Geography - US and Canada Review
|
|
|
- Nigel Weaver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Class: Date: Geography - US and Canada Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. KEY GEOGRAPHIC CONCEPTS AND SKILLS 1. All of the following landforms are located in both the United States and Canada except the a. Rocky Mountains. b. Great Plains. c. Laurentian Highlands. d. Gulf Atlantic Coastal Plain. 2. The peaks of the Rocky Mountains are higher and more jagged than the peaks of the Appalachian Mountains because a. glaciers moved across the Rockies during the last ice age. b. the tectonic forces that created the Rockies were very strong. c. volcanoes formed the peaks of the Appalachians. d. the Appalachians have been worn down by rain, ice, and wind over time. 3. Canada s climates are generally colder than those of the United States because a. there are no coastal ranges in Canada. b. Canada is located farther north of the Equator than is the United States. c. Canada does not lie near any warm bodies of water. d. the Canadian Shield blocks ocean winds from blowing onto the land. 4. The two most common climate regions found in Canada are a. subarctic and tundra. b. marine west coast and highlands. c. subarctic and semiarid. d. tundra and highlands. 5. The Canadian Shield, a vast expanse of ancient rock, is located a. along the Pacific coast of Canada. b. along the banks of the St. Lawrence River. c. around Hudson Bay. d. in the far northern regions of Canada. 6. Which of the following is an accurate statement about the ecosystems of the United States and Canada? a. A large part of Canada is coniferous forest. b. The northeastern regions of Canada are primarily temperate grasslands. c. Part of the southeastern United States is a tropical rain forest. d. Part of both the United States and Canada is a desert scrub region. 7. All of the following features are shared by the populations of the United States and Canada except a. a high standard of living. c. a predominantly rural lifestyle. b. cultural diversity. d. a long life expectancy. 1
2 8. The majority of the people in the United States and Canada live a. on the coastal plains. b. in or near urban centers. c. in the Great Plains region. d. in or near regions with rich mineral deposits. 9. For most of their histories, the United States and Canada have been a. closely tied economically and culturally. b. distrustful neighbors of each other. c. economic competitors. d. linked only by a common landmass. 10. Which of the following is not an accurate statement about energy use in Canada? a. Canada uses more electricity per capita than the United States. b. Canada is the world s leading user of nuclear energy. c. Canada is self-sufficient in its energy needs. d. Canada relies more on hydroelectricity than the United States. 11. The major landforms of North America generally extend a. from east to west. c. from north to south. b. along the coasts. d. in all directions. 12. Two major landforms stretching across both the United States and Canada are the a. Appalachian Mountains and the Laurentian Highlands. b. Rocky Mountains and the Great Plains. c. Canadian Shield and the Interior Plains. d. Gulf Atlantic Coastal Plain and the Sierra Nevada. 13. Which of the following is not an accurate statement about the climate of the United States and Canada? a. Part of the United States has a humid subtropical climate. b. A large region of Canada has a subarctic climate. c. The dominant climate in the United States is semiarid. d. Both the United States and Canada have tundra regions. 14. Because Canada is located farther north than the United States, a. interior regions in Canada have a continental climate. b. the climate of Canada is generally colder than that of the United States. c. coastal cities in Canada have a more moderate climate than do coastal cities in the United States. d. eastern Canada is drier than the eastern United States. 15. Which of the following is an accurate statement about the ecosystems of the United States and Canada? a. A large part of the United States is coniferous forest. b. The southwestern region of Canada includes a desert scrub region. c. While Canada has mixed forest regions, the United States does not. d. Both the United States and Canada have temperate grassland regions. 16. The people of the United States and Canada share all of the following traits except a. a long life expectancy. c. a high literacy rate. b. a high standard of living. d. little cultural diversity. 2
3 17. Which of the following is an accurate statement about the population distribution of Canada? a. Most Canadians live in the northern two thirds of the country. b. The Canadian population is evenly distributed throughout the country. c. Most Canadians live within 200 miles (322 km) of the United States. d. About half of all Canadians live in the province of Nova Scotia. 18. Which of the following pairs of cities is located on the Great Lakes? a. New York City and Ottawa c. Buffalo and Quebec b. Chicago and Toronto d. Boston and Vancouver 19. The most densely populated region of Canada lies along the St. Lawrence River and in the a. Canadian Shield. c. Northwest Territories. b. Interior Plains. d. Great Lakes region. 20. Which of the following is an accurate statement about energy use in Canada? a. Canada relies more on hydroelectricity than the United States. b. Canada has larger reserves of coal than the United States. c. Canada is a larger energy consumer than the United States. d. Canada relies more on nuclear power than the United States. 21. Which of the following factors did not influence the economic development of the United States? a. an abundance of land b. transportation technology c. strict immigration laws d. an economic system based on capitalism 22. Which of the following did not contribute to the growth of the suburbs? a. the availability of automobiles b. the building of the interstate highway system c. the availability of inexpensive land in major cities d. the availability of public transportation 23. All of the following are nonrenewable resources vital to the energy supply and economy of the United States except a. coal. c. natural gas. b. oil. d. forests. 24. After the Civil War, which ended in 1865, Chicago grew to become the largest city in the Midwest because a. many people from the South and the West migrated to the area. b. the construction of the Erie Canal made the city an important center of trade. c. most of the agricultural industries were located near the city. d. Chicago had the best location along the railroad network, located centrally between the coasts. 25. Which of the following is an accurate statement about the lumber industry in the United States? a. Logging in the Northwest was never a profitable industry because of seasonal variations in climate. b. The logging industry moved west when the forests of the east were depleted. c. Strict regulation of logging in the Northeast allowed the industry to thrive in that region. d. Logging has depleted forests to the point where the lumber industry in the United States has all but disappeared. 3
4 26. In the early to mid-1800s, the most efficient means of transporting raw materials and finished goods around the country was the a. steamboat. c. sailing ship. b. covered wagon. d. railroad. 27. The entire United States and the rest of the world serve as the hinterland for all of the following cities except a. New York. c. Tucson. b. Chicago. d. Los Angeles. 28. Cities in the South and the West have flourished in recent years because of popular preferences to live in cities that a. have mild year-round climates. b. offer a variety of jobs and activities. c. are the site of large industrial centers. d. provide easy access to important waterways. 29. Today the majority of the American population lives in a. a suburb. c. or near a major city. b. a small city. d. a small town or rural area. 30. Why was the invention of the telegraph important to the economic success of the United States? a. It provided an inexpensive way for businesses to communicate. b. It provided speedy communication across long distances. c. It introduced the technology that led to the invention of the telephone. d. It allowed for confidential business information to be sent without the risk of interception or theft. 31. In order to encourage farming in the Great Plains during the 1800s, the government a. gave parcels of land to settlers who agreed to farm. b. cleared the land and offered it for sale at reasonable rates. c. paid immigrants with farming backgrounds to settle in the region. d. encouraged the logging industry to clear land so it could be converted for agricultural use. 32. The steam engine was important because it a. gave boats the power to travel against both wind and current. b. made possible the building of canals. c. made fishing more efficient. d. created a need for fossil fuels. 33. Which of the following resources was not vital to the economic success of the United States? a. land c. lead b. coal d. forests 34. The construction of the Erie Canal was important because it a. linked the Hudson River in New York and the Great Lakes in the Midwest, greatly increasing the trade between the two regions. b. helped eastern cities such as Boston and Philadelphia become important port cities. c. allowed eastern crops to be transported faster and more efficiently to cities in the South and the West. d. provided the best access to the Pacific Ocean. 4
5 35. An important part of the free enterprise system is a. government regulation of industry in order to protect the interests of consumers. b. the belief that individuals acting in their own interest may also serve the interests of others. c. the belief that privately owned companies should not have to compete with each other for business. d. imposing taxes on all companies that do business in the country. 36. Which of the following is an accurate description about the use of land in the United States? a. The lumber industry is centered primarily in the East, where forests are plentiful. b. Coal mining in the United States provides about half of the world s coal resources. c. While only a small percentage of the population works on farms, nearly half of the land is devoted to agriculture. d. Drilling for oil and natural gas takes place primarily in the Northeast and Southwest. 37. A regional metropolis such as Atlanta differs from a city such as Tucson in that a regional metropolis a. has a larger hinterland and a wider range of activities. b. has a smaller hinterland and a narrower range of activities. c. is generally the same size as a smaller city but with fewer activities. d. is generally twice as large and has twice as many activities. 38. Which of the following is not an accurate statement about the effects of the transcontinental railway system? a. It made it easier to transport goods and people across the country. b. It helped make Chicago an important center of business. c. It signaled the decline of major east and west coast cities. d. It contributed to the growth of the suburbs. 39. All major American cities during the first 50 years of independence were located a. near the Great Lakes. b. along the Erie Canal. c. along the Mississippi River. d. along the Atlantic Coast. 40. What is the primary reason the South and the West have increased in population in recent years? a. new systems of transportation b. new methods of communication c. newly discovered natural resources d. popular preference for warmer climates 41. Industry and trade grew rapidly in the Northeast during the nineteenth century because a. the region is rich in mineral resources. b. people were eager to move from the farm to the suburbs. c. a well-planned system of roads connected the major cities. d. rivers provided transportation routes and water power for factories. 42. Settlers were originally attracted to the South primarily for which of the following reasons? a. rich soil c. varied climate b. extensive forest areas d. relatively flat landscape 5
6 43. The growth of industry in the South was not affected by a. the discovery of oil in Texas. b. its access to ocean ports along the Gulf of Mexico. c. the rich natural resources in Appalachia. d. the abundance of fast-moving streams in the Carolinas. 44. Which of the following is not a reason many industries moved south from northern cities? a. Land was cheaper in the South. b. Industrial plants were often newer, in better condition, and more efficient than those in the North. c. Labor unions were less common in the South. d. The South had a more diverse population. 45. The Midwest is called the nation s breadbasket because a. millions of loaves of bread are produced there every day. b. it is the crossroads of the United States. c. it is the region that produces most of the nation s grain, dairy products, and hogs. d. most of the nation s fruit and vegetables are grown there. 46. Which of the following is not a reason the Midwest became an industrial center? a. It is where labor costs were most reasonable. b. It has a rich supply of natural resources. c. It has easy access to water transportation routes. d. It is the link, by railroad, of the east and west coasts. 47. Family farms in the Midwest have been replaced by large farms for all of the following reasons except a. modern machinery. c. pressure from foreign competition. b. push and pull migration factors. d. increase in the yields of the harvest. 48. In contrast to San Diego and Reno, the city of Seattle has a. far fewer trees. b. a wetter climate. c. a warmer climate despite its more northern location. d. a milder climate because of its coastal location. 49. The rapid increase of population in the West resulted from the discovery of a. gold and silver deposits. c. the lush forests of the Northwest. b. a major oil field in Alaska. d. plentiful fish off the coast. 50. Residents of the West have adapted to their environment in all of the following ways except by a. building aqueducts. b. working in forestry. c. surmounting distances by traveling by boat and airplane. d. moving from the cities to the countryside. 51. The jagged shoreline of the Northeast a. has hindered farming in the region. c. provides many excellent harbors. b. makes fishing nearly impossible. d. contains few sandy beaches. 52. Which of the following has not been a problem for the northeastern megalopolis? a. a decline in population. c. a trash disposal problem. b. an inadequate water supply. d. a decline in professional-level jobs. 6
7 53. The Northeast became a leader in commerce because of its a. abundant mineral resources. c. rolling farmlands and lush forests. b. many rivers. d. agricultural diversity. 54. Industrial development in the South has been influenced primarily by a. the availability of natural resources. b. the region s humid, subtropical climate. c. large areas of rocky soil that made farming too difficult. d. competition from the Midwest, where farming was more profitable. 55. The most common ecosystem found in the South is a. tropical rain forest. c. temperate grassland. b. coniferous forest. d. mixed forest. 56. During the 1970s, the population of the South increased greatly because of a. the discovery of oil in eastern Texas. b. increased farm productivity. c. job opportunities in industries that had moved south. d. the migration of many Europeans to the region. 57. One characteristic common to all the states in the Midwest is a. productive farmland. c. heavy industry. b. a mild, predictable climate. d. a lush, wooded, hilly landscape. 58. All of the following are accurate statements about the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River system except: a. They aided the growth of industry in the Midwest. b. They are still important trade routes today. c. Cities connected by this transportation network are home to heavy manufacturing. d. They have helped the region become the nation s center of business and finance. 59. Because of the West s natural resources, two important economic activities in the region are a. heavy manufacturing and commerce. c. forestry and fishing. b. shipbuilding and trade. d. oil refining and agriculture. 60. Which of the following is an accurate statement about Alaska and Hawaii? a. Alaska lies closer to the mainland of the United States than Hawaii. b. In comparison to Hawaii, Alaska is a smaller state in terms of both population density and area. c. Both states were ceded to the United States as a result of a war. d. An extensive road-building effort has made travel within both states much easier than in the past. 61. Which of the following is an accurate statement about the economy of the Atlantic Provinces? a. Tourism is the region s major economic activity. b. A recent economic slump has resulted in a large decline in the population of the region. c. Forestry and farming are important economic activities in the region. d. Overfishing of shrimp and crab has largely destroyed the fishing industry in the region. 7
8 62. Compared with people in the Prairie Provinces, the residents of British Columbia are a. more likely to have higher incomes. b. less likely to live in cities. c. more likely to be employed in the oil industry. d. less likely to be immigrants. 63. The economic development of Ontario and Quebec was greatly influenced by their location a. bordering the United States. b. bordering the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River. c. along the Grand Banks. d. in the Canadian Shield. 64. Many of the mineral deposits and oil reserves in Nunavut, the Yukon, and the Northwest Territories have not been developed because a. environmental laws prohibit the mining of land in these territories. b. native Inuit refuse to give up their lands. c. the area is sparsely settled. d. harsh climate and rugged terrain make mining difficult. 65. Which of the following is an accurate statement about Canada? a. It was not until 1974 that the Canadian government passed laws officially permitting French Canadians to speak their own language. b. When the province of Quebec declared French to be its official language, many English-speaking residents and businesses left the province. c. French Canadians make up almost half of the total population of Canada, with the majority living in the province of Ontario. d. Only about 15 percent of the French Canadian population speaks fluent French. 66. Warfare between British and French colonists in North America between 1689 and 1763 ended with a. the British defeat in the Battle of Quebec. b. France surrendering most of its lands to Britain. c. independence for Canada. d. France gaining control of Canada. 67. Relations between the United States and Canada can best be summarized as a. generally good with occasional periods of political tension and conflict. b. strained because of high tariffs on both sides. c. generally good although many Canadians feel overshadowed by the United States. d. strained because of ongoing border disputes. 68. The diversity of the Canadian population is most accurately reflected in which of the following statements? a. The great diversity of the population has made a sense of national unity difficult to achieve. b. In order to promote a stronger sense of national unity, the government has limited immigration to the country. c. Because of liberal immigration policies, people of European ancestry no longer make up the majority of the population. d. In recent years the Inuit population has largely left behind their traditional way of life and has become just one more of a large number of ethnic minorities. 8
9 69. Building a pipeline above ground to transport Canada s oil and mineral resources a. creates barriers to the migration of arctic animals. b. causes acid rain. c. disrupts the permafrost of the fragile environment. d. permanently damages the natural vegetation. 70. In contrast to the United States, Canada is more likely to do which of the following? a. engage in armed combat with developing nations b. have positive relations with Japan and other Asian countries c. play the role of middle power in the global community d. engage in direct competition with European countries for business 71. The most important natural resource of the Atlantic Provinces is a. wildlife. c. the sea. b. rich soil. d. petroleum. 72. Quebec and Ontario developed as Canada s economic heart because of the provinces locations a. on the major waterway linking the Canadian interior and the Atlantic Ocean. b. along Canada s major railroad lines. c. bordering the Hudson Bay. d. in the southeastern corner of Canada near the United States. 73. The large cities of the Prairie Provinces developed in the late 1800s a. along the newly built railroads. b. along major waterways. c. around mining centers. d. around oil fields. 74. The rich mineral deposits and large reserves of petroleum in the northern territories are a. being exploited at the expense of the environment. b. causing a population boom in the region. c. largely undeveloped because of the harsh climate and terrain. d. forcing the native Inuit to radically alter their lifestyle. 75. All of the following factors have contributed to making national unity difficult to achieve except a. many Canadians strong ties to regional and ethnic groups. b. rivalry between Canadians of English and French heritage. c. great differences among the provinces and territories. d. immigration of central and eastern Europeans to Canada. 76. Which of the following distinguishes the province of Quebec from the rest of Canada? a. It has the largest Inuit population. b. It has the closest ties to the customs and culture of France. c. It has the largest Asian immigrant community. d. It was the only province that voted against becoming independent from Great Britain. 77. When Canada became an independent nation in 1931, the government a. continued to protect the rights of French-speaking citizens. b. made English the official language of Canada. c. passed laws to end the influence of French culture. d. established Quebec as a distinct society within the nation. 9
10 78. Today, Canada must balance the opportunities of developing its northern resources with the challenge of a. competing for markets with the United States. b. protecting the fragile environment. c. building transportation and communication facilities in the region. d. supplying a labor force large enough to mine the area. 79. In the very important economic link between the United States and Canada, the United States buys a. about 85 percent of all Canadian exports. b. almost 25 percent of all Canadian exports. c. all of Canada s petroleum and natural gas. d. manufactured goods only. 80. Canada plays an important role in the global community in all of the following ways except by a. promoting arms control and disarmament. b. working with the Commonwealth of Nations to promote trade. c. acting as superpower with influence over Europe and Asia. d. promoting trade with Japan and other Asian countries. 10
11 ID: A Geography - US and Canada Review Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: OBJ: TOP: United States Landforms Canada Landforms 2. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Rocky Mountains Appalachian Mountains 3. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: United States Climates Canada Climates 4. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Canada Climates 5. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Canada Physical Characteristics Canadian Shield 6. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: United States Ecosystems Canada Ecosystems 7. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: United States Population Canada Population 8. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: United States Population Canada Population 9. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: 126 OBJ: TOP: United States History Canada History 10. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: Canada Energy Use 11. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: United States Landforms Canada Landforms 12. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: United States Landforms Canada Landforms 13. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: United States Climate Canada Climate 14. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: United States Climate Canada Climate 15. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: United States Ecosystems Canada Ecosystem 16. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: United States Population Canada Population 17. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: United States Population Distribution Canada 18. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Great Lakes Cities 19. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Canada Population Density 20. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: Canada Energy Use 21. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Economic Development United States 1
12 ID: A 22. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 150 OBJ: TOP: Growth of Suburbs 23. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: OBJ: TOP: Natural Resources United States 24. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Growth of Cities and United States Railroad 25. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 144 OBJ: TOP: Natural Resources United States 26. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: OBJ: TOP: Transportation United States 27. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Urban Hierarchy 28. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Growth of Cities and United States 29. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 151 OBJ: TOP: Cities United States Metropolitan Areas United States 30. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Communication Technology 31. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: OBJ: TOP: Agriculture in the Great Plains United States 32. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 145 OBJ: TOP: Transportation United States Steam Engine 33. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: OBJ: TOP: Natural Resources Economic Development United States 34. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 149 OBJ: TOP: Transportation United States Erie Canal 35. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 147 OBJ: TOP: Free Enterprise Economic Systems & United States 36. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Natural Resources and United States 37. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: Metropolitan Areas Urban Hierarchy Atlanta Tucson 38. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Transcontinental Railroad 39. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 149 OBJ: TOP: Growth of Cities and United States 40. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Patterns of Settlement Movement 41. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Industry and Trade in the Northeast 42. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: OBJ: TOP: Settlement Patterns in the South 43. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Industry in the South 44. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Industry in the South 45. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Agriculture in the Midwest 2
13 ID: A 46. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Industry in the Midwest 47. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Agriculture in the Midwest 48. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: 174 OBJ: TOP: Growth of Cities in the West 49. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Population Growth in the West 50. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Human-Environment Interaction in the West 51. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: 157 OBJ: TOP: Physical Features of the Northeast 52. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Megalopolis 53. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Industry in the Northeast 54. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Industry in the South 55. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Ecosystems in the South 56. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Population in the South 57. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: The Midwest 58. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: 170 OBJ: TOP: Transportation and Industry in the Midwest 59. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Natural Resources and the Economy in the West 60. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Alaska Hawaii 61. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Atlantic Provinces 62. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: Prairie Provinces British Colombia 63. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: Ontario Quebec 64. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Natural Resources and Northern Territories 65. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: Canadian Culture 66. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 189 OBJ: TOP: Colonialism in North America Battle of Quebec 67. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Canada and the United States 68. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 191 OBJ: TOP: Diversity in Canada 69. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 193 OBJ: TOP: Natural Resources Canada 3
14 ID: A 70. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 195 OBJ: TOP: Canada's Links With the World 71. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: OBJ: TOP: Atlantic Provinces 72. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Ontario Quebec 73. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Prairie Provinces 74. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: Natural Resources and Northern Territories 75. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: National Unity and Canada 76. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: Quebec 77. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 190 OBJ: TOP: Canadian Independence 78. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: OBJ: TOP: Natural Resources and Northern Territories 79. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: OBJ: TOP: Canada and the United States 80. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: 195 OBJ: TOP: Canada's World Role 4
15 Geography - US and Canada Review [Answer Strip] ID: A _ B 8. _ C 17. _ A 26. _ B 35. _ A 9. _ B 18. _ C 27. _ C 1. _ D 19. _ A 28. _ C 36. _ B 10. _ D 2. _ A 20. _ C 29. _ A 37. _ C 11. _ B 3. _ B 12. _ C 21. _ B 30. _ C 38. _ A 4. _ C 13. _ C 22. _ A 31. _ D 39. _ C 5. _ B 14. _ D 23. _ A 32. _ D 40. _ D 24. _ A 6. _ D 15. _ C 33. _ D 41. _ C 7. _ B 25. _ A 34. _ A 42. _ D 16.
16 Geography - US and Canada Review [Answer Strip] ID: A _ C 43. _ B 53. _ A 62. _ A 69. _ B 78. _ A 54. _ D 44. _ B 63. _ C 70. _ A 79. _ D 55. _ C 45. _ C 56. _ D 64. _ C 71. _ C 80. _ A 72. _ A 46. _ A 57. _ B 65. _ A 73. _ C 47. _ D 58. _ B 48. _ C 59. _ B 66. _ C 74. _ A 49. _ A 60. _ C 67. _ D 75. _ D 50. _ A 68. _ B 76. _ C 61. _ C 51. _ A 77. _ D 52.
Post Test Trimester 1 US & Canada 6th Grade-Study Guide
 Post Test Trimester 1 US & Canada 6th Grade-Study Guide Matching Fill in the blank by writing the letter of the correct term below. a. dominion f. indigenous b. Industrial Revolution g. interdependent
Post Test Trimester 1 US & Canada 6th Grade-Study Guide Matching Fill in the blank by writing the letter of the correct term below. a. dominion f. indigenous b. Industrial Revolution g. interdependent
Physical Geography of the United States and Canada Chapter 5 A Land of Contrasts
 Physical Geography of the United States and Canada Chapter 5 A Land of Contrasts Land Area Together the U.S. and Canada cover more than 7 million square miles. In total area, Canada ranks 2 nd and the
Physical Geography of the United States and Canada Chapter 5 A Land of Contrasts Land Area Together the U.S. and Canada cover more than 7 million square miles. In total area, Canada ranks 2 nd and the
Landforms. Lesson 1: Physical Geography of Canada Mexico. Canada s mountainous eastern and western edges create a central region of fertile plains.
 Lesson 1: Physical Geography of Canada Mexico Landforms Canada s mountainous eastern and western edges create a central region of fertile plains. Collisions of tectonic plates thrust up a series of sharp-peaked
Lesson 1: Physical Geography of Canada Mexico Landforms Canada s mountainous eastern and western edges create a central region of fertile plains. Collisions of tectonic plates thrust up a series of sharp-peaked
MARS AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GRADE: Grade 4
 MARS AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GRADE: Grade 4 Course Title: Social Studies Brief Description Overview: Students will explore the history, geography, government, and economy of the United States with
MARS AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GRADE: Grade 4 Course Title: Social Studies Brief Description Overview: Students will explore the history, geography, government, and economy of the United States with
Guided Reading Activity
 Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Physical Features Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? A Vast Land Directions: Read the lesson and use your text to decide whether each
Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Physical Features Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? A Vast Land Directions: Read the lesson and use your text to decide whether each
The United States & Canada. A Regional Study of Anglo America
 A Regional Study of Anglo America Landform Regions of the United States & Canada world leaders in agricultural and industrial production because of... VAST LANDS stretch from the Atlantic Ocean on the
A Regional Study of Anglo America Landform Regions of the United States & Canada world leaders in agricultural and industrial production because of... VAST LANDS stretch from the Atlantic Ocean on the
Explain the impact of location, climate, natural resources, and population distribution on Europe. a. Compare how the location, climate, and natural
 SS6G10 Explain the impact of location, climate, natural resources, and population distribution on Europe. a. Compare how the location, climate, and natural resources of Germany, the United Kingdom and
SS6G10 Explain the impact of location, climate, natural resources, and population distribution on Europe. a. Compare how the location, climate, and natural resources of Germany, the United Kingdom and
Unit 1: Geography. For additional information, refer to this website: 1 G e o g r a p h y
 Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
Socials Studies. Chapter 3 Canada s People 3.0-Human Geography
 Socials Studies Chapter 3 Canada s People 3.0-Human Geography Physical Geography Study of the natural features of the Earth s surface including landforms, climate, ocean currents and flora and fauna Human
Socials Studies Chapter 3 Canada s People 3.0-Human Geography Physical Geography Study of the natural features of the Earth s surface including landforms, climate, ocean currents and flora and fauna Human
4th Grade U.S. Regional Geography
 4th Grade U.S. Regional Geography Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. What does the term mainland mean in the sentence above? A the continent
4th Grade U.S. Regional Geography Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. What does the term mainland mean in the sentence above? A the continent
Unit 2. United States Physical Geography
 Unit 2 United States Physical Geography Physical Geography U.S. extends from the Atlantic to Pacific U.S. is the 3rd largest country U.S. has fertile soils, vast forests, and variety of minerals All major
Unit 2 United States Physical Geography Physical Geography U.S. extends from the Atlantic to Pacific U.S. is the 3rd largest country U.S. has fertile soils, vast forests, and variety of minerals All major
The study of Geography and the use of geographic tools help us view the world in new ways.
 S How does Geography help us understand our world? What factors shape the Earth s different environments? 7.1.9 7.2.9 BIG IDEAS COMPETENCIES Text pages or The study of Geography and the use of geographic
S How does Geography help us understand our world? What factors shape the Earth s different environments? 7.1.9 7.2.9 BIG IDEAS COMPETENCIES Text pages or The study of Geography and the use of geographic
Factors Affecting Human Settlement
 Factors Affecting Human Settlement Physical Factors One of the most basic factors affecting settlement patterns is the physical geography of the land. Climate is key, because if a place is too dry, too
Factors Affecting Human Settlement Physical Factors One of the most basic factors affecting settlement patterns is the physical geography of the land. Climate is key, because if a place is too dry, too
EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles.
 EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles. Places & Terms for Discussion Appalachian Mountains Great Plains Canadian Shield
EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles. Places & Terms for Discussion Appalachian Mountains Great Plains Canadian Shield
A Profile of the United States
 Chapter 6, Section World Geography Chapter 6 A Profile of the United States Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter
Chapter 6, Section World Geography Chapter 6 A Profile of the United States Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: Thinking Geographically Section 2: Land and Climates of the United States Section 3: The Tools of History Section 4: Economics and Other Social Sciences Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: Thinking Geographically Section 2: Land and Climates of the United States Section 3: The Tools of History Section 4: Economics and Other Social Sciences Grade 7 History
Chapter 6, Part Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great.
 Social Studies 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great. 2. The Earth is years old and is composed
Social Studies 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great. 2. The Earth is years old and is composed
4th Grade Social Studies First Nine Weeks
 4th Grade Social Studies First Nine Weeks Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Name the mountains that are located in the eastern United States.
4th Grade Social Studies First Nine Weeks Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Name the mountains that are located in the eastern United States.
Terms. divide headwaters tributary fall line fishery
 Chapter 5 Preview Section 1 The Land Objectives Identify some key similarities and differences in the physical geography of the United States and Canada. Explain why rivers have played such an important
Chapter 5 Preview Section 1 The Land Objectives Identify some key similarities and differences in the physical geography of the United States and Canada. Explain why rivers have played such an important
Borchert s Epochs of American Urbanization
 Borchert s Epochs of American Urbanization Geographers define cities as intersecting points of communication and transportation. Cities serve multiple social, political, economic and cultural purposes.
Borchert s Epochs of American Urbanization Geographers define cities as intersecting points of communication and transportation. Cities serve multiple social, political, economic and cultural purposes.
LATITUDE. Latitude lines run to, but are measured & The 0 of latitude that circles the earth is called the?
 LATITUDE Latitude lines run to, but are measured & The 0 of latitude that circles the earth is called the? LATITUDE 0 0 Latitude lines run east to west, but are measured north & south The 0 of latitude
LATITUDE Latitude lines run to, but are measured & The 0 of latitude that circles the earth is called the? LATITUDE 0 0 Latitude lines run east to west, but are measured north & south The 0 of latitude
Grade Five Social Studies Assessment Regions/Native Americans
 Name Grade Five Social Studies Assessment Regions/Native Americans Use the map below to answer questions 1 and 2 1. (Geo 1) For this location give the name of the city found there. 38 N, 100 W a. Scottsbluff
Name Grade Five Social Studies Assessment Regions/Native Americans Use the map below to answer questions 1 and 2 1. (Geo 1) For this location give the name of the city found there. 38 N, 100 W a. Scottsbluff
4 th Grade Virginia Studies SOL Review Packet Geography of Virginia. 1. The Algonquian language group of Indians lived in what region of Virginia?
 4 th Grade Virginia Studies SOL Review Packet Geography of Virginia 1. The Algonquian language group of Indians lived in what region of Virginia? A. Allegheny B. Piedmont C. Ridge and Valley D. Tidewater
4 th Grade Virginia Studies SOL Review Packet Geography of Virginia 1. The Algonquian language group of Indians lived in what region of Virginia? A. Allegheny B. Piedmont C. Ridge and Valley D. Tidewater
Wednesday, May 23, 2018
 Wednesday, May 23, 2018 Physical Geography of West Africa Objective: Summarize the main geographic aspects of each country in West Africa. Understand each country s development pattern and their current
Wednesday, May 23, 2018 Physical Geography of West Africa Objective: Summarize the main geographic aspects of each country in West Africa. Understand each country s development pattern and their current
World Geography Fall 2013 Semester Review Project
 Reporting Category RC 1: History, Government and Citizenship Standard WG.1 History. The student understands how geography and processes of spatial exchange (diffusion) influenced events in the past and
Reporting Category RC 1: History, Government and Citizenship Standard WG.1 History. The student understands how geography and processes of spatial exchange (diffusion) influenced events in the past and
TYPES OF GOVERNMENTS
 While the terms country, state, and nation are often used interchangeably, there is a difference. A State (note the capital "S") is a self-governing political entity. The term State can be used interchangeably
While the terms country, state, and nation are often used interchangeably, there is a difference. A State (note the capital "S") is a self-governing political entity. The term State can be used interchangeably
discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms and bodies of
 Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Life East of the Mississippi
 Life East of the Mississippi Physical Features ESSENTIAL QUESTION: How does geography influence the way people live? ~The United States can be divided into regions based on physical characteristics. Learning
Life East of the Mississippi Physical Features ESSENTIAL QUESTION: How does geography influence the way people live? ~The United States can be divided into regions based on physical characteristics. Learning
Regional Geography C. LANGDON WHITE. Professor Emeritus Stanford University EDWIN J. FOSCUE TOM L. MCKNIGHT
 Regional Geography of Anglo-America Sixth Edition C. LANGDON WHITE Professor Emeritus Stanford University EDWIN J. FOSCUE Late of Southern Methodist University TOM L. MCKNIGHT Professor of Geography University
Regional Geography of Anglo-America Sixth Edition C. LANGDON WHITE Professor Emeritus Stanford University EDWIN J. FOSCUE Late of Southern Methodist University TOM L. MCKNIGHT Professor of Geography University
5th social studies geography (5thsocstud_geography)
 Name: Date: 1. Many of the Native Americans who lived on the Great Plains were nomadic people. Why did they move from place to place? A. They were finding new areas to mine. B. They were looking for fertile
Name: Date: 1. Many of the Native Americans who lived on the Great Plains were nomadic people. Why did they move from place to place? A. They were finding new areas to mine. B. They were looking for fertile
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore ISTHMU S tombolo For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore ISTHMU S tombolo For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Landforms and Bodies of Water
 Chapter 5, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 115 120. The Land Terms to Know divide A high point or ridge that determines the direction that rivers flow (page 118) headwaters The source waters of a
Chapter 5, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 115 120. The Land Terms to Know divide A high point or ridge that determines the direction that rivers flow (page 118) headwaters The source waters of a
Subunit 4.1: 2.5 hours. Subunit 4.2: 2.75 hours. Subunit 4.3: 1.5 hours. Subunit 4.4: 3.5 hours. Subunit 4.5: 1.5 hours Unit 4 Learning Outcomes close
 Unit 4: North America The realm of North America extends from the polar regions of the Arctic in northern Canada and Alaska, all the way south through Mexico and the countries of Central America. Geographers
Unit 4: North America The realm of North America extends from the polar regions of the Arctic in northern Canada and Alaska, all the way south through Mexico and the countries of Central America. Geographers
Tropical Moist Rainforest
 Tropical or Lowlatitude Climates: Controlled by equatorial tropical air masses Tropical Moist Rainforest Rainfall is heavy in all months - more than 250 cm. (100 in.). Common temperatures of 27 C (80 F)
Tropical or Lowlatitude Climates: Controlled by equatorial tropical air masses Tropical Moist Rainforest Rainfall is heavy in all months - more than 250 cm. (100 in.). Common temperatures of 27 C (80 F)
CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS
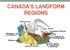 CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS Canada s Regions Canada is divided into Eight major regions. A Region is an area that is defined on the basis of the presence or absence of certain characteristics: Age of rock
CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS Canada s Regions Canada is divided into Eight major regions. A Region is an area that is defined on the basis of the presence or absence of certain characteristics: Age of rock
Oklahoma Academic Standards Science Grade: 6 - Adopted: 2014
 Main Criteria: Oklahoma Academic Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 6 Correlation Options: Show Correlated OK.6-LS. Oklahoma Academic Standards Science Grade: 6 - Adopted:
Main Criteria: Oklahoma Academic Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 6 Correlation Options: Show Correlated OK.6-LS. Oklahoma Academic Standards Science Grade: 6 - Adopted:
GEOGRAPHY OF THE WEST
 GEOGRAPHY OF THE WEST ROCKIES TO THE PACIFIC The Rocky Mountains run through North America from north to south. They mark the end of the Midwest and the beginning of the West. MOUNTAINS AND MORE The Rocky
GEOGRAPHY OF THE WEST ROCKIES TO THE PACIFIC The Rocky Mountains run through North America from north to south. They mark the end of the Midwest and the beginning of the West. MOUNTAINS AND MORE The Rocky
Chapter 32. Australia & New Zealand
 Chapter 32 Australia & New Zealand Lesson 1: Physical Geography of Australia & New Zealand Landforms Australia lies between the Pacific and Indian Oceans in the Southern Hemisphere. Although an island,
Chapter 32 Australia & New Zealand Lesson 1: Physical Geography of Australia & New Zealand Landforms Australia lies between the Pacific and Indian Oceans in the Southern Hemisphere. Although an island,
Chapter 32. Australia & New Zealand
 Chapter 32 Australia & New Zealand Lesson 1: Physical Geography of Australia & New Zealand Landforms Australia lies between the Pacific and Indian Oceans in the Southern Hemisphere. Although an island,
Chapter 32 Australia & New Zealand Lesson 1: Physical Geography of Australia & New Zealand Landforms Australia lies between the Pacific and Indian Oceans in the Southern Hemisphere. Although an island,
Five Themes of Geography Project Ms. Kiesel, Per 5. The United States of America
 Five Themes of Geography Project Ms. Kiesel, Per 5 The United States of America Location Absolute Location : The USA is located in the continent of North America in the northern and western hemispheres.
Five Themes of Geography Project Ms. Kiesel, Per 5 The United States of America Location Absolute Location : The USA is located in the continent of North America in the northern and western hemispheres.
Markville. CGC 1DL/PL Geography. Geography of Canada. Natural Environment Unit Test
 Markville CGC 1DL/PL Geography Geography of Canada Natural Environment Unit Test Name: Thinking /10 Knowledge /10 Application /10 Communication /10 Part A: Blanks (1 mark each) Thinking Choose the correct
Markville CGC 1DL/PL Geography Geography of Canada Natural Environment Unit Test Name: Thinking /10 Knowledge /10 Application /10 Communication /10 Part A: Blanks (1 mark each) Thinking Choose the correct
GUIDED READING CHAPTER 1: THE LAY OF THE LAND (Page 1)
 CHAPTER 1: THE LAY OF THE LAND (Page 1) Section 1 The Tidewater Region Directions: Use the information from pages 6-11 to complete the following statements. 1. In the southern part of the coast, the Tidewater
CHAPTER 1: THE LAY OF THE LAND (Page 1) Section 1 The Tidewater Region Directions: Use the information from pages 6-11 to complete the following statements. 1. In the southern part of the coast, the Tidewater
Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands
 Name Hour Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands Essential Question: How has the physical geography of Asia influenced the development of these regions (i.e. history, population distribution, &
Name Hour Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands Essential Question: How has the physical geography of Asia influenced the development of these regions (i.e. history, population distribution, &
2 Georgia: Its Heritage and Its Promise
 TERMS region, erosion, fault, elevation, Fall Line, aquifer, marsh, climate, weather, precipitation, drought, tornado, hurricane, wetland, estuary, barrier island, swamp PLACES Appalachian Mountains, Appalachian
TERMS region, erosion, fault, elevation, Fall Line, aquifer, marsh, climate, weather, precipitation, drought, tornado, hurricane, wetland, estuary, barrier island, swamp PLACES Appalachian Mountains, Appalachian
8th Geography Pre-Test
 Quiz Preview Go back Student's Name appears here Course Name appears here QuizStar 8th Geography Pre-Test Quiz Directions Choose the BEST answer for each question. Directions: 1. Answer the questions below
Quiz Preview Go back Student's Name appears here Course Name appears here QuizStar 8th Geography Pre-Test Quiz Directions Choose the BEST answer for each question. Directions: 1. Answer the questions below
What is the largest country in the world? Russia
 What is the largest country in the world? #1 Russia CSCOPE 2007 2 Russia Dimensions #2-3 Spans 11 Time Zones From East to West: Gulf of Finland to Alaska From North to South: Above the Arctic Circle to
What is the largest country in the world? #1 Russia CSCOPE 2007 2 Russia Dimensions #2-3 Spans 11 Time Zones From East to West: Gulf of Finland to Alaska From North to South: Above the Arctic Circle to
LOUISIANA STUDENT STANDARDS FOR SOCIAL STUDIES THAT CORRELATE WITH A FIELD TRIP TO DESTREHAN PLANTATION KINDERGARTEN
 LOUISIANA STUDENT STANDARDS FOR SOCIAL STUDIES THAT CORRELATE WITH A FIELD TRIP TO DESTREHAN PLANTATION KINDERGARTEN Standard 2 Historical Thinking Skills Students distinguish between events, people, and
LOUISIANA STUDENT STANDARDS FOR SOCIAL STUDIES THAT CORRELATE WITH A FIELD TRIP TO DESTREHAN PLANTATION KINDERGARTEN Standard 2 Historical Thinking Skills Students distinguish between events, people, and
Terms to Know. divide headwaters tributary fall line fishery
 Chapter Objectives Describe the dominant landforms and natural resources of the United States and Canada. Discuss climate and vegetation in the United States and Canada. Section 1 The Land Section Objectives
Chapter Objectives Describe the dominant landforms and natural resources of the United States and Canada. Discuss climate and vegetation in the United States and Canada. Section 1 The Land Section Objectives
GREAT BRITAIN: INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION TO 1851 Student Worksheet
 GREAT BRITAIN: INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION TO 1851 Student Worksheet Theme of Map This thematic map captures the industrial development of Britain at a time when it had transformed the British economy and society.
GREAT BRITAIN: INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION TO 1851 Student Worksheet Theme of Map This thematic map captures the industrial development of Britain at a time when it had transformed the British economy and society.
Simple Solutions Social Studies Level 2. Level 2. Social Studies. Help Pages
 Level 2 Social Studies 147 148 adobe houses with bricks made of clay and straw ancestor a family member who lived before us appoint choose; leaders can appoint others barter trading one thing for another
Level 2 Social Studies 147 148 adobe houses with bricks made of clay and straw ancestor a family member who lived before us appoint choose; leaders can appoint others barter trading one thing for another
Landforms in Canada. Canada is made up of three dis;nct types of landforms: Canadian Shield Highlands Lowlands
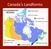 Canada s Landforms What is a Landform? A landform is any physical feature of the Earth s surface having a characteris;c, recognizable shape, produced by natural causes. Landforms include major features
Canada s Landforms What is a Landform? A landform is any physical feature of the Earth s surface having a characteris;c, recognizable shape, produced by natural causes. Landforms include major features
World Geography Chapter 3
 World Geography Chapter 3 Section 1 A. Introduction a. Weather b. Climate c. Both weather and climate are influenced by i. direct sunlight. ii. iii. iv. the features of the earth s surface. B. The Greenhouse
World Geography Chapter 3 Section 1 A. Introduction a. Weather b. Climate c. Both weather and climate are influenced by i. direct sunlight. ii. iii. iv. the features of the earth s surface. B. The Greenhouse
Vocabulary. geography. landform. plateau. climate. equator. Lesson Main Ideas What do they think about? What questions do they ask?
 Grade 5 U.S. History Chapter 1: America's Land Lesson 1: Land and Climate Objectives 1. Geography: Describe landforms and other physical features of the United States. 2. Geography: Explain how and why
Grade 5 U.S. History Chapter 1: America's Land Lesson 1: Land and Climate Objectives 1. Geography: Describe landforms and other physical features of the United States. 2. Geography: Explain how and why
Monday September 11, 2017
 Monday September 11, 2017 Need: 9/11 Interview Paper Agenda: Good things Warm Up: Video and Reflection Circles Sharing Interview Stories Discussion Questions Whole group sharing Summarizer: Living in a
Monday September 11, 2017 Need: 9/11 Interview Paper Agenda: Good things Warm Up: Video and Reflection Circles Sharing Interview Stories Discussion Questions Whole group sharing Summarizer: Living in a
The Region in Canadian Geography
 The Region in Canadian Geography Reading Course website (www.yorku.ca/anderson) Lists today s reading Laliberté et al (2015) Teaching the geographies of Canada: Reflections on pedagogy, curriculum, and
The Region in Canadian Geography Reading Course website (www.yorku.ca/anderson) Lists today s reading Laliberté et al (2015) Teaching the geographies of Canada: Reflections on pedagogy, curriculum, and
Content Area: Social Studies Standard: 1. History Prepared Graduates: Develop an understanding of how people view, construct, and interpret history
 Standard: 1. History Develop an understanding of how people view, construct, and interpret history 1. Organize and sequence events to understand the concepts of chronology and cause and effect in the history
Standard: 1. History Develop an understanding of how people view, construct, and interpret history 1. Organize and sequence events to understand the concepts of chronology and cause and effect in the history
Sixth Grade Social Studies. QPA Schedule
 2017 2018 Sixth Grade Social Studies Unit 1: Concepts Used in Global Studies 5 Weeks Unit 2: History & Geography of Europe 5 Weeks Unit 3: Europe Today 6 Weeks Unit 4: History & Geography of Latin America
2017 2018 Sixth Grade Social Studies Unit 1: Concepts Used in Global Studies 5 Weeks Unit 2: History & Geography of Europe 5 Weeks Unit 3: Europe Today 6 Weeks Unit 4: History & Geography of Latin America
1. Canadian Energy Use
 1 Unit 3 Energy 2 1. Canadian Energy Use Why are Canadians the sixth highest energy users in the world? Our major industries are energy intensive, overall industry consumes 31% of all energy in Canada.
1 Unit 3 Energy 2 1. Canadian Energy Use Why are Canadians the sixth highest energy users in the world? Our major industries are energy intensive, overall industry consumes 31% of all energy in Canada.
Standards Content Skills/Competency Assessment A:
 4 th Grade Course Title: Social Studies Month: Sept., & Oct Big Ideas/Enduring Understandings The political, economic, historical and geographic development of Pennsylvania is a model of the pattern for
4 th Grade Course Title: Social Studies Month: Sept., & Oct Big Ideas/Enduring Understandings The political, economic, historical and geographic development of Pennsylvania is a model of the pattern for
Unit 1: Geography CLASS WEBSITE: QUIZLET GAMES: ONLINE RESOURCES
 Unit 1: Geography ONLINE RESOURCES CLASS WEBSITE: HTTPS://MRYOUNGTMS.WEEBLY.COM/GEOGRAPHY.HTML QUIZLET GAMES: HTTPS://QUIZLET.COM/JOIN/MSFYY94T5 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans The Seven Continents
Unit 1: Geography ONLINE RESOURCES CLASS WEBSITE: HTTPS://MRYOUNGTMS.WEEBLY.COM/GEOGRAPHY.HTML QUIZLET GAMES: HTTPS://QUIZLET.COM/JOIN/MSFYY94T5 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans The Seven Continents
Social Studies. Chapter 2 Canada s Physical Landscape
 Social Studies Chapter 2 Canada s Physical Landscape Introduction Canada s geography its landforms and climate - has a great impact on Canadians sense of identity. Planet Earth The earth is divided into
Social Studies Chapter 2 Canada s Physical Landscape Introduction Canada s geography its landforms and climate - has a great impact on Canadians sense of identity. Planet Earth The earth is divided into
Minnesota K-12 Academic Standards in Social Studies. Grade 4: Geography of North America
 Minnesota K-12 Academic s in Social Studies Grade 4: Geography of North America 4 Describe how people take 1. Democratic government action to influence a depends on informed and decision on a specific
Minnesota K-12 Academic s in Social Studies Grade 4: Geography of North America 4 Describe how people take 1. Democratic government action to influence a depends on informed and decision on a specific
CHAPTER 1: EXPLORING GEOGRAPHY
 CHAPTER 1: EXPLORING GEOGRAPHY Please Do Now: In your PDN section of your binder answer the following with one or two sentences: What is Geography? What is Geography? The study of where people, places,
CHAPTER 1: EXPLORING GEOGRAPHY Please Do Now: In your PDN section of your binder answer the following with one or two sentences: What is Geography? What is Geography? The study of where people, places,
Chapter 2 - Lessons 1 & 2 Studying Geography, Economics
 Chapter 2 - Lessons 1 & 2 Studying Geography, Economics How does geography influence the way people live? Why do people trade? Why do people form governments? Lesson 1 - How Does Geography Influence the
Chapter 2 - Lessons 1 & 2 Studying Geography, Economics How does geography influence the way people live? Why do people trade? Why do people form governments? Lesson 1 - How Does Geography Influence the
World Industrial Regions
 World Industrial Regions North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern Europe East Asia Manufacturing Regions Fig. 11-3:
World Industrial Regions North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern Europe East Asia Manufacturing Regions Fig. 11-3:
September 14, 2013 Objective: How does geography impact history? What important features exist that have shaped societies?
 Lowenhaupt 1 September 14, 2013 Objective: How does geography impact history? What important features exist that have shaped societies? Warm-Up: In your binder, answer the following question: Imagine you
Lowenhaupt 1 September 14, 2013 Objective: How does geography impact history? What important features exist that have shaped societies? Warm-Up: In your binder, answer the following question: Imagine you
A Shift to the Sunbelt
 Adam Giladi 4/1/13 A Shift to the Sunbelt The changing global economy has lead to an increased interconnection between nations and the mass movement of individuals from one area to another. This movement
Adam Giladi 4/1/13 A Shift to the Sunbelt The changing global economy has lead to an increased interconnection between nations and the mass movement of individuals from one area to another. This movement
Answers to British Columbia Quizzes
 Answers to British Columbia Quizzes p. 1 Test Your Knowledge What do you remember from your review of the British Columbia section of the E-atlas? 1. What percentage of Canada's total area does British
Answers to British Columbia Quizzes p. 1 Test Your Knowledge What do you remember from your review of the British Columbia section of the E-atlas? 1. What percentage of Canada's total area does British
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore urban area For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore urban area For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
5 th Grade Social Studies Goals for the First Trimester Miss Gaull
 5 th Grade Social Studies Goals for the First Trimester Overview: American People, American Land The American People Government by the People Free Enterprise Lands and Regions Resources and the Environment
5 th Grade Social Studies Goals for the First Trimester Overview: American People, American Land The American People Government by the People Free Enterprise Lands and Regions Resources and the Environment
Chapter 2 Geography Study Guide
 Chapter 2 Geography Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the largest and deepest ocean? a. the Indian Ocean
Chapter 2 Geography Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the largest and deepest ocean? a. the Indian Ocean
Unit 1 Test - Version A
 Unit 1 Test - Version A 1. Approximately, how many degrees of longitude equal one time zone change? a. 5 b. 10 c. 15 d. 20 e. 25 2. The city of Lewisville has a population of 1,000 people living in 100
Unit 1 Test - Version A 1. Approximately, how many degrees of longitude equal one time zone change? a. 5 b. 10 c. 15 d. 20 e. 25 2. The city of Lewisville has a population of 1,000 people living in 100
Massachusetts Curriculum Frameworks Science Grade: 4 - Adopted: 2016
 Main Criteria: Massachusetts Curriculum Frameworks Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 4 Correlation Options: Show Correlated Massachusetts Curriculum Frameworks Science Grade:
Main Criteria: Massachusetts Curriculum Frameworks Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 4 Correlation Options: Show Correlated Massachusetts Curriculum Frameworks Science Grade:
Chapter 27. Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka
 Chapter 27 Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka Physical Geography of Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal & Sri Lanka Landforms Their locations on the fringe of South Asia means their physical and human geography
Chapter 27 Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka Physical Geography of Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal & Sri Lanka Landforms Their locations on the fringe of South Asia means their physical and human geography
Chapter 23. Equatorial Africa
 Chapter 23 Equatorial Africa Section 1 - Physical Geography of Equatorial Africa Landforms Equatorial Africa, or the Heart of Africa, is a tropical subregion located on and near the Equator in Central
Chapter 23 Equatorial Africa Section 1 - Physical Geography of Equatorial Africa Landforms Equatorial Africa, or the Heart of Africa, is a tropical subregion located on and near the Equator in Central
Most people used to live like this
 Urbanization Most people used to live like this Increasingly people live like this. For the first time in history, there are now more urban residents than rural residents. Land Cover & Land Use Land cover
Urbanization Most people used to live like this Increasingly people live like this. For the first time in history, there are now more urban residents than rural residents. Land Cover & Land Use Land cover
APPENDIX V VALLEYWIDE REPORT
 APPENDIX V VALLEYWIDE REPORT Page Intentionally Left Blank 1.2 San Joaquin Valley Profile Geography The San Joaquin Valley is the southern portion of the Great Central Valley of California (Exhibit 1-1).
APPENDIX V VALLEYWIDE REPORT Page Intentionally Left Blank 1.2 San Joaquin Valley Profile Geography The San Joaquin Valley is the southern portion of the Great Central Valley of California (Exhibit 1-1).
By Geri Flanary To accompany AP Human Geography: A Study Guide 3 rd edition By Ethel Wood
 Session 1 By Geri Flanary To accompany AP Human Geography: A Study Guide 3 rd edition By Ethel Wood WHAT IS DEMOGRAPHY? It is the scientific or statistical study of population. It comes from the Greek
Session 1 By Geri Flanary To accompany AP Human Geography: A Study Guide 3 rd edition By Ethel Wood WHAT IS DEMOGRAPHY? It is the scientific or statistical study of population. It comes from the Greek
Following the Civil War, many Americans and Europeans continued to move into the WEST
 1860-1900 Following the Civil War, many Americans and Europeans continued to move into the WEST as far as the eye can see millions of acres of treeless grassland. Between the Mississippi River and the
1860-1900 Following the Civil War, many Americans and Europeans continued to move into the WEST as far as the eye can see millions of acres of treeless grassland. Between the Mississippi River and the
Urban Geography Unit Test (Version B)
 Urban Geography Unit Test (Version B) 1. What function do the majority of the world s ten most populated cities serve? a. a fortress city to resist foreign invasion b. a port city for transporting people
Urban Geography Unit Test (Version B) 1. What function do the majority of the world s ten most populated cities serve? a. a fortress city to resist foreign invasion b. a port city for transporting people
Climate Change in Canada
 1 Climate Change in Canada Climate change is an urgent, global concern. The implications of climate change are significant and far reaching, with the potential of impacting future generations throughout
1 Climate Change in Canada Climate change is an urgent, global concern. The implications of climate change are significant and far reaching, with the potential of impacting future generations throughout
Chapter 24 Southern Africa
 Chapter 24 Southern Africa Section 1 - Physical Geography of Southern Africa Landforms Southern Africa consists of ten mainland countries and four island countries. Most of Southern Africa sits at a high
Chapter 24 Southern Africa Section 1 - Physical Geography of Southern Africa Landforms Southern Africa consists of ten mainland countries and four island countries. Most of Southern Africa sits at a high
Prentice Hall World Studies, Western Hemisphere 2005 Correlated to: Mississippi Social Studies Frameworks, Western Hemisphere Studies (Grade 6)
 Mississippi Social Studies Frameworks, Western Hemisphere Studies (Grade 6) SIXTH GRADE (Western Hemisphere Studies) STRANDS: (C-Civics); (H-History); (G-Geography); (E-Economics) COMPETENCIES and Suggested
Mississippi Social Studies Frameworks, Western Hemisphere Studies (Grade 6) SIXTH GRADE (Western Hemisphere Studies) STRANDS: (C-Civics); (H-History); (G-Geography); (E-Economics) COMPETENCIES and Suggested
Changes in Texas Ecoregions
 Comment On Lesson Changes in Texas Ecoregions The state of Texas can be divided into 10 distinct areas based on unique combinations of vegetation, topography, landforms, wildlife, soil, rock, climate,
Comment On Lesson Changes in Texas Ecoregions The state of Texas can be divided into 10 distinct areas based on unique combinations of vegetation, topography, landforms, wildlife, soil, rock, climate,
Unit 1 Basic Geographical Concepts and Themes of Geography
 Unit 1 Basic Geographical Concepts and Themes of Geography Physical: Mount Everest Political: Nepalese Sherpa What is Geography? -Geography, simply put, is the study of the Earth s surface. This includes
Unit 1 Basic Geographical Concepts and Themes of Geography Physical: Mount Everest Political: Nepalese Sherpa What is Geography? -Geography, simply put, is the study of the Earth s surface. This includes
Chapter 27. Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka
 Chapter 27 Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka Physical Geography of Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal & Sri Lanka Landforms Their locations on the fringe of South Asia means their physical and human geography
Chapter 27 Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka Physical Geography of Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal & Sri Lanka Landforms Their locations on the fringe of South Asia means their physical and human geography
Section Reference: Defining The North American Realm and Its Population Clusters Population Clusters
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: The World Today 7e Chapter Number: Chapter 01 Question type: Multiple-Choice 1) The two leading languages spoken in Canada are: a) English and Spanish b) English and
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: The World Today 7e Chapter Number: Chapter 01 Question type: Multiple-Choice 1) The two leading languages spoken in Canada are: a) English and Spanish b) English and
Augusta Canal National Heritage Area 8 Grade Lesson Plans. Stage 1 Desired Results
 Title: Falling into Place Stage 1 Desired Results Subject/Course: Grade: 8th Instructional Time: 10 hrs. Big Ideas: Geographic Regions, The Fall Line and Early Settlements, Rivers and Water Power, The
Title: Falling into Place Stage 1 Desired Results Subject/Course: Grade: 8th Instructional Time: 10 hrs. Big Ideas: Geographic Regions, The Fall Line and Early Settlements, Rivers and Water Power, The
GLOBAL CLIMATES FOCUS
 which you will learn more about in Chapter 6. Refer to the climate map and chart on pages 28-29 as you read the rest of this chapter. FOCUS GLOBAL CLIMATES What are the major influences on climate? Where
which you will learn more about in Chapter 6. Refer to the climate map and chart on pages 28-29 as you read the rest of this chapter. FOCUS GLOBAL CLIMATES What are the major influences on climate? Where
Pacemaker World Geography and Cultures. correlated to. Louisiana Social Studies Grade Level Expectations: World Geography Geography Grades 9-12
 Pacemaker World and Cultures correlated to Louisiana Social Studies Grade Level Expectations: World Grades 9-12 Pacemaker World and Cultures Pearson Learning Group correlated to Louisiana Social Studies
Pacemaker World and Cultures correlated to Louisiana Social Studies Grade Level Expectations: World Grades 9-12 Pacemaker World and Cultures Pearson Learning Group correlated to Louisiana Social Studies
ELEMENTS OF BASIC WORLD GEOGRAPHY TABLE OF CONTENTS UNIT 1 THE BASICS OF GEOGRAPHY AND NORTH AMERICA
 TABLE OF CONTENTS UNIT 1 THE BASICS OF GEOGRAPHY AND NORTH AMERICA IMPORTANT WORDS TO KNOW... 1 CHAPTER 1 THE BASICS OF GEOGRAPHY GEOGRAPHY... 2 TOOLS OF GEOGRAPHY... 3 EARTH...4 SEASONS, CLIMATE, AND
TABLE OF CONTENTS UNIT 1 THE BASICS OF GEOGRAPHY AND NORTH AMERICA IMPORTANT WORDS TO KNOW... 1 CHAPTER 1 THE BASICS OF GEOGRAPHY GEOGRAPHY... 2 TOOLS OF GEOGRAPHY... 3 EARTH...4 SEASONS, CLIMATE, AND
Stillwater Area Schools Curriculum Guide for Elementary Social Studies
 Stillwater Area Schools Curriculum Guide for Elementary Social Studies Grade Four Draft March 21, 2006 Minnesota and the St. Croix Valley I. Historical Skills A. The student will acquire skills of chronological
Stillwater Area Schools Curriculum Guide for Elementary Social Studies Grade Four Draft March 21, 2006 Minnesota and the St. Croix Valley I. Historical Skills A. The student will acquire skills of chronological
Social Studies 9 UNIT 2 GEOGRAPHIC INFLUENCES ON IDENTITY: PLACE AND PEOPLE
 Social Studies 9 UNIT 2 GEOGRAPHIC INFLUENCES ON IDENTITY: PLACE AND PEOPLE The Structure of the Earth To understand the forces that create Canada's physical landscape we must understand the structure
Social Studies 9 UNIT 2 GEOGRAPHIC INFLUENCES ON IDENTITY: PLACE AND PEOPLE The Structure of the Earth To understand the forces that create Canada's physical landscape we must understand the structure
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 3 POPULATION AND CULTURE SECTION 1: THE STUDY OF HUMAN GEOGRAPHY
 CHAPTER 3 POPULATION AND CULTURE SECTION 1: THE STUDY OF HUMAN GEOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF HUMAN GEOGRAPHY Human geography includes many topics Language Religion Customs Economics Political Systems One particular
CHAPTER 3 POPULATION AND CULTURE SECTION 1: THE STUDY OF HUMAN GEOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF HUMAN GEOGRAPHY Human geography includes many topics Language Religion Customs Economics Political Systems One particular
August 19 students first day of class (M1-M17) Place. Movement. Human- Environment Interaction. Cartography. Elevation
 Month August 2010 6 th Grade Western Hemisphere 2010-2011 Curriculum Map Pacing Vocabulary Assessment Resources Content Skills Mapmaster 7. Location August 19 Skills students first Handbook 7.6.1 Region
Month August 2010 6 th Grade Western Hemisphere 2010-2011 Curriculum Map Pacing Vocabulary Assessment Resources Content Skills Mapmaster 7. Location August 19 Skills students first Handbook 7.6.1 Region
Social Studies Continuum
 Historical Skills chronological thinking understand that we can learn about the past from different sorts of evidence begin to use historical resources apply research skills by investigating a topic in
Historical Skills chronological thinking understand that we can learn about the past from different sorts of evidence begin to use historical resources apply research skills by investigating a topic in
Why Do We Live Here? : A Historical Geographical Study of La Tabatiere, Quebec North Shore
 Why Do We Live Here? : A Historical Geographical Study of La Tabatiere, Quebec North Shore Lesson Overview Many communities and their occupants have historical connections to exploration routes and traditional
Why Do We Live Here? : A Historical Geographical Study of La Tabatiere, Quebec North Shore Lesson Overview Many communities and their occupants have historical connections to exploration routes and traditional
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Educator Version TRACKING GRO W TH IN THE U.S. Late 19th century
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Educator Version TRACKING GRO W TH IN THE U.S. Late 19th century
Chapter 1. Social Studies History and Geography
 Chapter 1 Social Studies History and Geography Unit 01 Geography Skills 1 Reading Maps Key Words border landform rely on display focus on route locater 1 There are many different kinds of maps. A political
Chapter 1 Social Studies History and Geography Unit 01 Geography Skills 1 Reading Maps Key Words border landform rely on display focus on route locater 1 There are many different kinds of maps. A political
