Supplementary Materials for mplr-loc Web-server
|
|
|
- Marcia Patrick
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Materials for mplr-loc Web-server Shibiao Wan and Man-Wai Mak June 2014 Back to mplr-loc Server Contents 1 Introduction to mplr-loc Server 2 2 Web-server Functions Inputting Protein Accession Numbers via Copy-and-Paste Inputting Protein Sequences via Copy-and-Paste Inputting Protein Accession Numbers via File-Upload Inputting Protein Sequences via File-Upload Statistical Methods 12 4 Dataset Construction 17 1
2 1 Introduction to mplr-loc Server mplr-loc is a subcellular-localization predictor which can deal with datasets with both single-label and multi-label proteins. The mplr-loc server can predict two different species (virus and plant) and two different input types (amino acid sequences in FASTA format and protein accession numbers 1 in UniProtKB [1] format). mplr-loc stands for multi-label Penalized Logistic Regression for protein subcellular Localization, meaning that this predictor extracts the feature information from the gene ontology information and then processes the information by a multi-label multi-class penalized logistic regression classifier with an adaptive decision strategy. The mplr- Loc predictor can deal with both single-location proteins and multi-location proteins. Compared to traditional GO-based predictors [2, 3, 4, 5], mplr-loc can not only rapidly and accurately predict subcellular localization of single- and multi-label proteins, but also provide probabilistic confidence scores for the prediction decisions. For each query protein, the mplr-loc web-server can give both the prediction results and a figure which shows the probabilistic confidence scores for each location. The specific algorithms can be found in the paper. For virus proteins, mplr-loc is designed to predict 6 subcellular locations of multilabel viral proteins. The 6 subcellular locations include: (1) viral capsid; (2) host cell membrane; (3) host endoplasmic reticulum; (4) host cytoplasm; (5) host nucleus; and (6) secreted. The predictor is not designed for predicting the subcellular localization of non-viral proteins. Therefore, the prediction results of non-viral proteins are arbitrary 1 numbers 2
3 Figure 1: Interface of the mplr-loc web-server. and meaningless. For plant proteins, mplr-loc is designed to predict 12 subcellular locations of multilabel plant proteins. The 12 subcellular locations include: (1) cell membrane; (2) cell wall; (3) chloroplast; (4) cytoplasm; (5) endoplasmic reticulum; (6) extracellular; (7) golgi apparatus; (8) mitochondrion; (9) nucleus; (10) peroxisome; (11) plastid; and (12) vacuole. Note (11) plastid here includes those plastid groups except for (3) chloroplast. The predictor is not designed for predicting the subcellular localization of non-plant proteins. Therefore, the prediction results of non-plant proteins are arbitrary and meaningless. 3
4 Input format and type selection Input format and type selection Figure 2: Different formats and types of input. 2 Web-server Functions Fig. 1 shows the interface of the mplr-loc web-server. As can be seen, there are two steps to use mplr-loc: 1. select the species type and input type. Fig. 2 shows the four combinations of species types and input types: plant protein amino acid sequences in FASTA format, plant protein UNIPROTKB accession numbers, virus protein amino acid sequences in FASTA format and virus protein UNIPROTKB accession numbers. 4
5 2. Input the query proteins in the form of either FASTA sequences or accession numbers (ACs). There are also two ways to input the proteins: copyand-paste the protein information into the textbox or upload a file containing the proteins. Inputting a batch of proteins in either formats (ACs or amino acid sequences) are supported in mplr-loc web-server for large-scale prediction. For users convenience, several examples of plant sequences, plant accession numbers, virus sequences and virus accession numbers are provided in the mplr-loc web-server. Besides, the two benchmark datasets are downloadable from the hyperlinks in the webserver, and the new independent test set can be directly downloaded from the web-server. Some simple yet informative instructions, which include significance of subcellular localization prediction, specific information about mplr-loc and some notes, are also provided thereafter. In addition to being able to rapidly and accurately predict subcellular localization of single- and multi-label proteins, mplr-loc can also provide probabilistic confidence scores for the prediction decisions. For each query protein, a figure showing the probabilistic confidence in assigning the query protein to each location is also provided. For readers ease of using the mplr-loc web-server, different combinations of species types, input types and ways to input proteins are specifically presented in the following subsections. 5
6 Select virus accession numbers Input accession numbers Figure 3: An example of using accession numbers as input. 2.1 Inputting Protein Accession Numbers via Copy-and-Paste Fig. 3 shows an example of using accession numbers (AC) as input. Note that mplr-loc can deal with one or more accession numbers for each submission. 2 After prediction, a prediction page similar to Fig. 4 will be shown, in which the input statistics and prediction results are listed. Fig. 5(a) and Fig. 5(b) specify the confidence scores for the two virus protein accession numbers (ACs) input. The red bar(s) represent the predicted locations and the blue bars are those locations where are predicted as not located. As can be 2 Note that the server can allow users to input maximum 100 accession numbers for each submission. 6
7 Figure 4: Prediction results page for using accession numbers as input. seen, the first virus AC is predicted as host-nucleus with a probabilistic confidence of more than 0.9; while the second virus ACs is predicted as host cell membrane and host endoplasmic reticulum, both with confidence of more than Inputting Protein Sequences via Copy-and-Paste Fig. 6 shows an example of using protein amino acid sequences as input. Note that mplr- Loc can deal with one or more protein sequences (maximum 50) 3 for each submission. After prediction, a prediction page similar to Fig. 7 will be shown, where the input statistics, prediction results are listed. Within the prediction results, besides the final subcellular locations, the BLAST E-value is also shown for each query protein sequence. Fig. 8(a) and Fig. 8(b) specify the confidence scores for the two plant protein sequences 3 Note that the updated server can allow users to input maximum 50 sequences for each submission. 7
8 (a) The 1-st virus accession number (b) The 2-nd virus accession number Figure 5: Confidence scores of the mplr-loc server for the virus protein accession numbers input in Fig. 3. 8
9 Select plant protein sequences Input protein sequences Figure 6: An example of using protein amino acid sequences as input. input. 2.3 Inputting Protein Accession Numbers via File-Upload mplr-loc allows users to upload a text file containing a list of accession numbers or sequences in FASTA format. Fig. 9 shows an example of uploading a file with a list of accession numbers. In this case, mplr-loc will present the prediction results in HTML format, as shown in Fig. 10. Fig. 11(a) and Fig. 11(b) specify the confidence scores for the two plant protein accession numbers input. 9
10 Figure 7: Prediction results page for using accession numbers as input. 2.4 Inputting Protein Sequences via File-Upload mplr-loc allows users to upload a text file containing a list of accession numbers or sequences in FASTA format. Fig. 12 shows an example of uploading a file with a list of protein sequences. In this case, mplr-loc will present the prediction results in HTML format, as shown in Fig. 13. Fig. 14 specifies the confidence scores for the plant protein sequence input. 10
11 (a) The 1-st plant amino-acid sequence (b) The 2-nd plant amino-acid sequence Figure 8: Confidence scores of the mplr-loc server for the plant protein sequences input in Fig
12 Select plant accession numbers Input file (with a list of protein accession numbers) Figure 9: An example of using a file with a list accession numbers as input. 3 Statistical Methods In statistical prediction, there are three methods that are often used for testing the generalization capabilities of predictors: independent tests, subsampling tests (or K-fold crossvalidation) and jackknife tests (or leave-one-out cross validation, short for LOOCV). In independent tests, the training set and the testing set were fixed, thus enabling us to obtain a fixed accuracy for the predictors. However, the selection of independent dataset often bears some sort of arbitrariness [6], which inevitably leads to non-bias-free accuracy for the predictors. 12
13 Figure 10: as input. Prediction results page for using a file with a list accession numbers In subsampling tests, here we use five-fold cross validation as an example. The whole dataset was randomly divided into 5 disjoint parts with equal size. The last part may have 1-4 more examples than the former 4 parts in order for each example to be evaluated on the model. Then one part of the dataset was used as the test set and the remained parts are jointly used as the training set. This procedure is repeated five times, and each time a different part was chosen as the test set. The number of the selections in dividing the benchmark dataset is obviously an astronomical figure even for a small-size dataset. This means that different selections lead to different results even for the same benchmark dataset, thus still being liable to statistical arbitrariness. Subsampling tests with a smaller K work definitely faster than that with a larger K. Thus, subsampling tests are faster than LOOCV, which can be regarded as N-fold cross-validation, where 13
14 (a) The 1-st plant accession number (b) The 2-nd plant accession number Figure 11: Confidence scores of the mplr-loc server for the plant protein accession numbers input in Fig
15 Select plant sequences Input file (with a list of protein sequences) Figure 12: An example of using a file with a list of protein sequences as input. N is the number of samples in the dataset, and N > K. At the same time, it is also statistically acceptable and usually regarded as less biased than the independent tests. In LOOCV, every protein in the benchmark dataset will be singled out one-by-one and is tested by the classifier trained by the remaining proteins. In this case, the arbitrariness can be avoided because LOOCV will yield a unique outcome for the predictors. Therefore, LOOCV is considered to be the most rigorous and bias-free method [7]. Hence, LOOCV was used to examine the performance of mplr-loc against other state-of-the-art predictors. 15
16 Figure 13: Prediction results page for using a file with a list of protein sequences as input. Figure 14: Confidence scores of the mplr-loc server for the plant protein sequences input in Fig
17 Table 1: Breakdown of the multi-label virus protein dataset. The sequence identity is cut off at 25%. The superscripts v stand for the virus dataset. Label Subcellular Location No. of Locative Proteins 1 Viral capsid 8 2 Host cell membrane 33 3 Host endoplasmic reticulum 20 4 Host cytoplasm 87 5 Host nucleus 84 6 Secreted 20 Total number of locative proteins (N loc v ) 252 Total number of actual proteins (N act v ) Dataset Construction mplr-loc uses two benchmark datasets [8, 9] and a new independent test set [4] to evaluate its performance. All of them were constructed by using the same standard procedures. The differences are the species (i.e., virus or plant), the Swiss-Prot versions and date of construction (i.e., Swiss-Prot 57.9 released on 22-Sept-2009 for benchmark virus dataset, Swiss-Prot 55.3 on 29-Apr-2008 for the benchmark plant dataset, and the date between 08-Mar-2011 and 18-Apr-2012 for the new plant dataset). Here, we take the new plant dataset as an example to illustrate the details of the procedures, which are specified as follows: 1. Go to the UniProt/SwissProt official webpage ( 2. Go to the Search section and select Protein Knowledgebase (UniProtKB) (default) in the Search in option; 3. In the Query option, select or type reviewered: yes ; 17
18 Table 2: Breakdown of the multi-label plant protein dataset. The sequence identity is cut off at 25%. The superscripts p stand for the plant dataset. Label Subcellular Location No. of Locative Proteins 1 Cell membrane 56 2 Cell wall 32 3 Chloroplast Cytoplasm Endoplasmic reticulum 42 6 Extracellular 22 7 Golgi apparatus 21 8 Mitochondrion Nucleus Peroxisome Plastid Vacuole 52 Total number of locative proteins (N loc p ) 1055 Total number of actual proteins (N act p ) Select AND in the Advanced Search option, and then select Taxonomy [OC] and type in Viridiplantae ; 5. Select AND in the Advanced Search option, and then select Fragment: no ; 6. Select AND in the Advanced Search option, and then select Sequence length and type in 50 - (no less than 50); 7. Select AND in the Advanced Search option, and then select Date entry integrated and type in ; 8. Select AND in the Advanced Search option, and then select Subcellular location: XXX Confidence: Experimental ; (XXX means the specific subcellular locations. 18
19 Table 3: Breakdown of the new plant dataset. The dataset was constructed from Swiss- Prot created between 08-Mar-2011 and 18-Apr The sequence identity of the dataset is below 25%. Label Subcellular Location No. of Locative Proteins 1 Cell membrane 16 2 Cell wall 1 3 Chloroplast 54 4 Cytoplasm 38 5 Endoplasmic reticulum 9 6 Extracellular 3 7 Golgi apparatus 7 8 Mitochondrion 16 9 Nucleus Peroxisome 6 11 Plastid 1 12 Vacuole 7 Total number of locative proteins 204 Total number of actual proteins 175 Here it includes 12 different locations: cell membrane; cell wall; chloroplast; endoplasmic reticulum; extracellular; golgi apparatus; mitochondrion; nucleus; peroxisome; plastid; vacuole.) 9. Further exclude those proteins which are not experimentally annotated (This is to recheck the proteins to guarantee they are all experimentally annotated). After selecting the proteins, Blastclust 4 was applied to reduce the redundancy in the dataset so that none of the sequence pairs has sequence identity higher than 25%
20 The details of the breakdown of the two benchmark datasets and the new plant dataset are listed in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3, respectively. All the datasets can be accessible from the page of Datasets of mplr-loc web-server. mplr-loc server is available at References [1] R. Apweiler, A. Bairoch, C. H. Wu, W. C. Barker, B. Boeckmann, S. Ferro, E. Gasteiger, H. Huang, R. Lopez, M. Magrane, M. J. Martin, D. A. Ntale, C. O Donovan, N. Redaschi, and L. S. Yeh, UniProt: the Universal Protein knowledgebase, Nucleic Acids Res, vol. 32, pp. D115 D119, [2] K. C. Chou, Z. C. Wu, and X. Xiao, iloc-euk: A multi-label classifier for predicting the subcellular localization of singleplex and multiplex eukaryotic proteins, PLoS ONE, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. e18258, [3] S. Wan, M. W. Mak, and S. Y. Kung, GOASVM: A subcellular location predictor by incorporating term-frequency gene ontology into the general form of Chou s pseudoamino acid composition, Journal of Theoretical Biology, vol. 323, pp , [4] S. Wan, M. W. Mak, and S. Y. Kung, mgoasvm: Multi-label protein subcellular localization based on gene ontology and support vector machines, BMC Bioinformatics, vol. 13, pp. 290,
21 [5] S. Wan, M. W. Mak, and S. Y. Kung, HybridGO-Loc: Mining hybrid features on gene ontology for predicting subcellular localization of multi-location proteins, PLoS ONE, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. e89545, [6] K. C. Chou and C. T. Zhang, Review: Prediction of protein structural classes, Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, vol. 30, no. 4, pp , [7] T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, and J. Friedman, The element of statistical learning, Springer-Verlag, [8] X. Xiao, Z. C. Wu, and K. C. Chou, iloc-virus: A multi-label learning classifier for identifying the subcellular localization of virus proteins with both single and multiple sites, Journal of Theoretical Biology, vol. 284, pp , [9] Z. C. Wu, X. Xiao, and K. C. Chou, iloc-plant: A multi-label classifier for predicting the subcellular localization of plant proteins with both single and multiple sites, Molecular BioSystems, vol. 7, pp ,
Supplementary Materials for R3P-Loc Web-server
 Supplementary Materials for R3P-Loc Web-server Shibiao Wan and Man-Wai Mak email: shibiao.wan@connect.polyu.hk, enmwmak@polyu.edu.hk June 2014 Back to R3P-Loc Server Contents 1 Introduction to R3P-Loc
Supplementary Materials for R3P-Loc Web-server Shibiao Wan and Man-Wai Mak email: shibiao.wan@connect.polyu.hk, enmwmak@polyu.edu.hk June 2014 Back to R3P-Loc Server Contents 1 Introduction to R3P-Loc
Shibiao Wan and Man-Wai Mak December 2013 Back to HybridGO-Loc Server
 Shibiao Wan and Man-Wai Mak December 2013 Back to HybridGO-Loc Server Contents 1 Functions of HybridGO-Loc Server 2 1.1 Webserver Interface....................................... 2 1.2 Inputing Protein
Shibiao Wan and Man-Wai Mak December 2013 Back to HybridGO-Loc Server Contents 1 Functions of HybridGO-Loc Server 2 1.1 Webserver Interface....................................... 2 1.2 Inputing Protein
SUB-CELLULAR LOCALIZATION PREDICTION USING MACHINE LEARNING APPROACH
 SUB-CELLULAR LOCALIZATION PREDICTION USING MACHINE LEARNING APPROACH Ashutosh Kumar Singh 1, S S Sahu 2, Ankita Mishra 3 1,2,3 Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, Ranchi Email: 1 ashutosh.4kumar.4singh@gmail.com,
SUB-CELLULAR LOCALIZATION PREDICTION USING MACHINE LEARNING APPROACH Ashutosh Kumar Singh 1, S S Sahu 2, Ankita Mishra 3 1,2,3 Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, Ranchi Email: 1 ashutosh.4kumar.4singh@gmail.com,
Supervised Ensembles of Prediction Methods for Subcellular Localization
 In Proc. of the 6th Asia-Pacific Bioinformatics Conference (APBC 2008), Kyoto, Japan, pp. 29-38 1 Supervised Ensembles of Prediction Methods for Subcellular Localization Johannes Aßfalg, Jing Gong, Hans-Peter
In Proc. of the 6th Asia-Pacific Bioinformatics Conference (APBC 2008), Kyoto, Japan, pp. 29-38 1 Supervised Ensembles of Prediction Methods for Subcellular Localization Johannes Aßfalg, Jing Gong, Hans-Peter
Large-Scale Plant Protein Subcellular Location Prediction
 Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 100:665 678 (2007) Large-Scale Plant Protein Subcellular Location Prediction Kuo-Chen Chou 1,2 * and Hong-Bin Shen 2 1 Gordon Life Science Institute, 13784 Torrey Del Mar
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 100:665 678 (2007) Large-Scale Plant Protein Subcellular Location Prediction Kuo-Chen Chou 1,2 * and Hong-Bin Shen 2 1 Gordon Life Science Institute, 13784 Torrey Del Mar
Efficient Classification of Multi-label and Imbalanced Data Using Min-Max Modular Classifiers
 2006 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks Sheraton Vancouver Wall Centre Hotel, Vancouver, BC, Canada July 16-21, 2006 Efficient Classification of Multi-label and Imbalanced Data Using Min-Max
2006 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks Sheraton Vancouver Wall Centre Hotel, Vancouver, BC, Canada July 16-21, 2006 Efficient Classification of Multi-label and Imbalanced Data Using Min-Max
STUDY OF PROTEIN SUBCELLULAR LOCALIZATION PREDICTION: A REVIEW ABSTRACT
 STUDY OF PROTEIN SUBCELLULAR LOCALIZATION PREDICTION: A REVIEW SHALINI KAUSHIK 1 *, USHA CHOUHAN 2 AND ASHOK DWIVEDI 3 *1,2,3 Department of Mathematics, and Computer applications, Maulana Azad National
STUDY OF PROTEIN SUBCELLULAR LOCALIZATION PREDICTION: A REVIEW SHALINI KAUSHIK 1 *, USHA CHOUHAN 2 AND ASHOK DWIVEDI 3 *1,2,3 Department of Mathematics, and Computer applications, Maulana Azad National
Biology. 7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure 10/29/2013. Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Biology Biology 1of 49 2of 49 Eukaryotic Cell Structures Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists
Biology Biology 1of 49 2of 49 Eukaryotic Cell Structures Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists
Cell Alive Homeostasis Plants Animals Fungi Bacteria. Loose DNA DNA Nucleus Membrane-Bound Organelles Humans
 UNIT 3: The Cell DAYSHEET 45: Introduction to Cellular Organelles Name: Biology I Date: Bellringer: Place the words below into the correct space on the Venn Diagram: Cell Alive Homeostasis Plants Animals
UNIT 3: The Cell DAYSHEET 45: Introduction to Cellular Organelles Name: Biology I Date: Bellringer: Place the words below into the correct space on the Venn Diagram: Cell Alive Homeostasis Plants Animals
Genome-wide multilevel spatial interactome model of rice
 Sino-German Workshop on Multiscale Spatial Computational Systems Biology, Beijing, Oct 8-12, 2015 Genome-wide multilevel spatial interactome model of rice Ming CHEN ( 陈铭 ) mchen@zju.edu.cn College of Life
Sino-German Workshop on Multiscale Spatial Computational Systems Biology, Beijing, Oct 8-12, 2015 Genome-wide multilevel spatial interactome model of rice Ming CHEN ( 陈铭 ) mchen@zju.edu.cn College of Life
UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure
 UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure Page CP: CHAPTER 3, Sections 1-3; HN: CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-2 Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their
UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure Page CP: CHAPTER 3, Sections 1-3; HN: CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-2 Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their
Cell Organelles Tutorial
 1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction with WoLF PSORT
 Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction with WoLF PSORT Paul Horton Computational Biology Research Center National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology Tokyo, Japan horton-p@aist.go.jp
Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction with WoLF PSORT Paul Horton Computational Biology Research Center National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology Tokyo, Japan horton-p@aist.go.jp
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
 Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
The Discovery of Cells
 The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab
 Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 1 of 49 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic
1 of 49 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic
Complete the table by stating the function associated with each organelle. contains the genetic material.... lysosome ribosome... Table 6.
 1 (a) Table 6.1 gives the functions of certain organelles in a eukaryotic cell. Complete the table by stating the function associated with each organelle. The first row has been completed for you. Organelle
1 (a) Table 6.1 gives the functions of certain organelles in a eukaryotic cell. Complete the table by stating the function associated with each organelle. The first row has been completed for you. Organelle
EXAMPLE-BASED CLASSIFICATION OF PROTEIN SUBCELLULAR LOCATIONS USING PENTA-GRAM FEATURES
 EXAMPLE-BASED CLASSIFICATION OF PROTEIN SUBCELLULAR LOCATIONS USING PENTA-GRAM FEATURES Jinsuk Kim 1, Ho-Eun Park 2, Mi-Nyeong Hwang 1, Hyeon S. Son 2,3 * 1 Information Technology Department, Korea Institute
EXAMPLE-BASED CLASSIFICATION OF PROTEIN SUBCELLULAR LOCATIONS USING PENTA-GRAM FEATURES Jinsuk Kim 1, Ho-Eun Park 2, Mi-Nyeong Hwang 1, Hyeon S. Son 2,3 * 1 Information Technology Department, Korea Institute
Identifying Extracellular Plant Proteins Based on Frequent Subsequences
 Identifying Extracellular Plant Proteins Based on Frequent Subsequences Yang Wang, Osmar R. Zaïane, Randy Goebel and Gregory Taylor University of Alberta {wyang, zaiane, goebel}@cs.ualberta.ca Abstract
Identifying Extracellular Plant Proteins Based on Frequent Subsequences Yang Wang, Osmar R. Zaïane, Randy Goebel and Gregory Taylor University of Alberta {wyang, zaiane, goebel}@cs.ualberta.ca Abstract
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.2 Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions 1. Which two domains consist of prokaryotic cells? 2. A major difference between
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.2 Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions 1. Which two domains consist of prokaryotic cells? 2. A major difference between
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Organelles & Cells Student Edition. A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole
 Name: Date: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains DNA? A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole 2. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure
Name: Date: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains DNA? A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole 2. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure
9/11/18. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 3. The Cell From Genes to Proteins. key processes
 Molecular and Cellular Biology Animal Cell ((eukaryotic cell) -----> compare with prokaryotic cell) ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) Rough ER Smooth ER Flagellum Nuclear envelope Nucleolus NUCLEUS Chromatin
Molecular and Cellular Biology Animal Cell ((eukaryotic cell) -----> compare with prokaryotic cell) ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) Rough ER Smooth ER Flagellum Nuclear envelope Nucleolus NUCLEUS Chromatin
AS Biology Summer Work 2015
 AS Biology Summer Work 2015 You will be following the OCR Biology A course and in preparation for this you are required to do the following for September 2015: Activity to complete Date done Purchased
AS Biology Summer Work 2015 You will be following the OCR Biology A course and in preparation for this you are required to do the following for September 2015: Activity to complete Date done Purchased
Supplementary Information 16
 Supplementary Information 16 Cellular Component % of Genes 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 human mouse extracellular other membranes plasma membrane cytosol cytoskeleton mitochondrion ER/Golgi translational
Supplementary Information 16 Cellular Component % of Genes 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 human mouse extracellular other membranes plasma membrane cytosol cytoskeleton mitochondrion ER/Golgi translational
Biology Test 2 The Cell. For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form.
 Name Block Date Biology Test 2 The Cell For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form. 1. Which pair of structures best shows that plant cells have functions
Name Block Date Biology Test 2 The Cell For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form. 1. Which pair of structures best shows that plant cells have functions
3.2. Eukaryotic Cells and Cell Organelles. Teacher Notes and Answers. section
 section 3.2 Eukaryotic Cells and Cell Organelles Teacher Notes and Answers SECTION 2 Instant Replay 1. Answers will vary. An example answer is a shapeless bag. 2. store and protect the DNA 3. mitochondria
section 3.2 Eukaryotic Cells and Cell Organelles Teacher Notes and Answers SECTION 2 Instant Replay 1. Answers will vary. An example answer is a shapeless bag. 2. store and protect the DNA 3. mitochondria
9/2/17. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 3. The Cell From Genes to Proteins. key processes
 Molecular and Cellular Biology Animal Cell ((eukaryotic cell) -----> compare with prokaryotic cell) ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) Rough ER Smooth ER Flagellum Nuclear envelope Nucleolus NUCLEUS Chromatin
Molecular and Cellular Biology Animal Cell ((eukaryotic cell) -----> compare with prokaryotic cell) ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) Rough ER Smooth ER Flagellum Nuclear envelope Nucleolus NUCLEUS Chromatin
Hands-On Nine The PAX6 Gene and Protein
 Hands-On Nine The PAX6 Gene and Protein Main Purpose of Hands-On Activity: Using bioinformatics tools to examine the sequences, homology, and disease relevance of the Pax6: a master gene of eye formation.
Hands-On Nine The PAX6 Gene and Protein Main Purpose of Hands-On Activity: Using bioinformatics tools to examine the sequences, homology, and disease relevance of the Pax6: a master gene of eye formation.
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function
 Name: Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function a. Define the word cell: 1. I know the history of the cell: b. Who discovered the cell? What did he observe? 2. I can list the three parts of
Name: Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function a. Define the word cell: 1. I know the history of the cell: b. Who discovered the cell? What did he observe? 2. I can list the three parts of
Introduction 1) List the 3 types of cells you will be comparing in today s lesson. a. b. c.
 Name: Date: Period: Cell Structure Internet Lesson Directions: Answer the following question by visiting the web site below. http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_structure.htm
Name: Date: Period: Cell Structure Internet Lesson Directions: Answer the following question by visiting the web site below. http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_structure.htm
Frequent Subsequence-based Protein Localization
 Submitted to ICDM 05 - Paper ID #.. Frequent Subsequence-based Protein Localization Yang Wang, Osmar R. Zaïane, and Randy Goebel University of Alberta wyang, zaiane, goebel @cs.ualberta.ca Abstract Extracellular
Submitted to ICDM 05 - Paper ID #.. Frequent Subsequence-based Protein Localization Yang Wang, Osmar R. Zaïane, and Randy Goebel University of Alberta wyang, zaiane, goebel @cs.ualberta.ca Abstract Extracellular
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Eukaryotic Cell Structure. 7.2 Biology Mr. Hines
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure 7.2 Biology Mr. Hines Comparing the cell to a factory In order for a cell to maintain its internal environment (homeostasis), many things must go on. This is similar to a factory.
Eukaryotic Cell Structure 7.2 Biology Mr. Hines Comparing the cell to a factory In order for a cell to maintain its internal environment (homeostasis), many things must go on. This is similar to a factory.
Know how to read a balance, graduated cylinder, ruler. Know the SI unit of each measurement.
 Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2012-2013 Due the day of your final for a maximum of 5 extra credit points. You will be able to use this review on your exam for 15 minutes! Safety and Lab Measurement:
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2012-2013 Due the day of your final for a maximum of 5 extra credit points. You will be able to use this review on your exam for 15 minutes! Safety and Lab Measurement:
Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards
 Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students
Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students
Frequent Subsequence-based Protein Localization
 Submitted to ICDM 05 - Paper ID #.. Frequent Subsequence-based Protein Localization Yang Wang, Osmar R. Zaïane, and Randy Goebel University of Alberta wyang, zaiane, goebel @cs.ualberta.ca Abstract Extracellular
Submitted to ICDM 05 - Paper ID #.. Frequent Subsequence-based Protein Localization Yang Wang, Osmar R. Zaïane, and Randy Goebel University of Alberta wyang, zaiane, goebel @cs.ualberta.ca Abstract Extracellular
Biology Exam #1 Study Guide. True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. F 1. All living things are composed of many cells.
 Biology Exam #1 Study Guide True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. F 1. All living things are composed of many cells. T 2. Membranes are selectively permeable if they allow only certain
Biology Exam #1 Study Guide True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. F 1. All living things are composed of many cells. T 2. Membranes are selectively permeable if they allow only certain
3.2 Cell Organelles. KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities.
 KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
Just Print Science. Pack
 Just Print Science Pack Plant and Animal Cells Jennifer Findley Note to Teacher This resource includes several resources for teaching and reviewing plant and animal cells. The resource includes a one-page
Just Print Science Pack Plant and Animal Cells Jennifer Findley Note to Teacher This resource includes several resources for teaching and reviewing plant and animal cells. The resource includes a one-page
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote Eukaryotes animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria 1-10 microns eukaryotic
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote Eukaryotes animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria 1-10 microns eukaryotic
Chapter 7.2. Cell Structure
 Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Exam 1-6 Review Homework Answer the following in complete sentences.
 Exam 1-6 Review Homework Answer the following in complete sentences. 1. Explain the relationship between enzymes and activation energy. (Clue: How are enzymes and activation energy related?) http://raeonscience.weebly.com/enzymes.html
Exam 1-6 Review Homework Answer the following in complete sentences. 1. Explain the relationship between enzymes and activation energy. (Clue: How are enzymes and activation energy related?) http://raeonscience.weebly.com/enzymes.html
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
 Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Function and Illustration. Nucleus. Nucleolus. Cell membrane. Cell wall. Capsule. Mitochondrion
 Intro to Organelles Name: Block: Organelles are small structures inside cells. They are often covered in membranes. Each organelle has a job to do in the cell. Their name means little organ. Just like
Intro to Organelles Name: Block: Organelles are small structures inside cells. They are often covered in membranes. Each organelle has a job to do in the cell. Their name means little organ. Just like
Exam: Introduction to Cells and Cell Function
 Name: Date: Exam: Introduction to Cells and Cell Function Georgia Performance Standard SB1: Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. 1. What
Name: Date: Exam: Introduction to Cells and Cell Function Georgia Performance Standard SB1: Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. 1. What
Prediction of human protein subcellular localization using deep learning
 Accepted Manuscript Prediction of human protein subcellular localization using deep learning Leyi Wei, Yijie Ding, Ran Su, Jijun Tang, Quan Zou PII: S0743-7315(17)30239-3 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2017.08.009
Accepted Manuscript Prediction of human protein subcellular localization using deep learning Leyi Wei, Yijie Ding, Ran Su, Jijun Tang, Quan Zou PII: S0743-7315(17)30239-3 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2017.08.009
Truncated Profile Hidden Markov Models
 Boise State University ScholarWorks Electrical and Computer Engineering Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 11-1-2005 Truncated Profile Hidden Markov
Boise State University ScholarWorks Electrical and Computer Engineering Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 11-1-2005 Truncated Profile Hidden Markov
ProtoNet 4.0: A hierarchical classification of one million protein sequences
 ProtoNet 4.0: A hierarchical classification of one million protein sequences Noam Kaplan 1*, Ori Sasson 2, Uri Inbar 2, Moriah Friedlich 2, Menachem Fromer 2, Hillel Fleischer 2, Elon Portugaly 2, Nathan
ProtoNet 4.0: A hierarchical classification of one million protein sequences Noam Kaplan 1*, Ori Sasson 2, Uri Inbar 2, Moriah Friedlich 2, Menachem Fromer 2, Hillel Fleischer 2, Elon Portugaly 2, Nathan
PREDICTING HUMAN AND ANIMAL PROTEIN SUBCELLULAR LOCATION. Sepideh Khavari
 PREDICTING HUMAN AND ANIMAL PROTEIN SUBCELLULAR LOCATION by Sepideh Khavari Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE in the Department of Mathematics and
PREDICTING HUMAN AND ANIMAL PROTEIN SUBCELLULAR LOCATION by Sepideh Khavari Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE in the Department of Mathematics and
Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018
 Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Biology 160 Cell Lab. Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm. Student Learning Outcomes:
 Biology 160 Cell Lab Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm Student Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of today s lab you will be able to do the following: Properly use a compound light microscope Discuss the
Biology 160 Cell Lab Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm Student Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of today s lab you will be able to do the following: Properly use a compound light microscope Discuss the
Chapter 4. Table of Contents. Section 1 The History of Cell Biology. Section 2 Introduction to Cells. Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features
 Cell Structure and Function Table of Contents Section 1 The History of Cell Biology Section 2 Introduction to Cells Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features Section 4 Unique Features of Plant Cells Section
Cell Structure and Function Table of Contents Section 1 The History of Cell Biology Section 2 Introduction to Cells Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features Section 4 Unique Features of Plant Cells Section
Protein subcellular location prediction
 Protein Engineering vol.12 no.2 pp.107 118, 1999 Protein subcellular location prediction Kuo-Chen Chou 1 and David W.Elrod Computer-Aided Drug Discovery, Pharmacia & Upjohn, Kalamazoo, MI 49007-4940, USA
Protein Engineering vol.12 no.2 pp.107 118, 1999 Protein subcellular location prediction Kuo-Chen Chou 1 and David W.Elrod Computer-Aided Drug Discovery, Pharmacia & Upjohn, Kalamazoo, MI 49007-4940, USA
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from p. 93-121, mostly skimming Concept 6.1 on microscopy. Figure 6.8 on pp. 100-101 is really helpful in showing
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from p. 93-121, mostly skimming Concept 6.1 on microscopy. Figure 6.8 on pp. 100-101 is really helpful in showing
Biology Cell Test. Name: Class: Date: ID: A. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: Biology Cell Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1, Who. wasone of the first people to-identify and seecorkeells? -,- ; -...
Class: Date: Biology Cell Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1, Who. wasone of the first people to-identify and seecorkeells? -,- ; -...
Biochemistry: A Review and Introduction
 Biochemistry: A Review and Introduction CHAPTER 1 Chem 40/ Chem 35/ Fundamentals of 1 Outline: I. Essence of Biochemistry II. Essential Elements for Living Systems III. Classes of Organic Compounds IV.
Biochemistry: A Review and Introduction CHAPTER 1 Chem 40/ Chem 35/ Fundamentals of 1 Outline: I. Essence of Biochemistry II. Essential Elements for Living Systems III. Classes of Organic Compounds IV.
Cell-ebrate Cells Cell Structure & Function Notes. April 11, 2017
 Cell-ebrate Cells Cell Structure & Notes April 11, 2017 Warm-Up: Tuesday True or False? True Cells can only come from other cells Today we are Learning: I can describe that cells are the basic unit of
Cell-ebrate Cells Cell Structure & Notes April 11, 2017 Warm-Up: Tuesday True or False? True Cells can only come from other cells Today we are Learning: I can describe that cells are the basic unit of
From the Bioinformatics Centre, Institute of Microbial Technology, Sector 39A, Chandigarh, India
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 280, No.??, Issue of??????, pp. 1 xxx, 2005 2005 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. AQ: A Support Vector Machine-based
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 280, No.??, Issue of??????, pp. 1 xxx, 2005 2005 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. AQ: A Support Vector Machine-based
Cell Structure and Function How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive?
 Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic. Record
Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic. Record
The Cell. The basic unit of all living things
 The Cell The basic unit of all living things 1 Robert Hooke was the first to name the cell (1665) 2 The Cell Theory The cell is the unit of Structure of all living things. The cell is the unit of Function
The Cell The basic unit of all living things 1 Robert Hooke was the first to name the cell (1665) 2 The Cell Theory The cell is the unit of Structure of all living things. The cell is the unit of Function
Learning Classifiers from Only Positive and Unlabeled Data
 Learning Classifiers from Only Positive and Unlabeled Data Charles Elkan Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093-0404 elkan@cs.ucsd.edu Keith Noto Computer
Learning Classifiers from Only Positive and Unlabeled Data Charles Elkan Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093-0404 elkan@cs.ucsd.edu Keith Noto Computer
02/02/ Living things are organized. Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures. Learning Outcome B1
 Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
The Cell. What is a cell?
 The Cell What is a cell? The Cell What is a cell? Structure which makes up living organisms. The Cell Theory l All living things are composed of cells. l Cells are the basic unit of life. l Cells come
The Cell What is a cell? The Cell What is a cell? Structure which makes up living organisms. The Cell Theory l All living things are composed of cells. l Cells are the basic unit of life. l Cells come
Biology Cell Organelle Webquest. Name Period Date
 Biology Cell Organelle Webquest Name Period Date This webquest has TWO parts to it. You need to go to www.rodensclassroom.com and click on the "BIOLOGY" link. Once there click on the Unit 3-Cell Organelles
Biology Cell Organelle Webquest Name Period Date This webquest has TWO parts to it. You need to go to www.rodensclassroom.com and click on the "BIOLOGY" link. Once there click on the Unit 3-Cell Organelles
Unit 4: Cells. Biology 309/310. Name: Review Guide
 Unit 4: Cells Review Guide LEARNING TARGETS Place a checkmark next to the learning targets you feel confident on. Then go back and focus on the learning targets that are not checked. Identify the parts
Unit 4: Cells Review Guide LEARNING TARGETS Place a checkmark next to the learning targets you feel confident on. Then go back and focus on the learning targets that are not checked. Identify the parts
Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
 Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were
Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were
Biology. Mrs. Michaelsen. Types of cells. Cells & Cell Organelles. Cell size comparison. The Cell. Doing Life s Work. Hooke first viewed cork 1600 s
 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Clicker Question. Clicker Question
 Which organelle provides a cell with protection? A. Mitochondria B. Cell membrane C. Nucleus D. Chloroplast This organelle uses sunlight in order to make glucose. A. Chloroplast B. Mitochondria C. Golgi
Which organelle provides a cell with protection? A. Mitochondria B. Cell membrane C. Nucleus D. Chloroplast This organelle uses sunlight in order to make glucose. A. Chloroplast B. Mitochondria C. Golgi
Now starts the fun stuff Cell structure and function
 Now starts the fun stuff Cell structure and function Cell Theory The three statements of the cell theory are: All organisms are composed of one or more cells and the processes of life occur in these cells.
Now starts the fun stuff Cell structure and function Cell Theory The three statements of the cell theory are: All organisms are composed of one or more cells and the processes of life occur in these cells.
Unicellular Marine Organisms. Chapter 4
 Unicellular Marine Organisms Chapter 4 The Cellular Structure of Life: Review Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists;
Unicellular Marine Organisms Chapter 4 The Cellular Structure of Life: Review Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists;
PA-GOSUB: A Searchable Database of Model Organism Protein Sequences With Their Predicted GO Molecular Function and Subcellular Localization
 PA-GOSUB: A Searchable Database of Model Organism Protein Sequences With Their Predicted GO Molecular Function and Subcellular Localization Paul Lu, Duane Szafron, Russell Greiner, David S. Wishart, Alona
PA-GOSUB: A Searchable Database of Model Organism Protein Sequences With Their Predicted GO Molecular Function and Subcellular Localization Paul Lu, Duane Szafron, Russell Greiner, David S. Wishart, Alona
Biology A level induction
 1 Biology A level induction work Name: 2 Summer Induction work Year 12 Biology When you start biology in September you will have two teachers for three lessons each. Each teacher will cover a different
1 Biology A level induction work Name: 2 Summer Induction work Year 12 Biology When you start biology in September you will have two teachers for three lessons each. Each teacher will cover a different
Name Hour. Section 7-1 Life Is Cellular (pages )
 Name Hour Section 7-1 Life Is Cellular (pages 169-173) Introduction (page 169) 1. What is the structure that makes up every living thing? The Discovery of the Cell (pages 169-170) 2. What was Anton van
Name Hour Section 7-1 Life Is Cellular (pages 169-173) Introduction (page 169) 1. What is the structure that makes up every living thing? The Discovery of the Cell (pages 169-170) 2. What was Anton van
1. Looking at the data above, what was the questions that was being tested?
 UCS BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE FOR 1 ST SEMESTER MIDTERM EXAM 2017-2018 CHAPTER 1 Use the data table and graph below to answer the 7 questions that follow. 1. Looking at the data above, what was the questions
UCS BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE FOR 1 ST SEMESTER MIDTERM EXAM 2017-2018 CHAPTER 1 Use the data table and graph below to answer the 7 questions that follow. 1. Looking at the data above, what was the questions
Chapter 1. DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d
 Chapter 1 1. Matching Questions DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d 2. Matching Questions : Unbranched polymer that, when folded into its three-dimensional shape,
Chapter 1 1. Matching Questions DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d 2. Matching Questions : Unbranched polymer that, when folded into its three-dimensional shape,
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms. Section 2: Inside Cells
 Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 2: 42 Essential Question: Are all cells the same? - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Organelle Plant Cell Animal Cell Chloroplast
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 2: 42 Essential Question: Are all cells the same? - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Organelle Plant Cell Animal Cell Chloroplast
Introduction to Bioinformatics Online Course: IBT
 Introduction to Bioinformatics Online Course: IBT Multiple Sequence Alignment Building Multiple Sequence Alignment Lec1 Building a Multiple Sequence Alignment Learning Outcomes 1- Understanding Why multiple
Introduction to Bioinformatics Online Course: IBT Multiple Sequence Alignment Building Multiple Sequence Alignment Lec1 Building a Multiple Sequence Alignment Learning Outcomes 1- Understanding Why multiple
Prediction of the subcellular location of apoptosis proteins based on approximate entropy
 Prediction of the subcellular location of apoptosis proteins based on approximate entropy Chaohong Song Feng Shi* Corresponding author Xuan Ma College of Science, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan,
Prediction of the subcellular location of apoptosis proteins based on approximate entropy Chaohong Song Feng Shi* Corresponding author Xuan Ma College of Science, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan,
Chapter 4: Cells: The Working Units of Life
 Name Period Chapter 4: Cells: The Working Units of Life 1. What are the three critical components of the cell theory? 2. What are the two important conceptual implications of the cell theory? 3. Which
Name Period Chapter 4: Cells: The Working Units of Life 1. What are the three critical components of the cell theory? 2. What are the two important conceptual implications of the cell theory? 3. Which
Biology. Introduction to Cells. Tuesday, February 9, 16
 Biology Introduction to Cells Biology Biology is the study of life. In Biology, we are going to start small (the cell) and end with explaining a larger system (organisms) How small? http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/
Biology Introduction to Cells Biology Biology is the study of life. In Biology, we are going to start small (the cell) and end with explaining a larger system (organisms) How small? http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/
Synteny Portal Documentation
 Synteny Portal Documentation Synteny Portal is a web application portal for visualizing, browsing, searching and building synteny blocks. Synteny Portal provides four main web applications: SynCircos,
Synteny Portal Documentation Synteny Portal is a web application portal for visualizing, browsing, searching and building synteny blocks. Synteny Portal provides four main web applications: SynCircos,
EUBACTERIA CYTOLOGY CHLOROPLAST: ABSENT RIBOSOME CAPSULE CELL WALL PROTOPLAST CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOID MESOSOME CYTOSOL FLAGELLA
 EUBACTERIA CYTOLOGY * PERIFERAL MEMBRANE BOND ORGANELLES ABSENT RIBOSOME CAPSULE PROTOPLAST CELL WALL CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOID CYTOSOL MESOSOME FLAGELLA CHLOROPLAST: ABSENT ^ MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES ABSENT
EUBACTERIA CYTOLOGY * PERIFERAL MEMBRANE BOND ORGANELLES ABSENT RIBOSOME CAPSULE PROTOPLAST CELL WALL CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOID CYTOSOL MESOSOME FLAGELLA CHLOROPLAST: ABSENT ^ MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES ABSENT
Components of a functional cell. Boundary-membrane Cytoplasm: Cytosol (soluble components) & particulates DNA-information Ribosomes-protein synthesis
 Cell (Outline) - Components of a functional cell - Major Events in the History of Earth: abiotic and biotic phases; anaerobic and aerobic atmosphere - Prokaryotic cells impact on the biosphere - Origin
Cell (Outline) - Components of a functional cell - Major Events in the History of Earth: abiotic and biotic phases; anaerobic and aerobic atmosphere - Prokaryotic cells impact on the biosphere - Origin
Term Generalization and Synonym Resolution for Biological Abstracts: Using the Gene Ontology for Subcellular Localization Prediction
 Term Generalization and Synonym Resolution for Biological Abstracts: Using the Gene Ontology for Subcellular Localization Prediction Alona Fyshe Department of Computing Science University of Alberta Edmonton,
Term Generalization and Synonym Resolution for Biological Abstracts: Using the Gene Ontology for Subcellular Localization Prediction Alona Fyshe Department of Computing Science University of Alberta Edmonton,
Fast and accurate semi-supervised protein homology detection with large uncurated sequence databases
 Rutgers Computer Science Technical Report RU-DCS-TR634 May 2008 Fast and accurate semi-supervised protein homology detection with large uncurated sequence databases by Pai-Hsi Huang, Pavel Kuksa, Vladimir
Rutgers Computer Science Technical Report RU-DCS-TR634 May 2008 Fast and accurate semi-supervised protein homology detection with large uncurated sequence databases by Pai-Hsi Huang, Pavel Kuksa, Vladimir
Cell Organelles. Wednesday, October 22, 14
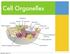 Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Chapter 4 Active Reading Guide A Tour of the Cell
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 4 Active Reading Guide A Tour of the Cell Section 1 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 4 Active Reading Guide A Tour of the Cell Section 1 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when
Cells. Structural and functional units of living organisms
 Cells Structural and functional units of living organisms Eukaryotic ( true nucleus ) vs. Prokaryotic ( before nucleus ) cells Proks Eukaryotic ( true nucleus ) vs. Prokaryotic ( before nucleus ) cells
Cells Structural and functional units of living organisms Eukaryotic ( true nucleus ) vs. Prokaryotic ( before nucleus ) cells Proks Eukaryotic ( true nucleus ) vs. Prokaryotic ( before nucleus ) cells
Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Organelles in Animal & Plant Cells Why are organelles important and how are plants and animals different?
 Why? Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Organelles in Animal & Plant Cells Why are organelles important and how are plants and animals different? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things.
Why? Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Organelles in Animal & Plant Cells Why are organelles important and how are plants and animals different? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things.
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Biology Summer Assignments
 Biology Summer Assignments Welcome Mustangs! The following summer assignments are to assist you in obtaining background information for topics we will be learning during 1 st quarter, in Biology. Please
Biology Summer Assignments Welcome Mustangs! The following summer assignments are to assist you in obtaining background information for topics we will be learning during 1 st quarter, in Biology. Please
Unit 7: Cells and Life
 Unit 7: Cells and Life Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Due Date VIRUS vs CELLS CHECKLIST 3 Warm-ups 4-5 Virus Notes 6-7 Viral Reproduction Notes 8 Viruses VS Cells
Unit 7: Cells and Life Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Due Date VIRUS vs CELLS CHECKLIST 3 Warm-ups 4-5 Virus Notes 6-7 Viral Reproduction Notes 8 Viruses VS Cells
Essential Question: How do the parts of a cell work together to function as a system?
 Topic: Cell Organelles Essential Question: How do the parts of a cell work together to function as a system? All those who believe in psychokinesis raise my hand. -Steven Wright 9/16/14 INB page 12-13
Topic: Cell Organelles Essential Question: How do the parts of a cell work together to function as a system? All those who believe in psychokinesis raise my hand. -Steven Wright 9/16/14 INB page 12-13
PROTEIN FUNCTION PREDICTION WITH AMINO ACID SEQUENCE AND SECONDARY STRUCTURE ALIGNMENT SCORES
 PROTEIN FUNCTION PREDICTION WITH AMINO ACID SEQUENCE AND SECONDARY STRUCTURE ALIGNMENT SCORES Eser Aygün 1, Caner Kömürlü 2, Zafer Aydin 3 and Zehra Çataltepe 1 1 Computer Engineering Department and 2
PROTEIN FUNCTION PREDICTION WITH AMINO ACID SEQUENCE AND SECONDARY STRUCTURE ALIGNMENT SCORES Eser Aygün 1, Caner Kömürlü 2, Zafer Aydin 3 and Zehra Çataltepe 1 1 Computer Engineering Department and 2
Cell (Learning Objectives)
 Cell (Learning Objectives) 1. Understand & describe the basic components necessary for a functional cell. 2. Review the order of appearance of cells on earth and explain the endosymbiotic theory. 3. Compare
Cell (Learning Objectives) 1. Understand & describe the basic components necessary for a functional cell. 2. Review the order of appearance of cells on earth and explain the endosymbiotic theory. 3. Compare
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 4-1 The History of Cell Biology
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 4-1 The History of Cell Biology Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. One early piece of evidence supporting the cell theory was the observation
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 4-1 The History of Cell Biology Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. One early piece of evidence supporting the cell theory was the observation
Cell Theory. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century!
 Cell Notes Cell Theory All living organisms are made of. cells The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century! In 1665,
Cell Notes Cell Theory All living organisms are made of. cells The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century! In 1665,
