Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007
|
|
|
- Sherman Smith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology 4361 Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007 Name: ID: Multiple choice (1 point each. Indicate the best answer.) 1. During Drosophila gastrulation, mesoderm moves in through the a. primitives streak. b. node. c. dorsal lip. d. ventral furrow. 2. During development of Drosophila eggs, the nurse cells a. contribute mrna to the egg. b. are joined to the egg by cytoplasmic bridges. c. donate cytoplasm to the egg. d. all of the above. 3. The gurken gene is synthesized by Drosophila nurse cells and is transported into the oocyte. This results in the posteriorization of the a. nurse cells. b. follicle cells. c. oocyte. d. none of the above. 4. Drosophila bicoid mrna binds to a. kinesin, which moves to the (-) end of the microtubules. b. kinesin, which moves to the (+) end of the microtubules. c. dynein, which moves to the (-) end of the microtubules. d. dynein, which moves to the (+) end of the microtubules. 5. In general, the hierarchical order of gene expression in early Drosophila development is a. Maternal Effect, Gap, Pair-rule, Segment Polarity. b. Maternal Effect, Pair-rule, Segment Polarity, Gap. c. Gap, Maternal Effect, Segment Polarity, Pair-rule. d. none of the above. 6. If you created a Drosophila embryo with a homeotic selector gene knockout, where might a typical phenotypic effect be found? a. anterior-posterior axis development. b. gastrulation. c. segmentation. d. wing development. 7. Chicks undergo a. bilateral cleavage. b. rotational cleavage. c. discoidal cleavage. d. syncytial cleavage. 1
2 8. During chick gastrulation, cells move into the blastocoel through a. the primitive pit b. the primitive groove. c. Hensen s node. d. all of the above 9. Gastrulation in mammals most closely resembles which of the following? a. reptiles b. amphibians c. sea urchins d. Drosophila 10. is seen as a hallmark of early mammalian development. a. Asynchronous cleavage b. Rotational cleavage c. Compaction d. all of the above 11. The portion of the trophoblast the erodes the uterine tissue is referred to as the a. cytotrophoblast. b. choriotrophoblast. c. syncytiotrophoblast. d. amniotrophoblast. 12. If expression of all copies of a particular Hox gene were knocked out, what would the expected result be regarding the identity of the affected region? a. The region would take on the identity of the next most anterior region. b. The region would take on the identity of the next most posterior region. c. The region would revert to a default identity (i.e. would not differentiate into any structure) d. none of the above. 13. Primary neurulation occurs in a. the anterior neural tube. b. the posterior neural tube. c. the entire neural tube. d. none of the neural tube. 14. Folding of the floor plate of the neural tube is facilitated by a. notochord cells. b. mesenchymal mesoderm. c. columnar epithelium cells. d. medial hinge point cells. 15. The force that closes the neural tube is supplied in part by the a. neural tube. b. epidermal ectoderm. c. both a and b d. neither a nor b 2
3 16. Anencephaly results form the failure of the to close. a. anterior neuropore b. posterior neuropore c. dorsolateral hinge points d. neural crest 17. Myelination is carried out in the peripheral nervous system by a. oligodendrocytes. b. glial cells. c. Schwann cells. d. dendrites. 18. The neural tube floor plate is primarily specified by a. BMPs b. Shh c. Nodal d. Notch 19. Trunk neural crest cells that migrate through the dorsolateral pathway a. migrate before those traveling through the ventrolateral pathway. b. migrate after those traveling through the ventrolateral pathway. c. migrate at the same time as those traveling through the ventrolateral pathway. d. prevent migration through the ventrolateral pathway. 20. The parasympathetic (enteric) ganglia of the gut are formed by a. cranial neural crest cells. b. trunk neural crest cells. c. vagal and sacral neural crest cells. d. cardiac neural crest cells. 21. During intramembranous ossification the osteoid matrix that binds calcium is formed by a. osteoblasts. b. osteoclasts. c. osteocytes. d. osteoforms. 22. In general, the major mesodermal lineages are determined by gradients of a. retinoic acid. b. sonic hedgehog. c. FGFs. d. BMPs. 23. In the process of mammalian somite formation, the clock for periodic somite formation is considered a. Notch. b. Fgf8. c. Hairy 1. d. none of the above 3
4 24. During somite formation, the paraxial mesoderm undergoes a. convergent extension. b. an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation. c. a mesenchymal-to-epithelial transformation. d. none of the above. 25. Which of the following bones are formed by endochondral ossification? a. inner ear. b. facial. c. wrist. d. all of the above. 26. What portion of the pronephric kidney is functional in the adult mammal? a. pronephros b. nephric duct c. nephrons d. none of the above 27. The mesonephric kidney supplies the adult mammal with which structures? a. vas deferens b. epididymus c. efferent ducts d. all of the above 28. The growth factor responsible for initiating angiogenesis is called a. FGF b. TGFβ c. BMP d. VEGF 29. The thymus gland is derived from a. branchial arch. b. pharyngeal pouch. c. pharyngeal arch. d. aortic arch. 30. Amniote eggs prevent desiccation by developing the a. amnion. b. chorion. c. allantois. d. yolk sac. 4
5 True / False (1 point each.) 31. Torso, the Drosophila terminal determinant, is a receptor tyrosine kinase. True / False 32. In chick embryos the endoderm layer is derived from the secondary hypoblast. True / False 33. Mammalian Hox genes are homologs of Drosophila homeotic selector genes. True / False 34. Neurons are guided to their ultimate destinations by oligodendrocyte cells. True / False 35. The mammalian brain is structurally organized both horizontally and vertically. True / False 36. All neural crest cells undergo epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation. True / False 37. Cells destined to be tendons can be identified by the presence of the MyoD protein. True / False 38. The human face is primarily a product of neural crest cells. True / False 39. Cardiogenic mesoderm forms the heart and blood vessels. True / False 40. The foregut is derived from an outpocketing of the respiratory diverticulum. True / False Fill in. (1 point per answer) Use the terms from the Term Banks to make the most accurate sentence. Terms may be used more than once. Term Bank: Drosophila dorsal-ventral axis specification Cactus Dorsal dorsal Frizzeled Gurken nuclear Nudel Pipe Toll Torpedo Spätzle ventral In Drosophila the process of dorsal-ventral axis specification starts with protein expression in the dorsal region of the oocyte, where it binds to the receptor and blocks the expression of the protein. In the region, expression of starts a cascade of enzymatic activity that eventually causes the binding and activation of the receptor, which subsequently causes the activation of the transcription factor, which stimulates genes that specify fates. 5
6 Term Bank: Mammalian blastocyst derivatives allantois amnion blastocyst chorion cytotrophoblast decidua embryo hypoblast inner cell mass epiblast trophoblast syncytiotrophoblast The mammalian blastocyst is divided into two major portions: The, which will eventually form the embryonic portion of the placenta, is composed of the and. The embryonic placenta is referred to as the. The second portion of the blastocyst, the splits into the and the, with the former creating the and the latter forming the extraembryonic yolk sac. Short answer. (6 points each; answer any four.) Be as specific as possible and completely answer all parts of each question. 58. Two opposing gene activities specify the dorsal and ventral regions of the neural tube. List these genes and describe what portions of the neural tube that they specify. 59. Describe the role of gravity in determining the position of the primitive streak in chick embryos. 60. Describe the formation of intramembranous bone. 6
7 61. List the four major mesodermal lineages and provide one structure that arises from each one. 62. Describe the mechanism that veins and arteries use to connect to each other during angiogenesis; specifically, how do veins attach to arteries and avoid attachment to other veins? 63. Define the following terms dealing with mammalian early mammalian development: compaction, morula, cavitation. Short Essay. (Ten points each; answer any two) Be sure to address and completely answer all parts to the questions. 64. Describe the establishment of the anterior-posterior axis in Drosophila, specifically involving the bicoid, nanos, hunchback, and caudal genes and proteins. 7
8 65. Describe the formation of endochondral bone. 66. Drosophila embryos develop parasegments and segments. Describe how these are organized structurally and how they function in the adult organism. 8
9 67. Mammalian somites are periodic structures that form during embryogenesis. Describe in general terms what forms of gene or protein activities that would be necessary to create somites. Short Essay II. (15 points each. Answer any three.) 68. The establishment of the left-right axis has some similarities and some differences among different species. For two of the species that we have studied, describe the major gene(s), paracrine factors, or other proteins involved and describe how they operate structurally to establish the left and right sides. 9
10 69. Most of the model species we have studies have a certain region or structure referred to as an organizer. What does this term mean? What functional test would you use to determine whether a particular region or structure had organizer properties? For two of the models we studied, list the organizer structure or region. 70. Transformations of cells between epithelia and mesenchyme are very common during development. Describe one situation in which epithelial cells transform into mesenchyme and one in which mesenchymal cells transform into epithelia. Be specific regarding species, tissue, developmental stage, and the developmental process that the cells or tissue is undergoing. 10
11 71. Your task in the lab is to design experiments that will determine which migration pathway a certain set of neural crest cells takes, and where (or when) during their journey they become specified. Describe at least two experiments that use different techniques of experimental developmental biology that would address these questions. Be as specific as possible in your explanation of the experimental design and the possible results. 11
12 72. Describe one area or subject that we covered in the class that you feel needs further attention, clarification, or explanation. (2 pt.) 73. List one area or subject that you would like to see covered in more detail or one that we didn t discuss that you wish we had. (2 pt.) 74. List one fact that we covered that surprised, fascinated, or repelled you. (1 pt.) Bonus question. (1 pt.) Dr. James Thomson and Dr. Shinya Yamanaka recently made headlines by announcing what scientific discovery? Bonus bonus question. (1 pt). This is the second time that Dr. James Thomson has made the news in the last few years. What was his first newsworthy accomplishment announced in 1998? 12
4. Neural tube cells are specified by opposing dorsal-ventral gradients of a. Wnts and Nodal. b. FGF and Shh. c. BMPs and Wnts. d. BMPs and Shh.
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: August 1, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: August 1, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Exam 3 ID#: July 31, 2009
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 3 ID#: July 31, 2009 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 3 ID#: July 31, 2009 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos
 Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 6, 2007 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 6, 2007 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm July 28, 2008 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm Overview Development of major mesodermal lineages Somites: formation specification and differentiation Mesodermal
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm July 28, 2008 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm Overview Development of major mesodermal lineages Somites: formation specification and differentiation Mesodermal
Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006 Multiple choice (one point each) Circle the best answer. 1. Inducers of Xenopus lens and optic vesicle include a. pharyngeal endoderm and anterior neural
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006 Multiple choice (one point each) Circle the best answer. 1. Inducers of Xenopus lens and optic vesicle include a. pharyngeal endoderm and anterior neural
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila July 9, 2008 Drosophila Development Overview Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation Genetic control
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila July 9, 2008 Drosophila Development Overview Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation Genetic control
Mesoderm Development
 Quiz rules: Spread out across available tables No phones, text books, or (lecture) notes on your desks No consultation with your colleagues No websites open other than the Quiz page No screen snap shots
Quiz rules: Spread out across available tables No phones, text books, or (lecture) notes on your desks No consultation with your colleagues No websites open other than the Quiz page No screen snap shots
Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006
 Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
Drosophila Life Cycle
 Drosophila Life Cycle 1 Early Drosophila Cleavage Nuclei migrate to periphery after 10 nuclear divisions. Cellularization occurs when plasma membrane folds in to divide nuclei into cells. Drosophila Superficial
Drosophila Life Cycle 1 Early Drosophila Cleavage Nuclei migrate to periphery after 10 nuclear divisions. Cellularization occurs when plasma membrane folds in to divide nuclei into cells. Drosophila Superficial
Name KEY. Biology Developmental Biology Winter Quarter Midterm 3 KEY
 Name KEY 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2009 Midterm 3 KEY All of the 25 multi-choice questions are single-answer. Choose the best answer. (4 pts each) Place
Name KEY 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2009 Midterm 3 KEY All of the 25 multi-choice questions are single-answer. Choose the best answer. (4 pts each) Place
Developmental processes Differential gene expression Introduction to determination The model organisms used to study developmental processes
 Date Title Topic(s) Learning Outcomes: Sept 28 Oct 3 1. What is developmental biology and why should we care? 2. What is so special about stem cells and gametes? Developmental processes Differential gene
Date Title Topic(s) Learning Outcomes: Sept 28 Oct 3 1. What is developmental biology and why should we care? 2. What is so special about stem cells and gametes? Developmental processes Differential gene
9/4/2015 INDUCTION CHAPTER 1. Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology. Fig 1.
 INDUCTION CHAPTER 1 Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology Fig 1.1 1 EVOLUTION OF METAZOAN BRAINS GASTRULATION MAKING THE 3 RD GERM LAYER
INDUCTION CHAPTER 1 Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology Fig 1.1 1 EVOLUTION OF METAZOAN BRAINS GASTRULATION MAKING THE 3 RD GERM LAYER
Bio Section III Organogenesis. The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification. Student Learning Objectives. Student Learning Objectives
 Bio 127 - Section III Organogenesis The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification Gilbert 9e Chapter 10 Student Learning Objectives 1. You should understand that the neural crest is an evolutionary advancement
Bio 127 - Section III Organogenesis The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification Gilbert 9e Chapter 10 Student Learning Objectives 1. You should understand that the neural crest is an evolutionary advancement
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning
 MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines
 Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Early Development in Invertebrates
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Early Development in Invertebrates October 25, 2006 Early Development Overview Cleavage rapid cell divisions divisions of fertilized egg into many cells Gastrulation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Early Development in Invertebrates October 25, 2006 Early Development Overview Cleavage rapid cell divisions divisions of fertilized egg into many cells Gastrulation
!!!!!!!! DB3230 Midterm 2 12/13/2013 Name:
 1. (10 pts) Draw or describe the fate map of a late blastula stage sea urchin embryo. Draw or describe the corresponding fate map of the pluteus stage larva. Describe the sequence of gastrulation events
1. (10 pts) Draw or describe the fate map of a late blastula stage sea urchin embryo. Draw or describe the corresponding fate map of the pluteus stage larva. Describe the sequence of gastrulation events
Development of Drosophila
 Development of Drosophila Hand-out CBT Chapter 2 Wolpert, 5 th edition March 2018 Introduction 6. Introduction Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is found in all warm countries. In cooler regions,
Development of Drosophila Hand-out CBT Chapter 2 Wolpert, 5 th edition March 2018 Introduction 6. Introduction Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is found in all warm countries. In cooler regions,
Developmental Zoology. Ectodermal derivatives (ZOO ) Developmental Stages. Developmental Stages
 Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? 2. What embryonic regions contribute to the developing limb bud?
 Study Questions - Lecture 17 & 18 1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? The three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb are the proximal stylopod, zeugopod, and
Study Questions - Lecture 17 & 18 1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? The three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb are the proximal stylopod, zeugopod, and
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Life Sciences For NET & SLET Exams Of UGC-CSIR. Section B and C. Volume-08. Contents A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1
 Section B and C Volume-08 Contents 5. DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1 B. GAMETOGENESIS, FERTILIZATION AND EARLY DEVELOPMENT 23 C. MORPHOGENESIS AND ORGANOGENESIS IN ANIMALS 91 0
Section B and C Volume-08 Contents 5. DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1 B. GAMETOGENESIS, FERTILIZATION AND EARLY DEVELOPMENT 23 C. MORPHOGENESIS AND ORGANOGENESIS IN ANIMALS 91 0
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology The Genetics of Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology The Genetics of Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 EARLY DROSOPHILA DEVELOPMENT Fertilization 1) Drosophila egg activation occurs at ovulation - eggs are
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology The Genetics of Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 EARLY DROSOPHILA DEVELOPMENT Fertilization 1) Drosophila egg activation occurs at ovulation - eggs are
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology. Cell Cell Communication in Development. Developmental Activities Coordinated in this Way
 Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic)
 Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic) Fates of Mesoderm Paraxial - Dermis of skin - Axial Skeleton - Axial and limb muscles/tendons
Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic) Fates of Mesoderm Paraxial - Dermis of skin - Axial Skeleton - Axial and limb muscles/tendons
MOLECULAR CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC PATTERN FORMATION
 MOLECULAR CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC PATTERN FORMATION Drosophila is the best understood of all developmental systems, especially at the genetic level, and although it is an invertebrate it has had an enormous
MOLECULAR CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC PATTERN FORMATION Drosophila is the best understood of all developmental systems, especially at the genetic level, and although it is an invertebrate it has had an enormous
Name. Biology Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY. Midterm 3
 Name 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY Midterm 3 Read the Following Instructions: * Answer 20 questions (5 points each) out of the available 25 questions
Name 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY Midterm 3 Read the Following Instructions: * Answer 20 questions (5 points each) out of the available 25 questions
BIOLOGY 340 Exam Study Guide All Exams Comparative Embryology Dr. Stuart S. Sumida California State University San Bernardino; Department of Biology
 BIOLOGY 340 Exam Study Guide All Exams Comparative Embryology Dr. Stuart S. Sumida California State University San Bernardino; Department of Biology Midterm and final exams may include materials studied
BIOLOGY 340 Exam Study Guide All Exams Comparative Embryology Dr. Stuart S. Sumida California State University San Bernardino; Department of Biology Midterm and final exams may include materials studied
Midterm 1. Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77
 Midterm 1 Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77 NAME: TA (circle one) Jody Westbrook or Jessica Piel Section (circle one) Tue Wed Thur MCB 141 First Midterm Feb. 21, 2008 Only answer 4 of these 5 problems.
Midterm 1 Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77 NAME: TA (circle one) Jody Westbrook or Jessica Piel Section (circle one) Tue Wed Thur MCB 141 First Midterm Feb. 21, 2008 Only answer 4 of these 5 problems.
Head and Face Development
 Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
Chapter 10 Development and Differentiation
 Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter Since ancient times, people have wondered how organisms are formed during the developmental process, and many researchers have worked tirelessly in search
Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter Since ancient times, people have wondered how organisms are formed during the developmental process, and many researchers have worked tirelessly in search
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo
 Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo In the first part of this thesis work the physical properties of cilia-driven leftward flow were characterised in the rabbit embryo. Since its discovery
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo In the first part of this thesis work the physical properties of cilia-driven leftward flow were characterised in the rabbit embryo. Since its discovery
Exam 1 ID#: October 4, 2007
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 1 ID#: October 4, 2007 Multiple choice (one point each) (1-25) 1. The process of cells forming tissues and organs is called a. morphogenesis. b. differentiation. c. allometry.
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 1 ID#: October 4, 2007 Multiple choice (one point each) (1-25) 1. The process of cells forming tissues and organs is called a. morphogenesis. b. differentiation. c. allometry.
presumptiv e germ layers during Gastrulatio n and neurulation Somites
 Vertebrate embryos are similar at the phylotypic stage Patterning the Vertebrate Body Plan II: Mesoderm & Early Nervous System Wolpert L, Beddington R, Jessell T, Lawrence P, Meyerowitz E, Smith J. (2001)
Vertebrate embryos are similar at the phylotypic stage Patterning the Vertebrate Body Plan II: Mesoderm & Early Nervous System Wolpert L, Beddington R, Jessell T, Lawrence P, Meyerowitz E, Smith J. (2001)
Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle.
 Spatial organization is a key difference between unicellular organisms and metazoans Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle. Cells differentiate as a
Spatial organization is a key difference between unicellular organisms and metazoans Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle. Cells differentiate as a
Axis determination in flies. Sem 9.3.B.5 Animal Science
 Axis determination in flies Sem 9.3.B.5 Animal Science All embryos are in lateral view (anterior to the left). Endoderm, midgut; mesoderm; central nervous system; foregut, hindgut and pole cells in yellow.
Axis determination in flies Sem 9.3.B.5 Animal Science All embryos are in lateral view (anterior to the left). Endoderm, midgut; mesoderm; central nervous system; foregut, hindgut and pole cells in yellow.
Cell Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
2. Fertilization activates the egg and bring together the nuclei of sperm and egg
 2. Fertilization activates the egg and bring together the nuclei of sperm and egg Sea urchins (what phylum?) are models for the study of the early development of deuterostomes (like us, right?). Sea urchin
2. Fertilization activates the egg and bring together the nuclei of sperm and egg Sea urchins (what phylum?) are models for the study of the early development of deuterostomes (like us, right?). Sea urchin
Principles of Experimental Embryology
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology June 16, 2008 Overview What forces affect embryonic development? The embryonic environment: external and internal How do forces
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology June 16, 2008 Overview What forces affect embryonic development? The embryonic environment: external and internal How do forces
The wild imaginings of midterm content. Fill your soul
 The wild imaginings of midterm content. Fill your soul 1-2 Is the sperm activation the same as capacitation? sea urchin and mammal -- acrosomal reaction must occur. Acrosomal Reaction is sperm activation.
The wild imaginings of midterm content. Fill your soul 1-2 Is the sperm activation the same as capacitation? sea urchin and mammal -- acrosomal reaction must occur. Acrosomal Reaction is sperm activation.
2/23/09. Regional differentiation of mesoderm. Morphological changes at early postgastrulation. Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
 Regional differentiation of mesoderm Axial Paraxial Intermediate Somatic Splanchnic Chick embryo Morphological changes at early postgastrulation stages Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
Regional differentiation of mesoderm Axial Paraxial Intermediate Somatic Splanchnic Chick embryo Morphological changes at early postgastrulation stages Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
Development Team. Developmental Biology Axis Specification in Drosophila. Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi
 Paper No. : 11 Module : 6 Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof. Namita Agrawal Department of Zoology, University
Paper No. : 11 Module : 6 Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof. Namita Agrawal Department of Zoology, University
Developmental Biology Biology Ectodermal Organs. November 22, 2005
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Ectodermal Organs November 22, 2005 Germinal neuroepithelium external limiting membrane neural tube neuroepithelium (stem cells) Figure 13.3 Figure 13.4 Neuroepithelial
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Ectodermal Organs November 22, 2005 Germinal neuroepithelium external limiting membrane neural tube neuroepithelium (stem cells) Figure 13.3 Figure 13.4 Neuroepithelial
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.32 - OVERVIEW OF ANIMALS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
!! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
Homeotic genes in flies. Sem 9.3.B.6 Animal Science
 Homeotic genes in flies Sem 9.3.B.6 Animal Science So far We have seen that identities of each segment is determined by various regulators of segment polarity genes In arthopods, and in flies, each segment
Homeotic genes in flies Sem 9.3.B.6 Animal Science So far We have seen that identities of each segment is determined by various regulators of segment polarity genes In arthopods, and in flies, each segment
QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY"
 QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY" 1. The structure of the Plasmolemma. 2. Characteristic of receptive and transport functions of the plasmolemma. 3. The structure of intercellular contacts: Simple contact,
QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY" 1. The structure of the Plasmolemma. 2. Characteristic of receptive and transport functions of the plasmolemma. 3. The structure of intercellular contacts: Simple contact,
Questions in developmental biology. Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration
 Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA
 Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA Instructor: Marianne Bronner Exam Length: 6 hours plus one 30-minute break at your discretion. It should take
Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA Instructor: Marianne Bronner Exam Length: 6 hours plus one 30-minute break at your discretion. It should take
Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure
 The embryo is a Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure WEEK 4 EMBRYO General features Primordia of the brain Somites Primordia of the heart Branchial arches Primordia
The embryo is a Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure WEEK 4 EMBRYO General features Primordia of the brain Somites Primordia of the heart Branchial arches Primordia
Lecture 7. Development of the Fruit Fly Drosophila
 BIOLOGY 205/SECTION 7 DEVELOPMENT- LILJEGREN Lecture 7 Development of the Fruit Fly Drosophila 1. The fruit fly- a highly successful, specialized organism a. Quick life cycle includes three larval stages
BIOLOGY 205/SECTION 7 DEVELOPMENT- LILJEGREN Lecture 7 Development of the Fruit Fly Drosophila 1. The fruit fly- a highly successful, specialized organism a. Quick life cycle includes three larval stages
MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 19, 2009
 Write your name and student ID# on EVERY PAGE of your exam MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 19, 2009 Circle the name of your TA Jessica Lyons Alberto Stolfi Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 TOTAL
Write your name and student ID# on EVERY PAGE of your exam MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 19, 2009 Circle the name of your TA Jessica Lyons Alberto Stolfi Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 TOTAL
Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018
 Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018 Introduction 3. Books This module is based on the following books: - 'Principles of Developement', Lewis Wolpert, et al., fifth edition, 2015 - 'Developmental
Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018 Introduction 3. Books This module is based on the following books: - 'Principles of Developement', Lewis Wolpert, et al., fifth edition, 2015 - 'Developmental
PRACTICE EXAM. 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos.
 PRACTICE EXAM 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos. No Low [] Fly Embryo Embryo Non-neural Genes Neuroectoderm Genes
PRACTICE EXAM 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos. No Low [] Fly Embryo Embryo Non-neural Genes Neuroectoderm Genes
Why Flies? stages of embryogenesis. The Fly in History
 The Fly in History 1859 Darwin 1866 Mendel c. 1890 Driesch, Roux (experimental embryology) 1900 rediscovery of Mendel (birth of genetics) 1910 first mutant (white) (Morgan) 1913 first genetic map (Sturtevant
The Fly in History 1859 Darwin 1866 Mendel c. 1890 Driesch, Roux (experimental embryology) 1900 rediscovery of Mendel (birth of genetics) 1910 first mutant (white) (Morgan) 1913 first genetic map (Sturtevant
THE PROBLEMS OF DEVELOPMENT. Cell differentiation. Cell determination
 We emphasize these points from Kandel in Bi/CNS 150 Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience Read Lecture Lecture Friday, October 2, 2015 Development 1: pp 5-10 Introduction Brains evolved All higher animals have brains
We emphasize these points from Kandel in Bi/CNS 150 Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience Read Lecture Lecture Friday, October 2, 2015 Development 1: pp 5-10 Introduction Brains evolved All higher animals have brains
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
10/15/09. Tetrapod Limb Development & Pattern Formation. Developing limb region is an example of a morphogenetic field
 Tetrapod Limb Development & Pattern Formation Figure 16.5(1) Limb Bud Formation derived from lateral plate (somatic) & paraxial (myotome) Fig. 16.2 Prospective Forelimb Field of Salamander Ambystoma maculatum
Tetrapod Limb Development & Pattern Formation Figure 16.5(1) Limb Bud Formation derived from lateral plate (somatic) & paraxial (myotome) Fig. 16.2 Prospective Forelimb Field of Salamander Ambystoma maculatum
Unit 4 Evaluation Question 1:
 Name: Unit 4 Evaluation Question 1: /7 points A naturally occurring dominant mutant in mice is the Doublefoot (Dbf) mutant. Below is an image of the bones from a wildtype (wt) and Doublefoot mutant mouse.
Name: Unit 4 Evaluation Question 1: /7 points A naturally occurring dominant mutant in mice is the Doublefoot (Dbf) mutant. Below is an image of the bones from a wildtype (wt) and Doublefoot mutant mouse.
Organization of Vertebrate Body. Organization of Vertebrate Body
 The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
The Radiata-Bilateria split. Second branching in the evolutionary tree
 The Radiata-Bilateria split Second branching in the evolutionary tree Two very important characteristics are used to distinguish between the second bifurcation of metazoans Body symmetry Germinal layers
The Radiata-Bilateria split Second branching in the evolutionary tree Two very important characteristics are used to distinguish between the second bifurcation of metazoans Body symmetry Germinal layers
MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I. Slide #1. Cell Differentiation
 MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I Slide #1 Cell Differentiation Cell Differentiation I -Basic principles of differentiation (p1305-1320) -C-elegans (p1321-1327) Cell Differentiation II
MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I Slide #1 Cell Differentiation Cell Differentiation I -Basic principles of differentiation (p1305-1320) -C-elegans (p1321-1327) Cell Differentiation II
Drosophila Somatic Anterior-Posterior Axis (A-P Axis) Formation
 Home Biol 4241 Luria-Delbruck 1943 Hershey-Chase 1952 Meselson-Stahl 1958 Garapin et al. 1978 McClintock 1953 King-Wilson 1975 Sanger et al. 1977 Rothberg et al. 2011 Jeffreys et al. 1985 Bacterial Genetics
Home Biol 4241 Luria-Delbruck 1943 Hershey-Chase 1952 Meselson-Stahl 1958 Garapin et al. 1978 McClintock 1953 King-Wilson 1975 Sanger et al. 1977 Rothberg et al. 2011 Jeffreys et al. 1985 Bacterial Genetics
Genes, Development, and Evolution
 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Chapter 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Key Concepts 14.1 Development Involves Distinct but Overlapping Processes 14.2 Changes in Gene Expression Underlie Cell
14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Chapter 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Key Concepts 14.1 Development Involves Distinct but Overlapping Processes 14.2 Changes in Gene Expression Underlie Cell
Chapter 32. Objectives. Table of Contents. Characteristics. Characteristics, continued. Section 1 The Nature of Animals
 Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Chapter 18 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Developmental Genetics
 Chapter 18 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Developmental Genetics Chapter Contents 18.1 Differentiated States Develop from Coordinated Programs of Gene Expression 18.2 Evolutionary Conservation
Chapter 18 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Developmental Genetics Chapter Contents 18.1 Differentiated States Develop from Coordinated Programs of Gene Expression 18.2 Evolutionary Conservation
Morphogens in biological development: Drosophila example
 LSM5194 Morphogens in biological development: Drosophila example Lecture 29 The concept of morphogen gradients The concept of morphogens was proposed by L. Wolpert as a part of the positional information
LSM5194 Morphogens in biological development: Drosophila example Lecture 29 The concept of morphogen gradients The concept of morphogens was proposed by L. Wolpert as a part of the positional information
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Review of Early Development of Humans.
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Review of Early Development of Humans Special Senses Review: Historical and Developmental Perspectives Ontogeny
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Review of Early Development of Humans Special Senses Review: Historical and Developmental Perspectives Ontogeny
MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 14, 2012
 Write your name and student ID# on EVERY PAGE of your exam MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 14, 2012 Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 BONUS / 28 pts / 27 pts / 25 pts / 20 pts / 1 pt TOTAL / 100 pts
Write your name and student ID# on EVERY PAGE of your exam MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 14, 2012 Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 BONUS / 28 pts / 27 pts / 25 pts / 20 pts / 1 pt TOTAL / 100 pts
Pamela E. Knapp, Ph.D. Dept. of Anatomy & Neurobiology DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHARYNGEAL (BRANCHIAL) ARCHES
 Embryology Pamela E. Knapp, Ph.D. Dept. of Anatomy & Neurobiology DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHARYNGEAL (BRANCHIAL) ARCHES READING: Larsen, 4 th Edition, Chapter 16; or, Langman, 8 th Edition, pp. 345-365 OBJECTIVES:
Embryology Pamela E. Knapp, Ph.D. Dept. of Anatomy & Neurobiology DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHARYNGEAL (BRANCHIAL) ARCHES READING: Larsen, 4 th Edition, Chapter 16; or, Langman, 8 th Edition, pp. 345-365 OBJECTIVES:
Comparative Anatomy Biology 440 Fall semester
 Comparative Anatomy Biology 440 Fall semester TuTh 10:00 11:15 G23 Lab at 1:00 in 3106 or 3108 Comparative Anatomy Biology 440 Spring semester TuTh 11:30-12:45 G23 Lab at 2:00 in either 3108 or 3106 Dr.
Comparative Anatomy Biology 440 Fall semester TuTh 10:00 11:15 G23 Lab at 1:00 in 3106 or 3108 Comparative Anatomy Biology 440 Spring semester TuTh 11:30-12:45 G23 Lab at 2:00 in either 3108 or 3106 Dr.
Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002
 Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002 1) A variety of reagents and approaches are frequently used by developmental biologists to understand the tissue interactions and molecular signaling pathways
Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002 1) A variety of reagents and approaches are frequently used by developmental biologists to understand the tissue interactions and molecular signaling pathways
Sample paper 6. Question: 1. Which of the following pairing is incorrect?
 Sample paper 6 Question: 1 Which of the following pairing is incorrect? A. Mesosomes : infolding of bacterial cell wall B. Ribosomes : sites of protein synthesis C. Flagella : locomotory organ of bacteria
Sample paper 6 Question: 1 Which of the following pairing is incorrect? A. Mesosomes : infolding of bacterial cell wall B. Ribosomes : sites of protein synthesis C. Flagella : locomotory organ of bacteria
Maternal Control of GermLayer Formation in Xenopus
 Maternal Control of GermLayer Formation in Xenopus The zygotic genome is activated at the mid-blastula transition mid-blastula fertilized egg Xenopus gastrulae early-gastrula 7 hrs 10 hrs control not VP
Maternal Control of GermLayer Formation in Xenopus The zygotic genome is activated at the mid-blastula transition mid-blastula fertilized egg Xenopus gastrulae early-gastrula 7 hrs 10 hrs control not VP
Exam 4 ID#: July 7, 2008
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: July 7, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. RNA polymerase II is not able to transcribe RNA unless a. it is first bound to TFIIB. b. its
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: July 7, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. RNA polymerase II is not able to transcribe RNA unless a. it is first bound to TFIIB. b. its
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Lecture 2 - Making babies: Organ formation in the Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm and Neural Crest. Outline August 15, 2016 Eddy De Robertis, M.D., Ph.D.
 Lecture 2 - Making babies: Organ formation in the Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm and Neural Crest Lecture Objectives Outline August 15, 2016, M.D., Ph.D. - To examine how the main organ systems are formed
Lecture 2 - Making babies: Organ formation in the Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm and Neural Crest Lecture Objectives Outline August 15, 2016, M.D., Ph.D. - To examine how the main organ systems are formed
UNIVERSITY OF YORK BIOLOGY. Developmental Biology
 Examination Candidate Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Developmental Biology Desk Number: Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total
Examination Candidate Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Developmental Biology Desk Number: Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total
craniofacial development and WNT signaling. Shachi Bhatt
 MED23: a Mediator subunit's role in global gene transcription, regulation of craniofacial development and WNT signaling. BY 2013 Shachi Bhatt Submitted to the graduate degree program in Anatomy and Cell
MED23: a Mediator subunit's role in global gene transcription, regulation of craniofacial development and WNT signaling. BY 2013 Shachi Bhatt Submitted to the graduate degree program in Anatomy and Cell
Principles of Experimental Embryology
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology September 19, 2006 Major Research Questions How do forces outside the embryo affect its development? (Environmental Developmental
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology September 19, 2006 Major Research Questions How do forces outside the embryo affect its development? (Environmental Developmental
Gut Tube Development. For it s rare that a man thinks of anything so seriously as his dinner!
 For it s rare that a man thinks of anything so seriously as his dinner! Ben Johnson Gut Tube Development This chapter will follow the development of the embryonic gut caudal to the developing pharynx,
For it s rare that a man thinks of anything so seriously as his dinner! Ben Johnson Gut Tube Development This chapter will follow the development of the embryonic gut caudal to the developing pharynx,
Biology 7 Study Guide Exam #3
 Biology 7 Study Guide Exam #3 This is a list of general topics you should be prepared to answer questions on for each chapter. This guide is NOT what you should study but rather is a guide to help organize
Biology 7 Study Guide Exam #3 This is a list of general topics you should be prepared to answer questions on for each chapter. This guide is NOT what you should study but rather is a guide to help organize
Biology 218, practise Exam 2, 2011
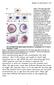 Figure 3 The long-range effect of Sqt does not depend on the induction of the endogenous cyc or sqt genes. a, Design and predictions for the experiments shown in b-e. b-e, Single-cell injection of 4 pg
Figure 3 The long-range effect of Sqt does not depend on the induction of the endogenous cyc or sqt genes. a, Design and predictions for the experiments shown in b-e. b-e, Single-cell injection of 4 pg
Neural development its all connected
 Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
1/30/2009. Copyright The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 CHAPTER 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal New Designs for Living Zoologists recognize 34 major phyla of living multicellular animals Survivors of around 100 phyla that appeared 600 million years ago
CHAPTER 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal New Designs for Living Zoologists recognize 34 major phyla of living multicellular animals Survivors of around 100 phyla that appeared 600 million years ago
Skeletal Development in Human
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Skeletal Development in Human Skeletal development in human - Long version I. Introduction I.1 Developmental genes in Drosophila I.2 Skeletal
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Skeletal Development in Human Skeletal development in human - Long version I. Introduction I.1 Developmental genes in Drosophila I.2 Skeletal
Chapter 9. Benefits of Being Large. Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity. Hierarchical Organization of Animal Complexity. Fig. 9.
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity Zoologists recognize
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity Zoologists recognize
Mesoderm induction: from caps to chips
 Mesoderm induction: from caps to chips David Kimelman Abstract Vertebrate mesoderm induction is one of the classical problems in developmental biology. Various developmental biology approaches, particularly
Mesoderm induction: from caps to chips David Kimelman Abstract Vertebrate mesoderm induction is one of the classical problems in developmental biology. Various developmental biology approaches, particularly
Mechanisms of Human Health and Disease. Developmental Biology
 Mechanisms of Human Health and Developmental Biology Joe Schultz joe.schultz@nationwidechildrens.org D6 1 Dev Bio: Mysteries How do fertilized eggs become adults? How do adults make more adults? Why and
Mechanisms of Human Health and Developmental Biology Joe Schultz joe.schultz@nationwidechildrens.org D6 1 Dev Bio: Mysteries How do fertilized eggs become adults? How do adults make more adults? Why and
Drosophila melanogaster- Morphogen Gradient
 NPTEL Biotechnology - Systems Biology Drosophila melanogaster- Morphogen Gradient Dr. M. Vijayalakshmi School of Chemical and Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by
NPTEL Biotechnology - Systems Biology Drosophila melanogaster- Morphogen Gradient Dr. M. Vijayalakshmi School of Chemical and Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 4 Dr. Stuart Sumida. Overview of Pre-Metazoan. and Protostome Development (Insects)
 Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 4 Dr. Stuart Sumida Overview of Pre-Metazoan and Protostome Development (Insects) Plants Fungi Animals In1998 fossilized animal embryos were reported from the
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 4 Dr. Stuart Sumida Overview of Pre-Metazoan and Protostome Development (Insects) Plants Fungi Animals In1998 fossilized animal embryos were reported from the
A systems approach to biology
 A systems approach to biology SB200 Lecture 7 7 October 2008 Jeremy Gunawardena jeremy@hms.harvard.edu Recap of Lecture 6 In phage lambda, cooperativity leads to bistability and hysteresis In HIV-1, sequestration
A systems approach to biology SB200 Lecture 7 7 October 2008 Jeremy Gunawardena jeremy@hms.harvard.edu Recap of Lecture 6 In phage lambda, cooperativity leads to bistability and hysteresis In HIV-1, sequestration
Lecture 3 - Molecular Regulation of Development. Growth factor signaling, Hox genes and the body plan
 Lecture 3 - Molecular Regulation of Development. Growth factor signaling, Hox genes and the body plan Lecture Objectives Outline August 18, 2015, M.D., Ph.D. To understand how cell differentiation and
Lecture 3 - Molecular Regulation of Development. Growth factor signaling, Hox genes and the body plan Lecture Objectives Outline August 18, 2015, M.D., Ph.D. To understand how cell differentiation and
What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics. I. Characteristics of Animals. Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen
 What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. Characteristics of Animals A. All animals are eukaryotic, multicellular, have ways of moving to reproduce, obtain
What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. Characteristics of Animals A. All animals are eukaryotic, multicellular, have ways of moving to reproduce, obtain
Limb Development Involving the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles
 Limb Development Involving the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles 1 Objectives Timing and location of limb bud development The tissues from which limb buds are made Determining the position
Limb Development Involving the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles 1 Objectives Timing and location of limb bud development The tissues from which limb buds are made Determining the position
