EE 505. Lecture 13. String DACs
|
|
|
- Aron Webb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EE 505 Lecture 13 Strig DACs
2 -Strig DAC V FF S 1 S 2 Simple structure Iheretly mootoe Very low DNL Challeges: S N-2 S N-1 S N S k d k Maagig INL Large umber of devices for large outig thermometer/bubble clocks Switch implemetatio Thevei impedace facig highly code depedet M k Coceptual
3 -Strig DAC V FF V FF /2 S 1 S 1 S 2 S 2 S N-2 S N-2 S N-1 S N-1 S N /2 S N Practical level shift
4 Switch Implemetatio Basic Switch Large umber required for large resolutio Simple structure ofte used φ sigle -chael device Good whe switch termials ear gd Will ot tur o whe termials ear V DD φ sigle p-chael device Good whe switch termials ear V DD Will ot tur o whe termials ear gd φ φ trasmissio gate switch Use devices where cross-over occurs Good for both high ad low term voltages Extra clock sigal required Try to avoid this complexity Other switch structures (such as bootstrapped switch) used but ot for basic strig DACs
5 Switch Assigmet V FF Challeges: S 1 p-chael regio S 2 S N-2 S N-1 -chael regio S N
6 Switch Impedaces SW V G =V DD SWp V G =0V SW_mi SWp_mi V Term V Term V DD V DD -V TH -V THp V DD φ φ
7 Switch Impedaces φ φ SWTG SWTG V Gp =0V,V G =V DD V Gp =0V,V G =V DD Crossover Crossover V Term V Term -V THp V DD -V TH V DD V DD -V THp V DD -V TH SWTG Switch impedace sigificatly both positio ad device size depedet Crossover V Gp =0V,V G =V DD V Term -V THp VDD -V TH V DD
8 Switch Parasitics S G D C GSOL C GDOL φ C BS C GB whe off C GC whe o C BD S G D φ C BS C GSOL C GB whe off C GC whe o C BD C GDOL C WELLSSUB C BD ad C BS ca be sigificat ad cause rise-fall times to be positio depedet C GDOL ca cause kickback or feed-forward C GS ca slow tur-o ad tur-off time of switch
9 -Strig DAC V FF Challeges: S 1 S 2 S N-2 S N-1 S N Maagig INL Large umber of devices for large outig thermometer/bubble clocks(2 or 2 +1 lies) Capacitace o ca be large larger for p-chael devices eve larger for TG switches Switch impedaces positio depedet Kickback from switches to -strig Capacitace o each ode (though small) of - strig from switch Thevei impedace facig highly code depedet
10 -Strig DAC V FF 2 S 1 Biary to Thermometer Decoder S 2 Challeges S N-2 S N-1 S N May output sigals to route Delay i Decoder may be sigificat Delay i Decoder may be previous code ad curret code depedet Itermediate udesired Boolea outputs may occur o o o These may cause udesired opeig ad closig of switches Could mometarily short out taps o -strig Could itroduce trasiets o all odes of -strig that are code ad previous code depedet
11 -Strig DAC V FF M 1 d 1 d 2 2 Biary to Thermometer Decoder M 2 d N-2 M N-2 d N-1 C L M N-1 d N M N Capacitive loadig due to switches
12 -Strig DAC V EF Decoder b 3 b 3 b 2 b 2 b 1 b 1 Uses matrix decoder as aalog MUX Implemets biary to decimal coversio with pass trasistor aalog logic Very structured layout Itercoectio poits are switches (combiatio of -chael ad p-chael) -Strig Challeges Tree Decoder Still may sigals to route Large capacitace o (over 2 +1 diff caps) Multiple previous code depedecies cause output trasitio time to be quite upredictable Cosiderable trasiets itroduced o -strig
13 -Strig DAC V EF Decoder b 3 b 3 b 2 b 2 b 1 b 1 -Strig Tree Decoder Parasitic Capacitaces i Tree Decoder
14 -Strig DAC V EF Decoder Example: < > b 3 b 3 b 2 b 2 b 1 b 1 -Strig V 3 Tree Decoder Previous-Code Depedet Settlig Assume all C s iitially with 0V ed deotes V, black deotes 0V, Purple some other voltage
15 Previous-Code Depedet Settlig Assume all C s iitially with 0V ed deotes V, gree deotes V, black deotes 0V, Purple some other vo V EF -Strig DAC Trasitio from <010> to <101> Example: < > Decoder b 3 b 3 b 2 b 2 b 1 b 1 V 6 -Strig V 3 Tree Decoder
16 Trasitio from <010> to <101> V EF -Strig DAC Decoder b 3 b 3 b 2 b 2 b 1 b 1 White boxes show capacitors depede upo previous code <010> Example: < > V 6 -Strig V 3 Tree Decoder Previous-Code Depedet Settlig Assume all C s iitially with 0V ed deotes V 3, gree deotes V 6, black deotes 0V, Purple some other voltage
17 -Strig DAC V EF Decoder b 3 b 3 b 2 b 2 b 1 b 1 Uses tree decoder as aalog MUX Implemets biary to decimal coversio with pass trasistor aalog logic Very structured layout Itercoectio poits are switches (combiatio of -chael ad p-chael) Dramatically reduces capacitace o output ad switchig capacitaces -Strig Challeges Still may sigals to route Multiple previous code depedecies cause output trasitio time to be quite upredictable Tree Decoder
18 -Strig DAC V DD Decoder b 3 b 3 b 2 b 2 b 1 b 1 Tree Decoder Tree-Decoder i Digital Domai Sigle trasistor used at each marked itersectio to for PTL AND gates Do the resistors that form part of PTL dissipate ay substatial power? No because oly oe will be coductig for ay DAC output
19 -Strig DAC Strig DAC with ow-colum Decoder V EF F F F F F Colum Decoder F F F F F F F 2 = 1:2 1 Dramatic reductio i decoder complexity Dramatic reductio of capacitive loadig o output Chages decoder from a oedimesioal to a two-dimesioal solutio (ca be thought of as foldig) Logic gates could be placed at each ode to elimiate aalog row decoder F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F ow Decoder Challeges (most were preset i earlier structures too) Some previous code depedece INL large Difficult to cacel gradiet effects i layout Switchig sequecig ca help a lot Switch impedaces code depedet Settlig times code depedet
20 -Strig DAC V EF F F F F F Colum Decoder F F F F F F F 2 = 1:2 1 Ca this cocept be exteded further? Dramatic reductio i decoder complexity Dramatic reductio of capacitive loadig o output Chages decoder from a oedimesioal to a m-dimesioal solutio (foldig) Logic gates could be placed at each ode to elimiate aalog row decoder F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F ow Decoder F F F F
21 -Strig DAC What about this parallel -strig? V FF S 1 Added two resistors tapped at middle of origial -strig 1 S 2 1 S N-2 S N-1 S N
22 -Strig DAC What about this parallel -strig? V FF Added six resistors tapped at middle of origial -strig 1 S 1 2 S S N-2 S N-1 1 S N
23 -Strig DAC V EF MSB ow Decoder 2 1 LSB Aalog MUX 2 2
24 -Strig DAC V EF = 1:2 1 2 F F F F C F F F F F F F F C F F F F F F F F C F F F F F F F F Colum Decoder ow Decoder C F F F F Note Dual Ladder is used!
25 Cited by 51 (4/5/10) Cited by 94 (4/6/14) Cited by 109 (4/5/16)
26 Pelgrom Paper Assessmet
27 Pelgrom Paper Assessmet
28 Pelgrom Paper Assessmet
29 Pelgrom Paper Assessmet
30 Pelgrom Paper Assessmet
31 Pelgrom Paper Assessmet
32 Pelgrom Paper Assessmet
33 Pelgrom Paper Assessmet
34 Ed of Lecture 13
EE 505. Lecture 28. ADC Design SAR
 EE 505 Lecture 28 ADC Desig SAR Review from Last Lecture Elimiatio of Iput S/H C LK X IN S/H Stage 1 r 1 Stage 2 r 2 Stage k r k Stage m r m 1 2 k m Pipelied Assembler (Shift Register
EE 505 Lecture 28 ADC Desig SAR Review from Last Lecture Elimiatio of Iput S/H C LK X IN S/H Stage 1 r 1 Stage 2 r 2 Stage k r k Stage m r m 1 2 k m Pipelied Assembler (Shift Register
EE 435. Lecture 25. Data Converters. Architectures. Characterization
 EE 435 Lecture 5 Data Coverters Architectures Characterizatio . eview from last lecture. Data Coverters Types: A/D (Aalog to Digital) Coverts Aalog Iput to a Digital Output D/A (Digital to Aalog) Coverts
EE 435 Lecture 5 Data Coverters Architectures Characterizatio . eview from last lecture. Data Coverters Types: A/D (Aalog to Digital) Coverts Aalog Iput to a Digital Output D/A (Digital to Aalog) Coverts
EE 505. Lecture 29. ADC Design. Oversampled
 EE 505 Lecture 29 ADC Desig Oversampled Review from Last Lecture SAR ADC V IN Sample Hold C LK V REF DAC DAC Cotroller DAC Cotroller stores estimates of iput i Successive Approximatio Register (SAR) At
EE 505 Lecture 29 ADC Desig Oversampled Review from Last Lecture SAR ADC V IN Sample Hold C LK V REF DAC DAC Cotroller DAC Cotroller stores estimates of iput i Successive Approximatio Register (SAR) At
EE260: Digital Design, Spring n MUX Gate n Rudimentary functions n Binary Decoders. n Binary Encoders n Priority Encoders
 EE260: Digital Desig, Sprig 2018 EE 260: Itroductio to Digital Desig MUXs, Ecoders, Decoders Yao Zheg Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Hawaiʻi at Māoa Overview of Ecoder ad Decoder MUX Gate
EE260: Digital Desig, Sprig 2018 EE 260: Itroductio to Digital Desig MUXs, Ecoders, Decoders Yao Zheg Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Hawaiʻi at Māoa Overview of Ecoder ad Decoder MUX Gate
EE 435. Lecture 37. Parasitic Capacitances in MOS Devices. String DAC Parasitic Capacitances
 EE 435 Lecture 37 Parasitic Capacitances in MOS Devices String DAC Parasitic Capacitances Parasitic Capacitors in MOSFET (will initially consider two) Parasitic Capacitors in MOSFET C GCH Parasitic Capacitors
EE 435 Lecture 37 Parasitic Capacitances in MOS Devices String DAC Parasitic Capacitances Parasitic Capacitors in MOSFET (will initially consider two) Parasitic Capacitors in MOSFET C GCH Parasitic Capacitors
EE 435. Lecture 38. DAC Design Current Steering DACs Charge Redistribution DACs ADC Design
 EE 435 Lecture 38 DAC Design Current Steering DACs Charge edistribution DACs ADC Design eview from last lecture Current Steering DACs X N Binary to Thermometer ndecoder (all ON) S S N- S N V EF F nherently
EE 435 Lecture 38 DAC Design Current Steering DACs Charge edistribution DACs ADC Design eview from last lecture Current Steering DACs X N Binary to Thermometer ndecoder (all ON) S S N- S N V EF F nherently
EE 505. Lecture 14. Offset Voltages DAC Design
 EE 505 Lecture 14 Offset Voltages DAC Desig Review from previous lecture: Cosider First Offset i Operatioal Amplifiers Iput-referred Offset Voltage: Differetial Voltage that must be applied to the iput
EE 505 Lecture 14 Offset Voltages DAC Desig Review from previous lecture: Cosider First Offset i Operatioal Amplifiers Iput-referred Offset Voltage: Differetial Voltage that must be applied to the iput
EE247 Lecture 16. Serial Charge Redistribution DAC
 EE47 Lecture 16 D/A Converters D/A examples Serial charge redistribution DAC Practical aspects of current-switch DACs Segmented current-switch DACs DAC self calibration techniques Current copiers Dynamic
EE47 Lecture 16 D/A Converters D/A examples Serial charge redistribution DAC Practical aspects of current-switch DACs Segmented current-switch DACs DAC self calibration techniques Current copiers Dynamic
EE 505 Lecture 9. Statistical Circuit Modeling
 EE 505 Lecture 9 Statistical Circuit Modelig eview from previous lecture: Statistical Aalysis Strategy Will first focus o statistical characterizatio of resistors, the exted to capacitors ad trasistors
EE 505 Lecture 9 Statistical Circuit Modelig eview from previous lecture: Statistical Aalysis Strategy Will first focus o statistical characterizatio of resistors, the exted to capacitors ad trasistors
Annotations to the assignments and the solution sheet. Note the following points
 WS 26/7 Trial Exam: Fudametals of Computer Egieerig Seite: Aotatios to the assigmets ad the solutio sheet This is a multiple choice examiatio, that meas: Solutio approaches are ot assessed. For each sub-task
WS 26/7 Trial Exam: Fudametals of Computer Egieerig Seite: Aotatios to the assigmets ad the solutio sheet This is a multiple choice examiatio, that meas: Solutio approaches are ot assessed. For each sub-task
Nyquist-Rate D/A Converters. D/A Converter Basics.
 Nyquist-Rate D/A Converters David Johns and Ken Martin (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) slide 1 of 20 D/A Converter Basics. B in D/A is a digital signal (or word), B in b i B in = 2 1
Nyquist-Rate D/A Converters David Johns and Ken Martin (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) slide 1 of 20 D/A Converter Basics. B in D/A is a digital signal (or word), B in b i B in = 2 1
CMOS. Dynamic Logic Circuits. Chapter 9. Digital Integrated Circuits Analysis and Design
 MOS Digital Itegrated ircuits Aalysis ad Desig hapter 9 Dyamic Logic ircuits 1 Itroductio Static logic circuit Output correspodig to the iput voltage after a certai time delay Preservig its output level
MOS Digital Itegrated ircuits Aalysis ad Desig hapter 9 Dyamic Logic ircuits 1 Itroductio Static logic circuit Output correspodig to the iput voltage after a certai time delay Preservig its output level
EE 435. Lecture 25. Data Converters
 EE 435 Lecture 5 Data Coverters . Review from last lecture. Basic Operatio of CMFB Block V DD V FB V O1 V O CMFB Circuit V FB V OUT C L M 3 M 4 V OUT V IN M 1 M V IN C L V OXX CMFB Circuit V B M 9 V OXX
EE 435 Lecture 5 Data Coverters . Review from last lecture. Basic Operatio of CMFB Block V DD V FB V O1 V O CMFB Circuit V FB V OUT C L M 3 M 4 V OUT V IN M 1 M V IN C L V OXX CMFB Circuit V B M 9 V OXX
EE260: Digital Design, Spring n Binary Addition. n Complement forms. n Subtraction. n Multiplication. n Inputs: A 0, B 0. n Boolean equations:
 EE260: Digital Desig, Sprig 2018 EE 260: Itroductio to Digital Desig Arithmetic Biary Additio Complemet forms Subtractio Multiplicatio Overview Yao Zheg Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Hawaiʻi
EE260: Digital Desig, Sprig 2018 EE 260: Itroductio to Digital Desig Arithmetic Biary Additio Complemet forms Subtractio Multiplicatio Overview Yao Zheg Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Hawaiʻi
EE 435. Lecture 36. Quantization Noise ENOB Absolute and Relative Accuracy DAC Design. The String DAC
 EE 435 Lecture 36 Quantization Noise ENOB Absolute and elative Accuracy DAC Design The String DAC . eview from last lecture. Quantization Noise in ADC ecall: If the random variable f is uniformly distributed
EE 435 Lecture 36 Quantization Noise ENOB Absolute and elative Accuracy DAC Design The String DAC . eview from last lecture. Quantization Noise in ADC ecall: If the random variable f is uniformly distributed
A novel Capacitor Array based Digital to Analog Converter
 Chapter 4 A novel Capacitor Array based Digital to Analog Converter We present a novel capacitor array digital to analog converter(dac architecture. This DAC architecture replaces the large MSB (Most Significant
Chapter 4 A novel Capacitor Array based Digital to Analog Converter We present a novel capacitor array digital to analog converter(dac architecture. This DAC architecture replaces the large MSB (Most Significant
PARALLEL DIGITAL-ANALOG CONVERTERS
 CMOS Analog IC Design Page 10.2-1 10.2 - PARALLEL DIGITAL-ANALOG CONVERTERS CLASSIFICATION OF DIGITAL-ANALOG CONVERTERS CMOS Analog IC Design Page 10.2-2 CURRENT SCALING DIGITAL-ANALOG CONVERTERS GENERAL
CMOS Analog IC Design Page 10.2-1 10.2 - PARALLEL DIGITAL-ANALOG CONVERTERS CLASSIFICATION OF DIGITAL-ANALOG CONVERTERS CMOS Analog IC Design Page 10.2-2 CURRENT SCALING DIGITAL-ANALOG CONVERTERS GENERAL
Chapter 9 Computer Design Basics
 Logic ad Computer Desig Fudametals Chapter 9 Computer Desig Basics Part 1 Datapaths Overview Part 1 Datapaths Itroductio Datapath Example Arithmetic Logic Uit (ALU) Shifter Datapath Represetatio Cotrol
Logic ad Computer Desig Fudametals Chapter 9 Computer Desig Basics Part 1 Datapaths Overview Part 1 Datapaths Itroductio Datapath Example Arithmetic Logic Uit (ALU) Shifter Datapath Represetatio Cotrol
DESCRIPTION OF THE SYSTEM
 Sychroous-Serial Iterface for absolute Ecoders SSI 1060 BE 10 / 01 DESCRIPTION OF THE SYSTEM TWK-ELEKTRONIK GmbH D-001 Düsseldorf PB 1006 Heirichstr. Tel +9/11/6067 Fax +9/11/6770 e-mail: ifo@twk.de Page
Sychroous-Serial Iterface for absolute Ecoders SSI 1060 BE 10 / 01 DESCRIPTION OF THE SYSTEM TWK-ELEKTRONIK GmbH D-001 Düsseldorf PB 1006 Heirichstr. Tel +9/11/6067 Fax +9/11/6770 e-mail: ifo@twk.de Page
6.111 Lecture 6 Today: 1.Blocking vs. non-blocking assignments 2.Single clock synchronous circuits 3.Finite State Machines
 6. Lecture 6 Today:.Blockig vs. o-blockig assigmets 2.Sigle clock sychroous circuits 3.Fiite State Machies 6. Fall 25 Lecture 6, Slide I. Blockig vs. Noblockig Assigmets Coceptual eed for two kids of assigmet
6. Lecture 6 Today:.Blockig vs. o-blockig assigmets 2.Sigle clock sychroous circuits 3.Fiite State Machies 6. Fall 25 Lecture 6, Slide I. Blockig vs. Noblockig Assigmets Coceptual eed for two kids of assigmet
The Scattering Matrix
 2/23/7 The Scatterig Matrix 723 1/13 The Scatterig Matrix At low frequecies, we ca completely characterize a liear device or etwork usig a impedace matrix, which relates the currets ad voltages at each
2/23/7 The Scatterig Matrix 723 1/13 The Scatterig Matrix At low frequecies, we ca completely characterize a liear device or etwork usig a impedace matrix, which relates the currets ad voltages at each
EEC 118 Lecture #4: CMOS Inverters. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 118 Lecture #4: CMOS Iverters ajeeva Amirtharajah Uiversity of Califoria, Davis Jeff Parhurst Itel Cororatio Outlie eview: Iverter Trasfer Characteristics Lecture 3: Noise Margis, ise & Fall Times,
EEC 118 Lecture #4: CMOS Iverters ajeeva Amirtharajah Uiversity of Califoria, Davis Jeff Parhurst Itel Cororatio Outlie eview: Iverter Trasfer Characteristics Lecture 3: Noise Margis, ise & Fall Times,
Parasitic Resistance L R W. Polysilicon gate. Drain. contact L D. V GS,eff R S R D. Drain
 Parasitic Resistace G Polysilico gate rai cotact V GS,eff S R S R S, R S, R + R C rai Short Chael Effects Chael-egth Modulatio Equatio k ( V V ) GS T suggests that the trasistor i the saturatio mode acts
Parasitic Resistace G Polysilico gate rai cotact V GS,eff S R S R S, R S, R + R C rai Short Chael Effects Chael-egth Modulatio Equatio k ( V V ) GS T suggests that the trasistor i the saturatio mode acts
Chapter 9 - CD companion 1. A Generic Implementation; The Common-Merge Amplifier. 1 τ is. ω ch. τ io
 Chapter 9 - CD compaio CHAPTER NINE CD-9.2 CD-9.2. Stages With Voltage ad Curret Gai A Geeric Implemetatio; The Commo-Merge Amplifier The advaced method preseted i the text for approximatig cutoff frequecies
Chapter 9 - CD compaio CHAPTER NINE CD-9.2 CD-9.2. Stages With Voltage ad Curret Gai A Geeric Implemetatio; The Commo-Merge Amplifier The advaced method preseted i the text for approximatig cutoff frequecies
Module 5 EMBEDDED WAVELET CODING. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 5 EMBEDDED WAVELET CODING Versio ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesso 4 SPIHT algorithm Versio ECE IIT, Kharagpur Istructioal Objectives At the ed of this lesso, the studets should be able to:. State the limitatios
Module 5 EMBEDDED WAVELET CODING Versio ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesso 4 SPIHT algorithm Versio ECE IIT, Kharagpur Istructioal Objectives At the ed of this lesso, the studets should be able to:. State the limitatios
Digital to Analog Converters I
 Advanced Analog Building Blocks 2 Digital to Analog Converters I Albert Comerma (PI) (comerma@physi.uni-heidelberg.de) Course web WiSe 2017 DAC parameters DACs parameters DACs non ideal effects DACs performance
Advanced Analog Building Blocks 2 Digital to Analog Converters I Albert Comerma (PI) (comerma@physi.uni-heidelberg.de) Course web WiSe 2017 DAC parameters DACs parameters DACs non ideal effects DACs performance
EXTENDING THE RESOLUTION OF PARALLEL DIGITAL-ANALOG CONVERTERS
 CMOS Analog IC Design Page 10.3-1 10.3 - EXTENDING THE RESOLUTION OF PARALLEL DIGITAL-ANALOG CONVERTERS TECHNIQUE: Divide the total resolution N into k smaller sub-dacs each with a resolution of N k. Result:
CMOS Analog IC Design Page 10.3-1 10.3 - EXTENDING THE RESOLUTION OF PARALLEL DIGITAL-ANALOG CONVERTERS TECHNIQUE: Divide the total resolution N into k smaller sub-dacs each with a resolution of N k. Result:
EE C245 - ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design Fall Today s Lecture
 EE C45 ME C8 Itroductio to MEMS Desig Fall 003 Roger Howe ad Thara Sriiasa Lecture 3 Capacitie Positio Sesig: Electroic ad Mechaical Noise EE C45 ME C8 Fall 003 Lecture 3 Today s Lecture Basic CMOS buffer
EE C45 ME C8 Itroductio to MEMS Desig Fall 003 Roger Howe ad Thara Sriiasa Lecture 3 Capacitie Positio Sesig: Electroic ad Mechaical Noise EE C45 ME C8 Fall 003 Lecture 3 Today s Lecture Basic CMOS buffer
FIR Filter Design: Part II
 EEL335: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems. Itroductio I this set of otes, we cosider how we might go about desigig FIR filters with arbitrary frequecy resposes, through compositio of multiple sigle-peak
EEL335: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems. Itroductio I this set of otes, we cosider how we might go about desigig FIR filters with arbitrary frequecy resposes, through compositio of multiple sigle-peak
Optimal area and impedance allocation for maximizing yield and enhancing performance in dual string DACs
 Graduate Theses ad Dissertatios Graduate College 009 Optimal area ad impedace allocatio for maximizig yield ad ehacig performace i dual strig DACs Thu Thi Ah Duog Iowa State Uiversity Follow this ad additioal
Graduate Theses ad Dissertatios Graduate College 009 Optimal area ad impedace allocatio for maximizig yield ad ehacig performace i dual strig DACs Thu Thi Ah Duog Iowa State Uiversity Follow this ad additioal
Linearly Independent Sets, Bases. Review. Remarks. A set of vectors,,, in a vector space is said to be linearly independent if the vector equation
 Liearly Idepedet Sets Bases p p c c p Review { v v vp} A set of vectors i a vector space is said to be liearly idepedet if the vector equatio cv + c v + + c has oly the trivial solutio = = { v v vp} The
Liearly Idepedet Sets Bases p p c c p Review { v v vp} A set of vectors i a vector space is said to be liearly idepedet if the vector equatio cv + c v + + c has oly the trivial solutio = = { v v vp} The
Data Converters. Nyquist-rate D/A Converters. Overview. Introduction (II) Introduction
 Data Coverters Overview Nyquist-rate D/A Coverters Pietro Adreai Dept. of Electrical ad Iformatio Techology ud Uiversity, Swede Itroductio Type of coverters Architectures based o resistors Architectures
Data Coverters Overview Nyquist-rate D/A Coverters Pietro Adreai Dept. of Electrical ad Iformatio Techology ud Uiversity, Swede Itroductio Type of coverters Architectures based o resistors Architectures
Data Converters. Nyquist-rate D/A Converters. Overview. Introduction I. DAC applications
 Data Coverters Overview Nyquist-rate D/A Coverters Pietro Adreai Dept. of Electrical ad Iformatio Techology ud Uiversity, Swede Itroductio Type of coverters Architectures based o resistors Architectures
Data Coverters Overview Nyquist-rate D/A Coverters Pietro Adreai Dept. of Electrical ad Iformatio Techology ud Uiversity, Swede Itroductio Type of coverters Architectures based o resistors Architectures
ELE B7 Power Systems Engineering. Symmetrical Components
 ELE B7 Power Systems Egieerig Symmetrical Compoets Aalysis of Ubalaced Systems Except for the balaced three-phase fault, faults result i a ubalaced system. The most commo types of faults are sigle liegroud
ELE B7 Power Systems Egieerig Symmetrical Compoets Aalysis of Ubalaced Systems Except for the balaced three-phase fault, faults result i a ubalaced system. The most commo types of faults are sigle liegroud
Time-Domain Representations of LTI Systems
 2.1 Itroductio Objectives: 1. Impulse resposes of LTI systems 2. Liear costat-coefficiets differetial or differece equatios of LTI systems 3. Bloc diagram represetatios of LTI systems 4. State-variable
2.1 Itroductio Objectives: 1. Impulse resposes of LTI systems 2. Liear costat-coefficiets differetial or differece equatios of LTI systems 3. Bloc diagram represetatios of LTI systems 4. State-variable
Calculation of Inrush Current During Capacitor Bank Energization
 Protectio of lectrical Networks hristophe Preve opyright 0 006, IST td. Appedix B alculatio of Irush urret Durig apacitor Bak ergizatio Fixed bak The equivalet stream etwork sigle-phase diagram durig eergizatio
Protectio of lectrical Networks hristophe Preve opyright 0 006, IST td. Appedix B alculatio of Irush urret Durig apacitor Bak ergizatio Fixed bak The equivalet stream etwork sigle-phase diagram durig eergizatio
EE692 Applied EM- FDTD Method One-Dimensional Transmission Lines Notes- Lecture 4
 ee692_fdtd_d_tras_lie_lecture4.doc Page of 6 EE692 Applied EM FDTD Method OeDimesioal Trasmissio ies Notes ecture 4 FDTD Modelig of Voltage ources ad Termiatios with Parallel/eries R oads As the fial step
ee692_fdtd_d_tras_lie_lecture4.doc Page of 6 EE692 Applied EM FDTD Method OeDimesioal Trasmissio ies Notes ecture 4 FDTD Modelig of Voltage ources ad Termiatios with Parallel/eries R oads As the fial step
Fig. 1 CMOS Transistor Circuits (a) Inverter Out = NOT In, (b) NOR-gate C = NOT (A or B)
 1 Introduction to Transistor-Level Logic Circuits 1 By Prawat Nagvajara At the transistor level of logic circuits, transistors operate as switches with the logic variables controlling the open or closed
1 Introduction to Transistor-Level Logic Circuits 1 By Prawat Nagvajara At the transistor level of logic circuits, transistors operate as switches with the logic variables controlling the open or closed
CS276A Practice Problem Set 1 Solutions
 CS76A Practice Problem Set Solutios Problem. (i) (ii) 8 (iii) 6 Compute the gamma-codes for the followig itegers: (i) (ii) 8 (iii) 6 Problem. For this problem, we will be dealig with a collectio of millio
CS76A Practice Problem Set Solutios Problem. (i) (ii) 8 (iii) 6 Compute the gamma-codes for the followig itegers: (i) (ii) 8 (iii) 6 Problem. For this problem, we will be dealig with a collectio of millio
ENGI 9420 Engineering Analysis Assignment 3 Solutions
 ENGI 9 Egieerig Aalysis Assigmet Solutios Fall [Series solutio of ODEs, matri algebra; umerical methods; Chapters, ad ]. Fid a power series solutio about =, as far as the term i 7, to the ordiary differetial
ENGI 9 Egieerig Aalysis Assigmet Solutios Fall [Series solutio of ODEs, matri algebra; umerical methods; Chapters, ad ]. Fid a power series solutio about =, as far as the term i 7, to the ordiary differetial
Announcements, Nov. 19 th
 Aoucemets, Nov. 9 th Lecture PRS Quiz topic: results Chemical through Kietics July 9 are posted o the course website. Chec agaist Kietics LabChec agaist Kietics Lab O Fial Exam, NOT 3 Review Exam 3 ad
Aoucemets, Nov. 9 th Lecture PRS Quiz topic: results Chemical through Kietics July 9 are posted o the course website. Chec agaist Kietics LabChec agaist Kietics Lab O Fial Exam, NOT 3 Review Exam 3 ad
Run-length & Entropy Coding. Redundancy Removal. Sampling. Quantization. Perform inverse operations at the receiver EEE
 Geeral e Image Coder Structure Motio Video (s 1,s 2,t) or (s 1,s 2 ) Natural Image Samplig A form of data compressio; usually lossless, but ca be lossy Redudacy Removal Lossless compressio: predictive
Geeral e Image Coder Structure Motio Video (s 1,s 2,t) or (s 1,s 2 ) Natural Image Samplig A form of data compressio; usually lossless, but ca be lossy Redudacy Removal Lossless compressio: predictive
Unit 5 - Week 4. Week 4: Assignment. Course outline. Announcements Course Forum Progress Mentor
 14/12/2017 Electrical Machies - I - - Uit 5 - Week 4 X reviewer2@ptel.iitm.ac.i Courses» Electrical Machies - I Aoucemets Course Forum Progress Metor Uit 5 - Week 4 Course outlie How to access the portal
14/12/2017 Electrical Machies - I - - Uit 5 - Week 4 X reviewer2@ptel.iitm.ac.i Courses» Electrical Machies - I Aoucemets Course Forum Progress Metor Uit 5 - Week 4 Course outlie How to access the portal
USA Mathematical Talent Search Round 3 Solutions Year 27 Academic Year
 /3/27. Fill i each space of the grid with either a or a so that all sixtee strigs of four cosecutive umbers across ad dow are distict. You do ot eed to prove that your aswer is the oly oe possible; you
/3/27. Fill i each space of the grid with either a or a so that all sixtee strigs of four cosecutive umbers across ad dow are distict. You do ot eed to prove that your aswer is the oly oe possible; you
ln(i G ) 26.1 Review 26.2 Statistics of multiple breakdowns M Rows HBD SBD N Atoms Time
 EE650R: Reliability Physics of Naoelectroic Devices Lecture 26: TDDB: Statistics of Multiple Breadows Date: Nov 17, 2006 ClassNotes: Jaydeep P. Kulari Review: Pradeep R. Nair 26.1 Review I the last class
EE650R: Reliability Physics of Naoelectroic Devices Lecture 26: TDDB: Statistics of Multiple Breadows Date: Nov 17, 2006 ClassNotes: Jaydeep P. Kulari Review: Pradeep R. Nair 26.1 Review I the last class
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF ALIFORNIA, BERELEY ollege of Egieerig Deartmet of Electrical Egieerig ad omuter Scieces Ja M. Rabaey Homework #5 EES 4 SP0) [PROBLEM Elmore Delay 30ts) Due Friday, March 5, 5m, box i 40 ory
UNIVERSITY OF ALIFORNIA, BERELEY ollege of Egieerig Deartmet of Electrical Egieerig ad omuter Scieces Ja M. Rabaey Homework #5 EES 4 SP0) [PROBLEM Elmore Delay 30ts) Due Friday, March 5, 5m, box i 40 ory
(3) If you replace row i of A by its sum with a multiple of another row, then the determinant is unchanged! Expand across the i th row:
 Math 50-004 Tue Feb 4 Cotiue with sectio 36 Determiats The effective way to compute determiats for larger-sized matrices without lots of zeroes is to ot use the defiitio, but rather to use the followig
Math 50-004 Tue Feb 4 Cotiue with sectio 36 Determiats The effective way to compute determiats for larger-sized matrices without lots of zeroes is to ot use the defiitio, but rather to use the followig
2.CMOS Transistor Theory
 CMOS LSI esig.cmos rasistor heory Fu yuzhuo School of microelectroics,sju Itroductio omar fadhil,baghdad outlie PN juctio priciple CMOS trasistor itroductio Ideal I- characteristics uder static coditios
CMOS LSI esig.cmos rasistor heory Fu yuzhuo School of microelectroics,sju Itroductio omar fadhil,baghdad outlie PN juctio priciple CMOS trasistor itroductio Ideal I- characteristics uder static coditios
SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES
 SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES Read Sectio 1.5 (pages 5 9) Overview I Sectio 1.5 we lear to work with summatio otatio ad formulas. We will also itroduce a brief overview of sequeces,
SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES Read Sectio 1.5 (pages 5 9) Overview I Sectio 1.5 we lear to work with summatio otatio ad formulas. We will also itroduce a brief overview of sequeces,
Definitions and Theorems. where x are the decision variables. c, b, and a are constant coefficients.
 Defiitios ad Theorems Remember the scalar form of the liear programmig problem, Miimize, Subject to, f(x) = c i x i a 1i x i = b 1 a mi x i = b m x i 0 i = 1,2,, where x are the decisio variables. c, b,
Defiitios ad Theorems Remember the scalar form of the liear programmig problem, Miimize, Subject to, f(x) = c i x i a 1i x i = b 1 a mi x i = b m x i 0 i = 1,2,, where x are the decisio variables. c, b,
Lecture 9: Diffusion, Electrostatics review, and Capacitors. Context
 EECS 5 Sprig 4, Lecture 9 Lecture 9: Diffusio, Electrostatics review, ad Capacitors EECS 5 Sprig 4, Lecture 9 Cotext I the last lecture, we looked at the carriers i a eutral semicoductor, ad drift currets
EECS 5 Sprig 4, Lecture 9 Lecture 9: Diffusio, Electrostatics review, ad Capacitors EECS 5 Sprig 4, Lecture 9 Cotext I the last lecture, we looked at the carriers i a eutral semicoductor, ad drift currets
Data Converters. Nyquist-rate D/A Converters. Overview. Introduction I. DAC applications
 Data Coverters Overview Nyquist-rate D/ Coverters Pietro dreai Dept. of Electrical ad Iformatio Techology ud Uiversity, Swede Itroductio Type of coverters rchitectures based o resistors rchitectures based
Data Coverters Overview Nyquist-rate D/ Coverters Pietro dreai Dept. of Electrical ad Iformatio Techology ud Uiversity, Swede Itroductio Type of coverters rchitectures based o resistors rchitectures based
Filter banks. Separately, the lowpass and highpass filters are not invertible. removes the highest frequency 1/ 2and
 Filter bas Separately, the lowpass ad highpass filters are ot ivertible T removes the highest frequecy / ad removes the lowest frequecy Together these filters separate the sigal ito low-frequecy ad high-frequecy
Filter bas Separately, the lowpass ad highpass filters are ot ivertible T removes the highest frequecy / ad removes the lowest frequecy Together these filters separate the sigal ito low-frequecy ad high-frequecy
6.1 Analysis of frequency selective surfaces
 6.1 Aalysis of frequecy selective surfaces Basic theory I this paragraph, reflectio coefficiet ad trasmissio coefficiet are computed for a ifiite periodic frequecy selective surface. The attetio is tured
6.1 Aalysis of frequecy selective surfaces Basic theory I this paragraph, reflectio coefficiet ad trasmissio coefficiet are computed for a ifiite periodic frequecy selective surface. The attetio is tured
Introduction to Signals and Systems, Part V: Lecture Summary
 EEL33: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems Itroductio to Sigals ad Systems, Part V: Lecture Summary Itroductio to Sigals ad Systems, Part V: Lecture Summary So far we have oly looked at examples of o-recursive
EEL33: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems Itroductio to Sigals ad Systems, Part V: Lecture Summary Itroductio to Sigals ad Systems, Part V: Lecture Summary So far we have oly looked at examples of o-recursive
Bipolar Junction Transistors
 ipolar Juctio Trasistors ipolar juctio trasistor (JT) was iveted i 948 at ell Telephoe Laboratories Sice 97, the high desity ad low power advatage of the MOS techology steadily eroded the JT s early domiace.
ipolar Juctio Trasistors ipolar juctio trasistor (JT) was iveted i 948 at ell Telephoe Laboratories Sice 97, the high desity ad low power advatage of the MOS techology steadily eroded the JT s early domiace.
EE 230 Lecture 31. THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR
 EE 23 Lecture 3 THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR Quiz 3 Determine I X. Assume W=u, L=2u, V T =V, uc OX = - 4 A/V 2, λ= And the number is? 3 8 5 2? 6 4 9 7 Quiz 3
EE 23 Lecture 3 THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR Quiz 3 Determine I X. Assume W=u, L=2u, V T =V, uc OX = - 4 A/V 2, λ= And the number is? 3 8 5 2? 6 4 9 7 Quiz 3
Lecture 7 Circuit Delay, Area and Power
 Lecture 7 Circuit Delay, Area and Power lecture notes from S. Mitra Intro VLSI System course (EE271) Introduction to VLSI Systems 1 Circuits and Delay Introduction to VLSI Systems 2 Power, Delay and Area:
Lecture 7 Circuit Delay, Area and Power lecture notes from S. Mitra Intro VLSI System course (EE271) Introduction to VLSI Systems 1 Circuits and Delay Introduction to VLSI Systems 2 Power, Delay and Area:
CSE 191, Class Note 05: Counting Methods Computer Sci & Eng Dept SUNY Buffalo
 Coutig Methods CSE 191, Class Note 05: Coutig Methods Computer Sci & Eg Dept SUNY Buffalo c Xi He (Uiversity at Buffalo CSE 191 Discrete Structures 1 / 48 Need for Coutig The problem of coutig the umber
Coutig Methods CSE 191, Class Note 05: Coutig Methods Computer Sci & Eg Dept SUNY Buffalo c Xi He (Uiversity at Buffalo CSE 191 Discrete Structures 1 / 48 Need for Coutig The problem of coutig the umber
Summary of pn-junction (Lec )
 Lecture #12 OUTLNE Diode aalysis ad applicatios cotiued The MOFET The MOFET as a cotrolled resistor Pich-off ad curret saturatio Chael-legth modulatio Velocity saturatio i a short-chael MOFET Readig Howe
Lecture #12 OUTLNE Diode aalysis ad applicatios cotiued The MOFET The MOFET as a cotrolled resistor Pich-off ad curret saturatio Chael-legth modulatio Velocity saturatio i a short-chael MOFET Readig Howe
Quantum Computing Lecture 7. Quantum Factoring
 Quatum Computig Lecture 7 Quatum Factorig Maris Ozols Quatum factorig A polyomial time quatum algorithm for factorig umbers was published by Peter Shor i 1994. Polyomial time meas that the umber of gates
Quatum Computig Lecture 7 Quatum Factorig Maris Ozols Quatum factorig A polyomial time quatum algorithm for factorig umbers was published by Peter Shor i 1994. Polyomial time meas that the umber of gates
Castiel, Supernatural, Season 6, Episode 18
 13 Differetial Equatios the aswer to your questio ca best be epressed as a series of partial differetial equatios... Castiel, Superatural, Seaso 6, Episode 18 A differetial equatio is a mathematical equatio
13 Differetial Equatios the aswer to your questio ca best be epressed as a series of partial differetial equatios... Castiel, Superatural, Seaso 6, Episode 18 A differetial equatio is a mathematical equatio
7. Modern Techniques. Data Encryption Standard (DES)
 7. Moder Techiques. Data Ecryptio Stadard (DES) The objective of this chapter is to illustrate the priciples of moder covetioal ecryptio. For this purpose, we focus o the most widely used covetioal ecryptio
7. Moder Techiques. Data Ecryptio Stadard (DES) The objective of this chapter is to illustrate the priciples of moder covetioal ecryptio. For this purpose, we focus o the most widely used covetioal ecryptio
Minimum Source/Drain Area AS,AD = (0.48µm)(0.60µm) - (0.12µm)(0.12µm) = µm 2
 UNIERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Egieerig Departmet of Electrical Egieerig ad Computer Scieces Last modified o February 1 st, 005 by Chris Baer (crbaer@eecs Adrei ladimirescu Homewor #3 EECS141 Due Friday,
UNIERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Egieerig Departmet of Electrical Egieerig ad Computer Scieces Last modified o February 1 st, 005 by Chris Baer (crbaer@eecs Adrei ladimirescu Homewor #3 EECS141 Due Friday,
Mixtures of Gaussians and the EM Algorithm
 Mixtures of Gaussias ad the EM Algorithm CSE 6363 Machie Learig Vassilis Athitsos Computer Sciece ad Egieerig Departmet Uiversity of Texas at Arligto 1 Gaussias A popular way to estimate probability desity
Mixtures of Gaussias ad the EM Algorithm CSE 6363 Machie Learig Vassilis Athitsos Computer Sciece ad Egieerig Departmet Uiversity of Texas at Arligto 1 Gaussias A popular way to estimate probability desity
Lecture 10: P-N Diodes. Announcements
 EECS 15 Sprig 4, Lecture 1 Lecture 1: P-N Diodes EECS 15 Sprig 4, Lecture 1 Aoucemets The Thursday lab sectio will be moved a hour later startig this week, so that the TA s ca atted lecture i aother class
EECS 15 Sprig 4, Lecture 1 Lecture 1: P-N Diodes EECS 15 Sprig 4, Lecture 1 Aoucemets The Thursday lab sectio will be moved a hour later startig this week, so that the TA s ca atted lecture i aother class
Lecture 3. Digital Signal Processing. Chapter 3. z-transforms. Mikael Swartling Nedelko Grbic Bengt Mandersson. rev. 2016
 Lecture 3 Digital Sigal Processig Chapter 3 z-trasforms Mikael Swartlig Nedelko Grbic Begt Madersso rev. 06 Departmet of Electrical ad Iformatio Techology Lud Uiversity z-trasforms We defie the z-trasform
Lecture 3 Digital Sigal Processig Chapter 3 z-trasforms Mikael Swartlig Nedelko Grbic Begt Madersso rev. 06 Departmet of Electrical ad Iformatio Techology Lud Uiversity z-trasforms We defie the z-trasform
LECTURE 5 PART 2 MOS INVERTERS STATIC DESIGN CMOS. CMOS STATIC PARAMETERS The Inverter Circuit and Operating Regions
 LECTURE 5 PART 2 MOS INVERTERS STATIC ESIGN CMOS Objectives for Lecture 5 - Part 2* Uderstad the VTC of a CMOS iverter. Uderstad static aalysis of the CMOS iverter icludig breakpoits, VOL, V OH,, V IH,
LECTURE 5 PART 2 MOS INVERTERS STATIC ESIGN CMOS Objectives for Lecture 5 - Part 2* Uderstad the VTC of a CMOS iverter. Uderstad static aalysis of the CMOS iverter icludig breakpoits, VOL, V OH,, V IH,
Physics 310 Lecture 9a DAC and ADC
 Lecture 9a ad Mo. 3/19 Wed. 3/1 Thurs. 3/ Fri. 3/3 Mo. 3/6 Wed. 3/8 Thurs. 3/9 h 14.1,.6-.10; pp 373-374 (Samplig Frequecy); 1.6: & More of the same Lab 9: & More of the same; Quiz h 14 Project: ompoet
Lecture 9a ad Mo. 3/19 Wed. 3/1 Thurs. 3/ Fri. 3/3 Mo. 3/6 Wed. 3/8 Thurs. 3/9 h 14.1,.6-.10; pp 373-374 (Samplig Frequecy); 1.6: & More of the same Lab 9: & More of the same; Quiz h 14 Project: ompoet
MORE TUTORIALS FOR VERILOG DIGITAL ELECTRONICS SYSTEM DESIGN HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS DATASHEETS FOR PARTS 10/3/2018
 //8 DIGITA EECTRONICS SYSTEM DESIGN FA 8 PROFS. IRIS BAHAR & ROD BERESFORD OCTOBER, 8 ECTURE 9: CMOS TRANSIENT BEHAIOR MORE TUTORIAS FOR ERIOG O the course website you ca fid some useful liks to additioal
//8 DIGITA EECTRONICS SYSTEM DESIGN FA 8 PROFS. IRIS BAHAR & ROD BERESFORD OCTOBER, 8 ECTURE 9: CMOS TRANSIENT BEHAIOR MORE TUTORIAS FOR ERIOG O the course website you ca fid some useful liks to additioal
Lecture 3: August 31
 36-705: Itermediate Statistics Fall 018 Lecturer: Siva Balakrisha Lecture 3: August 31 This lecture will be mostly a summary of other useful expoetial tail bouds We will ot prove ay of these i lecture,
36-705: Itermediate Statistics Fall 018 Lecturer: Siva Balakrisha Lecture 3: August 31 This lecture will be mostly a summary of other useful expoetial tail bouds We will ot prove ay of these i lecture,
Chapter 8. Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology
 VLSI Design hapter 8 Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology Jin-Fu Li hapter 8 Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology Introduction Low-Power Gate-Level Design Low-Power Architecture-Level Design Algorithmic-Level
VLSI Design hapter 8 Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology Jin-Fu Li hapter 8 Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology Introduction Low-Power Gate-Level Design Low-Power Architecture-Level Design Algorithmic-Level
Diversity Combining Techniques
 Diversity Combiig Techiques Whe the required sigal is a combiatio of several waves (i.e, multipath), the total sigal amplitude may experiece deep fades (i.e, Rayleigh fadig), over time or space. The major
Diversity Combiig Techiques Whe the required sigal is a combiatio of several waves (i.e, multipath), the total sigal amplitude may experiece deep fades (i.e, Rayleigh fadig), over time or space. The major
. (24) If we consider the geometry of Figure 13 the signal returned from the n th scatterer located at x, y is
 .5 SAR SIGNA CHARACTERIZATION I order to formulate a SAR processor we first eed to characterize the sigal that the SAR processor will operate upo. Although our previous discussios treated SAR cross-rage
.5 SAR SIGNA CHARACTERIZATION I order to formulate a SAR processor we first eed to characterize the sigal that the SAR processor will operate upo. Although our previous discussios treated SAR cross-rage
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics D2 - DAC taxonomy and errors» Static and dynamic parameters» DAC taxonomy» DAC circuits» Error sources AY 2015-16
Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics D2 - DAC taxonomy and errors» Static and dynamic parameters» DAC taxonomy» DAC circuits» Error sources AY 2015-16
Fortgeschrittene Datenstrukturen Vorlesung 11
 Fortgeschrittee Datestruture Vorlesug 11 Schriftführer: Marti Weider 19.01.2012 1 Succict Data Structures (ctd.) 1.1 Select-Queries A slightly differet approach, compared to ra, is used for select. B represets
Fortgeschrittee Datestruture Vorlesug 11 Schriftführer: Marti Weider 19.01.2012 1 Succict Data Structures (ctd.) 1.1 Select-Queries A slightly differet approach, compared to ra, is used for select. B represets
Integer Linear Programming
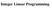 Iteger Liear Programmig Itroductio Iteger L P problem (P) Mi = s. t. a = b i =,, m = i i 0, iteger =,, c Eemple Mi z = 5 s. t. + 0 0, 0, iteger F(P) = feasible domai of P Itroductio Iteger L P problem
Iteger Liear Programmig Itroductio Iteger L P problem (P) Mi = s. t. a = b i =,, m = i i 0, iteger =,, c Eemple Mi z = 5 s. t. + 0 0, 0, iteger F(P) = feasible domai of P Itroductio Iteger L P problem
C.K. Ken Yang UCLA Courtesy of MAH EE 215B
 Decoders: Logical Effort Applied C.K. Ken Yang UCLA yang@ee.ucla.edu Courtesy of MAH 1 Overview Reading Rabaey 6.2.2 (Ratio-ed logic) W&H 6.2.2 Overview We have now gone through the basics of decoders,
Decoders: Logical Effort Applied C.K. Ken Yang UCLA yang@ee.ucla.edu Courtesy of MAH 1 Overview Reading Rabaey 6.2.2 (Ratio-ed logic) W&H 6.2.2 Overview We have now gone through the basics of decoders,
a for a 1 1 matrix. a b a b 2 2 matrix: We define det ad bc 3 3 matrix: We define a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a
 Math E-2b Lecture #8 Notes This week is all about determiats. We ll discuss how to defie them, how to calculate them, lear the allimportat property kow as multiliearity, ad show that a square matrix A
Math E-2b Lecture #8 Notes This week is all about determiats. We ll discuss how to defie them, how to calculate them, lear the allimportat property kow as multiliearity, ad show that a square matrix A
2 f(x) dx = 1, 0. 2f(x 1) dx d) 1 4t t6 t. t 2 dt i)
 Math PracTest Be sure to review Lab (ad all labs) There are lots of good questios o it a) State the Mea Value Theorem ad draw a graph that illustrates b) Name a importat theorem where the Mea Value Theorem
Math PracTest Be sure to review Lab (ad all labs) There are lots of good questios o it a) State the Mea Value Theorem ad draw a graph that illustrates b) Name a importat theorem where the Mea Value Theorem
Doped semiconductors: donor impurities
 Doped semicoductors: door impurities A silico lattice with a sigle impurity atom (Phosphorus, P) added. As compared to Si, the Phosphorus has oe extra valece electro which, after all bods are made, has
Doped semicoductors: door impurities A silico lattice with a sigle impurity atom (Phosphorus, P) added. As compared to Si, the Phosphorus has oe extra valece electro which, after all bods are made, has
Machine Learning. Ilya Narsky, Caltech
 Machie Learig Ilya Narsky, Caltech Lecture 4 Multi-class problems. Multi-class versios of Neural Networks, Decisio Trees, Support Vector Machies ad AdaBoost. Reductio of a multi-class problem to a set
Machie Learig Ilya Narsky, Caltech Lecture 4 Multi-class problems. Multi-class versios of Neural Networks, Decisio Trees, Support Vector Machies ad AdaBoost. Reductio of a multi-class problem to a set
EE241 - Spring 2000 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits. References
 EE241 - Spring 2000 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 26 Memory References Rabaey, Digital Integrated Circuits Memory Design and Evolution, VLSI Circuits Short Course, 1998.» Gillingham, Evolution
EE241 - Spring 2000 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 26 Memory References Rabaey, Digital Integrated Circuits Memory Design and Evolution, VLSI Circuits Short Course, 1998.» Gillingham, Evolution
Consider the circuit below. We have seen this one already. As before, assume that the BJT is on and in forward active operation.
 Saturatio Cosider the circuit below. We have see this oe already. As before, assume that the BJT is o ad i forward active operatio. VCC 0 V VBB ib RC 0 k! RB 3V 47 k! vbe ic vce βf 00. ( )( µ µ ). (. )(!!
Saturatio Cosider the circuit below. We have see this oe already. As before, assume that the BJT is o ad i forward active operatio. VCC 0 V VBB ib RC 0 k! RB 3V 47 k! vbe ic vce βf 00. ( )( µ µ ). (. )(!!
Lecture 8: Solving the Heat, Laplace and Wave equations using finite difference methods
 Itroductory lecture otes o Partial Differetial Equatios - c Athoy Peirce. Not to be copied, used, or revised without explicit writte permissio from the copyright ower. 1 Lecture 8: Solvig the Heat, Laplace
Itroductory lecture otes o Partial Differetial Equatios - c Athoy Peirce. Not to be copied, used, or revised without explicit writte permissio from the copyright ower. 1 Lecture 8: Solvig the Heat, Laplace
Chapter Vectors
 Chapter 4. Vectors fter readig this chapter you should be able to:. defie a vector. add ad subtract vectors. fid liear combiatios of vectors ad their relatioship to a set of equatios 4. explai what it
Chapter 4. Vectors fter readig this chapter you should be able to:. defie a vector. add ad subtract vectors. fid liear combiatios of vectors ad their relatioship to a set of equatios 4. explai what it
Chapter 9 Computer Design Basics
 Logic ad Computer Desig Fudametals Chapter 9 Computer Desig asics Part Datapaths Charles Kime & Thomas Kamiski 008 Pearso Educatio, Ic. (Hyperliks are active i View Show mode) Overview Part Datapaths Itroductio
Logic ad Computer Desig Fudametals Chapter 9 Computer Desig asics Part Datapaths Charles Kime & Thomas Kamiski 008 Pearso Educatio, Ic. (Hyperliks are active i View Show mode) Overview Part Datapaths Itroductio
Generalizing the DTFT. The z Transform. Complex Exponential Excitation. The Transfer Function. Systems Described by Difference Equations
 Geeraliig the DTFT The Trasform M. J. Roberts - All Rights Reserved. Edited by Dr. Robert Akl 1 The forward DTFT is defied by X e jω = x e jω i which = Ω is discrete-time radia frequecy, a real variable.
Geeraliig the DTFT The Trasform M. J. Roberts - All Rights Reserved. Edited by Dr. Robert Akl 1 The forward DTFT is defied by X e jω = x e jω i which = Ω is discrete-time radia frequecy, a real variable.
EE260: Digital Design, Spring n Binary logic and Gates n Boolean Algebra. n Basic Properties n Algebraic Manipulation
 EE26: Digital Desig, Sprig 28 2-Ja-8 EE 26: Itroductio to Digital Desig Boolea lgebra: Logic Represetatios ad alysis Yao Zheg Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Hawaiʻi at Māoa Overview Biary
EE26: Digital Desig, Sprig 28 2-Ja-8 EE 26: Itroductio to Digital Desig Boolea lgebra: Logic Represetatios ad alysis Yao Zheg Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Hawaiʻi at Māoa Overview Biary
On comparison of different approaches to the stability radius calculation. Olga Karelkina
 O compariso of differet approaches to the stability radius calculatio Olga Karelkia Uiversity of Turku 2011 Outlie Prelimiaries Problem statemet Exact method for calculatio stability radius proposed by
O compariso of differet approaches to the stability radius calculatio Olga Karelkia Uiversity of Turku 2011 Outlie Prelimiaries Problem statemet Exact method for calculatio stability radius proposed by
CHM 424 EXAM 2 - COVER PAGE FALL
 CHM 44 EXAM - COVER PAGE FALL 007 There are six umbered pages with five questios. Aswer the questios o the exam. Exams doe i ik are eligible for regrade, those doe i pecil will ot be regraded. coulomb
CHM 44 EXAM - COVER PAGE FALL 007 There are six umbered pages with five questios. Aswer the questios o the exam. Exams doe i ik are eligible for regrade, those doe i pecil will ot be regraded. coulomb
Integer Programming (IP)
 Iteger Programmig (IP) The geeral liear mathematical programmig problem where Mied IP Problem - MIP ma c T + h Z T y A + G y + y b R p + vector of positive iteger variables y vector of positive real variables
Iteger Programmig (IP) The geeral liear mathematical programmig problem where Mied IP Problem - MIP ma c T + h Z T y A + G y + y b R p + vector of positive iteger variables y vector of positive real variables
CS151 Complexity Theory
 Time ad Space CS151 Complexity Theory Lecture 2 April 1, 2004 A motivatig questio: Boolea formula with odes evaluate usig O(log ) space? depth-first traversal requires storig itermediate values idea: short-circuit
Time ad Space CS151 Complexity Theory Lecture 2 April 1, 2004 A motivatig questio: Boolea formula with odes evaluate usig O(log ) space? depth-first traversal requires storig itermediate values idea: short-circuit
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 18: March 27, 2018 Dynamic Logic, Charge Injection Lecture Outline! Sequential MOS Logic " D-Latch " Timing Constraints! Dynamic Logic " Domino
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 18: March 27, 2018 Dynamic Logic, Charge Injection Lecture Outline! Sequential MOS Logic " D-Latch " Timing Constraints! Dynamic Logic " Domino
Lecture 6 Power Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis 2010
 EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 6 Power Zhuo Feng 6.1 Outline Power and Energy Dynamic Power Static Power 6.2 Power and Energy Power is drawn from a voltage source attached to the V DD
EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 6 Power Zhuo Feng 6.1 Outline Power and Energy Dynamic Power Static Power 6.2 Power and Energy Power is drawn from a voltage source attached to the V DD
Charge Recycling in MTCMOS Circuits: Concept and Analysis Ehsan Pakbaznia University of Southern California
 Charge Recyclig i MTCMOS Circuits: Cocept ad Aalysis hsa akbazia Uiversity of Souther Califoria pakbazi@usc.edu Farza Fallah Fujitsu Labs of America farza@us.fujitsu.com Massoud edram Uiversity of Souther
Charge Recyclig i MTCMOS Circuits: Cocept ad Aalysis hsa akbazia Uiversity of Souther Califoria pakbazi@usc.edu Farza Fallah Fujitsu Labs of America farza@us.fujitsu.com Massoud edram Uiversity of Souther
MTH Assignment 1 : Real Numbers, Sequences
 MTH -26 Assigmet : Real Numbers, Sequeces. Fid the supremum of the set { m m+ : N, m Z}. 2. Let A be a o-empty subset of R ad α R. Show that α = supa if ad oly if α is ot a upper boud of A but α + is a
MTH -26 Assigmet : Real Numbers, Sequeces. Fid the supremum of the set { m m+ : N, m Z}. 2. Let A be a o-empty subset of R ad α R. Show that α = supa if ad oly if α is ot a upper boud of A but α + is a
Commutativity in Permutation Groups
 Commutativity i Permutatio Groups Richard Wito, PhD Abstract I the group Sym(S) of permutatios o a oempty set S, fixed poits ad trasiet poits are defied Prelimiary results o fixed ad trasiet poits are
Commutativity i Permutatio Groups Richard Wito, PhD Abstract I the group Sym(S) of permutatios o a oempty set S, fixed poits ad trasiet poits are defied Prelimiary results o fixed ad trasiet poits are
LECTURE 28. Analyzing digital computation at a very low level! The Latch Pipelined Datapath Control Signals Concept of State
 Today LECTURE 28 Analyzing digital computation at a very low level! The Latch Pipelined Datapath Control Signals Concept of State Time permitting, RC circuits (where we intentionally put in resistance
Today LECTURE 28 Analyzing digital computation at a very low level! The Latch Pipelined Datapath Control Signals Concept of State Time permitting, RC circuits (where we intentionally put in resistance
Lecture 16: Monotone Formula Lower Bounds via Graph Entropy. 2 Monotone Formula Lower Bounds via Graph Entropy
 15-859: Iformatio Theory ad Applicatios i TCS CMU: Sprig 2013 Lecture 16: Mootoe Formula Lower Bouds via Graph Etropy March 26, 2013 Lecturer: Mahdi Cheraghchi Scribe: Shashak Sigh 1 Recap Graph Etropy:
15-859: Iformatio Theory ad Applicatios i TCS CMU: Sprig 2013 Lecture 16: Mootoe Formula Lower Bouds via Graph Etropy March 26, 2013 Lecturer: Mahdi Cheraghchi Scribe: Shashak Sigh 1 Recap Graph Etropy:
