SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES AND THEIR LEGENDS. Transient infection of the zebrafish notochord triggers chronic inflammation
|
|
|
- Christian Antony Tucker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES AND THEIR LEGENDS Transient infection of the zebrafish notochord triggers chronic inflammation Mai Nguyen-Chi 1,2,5, Quang Tien Phan 1,2,5, Catherine Gonzalez 1,2, Jean-François Dubremetz 1,2, Jean-Pierre Levraud 3,4 and Georges Lutfalla 1,2. 1 Dynamique des Interactions Membranaires Normales et Pathologiques, Université Montpellier 2, UMR 5235, case 107, Place Eugène Bataillon, Montpellier Cedex 05, France. 2 CNRS; UMR 5235, Place Eugène Bataillon, Montpellier Cedex 05, France. 3 Macrophages et Développement de l Immunité, Institut Pasteur, Paris F-75015, France. 4 CNRS URA2578, Paris F-75015, France 5 These authors contributed equally to this work Correspondence to Mai Nguyen Chi and Georges Lutfalla, Dynamique des Interactions Membranaires Normales et Pathologiques, Université de Montpellier 2, UMR 5235, CNRS, case 107, Place Eugène Bataillon, Montpellier Cedex 05, France. addresses: mai.nguyen-chi@univ-montp2.fr and lutfalla@univ-montp2.fr
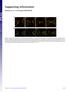
2 A pbm nc B V 2 1 col b C D b E pbm F col col b b b nc V Figure S1: E. coli remains extracellular in the notochord of infected larvae. Ultra-structural analysis using transmission electron microscopy of notochord infected larvae with E. coli, 15 min after infection (A-C) and 2 hpi (D-F). (B) and (C) are high magnification of regions boxed in (A), box 1 and 2, respectively. and (F) of region boxed in (E). Asterisks show bacteria whose morphology is altered. b: bacteria, pbm: peri-notochordal basement membrane, col: collagen sheath, nc: notochordal cell, v: vacuole. Scale bars : 5 μm in A and E, 0.5 μm in B, C, D and F.
3 PBS GFP PBS+fluo-dextran GFP/fluo-dextran Tg(mpx:GFP) 4 hpi 24 hpi 48 hpi 4 dpi Figure S2: Effect of PBS injection in the notochord on neutrophil recruitment. To check the effect of the injection in the notochord per se on neutrophil recruitment, PBS was injected in the notochord of Tg(mpx:GFP) larvae. No neutrophil was recruited to the notochord (visible with bright-field). To confirm and follow the injection in the notochord, PBS combined with Fluorecein-dextran (green) was injected in the notochord of Tg(mpx:GFP) larvae. Larvae were imaged at different time points following injection: 4, 24, 48 hpi and 4dpi and no recruited neutrophils (green) was detected..
4 PBS A B C 5 dpi 5 dpi 10 dpi E.coli 5 dpi 5 dpi 10 dpi PBS E. coli D E F G N PBS E. coli H I J # K Figure S3: Notochord infection induces notochord defects Bright-field images of PBS or E. coli injected larvae in the notochord at 5 dpi (A-B) and 10 dpi (C). A, C lateral views; B, dorsal view. Arrowheads show defects in the notochord anterior of the injection site (5 to 10 somites away). (D-G) 4 μm cross sections of PBS (D) or E. coli (E-G) injected larvae stained with Masson s Trichrome. While PBS injected larvae present a notochord (N, bracket) filled mainly with 2 or 3 big vacuolated cells (white) and delimited with a regular, unaffected collagen membrane (blue), E. coli injected larvae present several abnormalities of the notochord. Numerous cells and vacuoles are found inside the notochord. Increase of collagen deposition appears inside and outside the notochord (arrowhead). Many cells are embedded inside the collagen sheath (asterisks). (G) is a high magnification image of the region boxed in (F). (H-K) 4 μm longitudinal sections of PBS (H) or E. coli (I-K) infected larvae stained with Masson s Trichrome. As described above, PBS injected larvae present a notochord filled mainly with vacuolated cells (H), while E. coli infected larvae present several massive cell aggregates within the notochord (I). In these locations, the notochord is surrounded with cells embedded in the matrix (arrow heads) and cells with different morphologies are found inside the Disease notochord Models ( and & Mechanisms #) (J-K). Supplementary Material
5 Tg(il1b:GFP-F) A GFP B C D shield 17-somites E F G H 24hpf I J 35hpf 52hpf K L M 52hpf N O P 72hpf Figure S4: GFP expression in Tg(il1b:GFP-F) embryos and larvae during normal development. (A-B) GFP is not detected during gastrulation: Shield stage, side view with animal pole on top (A) and animal pole view (B). (C-D) GFP is first detected during segmentation in the tail bud, especially in the tip (arrow). (E-I) This expression pattern is seen at 24 and 35hpf, with in addition expression in the olfactory epithelium (F) and in scattered cells on the yolk sac (H). (J-P) From 50 hpf GFP is detected in the tip of the tail and of the caudal fin, especially in the keratinocytes. In addition it is observed in the pectoral fin bud, the retina and the neuromasts. This expression was constant during one month. (C-P) lateral views except (F) (front) and (M) (dorsal).
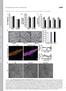
6 A B C uninfected infected uninfected 5dpf il1b AS il1b AS il1b S D 1 hpi Tg(il1b:F-GFP) E.coli-DsRed uninfected muscle notochord 24 hpi 48 hpi 96 hpi 168 hpi E E F F Figure S5: transcriptional activation of il1b upon infection with E. coli (A-B) Whole mount in situ hybridization with il1b anti-sense (il1b AS) probe in 5dpf larvae uninfected (A) and infected with E. coli in the notochord (3dpi) (B). Probe signal is detected in the tip of the caudal fin, the skin, the neuromast, eyes (arrows) and gills (asterisks). After infection, larvae overexpress il1b mrna in the inflamed region (arrowhead). (C) No signal is detected using il1b sense probe (il1b S) (C). (D) GFP (green) expression in Tg(il1b:GFP-F) larvae. Larvae were imaged without infection or at different time points following infection with a DsRed expressing E. coli (red) in the muscle or in notochord. Each column shows images from a single larva image repeatedly. (E-F) Confocal analysis of GFP expression in Tg(il1b:-GFP-F) in the head (G) and the tail (H) regions 24h following E. coli injection. Maximum projections, lateral views, scale bars=20μm. (E ) and (F ) are high magnification images of regions boxed in E and F, respectively.
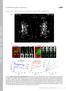
7 relative expression of mrna A mpeg1 macro neutro neg macro neutro neg PBS E. coli B mpx macro neutro neg macro neutro neg PBS E. coli relative expression of mrna C macro neutro neg il1b macro neutro neg D Tg(mpeg1:mCherryF; il1b:gfp-f) GFP mcherry Merge E Tg(Lyz:DsRed; il1b:gfp-f) GFP DsRed Merge PBS E. coli Figure S6 : GFP expression in Tg(il1b:GFP-F) line recapitulates endogenous il1b mrna expression in activated leukocytes Trypsinization of 4dpf larvae was used to generate single cell suspensions for FACS sorting, and was found to activate macrophages and neutrophils, allowing us to compare endogenous il1b transcription and GFP expression triggered by a stimulus irrespective of an infection, (A-C) To test whether Tg(il1b:GFP-F) can be used to study the dynamic expression of il1b in activated leukocytes, macrophages (macro), neutrophils (neutro), and non leukocyte cells (neg) were FACS sorted from Tg(mpx:GFP; mpeg1:mcherryf) 4dpf-larvae first injected with either PBS or E. coli. Q-RT-PCR was used to measure the relative expression of mpeg1 (A) and mpx (B) in the different populations, confirming purity of sorted populations. Measurement of il1b expression (C) shows that trypinization and cell dissociation of larvae induced high level of il1b expression in macrophages and neutrophils as compared to non leukocyte cells in both PBS and E. coli injected embryos. Quantifications using ef1a as a reference gene; light grey bar represent 95% confidence interval (student T test). Non-overlapping light grey means p<0.05. (D-E) Using similar conditions to dissociate the embryos, leukocytes were cultured from Tg(il1b:GFP-F; mpeg1:mcherryf) (D) or Tg(il1b:GFP-F; Lyz:DsRed) (E). While no expression of GFP was observed in leukocytes before dissociation (in living larvae, not shown), 90% of the macrophages (red, D) and 100% of the neutrophils (red, E) expressed GFP (green) (arrowheads), showing that Tg(il1b:GFP-F) is a good reporter transgene in leukocytes. Confocal images, Scale bar= 20µm
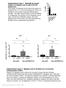
8 number of recruited macrophages hpi hpi scram MO il1b MO number of recruited macrophages scram MO il1b MO Figure S7: Macrophage recruitment is not affected by il1b loss-of-function upon notochord infection. To evaluate the effect of il1b loss-of-function on macrophage recruitment, Tg(mpeg1:mCherryF) larvae were injected with either il1b (il1b MO) or scramble (scram MO) morpholinos. Then the larvae were infected with E. coli-gfp in the notochord and recruited macrophages counted. Plots represent the number of recruited macrophages to the notochord at 4 hpi (A) and at 24 hpi (B). The number of recruited macrophages in il1b morphans was similar to that of controls. Graphs are mean value ± s.e.m. (A) p=0.80 and (B) p=0.69
9 accession number genes Fold s.e.m NM_ TNFa increased NM_ TNFa NM_ Il NM_ Il NM_ Il unchanged NM_ IFNφ NM_ Il XM_ CXC11L NM_ CXCR4b decreased XM_ CXC10L Table S1: Induction of cytokines upon notochord infection with E. coli The relative expression levels of cytokines and chemokines associated with E. coli infection in the notochord. Expressions were measured by real-time PCR (using ef1a as a reference gene) on cdna made from RNA isolated from larvae injected with PBS or with E. coli in the notochord at 48 hpi. Results are represented as fold change in E. coli infection relative to PBS injection +/- standard error of the mean. n=3 independent samples of 10 pooled larvae. We detected no significant expression of interferon φ1, φ2, γ1 and γ2 in the different conditions.
10 MOVIE LEGENDS Movie 1: General behaviour of neutrophils following notochord infection Tg(mpx:GFP) larvae were infected with crimson expressing E. coli (magenta) in the notochord at 48hpf. General behaviour of neutrophil (green) was imaged using 4- dimensional confocal microscopy at 2 hpi during 3 hours. Scale bar: 20µm. Movie 2: General behaviour of neutrophils following notochord infection Tg(mpx:GFP) larvae were infected with DsRed expressing E. coli (red) in the notochord at 48hpf. Scale bar: 50µm. Neutrophil behaviour (green) was imaged at 1 hpi during 2 hours and 50 min. Movie 3: Typical behaviour of one neutrophil following notochord infection High magnification of a region of movie S2 shows the representative behaviour of one neutrophil that fail to engulf bacteria. Scale bar: 20µm. Movie 4: General behaviour of macrophages following notochord infection Tg(mpeg1:mCherryF) larvae were infected with GFP expressing E. coli (green) at 48hpf in the notochord. The behaviour of macrophages (red) was imaged using 4-dimensional confocal microscopy at 1 hpi during 3 hours. Scale bar: 50μm. Movie 5: Typical behaviour of few macrophages following notochord infection The representative behaviour of few macrophages was image in a similar experiment that describe in movie S5 from 1hpi during 3 hours 20 min. Scale bar: 20µm.
11 Movie 6: General behaviour of macrophages following systemic infection Tg(mpeg1:mCherryF) larvae were infected with GFP expressing E. coli (green) at 48hpf in the posterior caudal vein. The behaviour of macrophages (red) was imaged using 4- dimensional confocal microscopy at 1 hpi during 1 hour. Scale bar: 50μm.
12 Movie 1. Movie 2. Movie 3.
13 Movie 4. Movie 5. Movie 6.
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its
 Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2662
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature1237 a b retinol retinal RA OH RDH (retinol dehydrogenase) O H Raldh2 O R/R.6.4.2 (retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 2) RA retinal retinol..1.1 1 Concentration (nm)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature1237 a b retinol retinal RA OH RDH (retinol dehydrogenase) O H Raldh2 O R/R.6.4.2 (retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 2) RA retinal retinol..1.1 1 Concentration (nm)
Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and
 Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and Lifeact-Ruby (red) were imaged in vivo to visualize secretion
Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and Lifeact-Ruby (red) were imaged in vivo to visualize secretion
Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo
 Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo (magenta), Fas2 (blue) and GFP (green) in overview (A) and
Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo (magenta), Fas2 (blue) and GFP (green) in overview (A) and
Actinobacteria Relative abundance (%) Co-housed CD300f WT. CD300f KO. Colon length (cm) Day 9. Microscopic inflammation score
 y groups y individuals 9 Actinobacteria Relative abundance (%) acteroidetes Cyanobacteria Deferribacteres Firmicutes Proteobacteria TM Tenericutes Unclassified CDf CDf Co-housed CDf Co-housed CDf CDf CDf
y groups y individuals 9 Actinobacteria Relative abundance (%) acteroidetes Cyanobacteria Deferribacteres Firmicutes Proteobacteria TM Tenericutes Unclassified CDf CDf Co-housed CDf Co-housed CDf CDf CDf
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A)
 Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A) and mutant (B) 4 dpf retinae. The central retina of the
Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A) and mutant (B) 4 dpf retinae. The central retina of the
Biology 218, practise Exam 2, 2011
 Figure 3 The long-range effect of Sqt does not depend on the induction of the endogenous cyc or sqt genes. a, Design and predictions for the experiments shown in b-e. b-e, Single-cell injection of 4 pg
Figure 3 The long-range effect of Sqt does not depend on the induction of the endogenous cyc or sqt genes. a, Design and predictions for the experiments shown in b-e. b-e, Single-cell injection of 4 pg
Ab1 (57-68) Ab2 ( ) Ab3 ( ) Ab4 ( ) GBP-N domain GBP-C domain CARD domain
 MDKPVCLIDTGSDGKLCVQQAALQVLQQIQQPVVVVAVVGLYRTGKSFLMNRLAG 55 KRTGFALSSNIKPKTEGIWMWCVPHPTKAGTSLVLLDTKGLGDVEKGDSKRDTYI 110 FSLTVLLSSTLVYNSRGVIDNKAMEELQYVTELIEHIKVTPDEDADDCTAFAKFF 165 PHFIWCLRDFTLELKLDGKDLTEDEYLEFALKLRPGTLKKVMMYNLPRECIQKFF
MDKPVCLIDTGSDGKLCVQQAALQVLQQIQQPVVVVAVVGLYRTGKSFLMNRLAG 55 KRTGFALSSNIKPKTEGIWMWCVPHPTKAGTSLVLLDTKGLGDVEKGDSKRDTYI 110 FSLTVLLSSTLVYNSRGVIDNKAMEELQYVTELIEHIKVTPDEDADDCTAFAKFF 165 PHFIWCLRDFTLELKLDGKDLTEDEYLEFALKLRPGTLKKVMMYNLPRECIQKFF
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2215 Figure S1 Number of egfp-vps4a bursts versus cellular expression levels. The total number of egfp-vps4a bursts, counted at the end of each movie (frame 2000, after 1h 28 min) are plotted
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2215 Figure S1 Number of egfp-vps4a bursts versus cellular expression levels. The total number of egfp-vps4a bursts, counted at the end of each movie (frame 2000, after 1h 28 min) are plotted
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
Functional analysis of a zebrafish myd88 mutant identifies key transcriptional components of the innate immune system
 Disease Models & Mechanisms 6, 841-854 (2013) doi:10.1242/dmm.010843 RESOURCE ARTICLE Functional analysis of a zebrafish myd88 mutant identifies key transcriptional components of the innate immune system
Disease Models & Mechanisms 6, 841-854 (2013) doi:10.1242/dmm.010843 RESOURCE ARTICLE Functional analysis of a zebrafish myd88 mutant identifies key transcriptional components of the innate immune system
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3848
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline. The pie-1 promoter and 3 utr were used to express yfp::gpr-1 in the germline. Expression levels from the yfp::gpr-1(cai 1.0)-expressing
Supplementary Figure 1 Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline. The pie-1 promoter and 3 utr were used to express yfp::gpr-1 in the germline. Expression levels from the yfp::gpr-1(cai 1.0)-expressing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3267 Supplementary Figure 1 A group of genes required for formation or orientation of annular F-actin bundles and aecm ridges: RNAi phenotypes and their validation by standard mutations.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3267 Supplementary Figure 1 A group of genes required for formation or orientation of annular F-actin bundles and aecm ridges: RNAi phenotypes and their validation by standard mutations.
Heather Currinn, Benjamin Guscott, Zita Balklava, Alice Rothnie and Thomas Wassmer*
 Online Resources APP controls the formation of PI(3,5)P 2 vesicles through its binding of the PIKfyve complex. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences Heather Currinn, Benjamin Guscott, Zita Balklava, Alice
Online Resources APP controls the formation of PI(3,5)P 2 vesicles through its binding of the PIKfyve complex. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences Heather Currinn, Benjamin Guscott, Zita Balklava, Alice
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterisation of IHG-1 overexpressing and knockdown cell lines. (A) Total cellular RNA was prepared from HeLa cells stably overexpressing IHG-1 or mts-ihg-1. IHG-1 mrna was quantified
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterisation of IHG-1 overexpressing and knockdown cell lines. (A) Total cellular RNA was prepared from HeLa cells stably overexpressing IHG-1 or mts-ihg-1. IHG-1 mrna was quantified
Spinal neurons require Islet1 for subtype-specific differentiation of electrical excitability
 Moreno and Ribera Neural Development 2014, 9:19 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Spinal neurons require Islet1 for subtype-specific differentiation of electrical excitability Rosa L Moreno * and Angeles B
Moreno and Ribera Neural Development 2014, 9:19 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Spinal neurons require Islet1 for subtype-specific differentiation of electrical excitability Rosa L Moreno * and Angeles B
Intravital Imaging Reveals Ghost Fibers as Architectural Units Guiding Myogenic Progenitors during Regeneration
 Cell Stem Cell Supplemental Information Intravital Imaging Reveals Ghost Fibers as Architectural Units Guiding Myogenic Progenitors during Regeneration Micah T. Webster, Uri Manor, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz,
Cell Stem Cell Supplemental Information Intravital Imaging Reveals Ghost Fibers as Architectural Units Guiding Myogenic Progenitors during Regeneration Micah T. Webster, Uri Manor, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Kasprowicz et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201310090/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. NMJ morphology of shi 12-12B ; shi-4c not treated
Supplemental material Kasprowicz et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201310090/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. NMJ morphology of shi 12-12B ; shi-4c not treated
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2717
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Dendrite length is not secondary to body length. Dendrite growth proceeds independently of the rate of body growth and decreases in rate in adults. n 20 on dendrite measurement, n
Supplementary Fig. 1. Dendrite length is not secondary to body length. Dendrite growth proceeds independently of the rate of body growth and decreases in rate in adults. n 20 on dendrite measurement, n
Zebrafish wnt8 and wnt8b share a common activity but are involved in distinct developmental pathways
 Development 121, 1787-1799 (1995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1995 1787 Zebrafish wnt8 and wnt8b share a common activity but are involved in distinct developmental pathways
Development 121, 1787-1799 (1995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1995 1787 Zebrafish wnt8 and wnt8b share a common activity but are involved in distinct developmental pathways
Nodal Signaling is Required for Closure of the Anterior Neural Tube in Zebrafish
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Biology Faculty Research Biology Department 11-8-2007 Nodal Signaling is Required for Closure of the Anterior Neural Tube in Zebrafish Allisan Aquilina-Beck
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Biology Faculty Research Biology Department 11-8-2007 Nodal Signaling is Required for Closure of the Anterior Neural Tube in Zebrafish Allisan Aquilina-Beck
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10923 Supplementary Figure 1 Ten-a and Ten-m antibody and cell type specificities. a c, Representative single confocal sections of a Drosophila NMJ stained with antibodies to Ten-a (red),
doi:10.1038/nature10923 Supplementary Figure 1 Ten-a and Ten-m antibody and cell type specificities. a c, Representative single confocal sections of a Drosophila NMJ stained with antibodies to Ten-a (red),
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fleissner et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907039106 Fig. S1. (A) MAK-2-GFP localized to CATs tips is not bound by membrane. his-3::pccg1 mak-2-gfp; mak-2 strain labeled with membrane dye FM4
Supporting Information Fleissner et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907039106 Fig. S1. (A) MAK-2-GFP localized to CATs tips is not bound by membrane. his-3::pccg1 mak-2-gfp; mak-2 strain labeled with membrane dye FM4
Role of Mitochondrial Remodeling in Programmed Cell Death in
 Developmental Cell, Vol. 12 Supplementary Data Role of Mitochondrial Remodeling in Programmed Cell Death in Drosophila melanogaster Gaurav Goyal, Brennan Fell, Apurva Sarin, Richard J. Youle, V. Sriram.
Developmental Cell, Vol. 12 Supplementary Data Role of Mitochondrial Remodeling in Programmed Cell Death in Drosophila melanogaster Gaurav Goyal, Brennan Fell, Apurva Sarin, Richard J. Youle, V. Sriram.
Comparison of the expression patterns of several sox genes between Oryzias latipes and Danio rerio
 Urun 1 Comparison of the expression patterns of several sox genes between Oryzias latipes and Danio rerio Fatma Rabia URUN ilkent University, nkara - TURKEY High mobility group domain containing transcription
Urun 1 Comparison of the expression patterns of several sox genes between Oryzias latipes and Danio rerio Fatma Rabia URUN ilkent University, nkara - TURKEY High mobility group domain containing transcription
Gene Duplication of the Zebrafish kit ligand and Partitioning of Melanocyte Development Functions to kit ligand a
 Gene Duplication of the Zebrafish kit ligand and Partitioning of Melanocyte Development Functions to kit ligand a Keith A. Hultman 1, Nathan Bahary 2, Leonard I. Zon 3,4, Stephen L. Johnson 1* 1 Department
Gene Duplication of the Zebrafish kit ligand and Partitioning of Melanocyte Development Functions to kit ligand a Keith A. Hultman 1, Nathan Bahary 2, Leonard I. Zon 3,4, Stephen L. Johnson 1* 1 Department
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2819 Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin a a Gαi3 a Actin Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT b b Gαi3 b Actin Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO # # Figure S1 Loss of protein
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2819 Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin a a Gαi3 a Actin Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT b b Gαi3 b Actin Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO # # Figure S1 Loss of protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle.
 Spatial organization is a key difference between unicellular organisms and metazoans Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle. Cells differentiate as a
Spatial organization is a key difference between unicellular organisms and metazoans Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle. Cells differentiate as a
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 PRC2 represses dedifferentiation of mature somatic cells in Arabidopsis Momoko Ikeuchi 1 *, Akira Iwase 1 *, Bart Rymen 1, Hirofumi Harashima 1, Michitaro Shibata 1, Mariko Ohnuma 1, Christian Breuer 1,
PRC2 represses dedifferentiation of mature somatic cells in Arabidopsis Momoko Ikeuchi 1 *, Akira Iwase 1 *, Bart Rymen 1, Hirofumi Harashima 1, Michitaro Shibata 1, Mariko Ohnuma 1, Christian Breuer 1,
Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA
 Himber et al. Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material 1. Short-range movement of GFP silencing affects a nearly
Himber et al. Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material 1. Short-range movement of GFP silencing affects a nearly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
Supplemental Data. Perrella et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Chapter 4 Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays.
 Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays. The data described in chapter 3 presented evidence that endogenous
Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays. The data described in chapter 3 presented evidence that endogenous
Developmental genetics: finding the genes that regulate development
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 9 Developmental genetics: finding the genes that regulate development Introduction The application of genetic analysis and DNA technology to the study of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 9 Developmental genetics: finding the genes that regulate development Introduction The application of genetic analysis and DNA technology to the study of
Supplemental Figures S1 S5
 Beyond reduction of atherosclerosis: PON2 provides apoptosis resistance and stabilizes tumor cells Ines Witte (1), Sebastian Altenhöfer (1), Petra Wilgenbus (1), Julianna Amort (1), Albrecht M. Clement
Beyond reduction of atherosclerosis: PON2 provides apoptosis resistance and stabilizes tumor cells Ines Witte (1), Sebastian Altenhöfer (1), Petra Wilgenbus (1), Julianna Amort (1), Albrecht M. Clement
Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1
 Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR
Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR
Modular scanning FCS quantifies receptor-ligand interactions in living multicellular organisms
 nature methods Modular scanning FCS quantifies receptor-ligand interactions in living multicellular organisms Jonas Ries, Shuizi Rachel Yu, Markus Burkhardt, Michael Brand & Petra Schwille Supplementary
nature methods Modular scanning FCS quantifies receptor-ligand interactions in living multicellular organisms Jonas Ries, Shuizi Rachel Yu, Markus Burkhardt, Michael Brand & Petra Schwille Supplementary
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo
 Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo In the first part of this thesis work the physical properties of cilia-driven leftward flow were characterised in the rabbit embryo. Since its discovery
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo In the first part of this thesis work the physical properties of cilia-driven leftward flow were characterised in the rabbit embryo. Since its discovery
Supplemental Information. Inferring Cell-State Transition. Dynamics from Lineage Trees. and Endpoint Single-Cell Measurements
 Cell Systems, Volume 3 Supplemental Information Inferring Cell-State Transition Dynamics from Lineage Trees and Endpoint Single-Cell Measurements Sahand Hormoz, Zakary S. Singer, James M. Linton, Yaron
Cell Systems, Volume 3 Supplemental Information Inferring Cell-State Transition Dynamics from Lineage Trees and Endpoint Single-Cell Measurements Sahand Hormoz, Zakary S. Singer, James M. Linton, Yaron
Life in an unusual intracellular niche a bacterial symbiont infecting the nucleus of amoebae
 Life in an unusual intracellular niche a bacterial symbiont infecting the nucleus of amoebae Frederik Schulz, Ilias Lagkouvardos, Florian Wascher, Karin Aistleitner, Rok Kostanjšek, Matthias Horn Supplementary
Life in an unusual intracellular niche a bacterial symbiont infecting the nucleus of amoebae Frederik Schulz, Ilias Lagkouvardos, Florian Wascher, Karin Aistleitner, Rok Kostanjšek, Matthias Horn Supplementary
FSC-W FSC-H CD4 CD62-L
 Supplementary Fig. 1 a SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H CD4 CD62-L b SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-A FSC-A 7-AAD FSC-A CD4 IL-9 CD4 c SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H 7-AAD KI67 Annexin-V 7-AAD d I L -5
Supplementary Fig. 1 a SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H CD4 CD62-L b SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-A FSC-A 7-AAD FSC-A CD4 IL-9 CD4 c SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H 7-AAD KI67 Annexin-V 7-AAD d I L -5
AP3162D: Lecture 4 - Basic modelling frameworks for developmental biology and cell-fate decisions
 AP162D: Lecture 4 - Basic modelling frameworks for developmental biology and cell-fate decisions Hyun Youk Delft University of Technology (Dated: March 15, 2018) In this lecture, we will derive the Berg-Purcell
AP162D: Lecture 4 - Basic modelling frameworks for developmental biology and cell-fate decisions Hyun Youk Delft University of Technology (Dated: March 15, 2018) In this lecture, we will derive the Berg-Purcell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09414 Supplementary Figure 1 FACS-isolated 8c hepatocytes are highly pure. a, Gating strategy for identifying hepatocyte populations based on DNA content. b, Detection of mchry and mchr9
doi:10.1038/nature09414 Supplementary Figure 1 FACS-isolated 8c hepatocytes are highly pure. a, Gating strategy for identifying hepatocyte populations based on DNA content. b, Detection of mchry and mchr9
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Eisner et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201312066/dc1 Figure S1. Mitochondrial continuity in adult skeletal muscle. (A)
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Eisner et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201312066/dc1 Figure S1. Mitochondrial continuity in adult skeletal muscle. (A)
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice Supplementary Figure 2.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018
 Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018 Introduction 3. Books This module is based on the following books: - 'Principles of Developement', Lewis Wolpert, et al., fifth edition, 2015 - 'Developmental
Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018 Introduction 3. Books This module is based on the following books: - 'Principles of Developement', Lewis Wolpert, et al., fifth edition, 2015 - 'Developmental
Essential roles of zebrafish rtn4/nogo paralogues in embryonic development
 Essential roles of zebrafish rtn4/nogo paralogues in embryonic development Pinzón-Olejua et al. Pinzón-Olejua et al. Neural Development 2014, 9:8 Pinzón-Olejua et al. Neural Development 2014, 9:8 RESEARCH
Essential roles of zebrafish rtn4/nogo paralogues in embryonic development Pinzón-Olejua et al. Pinzón-Olejua et al. Neural Development 2014, 9:8 Pinzón-Olejua et al. Neural Development 2014, 9:8 RESEARCH
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Sarcomere length-dependence of total fluorescence intensity in a relaxed muscle fibre containing BSR-RLC. a) Fluorescence intensity (I) relative to the value
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Sarcomere length-dependence of total fluorescence intensity in a relaxed muscle fibre containing BSR-RLC. a) Fluorescence intensity (I) relative to the value
Angiogenic network formation in the developing vertebrate trunk
 Research article Development and disease 5281 Angiogenic network formation in the developing vertebrate trunk Sumio Isogai 1,2, Nathan D. Lawson 1, *, Saioa Torrealday 1,, Masaharu Horiguchi 2, and Brant
Research article Development and disease 5281 Angiogenic network formation in the developing vertebrate trunk Sumio Isogai 1,2, Nathan D. Lawson 1, *, Saioa Torrealday 1,, Masaharu Horiguchi 2, and Brant
Supplementary Figure 1. CoMIC in 293T, HeLa, and HepG2 cells. (a) Mitochondrial morphology in 293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with
 Supplementary Figure 1. CoMIC in 293T, HeLa, and HepG2 cells. (a) Mitochondrial morphology in 293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with DsRed-mito. Right panels are time-course enlarged images
Supplementary Figure 1. CoMIC in 293T, HeLa, and HepG2 cells. (a) Mitochondrial morphology in 293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with DsRed-mito. Right panels are time-course enlarged images
Hes5. Hes Relative mrna levels
 A a Absolute mrna levels 6 5 4 3 2 1 hjag1 EP cdl1 EP Jag1 E2+1 b d m Hey1 c e EP Hey1 Dl1 E2+1 f h m Hey1 g i EP Hey1 1 a Hes5 Hes5 a Hes5 Hes5 B a b EP e 1.4 1.2 EP GFP GFP E2+1 c m Hey1 d Hey1 Relative
A a Absolute mrna levels 6 5 4 3 2 1 hjag1 EP cdl1 EP Jag1 E2+1 b d m Hey1 c e EP Hey1 Dl1 E2+1 f h m Hey1 g i EP Hey1 1 a Hes5 Hes5 a Hes5 Hes5 B a b EP e 1.4 1.2 EP GFP GFP E2+1 c m Hey1 d Hey1 Relative
microrna pseudo-targets
 microrna pseudo-targets Natalia Pinzón Restrepo Institut de Génétique Humaine (CNRS), Montpellier, France August, 2012 microrna target identification mir: target: 2 7 5 N NNNNNNNNNNNNNN NNNNNN 3 the seed
microrna pseudo-targets Natalia Pinzón Restrepo Institut de Génétique Humaine (CNRS), Montpellier, France August, 2012 microrna target identification mir: target: 2 7 5 N NNNNNNNNNNNNNN NNNNNN 3 the seed
Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006
 Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals unique sets of neuropeptides, transcription factors and receptors in specific types of sympathetic neurons (a) Dissection of paravertebral SGs
Supplementary Figure 1 Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals unique sets of neuropeptides, transcription factors and receptors in specific types of sympathetic neurons (a) Dissection of paravertebral SGs
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 reverse 3175 3175 F L C 318 318 3185 3185 319 319 3195 3195 315 8 1 315 3155 315 317 Supplementary Figure 3. Stability of expression of the GFP sensor constructs return to warm conditions. Semi-quantitative
reverse 3175 3175 F L C 318 318 3185 3185 319 319 3195 3195 315 8 1 315 3155 315 317 Supplementary Figure 3. Stability of expression of the GFP sensor constructs return to warm conditions. Semi-quantitative
Drosophila Life Cycle
 Drosophila Life Cycle 1 Early Drosophila Cleavage Nuclei migrate to periphery after 10 nuclear divisions. Cellularization occurs when plasma membrane folds in to divide nuclei into cells. Drosophila Superficial
Drosophila Life Cycle 1 Early Drosophila Cleavage Nuclei migrate to periphery after 10 nuclear divisions. Cellularization occurs when plasma membrane folds in to divide nuclei into cells. Drosophila Superficial
Segment boundary formation in Drosophila embryos
 Segment boundary formation in Drosophila embryos Development 130, August 2003 Camilla W. Larsen, Elizabeth Hirst, Cyrille Alexandre and Jean Paul Vincent 1. Introduction: - Segment boundary formation:
Segment boundary formation in Drosophila embryos Development 130, August 2003 Camilla W. Larsen, Elizabeth Hirst, Cyrille Alexandre and Jean Paul Vincent 1. Introduction: - Segment boundary formation:
Supporting Information Axial and transverse intensity profiles Figure S1. Relative axial coordinate of permeabilization events
 Supporting Information Localized Permeabilization of E. coli Membranes by the Antimicrobial Peptide Cecropin A Nambirajan Rangarajan, Somenath Bakshi, and James C. Weisshaar Axial and transverse intensity
Supporting Information Localized Permeabilization of E. coli Membranes by the Antimicrobial Peptide Cecropin A Nambirajan Rangarajan, Somenath Bakshi, and James C. Weisshaar Axial and transverse intensity
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information In situ generated catalyst: Copper (II) oxide and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information In situ generated catalyst: Copper (II) oxide and
Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos
 Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
V12 Gene Regulatory Networks, Boolean Networks
 V12 Gene Regulatory Networks, Boolean Networks Tue, May 28, 2018 1 Gene Expression Sequence of processes: from DNA to functional proteins transcription transcribed DNA mrna mrna RNA TFs regulation at every
V12 Gene Regulatory Networks, Boolean Networks Tue, May 28, 2018 1 Gene Expression Sequence of processes: from DNA to functional proteins transcription transcribed DNA mrna mrna RNA TFs regulation at every
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.32 - OVERVIEW OF ANIMALS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
!! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
GFP GAL bp 3964 bp
 Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
robustness: revisting the significance of mirna-mediated regulation
 : revisting the significance of mirna-mediated regulation Hervé Seitz IGH (CNRS), Montpellier, France October 13, 2012 microrna target identification .. microrna target identification mir: target: 2 7
: revisting the significance of mirna-mediated regulation Hervé Seitz IGH (CNRS), Montpellier, France October 13, 2012 microrna target identification .. microrna target identification mir: target: 2 7
Chapter 18 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Developmental Genetics
 Chapter 18 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Developmental Genetics Chapter Contents 18.1 Differentiated States Develop from Coordinated Programs of Gene Expression 18.2 Evolutionary Conservation
Chapter 18 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Developmental Genetics Chapter Contents 18.1 Differentiated States Develop from Coordinated Programs of Gene Expression 18.2 Evolutionary Conservation
UC Irvine UC Irvine Previously Published Works
 UC Irvine UC Irvine Previously Published Works Title Morphogenesis and Cell Fate Determination within the Adaxial Cell Equivalence Group of the Zebrafish Myotome Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/9921353k
UC Irvine UC Irvine Previously Published Works Title Morphogenesis and Cell Fate Determination within the Adaxial Cell Equivalence Group of the Zebrafish Myotome Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/9921353k
Lesson Overview. Gene Regulation and Expression. Lesson Overview Gene Regulation and Expression
 13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression THINK ABOUT IT Think of a library filled with how-to books. Would you ever need to use all of those books at the same time? Of course not. Now picture a tiny bacterium
13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression THINK ABOUT IT Think of a library filled with how-to books. Would you ever need to use all of those books at the same time? Of course not. Now picture a tiny bacterium
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. In vitro screening of recombinant R-CaMP2 variants.
 Supplementary Figure 1 In vitro screening of recombinant R-CaMP2 variants. Baseline fluorescence compared to R-CaMP1.07 at nominally zero calcium plotted versus dynamic range ( F/F) for 150 recombinant
Supplementary Figure 1 In vitro screening of recombinant R-CaMP2 variants. Baseline fluorescence compared to R-CaMP1.07 at nominally zero calcium plotted versus dynamic range ( F/F) for 150 recombinant
Guided Reading Activities
 Name Period Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell Guided Reading Activities Big Idea: Introduction to the Cell Answer the following questions as you read Modules 4.1 4.4: 1. A(n) uses a beam of light to illuminate
Name Period Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell Guided Reading Activities Big Idea: Introduction to the Cell Answer the following questions as you read Modules 4.1 4.4: 1. A(n) uses a beam of light to illuminate
Neural development its all connected
 Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Erythrocyte. Erythrocytes (unstained) thin membrane. refractive index varies by hemoglobin content; ghost cells seen with low hemoglobin
 Erythrocyte SYNONYMS RBC, red cell VITAL STATISTICS size... diameter 7-8 μm shape... round to slightly oval biconcave disk, crenated in hypertonic specimens with irregular edges and surfaces, spherical
Erythrocyte SYNONYMS RBC, red cell VITAL STATISTICS size... diameter 7-8 μm shape... round to slightly oval biconcave disk, crenated in hypertonic specimens with irregular edges and surfaces, spherical
Supplementary Information for. Single-cell dynamics of the chromosome replication and cell division cycles in mycobacteria
 Supplementary Information for Single-cell dynamics of the chromosome replication and cell division cycles in mycobacteria Isabella Santi 1 *, Neeraj Dhar 1, Djenet Bousbaine 1, Yuichi Wakamoto, John D.
Supplementary Information for Single-cell dynamics of the chromosome replication and cell division cycles in mycobacteria Isabella Santi 1 *, Neeraj Dhar 1, Djenet Bousbaine 1, Yuichi Wakamoto, John D.
Supplementary Figure 1. Fullerence has poor solubility in water while the C60S and LC60S nanoparticles can be stably dispersed in water.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Fullerence has poor solubility in water while the C60S and LC60S nanoparticles can be stably dispersed in water. (a) A typical photograph of fullerence (C60), C60S nanoparticles,
Supplementary Figure 1. Fullerence has poor solubility in water while the C60S and LC60S nanoparticles can be stably dispersed in water. (a) A typical photograph of fullerence (C60), C60S nanoparticles,
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses
 Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 2: Phagocytosis Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Salmonella Gram negative bacteria
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 2: Phagocytosis Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Salmonella Gram negative bacteria
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Ex vivo multiscale quantitation of skin biomechanics in wild-type and genetically-modified mice using multiphoton microscopy Stéphane Bancelin #(1), Barbara Lynch #(2), Christelle
Supplementary information Ex vivo multiscale quantitation of skin biomechanics in wild-type and genetically-modified mice using multiphoton microscopy Stéphane Bancelin #(1), Barbara Lynch #(2), Christelle
PHOTOLUMINESCENCE SPECTRA AND QUANTUM YIELDS OF GOLD NANOSPHERE MONOMERS AND DIMERS IN AQUEOUS SUSPENSION
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2016 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR PHOTOLUMINESCENCE SPECTRA AND QUANTUM
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2016 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR PHOTOLUMINESCENCE SPECTRA AND QUANTUM
Morphogen gradient interpretation by a regulated trafficking step during ligand receptor transduction
 Morphogen gradient interpretation by a regulated trafficking step during ligand receptor transduction Jerome Jullien and John Gurdon 1 Wellcome Trust/Cancer Research UK Gurdon Institute, University of
Morphogen gradient interpretation by a regulated trafficking step during ligand receptor transduction Jerome Jullien and John Gurdon 1 Wellcome Trust/Cancer Research UK Gurdon Institute, University of
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Photographs of the 3D-MTC device and the confocal fluorescence microscopy. I: The system consists of a Leica SP8-Confocal microscope (with an option of STED), a confocal PC, a 3D-MTC
Supplementary Figure 1 Photographs of the 3D-MTC device and the confocal fluorescence microscopy. I: The system consists of a Leica SP8-Confocal microscope (with an option of STED), a confocal PC, a 3D-MTC
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Statistical organelle dissection of Arabidopsis guard cells using image database LIPS Takumi Higaki *, Natsumaro Kutsuna, Yoichiroh Hosokawa, Kae Akita, Kazuo Ebine, Takashi Ueda,
Supplementary information Statistical organelle dissection of Arabidopsis guard cells using image database LIPS Takumi Higaki *, Natsumaro Kutsuna, Yoichiroh Hosokawa, Kae Akita, Kazuo Ebine, Takashi Ueda,
Waithe et al Supplementary Figures
 Waithe et al Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Expression and properties of WT and W391A mutant YFP- Ca V 2.2. A Immunoblot using Ca V 2.2 Ab for untransfected cells (UT, lane 1), YFP-Ca V 2.2
Waithe et al Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Expression and properties of WT and W391A mutant YFP- Ca V 2.2. A Immunoblot using Ca V 2.2 Ab for untransfected cells (UT, lane 1), YFP-Ca V 2.2
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Cao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1306220110 Gram - bacteria Hemolymph Cytoplasm PGRP-LC TAK1 signalosome Imd dfadd Dredd Dnr1 Ikk signalosome P Relish Nucleus AMP and effector genes Fig.
Supporting Information Cao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1306220110 Gram - bacteria Hemolymph Cytoplasm PGRP-LC TAK1 signalosome Imd dfadd Dredd Dnr1 Ikk signalosome P Relish Nucleus AMP and effector genes Fig.
2. Examine the external anatomy of the squid and identify the following structures: tentacles, arms, fins, siphon, mantle, eyes and collar.
 Cephalopod Anatomy As their name implies, members of the class Cephalopoda have modified head-foot which bears an array of prehensile tentacles and arms at the cranial end of the body. The visceral mass
Cephalopod Anatomy As their name implies, members of the class Cephalopoda have modified head-foot which bears an array of prehensile tentacles and arms at the cranial end of the body. The visceral mass
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Tuesday, December 27, 16
 Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.B: Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.B: Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information MAP2/Hoechst Hyp.-AP ph 6.5 Hyp.-SD ph 7.2 Norm.-SD ph 7.2 Supplementary Figure 1. Mitochondrial elongation in cortical neurons by acidosis. Representative images of neuronal
Supplementary Information MAP2/Hoechst Hyp.-AP ph 6.5 Hyp.-SD ph 7.2 Norm.-SD ph 7.2 Supplementary Figure 1. Mitochondrial elongation in cortical neurons by acidosis. Representative images of neuronal
TOXICOLOGICAL ENDPOINTS EASILY MEASURED IN DEVELOPING ZEBRAFISH. Robert L. Tanguay Environmental and Molecular Toxicology Oregon State University
 TOXICOLOGICAL ENDPOINTS EASILY MEASURED IN DEVELOPING ZEBRAFISH Robert L. Tanguay Environmental and Molecular Toxicology Oregon State University Why zebrafish for toxicity testing? Vertebrates.. Most importantly:
TOXICOLOGICAL ENDPOINTS EASILY MEASURED IN DEVELOPING ZEBRAFISH Robert L. Tanguay Environmental and Molecular Toxicology Oregon State University Why zebrafish for toxicity testing? Vertebrates.. Most importantly:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1 Sns and Duf co-localise in embryonic nephrocytes a-c, Wild-type stage 11 (a),14 (b) and 16 (c) embryos stained with anti-duf (green) and anti-sns (red). Higher magnification images
Supplementary Figure 1 Sns and Duf co-localise in embryonic nephrocytes a-c, Wild-type stage 11 (a),14 (b) and 16 (c) embryos stained with anti-duf (green) and anti-sns (red). Higher magnification images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09714 Supplementary Figure 1 The mouse olfactory system and summary of our results. a, Schematic of the mouse olfactory system (sagittal view). See text for more details. The red and
doi:10.1038/nature09714 Supplementary Figure 1 The mouse olfactory system and summary of our results. a, Schematic of the mouse olfactory system (sagittal view). See text for more details. The red and
Lecture 6: Non-Cortical Visual Pathways MCP 9.013/7.68, 03
 Lecture 6: Non-Cortical Visual Pathways MCP 9.013/7.68, 03 Roger W. Sperry The problem of central nervous reorganization after nerve regeneration and muscle transposition. R.W. Sperry. Quart. Rev. Biol.
Lecture 6: Non-Cortical Visual Pathways MCP 9.013/7.68, 03 Roger W. Sperry The problem of central nervous reorganization after nerve regeneration and muscle transposition. R.W. Sperry. Quart. Rev. Biol.
Supplementary Figures
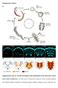 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1: Normal development and organization of the embryonic ventral nerve cord in Platynereis. (A) Life cycle of Platynereis dumerilii. (B-F) Axonal scaffolds and
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1: Normal development and organization of the embryonic ventral nerve cord in Platynereis. (A) Life cycle of Platynereis dumerilii. (B-F) Axonal scaffolds and
Behavioural properties of chick somitic mesoderm and lateral plate when explanted in vitro
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 56, pp. 41-58,1980 41 Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited 1980 Behavioural properties of chick somitic mesoderm and lateral plate when explanted in vitro
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 56, pp. 41-58,1980 41 Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited 1980 Behavioural properties of chick somitic mesoderm and lateral plate when explanted in vitro
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/ncb3492 In the format provided b the authors and unedited. Supplementar Figure 1 Fibronectin and interstitial fluid localization at the neurectoderm-to-prechordal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/ncb3492 In the format provided b the authors and unedited. Supplementar Figure 1 Fibronectin and interstitial fluid localization at the neurectoderm-to-prechordal
