Developmental processes Differential gene expression Introduction to determination The model organisms used to study developmental processes
|
|
|
- Valerie Gilbert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Date Title Topic(s) Learning Outcomes: Sept 28 Oct 3 1. What is developmental biology and why should we care? 2. What is so special about stem cells and gametes? Developmental processes Differential gene expression Introduction to determination The model organisms used to study developmental processes Germ cells, stem cells, and gametes Gametogenesis in Drosophila vs other organisms maternal mrna Imprinting Describe the basic cellular processes take place during development Define differential gene expression Describe experiments that proved that development does not occur through the differential inheritance of genetic material Define determination and describe how is it tested Name the pros and cons of different model organisms for studying development Compare and contrast spermatogenesis and oogenesis Describe the unique features of oogenesis in Drosophila Describe the experiment that demonstrates the importance of maternal mrna in sea urchins Describe mechanisms used to stabilize maternal mrnas (a) and (b) to localize them Define imprinting and in which species it occurs Oct 5 Oct 10 Oct How does fertilization kick start the formation of an embryo? 4. Getting down to business: How do we study gene expression and development in embryos? 5. The amazing oocyte: Ooplasmic (cytoplasmic) determinants and the emergence of pattern Fertilization Activation and cleavage of the newly formed embryo Compaction in the mammalian embryo Maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) Transcription factors and enhancers Post-translational modifications Methods to visualize gene expression in embryos Gain and loss of function approaches to study gene function Cytoplasmic determinants and maternal effect genes Consequences of cleavage on cell fate bicoid and nanos in Drosophila Outline the basic steps in fertilization Describe the slow and fast blocks to polyspermy Describe why cleavage of embryos is very rapid in many species, but not in mammals Compare and contrast the mammalian and Drosophila egg and early cleavage stage embryo with respect to yolk distribution and cleavage pattern Describe compaction and its consequences in the mammalian embryo Define the MZT and what controls its timing Describe what is meant by combinatorial action of transcription factors Name types of post-translational mechanisms that impact gene expression during development Draw positive and negative feedback loops and explain what impact can they have on gene expression patterns Describe methods used to visualize expression of specific (a) mrnas or (b) proteins expression in an embryo Describe methods are used to define all of the mrnas expressed in a particular embryo or part of an embryo Explain how gene targeting, CRISPR/Cas and transgenic (overexpression) methods can be used to introduce mutations into specific genes Describe types of experiments that provide evidence for the existence of cytoplasmic determinants Explain the differences between maternal mrnas in general vs cytoplasmic determinants
2 Oct 17 Oct 24 Oct 26 Oct Maternal control of pattern formation in the early Drosophila embryo 7. The transition from maternal to zygotic control of pattern formation in the Drosophila embryo 8. How is identity acquired along the anterior-posterior axis of the embryo? The conservation of homeotic gene function in Drosophila and 9. How do cell rearrangements and changes in cell shape drive changes in the form of the embryo? How are mrnas like bicoid and nanos localized? Morphogens Cleavage in the early Drosophila embryo Defining the A/P axis of the Drosophila oocyte Interactions between the Drosophila oocyte and surrounding follicle cells Toll signaling and dorsal/ventral axis Arranging developmental genes in hierarchies Hunchback and Krüppel as gap genes Even-skipped as a pair-rule gene Compartments Hedgehog and Wingless as segmentation genes Homeotic (Hox) genes Co-linearity Conservation of Hox gene function Cytoskeletal elements Adhesion Cell shape Types of cell movements/rearrangements during development Define what is meant by inductive interaction Describe experiments establishing that there are germ cell determinants in Drosophila and frog embryos Compare and contrast maternal effect vs. zygotic genes Explain the functions of bicoid and nanos Describe the key attributes of a morphogen Describe some mechanisms used to localize maternal mrnas in the Drosophila oocyte Outline how Gurken and Torpedo act define the A/P and D/V axes of the Drosophila egg Describe how Toll signaling refines the D/V axis and name some basic components of this pathway Describe how Dorsal activity specifies cell identity along the D/V axis Describe types of experiments used to arrange genes in a hierarchy of gene action Explain the effects of increasing or decreasing Hb, bicoid, nanos, levels on Kr expression Describe the main features of gap, pair-rule and segmentation genes. Provide examples of each type of gene. Describe experiments that were used to identify enhancers that control expression of eve Define compartments and describe the importance of compartmentalizing the Drosophila embryo Define planar cell polarity and describe why is it important for patterning the embryo Describe the key structural and functional features of Hox genes and Hox complexes Describe the consequences of loss or gain of Hox gene function Define co-linearity and describe mechanisms that control colinear Hox gene expression Describe the evidence that Hox gene function is conserved across the Animal Kingdom Outline the major differences between epithelial and mesenchymal cell types Describe how signal transduction pathways can impact cell shape/rearrangement Compare and contrast (de)compaction, delamination, ingression, apical constriction, invagination, convergent extension, epiboly, involution Recognize the main movements of gastrulation in (a) frogs, (b) sea urchin, (c) birds and mammals
3 Nov 2 Nov 7 Nov 14 Nov The emergence of form in the frog embryo: germ layer formation and gastrulation 11. Career decisions by cells in the frog embryo: developing or not into brain and neural tissue 12. On the importance of being flat: Gastrulation/Mesoderm formation in birds and mammals 13. Neural development in : Subdivision of the brain and spinal cord into discrete regions Gastrulation and germ layers Dorsal-ventral (D/V) axis formation Conservation of D/V axis formation in Drosophila and frogs BMPs and D/V axis formation Neural induction Formation of the dorsal/ventral axis in frogs Formation of the anterior/posterior axis in frogs Lateral Inhibition: Delta and Notch Events in mammalian/bird gastrulation: Initiation and elongation of the primitive streak The primitive streak and specification of the D/V axis Mesoderm/endodnerm induction in the primitive streak Somites Regionalization of the neural tube along the A/P axis in Compartments in Regionalization of the neural tube along the D/V axis Neuronal stem cells and the origins of differentiated neurons Define the difference between determination and specification Describe the experiments that demonstrated when different germ layers first arise in the frog embryo Describe cortical rotation and its impact on the frog embryo Describe the Neiuwkoop Center and experiments that demonstrate its importance Explain the functions of beta-catenin, Veg-T, and nodalrelated proteins Describe the Organizer and the experiments that demonstrate its role Compare and contrast the role of BMP/DPP in frog/drosophila D/V axis formation Describe experiments that demonstrated that the dorsal ectoderm becomes determined to form neural tissue Describe experiments that demonstrate the importance of the dorsal mesoderm for organizing the remaining tissues along dorsal/ventral axis Idenfity the molecules produced by the Organizer that are responsible for its properties, and explain how they work. Explain how Wnt activity specifies the anterior/posterior axis of the frog embryo Define lateral inhibition and describe its role in neurogenesis Describe how Delta and Notch mediate lateral inhibition Although the morphologies of frog and bird/mammalian embryos are different (round vs. flat), molecule mechanisms of D/V and A/P axis formation are conserved. Explain the conserved functions of Wnts, nodals, BMPs, BMP antagonists, Hox genes Compare the functions of the frog Organizer and the bird/mammalian node Explain how the neural tissue is formed in mammals/birds, and compare and contrast this to neural induction in frogs. Describe somites and the mechanisms that control their orderly formation along the A/P axis Explain how a negative feedback loop leads to periodic expression of a gene, and how is this related to periodic formation of somites. Describe the evidence that rhombomeres are compartments in. Explain the role of Hox genes in A/P axis formation in the neural tube in. Identify what mechanisms pattern the most anterior regions of the neural tube (i.e, brain). Discuss an experiment demonstrating the role of Shh in patterning the D/V axis of the neural tube
4 Lateral inhibition and Delta/Notch activity Describe how lateral inhibition regulate the timing of the production of neurons in Nov 21 Nov 28 Nov 30 Dec Cells on the move in the embryo: Directed cell migration. Axonal pathfinding and neural crest cells in 15. Making sense of sensory placodes and ectodermal appendages in 16. Branching morphogenesis and endodermal organs in 17. Limb Development: Charles Darwin and The Examples of long-range and shortrange cues that guide cell migration Mechanisms regulating responsiveness to guidance cues: Robo and Slit Retinotectal mapping: short-range cues in action Neural crest cells: formation, migration, and derivatives Placodes--definition Specification of sensory placodes that give rise to sensory structures and cell types (eyes, stereocilia of the ear, olfactory neurons) Development of the vertebrate eye Conserved function of Pax6 in Drosophila and Conserved features of formation of ectodermal appendages Endoderm formation in frogs and birds/mammals-review Establishment of left-right asymmetry in Regionalization of endoderm along the A/P axis: Hox genes and Cdx2 Branching morphogenesis in organ formation Intestinal villi and stem cells in : role of Wnt signaling Components of the limb bud: AER, ZPA/PR and Progress zone Describe long-range and short-range cues and provide examples of each (attractive and repulsive) Describe the experiments that support a role for netrin as a long-range cue Describe the key experiment that suggests netrin produced by the floorplate does NOT act as a long-range cue Explain how ephrins and ephrin receptors mediate retinotectile mapping. Explain where neural crest cells originate in the embryo and name some derivatives of neural crest cells Define ectodermal vs sensory placodes and their derivatives Describe the inductive interactions that give rise to the vertebrate eye Describe the role of Pax6 in eye formation and describe the loss-of-function and gain of function experiments (in Drosophila, mouse) that demonstrate conservation of function Describe why reduced Shh expression leads to cyclopia (one central eye) in humans and describe the consequences of gain of Shh expression in cavefish. How do these examples show conservation of Shh function in specifying D/V axis identity in the neural tube? Define regional and genetic specificity of induction and the experiments used to demonstrate these concepts Describe how mutations in Eda or Edar lead to ectodermal dysplasia Compare the process of endoderm specification in frogs vs. birds/mammals Describe left-right asymmetry, and explain how it is regulated by ciliary function in. Recognize the experiments and relevant mutations that demonstrate asymmetry. Explain experiments that demonstrate Hox genes and Cdx2 are involved in A/P axis identity in the endoderm in. Define branching morphogenesis, and describe the function FGF10 plays in this process in the lung Explain how Wnt signaling regulates stem cell maintenance in the intestine. Describe the impact of mutations in Wnt pathway components (TCF/LEF, beta-catenin, APC) in the intestine in. Discuss the results of experiments that demonstrated the roles of the AER and ZPA/PR in limb development.
5 Dec 7 Curious Case of the Bat Wing and the Porpoise Paddle 18. Sex and the Single Mammalian Embryo Hox genes and A/P and proximal-distal (P/D) identity SHH as a regulator of A/P and P/D identity Mechanisms that determine the position of limb buds in the embryo Molecular mechanisms that may have contributed to limb evolution Development of male and female gonads in mammals Primary vs secondary sexual characteristics--the importance of the testes and testosterone Origins of germ cells Role of the Y chromosome and the SRY gene Describe the genetic evidence that Hox genes regulate A/P and P/D identity in the limb Evaluate the findings from experiments that demonstrate how SHH regulates both A/P and P/D identity in the limb Describe the roles of FGFs, SHH, and Hox genes in positioning limb buds in the embryo Describe evidence that genetic changes in SHH expression have contributed to diversification of limb forms during evolution Identify experiments demonstrating that the mammalian testes produce soluble substances that define secondary sexual characteristics Predict the effects of mutations in these soluble substances and their receptors on primary and secondary sexual characteristics Describe the relationship of Sox9 and SRY, and how these genes control sex determination. Compare and contrast the fate of germ cells when they enter the developing gonads of male and female embryos.
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning
 MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines
 Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006 Multiple choice (one point each) Circle the best answer. 1. Inducers of Xenopus lens and optic vesicle include a. pharyngeal endoderm and anterior neural
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006 Multiple choice (one point each) Circle the best answer. 1. Inducers of Xenopus lens and optic vesicle include a. pharyngeal endoderm and anterior neural
1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? 2. What embryonic regions contribute to the developing limb bud?
 Study Questions - Lecture 17 & 18 1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? The three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb are the proximal stylopod, zeugopod, and
Study Questions - Lecture 17 & 18 1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? The three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb are the proximal stylopod, zeugopod, and
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila July 9, 2008 Drosophila Development Overview Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation Genetic control
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila July 9, 2008 Drosophila Development Overview Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation Genetic control
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 6, 2007 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 6, 2007 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Early Development in Invertebrates
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Early Development in Invertebrates October 25, 2006 Early Development Overview Cleavage rapid cell divisions divisions of fertilized egg into many cells Gastrulation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Early Development in Invertebrates October 25, 2006 Early Development Overview Cleavage rapid cell divisions divisions of fertilized egg into many cells Gastrulation
Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos
 Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Drosophila Life Cycle
 Drosophila Life Cycle 1 Early Drosophila Cleavage Nuclei migrate to periphery after 10 nuclear divisions. Cellularization occurs when plasma membrane folds in to divide nuclei into cells. Drosophila Superficial
Drosophila Life Cycle 1 Early Drosophila Cleavage Nuclei migrate to periphery after 10 nuclear divisions. Cellularization occurs when plasma membrane folds in to divide nuclei into cells. Drosophila Superficial
MOLECULAR CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC PATTERN FORMATION
 MOLECULAR CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC PATTERN FORMATION Drosophila is the best understood of all developmental systems, especially at the genetic level, and although it is an invertebrate it has had an enormous
MOLECULAR CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC PATTERN FORMATION Drosophila is the best understood of all developmental systems, especially at the genetic level, and although it is an invertebrate it has had an enormous
Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle.
 Spatial organization is a key difference between unicellular organisms and metazoans Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle. Cells differentiate as a
Spatial organization is a key difference between unicellular organisms and metazoans Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle. Cells differentiate as a
Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006
 Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
!!!!!!!! DB3230 Midterm 2 12/13/2013 Name:
 1. (10 pts) Draw or describe the fate map of a late blastula stage sea urchin embryo. Draw or describe the corresponding fate map of the pluteus stage larva. Describe the sequence of gastrulation events
1. (10 pts) Draw or describe the fate map of a late blastula stage sea urchin embryo. Draw or describe the corresponding fate map of the pluteus stage larva. Describe the sequence of gastrulation events
Morphogens in biological development: Drosophila example
 LSM5194 Morphogens in biological development: Drosophila example Lecture 29 The concept of morphogen gradients The concept of morphogens was proposed by L. Wolpert as a part of the positional information
LSM5194 Morphogens in biological development: Drosophila example Lecture 29 The concept of morphogen gradients The concept of morphogens was proposed by L. Wolpert as a part of the positional information
Chapter 10 Development and Differentiation
 Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter Since ancient times, people have wondered how organisms are formed during the developmental process, and many researchers have worked tirelessly in search
Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter Since ancient times, people have wondered how organisms are formed during the developmental process, and many researchers have worked tirelessly in search
Lecture 7. Development of the Fruit Fly Drosophila
 BIOLOGY 205/SECTION 7 DEVELOPMENT- LILJEGREN Lecture 7 Development of the Fruit Fly Drosophila 1. The fruit fly- a highly successful, specialized organism a. Quick life cycle includes three larval stages
BIOLOGY 205/SECTION 7 DEVELOPMENT- LILJEGREN Lecture 7 Development of the Fruit Fly Drosophila 1. The fruit fly- a highly successful, specialized organism a. Quick life cycle includes three larval stages
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
2. Fertilization activates the egg and bring together the nuclei of sperm and egg
 2. Fertilization activates the egg and bring together the nuclei of sperm and egg Sea urchins (what phylum?) are models for the study of the early development of deuterostomes (like us, right?). Sea urchin
2. Fertilization activates the egg and bring together the nuclei of sperm and egg Sea urchins (what phylum?) are models for the study of the early development of deuterostomes (like us, right?). Sea urchin
Development of Drosophila
 Development of Drosophila Hand-out CBT Chapter 2 Wolpert, 5 th edition March 2018 Introduction 6. Introduction Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is found in all warm countries. In cooler regions,
Development of Drosophila Hand-out CBT Chapter 2 Wolpert, 5 th edition March 2018 Introduction 6. Introduction Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is found in all warm countries. In cooler regions,
MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I. Slide #1. Cell Differentiation
 MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I Slide #1 Cell Differentiation Cell Differentiation I -Basic principles of differentiation (p1305-1320) -C-elegans (p1321-1327) Cell Differentiation II
MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I Slide #1 Cell Differentiation Cell Differentiation I -Basic principles of differentiation (p1305-1320) -C-elegans (p1321-1327) Cell Differentiation II
Cell Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
PRACTICE EXAM. 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos.
 PRACTICE EXAM 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos. No Low [] Fly Embryo Embryo Non-neural Genes Neuroectoderm Genes
PRACTICE EXAM 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos. No Low [] Fly Embryo Embryo Non-neural Genes Neuroectoderm Genes
Why Flies? stages of embryogenesis. The Fly in History
 The Fly in History 1859 Darwin 1866 Mendel c. 1890 Driesch, Roux (experimental embryology) 1900 rediscovery of Mendel (birth of genetics) 1910 first mutant (white) (Morgan) 1913 first genetic map (Sturtevant
The Fly in History 1859 Darwin 1866 Mendel c. 1890 Driesch, Roux (experimental embryology) 1900 rediscovery of Mendel (birth of genetics) 1910 first mutant (white) (Morgan) 1913 first genetic map (Sturtevant
Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007
 Biology 4361 Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007 Name: ID: Multiple choice (1 point each. Indicate the best answer.) 1. During Drosophila gastrulation, mesoderm moves in through the a. primitives streak.
Biology 4361 Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007 Name: ID: Multiple choice (1 point each. Indicate the best answer.) 1. During Drosophila gastrulation, mesoderm moves in through the a. primitives streak.
Neural development its all connected
 Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Axis determination in flies. Sem 9.3.B.5 Animal Science
 Axis determination in flies Sem 9.3.B.5 Animal Science All embryos are in lateral view (anterior to the left). Endoderm, midgut; mesoderm; central nervous system; foregut, hindgut and pole cells in yellow.
Axis determination in flies Sem 9.3.B.5 Animal Science All embryos are in lateral view (anterior to the left). Endoderm, midgut; mesoderm; central nervous system; foregut, hindgut and pole cells in yellow.
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.32 - OVERVIEW OF ANIMALS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
!! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
UNIVERSITY OF YORK BIOLOGY. Developmental Biology
 Examination Candidate Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Developmental Biology Desk Number: Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total
Examination Candidate Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Developmental Biology Desk Number: Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total
9/4/2015 INDUCTION CHAPTER 1. Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology. Fig 1.
 INDUCTION CHAPTER 1 Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology Fig 1.1 1 EVOLUTION OF METAZOAN BRAINS GASTRULATION MAKING THE 3 RD GERM LAYER
INDUCTION CHAPTER 1 Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology Fig 1.1 1 EVOLUTION OF METAZOAN BRAINS GASTRULATION MAKING THE 3 RD GERM LAYER
Exam 1 ID#: October 4, 2007
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 1 ID#: October 4, 2007 Multiple choice (one point each) (1-25) 1. The process of cells forming tissues and organs is called a. morphogenesis. b. differentiation. c. allometry.
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 1 ID#: October 4, 2007 Multiple choice (one point each) (1-25) 1. The process of cells forming tissues and organs is called a. morphogenesis. b. differentiation. c. allometry.
Developmental genetics: finding the genes that regulate development
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 9 Developmental genetics: finding the genes that regulate development Introduction The application of genetic analysis and DNA technology to the study of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 9 Developmental genetics: finding the genes that regulate development Introduction The application of genetic analysis and DNA technology to the study of
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology. Cell Cell Communication in Development. Developmental Activities Coordinated in this Way
 Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Life Sciences For NET & SLET Exams Of UGC-CSIR. Section B and C. Volume-08. Contents A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1
 Section B and C Volume-08 Contents 5. DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1 B. GAMETOGENESIS, FERTILIZATION AND EARLY DEVELOPMENT 23 C. MORPHOGENESIS AND ORGANOGENESIS IN ANIMALS 91 0
Section B and C Volume-08 Contents 5. DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1 B. GAMETOGENESIS, FERTILIZATION AND EARLY DEVELOPMENT 23 C. MORPHOGENESIS AND ORGANOGENESIS IN ANIMALS 91 0
Name KEY. Biology Developmental Biology Winter Quarter Midterm 3 KEY
 Name KEY 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2009 Midterm 3 KEY All of the 25 multi-choice questions are single-answer. Choose the best answer. (4 pts each) Place
Name KEY 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2009 Midterm 3 KEY All of the 25 multi-choice questions are single-answer. Choose the best answer. (4 pts each) Place
Midterm 1. Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77
 Midterm 1 Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77 NAME: TA (circle one) Jody Westbrook or Jessica Piel Section (circle one) Tue Wed Thur MCB 141 First Midterm Feb. 21, 2008 Only answer 4 of these 5 problems.
Midterm 1 Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77 NAME: TA (circle one) Jody Westbrook or Jessica Piel Section (circle one) Tue Wed Thur MCB 141 First Midterm Feb. 21, 2008 Only answer 4 of these 5 problems.
Drosophila Somatic Anterior-Posterior Axis (A-P Axis) Formation
 Home Biol 4241 Luria-Delbruck 1943 Hershey-Chase 1952 Meselson-Stahl 1958 Garapin et al. 1978 McClintock 1953 King-Wilson 1975 Sanger et al. 1977 Rothberg et al. 2011 Jeffreys et al. 1985 Bacterial Genetics
Home Biol 4241 Luria-Delbruck 1943 Hershey-Chase 1952 Meselson-Stahl 1958 Garapin et al. 1978 McClintock 1953 King-Wilson 1975 Sanger et al. 1977 Rothberg et al. 2011 Jeffreys et al. 1985 Bacterial Genetics
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology The Genetics of Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology The Genetics of Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 EARLY DROSOPHILA DEVELOPMENT Fertilization 1) Drosophila egg activation occurs at ovulation - eggs are
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology The Genetics of Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 EARLY DROSOPHILA DEVELOPMENT Fertilization 1) Drosophila egg activation occurs at ovulation - eggs are
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018
 Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018 Introduction 3. Books This module is based on the following books: - 'Principles of Developement', Lewis Wolpert, et al., fifth edition, 2015 - 'Developmental
Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018 Introduction 3. Books This module is based on the following books: - 'Principles of Developement', Lewis Wolpert, et al., fifth edition, 2015 - 'Developmental
Drosophila melanogaster- Morphogen Gradient
 NPTEL Biotechnology - Systems Biology Drosophila melanogaster- Morphogen Gradient Dr. M. Vijayalakshmi School of Chemical and Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by
NPTEL Biotechnology - Systems Biology Drosophila melanogaster- Morphogen Gradient Dr. M. Vijayalakshmi School of Chemical and Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by
10/2/2015. Chapter 4. Determination and Differentiation. Neuroanatomical Diversity
 Chapter 4 Determination and Differentiation Neuroanatomical Diversity 1 Neurochemical diversity: another important aspect of neuronal fate Neurotransmitters and their receptors Excitatory Glutamate Acetylcholine
Chapter 4 Determination and Differentiation Neuroanatomical Diversity 1 Neurochemical diversity: another important aspect of neuronal fate Neurotransmitters and their receptors Excitatory Glutamate Acetylcholine
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Name. Biology Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY. Midterm 3
 Name 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY Midterm 3 Read the Following Instructions: * Answer 20 questions (5 points each) out of the available 25 questions
Name 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY Midterm 3 Read the Following Instructions: * Answer 20 questions (5 points each) out of the available 25 questions
Chapter 18 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Developmental Genetics
 Chapter 18 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Developmental Genetics Chapter Contents 18.1 Differentiated States Develop from Coordinated Programs of Gene Expression 18.2 Evolutionary Conservation
Chapter 18 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Developmental Genetics Chapter Contents 18.1 Differentiated States Develop from Coordinated Programs of Gene Expression 18.2 Evolutionary Conservation
Development Team. Developmental Biology Axis Specification in Drosophila. Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi
 Paper No. : 11 Module : 6 Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof. Namita Agrawal Department of Zoology, University
Paper No. : 11 Module : 6 Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof. Namita Agrawal Department of Zoology, University
BIS &003 Answers to Assigned Problems May 23, Week /18.6 How would you distinguish between an enhancer and a promoter?
 Week 9 Study Questions from the textbook: 6 th Edition: Chapter 19-19.6, 19.7, 19.15, 19.17 OR 7 th Edition: Chapter 18-18.6 18.7, 18.15, 18.17 19.6/18.6 How would you distinguish between an enhancer and
Week 9 Study Questions from the textbook: 6 th Edition: Chapter 19-19.6, 19.7, 19.15, 19.17 OR 7 th Edition: Chapter 18-18.6 18.7, 18.15, 18.17 19.6/18.6 How would you distinguish between an enhancer and
From DNA to Diversity
 From DNA to Diversity Molecular Genetics and the Evolution of Animal Design Sean B. Carroll Jennifer K. Grenier Scott D. Weatherbee Howard Hughes Medical Institute and University of Wisconsin Madison,
From DNA to Diversity Molecular Genetics and the Evolution of Animal Design Sean B. Carroll Jennifer K. Grenier Scott D. Weatherbee Howard Hughes Medical Institute and University of Wisconsin Madison,
Biology 218, practise Exam 2, 2011
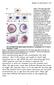 Figure 3 The long-range effect of Sqt does not depend on the induction of the endogenous cyc or sqt genes. a, Design and predictions for the experiments shown in b-e. b-e, Single-cell injection of 4 pg
Figure 3 The long-range effect of Sqt does not depend on the induction of the endogenous cyc or sqt genes. a, Design and predictions for the experiments shown in b-e. b-e, Single-cell injection of 4 pg
Homeotic genes in flies. Sem 9.3.B.6 Animal Science
 Homeotic genes in flies Sem 9.3.B.6 Animal Science So far We have seen that identities of each segment is determined by various regulators of segment polarity genes In arthopods, and in flies, each segment
Homeotic genes in flies Sem 9.3.B.6 Animal Science So far We have seen that identities of each segment is determined by various regulators of segment polarity genes In arthopods, and in flies, each segment
THE PROBLEMS OF DEVELOPMENT. Cell differentiation. Cell determination
 We emphasize these points from Kandel in Bi/CNS 150 Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience Read Lecture Lecture Friday, October 2, 2015 Development 1: pp 5-10 Introduction Brains evolved All higher animals have brains
We emphasize these points from Kandel in Bi/CNS 150 Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience Read Lecture Lecture Friday, October 2, 2015 Development 1: pp 5-10 Introduction Brains evolved All higher animals have brains
Genes, Development, and Evolution
 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Chapter 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Key Concepts 14.1 Development Involves Distinct but Overlapping Processes 14.2 Changes in Gene Expression Underlie Cell
14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Chapter 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Key Concepts 14.1 Development Involves Distinct but Overlapping Processes 14.2 Changes in Gene Expression Underlie Cell
Faculty of Science Course Syllabus Department of Biology BIOL 3050: Developmental Biology Fall 2018
 Faculty of Science Course Syllabus Department of Biology BIOL 3050: Developmental Biology Fall 2018 Instructor(s): Margaret Cooper Margaret.Cooper@dal.ca LSC 4014 Lectures: 1:35 2:25 MWF LSC Common Area
Faculty of Science Course Syllabus Department of Biology BIOL 3050: Developmental Biology Fall 2018 Instructor(s): Margaret Cooper Margaret.Cooper@dal.ca LSC 4014 Lectures: 1:35 2:25 MWF LSC Common Area
Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002
 Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002 1) A variety of reagents and approaches are frequently used by developmental biologists to understand the tissue interactions and molecular signaling pathways
Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002 1) A variety of reagents and approaches are frequently used by developmental biologists to understand the tissue interactions and molecular signaling pathways
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Developmental. Biology SCOTT F. GILBERT SWARTHMORE COLLEGE
 Developmental SCOTT F. GILBERT SWARTHMORE COLLEGE Biology Preface xi PART I : PATTERNS OF DEVELOPMENT Chapter 1 : An introduction to animal development 3 Introduction 4 Origins of sexual reproduction
Developmental SCOTT F. GILBERT SWARTHMORE COLLEGE Biology Preface xi PART I : PATTERNS OF DEVELOPMENT Chapter 1 : An introduction to animal development 3 Introduction 4 Origins of sexual reproduction
Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
 KAP Biology Dept Kenyon College Differential gene expression and development Mechanisms of cellular determination Induction Pattern formation Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
KAP Biology Dept Kenyon College Differential gene expression and development Mechanisms of cellular determination Induction Pattern formation Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
Bio Section III Organogenesis. The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification. Student Learning Objectives. Student Learning Objectives
 Bio 127 - Section III Organogenesis The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification Gilbert 9e Chapter 10 Student Learning Objectives 1. You should understand that the neural crest is an evolutionary advancement
Bio 127 - Section III Organogenesis The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification Gilbert 9e Chapter 10 Student Learning Objectives 1. You should understand that the neural crest is an evolutionary advancement
Conclusions. The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights
 C h a p t e r 5 Conclusions 5.1 Summary The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights into the cellular processes of assembly, and aggregation of neural crest and
C h a p t e r 5 Conclusions 5.1 Summary The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights into the cellular processes of assembly, and aggregation of neural crest and
BIOLOGY 340 Exam Study Guide All Exams Comparative Embryology Dr. Stuart S. Sumida California State University San Bernardino; Department of Biology
 BIOLOGY 340 Exam Study Guide All Exams Comparative Embryology Dr. Stuart S. Sumida California State University San Bernardino; Department of Biology Midterm and final exams may include materials studied
BIOLOGY 340 Exam Study Guide All Exams Comparative Embryology Dr. Stuart S. Sumida California State University San Bernardino; Department of Biology Midterm and final exams may include materials studied
Axon Guidance. Multiple decision points along a growing axon s trajectory Different types of axon guidance cues:
 Axon Guidance Multiple decision points along a growing axon s trajectory Different types of axon guidance cues: Contact mediated - requires direct contact by growth cone Long range - growth cone responds
Axon Guidance Multiple decision points along a growing axon s trajectory Different types of axon guidance cues: Contact mediated - requires direct contact by growth cone Long range - growth cone responds
MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 14, 2012
 Write your name and student ID# on EVERY PAGE of your exam MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 14, 2012 Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 BONUS / 28 pts / 27 pts / 25 pts / 20 pts / 1 pt TOTAL / 100 pts
Write your name and student ID# on EVERY PAGE of your exam MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 14, 2012 Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 BONUS / 28 pts / 27 pts / 25 pts / 20 pts / 1 pt TOTAL / 100 pts
10/15/09. Tetrapod Limb Development & Pattern Formation. Developing limb region is an example of a morphogenetic field
 Tetrapod Limb Development & Pattern Formation Figure 16.5(1) Limb Bud Formation derived from lateral plate (somatic) & paraxial (myotome) Fig. 16.2 Prospective Forelimb Field of Salamander Ambystoma maculatum
Tetrapod Limb Development & Pattern Formation Figure 16.5(1) Limb Bud Formation derived from lateral plate (somatic) & paraxial (myotome) Fig. 16.2 Prospective Forelimb Field of Salamander Ambystoma maculatum
BILD7: Problem Set. 2. What did Chargaff discover and why was this important?
 BILD7: Problem Set 1. What is the general structure of DNA? 2. What did Chargaff discover and why was this important? 3. What was the major contribution of Rosalind Franklin? 4. How did solving the structure
BILD7: Problem Set 1. What is the general structure of DNA? 2. What did Chargaff discover and why was this important? 3. What was the major contribution of Rosalind Franklin? 4. How did solving the structure
Exam 4 ID#: July 7, 2008
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: July 7, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. RNA polymerase II is not able to transcribe RNA unless a. it is first bound to TFIIB. b. its
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: July 7, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. RNA polymerase II is not able to transcribe RNA unless a. it is first bound to TFIIB. b. its
MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 19, 2009
 Write your name and student ID# on EVERY PAGE of your exam MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 19, 2009 Circle the name of your TA Jessica Lyons Alberto Stolfi Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 TOTAL
Write your name and student ID# on EVERY PAGE of your exam MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 19, 2009 Circle the name of your TA Jessica Lyons Alberto Stolfi Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 TOTAL
Principles of Development
 Principles of Development Fourth Edition Lewis Wolpert I Cheryll Tickle Thomas jessell Peter Lawrence Elliot Meyerowitz Elizabeth Robertson Jim Smith OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS --.:. - of contents Preface
Principles of Development Fourth Edition Lewis Wolpert I Cheryll Tickle Thomas jessell Peter Lawrence Elliot Meyerowitz Elizabeth Robertson Jim Smith OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS --.:. - of contents Preface
2/23/09. Regional differentiation of mesoderm. Morphological changes at early postgastrulation. Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
 Regional differentiation of mesoderm Axial Paraxial Intermediate Somatic Splanchnic Chick embryo Morphological changes at early postgastrulation stages Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
Regional differentiation of mesoderm Axial Paraxial Intermediate Somatic Splanchnic Chick embryo Morphological changes at early postgastrulation stages Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
Principles of Experimental Embryology
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology June 16, 2008 Overview What forces affect embryonic development? The embryonic environment: external and internal How do forces
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology June 16, 2008 Overview What forces affect embryonic development? The embryonic environment: external and internal How do forces
Development. 27 April 2017
 Development 27 April 2017 Development Development in multicellular organisms allow for cells and organ structures with specialized functions Development occurs at many points in the life cycle of an animal
Development 27 April 2017 Development Development in multicellular organisms allow for cells and organ structures with specialized functions Development occurs at many points in the life cycle of an animal
Segment boundary formation in Drosophila embryos
 Segment boundary formation in Drosophila embryos Development 130, August 2003 Camilla W. Larsen, Elizabeth Hirst, Cyrille Alexandre and Jean Paul Vincent 1. Introduction: - Segment boundary formation:
Segment boundary formation in Drosophila embryos Development 130, August 2003 Camilla W. Larsen, Elizabeth Hirst, Cyrille Alexandre and Jean Paul Vincent 1. Introduction: - Segment boundary formation:
AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review
 AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review 1. What does the regulatory gene code for? 2. Is the repressor by default active/inactive? 3. What changes the repressor activity? 4. What does repressor
AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review 1. What does the regulatory gene code for? 2. Is the repressor by default active/inactive? 3. What changes the repressor activity? 4. What does repressor
18.4 Embryonic development involves cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis
 18.4 Embryonic development involves cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis An organism arises from a fertilized egg cell as the result of three interrelated processes: cell division, cell
18.4 Embryonic development involves cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis An organism arises from a fertilized egg cell as the result of three interrelated processes: cell division, cell
Coordination of Cell Differentiation and Migration in Mathematical Models of Caudal Embryonic Axis Extension
 Coordination of Cell Differentiation and Migration in Mathematical Models of Caudal Embryonic Axis Extension Nigel C. Harrison 1, Ruth Diez del Corral 2 *, Bakhtier Vasiev 1 * 1 Department of Mathematical
Coordination of Cell Differentiation and Migration in Mathematical Models of Caudal Embryonic Axis Extension Nigel C. Harrison 1, Ruth Diez del Corral 2 *, Bakhtier Vasiev 1 * 1 Department of Mathematical
Maternal Control of GermLayer Formation in Xenopus
 Maternal Control of GermLayer Formation in Xenopus The zygotic genome is activated at the mid-blastula transition mid-blastula fertilized egg Xenopus gastrulae early-gastrula 7 hrs 10 hrs control not VP
Maternal Control of GermLayer Formation in Xenopus The zygotic genome is activated at the mid-blastula transition mid-blastula fertilized egg Xenopus gastrulae early-gastrula 7 hrs 10 hrs control not VP
Biology 376 Animal Development
 The stories are in every newspaper: cloning, stem cells, genetic engineering, in vitro fertilization, cancer therapies, organ regeneration, and protocols for prolonging our lifespan. In the past five years,
The stories are in every newspaper: cloning, stem cells, genetic engineering, in vitro fertilization, cancer therapies, organ regeneration, and protocols for prolonging our lifespan. In the past five years,
Introduction to Embryology. He who sees things grow from the beginning will have the finest view of them.
 He who sees things grow from the beginning will have the finest view of them. Aristotle 384 322 B.C. Introduction to Embryology This lecture will introduce you to the science of developmental biology or
He who sees things grow from the beginning will have the finest view of them. Aristotle 384 322 B.C. Introduction to Embryology This lecture will introduce you to the science of developmental biology or
Biology of Reproduction Spring 2007
 Biology of Reproduction Spring 2007 Louis Guillette Office: 528 Bartram Hall Office Hours: Tuesday/Thursday period 4 (10:40-11:25) Phone: 392-1098; Email: ljg@zoo.ufl.edu http://www.zoo.ufl.edu/ljg/courses/index.htm
Biology of Reproduction Spring 2007 Louis Guillette Office: 528 Bartram Hall Office Hours: Tuesday/Thursday period 4 (10:40-11:25) Phone: 392-1098; Email: ljg@zoo.ufl.edu http://www.zoo.ufl.edu/ljg/courses/index.htm
Reading. Lecture VI. Making Connections 9/17/12. Bio 3411 Lecture VI. Making Connections. Bio 3411 Monday September 17, 2012
 Lecture VI. Making Connections Bio 3411 Monday September 17, 2012!! 1! Reading NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp!507?536! 4 th ed, pp 577-609 Bentley, D., & Caudy, M. (1983). Nature, 304(5921), 62-65. Dickson,
Lecture VI. Making Connections Bio 3411 Monday September 17, 2012!! 1! Reading NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp!507?536! 4 th ed, pp 577-609 Bentley, D., & Caudy, M. (1983). Nature, 304(5921), 62-65. Dickson,
Questions in developmental biology. Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration
 Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
A systems approach to biology
 A systems approach to biology SB200 Lecture 7 7 October 2008 Jeremy Gunawardena jeremy@hms.harvard.edu Recap of Lecture 6 In phage lambda, cooperativity leads to bistability and hysteresis In HIV-1, sequestration
A systems approach to biology SB200 Lecture 7 7 October 2008 Jeremy Gunawardena jeremy@hms.harvard.edu Recap of Lecture 6 In phage lambda, cooperativity leads to bistability and hysteresis In HIV-1, sequestration
Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA
 Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA Instructor: Marianne Bronner Exam Length: 6 hours plus one 30-minute break at your discretion. It should take
Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA Instructor: Marianne Bronner Exam Length: 6 hours plus one 30-minute break at your discretion. It should take
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm July 28, 2008 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm Overview Development of major mesodermal lineages Somites: formation specification and differentiation Mesodermal
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm July 28, 2008 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm Overview Development of major mesodermal lineages Somites: formation specification and differentiation Mesodermal
Axon guidance I. Paul Garrity March 15, /9.013
 Axon guidance I Paul Garrity March 15, 2004 7.68/9.013 Neuronal Wiring: Functional Framework of the Nervous System Stretch reflex circuit Early theories of axonogenesis Schwann: many neurons link to form
Axon guidance I Paul Garrity March 15, 2004 7.68/9.013 Neuronal Wiring: Functional Framework of the Nervous System Stretch reflex circuit Early theories of axonogenesis Schwann: many neurons link to form
presumptiv e germ layers during Gastrulatio n and neurulation Somites
 Vertebrate embryos are similar at the phylotypic stage Patterning the Vertebrate Body Plan II: Mesoderm & Early Nervous System Wolpert L, Beddington R, Jessell T, Lawrence P, Meyerowitz E, Smith J. (2001)
Vertebrate embryos are similar at the phylotypic stage Patterning the Vertebrate Body Plan II: Mesoderm & Early Nervous System Wolpert L, Beddington R, Jessell T, Lawrence P, Meyerowitz E, Smith J. (2001)
Control of Gene Expression
 Control of Gene Expression Mechanisms of Gene Control Gene Control in Eukaryotes Master Genes Gene Control In Prokaryotes Epigenetics Gene Expression The overall process by which information flows from
Control of Gene Expression Mechanisms of Gene Control Gene Control in Eukaryotes Master Genes Gene Control In Prokaryotes Epigenetics Gene Expression The overall process by which information flows from
The Radiata-Bilateria split. Second branching in the evolutionary tree
 The Radiata-Bilateria split Second branching in the evolutionary tree Two very important characteristics are used to distinguish between the second bifurcation of metazoans Body symmetry Germinal layers
The Radiata-Bilateria split Second branching in the evolutionary tree Two very important characteristics are used to distinguish between the second bifurcation of metazoans Body symmetry Germinal layers
Unit 4 Evaluation Question 1:
 Name: Unit 4 Evaluation Question 1: /7 points A naturally occurring dominant mutant in mice is the Doublefoot (Dbf) mutant. Below is an image of the bones from a wildtype (wt) and Doublefoot mutant mouse.
Name: Unit 4 Evaluation Question 1: /7 points A naturally occurring dominant mutant in mice is the Doublefoot (Dbf) mutant. Below is an image of the bones from a wildtype (wt) and Doublefoot mutant mouse.
Chapter 10, 11, 14: Gene Expression, Regulation, and Development Exam
 Chapter 10, 11, 14: Gene Expression, Regulation, and Development Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Why did the original one-gene, one-enzyme
Chapter 10, 11, 14: Gene Expression, Regulation, and Development Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Why did the original one-gene, one-enzyme
Animal Origins and Evolution
 Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
Chapter 32. Objectives. Table of Contents. Characteristics. Characteristics, continued. Section 1 The Nature of Animals
 Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo
 Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo In the first part of this thesis work the physical properties of cilia-driven leftward flow were characterised in the rabbit embryo. Since its discovery
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo In the first part of this thesis work the physical properties of cilia-driven leftward flow were characterised in the rabbit embryo. Since its discovery
Extranuclear Inheritance
 Extranuclear Inheritance Extranuclear Inheritance The past couple of lectures, we ve been exploring exceptions to Mendel s principles of transmission inheritance. Scientists have observed inheritance patterns
Extranuclear Inheritance Extranuclear Inheritance The past couple of lectures, we ve been exploring exceptions to Mendel s principles of transmission inheritance. Scientists have observed inheritance patterns
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Differential gene expression Every somatic cell in an individual organism contains the same genetic information and replicated from the same original fertilized
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Differential gene expression Every somatic cell in an individual organism contains the same genetic information and replicated from the same original fertilized
Mesoderm induction: from caps to chips
 Mesoderm induction: from caps to chips David Kimelman Abstract Vertebrate mesoderm induction is one of the classical problems in developmental biology. Various developmental biology approaches, particularly
Mesoderm induction: from caps to chips David Kimelman Abstract Vertebrate mesoderm induction is one of the classical problems in developmental biology. Various developmental biology approaches, particularly
Principles of Experimental Embryology
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology September 19, 2006 Major Research Questions How do forces outside the embryo affect its development? (Environmental Developmental
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology September 19, 2006 Major Research Questions How do forces outside the embryo affect its development? (Environmental Developmental
Limb Development Involving the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles
 Limb Development Involving the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles 1 Objectives Timing and location of limb bud development The tissues from which limb buds are made Determining the position
Limb Development Involving the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles 1 Objectives Timing and location of limb bud development The tissues from which limb buds are made Determining the position
3/8/ Complex adaptations. 2. often a novel trait
 Chapter 10 Adaptation: from genes to traits p. 302 10.1 Cascades of Genes (p. 304) 1. Complex adaptations A. Coexpressed traits selected for a common function, 2. often a novel trait A. not inherited from
Chapter 10 Adaptation: from genes to traits p. 302 10.1 Cascades of Genes (p. 304) 1. Complex adaptations A. Coexpressed traits selected for a common function, 2. often a novel trait A. not inherited from
