Structure of the quaternary complex between SRP, SR, and translocon bound to the translating ribosome
|
|
|
- Kenneth Sanders
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Structure of the quaternary complex between SRP, SR, and translocon bound to the translating ribosome Ahmad Jomaa 1, Yu-Hsien Hwang Fu 2, Daniel Boehringer 1, Marc Leibundgut 1, Shu-ou Shan 2, and Nenad Ban 1 * 1 Department of Biology, Institute of Molecular Biology and Biophysics, Otto-Stern-Weg 5, ETH Zurich, CH-8093, Switzerland 2 Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA *Correspondence to: ban@mol.biol.ethz.ch Supplementary Information:
2 Supplementary Figure 1: Assembly of the RNC-SRP-SR-Sec translocon quaternary complex. Purified components were mixed in 1:5:5:5 molar rations as described (Material and Methods) and incubated for 30 minutes at 25 C in the presence of either GMPPNP or GDP:AlFx before applying the sample on a 40% (w/v) sucrose cushion and pelleting by ultra-centrifugation. a, Pellets were resuspended in Buffer B, resolved by 12% SDS PAGE, and stained by Comassie brilliant blue. b, Supernatant fraction of lane 2 in Panel a was resolved separately by SDS PAGE as a control. In the presence of GTP analogues (GMPPNP or GDP:AlFx), we observe stoichiometric binding of all components of the quaternary complex.
3
4 Supplementary Figure 2: 2D and 3D classification and refinement scheme. A total of 1,029,950 particles of the reaction containing RNC 1A9L -85, SRP, SR, and Sec translocon assembled in the presence of GDP:AlFx were semi-automatically picked with BOXER in the EMAN package. Two-dimensional classification (ML2D) was performed for 30 iterations using RELION on 4-fold binned images (80x80 pixels) with a sampling of 5.56 Å/pixel. 791,642 particles from good 2D class averages were retained and refined with an empty 70S model low-pass filtered to 60 Å resolution. Initial focused classification was performed for 30 iterations with the skip-align option and by applying a circular mask on the polypeptide exit tunnel region. Selected classes were then refined using information up to Nyquist frequency with a sampling of 1.39 Å/pixel. 121,952 particles (16%) depicted a quaternary complex with the kinked RNA structure and a density for the detergent embedded translocon, and were refined to 3.8 Å resolution. To improve the density of the translocon, an additional round of focused classification using the skipalign option was performed by applying a mask on the SRP distal region and the translocon and excluding the ribosome and the SRP M-domain regions. Further local classification was then performed using the signal subtraction approach implemented in RELION 1 by subtracting the signal of the ribosome. This was followed by a focused refinement to 4.8 Å of the particles by masking out the small ribosomal subunit. The resolution was determined based on the gold standard FSC (0.143 criterion).
5
6 Supplementary Figure 3: Local resolution estimation and Fourier shell correlation plot of the cryo-em map of the quaternary complex. a, Representative cryo-em micrograph of the assembled reaction containing SRP, SR, Sec translocon and RNC assembled in the presence of GDP:AlFx. b, Corresponding Thon rings extending to 4.5 Å resolution. c, Representative 2D class averages obtained after running 30 cycles of maximum-likelihood classification. d and e, Unsharpened cryo-em map of the quaternary complex colored based on local resolution calculated using ResMap 2. The resolution extends to better than 4 Å in the core of the ribosome. The local resolution of the NG-heterodimer is ~7 Å, of the M-domain ~5 Å, and of the Sec translocon ~7-10 Å. f, Close-up view of the SRP RNA and the M-domain (SRP core) bound to the ribosome with resolved protein α helices of the M-domain and the signal sequence (SS). g, Fourier shell correlation curves for the full two half maps (black), masked half maps by masking the area of the SRP-SR-Sec translocon and excluding the ribosome (green), and map versus model (blue) are shown. Resolutions of the full map and of the map area masked around the factors were estimated according to the gold standard FSC=0.143 criterion as implemented in RELION. The resolution of the model versus map was estimated based on the FSC=0.5 criterion.
7
8 Supplementary Figure 4: Conformation of the SRP RNA in the quaternary complex. a and b, Close-up views of the SRP-SR NG heterodimer in the activated state solved in the presence of the transition state analogue (GDP:AlFx; this study) and the SRP-SR in the closed state solved in the presence of the non-hydrolysable GTP analogue (GMPPNP; EMDB-8003). Atomic model of the NG-heterodimer in Panel b was generated by docking the x-ray structure of SRP-SR at the distal site (PDB:2XXA) into the EM map (EMDB-8003) and by using the M-domain as a reference (PDB: 5GAG). c, Close-up view of the GM-linker region shown at lower contour level (1.5 σ). Cryo-EM densities were filtered to 6 Å for clarity. d and e, Overlay of the atomic models in Panels a and b. Coordinates of the closed complex are colored gray. f, Sequence alignment of the NGloop depicts the sequence conservation in bacterial systems and was produced using the ClustalW WebServer 3,4.
9 Supplementary Figure 5: Secondary structure diagrams of SRP RNA from different organisms. a, Schematic and nomenclature of all SRP RNAs 5. Secondary structure of SRP RNA from a, Escherichia coli, b, Bacillus subtilis, c, Methanocaldococcus jannaschi, d, and Homo sapiens, e. RNA secondary structure diagrams were downloaded from the SRP database ( Circled regions indicate the hinge region observed in this study, also known as C- and E-loops, where the SRP RNA is kinked and untwisted, respectively.
10 Supplementary Figure 6: Orientation of the observed Sec translocon relative to the membrane. a, Cross-section of the unsharpened EM-density map of the quaternary complex showing secondary structural elements of the Sec translocon within the unstructured detergent micelle. b and c, Cut-through snapshots of the Sec translocon into the EM-density filtered to 8 Å with the homology model based on the x-ray coordinates of the isolated SecYEG (PDB:5CH4) docked as a rigid body (red). d, The proposed 20 tilt in the position of the translocon to prevent clashes with SRP and SR. The plane of the membrane is shown schematically as resolved in the structures of the native Sec translocon 6 or in nano-discs 7 bound at the ribosomal exit tunnel.
11 Supplementary Figure 7: Position of the A-domain of SR in the quaternary complex. a, Snapshot of the cryo-em density of the quaternary complex with fitted atomic coordinates. b and c, Close-up view of the circled area in Panel a, filtered to 20 Å and displayed at high and low density thresholds. Densities of the Sec translocon, SRP, and A-domain and NG-domain of SR are indicated. The surface of the ribosome is removed for clarity.
12 Supplementary Figure 8: Cryo-EM analysis of the RNC 1A9L -135 in the presence of the SRP, SR, Sec translocon and GDP:AlFx. The dataset was subjected to a similar processing approach as described in Extended Data Figure 2. Only subclasses of the focused 3D classification with recognizable features of either SRP, SR, or Sec translocon are shown. EMDB-8001 is filtered to a similar resolution as the final reconstruction for comparison.
13 DATA COLLECTION 50S-SRP-SR-SecYEG (SRP-SR-SecYEG) Final number of Particles 13,926 Pixel size (Å) 1.39 Defocus range (μm) Voltage (kv) 300 Electron does (e - Å -2 ) 20 Model Refinement Refinement Resolution (Å) 4.8 (8.4) Map Sharpening B-factor (Å 2 ) -218 Average B-factor (Å 2 ) 280 R.m.s deviations Bond length (Å) Bond angles ( o ) VALIDATION STATISTICS Validation Molprobity Score 2.35 (2.53) Clashscore, all atoms 8.37 (16.6) Good rotamers (%) 91.5 (91.3) Ramachandran Plot Favored (%) 96.8 (94.7) Allowed (%) 3.1 (4.44) Outliers(%) 0.08 (0.86) Validation (RNA) Correct sugar puckers (%) 99.5 (98.1) Good backbone conformation (%) 82.2 (71.2) Supplementary Table 1. Model and refinement statistics
14 COMPONENT CHAIN ID SOURCE COMMENT SRP RNA (distal site) 1 PDB ID 4C7O Fitted as a rigid model SRP RNA (core) 1 PDB ID 5GAG Fitted as a rigid model SRP RNA (kinked region) (res. 28:44, 70:80) 1 - Modeled Ffh (M-domain) i PDB ID 5GAG Fitted as a rigid model Ffh (NG-domain) i PDB ID 4C7O Fitted as a rigid model Ffh (GM-linker) i PDB ID 2XXA Fitted as a rigid model FtsY (NG-domain) l PDB ID 4C7O Fitted as a rigid model Signal sequence k - Modeled SecY g PDB ID 5CH4 Homology model SecE h PDB ID 5CH4 Homology model SecG j PDB ID 5CH4 Homology model 50S - PDB ID 5GAG Fitted as a rigid body Supplementary Table 2. Components of the final model used for rigid body docking and modeling
15 Region Chain ID Resolution (ResMap) SRP protein M- domain i (res ) 6.5 Signal sequence k 6.7 SRP protein NG- domain i (res ) 8.0 SRP RNA SR NG- domain l 9.2 SecYEG g,h,j 9.5 Supplementary Table 3. Local- resolution based on the atom position of the fitted model
16 References 1. Bai, X.C., Rajendra, E., Yang, G., Shi, Y. & Scheres, S.H. Sampling the conformational space of the catalytic subunit of human gamma-secretase. Elife 4(2015). 2. Kucukelbir, A., Sigworth, F.J. & Tagare, H.D. Quantifying the local resolution of cryo-em density maps. Nat Methods 11, 63-5 (2014). 3. Larkin, M.A. et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23, (2007). 4. Goujon, M. et al. A new bioinformatics analysis tools framework at EMBL-EBI. Nucleic Acids Res 38, W695-9 (2010). 5. Zwieb, C., van Nues, R.W., Rosenblad, M.A., Brown, J.D. & Samuelsson, T. A nomenclature for all signal recognition particle RNAs. RNA 11, 7-13 (2005). 6. Pfeffer, S. et al. Structure of the native Sec61 protein-conducting channel. Nat Commun 6, 8403 (2015). 7. Frauenfeld, J. et al. Cryo-EM structure of the ribosome-secye complex in the membrane environment. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18, (2011).
Cryo-EM data collection, refinement and validation statistics
 1 Table S1 Cryo-EM data collection, refinement and validation statistics Data collection and processing CPSF-160 WDR33 (EMDB-7114) (PDB 6BM0) CPSF-160 WDR33 (EMDB-7113) (PDB 6BLY) CPSF-160 WDR33 CPSF-30
1 Table S1 Cryo-EM data collection, refinement and validation statistics Data collection and processing CPSF-160 WDR33 (EMDB-7114) (PDB 6BM0) CPSF-160 WDR33 (EMDB-7113) (PDB 6BLY) CPSF-160 WDR33 CPSF-30
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/310/5753/1513/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Structural Roles for Human Translation Factor eif3 in Initiation of Protein Synthesis Bunpote Siridechadilok, Christopher
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/310/5753/1513/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Structural Roles for Human Translation Factor eif3 in Initiation of Protein Synthesis Bunpote Siridechadilok, Christopher
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLMTARY IFORMATIO a doi:10.108/nature10402 b 100 nm 100 nm c SAXS Model d ulers assigned to reference- Back-projected free class averages class averages Refinement against single particles Reconstructed
SUPPLMTARY IFORMATIO a doi:10.108/nature10402 b 100 nm 100 nm c SAXS Model d ulers assigned to reference- Back-projected free class averages class averages Refinement against single particles Reconstructed
Translocation through the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Institute of Biochemistry Benoît Kornmann
 Translocation through the endoplasmic reticulum membrane Institute of Biochemistry Benoît Kornmann Endomembrane system Protein sorting Permeable to proteins but not to ions IgG tetramer (16 nm) Fully hydrated
Translocation through the endoplasmic reticulum membrane Institute of Biochemistry Benoît Kornmann Endomembrane system Protein sorting Permeable to proteins but not to ions IgG tetramer (16 nm) Fully hydrated
Supplementary Information: Long range allosteric regulation of the human 26S proteasome by 20S proteasome-targeting cancer drugs
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Information: Long range allosteric regulation of the human 26S proteasome by 20S proteasome-targeting cancer drugs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Information: Long range allosteric regulation of the human 26S proteasome by 20S proteasome-targeting cancer drugs
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cryo-EM structure and model of the C. thermophilum 90S preribosome. a, Gold standard FSC curve showing the average resolution of the 90S preribosome masked and unmasked (left). FSC
Supplementary Figure 1 Cryo-EM structure and model of the C. thermophilum 90S preribosome. a, Gold standard FSC curve showing the average resolution of the 90S preribosome masked and unmasked (left). FSC
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of the ScDcp2 minimal region interacting with both ScDcp1 and the ScEdc3 LSm domain. Pull-down experiment of untagged ScEdc3 LSm with various ScDcp1-Dcp2-His 6 fragments.
Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of the ScDcp2 minimal region interacting with both ScDcp1 and the ScEdc3 LSm domain. Pull-down experiment of untagged ScEdc3 LSm with various ScDcp1-Dcp2-His 6 fragments.
Tools for Cryo-EM Map Fitting. Paul Emsley MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology
 Tools for Cryo-EM Map Fitting Paul Emsley MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology April 2017 Cryo-EM model-building typically need to move more atoms that one does for crystallography the maps are lower resolution
Tools for Cryo-EM Map Fitting Paul Emsley MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology April 2017 Cryo-EM model-building typically need to move more atoms that one does for crystallography the maps are lower resolution
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12045 Supplementary Table 1 Data collection and refinement statistics. Native Pt-SAD X-ray source SSRF BL17U SPring-8 BL41XU Wavelength (Å) 0.97947 1.07171 Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2
doi:10.1038/nature12045 Supplementary Table 1 Data collection and refinement statistics. Native Pt-SAD X-ray source SSRF BL17U SPring-8 BL41XU Wavelength (Å) 0.97947 1.07171 Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2
Spliceosome and Localization of Its Catalytic Core
 Molecular Cell, Volume 40 Supplemental Information 3D Cryo-EM Structure of an Active Step I Spliceosome and Localization of Its Catalytic Core Monika M. Golas, Bjoern Sander, Sergey Bessonov, Michael Grote,
Molecular Cell, Volume 40 Supplemental Information 3D Cryo-EM Structure of an Active Step I Spliceosome and Localization of Its Catalytic Core Monika M. Golas, Bjoern Sander, Sergey Bessonov, Michael Grote,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES. Structure of the cholera toxin secretion channel in its. closed state
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Structure of the cholera toxin secretion channel in its closed state Steve L. Reichow 1,3, Konstantin V. Korotkov 1,3, Wim G. J. Hol 1$ and Tamir Gonen 1,2$ 1, Department of Biochemistry
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Structure of the cholera toxin secretion channel in its closed state Steve L. Reichow 1,3, Konstantin V. Korotkov 1,3, Wim G. J. Hol 1$ and Tamir Gonen 1,2$ 1, Department of Biochemistry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary materials Figure S1 Fusion protein of Sulfolobus solfataricus SRP54 and a signal peptide. a, Expression vector for the fusion protein. The signal peptide of yeast dipeptidyl aminopeptidase
Supplementary materials Figure S1 Fusion protein of Sulfolobus solfataricus SRP54 and a signal peptide. a, Expression vector for the fusion protein. The signal peptide of yeast dipeptidyl aminopeptidase
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
Purification, SDS-PAGE and cryo-em characterization of the MCM hexamer and Cdt1 MCM heptamer samples.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Purification, SDS-PAGE and cryo-em characterization of the MCM hexamer and Cdt1 MCM heptamer samples. (a-b) SDS-PAGE analysis of the hexamer and heptamer samples. The eluted hexamer
Supplementary Figure 1 Purification, SDS-PAGE and cryo-em characterization of the MCM hexamer and Cdt1 MCM heptamer samples. (a-b) SDS-PAGE analysis of the hexamer and heptamer samples. The eluted hexamer
ParM filament images were extracted and from the electron micrographs and
 Supplemental methods Outline of the EM reconstruction: ParM filament images were extracted and from the electron micrographs and straightened. The digitized images were corrected for the phase of the Contrast
Supplemental methods Outline of the EM reconstruction: ParM filament images were extracted and from the electron micrographs and straightened. The digitized images were corrected for the phase of the Contrast
Table S1. Overview of used PDZK1 constructs and their binding affinities to peptides. Related to figure 1.
 Table S1. Overview of used PDZK1 constructs and their binding affinities to peptides. Related to figure 1. PDZK1 constru cts Amino acids MW [kda] KD [μm] PEPT2-CT- FITC KD [μm] NHE3-CT- FITC KD [μm] PDZK1-CT-
Table S1. Overview of used PDZK1 constructs and their binding affinities to peptides. Related to figure 1. PDZK1 constru cts Amino acids MW [kda] KD [μm] PEPT2-CT- FITC KD [μm] NHE3-CT- FITC KD [μm] PDZK1-CT-
Table 1. Crystallographic data collection, phasing and refinement statistics. Native Hg soaked Mn soaked 1 Mn soaked 2
 Table 1. Crystallographic data collection, phasing and refinement statistics Native Hg soaked Mn soaked 1 Mn soaked 2 Data collection Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 Cell
Table 1. Crystallographic data collection, phasing and refinement statistics Native Hg soaked Mn soaked 1 Mn soaked 2 Data collection Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 Cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. doi: /nature07461
 Figure S1 Electrophysiology. a ph-activation of. Two-electrode voltage clamp recordings of Xenopus oocytes expressing in comparison to waterinjected oocytes. Currents were recorded at 40 mv. The ph of
Figure S1 Electrophysiology. a ph-activation of. Two-electrode voltage clamp recordings of Xenopus oocytes expressing in comparison to waterinjected oocytes. Currents were recorded at 40 mv. The ph of
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/6/e1700147/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Ribosome rearrangements at the onset of translational bypassing Xabier Agirrezabala, Ekaterina Samatova, Mariia Klimova,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/6/e1700147/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Ribosome rearrangements at the onset of translational bypassing Xabier Agirrezabala, Ekaterina Samatova, Mariia Klimova,
MCB 110. "Molecular Biology: Macromolecular Synthesis and Cellular Function" Spring, 2018
 MCB 110 "Molecular Biology: Macromolecular Synthesis and Cellular Function" Spring, 2018 Faculty Instructors: Prof. Jeremy Thorner Prof. Qiang Zhou Prof. Eva Nogales GSIs:!!!! Ms. Samantha Fernandez Mr.
MCB 110 "Molecular Biology: Macromolecular Synthesis and Cellular Function" Spring, 2018 Faculty Instructors: Prof. Jeremy Thorner Prof. Qiang Zhou Prof. Eva Nogales GSIs:!!!! Ms. Samantha Fernandez Mr.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1: Data collection, phasing and refinement statistics ChbC/Ta 6 Br 12 Native ChbC Data collection Space group P4 3 2 1 2 P4 3 2 1 2 Cell dimensions a, c (Å) 132.75, 453.57 132.81, 452.95
Supplementary Table 1: Data collection, phasing and refinement statistics ChbC/Ta 6 Br 12 Native ChbC Data collection Space group P4 3 2 1 2 P4 3 2 1 2 Cell dimensions a, c (Å) 132.75, 453.57 132.81, 452.95
 Supplemental Figure and Movie Legends Figure S1. Time course experiments on the thermal stability of apo AT cpn-α by native PAGE (related to Figure 2B). The samples were heated, respectively, to (A) 45
Supplemental Figure and Movie Legends Figure S1. Time course experiments on the thermal stability of apo AT cpn-α by native PAGE (related to Figure 2B). The samples were heated, respectively, to (A) 45
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11991 Supplementary Figure 1 - Refinement strategy for PIC intermediate assemblies by negative stain EM. The cryo-negative stain structure of free Pol II 1 (a) was used as initial reference
doi:10.1038/nature11991 Supplementary Figure 1 - Refinement strategy for PIC intermediate assemblies by negative stain EM. The cryo-negative stain structure of free Pol II 1 (a) was used as initial reference
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Protein sequence alignment of Vibrionaceae with either a 40-residue insertion or a 44-residue insertion. Identical residues are indicated by red background.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Protein sequence alignment of Vibrionaceae with either a 40-residue insertion or a 44-residue insertion. Identical residues are indicated by red background.
Introduction to Evolutionary Concepts
 Introduction to Evolutionary Concepts and VMD/MultiSeq - Part I Zaida (Zan) Luthey-Schulten Dept. Chemistry, Beckman Institute, Biophysics, Institute of Genomics Biology, & Physics NIH Workshop 2009 VMD/MultiSeq
Introduction to Evolutionary Concepts and VMD/MultiSeq - Part I Zaida (Zan) Luthey-Schulten Dept. Chemistry, Beckman Institute, Biophysics, Institute of Genomics Biology, & Physics NIH Workshop 2009 VMD/MultiSeq
A conserved P-loop anchor limits the structural dynamics that mediate. nucleotide dissociation in EF-Tu.
 Supplemental Material for A conserved P-loop anchor limits the structural dynamics that mediate nucleotide dissociation in EF-Tu. Evan Mercier 1,2, Dylan Girodat 1, and Hans-Joachim Wieden 1 * 1 Alberta
Supplemental Material for A conserved P-loop anchor limits the structural dynamics that mediate nucleotide dissociation in EF-Tu. Evan Mercier 1,2, Dylan Girodat 1, and Hans-Joachim Wieden 1 * 1 Alberta
Application examples of single particle 3D reconstruction. Ning Gao Tsinghua University
 Application examples of single particle 3D reconstruction Ning Gao Tsinghua University ninggao@tsinghua.edu.cn Electron Microscopes First electron microscope constructed by Ernst Ruska in 1930 s (1986
Application examples of single particle 3D reconstruction Ning Gao Tsinghua University ninggao@tsinghua.edu.cn Electron Microscopes First electron microscope constructed by Ernst Ruska in 1930 s (1986
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/309/5742/1868/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Toward High-Resolution de Novo Structure Prediction for Small Proteins Philip Bradley, Kira M. S. Misura, David Baker*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/309/5742/1868/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Toward High-Resolution de Novo Structure Prediction for Small Proteins Philip Bradley, Kira M. S. Misura, David Baker*
Three-dimensional structure of a viral genome-delivery portal vertex
 Three-dimensional structure of a viral genome-delivery portal vertex Adam S. Olia 1, Peter E. Prevelige Jr. 2, John E. Johnson 3 and Gino Cingolani 4 1 Department of Biological Sciences, Purdue University,
Three-dimensional structure of a viral genome-delivery portal vertex Adam S. Olia 1, Peter E. Prevelige Jr. 2, John E. Johnson 3 and Gino Cingolani 4 1 Department of Biological Sciences, Purdue University,
type GroEL-GroES complex. Crystals were grown in buffer D (100 mm HEPES, ph 7.5,
 Supplementary Material Supplementary Materials and Methods Structure Determination of SR1-GroES-ADP AlF x SR1-GroES-ADP AlF x was purified as described in Materials and Methods for the wild type GroEL-GroES
Supplementary Material Supplementary Materials and Methods Structure Determination of SR1-GroES-ADP AlF x SR1-GroES-ADP AlF x was purified as described in Materials and Methods for the wild type GroEL-GroES
The Biogenesis of E. coli Inner Membrane Proteins Dr. Joen Luirink
 The Biogenesis of E. coli Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, The Netherlands 1 Talk SRP-mediated targeting to the mammalian ER and to the bacterial inner membrane Insertion of membrane proteins at the Sec complex
The Biogenesis of E. coli Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, The Netherlands 1 Talk SRP-mediated targeting to the mammalian ER and to the bacterial inner membrane Insertion of membrane proteins at the Sec complex
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11539 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of plant (A) and mammalian (B) P 2B -ATPase domain organization. Actuator (A-), nucleotide binding (N-),
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11539 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of plant (A) and mammalian (B) P 2B -ATPase domain organization. Actuator (A-), nucleotide binding (N-),
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information The direct role of selenocysteine in [NiFeSe] hydrogenase maturation and catalysis Marta C. Marques a, Cristina Tapia b, Oscar Gutiérrez-Sanz b, Ana Raquel Ramos a, Kimberly L.
Supplementary Information The direct role of selenocysteine in [NiFeSe] hydrogenase maturation and catalysis Marta C. Marques a, Cristina Tapia b, Oscar Gutiérrez-Sanz b, Ana Raquel Ramos a, Kimberly L.
Full wwpdb/emdatabank EM Map/Model Validation Report i
 Full wwpdb/emdatabank EM Map/Model Validation Report i Sep 25, 2018 07:01 PM EDT PDB ID : 6C0V EMDB ID: : EMD-7325 Title : Molecular structure of human P-glycoprotein in the ATP-bound, outwardfacing conformation
Full wwpdb/emdatabank EM Map/Model Validation Report i Sep 25, 2018 07:01 PM EDT PDB ID : 6C0V EMDB ID: : EMD-7325 Title : Molecular structure of human P-glycoprotein in the ATP-bound, outwardfacing conformation
Model building and validation for cryo-em maps at low resolution
 International Workshop of Advanced Image Processing of Cryo-Electron Microscopy 2015 Tsinghua University, Beijing, China June 3-7, 2015 Model building and validation for cryo-em maps at low resolution
International Workshop of Advanced Image Processing of Cryo-Electron Microscopy 2015 Tsinghua University, Beijing, China June 3-7, 2015 Model building and validation for cryo-em maps at low resolution
Procheck output. Bond angles (Procheck) Structure verification and validation Bond lengths (Procheck) Introduction to Bioinformatics.
 Structure verification and validation Bond lengths (Procheck) Introduction to Bioinformatics Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu ----------------------------------------------------------------- Bond
Structure verification and validation Bond lengths (Procheck) Introduction to Bioinformatics Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu ----------------------------------------------------------------- Bond
Molecular Dynamics Flexible Fitting
 Molecular Dynamics Flexible Fitting Ryan McGreevy Research Programmer University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign NIH Resource for Macromolecular Modeling and Bioinformatics Molecular Dynamics Flexible
Molecular Dynamics Flexible Fitting Ryan McGreevy Research Programmer University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign NIH Resource for Macromolecular Modeling and Bioinformatics Molecular Dynamics Flexible
Image Assessment San Diego, November 2005
 Image Assessment San Diego, November 005 Pawel A. Penczek The University of Texas Houston Medical School Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 6431 Fannin, MSB6.18, Houston, TX 77030, USA phone:
Image Assessment San Diego, November 005 Pawel A. Penczek The University of Texas Houston Medical School Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 6431 Fannin, MSB6.18, Houston, TX 77030, USA phone:
Building a Homology Model of the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Glycine α-1 Receptor
 Building a Homology Model of the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Glycine α-1 Receptor Presented by Stephanie Lee Research Mentor: Dr. Rob Coalson Glycine Alpha 1 Receptor (GlyRa1) Member of the superfamily
Building a Homology Model of the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Glycine α-1 Receptor Presented by Stephanie Lee Research Mentor: Dr. Rob Coalson Glycine Alpha 1 Receptor (GlyRa1) Member of the superfamily
Homology Modeling (Comparative Structure Modeling) GBCB 5874: Problem Solving in GBCB
 Homology Modeling (Comparative Structure Modeling) Aims of Structural Genomics High-throughput 3D structure determination and analysis To determine or predict the 3D structures of all the proteins encoded
Homology Modeling (Comparative Structure Modeling) Aims of Structural Genomics High-throughput 3D structure determination and analysis To determine or predict the 3D structures of all the proteins encoded
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature17991 Supplementary Discussion Structural comparison with E. coli EmrE The DMT superfamily includes a wide variety of transporters with 4-10 TM segments 1. Since the subfamilies of the
doi:10.1038/nature17991 Supplementary Discussion Structural comparison with E. coli EmrE The DMT superfamily includes a wide variety of transporters with 4-10 TM segments 1. Since the subfamilies of the
Processing Heterogeneity
 New Challenges for Processing Heterogeneity Nikolaus Grigorieff Larson, The Far Side Heterogeneity and Biology Translocation, Brilot et al 2013 Glutamate receptor, Dürr et al 2014 Spliceosome, Wahl et
New Challenges for Processing Heterogeneity Nikolaus Grigorieff Larson, The Far Side Heterogeneity and Biology Translocation, Brilot et al 2013 Glutamate receptor, Dürr et al 2014 Spliceosome, Wahl et
Acta Crystallographica Section D
 Supporting information Acta Crystallographica Section D Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structural characterization of the virulence factor Nuclease A from Streptococcus agalactiae
Supporting information Acta Crystallographica Section D Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structural characterization of the virulence factor Nuclease A from Streptococcus agalactiae
Improving cryo-em maps: focused 2D & 3D classifications and focused refinements
 Improving cryo-em maps: focused 2D & 3D classifications and focused refinements 3rd International Symposium on Cryo-3D Image Analysis 23.3.2018, Tahoe Bruno Klaholz Centre for Integrative Biology, IGBMC,
Improving cryo-em maps: focused 2D & 3D classifications and focused refinements 3rd International Symposium on Cryo-3D Image Analysis 23.3.2018, Tahoe Bruno Klaholz Centre for Integrative Biology, IGBMC,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wilson et al. 10.1073/pnas.0804276105 Fig. S1. Sites of oxazolidinone resistance mutations in bacteria and archaea. (a) Secondary structure of the peptidyltransferase ring of the
Supporting Information Wilson et al. 10.1073/pnas.0804276105 Fig. S1. Sites of oxazolidinone resistance mutations in bacteria and archaea. (a) Secondary structure of the peptidyltransferase ring of the
Three-Dimensional Electron Microscopy of Macromolecular Assemblies
 Three-Dimensional Electron Microscopy of Macromolecular Assemblies Joachim Frank Wadsworth Center for Laboratories and Research State of New York Department of Health The Governor Nelson A. Rockefeller
Three-Dimensional Electron Microscopy of Macromolecular Assemblies Joachim Frank Wadsworth Center for Laboratories and Research State of New York Department of Health The Governor Nelson A. Rockefeller
Stabilizing the CH2 domain of an Antibody by Engineering in an Enhanced Aromatic Sequon
 Stabilizing the CH2 domain of an Antibody by Engineering in an Enhanced Aromatic Sequon Wentao Chen,, Leopold Kong, Stephen Connelly, Julia M. Dendle,, Yu Liu,, Ian A. Wilson,#, Evan T. Powers, *, Jeffery
Stabilizing the CH2 domain of an Antibody by Engineering in an Enhanced Aromatic Sequon Wentao Chen,, Leopold Kong, Stephen Connelly, Julia M. Dendle,, Yu Liu,, Ian A. Wilson,#, Evan T. Powers, *, Jeffery
Introduction to" Protein Structure
 Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Supplementary Information. Autocatalytic backbone N-methylation in a family of ribosomal peptide natural products
 Supplementary Information Autocatalytic backbone -methylation in a family of ribosomal peptide natural products iels S. van der Velden 1, oemi Kälin 1, Maximilian J. Helf 1, Jörn Piel 1, Michael F. Freeman
Supplementary Information Autocatalytic backbone -methylation in a family of ribosomal peptide natural products iels S. van der Velden 1, oemi Kälin 1, Maximilian J. Helf 1, Jörn Piel 1, Michael F. Freeman
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.1290 Metal-directed, chemically tunable assembly of one-, two- and threedimensional crystalline protein arrays 1 2 1 1 1,3 Jeffrey D. Brodin 1, X. I. Ambroggio 2, Chunyan Tang 1, Kristin
DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.1290 Metal-directed, chemically tunable assembly of one-, two- and threedimensional crystalline protein arrays 1 2 1 1 1,3 Jeffrey D. Brodin 1, X. I. Ambroggio 2, Chunyan Tang 1, Kristin
Protein structure analysis. Risto Laakso 10th January 2005
 Protein structure analysis Risto Laakso risto.laakso@hut.fi 10th January 2005 1 1 Summary Various methods of protein structure analysis were examined. Two proteins, 1HLB (Sea cucumber hemoglobin) and 1HLM
Protein structure analysis Risto Laakso risto.laakso@hut.fi 10th January 2005 1 1 Summary Various methods of protein structure analysis were examined. Two proteins, 1HLB (Sea cucumber hemoglobin) and 1HLM
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1737 Supplementary Table 1 variant Description FSEC - 2B12 a FSEC - 6A1 a K d (leucine) c Leucine uptake e K (wild-type like) K (Y18F) K (TS) K (TSY) K288A mutant, lipid facing side chain
doi:1.138/nature1737 Supplementary Table 1 variant Description FSEC - 2B12 a FSEC - 6A1 a K d (leucine) c Leucine uptake e K (wild-type like) K (Y18F) K (TS) K (TSY) K288A mutant, lipid facing side chain
Protein Structures: Experiments and Modeling. Patrice Koehl
 Protein Structures: Experiments and Modeling Patrice Koehl Structural Bioinformatics: Proteins Proteins: Sources of Structure Information Proteins: Homology Modeling Proteins: Ab initio prediction Proteins:
Protein Structures: Experiments and Modeling Patrice Koehl Structural Bioinformatics: Proteins Proteins: Sources of Structure Information Proteins: Homology Modeling Proteins: Ab initio prediction Proteins:
Protein Structure Prediction
 Page 1 Protein Structure Prediction Russ B. Altman BMI 214 CS 274 Protein Folding is different from structure prediction --Folding is concerned with the process of taking the 3D shape, usually based on
Page 1 Protein Structure Prediction Russ B. Altman BMI 214 CS 274 Protein Folding is different from structure prediction --Folding is concerned with the process of taking the 3D shape, usually based on
Design of a Novel Globular Protein Fold with Atomic-Level Accuracy
 Design of a Novel Globular Protein Fold with Atomic-Level Accuracy Brian Kuhlman, Gautam Dantas, Gregory C. Ireton, Gabriele Varani, Barry L. Stoddard, David Baker Presented by Kate Stafford 4 May 05 Protein
Design of a Novel Globular Protein Fold with Atomic-Level Accuracy Brian Kuhlman, Gautam Dantas, Gregory C. Ireton, Gabriele Varani, Barry L. Stoddard, David Baker Presented by Kate Stafford 4 May 05 Protein
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Fall 2017 Databases and Protein Structure Representation October 2, 2017 Molecular Biology as Information Science > 12, 000 genomes sequenced, mostly bacterial (2013) > 5x10 6 unique sequences available
Fall 2017 Databases and Protein Structure Representation October 2, 2017 Molecular Biology as Information Science > 12, 000 genomes sequenced, mostly bacterial (2013) > 5x10 6 unique sequences available
Supplementary Figure 1. Aligned sequences of yeast IDH1 (top) and IDH2 (bottom) with isocitrate
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Aligned sequences of yeast IDH1 (top) and IDH2 (bottom) with isocitrate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli [ICD, pdb 1PB1, Mesecar, A. D., and Koshland,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Aligned sequences of yeast IDH1 (top) and IDH2 (bottom) with isocitrate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli [ICD, pdb 1PB1, Mesecar, A. D., and Koshland,
Supplementary Information. Cryo-EM Studies of Drp1 Reveal Cardiolipin Interactions that Activate
 Supplementary Information Cryo-EM Studies of Drp1 Reveal Cardiolipin Interactions that Activate the Helical Oligomer Christopher A. Francy 1, 2, 3, Ryan W. Clinton 1, 2, 3, Chris Fröhlich 4, 5, Colleen
Supplementary Information Cryo-EM Studies of Drp1 Reveal Cardiolipin Interactions that Activate the Helical Oligomer Christopher A. Francy 1, 2, 3, Ryan W. Clinton 1, 2, 3, Chris Fröhlich 4, 5, Colleen
Published online 5 June 2017 Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, Vol. 45, No doi: /nar/gkx499
 Published online 5 June 2017 Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, Vol. 45, No. 14 8581 8595 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx499 Unique localization of the plastid-specific ribosomal proteins in the chloroplast ribosome small
Published online 5 June 2017 Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, Vol. 45, No. 14 8581 8595 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx499 Unique localization of the plastid-specific ribosomal proteins in the chloroplast ribosome small
IgE binds asymmetrically to its B cell receptor CD23
 Supplementary Information IgE binds asymmetrically to its B cell receptor CD23 Balvinder Dhaliwal 1*, Marie O. Y. Pang 2, Anthony H. Keeble 2,3, Louisa K. James 2,4, Hannah J. Gould 2, James M. McDonnell
Supplementary Information IgE binds asymmetrically to its B cell receptor CD23 Balvinder Dhaliwal 1*, Marie O. Y. Pang 2, Anthony H. Keeble 2,3, Louisa K. James 2,4, Hannah J. Gould 2, James M. McDonnell
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal contacts in COP apo structure (PDB code 3S0R)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal contacts in COP apo structure (PDB code 3S0R) Shown in cyan and green are two adjacent tetramers from the crystallographic lattice of COP, forming the only unique inter-tetramer
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal contacts in COP apo structure (PDB code 3S0R) Shown in cyan and green are two adjacent tetramers from the crystallographic lattice of COP, forming the only unique inter-tetramer
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 www.nature.com/nature 1 Figure S1 Sequence alignment. a Structure based alignment of the plgic of E. chrysanthemi (ELIC), the acetylcholine binding protein from the snail Lymnea stagnalis (AchBP, PDB code
www.nature.com/nature 1 Figure S1 Sequence alignment. a Structure based alignment of the plgic of E. chrysanthemi (ELIC), the acetylcholine binding protein from the snail Lymnea stagnalis (AchBP, PDB code
Alpha-helical Topology and Tertiary Structure Prediction of Globular Proteins Scott R. McAllister Christodoulos A. Floudas Princeton University
 Alpha-helical Topology and Tertiary Structure Prediction of Globular Proteins Scott R. McAllister Christodoulos A. Floudas Princeton University Department of Chemical Engineering Program of Applied and
Alpha-helical Topology and Tertiary Structure Prediction of Globular Proteins Scott R. McAllister Christodoulos A. Floudas Princeton University Department of Chemical Engineering Program of Applied and
Protein synthesis I Biochemistry 302. February 17, 2006
 Protein synthesis I Biochemistry 302 February 17, 2006 Key features and components involved in protein biosynthesis High energy cost (essential metabolic activity of cell Consumes 90% of the chemical energy
Protein synthesis I Biochemistry 302 February 17, 2006 Key features and components involved in protein biosynthesis High energy cost (essential metabolic activity of cell Consumes 90% of the chemical energy
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling. Chapter 4 Part I
 Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08 Å resolution: comparison with the Azotobacter vinelandii MoFe protein
 Acta Cryst. (2015). D71, 274-282, doi:10.1107/s1399004714025243 Supporting information Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08
Acta Cryst. (2015). D71, 274-282, doi:10.1107/s1399004714025243 Supporting information Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08
Targeting proteins to membranes: structure of the signal recognition particle Pascal F Egea 1, Robert M Stroud 1 and Peter Walter 2
 Targeting proteins to membranes: structure of the signal recognition particle Pascal F Egea 1, Robert M Stroud 1 and Peter Walter 2 In all three kingdoms of life, co-translational targeting of secretory
Targeting proteins to membranes: structure of the signal recognition particle Pascal F Egea 1, Robert M Stroud 1 and Peter Walter 2 In all three kingdoms of life, co-translational targeting of secretory
7.88 Lecture Notes /7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding Problem. Ribosomes and In Vivo Folding
 7.88 Lecture Notes - 15 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding Problem Ribosomes and In Vivo Folding A. Ribosomes Ribosomes: Source of all Proteins! In prokaryotes, all ribosomes within cytoplasm; However,
7.88 Lecture Notes - 15 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding Problem Ribosomes and In Vivo Folding A. Ribosomes Ribosomes: Source of all Proteins! In prokaryotes, all ribosomes within cytoplasm; However,
Computational Molecular Modeling
 Computational Molecular Modeling Lecture 1: Structure Models, Properties Chandrajit Bajaj Today s Outline Intro to atoms, bonds, structure, biomolecules, Geometry of Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Ribosomes,
Computational Molecular Modeling Lecture 1: Structure Models, Properties Chandrajit Bajaj Today s Outline Intro to atoms, bonds, structure, biomolecules, Geometry of Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Ribosomes,
Table S1. Primers used for the constructions of recombinant GAL1 and λ5 mutants. GAL1-E74A ccgagcagcgggcggctgtctttcc ggaaagacagccgcccgctgctcgg
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1. Primers used for the constructions of recombinant GAL1 and λ5 mutants Sense primer (5 to 3 ) Anti-sense primer (5 to 3 ) GAL1 mutants GAL1-E74A ccgagcagcgggcggctgtctttcc ggaaagacagccgcccgctgctcgg
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1. Primers used for the constructions of recombinant GAL1 and λ5 mutants Sense primer (5 to 3 ) Anti-sense primer (5 to 3 ) GAL1 mutants GAL1-E74A ccgagcagcgggcggctgtctttcc ggaaagacagccgcccgctgctcgg
Molecular Modeling. Prediction of Protein 3D Structure from Sequence. Vimalkumar Velayudhan. May 21, 2007
 Molecular Modeling Prediction of Protein 3D Structure from Sequence Vimalkumar Velayudhan Jain Institute of Vocational and Advanced Studies May 21, 2007 Vimalkumar Velayudhan Molecular Modeling 1/23 Outline
Molecular Modeling Prediction of Protein 3D Structure from Sequence Vimalkumar Velayudhan Jain Institute of Vocational and Advanced Studies May 21, 2007 Vimalkumar Velayudhan Molecular Modeling 1/23 Outline
V19 Topology of Protein Complexes on Graphs
 V19 Topology of Protein Complexes on Graphs (1) CombDock (2) Nuclear Pore Complex 19. Lecture WS 2013/14 Bioinformatics III 1 Prediction Structures of Protein Complexes from Connectivities CombDock: automated
V19 Topology of Protein Complexes on Graphs (1) CombDock (2) Nuclear Pore Complex 19. Lecture WS 2013/14 Bioinformatics III 1 Prediction Structures of Protein Complexes from Connectivities CombDock: automated
Structure of the α-helix
 Structure of the α-helix Structure of the β Sheet Protein Dynamics Basics of Quenching HDX Hydrogen exchange of amide protons is catalyzed by H 2 O, OH -, and H 3 O +, but it s most dominated by base
Structure of the α-helix Structure of the β Sheet Protein Dynamics Basics of Quenching HDX Hydrogen exchange of amide protons is catalyzed by H 2 O, OH -, and H 3 O +, but it s most dominated by base
ml. ph 7.5 ph 6.5 ph 5.5 ph 4.5. β 2 AR-Gs complex + GDP β 2 AR-Gs complex + GTPγS
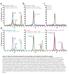 a UV28 absorption (mau) 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex + GDP β 2 AR-Gs complex + GTPγS β 2 AR-Gs complex dissociated complex excess nucleotides b 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex
a UV28 absorption (mau) 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex + GDP β 2 AR-Gs complex + GTPγS β 2 AR-Gs complex dissociated complex excess nucleotides b 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12890 Supplementary Table 1 Summary of protein components in the 39S subunit model. MW, molecular weight; aa amino acids; RP, ribosomal protein. Protein* MRP size MW (kda) Sequence accession
doi:10.1038/nature12890 Supplementary Table 1 Summary of protein components in the 39S subunit model. MW, molecular weight; aa amino acids; RP, ribosomal protein. Protein* MRP size MW (kda) Sequence accession
Supplementary Figures. Measuring Similarity Between Dynamic Ensembles of Biomolecules
 Supplementary Figures Measuring Similarity Between Dynamic Ensembles of Biomolecules Shan Yang, Loïc Salmon 2, and Hashim M. Al-Hashimi 3*. Department of Chemistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI,
Supplementary Figures Measuring Similarity Between Dynamic Ensembles of Biomolecules Shan Yang, Loïc Salmon 2, and Hashim M. Al-Hashimi 3*. Department of Chemistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Table of Contents Page Supplementary Table 1. Diffraction data collection statistics 2 Supplementary Table 2. Crystallographic refinement statistics 3 Supplementary Fig. 1. casic1mfc packing in the R3
Table of Contents Page Supplementary Table 1. Diffraction data collection statistics 2 Supplementary Table 2. Crystallographic refinement statistics 3 Supplementary Fig. 1. casic1mfc packing in the R3
Better Bond Angles in the Protein Data Bank
 Better Bond Angles in the Protein Data Bank C.J. Robinson and D.B. Skillicorn School of Computing Queen s University {robinson,skill}@cs.queensu.ca Abstract The Protein Data Bank (PDB) contains, at least
Better Bond Angles in the Protein Data Bank C.J. Robinson and D.B. Skillicorn School of Computing Queen s University {robinson,skill}@cs.queensu.ca Abstract The Protein Data Bank (PDB) contains, at least
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i
 Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Mar 8, 2018 08:34 pm GMT PDB ID : 1RUT Title : Complex of LMO4 LIM domains 1 and 2 with the ldb1 LID domain Authors : Deane, J.E.; Ryan, D.P.; Maher, M.J.;
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Mar 8, 2018 08:34 pm GMT PDB ID : 1RUT Title : Complex of LMO4 LIM domains 1 and 2 with the ldb1 LID domain Authors : Deane, J.E.; Ryan, D.P.; Maher, M.J.;
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Purification of yeast CKM. (a) Silver-stained SDS-PAGE analysis of CKM purified through a TAP-tag engineered into the Cdk8 C-terminus. (b) Kinase activity
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Purification of yeast CKM. (a) Silver-stained SDS-PAGE analysis of CKM purified through a TAP-tag engineered into the Cdk8 C-terminus. (b) Kinase activity
Bioinformatics. Macromolecular structure
 Bioinformatics Macromolecular structure Contents Determination of protein structure Structure databases Secondary structure elements (SSE) Tertiary structure Structure analysis Structure alignment Domain
Bioinformatics Macromolecular structure Contents Determination of protein structure Structure databases Secondary structure elements (SSE) Tertiary structure Structure analysis Structure alignment Domain
Structure of the signal recognition particle interacting with the elongation-arrested ribosome
 Structure of the signal recognition particle interacting with the elongation-arrested ribosome Mario Halic 1, Thomas Becker 1, Martin R. Pool 2, Christian M. T. Spahn 3, Robert A. Grassucci 4, Joachim
Structure of the signal recognition particle interacting with the elongation-arrested ribosome Mario Halic 1, Thomas Becker 1, Martin R. Pool 2, Christian M. T. Spahn 3, Robert A. Grassucci 4, Joachim
Measuring quaternary structure similarity using global versus local measures.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Measuring quaternary structure similarity using global versus local measures. (a) Structural similarity of two protein complexes can be inferred from a global superposition, which
Supplementary Figure 1 Measuring quaternary structure similarity using global versus local measures. (a) Structural similarity of two protein complexes can be inferred from a global superposition, which
Motif Prediction in Amino Acid Interaction Networks
 Motif Prediction in Amino Acid Interaction Networks Omar GACI and Stefan BALEV Abstract In this paper we represent a protein as a graph where the vertices are amino acids and the edges are interactions
Motif Prediction in Amino Acid Interaction Networks Omar GACI and Stefan BALEV Abstract In this paper we represent a protein as a graph where the vertices are amino acids and the edges are interactions
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2938
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of designed leucine-rich-repeat proteins. (a) Water-mediate hydrogen-bond network is frequently visible in the convex region of LRR crystal structures. Examples
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of designed leucine-rich-repeat proteins. (a) Water-mediate hydrogen-bond network is frequently visible in the convex region of LRR crystal structures. Examples
Crystal lattice Real Space. Reflections Reciprocal Space. I. Solving Phases II. Model Building for CHEM 645. Purified Protein. Build model.
 I. Solving Phases II. Model Building for CHEM 645 Purified Protein Solve Phase Build model and refine Crystal lattice Real Space Reflections Reciprocal Space ρ (x, y, z) pronounced rho F hkl 2 I F (h,
I. Solving Phases II. Model Building for CHEM 645 Purified Protein Solve Phase Build model and refine Crystal lattice Real Space Reflections Reciprocal Space ρ (x, y, z) pronounced rho F hkl 2 I F (h,
Homology models of the tetramerization domain of six eukaryotic voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.1-Kv1.6
 Homology models of the tetramerization domain of six eukaryotic voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.1-Kv1.6 Hsuan-Liang Liu* and Chin-Wen Chen Department of Chemical Engineering and Graduate Institute
Homology models of the tetramerization domain of six eukaryotic voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.1-Kv1.6 Hsuan-Liang Liu* and Chin-Wen Chen Department of Chemical Engineering and Graduate Institute
Lecture CIMST Winter School. 1. What can you see by TEM?
 Lecture CIMST Winter School Cryo-electron microscopy and tomography of biological macromolecules 20.1.2011 9:00-9:45 in Y03G91 Dr. Takashi Ishikawa OFLB/005 Tel: 056 310 4217 e-mail: takashi.ishikawa@psi.ch
Lecture CIMST Winter School Cryo-electron microscopy and tomography of biological macromolecules 20.1.2011 9:00-9:45 in Y03G91 Dr. Takashi Ishikawa OFLB/005 Tel: 056 310 4217 e-mail: takashi.ishikawa@psi.ch
Supporting Protocol This protocol describes the construction and the force-field parameters of the non-standard residue for the Ag + -site using CNS
 Supporting Protocol This protocol describes the construction and the force-field parameters of the non-standard residue for the Ag + -site using CNS CNS input file generatemetal.inp: remarks file generate/generatemetal.inp
Supporting Protocol This protocol describes the construction and the force-field parameters of the non-standard residue for the Ag + -site using CNS CNS input file generatemetal.inp: remarks file generate/generatemetal.inp
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
Supplemental Data SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES
 Supplemental Data CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE MG.ADP-INHIBITED STATE OF THE YEAST F 1 C 10 ATP SYNTHASE Alain Dautant*, Jean Velours and Marie-France Giraud* From Université Bordeaux 2, CNRS; Institut de
Supplemental Data CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE MG.ADP-INHIBITED STATE OF THE YEAST F 1 C 10 ATP SYNTHASE Alain Dautant*, Jean Velours and Marie-France Giraud* From Université Bordeaux 2, CNRS; Institut de
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Superagonist, Full Agonist, Partial Agonist and Antagonist Actions of Arylguanidines at 5-Hydroxytryptamine-3 (5-HT 3 ) Subunit A Receptors Katie Alix, Shailesh Khatri, Philip D.
Supporting Information Superagonist, Full Agonist, Partial Agonist and Antagonist Actions of Arylguanidines at 5-Hydroxytryptamine-3 (5-HT 3 ) Subunit A Receptors Katie Alix, Shailesh Khatri, Philip D.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1: The HpUreI crystal used for collection of native diffraction data. The crystal belongs to spacegroup P4 2 2 1 2 and has an approximate maximal dimension of 0.25 mm. Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1: The HpUreI crystal used for collection of native diffraction data. The crystal belongs to spacegroup P4 2 2 1 2 and has an approximate maximal dimension of 0.25 mm. Supplementary
Single Particle Reconstruction with EMAN. GroEL. GroEL 2000 (15 Å) GroEL 2001 (11.5 Å) GroEL 2003 (6 Å)
 Single Reconstruction with EMAN Methods for High Resolution Refinement in Single Processing Steve Ludtke Asst. Professor, Biochemistry, BCM Co-director,NCMI Donghua Chen Joanita Jakana Wah Chiu GroEL Jiu-Li
Single Reconstruction with EMAN Methods for High Resolution Refinement in Single Processing Steve Ludtke Asst. Professor, Biochemistry, BCM Co-director,NCMI Donghua Chen Joanita Jakana Wah Chiu GroEL Jiu-Li
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11744 Supplementary Table 1. Crystallographic data collection and refinement statistics. Wild-type Se-Met-BcsA-B SmCl 3 -soaked EMTS-soaked Data collection Space
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11744 Supplementary Table 1. Crystallographic data collection and refinement statistics. Wild-type Se-Met-BcsA-B SmCl 3 -soaked EMTS-soaked Data collection Space
Protein Structure Prediction, Engineering & Design CHEM 430
 Protein Structure Prediction, Engineering & Design CHEM 430 Eero Saarinen The free energy surface of a protein Protein Structure Prediction & Design Full Protein Structure from Sequence - High Alignment
Protein Structure Prediction, Engineering & Design CHEM 430 Eero Saarinen The free energy surface of a protein Protein Structure Prediction & Design Full Protein Structure from Sequence - High Alignment
Molecular Dynamics Flexible Fitting
 Molecular Dynamics Flexible Fitting Ryan McGreevy Research Programmer University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign NIH Resource for Macromolecular Modeling and Bioinformatics Molecular Dynamics Flexible
Molecular Dynamics Flexible Fitting Ryan McGreevy Research Programmer University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign NIH Resource for Macromolecular Modeling and Bioinformatics Molecular Dynamics Flexible
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
Supplementary Figures
 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Type I FGFR1 inhibitors (a) Chemical structures of a pyrazolylaminopyrimidine inhibitor (henceforth referred to as PAPI; PDB-code of the FGFR1-PAPI complex:
1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Type I FGFR1 inhibitors (a) Chemical structures of a pyrazolylaminopyrimidine inhibitor (henceforth referred to as PAPI; PDB-code of the FGFR1-PAPI complex:
