TOXICOLOGICAL ENDPOINTS EASILY MEASURED IN DEVELOPING ZEBRAFISH. Robert L. Tanguay Environmental and Molecular Toxicology Oregon State University
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Shields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TOXICOLOGICAL ENDPOINTS EASILY MEASURED IN DEVELOPING ZEBRAFISH Robert L. Tanguay Environmental and Molecular Toxicology Oregon State University
2 Why zebrafish for toxicity testing? Vertebrates.. Most importantly: Complex processes can be probed or interrogated by chemical exposures Experimental convenience of cell culture, with the added value of in vivo assessments Tools that permit mechanistic evaluations
3 Zebrafish: a tool to use developmental biology to protect and improve human health Evolutionary and Developmental Biology Human Health Risk Assessment Developmental Toxicology Zebrafish
4 Baer s Law "The general features of a large group of animals appear earlier in the embryo than the special features." Karl Ernst von Baer, In other words, early development is the period most well-conserved between species.
5 Why evaluate toxicity during early development? Processes of development are remarkably conserved Comparative genomics supports overall conservation of potential targets Generally more responsive to chemical insult Why? Signaling repertoire essential and most active If a chemical is developmentally toxic it must influence the activity of a molecular pathway or process
6 Embryonic Development: A platform to probe molecular signaling and cellular interactions Receptor tyrosine kinase pathways Apoptosis pathways G-protein signaling Inositol signaling NF kappa signaling FGF signaling TGF-beta Wnt signaling Sonic hedgehog signaling Nuclear Receptor signaling Notch delta signaling Etc.!
7 Consider startpoints - not endpoints Signaling pathways and molecular events are conserved..but fish are not rodents or humans Consequences of disrupted signaling often species specific In other words, the mechanism by which a target is hit is likely conserved, but the consequence of the hit may be distinct
8 Tier 1 Testing X Test Chemicals 96 OR 384 well plates Screening for TOXICITY 1-5 days
9 Amenable to rapid assessments small amounts of chemicals 384 well plate 4 embryos in Each well 23 hour embryo
10 Efficient housing of adults for embryo production Ex. 100 X 2 liter tank unit Produces up to 10,000 embryos/day. Chorion considerations We remove it to: Assay Considerations Eliminate a potential chemical barrier Early assessments are facilitated Start and duration of exposure?
11 KEY DEVELOPMENTAL EVENTS Zebrafish versus mammals Zebrafish Rat Human Blastula/Blastocyst 2-5 hr 3-5 days 4-6 days Neural Plate formation 10 hrs 9.5 days 18 days First Somite hrs 9-10 days days 10 Somite Stage 14 hrs days days Neural Tube Formation hrs 9-12 days days First Branchial arch 24 hrs 10 days 20 days Organogensisis 48 hrs 5-6 days days First Heartbeat 30 hrs 10.2 days 22 days Birth/Hatching hrs 21 days 253 days
12 Stages Of Zebrafish Development 1. 25hr 4 hr 8 hr 3 min 19 hr 24hr 120 hr 48hr
13 Tier 1 Endpoints (Assessed between 24 and 120 hpf) Morphological Malformations i.e. pericardial edema, yolk sac edema, body axis fin malformations, eye diameter Circulation Heart beat (rate) Pigmentation Developmental progression (developmental delay) Embryo viability Behavioral spontaneous movement (18-24 hpf) onset and frequency touch response (27 hpf) motility
14 Tier 1 examples
15 Early Life Stage Response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) SHORTENED SNOUT PERICARDIAL EDEMA HEAD EDEMA UNINFLATED GAS BLADDER YOLK SAC EDEMA TCDD GAS BLADDER CONTROL
16 Early Life Stage Responses to Ethanol
17 Early Life Stage Responses to Nanoparticle Exposures Control Exposed
18 Early Life Stage Responses to Dithiocarbamates (i.e Thiuram) Control N Yolk N Exposed Yolk
19 Tier 1 continued Early Behavioral Assessments
20 SPONTANEOUS BEHAVIOR
21 TOUCH RESPONSE
22 Touch Response Examples Normal Twitch Spasms Non-responsive
23 Drug Induced Behavioral Changes CONTROL Exposed 72 hpf
24 Tier 2 Testing Cellular Targets Cellular Response Assays Male Female Adult transgenic zebrafish Male Female Adult zebrafish Transgenic embryos embryos Add 1 embryo/well Fluorescence microscopy Add chemicals fluorescent dyes i.e. Cell death Oxidative stress Proliferation Fluorescence microscopy Evaluate cell morphology Specific cellular impact evaluated over time non-invasively Identify Localization of Responses
25 Transgenic Animals Islet-1 GFP Shin-ichi Higashiijima and Hitoshi Okamoto
26 Spinal Neuron Development Live Transgenic Imaging CONTROL EXPOSED 66hpf 66hpf Islet-1 GFP
27 Persistent Neuronal Branching Deficits LIVE TRANSGENIC IMAGING 120hpf Control 120hpf Exposure (22-66hpf)
28 Ethanol Induced Cell Death Live Animals Acridine Orange
29 Ethanol Induced Apoptosis TUNEL
30 Vascular CYP1a Expression Whole mount immunohistochemistry hpf PrA - prosencephalic artery PCeV- posterior cerebral vein AA - aortic arches DLV - dorsal longitudinal vein MsV - mesencephalic vein PMBC - primordial midbrain channel
31 Alterations in gene expression In situ hybridization Control Thiuram α-col2a
32 Tier 3 Testing Integrative and comparative studies Chemical Exposures Microarrays Investigate causality of gene expression changes zebrafish toolbox: transgenics, antisense, over expression, mutants chemical genetics Define gene responses - targets? Biomarkers of exposure, effect?
33 Interpreting Common Endpoints Common endpoints revealed by chemical and genetic screening Pericardial edema Yolk sac edema Reduced growth Bent body axis Lack of swim bladder inflation Mortality Common = nonspecific
34 Proof of Concept Startpoints SHORTENED SNOUT PERICARDIAL EDEMA HEAD EDEMA UNINFLATED GAS BLADDER YOLK SAC EDEMA TCDD GAS BLADDER CONTROL
35 FISH AHR SIGNALING PATHWAY TCDD hsp 90 hsp 90 AhR2 AIP + AhR1b AhR1a Cytoplasm hsp 90 hsp 90 TCDD AhR AIP hsp 90 hsp 90 TCDD AhR AIP hsp 90 hsp 90 AIP TCDD AhR2 ARNT1 Nucleus ARNT 2a, 2b, 2c ARNT1 DRE TCDD-Responsive Genes mrnas Increased expression Xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes Toxicity?
36 Assess gene functions - in vivo Morpholino Gene Repression General approach Antisense Morpholino AUG AAAAAAA(n) mrna Translational Repression- Protein levels reduced Since genome is sequenced, any gene can be targeted! Morpholino knock-down A B C 3 hpf
37 ARNT1 and AHR2 are Necessary for TCDD Toxicity Repression of ARNT1 OR AHR2 Makes Fish Non-responsive to TCDD TCDD AHR2 ARNT1 DRE TCDD-Responsive Genes No Toxic Response TCDD AHR2 ARNT1 DRE TCDD-Responsive Genes No Toxic Response
38 TCDD Toxicity is ARNT1 Dependent uninjected vehicle uninjected TCDD zfarnt1-mo TCDD Prasch AL, Tanguay RL, Mehta V, Heideman W, Peterson RE: Identification of zebrafish ARNT1 homologs: 2,3,7,8- tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin toxicity in the developing zebrafish requires ARNT1. Mol Pharmacol 2006;69(3):
39 Final Considerations No single model is sufficient to identify hazard or to assess risk. Zebrafish as a non-mammalian vertebrate model offers a number of powerful advantages Interpreting false negatives or false positives Comparative studies will help to explain differential species responses.embryonic ADME differences.no maternal contribution.molecular signaling well conserved (functionally), primary sequence not necessarily conserved!
40 Histone deacetylase 1 (HD1) Identities = 382/442 (86%), Positives = 406/442 (91%) Danio 5 SQGTKKKVCYYYDGDVGNYYYGQGHPMKPHRIRMTHNLLLNYGLYRKMEIYRPHKANAEE 64 +QGT++KVCYYYDGDVGNYYYGQGHPMKPHRIRMTHNLLLNYGLYRKMEIYRPHKANAEE Human 4 TQGTRRKVCYYYDGDVGNYYYGQGHPMKPHRIRMTHNLLLNYGLYRKMEIYRPHKANAEE 63 Danio 65 MTKYHSDDYIKFLRSIRPDNMSEYSKQMQRFNVGEDCPVFDGLFEFCQLSTGGSVAGAVK 124 MTKYHSDDYIKFLRSIRPDNMSEYSKQMQRFNVGEDCPVFDGLFEFCQLSTGGSVA AVK Human 64 MTKYHSDDYIKFLRSIRPDNMSEYSKQMQRFNVGEDCPVFDGLFEFCQLSTGGSVASAVK 123 Danio 125 LNKQQTDIAINWAGGLHHAKKSEASGFCYVNDIVLAILELLKYHQRVLYIDIDIHHGDGV 184 LNKQQTDIA+NWAGGLHHAKKSEASGFCYVNDIVLAILELLKYHQRVLYIDIDIHHGDGV Human 124 LNKQQTDIAVNWAGGLHHAKKSEASGFCYVNDIVLAILELLKYHQRVLYIDIDIHHGDGV 183 Danio 185 EEAFYTTDRVMTVSFHKYGEYFPGTGDLRDIGAGKGKYYAVNYPLRDGIDDESYEAIFKP 244 EEAFYTTDRVMTVSFHKYGEYFPGTGDLRDIGAGKGKYYAVNYPLRDGIDDESYEAIFKP Human 184 EEAFYTTDRVMTVSFHKYGEYFPGTGDLRDIGAGKGKYYAVNYPLRDGIDDESYEAIFKP 243 Danio 245 IMSKVMEMYQPSAVVLQCGADSLSGDRLGCFNLTIKGHAKCVEYMKSFNLPLLMLGGGGY 304 +MSKVMEM+QPSAVVLQCG+DSLSGDRLGCFNLTIKGHAKCVE++KSFNLP+LMLGGGGY Human 244 VMSKVMEMFQPSAVVLQCGSDSLSGDRLGCFNLTIKGHAKCVEFVKSFNLPMLMLGGGGY 303 Danio 305 TIRNVARCWTFETAVALDSTIPNELPYNDYFEYFGPDFKLHISPSNMTN TIRNVARCWT+ETAVALD+ IPNELPYNDYFEYFGPDFKLHISPSNMTN Human 304 TIRNVARCWTYETAVALDTEIPNELPYNDYFEYFGPDFKLHISPSNMTNQNTNEYLEKIK 363 Danio QMQAIPEDAV-QEDSGDEEDDPDKRISIRAHDKRIACDEEFSDS 396 QMQAIPEDA+ +E ++EDDPDKRISI + DKRIAC+EEFSDS Human 364 QRLFENLRMLPHAPGVQMQAIPEDAIPEESGDEDEDDPDKRISICSSDKRIACEEEFSDS 423 Danio 397 EDEGQGGRRNAANYKKPKRVKT 418 E+EG+GGR+N++N+KK KRVKT Human 424 EEEGEGGRKNSSNFKKAKRVKT 445
41 Transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-1) Identities = 164/371 (44%), Positives = 229/371 (61%) Danio Human Danio Human Danio Human Danio Human Danio Human Danio Human Danio Human MSTCKTLDLEVVRKKRIEAIRGQILSKLRMAKEPESGADDDGQKIPDSLLSLYNSTVELS +STCKT+D+E+V++KRIEAIRGQILSKLR+A P G G +P+++L+LYNST + LSTCKTIDMELVKRKRIEAIRGQILSKLRLASPPSQGEVPPG-PLPEAVLALYNSTRD-- EEMKTKIVPVQDEDEDYFGKEVHKFVFQQAQN NTKHQ--MFFNVSEMKRSIPD P + + DY+ KEV N + H MFFN SE++ ++P+ RVAGESAEPEPEPEADYYAKEVTRVLMVETHNEIYDKFKQSTHSIYMFFNTSELREAVPE YRLLSQAELRLRIKNPTMDQEQRLELYRGVGDQA-RYLGTRFVSKDLSNRWLSFDVKQTM + + LR+ + EQ +ELY+ + + RYL R ++ S WLSFDV + --PVLLSRAELRLLRLKLKVEQHVELYQKYSNNSWRYLSNRLLAPSDSPEWLSFDVTGVV IEWLQGSEDEETLELRLYCDCKA--NQQSTDKFLFTISGLDKQRGDTAGLADMMVKPYIL +WL + E L +C C + N D FT +RGD A + M +P++L RQWLSRGGEIEGFRLSAHCSCDSRDNTLQVDINGFTTG----RRGDLATIHGMN-RPFLL ALSLP-SNGNSLASVRKRRAVGTDETCDEKTETCCMRKLYIDFRKDLGWKWIHKPKGYFA ++ P L S R RRA+ T+ + CC+R+LYIDFRKDLGWKWIH+PKGY A LMATPLERAQHLQSSRHRRALDTNYCFSSTEKNCCVRQLYIDFRKDLGWKWIHEPKGYHA NYCMGSCTYIWNAENKYSQILALYKHHNPGASAQPCCVPAILDPLPILYYVGRQHKVEQL N+C+G C YIW+ + +YS++LALY HNPGASA PCCVP L+PLPI+YYVGR+ KVEQL NFCLGPCPYIWSLDTQYSKVLALYNQHNPGASAAPCCVPQALEPLPIVYYVGRKPKVEQL SNMVVRNCKCS SNM+VR+CKCS SNMIVRSCKCS
Zebrafish as a tool to study mechanisms of developmental toxicology of environmental chemicals. Jessica Legradi, P. Cenijn, R. Carvalho, J.
 Zebrafish as a tool to study mechanisms of developmental toxicology of environmental chemicals Jessica Legradi, P. Cenijn, R. Carvalho, J. Legler Overview Introduce zebrafish as model organism Zebrafish
Zebrafish as a tool to study mechanisms of developmental toxicology of environmental chemicals Jessica Legradi, P. Cenijn, R. Carvalho, J. Legler Overview Introduce zebrafish as model organism Zebrafish
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its
 Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
Exam 1 ID#: October 4, 2007
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 1 ID#: October 4, 2007 Multiple choice (one point each) (1-25) 1. The process of cells forming tissues and organs is called a. morphogenesis. b. differentiation. c. allometry.
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 1 ID#: October 4, 2007 Multiple choice (one point each) (1-25) 1. The process of cells forming tissues and organs is called a. morphogenesis. b. differentiation. c. allometry.
ZEBRAFISH, DANIO RERIO AS A
 ZEBRAFISH, DANIO RERIO AS A REPLACEMENT ALTERNATIVE MANGALA GUNATILAKE Dept. of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Colombo Overview: Introduction Objective Methods Concept of Replacement Alternatives
ZEBRAFISH, DANIO RERIO AS A REPLACEMENT ALTERNATIVE MANGALA GUNATILAKE Dept. of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Colombo Overview: Introduction Objective Methods Concept of Replacement Alternatives
9/4/2015 INDUCTION CHAPTER 1. Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology. Fig 1.
 INDUCTION CHAPTER 1 Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology Fig 1.1 1 EVOLUTION OF METAZOAN BRAINS GASTRULATION MAKING THE 3 RD GERM LAYER
INDUCTION CHAPTER 1 Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology Fig 1.1 1 EVOLUTION OF METAZOAN BRAINS GASTRULATION MAKING THE 3 RD GERM LAYER
Questions in developmental biology. Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration
 Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
Cell Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? 2. What embryonic regions contribute to the developing limb bud?
 Study Questions - Lecture 17 & 18 1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? The three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb are the proximal stylopod, zeugopod, and
Study Questions - Lecture 17 & 18 1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? The three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb are the proximal stylopod, zeugopod, and
Neural development its all connected
 Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2662
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007
 Biology 4361 Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007 Name: ID: Multiple choice (1 point each. Indicate the best answer.) 1. During Drosophila gastrulation, mesoderm moves in through the a. primitives streak.
Biology 4361 Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007 Name: ID: Multiple choice (1 point each. Indicate the best answer.) 1. During Drosophila gastrulation, mesoderm moves in through the a. primitives streak.
Types of biological networks. I. Intra-cellurar networks
 Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Integrated Approaches to Testing and Assessment in Developmental Toxicology
 Integrated Approaches to Testing and Assessment in Developmental Toxicology Aldert H. Piersma Center for Health Protection RIVM Bilthoven-NL 1 European Teratology Society Conference, Budapest, Hungary,
Integrated Approaches to Testing and Assessment in Developmental Toxicology Aldert H. Piersma Center for Health Protection RIVM Bilthoven-NL 1 European Teratology Society Conference, Budapest, Hungary,
Maternal Control of GermLayer Formation in Xenopus
 Maternal Control of GermLayer Formation in Xenopus The zygotic genome is activated at the mid-blastula transition mid-blastula fertilized egg Xenopus gastrulae early-gastrula 7 hrs 10 hrs control not VP
Maternal Control of GermLayer Formation in Xenopus The zygotic genome is activated at the mid-blastula transition mid-blastula fertilized egg Xenopus gastrulae early-gastrula 7 hrs 10 hrs control not VP
Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002
 Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002 1) A variety of reagents and approaches are frequently used by developmental biologists to understand the tissue interactions and molecular signaling pathways
Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002 1) A variety of reagents and approaches are frequently used by developmental biologists to understand the tissue interactions and molecular signaling pathways
Ecotoxicity testing for an environmentally safer-by-design nanotechnology industry : an overview
 Ecotoxicity testing for an environmentally safer-by-design nanotechnology industry : an overview Nanotechnology offers a huge range of opportunities for mankind and the global economy, but needs to be
Ecotoxicity testing for an environmentally safer-by-design nanotechnology industry : an overview Nanotechnology offers a huge range of opportunities for mankind and the global economy, but needs to be
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology. Cell Cell Communication in Development. Developmental Activities Coordinated in this Way
 Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Chapter 18 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Developmental Genetics
 Chapter 18 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Developmental Genetics Chapter Contents 18.1 Differentiated States Develop from Coordinated Programs of Gene Expression 18.2 Evolutionary Conservation
Chapter 18 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Developmental Genetics Chapter Contents 18.1 Differentiated States Develop from Coordinated Programs of Gene Expression 18.2 Evolutionary Conservation
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Developmental processes Differential gene expression Introduction to determination The model organisms used to study developmental processes
 Date Title Topic(s) Learning Outcomes: Sept 28 Oct 3 1. What is developmental biology and why should we care? 2. What is so special about stem cells and gametes? Developmental processes Differential gene
Date Title Topic(s) Learning Outcomes: Sept 28 Oct 3 1. What is developmental biology and why should we care? 2. What is so special about stem cells and gametes? Developmental processes Differential gene
3/8/ Complex adaptations. 2. often a novel trait
 Chapter 10 Adaptation: from genes to traits p. 302 10.1 Cascades of Genes (p. 304) 1. Complex adaptations A. Coexpressed traits selected for a common function, 2. often a novel trait A. not inherited from
Chapter 10 Adaptation: from genes to traits p. 302 10.1 Cascades of Genes (p. 304) 1. Complex adaptations A. Coexpressed traits selected for a common function, 2. often a novel trait A. not inherited from
Reception The target cell s detection of a signal coming from outside the cell May Occur by: Direct connect Through signal molecules
 Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Transmembrane distribution of kanamycin and chloramphenicol: Insights into the cytotoxicity of antibacterial drugs Text 1. The general Langmuir isothermal equation
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Transmembrane distribution of kanamycin and chloramphenicol: Insights into the cytotoxicity of antibacterial drugs Text 1. The general Langmuir isothermal equation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion Rationale for using maternal ythdf2 -/- mutants as study subject To study the genetic basis of the embryonic developmental delay that we observed, we crossed fish with different
Supplementary Discussion Rationale for using maternal ythdf2 -/- mutants as study subject To study the genetic basis of the embryonic developmental delay that we observed, we crossed fish with different
Cell Death & Trophic Factors II. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Death & Trophic Factors II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Remember? Neurotrophins are cell survival factors that neurons get from their target cells! There is a
Cell Death & Trophic Factors II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Remember? Neurotrophins are cell survival factors that neurons get from their target cells! There is a
Comparison of the expression patterns of several sox genes between Oryzias latipes and Danio rerio
 Urun 1 Comparison of the expression patterns of several sox genes between Oryzias latipes and Danio rerio Fatma Rabia URUN ilkent University, nkara - TURKEY High mobility group domain containing transcription
Urun 1 Comparison of the expression patterns of several sox genes between Oryzias latipes and Danio rerio Fatma Rabia URUN ilkent University, nkara - TURKEY High mobility group domain containing transcription
Adverse Outcome Pathways in Ecotoxicology Research
 Adverse Outcome Pathways in Ecotoxicology Research Michael W. Hornung US Environmental Protection Agency, Mid-Continent Ecology Division, Duluth, MN Meeting of the Northland Chapter of SOT October 7, 2010
Adverse Outcome Pathways in Ecotoxicology Research Michael W. Hornung US Environmental Protection Agency, Mid-Continent Ecology Division, Duluth, MN Meeting of the Northland Chapter of SOT October 7, 2010
Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018
 Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018 Introduction 3. Books This module is based on the following books: - 'Principles of Developement', Lewis Wolpert, et al., fifth edition, 2015 - 'Developmental
Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018 Introduction 3. Books This module is based on the following books: - 'Principles of Developement', Lewis Wolpert, et al., fifth edition, 2015 - 'Developmental
Biology 218, practise Exam 2, 2011
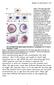 Figure 3 The long-range effect of Sqt does not depend on the induction of the endogenous cyc or sqt genes. a, Design and predictions for the experiments shown in b-e. b-e, Single-cell injection of 4 pg
Figure 3 The long-range effect of Sqt does not depend on the induction of the endogenous cyc or sqt genes. a, Design and predictions for the experiments shown in b-e. b-e, Single-cell injection of 4 pg
Developmental genetics: finding the genes that regulate development
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 9 Developmental genetics: finding the genes that regulate development Introduction The application of genetic analysis and DNA technology to the study of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 9 Developmental genetics: finding the genes that regulate development Introduction The application of genetic analysis and DNA technology to the study of
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES AND THEIR LEGENDS. Transient infection of the zebrafish notochord triggers chronic inflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES AND THEIR LEGENDS Transient infection of the zebrafish notochord triggers chronic inflammation Mai Nguyen-Chi 1,2,5, Quang Tien Phan 1,2,5, Catherine Gonzalez 1,2, Jean-François
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES AND THEIR LEGENDS Transient infection of the zebrafish notochord triggers chronic inflammation Mai Nguyen-Chi 1,2,5, Quang Tien Phan 1,2,5, Catherine Gonzalez 1,2, Jean-François
Spinal neurons require Islet1 for subtype-specific differentiation of electrical excitability
 Moreno and Ribera Neural Development 2014, 9:19 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Spinal neurons require Islet1 for subtype-specific differentiation of electrical excitability Rosa L Moreno * and Angeles B
Moreno and Ribera Neural Development 2014, 9:19 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Spinal neurons require Islet1 for subtype-specific differentiation of electrical excitability Rosa L Moreno * and Angeles B
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning
 MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
MOLECULAR CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC PATTERN FORMATION
 MOLECULAR CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC PATTERN FORMATION Drosophila is the best understood of all developmental systems, especially at the genetic level, and although it is an invertebrate it has had an enormous
MOLECULAR CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC PATTERN FORMATION Drosophila is the best understood of all developmental systems, especially at the genetic level, and although it is an invertebrate it has had an enormous
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature1237 a b retinol retinal RA OH RDH (retinol dehydrogenase) O H Raldh2 O R/R.6.4.2 (retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 2) RA retinal retinol..1.1 1 Concentration (nm)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature1237 a b retinol retinal RA OH RDH (retinol dehydrogenase) O H Raldh2 O R/R.6.4.2 (retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 2) RA retinal retinol..1.1 1 Concentration (nm)
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 6, 2007 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 6, 2007 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines
 Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
10/2/2015. Chapter 4. Determination and Differentiation. Neuroanatomical Diversity
 Chapter 4 Determination and Differentiation Neuroanatomical Diversity 1 Neurochemical diversity: another important aspect of neuronal fate Neurotransmitters and their receptors Excitatory Glutamate Acetylcholine
Chapter 4 Determination and Differentiation Neuroanatomical Diversity 1 Neurochemical diversity: another important aspect of neuronal fate Neurotransmitters and their receptors Excitatory Glutamate Acetylcholine
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
Variation in the genetic response to high temperature in Montastraea faveolata from the Florida Keys & Mexico
 Variation in the genetic response to high temperature in Montastraea faveolata from the Florida Keys & Mexico Nicholas R. Polato 1, Christian R. Voolstra 2, Julia Schnetzer 3, Michael K. DeSalvo 4, Carly
Variation in the genetic response to high temperature in Montastraea faveolata from the Florida Keys & Mexico Nicholas R. Polato 1, Christian R. Voolstra 2, Julia Schnetzer 3, Michael K. DeSalvo 4, Carly
AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review
 AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review 1. What does the regulatory gene code for? 2. Is the repressor by default active/inactive? 3. What changes the repressor activity? 4. What does repressor
AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review 1. What does the regulatory gene code for? 2. Is the repressor by default active/inactive? 3. What changes the repressor activity? 4. What does repressor
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
Supplemental table S7.
 Supplemental table S7. GO terms significantly enriched in significantly up-regulated genes of the microarray. K: number of genes from the input cluster in the given category. F: number of total genes in
Supplemental table S7. GO terms significantly enriched in significantly up-regulated genes of the microarray. K: number of genes from the input cluster in the given category. F: number of total genes in
Nrf2 and Nrf2-Related Proteins in Development and Developmental Toxicity: Insights from studies in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
 FRBM Special Issue: Nrf2 Regulated Redox Signaling and Metabolism in Physiology and Medicine FRBM-D-15-00377 (revised) Nrf2 and Nrf2-Related Proteins in Development and Developmental Toxicity: Insights
FRBM Special Issue: Nrf2 Regulated Redox Signaling and Metabolism in Physiology and Medicine FRBM-D-15-00377 (revised) Nrf2 and Nrf2-Related Proteins in Development and Developmental Toxicity: Insights
TWGHs Chen Zao Men College S3 Biology Teaching Schedule ( )
 TWGHs Chen Zao Men College S3 Biology Teaching Schedule (2015-2016) Date Period Topics Practical / Activities 2/9 4/9 1 Laboratory safety Note taking skills 7/9 20/10 11 Ch 1 Molecules of life Chemicals
TWGHs Chen Zao Men College S3 Biology Teaching Schedule (2015-2016) Date Period Topics Practical / Activities 2/9 4/9 1 Laboratory safety Note taking skills 7/9 20/10 11 Ch 1 Molecules of life Chemicals
Chapter 4 Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays.
 Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays. The data described in chapter 3 presented evidence that endogenous
Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays. The data described in chapter 3 presented evidence that endogenous
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo
 Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo In the first part of this thesis work the physical properties of cilia-driven leftward flow were characterised in the rabbit embryo. Since its discovery
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo In the first part of this thesis work the physical properties of cilia-driven leftward flow were characterised in the rabbit embryo. Since its discovery
OECD Conceptual Framework for Testing and Assessment of Endocrine Disrupters (as revised in 2012)
 OECD Conceptual Framework for Testing and Assessment of Endocrine Disrupters (as revised in 2012) This document presents the revised Conceptual Framework for Testing and Assessment of Endocrine Disrupters,
OECD Conceptual Framework for Testing and Assessment of Endocrine Disrupters (as revised in 2012) This document presents the revised Conceptual Framework for Testing and Assessment of Endocrine Disrupters,
Why Erosion and Sedimention Control is Important: A Fish s Point of View
 Why Erosion and Sedimention Control is Important: A Fish s Point of View Fisheries Protection Program Department of Fisheries and Oceans June 6, 2014 Basic definition: Sediment is defined as soil particles
Why Erosion and Sedimention Control is Important: A Fish s Point of View Fisheries Protection Program Department of Fisheries and Oceans June 6, 2014 Basic definition: Sediment is defined as soil particles
ZEBRAFISH CROSSWORD PUZZLE (LEVEL 1)
 ZEBRAFISH CROSSWORD PUZZLE (LEVEL 1) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 The organ that pumps blood through the body 6 An organ in the fish that takes oxygen from the water 7 Structures in the lung that take oxygen from
ZEBRAFISH CROSSWORD PUZZLE (LEVEL 1) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 The organ that pumps blood through the body 6 An organ in the fish that takes oxygen from the water 7 Structures in the lung that take oxygen from
Bio 3411, Fall 2006, Lecture 19-Cell Death.
 Types of Cell Death Questions : Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death) : Cell-Autonomous Stereotypic Rapid Clean (dead cells eaten) Necrosis : Not Self-Initiated Not Stereotypic Can Be Slow Messy (injury can
Types of Cell Death Questions : Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death) : Cell-Autonomous Stereotypic Rapid Clean (dead cells eaten) Necrosis : Not Self-Initiated Not Stereotypic Can Be Slow Messy (injury can
Lecture 7. Development of the Fruit Fly Drosophila
 BIOLOGY 205/SECTION 7 DEVELOPMENT- LILJEGREN Lecture 7 Development of the Fruit Fly Drosophila 1. The fruit fly- a highly successful, specialized organism a. Quick life cycle includes three larval stages
BIOLOGY 205/SECTION 7 DEVELOPMENT- LILJEGREN Lecture 7 Development of the Fruit Fly Drosophila 1. The fruit fly- a highly successful, specialized organism a. Quick life cycle includes three larval stages
Chapter 10, 11, 14: Gene Expression, Regulation, and Development Exam
 Chapter 10, 11, 14: Gene Expression, Regulation, and Development Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Why did the original one-gene, one-enzyme
Chapter 10, 11, 14: Gene Expression, Regulation, and Development Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Why did the original one-gene, one-enzyme
Classification and Phylogeny
 Classification and Phylogeny The diversity of life is great. To communicate about it, there must be a scheme for organization. There are many species that would be difficult to organize without a scheme
Classification and Phylogeny The diversity of life is great. To communicate about it, there must be a scheme for organization. There are many species that would be difficult to organize without a scheme
Neuronal Cell Health Assays. Real-time automated measurements of neuronal cell viability and neurite dynamics inside your incubator.
 I N C U C Y T E L I V E - C E L L A N A LY S I S S Y S T E M Neuronal Cell Health Assays Real-time automated measurements of neuronal cell viability and neurite dynamics inside your incubator. See what
I N C U C Y T E L I V E - C E L L A N A LY S I S S Y S T E M Neuronal Cell Health Assays Real-time automated measurements of neuronal cell viability and neurite dynamics inside your incubator. See what
The majority of environmental factors
 POINT-OF-VIEW Epigenetics 6:7, 838-842; July 2011; 2011 Landes Bioscience Environmental and somatic epigenetic mitotic stability Michael K. Skinner Center for Reproductive Biology; School of Biological
POINT-OF-VIEW Epigenetics 6:7, 838-842; July 2011; 2011 Landes Bioscience Environmental and somatic epigenetic mitotic stability Michael K. Skinner Center for Reproductive Biology; School of Biological
MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I. Slide #1. Cell Differentiation
 MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I Slide #1 Cell Differentiation Cell Differentiation I -Basic principles of differentiation (p1305-1320) -C-elegans (p1321-1327) Cell Differentiation II
MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I Slide #1 Cell Differentiation Cell Differentiation I -Basic principles of differentiation (p1305-1320) -C-elegans (p1321-1327) Cell Differentiation II
Classification and Phylogeny
 Classification and Phylogeny The diversity it of life is great. To communicate about it, there must be a scheme for organization. There are many species that would be difficult to organize without a scheme
Classification and Phylogeny The diversity it of life is great. To communicate about it, there must be a scheme for organization. There are many species that would be difficult to organize without a scheme
Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006 Multiple choice (one point each) Circle the best answer. 1. Inducers of Xenopus lens and optic vesicle include a. pharyngeal endoderm and anterior neural
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006 Multiple choice (one point each) Circle the best answer. 1. Inducers of Xenopus lens and optic vesicle include a. pharyngeal endoderm and anterior neural
Honors Biology Reading Guide Chapter 11
 Honors Biology Reading Guide Chapter 11 v Promoter a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA located near the start of a gene that is the binding site for RNA polymerase and the place where transcription begins
Honors Biology Reading Guide Chapter 11 v Promoter a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA located near the start of a gene that is the binding site for RNA polymerase and the place where transcription begins
2. Examine the external anatomy of the squid and identify the following structures: tentacles, arms, fins, siphon, mantle, eyes and collar.
 Cephalopod Anatomy As their name implies, members of the class Cephalopoda have modified head-foot which bears an array of prehensile tentacles and arms at the cranial end of the body. The visceral mass
Cephalopod Anatomy As their name implies, members of the class Cephalopoda have modified head-foot which bears an array of prehensile tentacles and arms at the cranial end of the body. The visceral mass
Early Development in Invertebrates
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Early Development in Invertebrates October 25, 2006 Early Development Overview Cleavage rapid cell divisions divisions of fertilized egg into many cells Gastrulation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Early Development in Invertebrates October 25, 2006 Early Development Overview Cleavage rapid cell divisions divisions of fertilized egg into many cells Gastrulation
Developmental Zoology. Ectodermal derivatives (ZOO ) Developmental Stages. Developmental Stages
 Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006
 Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
Evidence for the Existence of Non-monotonic Dose-response: Does it or Doesn t it?
 Evidence for the Existence of Non-monotonic Dose-response: Does it or Doesn t it? Scott M. Belcher, PhD University of Cincinnati Department of Pharmacology and Cell Biophysics Evidence for the Existence
Evidence for the Existence of Non-monotonic Dose-response: Does it or Doesn t it? Scott M. Belcher, PhD University of Cincinnati Department of Pharmacology and Cell Biophysics Evidence for the Existence
purpose of this Chapter is to highlight some problems that will likely provide new
 119 Chapter 6 Future Directions Besides our contributions discussed in previous chapters to the problem of developmental pattern formation, this work has also brought new questions that remain unanswered.
119 Chapter 6 Future Directions Besides our contributions discussed in previous chapters to the problem of developmental pattern formation, this work has also brought new questions that remain unanswered.
Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
 KAP Biology Dept Kenyon College Differential gene expression and development Mechanisms of cellular determination Induction Pattern formation Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
KAP Biology Dept Kenyon College Differential gene expression and development Mechanisms of cellular determination Induction Pattern formation Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
AN ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION OF. Britton C. Goodale for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Toxicology presented on August 12, 2013.
 AN ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION OF Britton C. Goodale for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Toxicology presented on August 12, 2013. Title: Developmental Toxicity of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons:
AN ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION OF Britton C. Goodale for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Toxicology presented on August 12, 2013. Title: Developmental Toxicity of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons:
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 5.1 Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of the genetic variation of the offspring.
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 5.1 Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of the genetic variation of the offspring.
8 th BioDetectors. Applications of bioassays to prioritize chemical food safety issues. Maricel Marin-Kuan
 8 th BioDetectors Applications of bioassays to prioritize chemical food safety issues Maricel Marin-Kuan maricel.marin-kuan@rdls.nestle.com Hazard identification in food industry substances potentially
8 th BioDetectors Applications of bioassays to prioritize chemical food safety issues Maricel Marin-Kuan maricel.marin-kuan@rdls.nestle.com Hazard identification in food industry substances potentially
Development of Drosophila
 Development of Drosophila Hand-out CBT Chapter 2 Wolpert, 5 th edition March 2018 Introduction 6. Introduction Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is found in all warm countries. In cooler regions,
Development of Drosophila Hand-out CBT Chapter 2 Wolpert, 5 th edition March 2018 Introduction 6. Introduction Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is found in all warm countries. In cooler regions,
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila July 9, 2008 Drosophila Development Overview Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation Genetic control
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila July 9, 2008 Drosophila Development Overview Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation Genetic control
Characterization of Biological Secretions Binding to Graphene Oxide in Water and the Specific Toxicological Mechanisms
 Supporting Information Characterization of Biological Secretions Binding to Graphene Oxide in Water and the Specific Toxicological Mechanisms Li Mu, Yue Gao, Xiangang Hu, Institute of Agro-environmental
Supporting Information Characterization of Biological Secretions Binding to Graphene Oxide in Water and the Specific Toxicological Mechanisms Li Mu, Yue Gao, Xiangang Hu, Institute of Agro-environmental
Signal Transduction. Dr. Chaidir, Apt
 Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
Department Curriculum and Assessment Outline
 Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
PRACTICE EXAM. 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos.
 PRACTICE EXAM 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos. No Low [] Fly Embryo Embryo Non-neural Genes Neuroectoderm Genes
PRACTICE EXAM 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos. No Low [] Fly Embryo Embryo Non-neural Genes Neuroectoderm Genes
Nodal Signaling is Required for Closure of the Anterior Neural Tube in Zebrafish
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Biology Faculty Research Biology Department 11-8-2007 Nodal Signaling is Required for Closure of the Anterior Neural Tube in Zebrafish Allisan Aquilina-Beck
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Biology Faculty Research Biology Department 11-8-2007 Nodal Signaling is Required for Closure of the Anterior Neural Tube in Zebrafish Allisan Aquilina-Beck
Regulation of gene expression. Premedical - Biology
 Regulation of gene expression Premedical - Biology Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cell Operon units system of negative feedback positive and negative regulation in eukaryotic cell - at any
Regulation of gene expression Premedical - Biology Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cell Operon units system of negative feedback positive and negative regulation in eukaryotic cell - at any
Course Descriptions Biology
 Course Descriptions Biology BIOL 1010 (F/S) Human Anatomy and Physiology I. An introductory study of the structure and function of the human organ systems including the nervous, sensory, muscular, skeletal,
Course Descriptions Biology BIOL 1010 (F/S) Human Anatomy and Physiology I. An introductory study of the structure and function of the human organ systems including the nervous, sensory, muscular, skeletal,
ACCELERATE ITS BIOCHEMICAL PROCESSES WHICH WERE SLOWED DOWN BY MITOSIS. THE LENGTH OF THE G1 PHASE CREATES THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FAST DIVIDING
 CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
18.4 Embryonic development involves cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis
 18.4 Embryonic development involves cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis An organism arises from a fertilized egg cell as the result of three interrelated processes: cell division, cell
18.4 Embryonic development involves cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis An organism arises from a fertilized egg cell as the result of three interrelated processes: cell division, cell
Cells to Tissues. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cells to Tissues Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology From one cell to ensembles of cells. Multicellular organisms require individual cells to work together in functional groups. This means cells
Cells to Tissues Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology From one cell to ensembles of cells. Multicellular organisms require individual cells to work together in functional groups. This means cells
Next Generation Computational Chemistry Tools to Predict Toxicity of CWAs
 Next Generation Computational Chemistry Tools to Predict Toxicity of CWAs William (Bill) Welsh welshwj@umdnj.edu Prospective Funding by DTRA/JSTO-CBD CBIS Conference 1 A State-wide, Regional and National
Next Generation Computational Chemistry Tools to Predict Toxicity of CWAs William (Bill) Welsh welshwj@umdnj.edu Prospective Funding by DTRA/JSTO-CBD CBIS Conference 1 A State-wide, Regional and National
Genes, Development, and Evolution
 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Chapter 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Key Concepts 14.1 Development Involves Distinct but Overlapping Processes 14.2 Changes in Gene Expression Underlie Cell
14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Chapter 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Key Concepts 14.1 Development Involves Distinct but Overlapping Processes 14.2 Changes in Gene Expression Underlie Cell
EVOLUTIONARY BIOLOGY FALL 2017
 EVOLUTIONARY BIOLOGY FALL 2017 WHEN: MWF 11:30 12:20 WHERE: 283 Galvin Life Science Center INSTRUCTOR: Mike Pfrender Course webpage: http://www3.nd.edu/~mpfrende/evolutionary_biology/homepage.htm Nothing
EVOLUTIONARY BIOLOGY FALL 2017 WHEN: MWF 11:30 12:20 WHERE: 283 Galvin Life Science Center INSTRUCTOR: Mike Pfrender Course webpage: http://www3.nd.edu/~mpfrende/evolutionary_biology/homepage.htm Nothing
TRANSCRIPTOMICS. (or the analysis of the transcriptome) Mario Cáceres. Main objectives of genomics. Determine the entire DNA sequence of an organism
 TRANSCRIPTOMICS (or the analysis of the transcriptome) Mario Cáceres Main objectives of genomics Determine the entire DNA sequence of an organism Identify and annotate the complete set of genes encoded
TRANSCRIPTOMICS (or the analysis of the transcriptome) Mario Cáceres Main objectives of genomics Determine the entire DNA sequence of an organism Identify and annotate the complete set of genes encoded
Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA
 Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA Instructor: Marianne Bronner Exam Length: 6 hours plus one 30-minute break at your discretion. It should take
Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA Instructor: Marianne Bronner Exam Length: 6 hours plus one 30-minute break at your discretion. It should take
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
BEFORE TAKING THIS MODULE YOU MUST ( TAKE BIO-4013Y OR TAKE BIO-
 2018/9 - BIO-4001A BIODIVERSITY Autumn Semester, Level 4 module (Maximum 150 Students) Organiser: Dr Harriet Jones Timetable Slot:DD This module explores life on Earth. You will be introduced to the major
2018/9 - BIO-4001A BIODIVERSITY Autumn Semester, Level 4 module (Maximum 150 Students) Organiser: Dr Harriet Jones Timetable Slot:DD This module explores life on Earth. You will be introduced to the major
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
 Evolutionary Developmental Biology a.k.a. EVO-DEVO Paedomorphosis is common among salamanders. Note how this hellbender (top) and mudpuppy (bottom) both have gills, paddle tails, and weaker limbs... Top:
Evolutionary Developmental Biology a.k.a. EVO-DEVO Paedomorphosis is common among salamanders. Note how this hellbender (top) and mudpuppy (bottom) both have gills, paddle tails, and weaker limbs... Top:
19/10/2015. Response to environmental manipulation. Its not as simple as it seems!
 Jackie Mitchell Department of Basic and Clinical Neuroscience - IoPPN Why do we need model genetic systems? What does it take to be a good model? Common in vivo model species Genetic manipulations (Lecture
Jackie Mitchell Department of Basic and Clinical Neuroscience - IoPPN Why do we need model genetic systems? What does it take to be a good model? Common in vivo model species Genetic manipulations (Lecture
Life Sciences 1a: Section 3B. The cell division cycle Objectives Understand the challenges to producing genetically identical daughter cells
 Life Sciences 1a: Section 3B. The cell division cycle Objectives Understand the challenges to producing genetically identical daughter cells Understand how a simple biochemical oscillator can drive the
Life Sciences 1a: Section 3B. The cell division cycle Objectives Understand the challenges to producing genetically identical daughter cells Understand how a simple biochemical oscillator can drive the
AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8
 AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test Name: 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms
AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test Name: 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms
Anthropogenic chemicals & nanomaterials: Persistent Concerns in Oceans and Human Health.
 Anthropogenic chemicals & nanomaterials: Persistent Concerns in Oceans and Human Health. John J. Stegeman Woods Hole Oceanographic Ins3tu3on Woods Hole Center for Oceans and Human Health Boston University
Anthropogenic chemicals & nanomaterials: Persistent Concerns in Oceans and Human Health. John J. Stegeman Woods Hole Oceanographic Ins3tu3on Woods Hole Center for Oceans and Human Health Boston University
Evaluation of Fish Early Life-Stage Toxicity Models of Chronic Embryonic Exposures to Complex Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Mixtures
 TOXICOLOGICAL SCIENCES 78, 60 67 (2004) DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfh051 Advance Access publication December 22, 2003 Evaluation of Fish Early Life-Stage Toxicity Models of Chronic Embryonic Exposures to Complex
TOXICOLOGICAL SCIENCES 78, 60 67 (2004) DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfh051 Advance Access publication December 22, 2003 Evaluation of Fish Early Life-Stage Toxicity Models of Chronic Embryonic Exposures to Complex
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
C. elegans L1 cell adhesion molecule functions in axon guidance
 C. elegans L1 cell adhesion molecule functions in axon guidance Biorad Lihsia Chen Dept. of Genetics, Cell Biology & Development Developmental Biology Center C. elegans embryogenesis Goldstein lab, UNC-Chapel
C. elegans L1 cell adhesion molecule functions in axon guidance Biorad Lihsia Chen Dept. of Genetics, Cell Biology & Development Developmental Biology Center C. elegans embryogenesis Goldstein lab, UNC-Chapel
