Emerging Memory Technologies
|
|
|
- Benedict McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Emerging Memory Technologies Minal Dubewar 1, Nibha Desai 2, Subha Subramaniam 3 1 Shah and Anchor kutchhi college of engineering, 2 Shah and Anchor kutchhi college of engineering, 3 Shah and Anchor kutchhi college of engineering, Abstract Current memory technologies, such as DRAM, SRAM, and NAND Flash, are approaching very difficult issues related their continued scaling to and beyond the 16nm generation [5]. Fortunately, research over the past ten fifteen years has led to discovery of several new memory technologies. This paper provides information on some of these emerging memories which includes some clarification and insight to their physical storage mechanisms and the limits of several of these approaches. Keywords: Memory, STT-RAM, Carbon nanotubes, 1. Introduction Memory is a device that is used to store data or programs (sequences of instructions) on a temporary or permanent basis. It is an integral part of any electronic circuit or system, particularly semiconductor memories. With the rapid growth in the requirement for semiconductor memories there have been a number of technologies and types of memory that have emerged such as ROM, RAM, EPROM, EEPROM, Flash memory, DRAM, SRAM, SDRAM, can now be seen in the electronics literature. Each one has its own advantages and area in which it may be used. In the past years, there has been a constant exponential growth in the capabilities of silicon-based microelectronics. However, it is unlikely that these advances will continue, because of the current designs when reduced to nanometer scale, will not function reliably due to their fundamental physical limitations. Also exponentially rising fabrication costs will make it prohibitive to raise integration levels [1]. Research over the past years has led to the discovery of some new memory technologies, which circumvents the issues of transistor scaling. These emerging research memory technologies include the Ferroelectric-gate FET, Nanoelectromechanical RAM, Spin Transfer Torque RAM, Nanoionic or Redox Memory, Nanowire Phase Change Memory, Electronic effects Memory (i.e., Charge trapping, Mott transition, Ferroelectric barrier effects), Macromolecular memory, and Molecular memory. Some of these emerging technologies are discussed here. 2. STT-RAM Spin-transfer torque random access memory (STT-RAM) is the solid state magnetic memory. STT-RAM, can have the density of DRAM, the speed of SRAM and the nonvolatility of flash, as well as unlimited endurance and moderate to low power consumption. The main component of STT-RAM is the magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ), which is a magnetic element consisting of two magnetic layers separated by a thin insulating layer. The information is stored in the magnetic state of one of the magnetic layers, called the free layer (FL). A second magnetic layer called the reference layer (RL) provides a stable reference magnetic orientation required for reading and writing. STT-RAM functionality depends on two phenomena: the tunneling magneto resistance (TMR) effect for reading and the spin-transfer torque (STT) effect for writing. The TMR effect causes the resistance of the MTJ to depend significantly on the relative orientation of the magnetic layers: the resistance in the antiparallel state can be several times larger than in the parallel state. It enables the magnetic state of the FL to be sensed and thus, stored information to be read. The STT effect enables electrons flowing through the MTJ to transfer spin angular momentum between the magnetic layers, which results in a torque on the magnetization of the FL. This enables the magnetic state of the FL to be changed if the torque is sufficiently strong, thus information can be written. 588
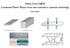
2 2.1 STT-RAM Cell Structure: An STT-RAM cell uses a Magnetic Tunnel Junction (MTJ) to store binary data. An MTJ consists of two ferromagnetic layers and one tunnel barrier layer. The two ferromagnetic layers are called the reference layer and the free layer. The magnetic direction of the reference layer remains fixed, while the magnetic direction of the free layer can be parallel or anti-parallel, which is used to represent the binary data stored in the cell. Figure1 shows an STT-RAM cell. write amplifier organization in STT-RAM are shown in Figure3. Fig.3 The organization of the sense and write circuitry for STT-RAM bitlines. Fig.1 STT-RAM cell STT-RAM cell has an access transistor that connects the storage device and the bitline. The other end of the storage device is not connected to ground; instead, it is connected to the sense line [6]. 2.2 STT-RAM Operation and Peripherals: In an MTJ, data is stored as magnetic orientation of the free layer. This orientation determines the electrical resistance of the device which is used to read the data stored in the cell. As shown in Figure 2, To read the data stored in a cell (i.e., activation operation), a small voltage is applied between sense and bit lines, and the amount of current flow is sensed. To write data to an MTJ, a large current must be pushed through the MTJ to change the magnetic orientation of the free layer. Depending on the direction of the current, the free layer becomes parallel or anti-parallel to the fixed layer. The amount of current required for writing into an MTJ is significantly larger than that needed for reading from it. Therefore, large write amplifiers are used [6]. While the STT-MRAM offers clear advantages listed above, it also faces several important challenges. The STT-MRAM cell structure requires different layers, deposited by physical vapor deposition processes for a thickness of ~ nm Robust production fabrication processes Thermal instability at the backend Narrow coercivity window 3. Carbon nanotube based memory devices Fig.2 MTJ in parallel and anti-parallel allignments when the magnetic field of the free layer and reference layer are parallel (i.e., aligned in the same direction), the MTJ resistance is low, representing a logical 0; and when they are anti-parallel to each other (i.e., aligned in the opposite direction), the MTJ resistance is high, representing a logical 1. In STT-RAM, it is the resistance of the MTJ that changes based on the stored data. Therefore, different sensing and writing mechanisms must be employed [6]. The sense and Carbon atoms can form a number of very different structures, two of the better known are diamond and graphite. A new carbon structure, the buckyball, was discovered in Soon after, the nanotube was discovered. These carbon structures, collectively known as fullerines. 589
3 Fig. 4 The atomic structure of graphite. The dashed lines indicate the weak connection betweenthe planes of graphite. Graphite consists of sheets of carbon atoms in a hexagonal arrangement as shown in figure 4. The sheets are very loosely connected to each other. Now imagine taking a single sheet of graphite and cutting a long narrow strip. If that strip is rolled into a long, narrow tube, it would be a nanotube. The ends of the tubes usually form caps, as the dangling atoms will be receptive to forming bonds with their neighbors. The resulting structure is shown in Figure 5. The electrical property of the newly created nanotube depends upon the exact angle at which the graphite was cut. charge. (The potassium ion is not shown in the figure). The state of the memory device is determined by the location of the shuttle: if it is on one side of the capsule, we treat it as a 1 ; on the other we treat it as a 0. The Van der Waals forces between the tube and the shuttle will tightly bind the shuttle to one end of the tube or the other. There is an unstable equilibrium point when the shuttle is in the exact middle of the capsule, but application of certain voltage to the capsule would prevent the shuttle from ever coming to rest there.[7] Fig. 7 An example nanomemory device Fig.5 A carbon nano tube Fig.6 Bucky ball A buckyball can be thought of as the smallest of the nanotubes. It is simply the connection of the two caps with no tube in between, and consists of exactly 60 carbon atoms (see Figure 6). Its combination of hexagons and pentagons is exactly the same as that found on a soccer ball. Very short nanotubes with 70, or even 80 atoms are sometimes also called buckyball. 3.1 The Nanomemory Device The proposed nanomemory device (NMD) consists of two parts: the capsule which holds the much smaller, charged shuttle. The shuttle is a buckyball and it contains a potassium ion (K+) which gives the shuttle its Writing to the NMD : Writing to the device is easier than reading from it. To write, voltage is applied to the capsule and shuttle will move to the either side of the capsule. To move the shuttle to the other side same voltage with opposite polarity is applied. In general the amount of voltage which needs to be applied depends upon the length of the capsule. A field of 0.1 volts/c is sufficient to move the shuttle from one side of the tube to the other. Because of a bouncing effect buckyball takes time to come to a stop. Time to settle will be about 20 picoseconds.[7] Reading from the NMD Number of ways are proposed to perform a read. The first requires three wires to be connected to the capsule: one on each end, and one in the middle. The position of the buckyball is detected by examining the resistance between the middle wire of the nanotube and the ends. A lower resistance will be found on the end that has the shuttle. This three-wire solution has a number of problems, not the least of which is that making a connection to the middle of a nanotube seems difficult. However, a long capsule and shuttle would perhaps make this solution viable. A device without the middle wire would be easier to fabricate. The notion of a destructive read could be applied here. A read would then be performed in the same way as a write. During that write some current will flow if the shuttle moves from one side of the nanotube to the other. The total current that will flow is limited by the amount of charge held in the shuttles. It is for this type of 590
4 a read that many shuttles can be used inside the capsule to increase the amount of the current flow.[7] 3.2 Bi-layer CNT RAM This device consists of a set of parallel SWNT(single wall nano tubes) or nanowires on a substrate and a set of perpendicular SWNTs that are suspended on a periodic array of supports (Figure 8 ). Each cross point in this structure corresponds to a device element with a SWNT suspended above a perpendicular nanoscale wire. Qualitatively, bistability can be envisioned as arising from the interplay of the elastic energy, which produces a potential energy minimum at finite separation (when the upper nanotube is freely suspended), and the attractive van der Waals (vdw) energy, which creates a second energy minimum when the suspended SWNT is deflected into contact with the lower nanotube. These two minima correspond to well defined OFF and ON states, respectively; that is, the separated upper-to-lower nanotube junction resistance will be very high, whereas the contact junction resistance will be orders of magnitude lower. A device element could be switched between these well-defined OFF and ON states by transiently charging the nanotubes to produce attractive or repulsive electrostatic forces. On the basis of this switching mode, we can characterize the elements as nano- or molecularscale electromechanical devices. [1] Fig. 8 Fig.9 Fig.10 Challenges with this device The distance between the crossed wires has to be controlled fairly precisely: one to two nanometers Aligning a large number of these cross-wires and to make this pattern of nanotubes with precise control of distance is going to be a difficulty. 4. Conclusions The potential and maturity of the emerging memory devices are reviewed in this paper to identify the most scientific and technological challenges that must be overcome by the device to become a viable technology. References [1] Thomas Rueckes, Kyoungha Kim, Ernesto Joselevich, Greg Y. Tseng, Chin Li Cheung, and Charles M. Lieber, Carbon Nanotube-Based Nonvolatile Random Access Memory for Molecular Computing, Science Vol. 289, no (July 7, 2000), pp [2] The international technology Roadmap for semiconductor [3] The international technology Roadmap for semiconductor [4] Yiming Huai, Spin-Transfer Torque MRAM (STT- MRAM):Challenges and Prospects AAPPS Bulletin December 2008, Vol. 18, No. 6 [5] Jim Hutchby & Mike Garner, "Assessment of the Potential & Maturity of Selected Emerging Research Memory Technologies ", in Workshop & ERD/ERM Working Group Meeting (April 6-7, 2010). [6] Emre kultu rsay, Mahmut kandemir, Anand sivasubramaniam, onur Mutlu, Evluating STT-RAM as an Energy Efficient Main Memory Alternative [7] M Brehob, The Potential of Carbon based Memory Systems, IEEE
5 Authors IJISET - International Journal of Innovative Science, Engineering & Technology, Vol. 2 Issue 5, May Minal Dubewar: She received B.E. degree in electronics and telecommunication from MGM College of Engineering affiliated to SRTM University in May-2007 and currently doing ME in Electronics from Shah & Anchor Kutchhi Engineering College affiliated to Mumbai University. Nibha Desai: She received B.E. degree in electrical engineering from L D College of Engineering affiliated to Gujrat University in July-2004 and ME in Electronics from FRCRCE affiliated to Mumbai University in Dec Currently she is working as Assistant Professor in Shah and Anchor college of engineering, Mumbai. Subha Subramaniam: She received B.E degree in Electronics and Communication Engineering from Govt. College of Engineering (GCE), Tirunelveli affiliated to Anna University in July 1998 and M.E degree in Electronics Engineering from Thadomal Shahani Engineering College (TSEC), Mumbai affiliated to Mumbai University in Nov She is currently pursuing Ph.D in Electronics Engineering from Veeramata Jijabai Technological Institute (VJTI), Mumbai. Presently she is working as Associate professor, Department of Electronics at Shah & Anchor Kutchhi Engineering College (SAKEC), Mumbai. Her research interest is in the area of Nanoelctronics. 592
DocumentToPDF trial version, to remove this mark, please register this software.
 PAPER PRESENTATION ON Carbon Nanotube - Based Nonvolatile Random Access Memory AUTHORS M SIVARAM PRASAD Sivaram.443@gmail.com B N V PAVAN KUMAR pavankumar.bnv@gmail.com 1 Carbon Nanotube- Based Nonvolatile
PAPER PRESENTATION ON Carbon Nanotube - Based Nonvolatile Random Access Memory AUTHORS M SIVARAM PRASAD Sivaram.443@gmail.com B N V PAVAN KUMAR pavankumar.bnv@gmail.com 1 Carbon Nanotube- Based Nonvolatile
The Potential of Carbon-based Memory Systems l
 The Potential of Carbon-based Memory Systems l Mark Brehob and Richard Enbody Young-Kyun Kwon and David Tomanek Department of Computer Science and Department of Physics and Astronomy Engineering Michigan
The Potential of Carbon-based Memory Systems l Mark Brehob and Richard Enbody Young-Kyun Kwon and David Tomanek Department of Computer Science and Department of Physics and Astronomy Engineering Michigan
EN2912C: Future Directions in Computing Lecture 08: Overview of Near-Term Emerging Computing Technologies
 EN2912C: Future Directions in Computing Lecture 08: Overview of Near-Term Emerging Computing Technologies Prof. Sherief Reda Division of Engineering Brown University Fall 2008 1 Near-term emerging computing
EN2912C: Future Directions in Computing Lecture 08: Overview of Near-Term Emerging Computing Technologies Prof. Sherief Reda Division of Engineering Brown University Fall 2008 1 Near-term emerging computing
Lecture 6 NEW TYPES OF MEMORY
 Lecture 6 NEW TYPES OF MEMORY Memory Logic needs memory to function (efficiently) Current memories Volatile memory SRAM DRAM Non-volatile memory (Flash) Emerging memories Phase-change memory STT-MRAM (Ferroelectric
Lecture 6 NEW TYPES OF MEMORY Memory Logic needs memory to function (efficiently) Current memories Volatile memory SRAM DRAM Non-volatile memory (Flash) Emerging memories Phase-change memory STT-MRAM (Ferroelectric
Ultralow-Power Reconfigurable Computing with Complementary Nano-Electromechanical Carbon Nanotube Switches
 Ultralow-Power Reconfigurable Computing with Complementary Nano-Electromechanical Carbon Nanotube Switches Presenter: Tulika Mitra Swarup Bhunia, Massood Tabib-Azar, and Daniel Saab Electrical Eng. And
Ultralow-Power Reconfigurable Computing with Complementary Nano-Electromechanical Carbon Nanotube Switches Presenter: Tulika Mitra Swarup Bhunia, Massood Tabib-Azar, and Daniel Saab Electrical Eng. And
Perpendicular MTJ stack development for STT MRAM on Endura PVD platform
 Perpendicular MTJ stack development for STT MRAM on Endura PVD platform Mahendra Pakala, Silicon Systems Group, AMAT Dec 16 th, 2014 AVS 2014 *All data in presentation is internal Applied generated data
Perpendicular MTJ stack development for STT MRAM on Endura PVD platform Mahendra Pakala, Silicon Systems Group, AMAT Dec 16 th, 2014 AVS 2014 *All data in presentation is internal Applied generated data
RAJASTHAN TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, KOTA
 RAJASTHAN TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, KOTA (Electronics & Communication) Submitted By: LAKSHIKA SOMANI E&C II yr, IV sem. Session: 2007-08 Department of Electronics & Communication Geetanjali Institute of Technical
RAJASTHAN TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, KOTA (Electronics & Communication) Submitted By: LAKSHIKA SOMANI E&C II yr, IV sem. Session: 2007-08 Department of Electronics & Communication Geetanjali Institute of Technical
CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Lec 13 Semiconductor Memories
 Lec 13 Semiconductor Memories 1 Semiconductor Memory Types Semiconductor Memories Read/Write (R/W) Memory or Random Access Memory (RAM) Read-Only Memory (ROM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Static RAM (SRAM) 1. Mask
Lec 13 Semiconductor Memories 1 Semiconductor Memory Types Semiconductor Memories Read/Write (R/W) Memory or Random Access Memory (RAM) Read-Only Memory (ROM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Static RAM (SRAM) 1. Mask
Introduction to magnetic recording + recording materials
 Introduction to magnetic recording + recording materials Laurent Ranno Institut Néel, Nanoscience Dept, CNRS-UJF, Grenoble, France I will give two lectures about magnetic recording. In the first one, I
Introduction to magnetic recording + recording materials Laurent Ranno Institut Néel, Nanoscience Dept, CNRS-UJF, Grenoble, France I will give two lectures about magnetic recording. In the first one, I
SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORIES
 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORIES Semiconductor Memory Classification RWM NVRWM ROM Random Access Non-Random Access EPROM E 2 PROM Mask-Programmed Programmable (PROM) SRAM FIFO FLASH DRAM LIFO Shift Register CAM
SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORIES Semiconductor Memory Classification RWM NVRWM ROM Random Access Non-Random Access EPROM E 2 PROM Mask-Programmed Programmable (PROM) SRAM FIFO FLASH DRAM LIFO Shift Register CAM
NRAM: High Performance, Highly Reliable Emerging Memory
 NRAM: High Performance, Highly Reliable Emerging Memory Sheyang Ning,2, Tomoko Ogura Iwasaki, Darlene Viviani 2, Henry Huang 2, Monte Manning 2, Thomas Rueckes 2, Ken Takeuchi Chuo University 2 Nantero
NRAM: High Performance, Highly Reliable Emerging Memory Sheyang Ning,2, Tomoko Ogura Iwasaki, Darlene Viviani 2, Henry Huang 2, Monte Manning 2, Thomas Rueckes 2, Ken Takeuchi Chuo University 2 Nantero
Lecture 25. Semiconductor Memories. Issues in Memory
 Lecture 25 Semiconductor Memories Issues in Memory Memory Classification Memory Architectures TheMemoryCore Periphery 1 Semiconductor Memory Classification RWM NVRWM ROM Random Access Non-Random Access
Lecture 25 Semiconductor Memories Issues in Memory Memory Classification Memory Architectures TheMemoryCore Periphery 1 Semiconductor Memory Classification RWM NVRWM ROM Random Access Non-Random Access
Semiconductor Memory Classification
 Semiconductor Memory Classification Read-Write Memory Non-Volatile Read-Write Memory Read-Only Memory Random Access Non-Random Access EPROM E 2 PROM Mask-Programmed Programmable (PROM) SRAM FIFO FLASH
Semiconductor Memory Classification Read-Write Memory Non-Volatile Read-Write Memory Read-Only Memory Random Access Non-Random Access EPROM E 2 PROM Mask-Programmed Programmable (PROM) SRAM FIFO FLASH
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Semiconductor. Memories. Memories
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Semiconductor Chapter Overview Memory Classification Memory Architectures The Memory Core Periphery Reliability Case Studies Semiconductor Memory Classification
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Semiconductor Chapter Overview Memory Classification Memory Architectures The Memory Core Periphery Reliability Case Studies Semiconductor Memory Classification
1. Introduction : 1.2 New properties:
 Nanodevices In Electronics Rakesh Kasaraneni(PID : 4672248) Department of Electrical Engineering EEL 5425 Introduction to Nanotechnology Florida International University Abstract : This paper describes
Nanodevices In Electronics Rakesh Kasaraneni(PID : 4672248) Department of Electrical Engineering EEL 5425 Introduction to Nanotechnology Florida International University Abstract : This paper describes
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 Semiconductor Memories Adapted from Chapter 12 of Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey et al. Copyright 2003 Prentice Hall/Pearson Outline Memory Classification Memory Architectures
Semiconductor Memories Adapted from Chapter 12 of Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey et al. Copyright 2003 Prentice Hall/Pearson Outline Memory Classification Memory Architectures
Semiconductor Memories
 Semiconductor References: Adapted from: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey UCB Principles of CMOS VLSI Design: A Systems Perspective, 2nd Ed., N. H. E. Weste and K. Eshraghian
Semiconductor References: Adapted from: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey UCB Principles of CMOS VLSI Design: A Systems Perspective, 2nd Ed., N. H. E. Weste and K. Eshraghian
MTJ-Based Nonvolatile Logic-in-Memory Architecture and Its Application
 2011 11th Non-Volatile Memory Technology Symposium @ Shanghai, China, Nov. 9, 20112 MTJ-Based Nonvolatile Logic-in-Memory Architecture and Its Application Takahiro Hanyu 1,3, S. Matsunaga 1, D. Suzuki
2011 11th Non-Volatile Memory Technology Symposium @ Shanghai, China, Nov. 9, 20112 MTJ-Based Nonvolatile Logic-in-Memory Architecture and Its Application Takahiro Hanyu 1,3, S. Matsunaga 1, D. Suzuki
Spintronics. Seminar report SUBMITTED TO: SUBMITTED BY:
 A Seminar report On Spintronics Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree of Electronics SUBMITTED TO: SUBMITTED BY: www.studymafia.org www.studymafia.org Preface I have
A Seminar report On Spintronics Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree of Electronics SUBMITTED TO: SUBMITTED BY: www.studymafia.org www.studymafia.org Preface I have
3/10/2013. Lecture #1. How small is Nano? (A movie) What is Nanotechnology? What is Nanoelectronics? What are Emerging Devices?
 EECS 498/598: Nanocircuits and Nanoarchitectures Lecture 1: Introduction to Nanotelectronic Devices (Sept. 5) Lectures 2: ITRS Nanoelectronics Road Map (Sept 7) Lecture 3: Nanodevices; Guest Lecture by
EECS 498/598: Nanocircuits and Nanoarchitectures Lecture 1: Introduction to Nanotelectronic Devices (Sept. 5) Lectures 2: ITRS Nanoelectronics Road Map (Sept 7) Lecture 3: Nanodevices; Guest Lecture by
Moores Law for DRAM. 2x increase in capacity every 18 months 2006: 4GB
 MEMORY Moores Law for DRAM 2x increase in capacity every 18 months 2006: 4GB Corollary to Moores Law Cost / chip ~ constant (packaging) Cost / bit = 2X reduction / 18 months Current (2008) ~ 1 micro-cent
MEMORY Moores Law for DRAM 2x increase in capacity every 18 months 2006: 4GB Corollary to Moores Law Cost / chip ~ constant (packaging) Cost / bit = 2X reduction / 18 months Current (2008) ~ 1 micro-cent
A Review of Spintronics based Data Storage. M.Tech Student Professor
 A Review of Spintronics based Data Storage By: Mohit P. Tahiliani S. Vadakkan M.Tech Student Professor NMAMIT, Nitte NMAMIT, Nitte CONTENTS Introduction Giant Magneto Resistance (GMR) Tunnel Magneto Resistance
A Review of Spintronics based Data Storage By: Mohit P. Tahiliani S. Vadakkan M.Tech Student Professor NMAMIT, Nitte NMAMIT, Nitte CONTENTS Introduction Giant Magneto Resistance (GMR) Tunnel Magneto Resistance
Author : Fabrice BERNARD-GRANGER September 18 th, 2014
 Author : September 18 th, 2014 Spintronic Introduction Spintronic Design Flow and Compact Modelling Process Variation and Design Impact Semiconductor Devices Characterisation Seminar 2 Spintronic Introduction
Author : September 18 th, 2014 Spintronic Introduction Spintronic Design Flow and Compact Modelling Process Variation and Design Impact Semiconductor Devices Characterisation Seminar 2 Spintronic Introduction
Mon., Feb. 04 & Wed., Feb. 06, A few more instructive slides related to GMR and GMR sensors
 Mon., Feb. 04 & Wed., Feb. 06, 2013 A few more instructive slides related to GMR and GMR sensors Oscillating sign of Interlayer Exchange Coupling between two FM films separated by Ruthenium spacers of
Mon., Feb. 04 & Wed., Feb. 06, 2013 A few more instructive slides related to GMR and GMR sensors Oscillating sign of Interlayer Exchange Coupling between two FM films separated by Ruthenium spacers of
From Hall Effect to TMR
 From Hall Effect to TMR 1 Abstract This paper compares the century old Hall effect technology to xmr technologies, specifically TMR (Tunnel Magneto-Resistance) from Crocus Technology. It covers the various
From Hall Effect to TMR 1 Abstract This paper compares the century old Hall effect technology to xmr technologies, specifically TMR (Tunnel Magneto-Resistance) from Crocus Technology. It covers the various
Wouldn t it be great if
 IDEMA DISKCON Asia-Pacific 2009 Spin Torque MRAM with Perpendicular Magnetisation: A Scalable Path for Ultra-high Density Non-volatile Memory Dr. Randall Law Data Storage Institute Agency for Science Technology
IDEMA DISKCON Asia-Pacific 2009 Spin Torque MRAM with Perpendicular Magnetisation: A Scalable Path for Ultra-high Density Non-volatile Memory Dr. Randall Law Data Storage Institute Agency for Science Technology
Chapter Overview. Memory Classification. Memory Architectures. The Memory Core. Periphery. Reliability. Memory
 SRAM Design Chapter Overview Classification Architectures The Core Periphery Reliability Semiconductor Classification RWM NVRWM ROM Random Access Non-Random Access EPROM E 2 PROM Mask-Programmed Programmable
SRAM Design Chapter Overview Classification Architectures The Core Periphery Reliability Semiconductor Classification RWM NVRWM ROM Random Access Non-Random Access EPROM E 2 PROM Mask-Programmed Programmable
Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1
 Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1 ChiiDong Chen Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica chiidong@phys.sinica.edu.tw 02 27896766 Section 5.2.1 Nature of the Carbon Bond
Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1 ChiiDong Chen Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica chiidong@phys.sinica.edu.tw 02 27896766 Section 5.2.1 Nature of the Carbon Bond
GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design 1
 ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter VIII Semiconductor Memory (chapter 12 in textbook) 1 Chapter Overview Memory Classification Memory Architectures The Memory Core Periphery Reliability Case Studies
ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter VIII Semiconductor Memory (chapter 12 in textbook) 1 Chapter Overview Memory Classification Memory Architectures The Memory Core Periphery Reliability Case Studies
Magnetic core memory (1951) cm 2 ( bit)
 Magnetic core memory (1951) 16 16 cm 2 (128 128 bit) Semiconductor Memory Classification Read-Write Memory Non-Volatile Read-Write Memory Read-Only Memory Random Access Non-Random Access EPROM E 2 PROM
Magnetic core memory (1951) 16 16 cm 2 (128 128 bit) Semiconductor Memory Classification Read-Write Memory Non-Volatile Read-Write Memory Read-Only Memory Random Access Non-Random Access EPROM E 2 PROM
Semiconductor memories
 Semiconductor memories Semiconductor Memories Data in Write Memory cell Read Data out Some design issues : How many cells? Function? Power consuption? Access type? How fast are read/write operations? Semiconductor
Semiconductor memories Semiconductor Memories Data in Write Memory cell Read Data out Some design issues : How many cells? Function? Power consuption? Access type? How fast are read/write operations? Semiconductor
MRAM: Device Basics and Emerging Technologies
 MRAM: Device Basics and Emerging Technologies Matthew R. Pufall National Institute of Standards and Technology 325 Broadway, Boulder CO 80305-3337 Phone: +1-303-497-5206 FAX: +1-303-497-7364 E-mail: pufall@boulder.nist.gov
MRAM: Device Basics and Emerging Technologies Matthew R. Pufall National Institute of Standards and Technology 325 Broadway, Boulder CO 80305-3337 Phone: +1-303-497-5206 FAX: +1-303-497-7364 E-mail: pufall@boulder.nist.gov
NANOTECHNOLOGY CHAPTER 1::INTRODUCTION
 ABSTRACT Nano-RAM is a proprietary computer memory technology from the company Nantero and NANOMOTOR is invented by University of bologna and California nano systems. NRAM is a type of nonvolatile random
ABSTRACT Nano-RAM is a proprietary computer memory technology from the company Nantero and NANOMOTOR is invented by University of bologna and California nano systems. NRAM is a type of nonvolatile random
Nanotechnology in Consumer Products
 Nanotechnology in Consumer Products June 17, 2015 October 31, 2014 The webinar will begin at 1pm Eastern Time Perform an audio check by going to Tools > Audio > Audio Setup Wizard Chat Box Chat Box Send
Nanotechnology in Consumer Products June 17, 2015 October 31, 2014 The webinar will begin at 1pm Eastern Time Perform an audio check by going to Tools > Audio > Audio Setup Wizard Chat Box Chat Box Send
Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1
 Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1 ChiiDong Chen Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica chiidong@phys.sinica.edu.tw 02 27896766 Carbon contains 6 electrons: (1s) 2,
Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1 ChiiDong Chen Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica chiidong@phys.sinica.edu.tw 02 27896766 Carbon contains 6 electrons: (1s) 2,
Topics. Dynamic CMOS Sequential Design Memory and Control. John A. Chandy Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
 Topics Dynamic CMOS Sequential Design Memory and Control Dynamic CMOS In static circuits at every point in time (except when switching) the output is connected to either GND or V DD via a low resistance
Topics Dynamic CMOS Sequential Design Memory and Control Dynamic CMOS In static circuits at every point in time (except when switching) the output is connected to either GND or V DD via a low resistance
Challenges for Materials to Support Emerging Research Devices
 Challenges for Materials to Support Emerging Research Devices C. Michael Garner*, James Hutchby +, George Bourianoff*, and Victor Zhirnov + *Intel Corporation Santa Clara, CA + Semiconductor Research Corporation
Challenges for Materials to Support Emerging Research Devices C. Michael Garner*, James Hutchby +, George Bourianoff*, and Victor Zhirnov + *Intel Corporation Santa Clara, CA + Semiconductor Research Corporation
EE141- Fall 2002 Lecture 27. Memory EE141. Announcements. We finished all the labs No homework this week Projects are due next Tuesday 9am EE141
 - Fall 2002 Lecture 27 Memory Announcements We finished all the labs No homework this week Projects are due next Tuesday 9am 1 Today s Lecture Memory:» SRAM» DRAM» Flash Memory 2 Floating-gate transistor
- Fall 2002 Lecture 27 Memory Announcements We finished all the labs No homework this week Projects are due next Tuesday 9am 1 Today s Lecture Memory:» SRAM» DRAM» Flash Memory 2 Floating-gate transistor
Memory Trend. Memory Architectures The Memory Core Periphery
 Semiconductor Memories: an Introduction ti Talk Overview Memory Trend Memory Classification Memory Architectures The Memory Core Periphery Reliability Semiconductor Memory Trends (up to the 90 s) Memory
Semiconductor Memories: an Introduction ti Talk Overview Memory Trend Memory Classification Memory Architectures The Memory Core Periphery Reliability Semiconductor Memory Trends (up to the 90 s) Memory
CMOS Inverter. Performance Scaling
 Announcements Exam #2 regrade requests due today. Homework #8 due today. Final Exam: Th June 12, 8:30 10:20am, CMU 120 (extension to 11:20am requested). Grades available for viewing via Catalyst. CMOS
Announcements Exam #2 regrade requests due today. Homework #8 due today. Final Exam: Th June 12, 8:30 10:20am, CMU 120 (extension to 11:20am requested). Grades available for viewing via Catalyst. CMOS
An Overview of Spin-based Integrated Circuits
 ASP-DAC 2014 An Overview of Spin-based Integrated Circuits Wang Kang, Weisheng Zhao, Zhaohao Wang, Jacques-Olivier Klein, Yue Zhang, Djaafar Chabi, Youguang Zhang, Dafiné Ravelosona, and Claude Chappert
ASP-DAC 2014 An Overview of Spin-based Integrated Circuits Wang Kang, Weisheng Zhao, Zhaohao Wang, Jacques-Olivier Klein, Yue Zhang, Djaafar Chabi, Youguang Zhang, Dafiné Ravelosona, and Claude Chappert
3-month progress Report
 3-month progress Report Graphene Devices and Circuits Supervisor Dr. P.A Childs Table of Content Abstract... 1 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Graphene gold rush... 1 1.2 Properties of graphene... 3 1.3 Semiconductor
3-month progress Report Graphene Devices and Circuits Supervisor Dr. P.A Childs Table of Content Abstract... 1 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Graphene gold rush... 1 1.2 Properties of graphene... 3 1.3 Semiconductor
Page 1. A portion of this study was supported by NEDO.
 MRAM : Materials and Devices Current-induced Domain Wall Motion High-speed MRAM N. Ishiwata NEC Corporation Page 1 A portion of this study was supported by NEDO. Outline Introduction Positioning and direction
MRAM : Materials and Devices Current-induced Domain Wall Motion High-speed MRAM N. Ishiwata NEC Corporation Page 1 A portion of this study was supported by NEDO. Outline Introduction Positioning and direction
A Perpendicular Spin Torque Switching based MRAM for the 28 nm Technology Node
 A Perpendicular Spin Torque Switching based MRAM for the 28 nm Technology Node U.K. Klostermann 1, M. Angerbauer 1, U. Grüning 1, F. Kreupl 1, M. Rührig 2, F. Dahmani 3, M. Kund 1, G. Müller 1 1 Qimonda
A Perpendicular Spin Torque Switching based MRAM for the 28 nm Technology Node U.K. Klostermann 1, M. Angerbauer 1, U. Grüning 1, F. Kreupl 1, M. Rührig 2, F. Dahmani 3, M. Kund 1, G. Müller 1 1 Qimonda
Magnetic Race- Track Memory: Current Induced Domain Wall Motion!
 Magnetic Race- Track Memory: Current Induced Domain Wall Motion! Stuart Parkin IBM Fellow IBM Almaden Research Center San Jose, California parkin@almaden.ibm.com Digital data storage Two main types of
Magnetic Race- Track Memory: Current Induced Domain Wall Motion! Stuart Parkin IBM Fellow IBM Almaden Research Center San Jose, California parkin@almaden.ibm.com Digital data storage Two main types of
Advanced Topics In Solid State Devices EE290B. Will a New Milli-Volt Switch Replace the Transistor for Digital Applications?
 Advanced Topics In Solid State Devices EE290B Will a New Milli-Volt Switch Replace the Transistor for Digital Applications? August 28, 2007 Prof. Eli Yablonovitch Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences
Advanced Topics In Solid State Devices EE290B Will a New Milli-Volt Switch Replace the Transistor for Digital Applications? August 28, 2007 Prof. Eli Yablonovitch Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences
Directions for simulation of beyond-cmos devices. Dmitri Nikonov, George Bourianoff, Mark Stettler
 Directions for simulation of beyond-cmos devices Dmitri Nikonov, George Bourianoff, Mark Stettler Outline Challenges and responses in nanoelectronic simulation Limits for electronic devices and motivation
Directions for simulation of beyond-cmos devices Dmitri Nikonov, George Bourianoff, Mark Stettler Outline Challenges and responses in nanoelectronic simulation Limits for electronic devices and motivation
NANOTECHNOLOGY FOR ELECTRONICS AND SENSORS APPLICATIONS
 NANOTECHNOLOGY FOR ELECTRONICS AND SENSORS APPLICATIONS SMALLER FASTER MORE SENSETIVE MORE EFFICIENT NANO CONNECT SCANDINAVIA www.nano-connect.org Chalmers University of Technology DTU Halmstad University
NANOTECHNOLOGY FOR ELECTRONICS AND SENSORS APPLICATIONS SMALLER FASTER MORE SENSETIVE MORE EFFICIENT NANO CONNECT SCANDINAVIA www.nano-connect.org Chalmers University of Technology DTU Halmstad University
Semiconductor Memories
 !"#"$%&'()$*#+%$*,' -"+./"$0 1'!*0"#)'2*+03*.$"4* Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Semiconductor Memories December 20, 2002 !"#$%&'()*&'*+&, Memory Classification Memory Architectures
!"#"$%&'()$*#+%$*,' -"+./"$0 1'!*0"#)'2*+03*.$"4* Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Semiconductor Memories December 20, 2002 !"#$%&'()*&'*+&, Memory Classification Memory Architectures
SPINTRONICS. Waltraud Buchenberg. Faculty of Physics Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg
 SPINTRONICS Waltraud Buchenberg Faculty of Physics Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg July 14, 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 WHAT IS SPINTRONICS? 2 MAGNETO-RESISTANCE STONER MODEL ANISOTROPIC MAGNETO-RESISTANCE
SPINTRONICS Waltraud Buchenberg Faculty of Physics Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg July 14, 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 WHAT IS SPINTRONICS? 2 MAGNETO-RESISTANCE STONER MODEL ANISOTROPIC MAGNETO-RESISTANCE
Advanced Flash and Nano-Floating Gate Memories
 Advanced Flash and Nano-Floating Gate Memories Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 1337 2011 Materials Research Society DOI: 10.1557/opl.2011.1028 Scaling Challenges for NAND and Replacement Memory Technology
Advanced Flash and Nano-Floating Gate Memories Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 1337 2011 Materials Research Society DOI: 10.1557/opl.2011.1028 Scaling Challenges for NAND and Replacement Memory Technology
Lecture 6. Alternative storage technologies. All optical recording. Racetrack memory. Topological kink solitons. Flash memory. Holographic memory
 Lecture 6 Alternative storage technologies All optical recording Racetrack memory Topological kink solitons Flash memory Holographic memory Millipede Ferroelectric memory All-optical recording It is possible
Lecture 6 Alternative storage technologies All optical recording Racetrack memory Topological kink solitons Flash memory Holographic memory Millipede Ferroelectric memory All-optical recording It is possible
Five-Input Complex Gate with an Inverter Using QCA
 Five-Input Complex Gate with an Inverter Using QCA Tina Suratkar 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering, St.Vincent Pallotti College Of Engineering and Technology,
Five-Input Complex Gate with an Inverter Using QCA Tina Suratkar 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering, St.Vincent Pallotti College Of Engineering and Technology,
FERROELECTRIC RAM [FRAM] Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree of Bachelor of Technology in Computer Science
![FERROELECTRIC RAM [FRAM] Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree of Bachelor of Technology in Computer Science FERROELECTRIC RAM [FRAM] Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree of Bachelor of Technology in Computer Science](/thumbs/72/67470194.jpg) A Seminar report On FERROELECTRIC RAM [FRAM] Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree of Bachelor of Technology in Computer Science SUBMITTED TO: www.studymafia.org SUBMITTED
A Seminar report On FERROELECTRIC RAM [FRAM] Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree of Bachelor of Technology in Computer Science SUBMITTED TO: www.studymafia.org SUBMITTED
PHYS 3313 Section 001 Lecture #21 Monday, Nov. 26, 2012
 PHYS 3313 Section 001 Lecture #21 Monday, Nov. 26, 2012 Superconductivity Theory, The Cooper Pair Application of Superconductivity Semi-Conductor Nano-technology Graphene 1 Announcements Your presentations
PHYS 3313 Section 001 Lecture #21 Monday, Nov. 26, 2012 Superconductivity Theory, The Cooper Pair Application of Superconductivity Semi-Conductor Nano-technology Graphene 1 Announcements Your presentations
New Approaches to Reducing Energy Consumption of MRAM write cycles, Ultra-high efficient writing (Voltage-Control) Spintronics Memory (VoCSM)
 New Approaches to Reducing Energy Consumption of MRAM write cycles, Ultra-high efficient writing (Voltage-Control) Spintronics Memory (VoCSM) Hiroaki Yoda Corporate Research & Development Center, Toshiba
New Approaches to Reducing Energy Consumption of MRAM write cycles, Ultra-high efficient writing (Voltage-Control) Spintronics Memory (VoCSM) Hiroaki Yoda Corporate Research & Development Center, Toshiba
From Spin Torque Random Access Memory to Spintronic Memristor. Xiaobin Wang Seagate Technology
 From Spin Torque Random Access Memory to Spintronic Memristor Xiaobin Wang Seagate Technology Contents Spin Torque Random Access Memory: dynamics characterization, device scale down challenges and opportunities
From Spin Torque Random Access Memory to Spintronic Memristor Xiaobin Wang Seagate Technology Contents Spin Torque Random Access Memory: dynamics characterization, device scale down challenges and opportunities
33 Electric Fields and Potential. An electric field is a storehouse of energy.
 An electric field is a storehouse of energy. The space around a concentration of electric charge is different from how it would be if the charge were not there. If you walk by the charged dome of an electrostatic
An electric field is a storehouse of energy. The space around a concentration of electric charge is different from how it would be if the charge were not there. If you walk by the charged dome of an electrostatic
From nanophysics research labs to cell phones. Dr. András Halbritter Department of Physics associate professor
 From nanophysics research labs to cell phones Dr. András Halbritter Department of Physics associate professor Curriculum Vitae Birth: 1976. High-school graduation: 1994. Master degree: 1999. PhD: 2003.
From nanophysics research labs to cell phones Dr. András Halbritter Department of Physics associate professor Curriculum Vitae Birth: 1976. High-school graduation: 1994. Master degree: 1999. PhD: 2003.
Low Dimensional System & Nanostructures Angel Rubio & Nerea Zabala. Carbon Nanotubes A New Era
 Low Dimensional System & Nanostructures Angel Rubio & Nerea Zabala Carbon Nanotubes A New Era By Afaf El-Sayed 2009 Outline World of Carbon - Graphite - Diamond - Fullerene Carbon Nanotubes CNTs - Discovery
Low Dimensional System & Nanostructures Angel Rubio & Nerea Zabala Carbon Nanotubes A New Era By Afaf El-Sayed 2009 Outline World of Carbon - Graphite - Diamond - Fullerene Carbon Nanotubes CNTs - Discovery
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 19: March 29, 2018 Memory Overview, Memory Core Cells Today! Charge Leakage/Charge Sharing " Domino Logic Design Considerations! Logic Comparisons!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 19: March 29, 2018 Memory Overview, Memory Core Cells Today! Charge Leakage/Charge Sharing " Domino Logic Design Considerations! Logic Comparisons!
single-electron electron tunneling (SET)
 single-electron electron tunneling (SET) classical dots (SET islands): level spacing is NOT important; only the charging energy (=classical effect, many electrons on the island) quantum dots: : level spacing
single-electron electron tunneling (SET) classical dots (SET islands): level spacing is NOT important; only the charging energy (=classical effect, many electrons on the island) quantum dots: : level spacing
Carbon Nanotubes in Interconnect Applications
 Carbon Nanotubes in Interconnect Applications Page 1 What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them? - Interconnects of the future? Comparison of electrical properties
Carbon Nanotubes in Interconnect Applications Page 1 What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them? - Interconnects of the future? Comparison of electrical properties
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 21: April 4, 2017 Memory Overview, Memory Core Cells Penn ESE 570 Spring 2017 Khanna Today! Memory " Classification " ROM Memories " RAM Memory
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 21: April 4, 2017 Memory Overview, Memory Core Cells Penn ESE 570 Spring 2017 Khanna Today! Memory " Classification " ROM Memories " RAM Memory
EE241 - Spring 2000 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits. References
 EE241 - Spring 2000 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 26 Memory References Rabaey, Digital Integrated Circuits Memory Design and Evolution, VLSI Circuits Short Course, 1998.» Gillingham, Evolution
EE241 - Spring 2000 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 26 Memory References Rabaey, Digital Integrated Circuits Memory Design and Evolution, VLSI Circuits Short Course, 1998.» Gillingham, Evolution
! Charge Leakage/Charge Sharing. " Domino Logic Design Considerations. ! Logic Comparisons. ! Memory. " Classification. " ROM Memories.
 ESE 57: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 9: March 9, 8 Memory Overview, Memory Core Cells Today! Charge Leakage/ " Domino Logic Design Considerations! Logic Comparisons! Memory " Classification
ESE 57: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 9: March 9, 8 Memory Overview, Memory Core Cells Today! Charge Leakage/ " Domino Logic Design Considerations! Logic Comparisons! Memory " Classification
Analysis of flip flop design using nanoelectronic single electron transistor
 Int. J. Nanoelectronics and Materials 10 (2017) 21-28 Analysis of flip flop design using nanoelectronic single electron transistor S.Rajasekaran*, G.Sundari Faculty of Electronics Engineering, Sathyabama
Int. J. Nanoelectronics and Materials 10 (2017) 21-28 Analysis of flip flop design using nanoelectronic single electron transistor S.Rajasekaran*, G.Sundari Faculty of Electronics Engineering, Sathyabama
Information processing in nanoscale systems
 Information processing in nanoscale systems Mark Rudner Niels Bohr International Academy Image from: www.upscale.utoronto.ca 100 years after Bohr, the basic laws and players are established 1913 2013 Image
Information processing in nanoscale systems Mark Rudner Niels Bohr International Academy Image from: www.upscale.utoronto.ca 100 years after Bohr, the basic laws and players are established 1913 2013 Image
EE141. EE141-Spring 2006 Digital Integrated Circuits. Administrative Stuff. Class Material. Flash Memory. Read-Only Memory Cells MOS OR ROM
 EE141-pring 2006 igital Integrated Circuits Lecture 29 Flash memory Administrative tuff reat job on projects and posters! Homework #10 due today Lab reports due this week Friday lab in 353 Final exam May
EE141-pring 2006 igital Integrated Circuits Lecture 29 Flash memory Administrative tuff reat job on projects and posters! Homework #10 due today Lab reports due this week Friday lab in 353 Final exam May
News from NBIA. Condensed Matter Physics: from new materials to quantum technology. time. Mark Rudner
 News from NBIA Condensed Matter Physics: from new materials to quantum technology Mark Rudner time ~100 years after Bohr, the basic laws and players are established 1913 2013 Image from www.periodni.com
News from NBIA Condensed Matter Physics: from new materials to quantum technology Mark Rudner time ~100 years after Bohr, the basic laws and players are established 1913 2013 Image from www.periodni.com
This document is an author-formatted work. The definitive version for citation appears as:
 This document is an author-formatted work. The definitive version for citation appears as: A. Roohi, R. Zand, D. Fan and R. F. DeMara, "Voltage-based Concatenatable Full Adder using Spin Hall Effect Switching,"
This document is an author-formatted work. The definitive version for citation appears as: A. Roohi, R. Zand, D. Fan and R. F. DeMara, "Voltage-based Concatenatable Full Adder using Spin Hall Effect Switching,"
Magnetic tunnel junction beyond memory from logic to neuromorphic computing WANJUN PARK DEPT. OF ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING, HANYANG UNIVERSITY
 Magnetic tunnel junction beyond memory from logic to neuromorphic computing WANJUN PARK DEPT. OF ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING, HANYANG UNIVERSITY Magnetic Tunnel Junctions (MTJs) Structure High density memory
Magnetic tunnel junction beyond memory from logic to neuromorphic computing WANJUN PARK DEPT. OF ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING, HANYANG UNIVERSITY Magnetic Tunnel Junctions (MTJs) Structure High density memory
ECE520 VLSI Design. Lecture 23: SRAM & DRAM Memories. Payman Zarkesh-Ha
 ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 23: SRAM & DRAM Memories Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last Lecture
ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 23: SRAM & DRAM Memories Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last Lecture
Semiconductor Memories
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Semiconductor Memories December 20, 2002 Chapter Overview Memory Classification Memory Architectures
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Semiconductor Memories December 20, 2002 Chapter Overview Memory Classification Memory Architectures
An Autonomous Nonvolatile Memory Latch
 Radiant Technologies, Inc. 2835D Pan American Freeway NE Albuquerque, NM 87107 Tel: 505-842-8007 Fax: 505-842-0366 e-mail: radiant@ferrodevices.com www.ferrodevices.com An Autonomous Nonvolatile Memory
Radiant Technologies, Inc. 2835D Pan American Freeway NE Albuquerque, NM 87107 Tel: 505-842-8007 Fax: 505-842-0366 e-mail: radiant@ferrodevices.com www.ferrodevices.com An Autonomous Nonvolatile Memory
Semiconductor Memories. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Paolo Spirito
 Semiconductor Memories Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Paolo Spirito Memory Classification Memory Classification Read-Write Memory Non-Volatile Read-Write Memory Read-Only Memory Random
Semiconductor Memories Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Paolo Spirito Memory Classification Memory Classification Read-Write Memory Non-Volatile Read-Write Memory Read-Only Memory Random
GRAPHENE NANORIBBONS Nahid Shayesteh,
 USC Department of Physics Graduate Seminar 1 GRAPHENE NANORIBBONS Nahid Shayesteh, Outlines 2 Carbon based material Discovery and innovation of graphen Graphene nanoribbons structure Application of Graphene
USC Department of Physics Graduate Seminar 1 GRAPHENE NANORIBBONS Nahid Shayesteh, Outlines 2 Carbon based material Discovery and innovation of graphen Graphene nanoribbons structure Application of Graphene
CURRICULUM VITAE HUAMIN LI UPDATED: DECEMBER 1, 2015 MAIN RESEARCH INTERESTS EDUCATION
 CURRICULUM VITAE HUAMIN LI UPDATED: DECEMBER 1, 2015 Postdoctoral Research Associate Center for Low Energy Systems Technology (LEAST), Department of Electrical Engineering University of Notre Dame, B20
CURRICULUM VITAE HUAMIN LI UPDATED: DECEMBER 1, 2015 Postdoctoral Research Associate Center for Low Energy Systems Technology (LEAST), Department of Electrical Engineering University of Notre Dame, B20
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 ) 287 292 5th International Biennial Conference on Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials, UFGNSM15 Tunneling
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 ) 287 292 5th International Biennial Conference on Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials, UFGNSM15 Tunneling
Nonvolatile CMOS Circuits Using Magnetic Tunnel Junction
 November 3-4, 2011 Berkeley, CA, USA Nonvolatile CMOS Circuits Using Magnetic Tunnel Junction Hideo Ohno 1,2 1 Center for Spintronics Integrated Systems, Tohoku University, Japan 2 Laboratory for Nanoelectronics
November 3-4, 2011 Berkeley, CA, USA Nonvolatile CMOS Circuits Using Magnetic Tunnel Junction Hideo Ohno 1,2 1 Center for Spintronics Integrated Systems, Tohoku University, Japan 2 Laboratory for Nanoelectronics
Administrative Stuff
 EE141- Spring 2004 Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 30 PERSPECTIVES 1 Administrative Stuff Homework 10 posted just for practice. No need to turn in (hw 9 due today). Normal office hours next week. HKN
EE141- Spring 2004 Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 30 PERSPECTIVES 1 Administrative Stuff Homework 10 posted just for practice. No need to turn in (hw 9 due today). Normal office hours next week. HKN
A Technology-Agnostic MTJ SPICE Model with User-Defined Dimensions for STT-MRAM Scalability Studies
 A Technology-Agnostic MTJ SPICE Model with User-Defined Dimensions for STT-MRAM Scalability Studies Model download website: mtj.umn.edu Jongyeon Kim 1, An Chen 2, Behtash Behin-Aein 2, Saurabh Kumar 1,
A Technology-Agnostic MTJ SPICE Model with User-Defined Dimensions for STT-MRAM Scalability Studies Model download website: mtj.umn.edu Jongyeon Kim 1, An Chen 2, Behtash Behin-Aein 2, Saurabh Kumar 1,
A Universal Memory Model for Design Exploration. Ketul Sutaria, Chi-Chao Wang, Yu (Kevin) Cao School of ECEE, ASU
 A Universal Memory Model for Design Exploration Ketul Sutaria, Chi-Chao Wang, Yu (Kevin) Cao School of ECEE, ASU Universal Memory Modeling because there is no universal memory device! Modeling needs in
A Universal Memory Model for Design Exploration Ketul Sutaria, Chi-Chao Wang, Yu (Kevin) Cao School of ECEE, ASU Universal Memory Modeling because there is no universal memory device! Modeling needs in
What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them?
 Growth and Properties of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them? - Interconnects of the future? - our vision Where do we stand - our
Growth and Properties of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them? - Interconnects of the future? - our vision Where do we stand - our
Nanotechnology where size matters
 Nanotechnology where size matters J Emyr Macdonald Overview Ways of seeing very small things What is nanotechnology and why is it important? Building nanostructures What we can do with nanotechnology?
Nanotechnology where size matters J Emyr Macdonald Overview Ways of seeing very small things What is nanotechnology and why is it important? Building nanostructures What we can do with nanotechnology?
From Physics to Logic
 From Physics to Logic This course aims to introduce you to the layers of abstraction of modern computer systems. We won t spend much time below the level of bits, bytes, words, and functional units, but
From Physics to Logic This course aims to introduce you to the layers of abstraction of modern computer systems. We won t spend much time below the level of bits, bytes, words, and functional units, but
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,944,054 B2
 USOO6944.054B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Rueckes et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) NRAM BIT SELECTABLE TWO-DEVICE 6,586,787 B1 * 7/2003 Shih et al.... 365/163 NANOTUBE ARRAY
USOO6944.054B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Rueckes et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) NRAM BIT SELECTABLE TWO-DEVICE 6,586,787 B1 * 7/2003 Shih et al.... 365/163 NANOTUBE ARRAY
During such a time interval, the MOS is said to be in "deep depletion" and the only charge present in the semiconductor is the depletion charge.
 Q1 (a) If we apply a positive (negative) voltage step to a p-type (n-type) MOS capacitor, which is sufficient to generate an inversion layer at equilibrium, there is a time interval, after the step, when
Q1 (a) If we apply a positive (negative) voltage step to a p-type (n-type) MOS capacitor, which is sufficient to generate an inversion layer at equilibrium, there is a time interval, after the step, when
TECHNOLOGY ROADMAP EMERGING RESEARCH DEVICES 2013 EDITION FOR
 INTERNATIONAL TECHNOLOGY ROADMAP FOR SEMICONDUCTORS 01 EDITION EMERGING RESEARCH DEVICES THE ITRS IS DEVISED AND INTENDED FOR TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT ONLY AND IS WITHOUT REGARD TO ANY COMMERCIAL CONSIDERATIONS
INTERNATIONAL TECHNOLOGY ROADMAP FOR SEMICONDUCTORS 01 EDITION EMERGING RESEARCH DEVICES THE ITRS IS DEVISED AND INTENDED FOR TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT ONLY AND IS WITHOUT REGARD TO ANY COMMERCIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Embedded MRAM Technology For logic VLSI Application
 2011 11th Non-Volatile Memory Technology Symposium Embedded MRAM Technology For logic VLSI Application November 7, 2011 Naoki Kasai 1, Shoji Ikeda 1,2, Takahiro Hanyu 1,3, Tetsuo Endoh 1,4, and Hideo Ohno
2011 11th Non-Volatile Memory Technology Symposium Embedded MRAM Technology For logic VLSI Application November 7, 2011 Naoki Kasai 1, Shoji Ikeda 1,2, Takahiro Hanyu 1,3, Tetsuo Endoh 1,4, and Hideo Ohno
The Franck-Hertz Experiment Physics 2150 Experiment No. 9 University of Colorado
 Experiment 9 1 Introduction The Franck-Hertz Experiment Physics 2150 Experiment No. 9 University of Colorado During the late nineteenth century, a great deal of evidence accumulated indicating that radiation
Experiment 9 1 Introduction The Franck-Hertz Experiment Physics 2150 Experiment No. 9 University of Colorado During the late nineteenth century, a great deal of evidence accumulated indicating that radiation
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics. Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D.
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
DRAMATIC advances in technology scaling have given us
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 39, NO. 6, JUNE 2004 919 Complementary Ferroelectric-Capacitor Logic for Low-Power Logic-in-Memory VLSI Hiromitsu Kimura, Member, IEEE, Takahiro Hanyu, Member,
IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 39, NO. 6, JUNE 2004 919 Complementary Ferroelectric-Capacitor Logic for Low-Power Logic-in-Memory VLSI Hiromitsu Kimura, Member, IEEE, Takahiro Hanyu, Member,
NEM Relay Design for Compact, Ultra-Low-Power Digital Logic Circuits
 NEM Relay Design for Compact, Ultra-Low-Power Digital Logic Circuits T.-J. K. Liu 1, N. Xu 1, I.-R. Chen 1, C. Qian 1, J. Fujiki 2 1 Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of
NEM Relay Design for Compact, Ultra-Low-Power Digital Logic Circuits T.-J. K. Liu 1, N. Xu 1, I.-R. Chen 1, C. Qian 1, J. Fujiki 2 1 Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of
Design of A Efficient Hybrid Adder Using Qca
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 PP30-34 Design of A Efficient Hybrid Adder Using Qca 1, Ravi chander, 2, PMurali Krishna 1, PG Scholar,
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 PP30-34 Design of A Efficient Hybrid Adder Using Qca 1, Ravi chander, 2, PMurali Krishna 1, PG Scholar,
Review of Semiconductor Physics. Lecture 3 4 Dr. Tayab Din Memon
 Review of Semiconductor Physics Lecture 3 4 Dr. Tayab Din Memon 1 Electronic Materials The goal of electronic materials is to generate and control the flow of an electrical current. Electronic materials
Review of Semiconductor Physics Lecture 3 4 Dr. Tayab Din Memon 1 Electronic Materials The goal of electronic materials is to generate and control the flow of an electrical current. Electronic materials
The Chemistry of Everything Kimberley Waldron. Chapter topics
 The Chemistry of Everything Kimberley Waldron Chapter 3 Diamonds Carbon allotropes, covalent bonding and the structure of simple organic molecules Richard Jarman, College of DuPage 2007 Pearson Prentice
The Chemistry of Everything Kimberley Waldron Chapter 3 Diamonds Carbon allotropes, covalent bonding and the structure of simple organic molecules Richard Jarman, College of DuPage 2007 Pearson Prentice
Hw 6 and 7 Graded and available Project Phase 2 Graded Project Phase 3 Launch Today
 EECS141 1 Hw 8 Posted Last one to be graded Due Friday April 30 Hw 6 and 7 Graded and available Project Phase 2 Graded Project Phase 3 Launch Today EECS141 2 1 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 Frequency
EECS141 1 Hw 8 Posted Last one to be graded Due Friday April 30 Hw 6 and 7 Graded and available Project Phase 2 Graded Project Phase 3 Launch Today EECS141 2 1 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 Frequency
CHAPTER I. Introduction. 1.1 State of the art for non-volatile memory
 CHAPTER I Introduction 1.1 State of the art for non-volatile memory 1.1.1 Basics of non-volatile memory devices In the last twenty years, microelectronics has been strongly developed, concerning higher
CHAPTER I Introduction 1.1 State of the art for non-volatile memory 1.1.1 Basics of non-volatile memory devices In the last twenty years, microelectronics has been strongly developed, concerning higher
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport. Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR)
 Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
