C. Body is platelike, no symmetry, organs, muscular or nervous systems present. D. 2-3 mm E. marine F. glide over food and secrete digestive enzyme an
|
|
|
- Eric Douglas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 9 (multicellularity) I. Similarities A. cells are grouped B. groups of cells are specialized for various functions C. All cells in an organism is interdependent. II. Multicelled life appeared ~ 550 mya III. 2 main ways this could have happened. A. colonial hypothesis: dividing cells remained together (similar to colonial protists) B. Syncytical hypothesis: formation of plasma membranes in the cytoplasm producing small multicellular organisms. IV. Divided into 3 groups or grades A. mesazoa: believed to be the link between unicellularity and multicellularity. 1. Ciliated wormlike animals 2. Parasites in marine invertebrates classes: Rhombozoa and Orthonectida B. Parazoa: the phylums Porifera and Placozoa C. Eumetazoa: all other phylum. Phylum Placazoa I. General information A. Greek:plakos=plate zoa=animals B. only 1 species included: Trichoplax adharens. 1
2 C. Body is platelike, no symmetry, organs, muscular or nervous systems present. D. 2-3 mm E. marine F. glide over food and secrete digestive enzyme and then absorb the products. Phylum Porifera I. General Characteristics A. latin: por=pore fera=to bear B. believed to be the most primitive C sponges recognized as animals D. mostly marine other then 3 freshwater families = ~150 species E. filter feeding systems consist of pores and canals F. this groups is basically a mass of cells embedded in gelatinous material stiffened by skeleton of calcium carbonate or cilica and collogen (spicules) G. size vary from a few mm to 2m or more. H. most are asymmetrical I. Totally sessile, live attached to the bottom of water. Most commonly to rocks, shells, corals, pilings and other hard surfaces (substrate) J. approximately 9,000 species. 2
3 II. Structure and Function A. cell types and body wall 1. Simplest sponge are shaped like a vase or tube 2. Atrium or spongocoel: the interior cavity of the sponge 3. Osculum: large opening at the top going into the spongocoel. 4. The body of the sponge surround the spongocoel is perforated by pores (hence the name porifera) 5. Pinacoderm makes up the outer surface of the sponge body 6. Pinacocytes: the layer of flattened cells that make up the pinacoderm. 7. Porocytes: cells that are perforated like a ring. These make up the pores. 8. Choanocytes (collar cells): flagellated cells that have a collarlike ring of microvilli surrounding a flagellum. 8a. The collar is a netlike mesh of microfillaments connecting the villi 8b. The flagellum creates a water current through the sponge. 8c. The collar filters microscopic food particles from the water. 9. Mesohyl: the layer in between the spongocoel and pinacoderm. 3
4 9a. It has a jelly-like consistency 9b. Mesenchyme are cells that move by amoeboid movement. 1. These are specialized for reproduction, secreting skeletal elements, transporting and storing food, forming contractile rings around the openings of the sponge wall. III. Structure and function (skeleton) A. supported by a skeleton that may consist of microscopic needle-like spike called spicules 1. Formed by the mesenchyme cells 2. Made of calcium carbonate or silica and collagen. 3. Have a variety of shapes. B. Skeleton may also be made of a fibrinous protein called spongin (usually made of collagen) 1. These type of sponges are dried, beaten and washed until all cells are removed to produce a commercial sponge. IV. Water currents and ingestion A. Water currents are created by choanocytes 1. Causes water to be sucked in through pores and driven up and out of the spongocoel through the osculum. B. The water current forces bacteria and other fine suspended organic material into the choanocytes. 4
5 1. 80% of organic particles collected by some tropical sponges are invisible to even the light microscope. 2. Trapped particles are moved to the base of the collar by the microvilli where it s engulfed by the cell 3. Food is transferred to a mesenchyme cell (amoebocyte) in the mesohyl. 4. After the food is ingested, the products are passed by diffusion, to other parts of the sponge. C. Water currents also provide gas exchange, waste removal, and transfer of gametes. D. Many species have symbiotic relationships with smaller cyanobacteria and algae. 1. Symbiosis: live as a parasite but both host and parasite benefit. 2. Algae has protection and sponge gets some food given off by the algae. V. Body Forms A. Ascon 1. Vase-like 2. Simplest and least common 3. Not more than a few centimeters tall. 5
6 3a. Size is limited because as the volume of spongocoel increases, the flagellated surface doesn t increase proportionately. Therefore if the asconoid was large it would contain more water than it s choanocytes could move. 4. Outer opening of the porocytes are called ostia and lead directly to the spongocoel. 5. Choanocytes line the spongocoel and the flagellar movements draw water into the spongocoel via the ostia and out by way of the osculum. B. Sycon 1. This sponge has finger-like projection folds 2. The inner layer of the projection are called the flagellated canal or the radial canal. 2a. In this area are the only place that the choanocytes are found. 3. The pinacoderm side is called the incurrent canals. 4. The path of water flow is the same as in ascons. C. Leucon 1. Extensively branched system 2. Choanocytes are found only in chambers 2a. This allows for more surface area 2b. There are approximately 10,000 to 18,000 choanocytes per cubed mm 6
7 3. Dermal pores are made by porocytes 4. The spongocoel is absent 4a. Water leaves the sponge body through excurrent canals 4b. The exiting pore is larger and the choanocytes push water that way. 5. One leuconoid sponge that was 10cm high and 1 cm in diameter was found to have 2,250,000 flagellated chambers. 5a. A sponge this size could pass 22.5 liters in 24 hours. 6. Irregular in shape with many oscula (plural for osculum) located over body. 7. They can grow to large sizes 7a. Most fit in a bushel basket. 7b. Some species reach over a meter in height. 8. Most species found in shallow water are leuconoid. 7
8 VI. Defense Mechanisms A. most defenses appear to be chemical. B. spicules are not a deterent. C. 50% Antarctic and 64-75% tropical sponges are toxic 1. Predators will usually feed on nontoxic or weakly toxic sponges. D. Predators include sea stars and sea slugs. VII. Reproduction A. most are monoecious 1. Both sexes occur in the same individual 2. Sperm and eggs are produced at different times, therefore not allowing for selffertilization. B. Sperm production and disbursement. 1. Certain choanocytes lose their collar cells and flagella 2. Through meiosis flagellated sperm are formed. 3. Sperm cells exit one sponge through the osculum and enter another sponge with incurrent water. 8
9 4. Sperm are trapped by the choanocytes of another sponge and put into a vacoule. 5. The sperm are stored in the choanocytes. These choanocytes lose their collar and flagellum, become amoeboid and transport the sperm to the egg cells in the mesohyl. C. egg production 1. Choanocytes go through meiosis to form eggs (again losing collar cells and flagella) 2. The egg moves into the mesohyl and is stored there until it is fertilized by the sperm. D. Post fertilization 1. Early development occurs in the mesohyl 2. The zygote, as a result of cleavage, develops into a flagellated larval stage (an immature stage that undergoes changes before attaining adult body form) 3. The larva breaks free of mesohyl and is carried by water currents out of the osculum and into regular water current. 4. After 2 days, at most, of free swimming the larva settles down into the substrate of water bottom and begins formation into the adult body form. 9
10 E. Asexual reproduction 1. Some marine and most freshwater sponges go through asexual reproduction. 2. Gemmules (latin for little bud.), which are resistant capsules containing amoeboid cells are stored in the adult sponge. 3. When the parent sponge dies in the winter gemmules are released. These are able to survive both freezing and drying environments. 4. Once favorable conditions are present the cells are releases out of an opening called the micropyle and organize into an adult sponge. *** NOTE*** Some sponges have the power of regeneration. This is where the sponge has the ability to grow back parts of its body that has been removed. 10
12.1. Advent of Multicellularity A. Advantages 1. Nature s experiments with larger organisms without cellular differentiation are limited. 2. Increasi
 Phylum: Porifera The Sponges 12.1. Advent of Multicellularity A. Advantages 1. Nature s experiments with larger organisms without cellular differentiation are limited. 2. Increasing the size of a cell
Phylum: Porifera The Sponges 12.1. Advent of Multicellularity A. Advantages 1. Nature s experiments with larger organisms without cellular differentiation are limited. 2. Increasing the size of a cell
Zoology Name: Block: Exercise #7: The Sponges, Phylum Porifera Lab Guide
 Zoology Name: Block: Exercise #7: The Sponges, Phylum Porifera Lab Guide Members of the phylum Porifera are considered the simplest metazoans, they are little more than a loose grouping of cells, with
Zoology Name: Block: Exercise #7: The Sponges, Phylum Porifera Lab Guide Members of the phylum Porifera are considered the simplest metazoans, they are little more than a loose grouping of cells, with
Simplest metazoan (multi-cellular) Lecture 5 - Sponges!
 Simplest metazoan (multi-cellular) Lecture 5 - Sponges! Metazoan origins unicellular ancestors Originated during the Precambrian (1.2 billion - 670 million years ago) From what? Two hypotheses: Multinucleated
Simplest metazoan (multi-cellular) Lecture 5 - Sponges! Metazoan origins unicellular ancestors Originated during the Precambrian (1.2 billion - 670 million years ago) From what? Two hypotheses: Multinucleated
Module 4: Marine Invertebrates I. Kingdom Animalia
 Module 4: Marine Invertebrates I Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Contains the largest number of species We will split them into 2 large groups Invertebrates- Animals w/o a backbone Vertebrates- Animals
Module 4: Marine Invertebrates I Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Contains the largest number of species We will split them into 2 large groups Invertebrates- Animals w/o a backbone Vertebrates- Animals
COMPARISON BETWEEN PORIFERA AND CNIDARIA. Colwyn Sleep
 COMPARISON BETWEEN PORIFERA AND CNIDARIA Colwyn Sleep INTRODUCTION Porifera Cnidaria Porifera and Cnidaria are organisms which share similar characteristics with one another. -They are both multicellular,
COMPARISON BETWEEN PORIFERA AND CNIDARIA Colwyn Sleep INTRODUCTION Porifera Cnidaria Porifera and Cnidaria are organisms which share similar characteristics with one another. -They are both multicellular,
Phylum Porifera. Phylum Porifera (sponges) Defining Characteristics of Phylum. Sponges
 Phylum Porifera Sponges Ancient group of animals that dates back to the late Precambrian about 600 million years ago Phylum Porifera (sponges) Sessile, aquatic, benthic, suspension feeders on bacteria
Phylum Porifera Sponges Ancient group of animals that dates back to the late Precambrian about 600 million years ago Phylum Porifera (sponges) Sessile, aquatic, benthic, suspension feeders on bacteria
Lab ( 3) Kingdom: Animalia
 Lab ( 3) Kingdom: Animalia Characteristics of animals: - Multicellular - Eukaryotic organisms - Cells with out cell wall Animalia is divided in two group : A/ Invertebrate ( animals with out backbones
Lab ( 3) Kingdom: Animalia Characteristics of animals: - Multicellular - Eukaryotic organisms - Cells with out cell wall Animalia is divided in two group : A/ Invertebrate ( animals with out backbones
Characteristics of Animals
 Characteristics of Animals Multicellular Cellular Organization What is this? Heterotrophic Adaptations CHAPTER 9 Cellular Organization 4 Major Functions of Animals Obtain food and water Sustain metabolism
Characteristics of Animals Multicellular Cellular Organization What is this? Heterotrophic Adaptations CHAPTER 9 Cellular Organization 4 Major Functions of Animals Obtain food and water Sustain metabolism
Bilateria. Radiata. Eumetazoa. Parazoa no true tissues. Multicellularity
 Quiz 1. What does porifera mean? 2. Class Hexactinellida's skeletal structure is made out of what material? 3. Characterized as large openings where water comes out 4. Cells responsible for the circulating
Quiz 1. What does porifera mean? 2. Class Hexactinellida's skeletal structure is made out of what material? 3. Characterized as large openings where water comes out 4. Cells responsible for the circulating
The Rise of the Animals
 The Rise of the Animals Animal or Plant? No eye spots Don t move No organs How can it be an animal? Or is it a plant? Meeting the Minimum Multicellular + Heterotrophic + Differentiated Cells + Structural
The Rise of the Animals Animal or Plant? No eye spots Don t move No organs How can it be an animal? Or is it a plant? Meeting the Minimum Multicellular + Heterotrophic + Differentiated Cells + Structural
Phyllum Porifera: Sponges
 Phyllum Porifera: Sponges Chapter 12 Ini5ally not considered animals but molecular evidence demonstrate that sponges are phylogene5cally grouped with other metazoa (animals) Sponges are the simplest mul5cellular
Phyllum Porifera: Sponges Chapter 12 Ini5ally not considered animals but molecular evidence demonstrate that sponges are phylogene5cally grouped with other metazoa (animals) Sponges are the simplest mul5cellular
Mesozoa, Parazoa, and Metazoa. Chapter 12 pg. 239
 Mesozoa, Parazoa, and Metazoa Chapter 12 pg. 239 3 Multicellular Groups: Mesozoa, Parazoa, Eumetazoa Multicellular organisms are divided into three groups: Mesozoa, Parazoa (phylum Porifera, phylum Placozoa)
Mesozoa, Parazoa, and Metazoa Chapter 12 pg. 239 3 Multicellular Groups: Mesozoa, Parazoa, Eumetazoa Multicellular organisms are divided into three groups: Mesozoa, Parazoa (phylum Porifera, phylum Placozoa)
basal animalia porifera, cnidaria
 basal animalia porifera, cnidaria PHYLUM PORIFERA porifera Sponges, no tissues or organs, cellular level of organization outer layer is made of cells called pinacocytes choanocytes (collar cells) Flagella
basal animalia porifera, cnidaria PHYLUM PORIFERA porifera Sponges, no tissues or organs, cellular level of organization outer layer is made of cells called pinacocytes choanocytes (collar cells) Flagella
Invertebrate Zoology. Unit 2: Phylums: Porifera, Cnidaria, and Ctenophora
 Invertebrate Zoology Unit 2: Phylums: Porifera, Cnidaria, and Ctenophora Objective 1: Differentiate between the 3 types of Poriferians (Asconoids, Syconoids, and Leuconoids) and the three main classes
Invertebrate Zoology Unit 2: Phylums: Porifera, Cnidaria, and Ctenophora Objective 1: Differentiate between the 3 types of Poriferians (Asconoids, Syconoids, and Leuconoids) and the three main classes
Sponges and Cnidarians
 The Animal Kingdom Multicellular Sponges and Cnidarians Biology : Chapter 26 Eukaryotic Heterotrophs Cells lack cell walls 95% are invertebrates What Animals Do to Survive Feeding Response Respiration
The Animal Kingdom Multicellular Sponges and Cnidarians Biology : Chapter 26 Eukaryotic Heterotrophs Cells lack cell walls 95% are invertebrates What Animals Do to Survive Feeding Response Respiration
Chapter 7. Marine Animals Without a Backbone
 Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone General Characteristics of Animals Multicellular, diploid organisms with tissues, organs or organ systems in most Heterotrophic Require oxygen for aerobic
Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone General Characteristics of Animals Multicellular, diploid organisms with tissues, organs or organ systems in most Heterotrophic Require oxygen for aerobic
Porifera. BIO2135 Animal Form & Function ACD. Page 1. Kingdom Animalia. Cladistics Useful terms. Cladistics - Useful terms
 Kingdom Animalia 1 Cladistics - Useful terms Apomorphies Derived characters within a group Plesiomorphies Primitive characters within a group Synapomorphies Derived characters shared between groups Symplesiomorphies
Kingdom Animalia 1 Cladistics - Useful terms Apomorphies Derived characters within a group Plesiomorphies Primitive characters within a group Synapomorphies Derived characters shared between groups Symplesiomorphies
09/12/2012. Classification. Characteristics. Learning Outcome G2. Student Achievement Indicators. Phylum Porifera The Sponges
 Learning Outcome G2 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Porifera and the Phylum Cnidaria Learning Outcome G2 Phylum Porifera & Phylum Cnidaria Student Achievement Indicators Students who have
Learning Outcome G2 Analyse the increasing complexity of the Phylum Porifera and the Phylum Cnidaria Learning Outcome G2 Phylum Porifera & Phylum Cnidaria Student Achievement Indicators Students who have
Ph. Porifera and Ph. Cnidaria
 I. Phylum Porifera (sponges; pore bearer ) A. General characteristics 1. simplest animals 2. asymmetric 3. aquatic habitats a. typically marine 4. live alone or in colonies a. often members of reef habitats
I. Phylum Porifera (sponges; pore bearer ) A. General characteristics 1. simplest animals 2. asymmetric 3. aquatic habitats a. typically marine 4. live alone or in colonies a. often members of reef habitats
BIO2135 Animal Form & Function 2 9:10 AM 1 9:10 AM. A= Symplesiomorphy C= Synapomorphy. (Autoapomorphy) 3 9:10 AM
 Kingdom nimalia Cladistics - Useful terms pomorphies Derived characters within a group Plesiomorphies Primitive characters within a group Synapomorphies Derived characters shared between groups Symplesiomorphies
Kingdom nimalia Cladistics - Useful terms pomorphies Derived characters within a group Plesiomorphies Primitive characters within a group Synapomorphies Derived characters shared between groups Symplesiomorphies
Unit 2. The pellicle acts as a membrane It maintains the shape of the protozoan but remains flexible Ectoplasm
 Kingdom Protista A polyphyletic group containing: Unit 2 Polyphyletic- The Protozoans (Unicellular - can be very complex) Individuals may group together to form colonies Colony Specialized organelles Pellicle
Kingdom Protista A polyphyletic group containing: Unit 2 Polyphyletic- The Protozoans (Unicellular - can be very complex) Individuals may group together to form colonies Colony Specialized organelles Pellicle
Learning Objectives. The Animal Kingdom: An Introduction to Animal Diversity. Sexual Reproduction
 Learning Objectives The Animal Kingdom: An Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 29 What characters are common to most animals? Advantages and disadvantages of different environments Searching for relationships
Learning Objectives The Animal Kingdom: An Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 29 What characters are common to most animals? Advantages and disadvantages of different environments Searching for relationships
Sponge and Cnidarian Review
 Name Period Date Sponge and Cnidarian Review Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the definition that matches each term. 1. Invertebrate 2. Filter feeder 3. Asymmetry 4. Radial 5. Medusa
Name Period Date Sponge and Cnidarian Review Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the definition that matches each term. 1. Invertebrate 2. Filter feeder 3. Asymmetry 4. Radial 5. Medusa
Intro to Animals. Chapter 32
 Intro to Animals Chapter 32 1) Multicellular Organization (Different cells have different functions) Specialization: adaptation of a cell for a particular function Remember: cells tissues organs organ
Intro to Animals Chapter 32 1) Multicellular Organization (Different cells have different functions) Specialization: adaptation of a cell for a particular function Remember: cells tissues organs organ
Notes - Porifera and Cnideria
 Notes - Porifera and Cnideria - Animals exist on every continent on the planet. Most people consider animals to be the most important kingdom as we are considered animals. But, what is an animal? What
Notes - Porifera and Cnideria - Animals exist on every continent on the planet. Most people consider animals to be the most important kingdom as we are considered animals. But, what is an animal? What
26-2: Sponges. I. Sponges A. An ancient life form; sponges date back to the beginning of the Cambrian period. Shape of Life VIDEO
 26-2: Sponges I. Sponges A. An ancient life form; sponges date back to the beginning of the Cambrian period Shape of Life VIDEO B. Habitat: live in the sea, although a few live in freshwater lakes and
26-2: Sponges I. Sponges A. An ancient life form; sponges date back to the beginning of the Cambrian period Shape of Life VIDEO B. Habitat: live in the sea, although a few live in freshwater lakes and
Lab 2 Phylum Porifera and phylum Cnidaria. Grantia. Phylum Porifera. Kingdom :- Animalia. Phylum:- Porifera. Class:- Calcarea. Order:- Leucosolenida
 Lab 2 Phylum Porifera and phylum Cnidaria Phylum Porifera Adults sessile and attached Radial symmetry or asymmetrical Multi-cellular ; loose aggregation of cells Skeleton made of collagen and spicules
Lab 2 Phylum Porifera and phylum Cnidaria Phylum Porifera Adults sessile and attached Radial symmetry or asymmetrical Multi-cellular ; loose aggregation of cells Skeleton made of collagen and spicules
What is a Cnidarian?
 Invertebrate What is a Cnidarian? 9000 species of jellyfishes, corals, sea anemones, hydras Mostly marine animals Radially symmetrical One body opening Two layers of cells organized into tissues with specific
Invertebrate What is a Cnidarian? 9000 species of jellyfishes, corals, sea anemones, hydras Mostly marine animals Radially symmetrical One body opening Two layers of cells organized into tissues with specific
Chapter 24 Introduction to Animals
 1 Chapter 24 Introduction to Animals I. Animal characteristics A. General Animal Features Multicellular B. Feeding and Digestion a. acquire nutrients from various sources obtaining nutrients unique to
1 Chapter 24 Introduction to Animals I. Animal characteristics A. General Animal Features Multicellular B. Feeding and Digestion a. acquire nutrients from various sources obtaining nutrients unique to
BIOLOGY. An Introduction to Invertebrates CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 33.UN08 Metazoa Eumetazoa
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 33 An Introduction to Invertebrates Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 33.UN08 Metazoa Eumetazoa
Animal Body Plans. Aggregate Blind sac Tube-within-a-tube Segmented Molluscan Arthropod. Sponges. Acoelomate -Eucoelomate Annelid Mollusca Arthropoda
 Animal Body Plans Aggregate Blind sac Tube-within-a-tube Segmented Molluscan Arthropod Sponges Cnidaria, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes Acoelomate -Eucoelomate Annelid Mollusca Arthropoda Size Constraints
Animal Body Plans Aggregate Blind sac Tube-within-a-tube Segmented Molluscan Arthropod Sponges Cnidaria, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes Acoelomate -Eucoelomate Annelid Mollusca Arthropoda Size Constraints
Chapter 8. Sponges Phylum Porifera Basic characteristics: simple asymmetric sessile
 Chapter 8 Key Concepts Sponges are asymmetric, sessile animals that filter food from the water circulating through their bodies. Sponges provide habitats for other animals. Cnidarians and ctenophores exhibit
Chapter 8 Key Concepts Sponges are asymmetric, sessile animals that filter food from the water circulating through their bodies. Sponges provide habitats for other animals. Cnidarians and ctenophores exhibit
SG 9.2 notes Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants
 Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
The Evolution of Animal Diversity. Dr. Stephen J. Salek Biology 130 Fayetteville State University
 The Evolution of Animal Diversity Dr. Stephen J. Salek Biology 130 Fayetteville State University Create your own animal? Start with a basic plant. Make the plant into a simple animal such as a worm. Consider:
The Evolution of Animal Diversity Dr. Stephen J. Salek Biology 130 Fayetteville State University Create your own animal? Start with a basic plant. Make the plant into a simple animal such as a worm. Consider:
What Is an Animal? Animals come in many shapes, forms, and sizes. About 98 percent of all animals are invertebrates. The Kingdom Animalia
 What Is an Animal? What characteristics do all animals have? Animals come in many shapes, forms, and sizes. Scientists estimate that there are between 1 and 2 million species of animals! Some, like whales
What Is an Animal? What characteristics do all animals have? Animals come in many shapes, forms, and sizes. Scientists estimate that there are between 1 and 2 million species of animals! Some, like whales
Porifera, Coelenterata, Ctenophora
 Porifera, Coelenterata, Ctenophora Contents Animal Classification - Flow Chart... 3 Phylum Porifera... 4 Phylum Cnidaria... 10 Phylum Ctenophora... 16 www.topperlearning.com 2 Animal Classification - Flow
Porifera, Coelenterata, Ctenophora Contents Animal Classification - Flow Chart... 3 Phylum Porifera... 4 Phylum Cnidaria... 10 Phylum Ctenophora... 16 www.topperlearning.com 2 Animal Classification - Flow
Sponges and Cnidarians *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m48094 1 Sponges and Cnidarians * Miranda Dudzik Based on Sponges and Cnidarians by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m48094 1 Sponges and Cnidarians * Miranda Dudzik Based on Sponges and Cnidarians by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
Importance of Protists
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
origin and evolution of species
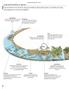 origin and evolution of species E V O L U T I O N O F L I F E Since its formation some 4.6 billion years ago, the Earth has witnessed the genesis of continents and oceans and the appearance of animals
origin and evolution of species E V O L U T I O N O F L I F E Since its formation some 4.6 billion years ago, the Earth has witnessed the genesis of continents and oceans and the appearance of animals
Kingdom Protista. The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists
 Kingdom Protista The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists DOMAIN EUKARYA PROTISTS KINGDOM PROTISTA Any eukaryote that is not classified as a fungus, plant, or
Kingdom Protista The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists DOMAIN EUKARYA PROTISTS KINGDOM PROTISTA Any eukaryote that is not classified as a fungus, plant, or
Intro to Invertebrate STUDENT NOTES Date: 1. Taxonomy : the science of classifying/grouping organisms
 Intro to Invertebrate STUDENT NOTES Date: 1 Warm up What does it mean to be an invertebrate? Taxonomy : the science of classifying/grouping organisms Who is the father of our modern day classification
Intro to Invertebrate STUDENT NOTES Date: 1 Warm up What does it mean to be an invertebrate? Taxonomy : the science of classifying/grouping organisms Who is the father of our modern day classification
3. Choanoflagellates resemble what? What is the significance of this resemblance?
 I. Animal Diversity 1. What are some basic characteristics of the animal kingdom? What characteristics make them different from plants? - Eukaryotic, heterotrophic (we don t make our own food), we store
I. Animal Diversity 1. What are some basic characteristics of the animal kingdom? What characteristics make them different from plants? - Eukaryotic, heterotrophic (we don t make our own food), we store
chapter six Sponges Phylum Porifera The Advent of Multicellularity
 6 chapter six Sponges Phylum The Advent of Multicellularity Sponges are the simplest multicellular animals. Because the cell is the elementary unit of life, organisms larger than unicellular protozoa arose
6 chapter six Sponges Phylum The Advent of Multicellularity Sponges are the simplest multicellular animals. Because the cell is the elementary unit of life, organisms larger than unicellular protozoa arose
Animals contain specialized cells
 What is an Animal? Kingdom Animalia Main Characteristics Members of the Animal Kingdom are: Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophic Have cells with membranes BUT NO cell wall Animals contain specialized
What is an Animal? Kingdom Animalia Main Characteristics Members of the Animal Kingdom are: Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophic Have cells with membranes BUT NO cell wall Animals contain specialized
Figure 1. Cladogram of the Major Animal Phyla based upon SSU-rRNA
 Biology 4B Laboratory Invertebrates I: Porifera, Cnidaria and Platyhelminthes Objectives To understand the basic differences among the invertebrate animal phyla To investigate and learn the obvious external
Biology 4B Laboratory Invertebrates I: Porifera, Cnidaria and Platyhelminthes Objectives To understand the basic differences among the invertebrate animal phyla To investigate and learn the obvious external
Invertebrate Diversity
 CHAPTER 23 Invertebrate Diversity Summary of Key Concepts Concept 23.1 Diverse animals share several key characteristics. (pp. 494 496) More than a million living species of animals are organized into
CHAPTER 23 Invertebrate Diversity Summary of Key Concepts Concept 23.1 Diverse animals share several key characteristics. (pp. 494 496) More than a million living species of animals are organized into
Chapter 32. Objectives. Table of Contents. Characteristics. Characteristics, continued. Section 1 The Nature of Animals
 Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Outline. v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: v Animal Phylogeny
 BIOSC 041 Overview of Animal Diversity: Animal Body Plans Reference: Chapter 32 Outline v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: Body symmetry Tissues
BIOSC 041 Overview of Animal Diversity: Animal Body Plans Reference: Chapter 32 Outline v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: Body symmetry Tissues
What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics. I. Characteristics of Animals. Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen
 What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. Characteristics of Animals A. All animals are eukaryotic, multicellular, have ways of moving to reproduce, obtain
What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. Characteristics of Animals A. All animals are eukaryotic, multicellular, have ways of moving to reproduce, obtain
v Scientists have identified 1.3 million living species of animals v The definition of an animal
 Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements BIOSC 041 v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements BIOSC 041 v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements
 Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal Body Plans
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal Body Plans
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Chapter 8. Sponges, Cnidarians, Comb Jellies, and Marine Worms
 Chapter 8 Sponges, Cnidarians, Comb Jellies, and Marine Worms Cnidarians: Animals with Stinging Cells Phylum Cnidaria Includes hydroids, corals, and sea anemones Coelenterate: synonym Named for their cnidocytes
Chapter 8 Sponges, Cnidarians, Comb Jellies, and Marine Worms Cnidarians: Animals with Stinging Cells Phylum Cnidaria Includes hydroids, corals, and sea anemones Coelenterate: synonym Named for their cnidocytes
Characteristics of Echinoderms
 Characteristics of Echinoderms Adult echinoderms have a body plan with five parts organized symmetrically around a center Does not have an anterior nor posterior end or a brain Most echinoderms are two
Characteristics of Echinoderms Adult echinoderms have a body plan with five parts organized symmetrically around a center Does not have an anterior nor posterior end or a brain Most echinoderms are two
Unicellular Marine Organisms. Chapter 4
 Unicellular Marine Organisms Chapter 4 The Cellular Structure of Life: Review Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists;
Unicellular Marine Organisms Chapter 4 The Cellular Structure of Life: Review Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists;
introduction to the Animal Kingdom (pages $55-560) Formulating a Definition: Building Vocabulary Skills
 STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER Sponges, Cnidarians, and Unsegmented Worms Section 26-1 introduction to the Animal Kingdom (pages $55-560) SECTION REVIEW With this section you began your study of the animal kingdom.
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER Sponges, Cnidarians, and Unsegmented Worms Section 26-1 introduction to the Animal Kingdom (pages $55-560) SECTION REVIEW With this section you began your study of the animal kingdom.
Animal Diversity. Features shared by all animals. Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers
 Animal Diversity Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers Nutritional mode Ingest food and use enzymes in the body to digest Cell structure and
Animal Diversity Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers Nutritional mode Ingest food and use enzymes in the body to digest Cell structure and
Resources. Visual Concepts. Chapter Presentation. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Section 2 Animal Body Systems Objectives Identify the features that animals have in
Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Section 2 Animal Body Systems Objectives Identify the features that animals have in
8/23/2014. Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 32 Objectives List the characteristics that combine to define animals Summarize key events of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras Distinguish between the
Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 32 Objectives List the characteristics that combine to define animals Summarize key events of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras Distinguish between the
Kingdom Animalia. Zoology the study of animals
 Kingdom Animalia Zoology the study of animals Summary Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. consume and digest organic materials thereby being heterotrophs. Most are motile at some time in their lives.
Kingdom Animalia Zoology the study of animals Summary Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. consume and digest organic materials thereby being heterotrophs. Most are motile at some time in their lives.
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Objective 1: I can describe protists. Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus.
 Kingdom Protista Objective 1: I can describe protists Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus. They are: Eukaryotic they contain a nucleus Can
Kingdom Protista Objective 1: I can describe protists Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus. They are: Eukaryotic they contain a nucleus Can
An Introduction to Animal Diversity
 An Introduction to Animal Diversity What defines an animal? Why so many species? The early history of animals life 7 Requirements of Animal Life What is an adaptation? Adapting to different habitats A
An Introduction to Animal Diversity What defines an animal? Why so many species? The early history of animals life 7 Requirements of Animal Life What is an adaptation? Adapting to different habitats A
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists
 Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
The Purple Encrusting Sponge: Haliclona permollis
 The Purple Encrusting Sponge: Haliclona permollis Susanna Flesher Section 04 http://calphotos.berkeley.edu/ There are many different aspects to Haliclona permollis, the purple encrusting sponge. Despite
The Purple Encrusting Sponge: Haliclona permollis Susanna Flesher Section 04 http://calphotos.berkeley.edu/ There are many different aspects to Haliclona permollis, the purple encrusting sponge. Despite
Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes. Chapter 22 Part 1
 Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes Chapter 22 Part 1 Impacts, Issues The Malaria Menace Plasmodium, a single-celled protist, causes malaria but also manipulates its mosquito and human hosts to maximize its
Protists The Simplest Eukaryotes Chapter 22 Part 1 Impacts, Issues The Malaria Menace Plasmodium, a single-celled protist, causes malaria but also manipulates its mosquito and human hosts to maximize its
Protist Classification the Saga Continues
 Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
Phylum Cnidaria Test True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. Mark a for true and b for false.
 PLEASE WRITE YOUR NAME HERE: 1 Phylum Cnidaria Test True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. Mark a for true and b for false. 1. Polyps are a body form of cnidarians that
PLEASE WRITE YOUR NAME HERE: 1 Phylum Cnidaria Test True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. Mark a for true and b for false. 1. Polyps are a body form of cnidarians that
There are two commonly accepted theories for how eukaryotic cells evolved: infolding and endosymbiosis. Infolding
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Eukaryote Phylogeny. Glycogen. Kingdom Animalia. Amoebozoa Animalia. Plantae. Chromalveolata Rhizaria. Fungi. Excavata
 Eukaryote Phylogeny most protozoans, brown algae, & water molds Excavata Chromalveolata Rhizaria Plantae Amoebozoa Animalia Fungi cpsts. w/ 2 memb. chitin, hyphae glycogen eukaryotic cells (nucleus, etc.)
Eukaryote Phylogeny most protozoans, brown algae, & water molds Excavata Chromalveolata Rhizaria Plantae Amoebozoa Animalia Fungi cpsts. w/ 2 memb. chitin, hyphae glycogen eukaryotic cells (nucleus, etc.)
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
 Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan &Talaro Chapter 5 Eucaryotic cells and microorganisms Chapter 5 2 3 Eucaryotic cells 3 Flagella 4 Cilia similar in overall structure to flagella, but
Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan &Talaro Chapter 5 Eucaryotic cells and microorganisms Chapter 5 2 3 Eucaryotic cells 3 Flagella 4 Cilia similar in overall structure to flagella, but
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.29 - PROTISTS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Eukrayotic cells are large, have a nucleus, contain membrane-bound organelles, and use a cytoskeleton The nucleus is the synapomorphy that unifies eukaryotes Endosymbiotic theory
!! www.clutchprep.com Eukrayotic cells are large, have a nucleus, contain membrane-bound organelles, and use a cytoskeleton The nucleus is the synapomorphy that unifies eukaryotes Endosymbiotic theory
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus Archaea & Eubacteria One circular chromosome Extremely small Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus!!! Membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, &
Basic Structure of a Cell Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus Archaea & Eubacteria One circular chromosome Extremely small Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus!!! Membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, &
The Microbial World. Chapter 5
 The Microbial World Chapter 5 Viruses Non-cellular infectious agents that have two basic characteristics: Not capable of reproduction without a host cell Structure: Nucleic acid core- can be DNA or RNA
The Microbial World Chapter 5 Viruses Non-cellular infectious agents that have two basic characteristics: Not capable of reproduction without a host cell Structure: Nucleic acid core- can be DNA or RNA
Introduction to Animal Diversity Lecture 7 Winter 2014
 Introduction to Animal Diversity Lecture 7 Winter 2014 Evolution of Animals 1 Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Prokaryotes No nucleus Nucleoid region Simple No membrane bound organelles Smaller (1-5 nm) Evolutionarily
Introduction to Animal Diversity Lecture 7 Winter 2014 Evolution of Animals 1 Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Prokaryotes No nucleus Nucleoid region Simple No membrane bound organelles Smaller (1-5 nm) Evolutionarily
Chapter 32, 10 th edition Q1.Which characteristic below is shared by plants, fungi, and animals? ( Concept 32.1)
 Chapter 32, 10 th edition Q1.Which characteristic below is shared by plants, fungi, and animals? ( Concept 32.1) A) They are multicellular eukaryotes. B) They are heterotrophs. C) Their cells are supported
Chapter 32, 10 th edition Q1.Which characteristic below is shared by plants, fungi, and animals? ( Concept 32.1) A) They are multicellular eukaryotes. B) They are heterotrophs. C) Their cells are supported
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Moving Forward Quizlet Each section we cover, 1 group will go to our class on Quizlet and create 20 flash cards on the topic (/5mks) If I warn you about talking while I m talking,
Introduction to Animals Moving Forward Quizlet Each section we cover, 1 group will go to our class on Quizlet and create 20 flash cards on the topic (/5mks) If I warn you about talking while I m talking,
Kingdom Animalia: Phyla Porifera and Cnidaria
 Kingdom Animalia: Phyla Porifera and Cnidaria Essential Question(s): What are key characteristics to the animal kingdom? Objectives: 1. Students will be able to distinguish essential characteristics in
Kingdom Animalia: Phyla Porifera and Cnidaria Essential Question(s): What are key characteristics to the animal kingdom? Objectives: 1. Students will be able to distinguish essential characteristics in
A. Incorrect! Sponges are mostly marine animals. This is a feature of sponges.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
Kingdom Protista. The following organisms will be examined in the lab today: Volvox, Oedogonium, Spirogyra, Ulva
 Kingdom Protista I. Introduction The protists are a diverse group of organisms. In the past they have been classified as fungi, plants and animals. They can be green, autotrophs or nongreen heterotrophs.
Kingdom Protista I. Introduction The protists are a diverse group of organisms. In the past they have been classified as fungi, plants and animals. They can be green, autotrophs or nongreen heterotrophs.
BIOS1101 Lab Notes. Contents ANIMALS. Lab 1: Animal Diversity invertebrates. Lab 2: Animal Diversity 2 vertebrates
 Contents ANIMALS Lab 1: Animal Diversity invertebrates Lab 2: Animal Diversity 2 vertebrates Lab 3: Animal Structure 1 Gross morphology Lab 4: Animal Structure 2 Histology Lab 5: The Nervous System & Sensory
Contents ANIMALS Lab 1: Animal Diversity invertebrates Lab 2: Animal Diversity 2 vertebrates Lab 3: Animal Structure 1 Gross morphology Lab 4: Animal Structure 2 Histology Lab 5: The Nervous System & Sensory
Biology. Slide 1of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Name Class Date. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 14 3 Invertebrates SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What structures and systems perform basic life functions
CHAPTER 14 3 Invertebrates SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What structures and systems perform basic life functions
Features of the Animal
 Features of the Animal Kingdom Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Even though members of the animal kingdom are incredibly diverse, animals share common features that distinguish them from organisms in other kingdoms.
Features of the Animal Kingdom Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Even though members of the animal kingdom are incredibly diverse, animals share common features that distinguish them from organisms in other kingdoms.
Cell Organelles. 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism Cells tissues organ organ system organism
 Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta
 Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
ZOOLOGY 101 SECTION 2 LECTURE NOTES
 ZOOLOGY 101 SECTION 2 LECTURE NOTES I. Protists - Commonly called protozoans - All single celled eukaryotes Three most important phyla: 1. Sarcomastigophora: includes the amebas and the flagellates 2.
ZOOLOGY 101 SECTION 2 LECTURE NOTES I. Protists - Commonly called protozoans - All single celled eukaryotes Three most important phyla: 1. Sarcomastigophora: includes the amebas and the flagellates 2.
Protista and Fungi. Fungi. Protista
 Protista and Fungi Protista -eukaryotic -multi and single cellular many singular -consumers, producers, and decomposers -some movement -algae like protists, plant like protists, and animal like protists
Protista and Fungi Protista -eukaryotic -multi and single cellular many singular -consumers, producers, and decomposers -some movement -algae like protists, plant like protists, and animal like protists
Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Diversity. Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Diversity Welcome to Your Kingdom The animal kingdom extends far beyond humans and other animals we may encounter 1.3 million living species of animals have been identified
Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Diversity Welcome to Your Kingdom The animal kingdom extends far beyond humans and other animals we may encounter 1.3 million living species of animals have been identified
29/11/2012. Characteristics. Protist Diversity. Characteristics. Kingdom Protista. Examples of Plant-like Protists
 Kingdom Protista Learning Outcome B1 Characteristics Appeared in the fossil record 1.5 billion years ago have an evolutionary advancement over bacteria, because they have a membranebound nucleus. also
Kingdom Protista Learning Outcome B1 Characteristics Appeared in the fossil record 1.5 billion years ago have an evolutionary advancement over bacteria, because they have a membranebound nucleus. also
What Are the Protists?
 Protists 1 What Are the Protists? 2 Protists are all the eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals. Protists are a paraphyletic group. Protists exhibit wide variation in morphology, size, and nutritional
Protists 1 What Are the Protists? 2 Protists are all the eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals. Protists are a paraphyletic group. Protists exhibit wide variation in morphology, size, and nutritional
2303ENV Zoology. Lecture week 1: Phylogeny and Classification
 Lecture week 1: Phylogeny and Classification 2303ENV Zoology Definition of animals: multicellular, eukaryotic, motile (can move independently and spontaneously), heterotrophic (must ingest other organisms
Lecture week 1: Phylogeny and Classification 2303ENV Zoology Definition of animals: multicellular, eukaryotic, motile (can move independently and spontaneously), heterotrophic (must ingest other organisms
Protists & Fungi. Words to Know: Chapters 19 & 20. Label the paramecium diagram above. (pg. 548)
 Words to Know: Protozoan Chapters 19 & 20 Protists & Fungi Microsporidium Contractile vacuole Pseudopod Bioluminescent Colony Plasmodium Chitin Hypha Septum Spore Sporangium Rhizoid Lichen Mycorrhiza Label
Words to Know: Protozoan Chapters 19 & 20 Protists & Fungi Microsporidium Contractile vacuole Pseudopod Bioluminescent Colony Plasmodium Chitin Hypha Septum Spore Sporangium Rhizoid Lichen Mycorrhiza Label
Kingdom Protista. Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 EXIT 2/16/2005
 Kingdom Protista Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 Kingdom Protista General Characteristics Animal-Like Protists Plant-Like Protists Fungus-Like Protists General Characteristics Protozoa - Greek name
Kingdom Protista Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 Kingdom Protista General Characteristics Animal-Like Protists Plant-Like Protists Fungus-Like Protists General Characteristics Protozoa - Greek name
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2007
 BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2007 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 8 Reproduction and Development 1.Asexual reproduction: a. Is the primary form
BIO 221 Invertebrate Zoology I Spring 2007 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 8 Reproduction and Development 1.Asexual reproduction: a. Is the primary form
Dearolf BIOL 220. Freshwater Brackish water Marine Terrestrial Parasitic
 CLADE METAZOA Phylum Porifera Hickman Chapter 12 The Origins of Multicellularity Phylum Porifera: Sponges Characteristics of Phylum Porifera (page 248) Figure 12.2 (page 248) Form and Function Figure 12.5
CLADE METAZOA Phylum Porifera Hickman Chapter 12 The Origins of Multicellularity Phylum Porifera: Sponges Characteristics of Phylum Porifera (page 248) Figure 12.2 (page 248) Form and Function Figure 12.5
From a Cell to an Organism
 From a Cell to an Organism Levels of Organization Life s Organization All matter is made of atoms. Atoms combine and form molecules. Molecules make up cells. A large animal, such as a Komodo dragon, is
From a Cell to an Organism Levels of Organization Life s Organization All matter is made of atoms. Atoms combine and form molecules. Molecules make up cells. A large animal, such as a Komodo dragon, is
Chapter 32 Intro to Animals. Image from:
 Chapter 32 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Animals Invertebrates (animals without a backbone) Porifera Cnidaria Worms Mollusks Echinoderms Arthropods Animals
Chapter 32 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Animals Invertebrates (animals without a backbone) Porifera Cnidaria Worms Mollusks Echinoderms Arthropods Animals
KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS
 KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS EUKARYOTIC MULTICELLULAR HETEROTROPHIC (by ingestion) MOVE AT SOME POINT IN LIFE (not all - sponges are sessile) DIGEST FOOD TO GET NUTRIENTS LACK CELL WALLS CHARACTERISTICS
KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS EUKARYOTIC MULTICELLULAR HETEROTROPHIC (by ingestion) MOVE AT SOME POINT IN LIFE (not all - sponges are sessile) DIGEST FOOD TO GET NUTRIENTS LACK CELL WALLS CHARACTERISTICS
