The Big Picture: A Review of Biology
|
|
|
- Amanda Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
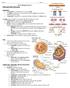
1 Name: Date: Block: Cells and Their Processes The Big Picture: A Review of Biology Organic Compounds A compound is a comination of 2 or more atoms An organic compound is a compound that contains caron atoms that have comined with each other An inorganic compound is a compound with no comination of caron atoms The Four Types of Organic Compounds (The Molecules of Life) Carohydrates: Sugars used for short term energy Lipids: Fats and oils used for long term energy Proteins: Made up of amino acids; used for construction materials and chemical reactions in the ody o Enzymes: Special types of proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the ody ut are not changed y the reactions Nucleic acids: DNA and RNA; contains genetic information Cells A cell is the smallest unit that is alive and can carry on all the processes of life Cells make up organisms (living things) o Unicellular organisms are made up of 1 cell o Multicellular organisms are made up of many cells Cells contain organelles, which are specialized compartments that carry out a specific function Types of cells o Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus, such as animal and plant cells o Prokaryotic cells contain no nucleus, such as acteria Animal Cells Usually round Organelles include o nucleus: controls cell activities o cell memrane: controls what enters and leaves the cell and also protects the cell o endoplasmic reticulum (ER): tunnels for compounds to move through the cell o Golgi ody: processes and stores protein o Riosomes: make proteins o Mitochondria: Makes energy for the cell o Lysosome: Has enzymes that digest waste and old organelles o Cytoplasm: Fills the empty space of the cell o Vacuole: Stores food, water, and waste o Centrioles: Help in cell division and is only found in animal, not plant, cells Plant Cells Usually square Organelles include o Everything that an animal cell has plus more o Chloroplast: Traps sunlight to make food for the plant o Cell wall: Protects the cell
2 Bacterial cells Smaller and simpler than plant or animal cells Bacteria are unicellular No nucleus Have a single closed loop of DNA, cell wall, cell memrane, cytoplasm and riosomes Some have a capsule (shell for protection), pili (short hair like structures to hold onto host cells), and flagella (whip like structure for movement) 2 Cell memrane Made up of molecules called phospholipids Phospholipid ilayer is the 2 layers of phospholipids that make up the cell memrane Cell memrane is fluid, which means that it is constantly flowing and moving over the cell Cell memrane is selectively permeale, which means that it allows small compounds, ut not large ones, to pass right through There are different ways that materials are transported across the cell memrane o Passive transport: requires no energy Diffusion: compounds move from high to low concentration Osmosis: diffusion of water o Active transport: requires energy Endocytosis: large compound are rought into the cell Exocytosis: large compounds are exported out of the cell Types of solutions o Hypotonic solutions cause water to move into the cell so the cell swells up o Hypertonic solutions cause water to move out of the cell so the cell shrivels up o Isotonic solutions cause no net movement of water into or out of the cell Photosynthesis Process y which organisms use energy from sunlight to make their own food (glucose) Glucose is a simple sugar Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells and some acteria Chloroplasts have a green pigment called chlorophyll Steps of photosynthesis o 1. Light reaction: chlorophyll in the chloroplasts asors sunlight o 2. Dark reaction: The energy from the sunlight is used to make glucose Light energy is completely changed into chemical energy (glucose) Chemical equation for photosynthesis 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + light energy C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 Cellular Respiration Process that reaks down glucose in order to make energy for an organism ATP: compound that stores energy in an organism Occurs in the mitochondria of the cell Two types of cellular respiration o Aeroic respiration: requires oxygen to occur Mostly happens in animals and plants
3 3 There are 3 steps in aeroic respiration Step 1 is glycolysis: glucose is cut in half Step 2 is the citric acid cycle: glucose halves get electrons chopped off of them Step 3 is the electron transport chain: electrons comine with oxygen and are used to make a lot of ATP Chemical equation for respiration C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + ATP energy Aeroic respiration is the opposite of photosynthesis o Anaeroic respiration: does not require oxygen to occur Mostly happens in acteria and yeast Also called fermentation Makes less ATP than aeroic respiration Chromosomes DNA strands in the nucleus that contain the directions on how to make and keep an organism alive Made up of genes, which are traits of an organism Cells will die if their DNA is damaged or removed Humans have mostly diploid cells, which means that we have 2 of each type of chromosome o Homologous chromosomes are 2 of the same type of chromosome o We have 23 types of chromosomes ut o We have 46 chromosomes in all, 23 chromosomes from mom + 23 chromosomes from dad Human gametes (sperm and egg cells) are haploid cells, which means that they have 1 of each type of chromosome o Sperm and egg cells have 23 chromosomes in all Autosomes: Chromosomes that do not determine gender Sex chromosomes: Chromosomes that determine gender o Girls are XX, Boys are XY Karyotype: ordered picture of an organism s chromosomes o Healthy individuals have 2 of each type of chromosome o Individuals with Down Syndrome have three #21 chromosomes Cell Cycle The cell cycle is the phases in the life of a cell o 1. M phase: Mitosis (cell division) occurs o 2. G1 phase: Cell grows o 3. S phase: DNA synthesis (chromosomes are copied) o 4. G2 phase: Cell grows o 5. M phase egins again Chromosomes must e copied efore mitosis so that new cells receive the same chromosomes found in the old cells
4 4 Mitosis Division of a cell into 2 identical cells Before mitosis: Chromosomes have copied themselves Sister chromatids: original chromosome and its exact copy are attached to each other Phases of mitosis o 1. Prophase: Nuclear memrane falls apart and spindle fiers start to form o 2. Metaphase: Sister chromatids line up along the middle of the spindle fiers o 3. Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell o 4. Telophase: Spindle fiers reak down and new nuclear memrane forms around each set of chromosomes Cytokinesis occurs when the cytoplasm actually divides, forming two new cells Genetics Meiosis Cell division that produces gametes (sex cells), such as sperm and egg cells Fertilization: Process of an egg and a sperm cell comining to produce a zygote o Zygote: Bay that is only 1 cell ig o Egg cell (23 chromosomes) + sperm cell (23 chromosomes) = ay (46 chromosomes) Steps in meiosis o 1. Before meiosis: 2 chromosomes of the same type come together to make a chromosome pair Each chromosome doules This gives 4 chromosomes stuck together o 2. Meiosis I: Chromosome pairs separate into two new cells o 3. Meiosis II: Each chromosome separates from its copy into 4 new cells In meiosis, one cell ecomes four cells ut in mitosis, one cell ecomes two cells DNA Deoxyrionucleic acid Makes up the chromosomes in the nucleus and never leaves the nucleus A chromosome is a chain of different genes DNA has a doule helix shape Has four types of ases: adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T), cytosine (C) A inds T and G inds C DNA is complementary, which means that the ases on one strand match up to the ases on the other strand o For example: Strand 1: ATG CCT GAC Strand 2: TAC GGA CTG Semi conservative replication is the process y which DNA copies itself and each new piece of DNA is made up of 1 old strand and 1 new strand RNA Rionucleic acid RNA is a copy of DNA that goes out into the cytoplasm to tell the cell what to do in order to stay alive RNA is single stranded and has uracil (U) rather than thymine (T) o U inds A and G inds C o If the DNA is ATG CCA AAG Then the RNA will e UAC GGU UUC
5 5 Using DNA to make protein 1. Transcription: DNA in the nucleus is used to make messenger RNA (mrna) o DNA has all the directions the cell needs to live 2. RNA moves out into the cytoplasm o RNA carries the directions to other parts of the cell 3. Translation: The RNA attaches to a riosome and directs the production of a protein o Proteins do all the work in the cell o Every 3 ases in RNA is called a codon and codes for 1 amino acid Mutations A mutation is a change in a gene or chromosome If the mutation happens in a ody cell, it only affects the organism that carries it If the mutation happens in a sex cell, it can e passed on to offspring Mutations can e o harmful if they reduce an organism s chances for reproduction or survival o helpful if they improve an organism s chances for survival o neutral if they do not produce an ovious changes in an organism o lethal if they result in the immediate death of an organism Mutations can occur spontaneously or e caused y a mutagen, which is a factor in the environment like UV and chemicals Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel is an Austrian monk credited with eginning the study of genetics Genetics is the study of heredity Humans have 2 genes for every trait o Alleles: Different forms of a single trait, like lue and rown are two eye color alleles Dominant gene: Stronger of 2 genes and shows up in the organism o Represented y a capital letter o B is the dominant gene for rown eyes Recessive gene: Weaker of 2 genes and only shows up when there is no dominant gene present o Represented y a lowercase letter o is the recessive gene for lue eyes Homozygous (purered): When 2 genes are alike for a trait o BB is homozygous for rown eyes, is homozygous for lue eyes Heterozygous (hyrid): When 2 genes are different for a trait o B is heterozygous Mendel s law of segregation states that the 2 genes we have for each trait get separated from one another when we make egg and sperm cells Mendel s law of independent assortment states that the gene for one trait is inherited independently of the genes for other traits o Only true when the genes are on different chromosomes
6 Punnett Squares Punnett squares are charts that are used to show the possile gene cominations in a cross etween 2 organisms * Let s say that B is the dominant gene for rown eyes and is the recessive gene for lue eyes* Genotype: The genes of an organism (B) Phenotype: The physical appearance of an organism (Brown eyes) 6 Parents Offspring genotype Parents B B x 50% B B x B 50% B B B Offspring phenotype 50% Brown eyes 50% lue eyes B B BB B B Offspring genotype 25% BB 50% B 25% Offspring phenotype 75% Brown eyes 25% lue eyes Human Genetics Multiple alleles are three or more alleles that exist for a single gene o For example, A, B, and O are the multiple alleles for lood type o The possile lood types are A, B, AB, and O You can e A+ or A-, B+ or B-, AB+ or AB-, O+ or O- depending on whether your lood cells have a special Rh protein Codominance occurs when 2 dominant genes are expressed and oth genes are seen in the organism o AB lood is codominant, a cat with lack and white spots is codominant Incomplete dominance occurs when 2 dominant genes are expressed and lended together in the organism o If the red flower color gene (R) is mixed with the white flower color gene (W) then the offspring will e pink (RW) A polygenic trait is a trait that is controlled y more than one pair of genes, like skin color A sex-linked trait is a trait that is found on the X chromosome, such as colorlindness o Females are XX so have 2 copies of sex-linked traits o Males are XY so have 1 copy of sex-linked traits Ecology Ecology Ecology is the study of how organisms fit into their environment A community is the organisms that live in a particular environment A haitat is the physical location of a community An ecosystem is a collection of organisms and their physical environment The diversity of an ecosystem is a measure of the numer of species living there There are different feeding groups of organisms o Autotrophs: Organisms that make their own food, like plants and some acteria o Heterotrophs: Organisms that cannot make their own food, like Herivores: Eat plants Carnivores: Eat meat Omnivores: Eat plants and meat
7 7 There are different factors is an ecosystem o Aiotic factors are nonliving things o Biotic factors are living things, such as Producers: Organisms that take in energy from their surroundings to make their own food Consumers: Organisms that eat other organisms for energy Decomposers: Special type of consumer that eats waste products and dead organisms for energy There are different trophic levels in a food chain o A trophic level is a feeding level in an ecosystem o A food chain is a lineup of organisms that shows who eats who o 1 st trophic level is usually a producer o 2 nd trophic level is a primary consumer o 3 rd trophic level is a secondary consumer o 4 th trophic level is a tertiary consumer o and so on o Last trophic level is a decomposer Every time an organism eats, it otains energy from its food o So energy is transferred from the 1 st to the 2 nd to the 3 rd trophic level and so on (ut some of this energy does get lost along the way) o Energy pyramid: Picture showing how much energy is transferred to the different trophic levels in a food chain A food we is a network of connected food chains Cycles of Matter Water, nitrogen, caron, and oxygen are recycled in the environment through cycles The nitrogen cycle o Nitrogen in the atmosphere is taken in y acteria that live in plant roots o The nitrogen is passed onto the plants and any animals that eat the plants o Once the plant or animal has died, decomposers (acteria) again take up the nitrogen in the dead material and send it ack to the atmosphere The water cycle o Precipitation, such as rain and snow, fall to the earth o The water either seeps into the ground for plants to use and the plants give off excess water ack to the atmosphere or runs off the land to lower-lying odies of water where it evaporates ack into the atmosphere The oxygen-caron cycle o Caron dioxide from the atmosphere is taken in y plants who use it during photosynthesis and release oxygen ack into the atmosphere o Oxygen in the atmosphere is taken in y animals and plants who use it during respiration and release caron dioxide ack into the atmosphere Interaction in an environment Each organism has a niche, or role, to play in its environment Competition is a struggle etween organisms for resources, such as food, water, shelter Predators are organisms that catch, kill, and eat other organisms called prey Symiosis is a close relationship etween 2 organisms in which one organism lives near, on, or even inside another organisms and in which at least one organism enefits o There are three types of symiosis
8 o 1. Commensalism is when one of the 2 organisms enefits from the symiosis o 2. Mutualism is when oth organisms enefit from the symiosis o 3. Parasitism is when one organism enefits (parasite) and the other organism is harmed (host) from the symiosis The parasite feeds on the host while it is still alive, weakening ut not killing it An adaptation is a change in the ehavior or physical characteristics of a species that make it etter suited to its environment Populations of organisms increase and decrease due to overpopulation of a competitor or predator, disease, lack of food or water or shelter, and extreme weather Ecosystems are constantly changing due to changing populations of organisms, changing weather, natural disasters, and human activity Every time a change occurs, the alance of the ecosystem has to e readjusted 8 The Theory of Evolution Evolution Evolution is a change in a species over time The theory of evolution was stated y Charles Darwin and is ased on natural selection Natural selection states that organisms with traits well suited to an environment are more likely to survive and produce more offspring than organisms without these favorale traits Biodiversity: Organisms ecome very different from each other as they evolve and ecome etter suited to their environments The theory of evolution is supported y evidence that includes o Adaptations: structures and ehaviors that organisms have evolved in order to survive etter in their environments o The fossil record which is information aout all known fossils o Comparative anatomy which is when the odies of different organisms are compared to see if they are related Homologous structures are ody structures on different organisms that are similar Vestigial structures are ody structures that may have served a purpose in ancient ancestors ut no longer are functional in current organisms o The fact that all verterate emryos look very similar as they develop efore irth o The fact that the DNA of closely related organisms looks very similar Taxonomy Taxonomy is the science of classifying living things Organisms are organized into 7 different levels of taxonomy (King Philip came over for good spaghetti) o 1. Kingdom most road o 5. Family o 2. Phylum o 6. Genus o 3. Class o 7. Species most specific o 4. Order Closely related organisms have more levels of taxonomy in common than unrelated organisms
9 There are six kingdoms of living things (Archie eats pretty fantastic apple pies) o 1. Archaeacteria: acteria that live o 4. Fungi: Mushrooms, yeasts, in extreme environments molds o 2. Euacteria: common acteria o 5. Animalia: animals o 3. Protista: Single-celled organisms o 6. Plantae: plants Every organism has a unique two-word scientific name that is written in Latin o The first word is the genus, the second word is the species (Humans are Homo sapiens) Some scientists prefer to organize organisms into domains rather than kingdoms o There are three domains (Archie eats eels) o 1. Archaea: Bacteria that live in extreme environments o 2. Euacteria: Common acteria o 3. Eukarya: Organisms whose DNA is in a nucleus 9
Name: Date: MCAS Biology Review! Cells and Their Processes
 Name: Date: MCAS Biology Review! Cells and Their Processes Compounds A compound is a combination of 2 or more atoms An organic compound is a compound that contains carbon atoms that have combined with
Name: Date: MCAS Biology Review! Cells and Their Processes Compounds A compound is a combination of 2 or more atoms An organic compound is a compound that contains carbon atoms that have combined with
Cells and Their Processes. 1. What element do organic compounds have that inorganic compounds do not?
 Name: Date: Cells and Their Processes 1. What element do organic compounds have that inorganic compounds do not? 2. List the four types of organic compounds, describe the function of each AND list a food
Name: Date: Cells and Their Processes 1. What element do organic compounds have that inorganic compounds do not? 2. List the four types of organic compounds, describe the function of each AND list a food
Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES.
 Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Biology EOC Review Study Questions
 Biology EOC Review Study Questions Microscopes and Characteristics of Life 1. How do you calculate total magnification on a compound light microscope? 2. What is the basic building block of all living
Biology EOC Review Study Questions Microscopes and Characteristics of Life 1. How do you calculate total magnification on a compound light microscope? 2. What is the basic building block of all living
Name: Date: Period: Biology End of Course Vocabulary 1. This is an organism s unique role in the environment that includes the habitat, function, and
 1. This is an organism s unique role in the environment that includes the habitat, function, and activities of the organism. a. Niche 2. This is a inter-species relationship in which one species benefits
1. This is an organism s unique role in the environment that includes the habitat, function, and activities of the organism. a. Niche 2. This is a inter-species relationship in which one species benefits
Biology Spring Final Exam Study Guide
 Name: Hour: Basic Biology Skills Graphing Know the keys to creating a graph Know how to interpret a graph Independent variable Dependent variable Biology Spring Final Exam Study Guide Levels of Organization
Name: Hour: Basic Biology Skills Graphing Know the keys to creating a graph Know how to interpret a graph Independent variable Dependent variable Biology Spring Final Exam Study Guide Levels of Organization
Define: Alleles. Define: Chromosome. In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways.
 Alleles Chromosome In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways. How do the bases A, C, G, T, and U match up in DNA? How about RNA? Summarize the cell process called protein synthesis!
Alleles Chromosome In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways. How do the bases A, C, G, T, and U match up in DNA? How about RNA? Summarize the cell process called protein synthesis!
7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Scranton School District Scranton, PA 7 th Grade Life Science Prerequisite: Completion of 6 th Grade Science Life Science establishes the study of living things and how they interact
7 th Grade Life Science Scranton School District Scranton, PA 7 th Grade Life Science Prerequisite: Completion of 6 th Grade Science Life Science establishes the study of living things and how they interact
Biology EOCT Review. Milton High School
 Biology EOCT Review Milton High School Cell Organelles Nucleus holds DNA Cell membrane what comes in and goes out Mitochondria powerhouse of the cell Ribosomes protein synthesis Lysosomes digestion Cell
Biology EOCT Review Milton High School Cell Organelles Nucleus holds DNA Cell membrane what comes in and goes out Mitochondria powerhouse of the cell Ribosomes protein synthesis Lysosomes digestion Cell
Biology 1 EOC Study Guide
 Name: Biology 1 EOC Study Guide Date: Standard 2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their organelles 1. What are three tenets of the cell theory?
Name: Biology 1 EOC Study Guide Date: Standard 2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their organelles 1. What are three tenets of the cell theory?
Honors Biology Midterm Exam Study Guide--January 2019
 Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Hypothesis. Levels of organization. Theory. Controlled experiment. Homeostasis. ph scale. Characteristics of living things
 Hypothesis Quantitative & Qualitative observations Theory Levels of organization Controlled experiment Homeostasis Characteristics of living things ph scale Quantitative- involves numbers, counting, measuring
Hypothesis Quantitative & Qualitative observations Theory Levels of organization Controlled experiment Homeostasis Characteristics of living things ph scale Quantitative- involves numbers, counting, measuring
End of Course Review. Review sheet
 Review Tips: Review ALL vocabulary, notes, assignments and worksheets Holt Biology CP: Review Science Skills on pages 1050 1063 and Lab safety on pages xxiv xxvii Modern Biology H: Review Lab safety &
Review Tips: Review ALL vocabulary, notes, assignments and worksheets Holt Biology CP: Review Science Skills on pages 1050 1063 and Lab safety on pages xxiv xxvii Modern Biology H: Review Lab safety &
Find your notes, old notebook, and a pencil * On Thursday please bring a calculator!
 Find your notes, old notebook, and a pencil * On Thursday please bring a calculator! Describe Photosynthesis: Inputs & outputs? Equation? Factors that impact it What types of organisms do Plants do it
Find your notes, old notebook, and a pencil * On Thursday please bring a calculator! Describe Photosynthesis: Inputs & outputs? Equation? Factors that impact it What types of organisms do Plants do it
Biology 2018 Final Review. Miller and Levine
 Biology 2018 Final Review Miller and Levine bones blood cells elements All living things are made up of. cells If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is a(n). eukaryote prokaryote plant
Biology 2018 Final Review Miller and Levine bones blood cells elements All living things are made up of. cells If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is a(n). eukaryote prokaryote plant
EOC Study Guide. CELLS SB1. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells.
 EOC Study Guide CELLS SB. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Unit. What are the characteristics that all living things share?. What
EOC Study Guide CELLS SB. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Unit. What are the characteristics that all living things share?. What
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Name Date Block. Biology EOCT Review
 Name Date Block Biology EOCT Review Section 1: Nature of Science 1. Bobby thinks that eating fish for breakfast will make people smarter. He gets 10 of his friends and divides them into 2 groups. Group
Name Date Block Biology EOCT Review Section 1: Nature of Science 1. Bobby thinks that eating fish for breakfast will make people smarter. He gets 10 of his friends and divides them into 2 groups. Group
Name: Hour: Cumulative Final Exam Review Guide
 Name: Hour: Cumulative Final Exam Review Guide Unit One: Nature of Science 1. On a separate sheet of paper write definitions for the following terms Biology d. Independent Variable Control Group e. Dependent
Name: Hour: Cumulative Final Exam Review Guide Unit One: Nature of Science 1. On a separate sheet of paper write definitions for the following terms Biology d. Independent Variable Control Group e. Dependent
Biology Concepts at a Glance. - Identify Endergonic vs Exergonic - Activation Energy (graphs of endergonic vs exergonic reactions)
 Biology Concepts at a Glance Unit 1 Inquiry Scientific Method: - Problem - Hypothesis - Experiment - collect data - analyze data - conclusion Dependent vs. Independent Variables Controlled Variables Control
Biology Concepts at a Glance Unit 1 Inquiry Scientific Method: - Problem - Hypothesis - Experiment - collect data - analyze data - conclusion Dependent vs. Independent Variables Controlled Variables Control
Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things are made of what?
 All living things are made of what? Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things respond to external conditions. This is called what? Which of the 7 traits of life is defined as the
All living things are made of what? Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things respond to external conditions. This is called what? Which of the 7 traits of life is defined as the
A.P. Biology Summer Assignment Mr. Moses
 A.P. Biology Summer Assignment 2018 - Mr. Moses Below, you will find items that you must cover during the summer. The review packet is designed to give students an understanding of the commitment necessary
A.P. Biology Summer Assignment 2018 - Mr. Moses Below, you will find items that you must cover during the summer. The review packet is designed to give students an understanding of the commitment necessary
Interphase & Cell Division
 1 Interphase & Cell Division 2 G1 = cell grows and carries out its normal job. S phase = DNA is copied (replicated/duplicated) G2 = Cell prepares for division 3 During mitosis, the nuclear membrane breaks
1 Interphase & Cell Division 2 G1 = cell grows and carries out its normal job. S phase = DNA is copied (replicated/duplicated) G2 = Cell prepares for division 3 During mitosis, the nuclear membrane breaks
Standards: A, C, E; A; A, B; B; B; C; A; B; A
 Unit: Tools, Techniques, Themes of Biology Standards: 3.1.10 A, C, E; 3.2.10 A; 3.3.10 A, B; 3.7.10 B; 3.8.10 B; 4.3.10 C; 4.6.10 A; 4.7.10 B; 4.8.10 A Unit Essential Question(s): 1. What is the study
Unit: Tools, Techniques, Themes of Biology Standards: 3.1.10 A, C, E; 3.2.10 A; 3.3.10 A, B; 3.7.10 B; 3.8.10 B; 4.3.10 C; 4.6.10 A; 4.7.10 B; 4.8.10 A Unit Essential Question(s): 1. What is the study
Parts of an experiment. CP Biology EOC Quick Review The Study of Life 1/6/2012
 CP Biology EOC Quick Review The Study of Life Parts of an experiment Independent variable the factor that is being tested. The factor that causes change. Dependent variable the measurable factor that changes
CP Biology EOC Quick Review The Study of Life Parts of an experiment Independent variable the factor that is being tested. The factor that causes change. Dependent variable the measurable factor that changes
Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis)
 Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis) DNA Structure o Discovered by Watson and Crick o Double-stranded o Shape is a double helix (twisted ladder) o Made of chains of nucleotides: o Has four types
Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis) DNA Structure o Discovered by Watson and Crick o Double-stranded o Shape is a double helix (twisted ladder) o Made of chains of nucleotides: o Has four types
Honors Biology Midterm Review
 Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
Name Date Period Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life?
 Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life? Eukaryotic cell parts you should be able a. to identify and label: Nucleus b. Nucleolus c. Rough/smooth ER Ribosomes d. Golgi
Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life? Eukaryotic cell parts you should be able a. to identify and label: Nucleus b. Nucleolus c. Rough/smooth ER Ribosomes d. Golgi
EOC MILESTONE REVIEW
 Introduction 1. What does the term biology mean? EOC MILESTONE REVIEW 2. What is homeostasis and why is it important to living things? Content Domain: Cells (SB1) 1. Define eukaryote: List 3 examples of
Introduction 1. What does the term biology mean? EOC MILESTONE REVIEW 2. What is homeostasis and why is it important to living things? Content Domain: Cells (SB1) 1. Define eukaryote: List 3 examples of
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology
 2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
2. Draw two water molecules. Using a dotted line, show a hydrogen bond that could form between them.
 Biology Final Review Packet Directions: Answer the questions below. You may use any notes, worksheets, or your textbook to find the answers. The questions are divided up based on the different units we
Biology Final Review Packet Directions: Answer the questions below. You may use any notes, worksheets, or your textbook to find the answers. The questions are divided up based on the different units we
Biology 1 Semester Review
 Chapter 1 What is Science? 1 1 What Is Science? Key Concept The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world, and to use those explanations
Chapter 1 What is Science? 1 1 What Is Science? Key Concept The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world, and to use those explanations
Biology Final Study for Multiple Choice Questions USE YOUR STUDY GUIDES & NOTES!!! Be able to explain, de<ine, & give examples for appropriate terms.
 Biology Final Study for Multiple Choice Questions USE YOUR STUDY GUIDES & NOTES!!! Be able to explain, de
Biology Final Study for Multiple Choice Questions USE YOUR STUDY GUIDES & NOTES!!! Be able to explain, de
Purpose of cytoplasm. Cell membrane. Cell membrane. Purpose of cell membrane. Cytoplasm. Contains organelles and site of many chemical reactions
 Cell membrane Purpose of cell membrane Cell membrane Cytoplasm Purpose of cytoplasm Contains organelles and site of many chemical reactions Plant cell wall Purpose of cell wall Provides support (plants
Cell membrane Purpose of cell membrane Cell membrane Cytoplasm Purpose of cytoplasm Contains organelles and site of many chemical reactions Plant cell wall Purpose of cell wall Provides support (plants
Biology Semester 2 Final Review
 Name Period Due Date: 50 HW Points Biology Semester 2 Final Review LT 15 (Proteins and Traits) Proteins express inherited traits and carry out most cell functions. 1. Give examples of structural and functional
Name Period Due Date: 50 HW Points Biology Semester 2 Final Review LT 15 (Proteins and Traits) Proteins express inherited traits and carry out most cell functions. 1. Give examples of structural and functional
Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline
 Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline Mitosis and Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences
Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline Mitosis and Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences
Name. Diversity of Life
 Review Guide Semester 1 End of Course Exam in Biology Name Diversity of Life Vocabulary to know and be able to apply: Prokaryotic, eukaryotic, unicellular, multicellular, sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction,
Review Guide Semester 1 End of Course Exam in Biology Name Diversity of Life Vocabulary to know and be able to apply: Prokaryotic, eukaryotic, unicellular, multicellular, sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction,
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014
 Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
Biology Mid-Term Study Guide
 Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
THINGS I NEED TO KNOW:
 THINGS I NEED TO KNOW: 1. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus. In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Both types of cells have ribosomes. Some
THINGS I NEED TO KNOW: 1. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus. In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Both types of cells have ribosomes. Some
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC
 BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) Biomolecules & Enzymes
 Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS!! WRITE ON YOUR OWN PAPER
 BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW Photosynthesis 1. Identify inputs and/or outputs of matter and/or energy in photosynthesis using words and/or chemical formulas Sun + CO 2 + H 2O -> C 6H 12O 6 + O 2 Light Energy + Carbon
BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW Photosynthesis 1. Identify inputs and/or outputs of matter and/or energy in photosynthesis using words and/or chemical formulas Sun + CO 2 + H 2O -> C 6H 12O 6 + O 2 Light Energy + Carbon
Use evidence of characteristics of life to differentiate between living and nonliving things.
 Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards All living things have a common set characteristic needs and functions that separate them from nonliving things such as:
Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards All living things have a common set characteristic needs and functions that separate them from nonliving things such as:
2. The following molecules are considered polymers except Mark all that apply a. Starch b. DNA c. Proteins d. Lipids e. Salt
 Life s Major Molecules 1. Which is an organic molecule? a. Ne b. O2 c. CH4 d. NaCl e. H2O 2. The following molecules are considered polymers except Mark all that apply a. Starch b. DNA c. Proteins d. Lipids
Life s Major Molecules 1. Which is an organic molecule? a. Ne b. O2 c. CH4 d. NaCl e. H2O 2. The following molecules are considered polymers except Mark all that apply a. Starch b. DNA c. Proteins d. Lipids
Name Period. 2. Name the 3 parts of interphase AND briefly explain what happens in each:
 Name Period GENERAL BIOLOGY Second Semester Study Guide Chapters 3, 4, 5, 6, 11, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16, and 17. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION AND MEIOSIS 1. The cell cycle consists of a growth stage and a division
Name Period GENERAL BIOLOGY Second Semester Study Guide Chapters 3, 4, 5, 6, 11, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16, and 17. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION AND MEIOSIS 1. The cell cycle consists of a growth stage and a division
Biology Fall Final Review 2005/2006 Mrs. Nuño
 Biology Fall Final Review 2005/2006 Mrs. Nuño Unit 1: The Nature of Science (Chapter 1) 7 characteristics of life. 7 major themes of biology, including the definitions of science terms describing those
Biology Fall Final Review 2005/2006 Mrs. Nuño Unit 1: The Nature of Science (Chapter 1) 7 characteristics of life. 7 major themes of biology, including the definitions of science terms describing those
Chapter 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS
 Chapter 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel I. Gregor Mendel A. Studied pea plants 1. Reproduce sexually (have two sex cells = gametes) 2. Uniting of male and female gametes = Fertilization
Chapter 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel I. Gregor Mendel A. Studied pea plants 1. Reproduce sexually (have two sex cells = gametes) 2. Uniting of male and female gametes = Fertilization
Describe the structure and composition of the cell membrane. (make a sketch) What does the Theory of Endosymbiosis state?
 Station 1. Analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell
Station 1. Analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell
Meiosis and Mendel. Chapter 6
 Meiosis and Mendel Chapter 6 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Key Concept Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Body Cells vs. Gametes You have body cells and gametes body cells
Meiosis and Mendel Chapter 6 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Key Concept Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Body Cells vs. Gametes You have body cells and gametes body cells
Peddie Summer Day School
 Peddie Summer Day School Course Syllabus: BIOLOGY Teacher: Mr. Jeff Tuliszewski Text: Biology by Miller and Levine, Prentice Hall, 2010 edition ISBN 9780133669510 Guided Reading Workbook for Biology ISBN
Peddie Summer Day School Course Syllabus: BIOLOGY Teacher: Mr. Jeff Tuliszewski Text: Biology by Miller and Levine, Prentice Hall, 2010 edition ISBN 9780133669510 Guided Reading Workbook for Biology ISBN
Name Period. 3. How many rounds of DNA replication and cell division occur during meiosis?
 Name Period GENERAL BIOLOGY Second Semester Study Guide Chapters 3, 4, 5, 6, 11, 14, 16, 17, 18 and 19. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION AND MEIOSIS 1. What is the purpose of meiosis? 2. Distinguish between diploid
Name Period GENERAL BIOLOGY Second Semester Study Guide Chapters 3, 4, 5, 6, 11, 14, 16, 17, 18 and 19. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION AND MEIOSIS 1. What is the purpose of meiosis? 2. Distinguish between diploid
The final product must be complete by Monday morning (8:30AM) May 21.
 Biology EOC Review Project Introduction: Over the course of this year in Biology, you have learned about living organisms through the lens of evolution. Earth is home to more than 8 million different species
Biology EOC Review Project Introduction: Over the course of this year in Biology, you have learned about living organisms through the lens of evolution. Earth is home to more than 8 million different species
CELLULAR ORGANIZATION UNICELLULAR & MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS
 7.2 CELL STRUCTURE The student will investigate and understand that all living things are composed of cells. Key concepts include a. cell structure and organelles b. similarities and differences between
7.2 CELL STRUCTURE The student will investigate and understand that all living things are composed of cells. Key concepts include a. cell structure and organelles b. similarities and differences between
Biology Semester 1 Study Guide
 Name Per Date Biology Semester 1 Study Guide The following Gizmos meet the standards assessed by the Biology EOC and should be reviewed during the first semester: 1. Rabbit Population by Season Gizmo 2.
Name Per Date Biology Semester 1 Study Guide The following Gizmos meet the standards assessed by the Biology EOC and should be reviewed during the first semester: 1. Rabbit Population by Season Gizmo 2.
Second Semester Biology Study Guide
 Second Semester Biology Study Guide All of the information on this review is fair game for the final Some information will be more prevalent on the test (Think about which topics we spent more time on
Second Semester Biology Study Guide All of the information on this review is fair game for the final Some information will be more prevalent on the test (Think about which topics we spent more time on
Biology Final Review Ch pg Biology is the study of
 Biology Final Review Ch. 1 1-3 pg. 17-25 1. Biology is the study of Ch.2 2-3 pg. 45-49 2. All organic compounds contain. 3. Starch is an example of which type of organic compound? 4. What monomers make
Biology Final Review Ch. 1 1-3 pg. 17-25 1. Biology is the study of Ch.2 2-3 pg. 45-49 2. All organic compounds contain. 3. Starch is an example of which type of organic compound? 4. What monomers make
NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions
 NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions Directions: Using your notes and book as a guide, complete the following questions to review everything we have learned about cells, their parts, and any functions
NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions Directions: Using your notes and book as a guide, complete the following questions to review everything we have learned about cells, their parts, and any functions
Name: Life Science Review Packet. Cell Structure and Function: What Defines Life:
 Name: Life Science Review Packet What Defines Life: An is anything capable of carrying on the processes or characteristics of life. = using materials from the surroundings to make more of oneself, or becoming
Name: Life Science Review Packet What Defines Life: An is anything capable of carrying on the processes or characteristics of life. = using materials from the surroundings to make more of oneself, or becoming
Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW
 Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW 2013-2014 CP Biology Student Name: School/Teacher: Date: SPS CP Biology Midterm Review, January 2014 Page 1 Dear Biology Student,
Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW 2013-2014 CP Biology Student Name: School/Teacher: Date: SPS CP Biology Midterm Review, January 2014 Page 1 Dear Biology Student,
Biology Semester Review
 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Biology Semester Review 1 1 What is Science? One goal of science is to provide natural explanations for events in the natural world. Science also aims to use those explanations
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Biology Semester Review 1 1 What is Science? One goal of science is to provide natural explanations for events in the natural world. Science also aims to use those explanations
1. The Chemistry of Life Chapter 3 Central Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life.
 Biology High School Standards Review Worksheet 1. The Chemistry of Life Chapter 3 Central Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize
Biology High School Standards Review Worksheet 1. The Chemistry of Life Chapter 3 Central Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize
2. How do plants get nitrogen? Explain how a symbiotic relationship allows this to happen.
 Unit 2 Interdependence of Organisms 1. What organism helps to carry out nitrogen fixation? 2. How do plants get nitrogen? Explain how a symbiotic relationship allows this to happen. 3. Using the diagram
Unit 2 Interdependence of Organisms 1. What organism helps to carry out nitrogen fixation? 2. How do plants get nitrogen? Explain how a symbiotic relationship allows this to happen. 3. Using the diagram
Semester II Final Exam Study Questions
 Semester II Final Exam Study Questions Unit 5: The Molecular Basis of Heredity DNA determines the characteristics of organisms. 1. Cells function according to the information contained in the master code
Semester II Final Exam Study Questions Unit 5: The Molecular Basis of Heredity DNA determines the characteristics of organisms. 1. Cells function according to the information contained in the master code
Reinforcement Unit 3 Resource Book. Meiosis and Mendel KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have.
 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Your body is made of two basic cell types. One basic type are somatic cells, also called body cells,
6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Your body is made of two basic cell types. One basic type are somatic cells, also called body cells,
Basic Biology. Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology
 Teacher: Lynn Dahring Basic Biology August 2014 Basic Biology CEQ (tri 1) 1. What are the parts of the biological scientific process? 2. What are the essential molecules and elements in living organisms?
Teacher: Lynn Dahring Basic Biology August 2014 Basic Biology CEQ (tri 1) 1. What are the parts of the biological scientific process? 2. What are the essential molecules and elements in living organisms?
UNIT 8 BIOLOGY: Meiosis and Heredity Page 148
 UNIT 8 BIOLOGY: Meiosis and Heredity Page 148 CP: CHAPTER 6, Sections 1-6; CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-4; HN: CHAPTER 11, Section 1-5 Standard B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular
UNIT 8 BIOLOGY: Meiosis and Heredity Page 148 CP: CHAPTER 6, Sections 1-6; CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-4; HN: CHAPTER 11, Section 1-5 Standard B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular
Jeopardy. Evolution Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300
 Jeopardy Mutations Crosses & Punnett Sqs. Meiosis & Variability Evolution Photo, Cell Resp, Energy, Matter Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300
Jeopardy Mutations Crosses & Punnett Sqs. Meiosis & Variability Evolution Photo, Cell Resp, Energy, Matter Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300
Biology Fall Semester Exam Review. Unit 1: Scientific method, characteristics of life What are the characteristics of life (pg. 6)
 Biology Fall Semester Exam Review Unit 1: Scientific method, characteristics of life What are the characteristics of life (pg. 6) Define the following terms: biology observation hypothesis dependent variable
Biology Fall Semester Exam Review Unit 1: Scientific method, characteristics of life What are the characteristics of life (pg. 6) Define the following terms: biology observation hypothesis dependent variable
Summer Work Biology. 1. If the sperm of a horse has 32 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will its body cells have? a. 16 c. 2 b. 64 d.
 Summer Work Biology Week One: A. Write the correct answer(s). 1. If the sperm of a horse has 32 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will its body cells have? a. 16 c. 2 b. 64 d. 62 2. Which of the following
Summer Work Biology Week One: A. Write the correct answer(s). 1. If the sperm of a horse has 32 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will its body cells have? a. 16 c. 2 b. 64 d. 62 2. Which of the following
genome a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another gene the passing of traits from one generation to the next
 genetics the study of heredity heredity sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait genome a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another gene trait the passing
genetics the study of heredity heredity sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait genome a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another gene trait the passing
Know how to read a balance, graduated cylinder, ruler. Know the SI unit of each measurement.
 Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2012-2013 Due the day of your final for a maximum of 5 extra credit points. You will be able to use this review on your exam for 15 minutes! Safety and Lab Measurement:
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2012-2013 Due the day of your final for a maximum of 5 extra credit points. You will be able to use this review on your exam for 15 minutes! Safety and Lab Measurement:
Biology Final Exam REVIEW ANSWERS 2015
 Biology Final Exam REVIEW ANSWERS 2015 Biology Final Review: Use this as a guide to assist you in preparing for the final. This is just an outline, and questions on the final reflect these concepts but
Biology Final Exam REVIEW ANSWERS 2015 Biology Final Review: Use this as a guide to assist you in preparing for the final. This is just an outline, and questions on the final reflect these concepts but
Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018
 Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
3 The Organization of Living Things
 CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
Turns sunlight, water & carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) into sugar & oxygen through photosynthesis
 CELL PART/ ORGANELLE FUNCTION (what it does) PICTURE Plant, Animal, or Both Cell Membrane controls what goes in & out of the cell protects the cell Nucleus directs all the cell s activities contains cell
CELL PART/ ORGANELLE FUNCTION (what it does) PICTURE Plant, Animal, or Both Cell Membrane controls what goes in & out of the cell protects the cell Nucleus directs all the cell s activities contains cell
c. 6CO2 + 6H2O 6O2 + C6H12O6 + Energy d. 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy 6O2 + C6H12O6
 AP Biology Pre-Test Name: Date: Points: AP Biology Prior Knowledge Multiple Choice-Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Organisms, such as plants, that make
AP Biology Pre-Test Name: Date: Points: AP Biology Prior Knowledge Multiple Choice-Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Organisms, such as plants, that make
Biology Massachusetts
 Tutorial Outline Massachusetts Tutorials are designed specifically for the Learning Standards found in the Massachusetts Curriculum Frameworks to prepare students for the MCAS tests. Biology Tutorials
Tutorial Outline Massachusetts Tutorials are designed specifically for the Learning Standards found in the Massachusetts Curriculum Frameworks to prepare students for the MCAS tests. Biology Tutorials
Notes: Cell Processes 1. Movement across cell membrane 2. Photosynthesis 3. Cellular respiration 4. Cell cycle
 Notes: Cell Processes 1. Movement across cell membrane 2. Photosynthesis 3. Cellular respiration 4. Cell cycle AMDG 1. Notes: Movement across a cell membrane Cell Membrane-see picture in text book What
Notes: Cell Processes 1. Movement across cell membrane 2. Photosynthesis 3. Cellular respiration 4. Cell cycle AMDG 1. Notes: Movement across a cell membrane Cell Membrane-see picture in text book What
Study Guide: Fall Final Exam H O N O R S B I O L O G Y : U N I T S 1-5
 Study Guide: Fall Final Exam H O N O R S B I O L O G Y : U N I T S 1-5 Directions: The list below identifies topics, terms, and concepts that will be addressed on your Fall Final Exam. This list should
Study Guide: Fall Final Exam H O N O R S B I O L O G Y : U N I T S 1-5 Directions: The list below identifies topics, terms, and concepts that will be addressed on your Fall Final Exam. This list should
Compare cellular structure and their functions in prokaryote and eukaryote cells.
 Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards DNA molecules contain genetic information that is found in all cells. Genes are sections of DNA that code for proteins,
Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards DNA molecules contain genetic information that is found in all cells. Genes are sections of DNA that code for proteins,
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
Cell Structure and Function
 Quarter 2 Review Biology Cell Structure and Function Identify the organelles AND give function of each. 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. Looking at the above diagram, what does the structure labeled 1 do? Why
Quarter 2 Review Biology Cell Structure and Function Identify the organelles AND give function of each. 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. Looking at the above diagram, what does the structure labeled 1 do? Why
Weeks Common Core Standards Unit/Topic Activities/Resources Learning Objectives Vocabulary
 Nine Weeks: First Curriculum Map Instructor: Kapiskosky Class: Biology Grade: 10 Shadyside Local Schools Building: High School Weeks Common Core Standards Unit/Topic Activities/Resources Learning Objectives
Nine Weeks: First Curriculum Map Instructor: Kapiskosky Class: Biology Grade: 10 Shadyside Local Schools Building: High School Weeks Common Core Standards Unit/Topic Activities/Resources Learning Objectives
8. Use the following terms: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, chromosome, spindle fibers, centrioles.
 Midterm Exam Study Guide: 2nd Quarter Concepts Cell Division 1. The cell spends the majority of its life in INTERPHASE. This phase is divided up into the G 1, S, and G 2 phases. During this stage, the
Midterm Exam Study Guide: 2nd Quarter Concepts Cell Division 1. The cell spends the majority of its life in INTERPHASE. This phase is divided up into the G 1, S, and G 2 phases. During this stage, the
TIPS TO PREPARE FOR THE BIOLOGY 2 nd SEMESTER FINAL EXAM:
 TIPS TO PREPARE FOR THE BIOLOGY 2 nd SEMESTER FINAL EXAM: FINAL EXAM DETAILS: 80 questions Multiple choice Will assess your mastery of the biological concepts covered in Units 3 and 4 Will assess your
TIPS TO PREPARE FOR THE BIOLOGY 2 nd SEMESTER FINAL EXAM: FINAL EXAM DETAILS: 80 questions Multiple choice Will assess your mastery of the biological concepts covered in Units 3 and 4 Will assess your
Study Guide Chapter
 Study Guide Chapter 4-10152015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. During the process of diffusion, a. cell surrounds and absorbs large particles.
Study Guide Chapter 4-10152015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. During the process of diffusion, a. cell surrounds and absorbs large particles.
Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide
 Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Information: Exam has 100 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencils and a four-function calculator on the day of the test. Review ALL vocabulary,
Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Information: Exam has 100 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencils and a four-function calculator on the day of the test. Review ALL vocabulary,
Grade 7 Science Learning Standards
 Grrade 7 Sciience Currrriicullum Overrviiew Middle School Science Hands-on, Minds-On, Science is the primary focus of the middle school science program, and includes content from Earth and Space Science,
Grrade 7 Sciience Currrriicullum Overrviiew Middle School Science Hands-on, Minds-On, Science is the primary focus of the middle school science program, and includes content from Earth and Space Science,
Cells and Genetics. Life Science. Cell parts. Cell parts cont. Cell processes. Cell Division 5/4/2015
 Cells and Genetics Life Science SOL Review Hooke was 1 st person to observe cells Cells Basic Unit of structure and function of life Prokaryote: bacteria/no nucleus Eukaryote: membrane structures; everything
Cells and Genetics Life Science SOL Review Hooke was 1 st person to observe cells Cells Basic Unit of structure and function of life Prokaryote: bacteria/no nucleus Eukaryote: membrane structures; everything
Biology study. Basic Principles of Biology Chapter One. Chapters
 1 April 27, 2010 Chapters Chapter One 1 Biology study Chapter Two 2 Chapter Three 3 Chapter Four 4 Chapter Five 5 Chapter Six/ Seven 6/7 Chapter Eight 8 Chapters continued.. Chapter Nine 9 Chapter Ten
1 April 27, 2010 Chapters Chapter One 1 Biology study Chapter Two 2 Chapter Three 3 Chapter Four 4 Chapter Five 5 Chapter Six/ Seven 6/7 Chapter Eight 8 Chapters continued.. Chapter Nine 9 Chapter Ten
Guided Reading Chapter 1: The Science of Heredity
 Name Number Date Guided Reading Chapter 1: The Science of Heredity Section 1-1: Mendel s Work 1. Gregor Mendel experimented with hundreds of pea plants to understand the process of _. Match the term with
Name Number Date Guided Reading Chapter 1: The Science of Heredity Section 1-1: Mendel s Work 1. Gregor Mendel experimented with hundreds of pea plants to understand the process of _. Match the term with
Cell Growth and Genetics
 Cell Growth and Genetics Cell Division (Mitosis) Cell division results in two identical daughter cells. The process of cell divisions occurs in three parts: Interphase - duplication of chromosomes and
Cell Growth and Genetics Cell Division (Mitosis) Cell division results in two identical daughter cells. The process of cell divisions occurs in three parts: Interphase - duplication of chromosomes and
Spring Break Packet. Name:
 Spring Break Packet Name: General Instructions All students are offered this extra credit assignment. This assignment is worth up to 40 points toward the Biology final exam. The assignment is broken down
Spring Break Packet Name: General Instructions All students are offered this extra credit assignment. This assignment is worth up to 40 points toward the Biology final exam. The assignment is broken down
Module B Unit 5 Cell Growth and Reproduction. Mr. Mitcheltree
 Module B Unit 5 Cell Growth and Reproduction Mr. Mitcheltree DNA and Genetics - The Cell and Inheritance Gene = group of codons that code for a specific protein Allele = alternate form of a gene A dominant,
Module B Unit 5 Cell Growth and Reproduction Mr. Mitcheltree DNA and Genetics - The Cell and Inheritance Gene = group of codons that code for a specific protein Allele = alternate form of a gene A dominant,
Biology 1 Spring 2010 Summative Exam
 Biology 1 Spring 2010 Summative Exam Short Answer USING SCIENCE SKILLS The pedigree shows the inheritance of free earlobes and attached earlobes in five generations of a family. Attached earlobes are caused
Biology 1 Spring 2010 Summative Exam Short Answer USING SCIENCE SKILLS The pedigree shows the inheritance of free earlobes and attached earlobes in five generations of a family. Attached earlobes are caused
Name: Date: Hour: Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis. Monomer Polymer Example Drawing Function in a cell DNA
 Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis I. Concept Review A. Why is carbon often called the building block of life? B. List the four major macromolecules. C. Complete the chart below. Monomer Polymer
Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis I. Concept Review A. Why is carbon often called the building block of life? B. List the four major macromolecules. C. Complete the chart below. Monomer Polymer
FCAT Review. Evolution & Ecosystems
 FCAT Review Evolution & Ecosystems Classifying Organisms Why would we classify organisms? To make them easier to study The science of studying how organisms are classified is called taxonomy Organisms
FCAT Review Evolution & Ecosystems Classifying Organisms Why would we classify organisms? To make them easier to study The science of studying how organisms are classified is called taxonomy Organisms
Unit 4 Review - Genetics. UNIT 4 Vocabulary topics: Cell Reproduction, Cell Cycle, Cell Division, Genetics
 Unit 4 Review - Genetics Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction Mendel s Laws of Heredity Patterns of Inheritance Meiosis and Genetic Variation Non-Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance Cell Reproduction/Cell Cycle/
Unit 4 Review - Genetics Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction Mendel s Laws of Heredity Patterns of Inheritance Meiosis and Genetic Variation Non-Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance Cell Reproduction/Cell Cycle/
