On Critical Path Selection Based Upon Statistical Timing Models -- Theory and Practice
|
|
|
- Colleen Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 On Critical Path Selection Based Upon Statistical Timing Models -- Theory and Practice Jing-Jia Liou, Angela Krstic, Li-C. Wang, and Kwang-Ting Cheng University of California - Santa Barbara
2 Problem Find a small set of paths for explicit testing Because we can t afford testing of all paths Important for Optimization Timing validation Speed test and binning Delay defect diagnosis
3 Why Path Selection Again? Traditional definition of a critical path A timing long path Defined under worst-case or nominal delay models Delays are discrete values In the DSM domain, the problem is different DSM process variation and defect effects can better be captured with statistical timings What if we change the delays with the statistical timing models?
4 Consider This Example a 15/1 e Most critical? b 13/2 10/1 g c 14/2 9/3 d 12/3 f Most critical? The most critical path can be different based upon which delay model you have in mind!
5 Statistical Simulation a b c 15/1 e 13/2 14/2 10/1 9/3 g P1: a, e, g P2: b, e, g P3: c, f, g P4: d, f, g d 12/3 f Suppose chip instances are produced: P1 P2 P3 P4 43.6% 19.1% 23.6% 13.7%
6 In the DSM Domain The most critical path in different chip instances can be different Statistical simulation can captures that variation But, How can we re-define the concept of a critical path?
7 Statistical Definition of Being Critical Critical Prob. Critical Not critical How critical a path is can be defined as the probability of exceeding the clock period T
8 Statistical Timing Analysis Framework Cell/interconnect delays (random variables) Cell-based netlist (Static analyzer) False-path-aware statistical timing analysis framework (DAC 2002) 1. True circuit delay distributions 2. A set of sensitizable, timing true and critical paths
9 1. Path Filtering & 2. Path Selection Logic and timing false paths or Non-critical paths U S: tested Suppose we have U, a set of critical and true paths which are ranked by their critical probabilities (p 1 >p 2 >p 3 > >p n ) How to select k paths as the critical paths? The critical path set S = {p 1,,p k } for a given k?
10 Critical Path Set In traditional delay test A critical path set contains the k longest paths Where k is the affordable # of tests Under the statistical models Pick a clock period T Select those k paths with the largest critical probabilities Does that really give us a good path set? This paper says No! And explains why
11 Consider This Example overlap B A C 24/3 25/3 22/2 After A is selected, should we select B or C?
12 Change of A distribution Path Correlation clk Return by testing A clk It is unclear whether B or C is a better choice after A Return by testing B Need to calculate the correlation pdf for B given that A is tested
13 Not Forget Another Important Thing Topological Coverage Captured Not captured
14 Problem Formulation (ICCAD02) Maximizing P capture = P obj1 * P obj2 Prob. that defects fall on the selected paths (locations and sizes are independent Prob. that defects can be random variables) detected by testing those paths Maximizing individual objective is NP-hard Approximate the optimal solution is NP-hard A heuristic maximizing one may not maximizing the other
15 Find A Well-Studied Problem Given an edge-weighted graph G and a number k Find a set of k vertices to cover the maximum weights Max-Weight-Vertex-Cover (MWVC) Problem Finding (1-ε)-approximation is NP-hard This is also true if G is a hypergraph (M-C) MWVC Log-Reduction Max-Coverage Log-Reduction Maximizing P obj1
16 Maximizing P obj2 Maximizing P obj2 is similar But it is harder because the weights corresponds to prob. Correlations Need a different analysis (ICCAD 02)
17 Main Results (ICCAD 02) Identify the best known heuristic to maximize P obj1 Identify the best known heuristic to maximize P obj2 Can we identify a unique answer for both problems? (P capture = P obj1 * P obj2 ) Answer with proof: The best heuristic to maximize P obj2 is also a good heuristic to maximize P obj1 (implicitly can maximize P obj1 as well ICCAD 02)
18 Path Selection Heuristics H-timing: Select the most critical k paths H-segment: best heuristic to maximize P obj1 first H-Opt: maximizing P obj2 1. Select the most critical un-selected path 2. Find all paths correlated to the path 3. Update their critical probabilities according to the path correlations For comparison, we also consider Traditional Select the most critical k paths Use 3σ bound worst-case delays
19 Statistical Evaluation of S (ASP-DAC 03) A chip instance (w/ defect injected) Is any path in S exceeding clk? no Is any path in U - S exceeding clk? yes yes Covered NotCovered Missing P = NotCovered Covered + NotCovered
20 Traditional Vs. H-Opt No defect injection Simulate process variation Small Defect (single size) Large Defect (single size)
21 Missing Prob. P Defect Free Traditional H-Opt # of Selected Paths
22 Small Size Defect Traditional H-Opt Missing Prob. P # of Selected Paths
23 Missing Prob. P Large Size Defect Traditional H-Opt # of Selected Paths
24 Comparison of The Three Heuristics Small Defects: exponential distribution between 0 and 40 units Larger Defects: exponential distribution between 0 and 100 units
25 Small Defects (Statistical Simulation I) Miss Prob # of Paths Selected H-Timing H-Segment H-Opt
26 Small Defects (Statistical Simulation II) Miss Prob # of Paths Selected H-Timing H-Segment H-Opt
27 Larger Defects (Statistical Simulation I) Miss Prob Defect Size H-Timing H-Segment H-Opt
28 Larger Defects (Statistical Simulation II) Miss Prob # of Paths Selected H-Timing H-Segment H-Opt
29 More Results (Traditional Vs. H-Opt) Results of selecting 10 critical paths: Circuit U Size Traditional H-Opt Memory Time S % 12.9% 6.8M 3M S % 5.4M 4M S % 0.0% 11M 6M S % 0.0% 39.5M 20M S % 47.4% 50M 24M s % 0.0% 41M 12M Statistical path analysis (Path filtering step) Quality evaluation
30 Conclusion Considering statistical timing is better than using traditional delay models Considering path correlation is crucial for critical path selection in the statistical domain Our path selection consists of 2 phases: Path filtering (DAC 2002) Critical path selection (ICCAD 02, ASP-DAC 03) Experimental results confirms our theoretical analysis H-Opt is the most feasible heuristic for path selection in the statistical domain
Performance Sensitivity Analysis Using Statistical Methods and Its Applications to Delay Testing
 Performance Sensitivity Analysis Using Statistical Methods and Its Applications to Delay Testing Jing-Jia Liou Angela Krstić Kwang-Ting Cheng Deb Aditya Mukherjee Sandip Kundu ECE Department, University
Performance Sensitivity Analysis Using Statistical Methods and Its Applications to Delay Testing Jing-Jia Liou Angela Krstić Kwang-Ting Cheng Deb Aditya Mukherjee Sandip Kundu ECE Department, University
Generation of High Quality Non-Robust Tests for Path Delay Faults
 Generation of High Quality Non-Robust Tests for Path Delay Faults Kwang-Ting Cheng Hsi-Chuan Chen Department of ECE AT&T Bell Laboratories University of California Murray Hill, NJ 07974 Santa Barbara,
Generation of High Quality Non-Robust Tests for Path Delay Faults Kwang-Ting Cheng Hsi-Chuan Chen Department of ECE AT&T Bell Laboratories University of California Murray Hill, NJ 07974 Santa Barbara,
Advanced Testing. EE5375 ADD II Prof. MacDonald
 Advanced Testing EE5375 ADD II Prof. MacDonald Functional Testing l Original testing method l Run chip from reset l Tester emulates the outside world l Chip runs functionally with internally generated
Advanced Testing EE5375 ADD II Prof. MacDonald Functional Testing l Original testing method l Run chip from reset l Tester emulates the outside world l Chip runs functionally with internally generated
PARADE: PARAmetric Delay Evaluation Under Process Variation * (Revised Version)
 PARADE: PARAmetric Delay Evaluation Under Process Variation * (Revised Version) Xiang Lu, Zhuo Li, Wangqi Qiu, D. M. H. Walker, Weiping Shi Dept. of Electrical Engineering Dept. of Computer Science Texas
PARADE: PARAmetric Delay Evaluation Under Process Variation * (Revised Version) Xiang Lu, Zhuo Li, Wangqi Qiu, D. M. H. Walker, Weiping Shi Dept. of Electrical Engineering Dept. of Computer Science Texas
PARADE: PARAmetric Delay Evaluation Under Process Variation *
 PARADE: PARAmetric Delay Evaluation Under Process Variation * Xiang Lu, Zhuo Li, Wangqi Qiu, D. M. H. Walker, Weiping Shi Dept. of Electrical Engineering Dept. of Computer Science Texas A&M University
PARADE: PARAmetric Delay Evaluation Under Process Variation * Xiang Lu, Zhuo Li, Wangqi Qiu, D. M. H. Walker, Weiping Shi Dept. of Electrical Engineering Dept. of Computer Science Texas A&M University
Longest Path Selection for Delay Test under Process Variation
 2093 1 Longest Path Selection for Delay Test under Process Variation Xiang Lu, Zhuo Li, Wangqi Qiu, D. M. H. Walker and Weiping Shi Abstract Under manufacturing process variation, a path through a net
2093 1 Longest Path Selection for Delay Test under Process Variation Xiang Lu, Zhuo Li, Wangqi Qiu, D. M. H. Walker and Weiping Shi Abstract Under manufacturing process variation, a path through a net
Delay Variation Tolerance for Domino Circuits
 Delay Variation Tolerance for Domino Circuits Student: Kai-Chiang Wu Advisor: Shih-Chieh Chang Department of Computer Science National Tsing Hua University Hsinchu, Taiwan 300, R.O.C. June, 2004 Abstract
Delay Variation Tolerance for Domino Circuits Student: Kai-Chiang Wu Advisor: Shih-Chieh Chang Department of Computer Science National Tsing Hua University Hsinchu, Taiwan 300, R.O.C. June, 2004 Abstract
Algorithms. NP -Complete Problems. Dong Kyue Kim Hanyang University
 Algorithms NP -Complete Problems Dong Kyue Kim Hanyang University dqkim@hanyang.ac.kr The Class P Definition 13.2 Polynomially bounded An algorithm is said to be polynomially bounded if its worst-case
Algorithms NP -Complete Problems Dong Kyue Kim Hanyang University dqkim@hanyang.ac.kr The Class P Definition 13.2 Polynomially bounded An algorithm is said to be polynomially bounded if its worst-case
Umans Complexity Theory Lectures
 Complexity Theory Umans Complexity Theory Lectures Lecture 1a: Problems and Languages Classify problems according to the computational resources required running time storage space parallelism randomness
Complexity Theory Umans Complexity Theory Lectures Lecture 1a: Problems and Languages Classify problems according to the computational resources required running time storage space parallelism randomness
Pre and post-silicon techniques to deal with large-scale process variations
 Pre and post-silicon techniques to deal with large-scale process variations Jaeyong Chung, Ph.D. Department of Electronic Engineering Incheon National University Outline Introduction to Variability Pre-silicon
Pre and post-silicon techniques to deal with large-scale process variations Jaeyong Chung, Ph.D. Department of Electronic Engineering Incheon National University Outline Introduction to Variability Pre-silicon
Test Generation for Designs with Multiple Clocks
 39.1 Test Generation for Designs with Multiple Clocks Xijiang Lin and Rob Thompson Mentor Graphics Corp. 8005 SW Boeckman Rd. Wilsonville, OR 97070 Abstract To improve the system performance, designs with
39.1 Test Generation for Designs with Multiple Clocks Xijiang Lin and Rob Thompson Mentor Graphics Corp. 8005 SW Boeckman Rd. Wilsonville, OR 97070 Abstract To improve the system performance, designs with
CSE241 VLSI Digital Circuits Winter Lecture 07: Timing II
 CSE241 VLSI Digital Circuits Winter 2003 Lecture 07: Timing II CSE241 L3 ASICs.1 Delay Calculation Cell Fall Cap\Tr 0.05 0.2 0.5 0.01 0.02 0.16 0.30 0.5 2.0 0.04 0.32 0.178 0.08 0.64 0.60 1.20 0.1ns 0.147ns
CSE241 VLSI Digital Circuits Winter 2003 Lecture 07: Timing II CSE241 L3 ASICs.1 Delay Calculation Cell Fall Cap\Tr 0.05 0.2 0.5 0.01 0.02 0.16 0.30 0.5 2.0 0.04 0.32 0.178 0.08 0.64 0.60 1.20 0.1ns 0.147ns
Yield Modeling and Analysis of Bundled Data and Ring-Oscillator Based Designs
 Yield Modeling and Analysis of Bundled Data and Ring-Oscillator Based Designs Yang Zhang, Ji Li, Huimei Cheng, Haipeng Zha, Jeffrey Draper, and Peter A. Beerel Computer Engineering Technical Report Number
Yield Modeling and Analysis of Bundled Data and Ring-Oscillator Based Designs Yang Zhang, Ji Li, Huimei Cheng, Haipeng Zha, Jeffrey Draper, and Peter A. Beerel Computer Engineering Technical Report Number
Computing Clock Skew Schedules Under Normal Process Variation
 Computing Clock Skew Schedules Under Normal Process Variation Aaron P. Hurst and Robert K. Brayton Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA
Computing Clock Skew Schedules Under Normal Process Variation Aaron P. Hurst and Robert K. Brayton Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA
Knapsack. Bag/knapsack of integer capacity B n items item i has size s i and profit/weight w i
 Knapsack Bag/knapsack of integer capacity B n items item i has size s i and profit/weight w i Goal: find a subset of items of maximum profit such that the item subset fits in the bag Knapsack X: item set
Knapsack Bag/knapsack of integer capacity B n items item i has size s i and profit/weight w i Goal: find a subset of items of maximum profit such that the item subset fits in the bag Knapsack X: item set
Unit 1A: Computational Complexity
 Unit 1A: Computational Complexity Course contents: Computational complexity NP-completeness Algorithmic Paradigms Readings Chapters 3, 4, and 5 Unit 1A 1 O: Upper Bounding Function Def: f(n)= O(g(n)) if
Unit 1A: Computational Complexity Course contents: Computational complexity NP-completeness Algorithmic Paradigms Readings Chapters 3, 4, and 5 Unit 1A 1 O: Upper Bounding Function Def: f(n)= O(g(n)) if
Lecture 8: Sequential Networks and Finite State Machines
 Lecture 8: Sequential Networks and Finite State Machines CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Spring 2014 CK Cheng, Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University
Lecture 8: Sequential Networks and Finite State Machines CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Spring 2014 CK Cheng, Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University
Predicting IC Defect Level using Diagnosis
 2014 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IEEE must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media, including reprinting/republishing this material for advertising
2014 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IEEE must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media, including reprinting/republishing this material for advertising
Lesson 3-7: Absolute Value Equations Name:
 Lesson 3-7: Absolute Value Equations Name: In this activity, we will learn to solve absolute value equations. An absolute value equation is any equation that contains an absolute value symbol. To start,
Lesson 3-7: Absolute Value Equations Name: In this activity, we will learn to solve absolute value equations. An absolute value equation is any equation that contains an absolute value symbol. To start,
Statistical Timing Analysis with Path Reconvergence and Spatial Correlations
 Statistical Timing Analysis with Path Reconvergence and Spatial Correlations Lizheng Zhang, Yuhen Hu, Charlie Chung-Ping Chen ECE Department, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI53706-1691, USA E-mail:
Statistical Timing Analysis with Path Reconvergence and Spatial Correlations Lizheng Zhang, Yuhen Hu, Charlie Chung-Ping Chen ECE Department, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI53706-1691, USA E-mail:
Delay Testing from the Ivory Tower to Tools in the Workshop
 Delay Testing from the Ivory Tower to Tools in the Workshop Einar Johan Aas Department of Electronics and Telecommunications, NTNU Nordic Test Forum, Tallinn, 25. November 2008 Name, title of the presentation
Delay Testing from the Ivory Tower to Tools in the Workshop Einar Johan Aas Department of Electronics and Telecommunications, NTNU Nordic Test Forum, Tallinn, 25. November 2008 Name, title of the presentation
Fast Buffer Insertion Considering Process Variation
 Fast Buffer Insertion Considering Process Variation Jinjun Xiong, Lei He EE Department University of California, Los Angeles Sponsors: NSF, UC MICRO, Actel, Mindspeed Agenda Introduction and motivation
Fast Buffer Insertion Considering Process Variation Jinjun Xiong, Lei He EE Department University of California, Los Angeles Sponsors: NSF, UC MICRO, Actel, Mindspeed Agenda Introduction and motivation
or 0101 Machine
 Synchronous State Graph or Synchronous State Graph or Detector Design a state graph for a machine with: One input X, one output Z. Z= after receiving the complete sequence or Overlapped sequences are detected.
Synchronous State Graph or Synchronous State Graph or Detector Design a state graph for a machine with: One input X, one output Z. Z= after receiving the complete sequence or Overlapped sequences are detected.
1 Submodular functions
 CS 369P: Polyhedral techniques in combinatorial optimization Instructor: Jan Vondrák Lecture date: November 16, 2010 1 Submodular functions We have already encountered submodular functions. Let s recall
CS 369P: Polyhedral techniques in combinatorial optimization Instructor: Jan Vondrák Lecture date: November 16, 2010 1 Submodular functions We have already encountered submodular functions. Let s recall
Sequential Logic (3.1 and is a long difficult section you really should read!)
 EECS 270, Fall 2014, Lecture 6 Page 1 of 8 Sequential Logic (3.1 and 3.2. 3.2 is a long difficult section you really should read!) One thing we have carefully avoided so far is feedback all of our signals
EECS 270, Fall 2014, Lecture 6 Page 1 of 8 Sequential Logic (3.1 and 3.2. 3.2 is a long difficult section you really should read!) One thing we have carefully avoided so far is feedback all of our signals
Timing Analysis. Andreas Kuehlmann. A k = max{a 1 +D k1, A 2 +D k2,a 3 +D k3 } S k. S j. Required times: S ki. given required times on primary outputs
 EECS 9B Spring 3 Timing Analysis - Delay Models Simple model : D k Ak A A A3 Timing Analysis A k = arrival time = max(a,a,a 3 ) + D k D k is the delay at node k, parameterized according to function f k
EECS 9B Spring 3 Timing Analysis - Delay Models Simple model : D k Ak A A A3 Timing Analysis A k = arrival time = max(a,a,a 3 ) + D k D k is the delay at node k, parameterized according to function f k
Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis
 Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis Given the circuit diagram of a state machine: Analyze the combinational logic to determine flip-flop input (excitation) equations: D i = F i (Q, inputs) The input
Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis Given the circuit diagram of a state machine: Analyze the combinational logic to determine flip-flop input (excitation) equations: D i = F i (Q, inputs) The input
Skew Management of NBTI Impacted Gated Clock Trees
 International Symposium on Physical Design 2010 Skew Management of NBTI Impacted Gated Clock Trees Ashutosh Chakraborty and David Z. Pan ECE Department, University of Texas at Austin ashutosh@cerc.utexas.edu
International Symposium on Physical Design 2010 Skew Management of NBTI Impacted Gated Clock Trees Ashutosh Chakraborty and David Z. Pan ECE Department, University of Texas at Austin ashutosh@cerc.utexas.edu
Energy-Efficient Real-Time Task Scheduling in Multiprocessor DVS Systems
 Energy-Efficient Real-Time Task Scheduling in Multiprocessor DVS Systems Jian-Jia Chen *, Chuan Yue Yang, Tei-Wei Kuo, and Chi-Sheng Shih Embedded Systems and Wireless Networking Lab. Department of Computer
Energy-Efficient Real-Time Task Scheduling in Multiprocessor DVS Systems Jian-Jia Chen *, Chuan Yue Yang, Tei-Wei Kuo, and Chi-Sheng Shih Embedded Systems and Wireless Networking Lab. Department of Computer
Time stealing: An adventure in tropical land
 1/ 21 Time stealing: An adventure in tropical land Marianne Johnson Manchester, 16th November 2010 2/ 21 Time stealing: An adventure in tropical land For Dave on the occasion of his 60th Birthday (with
1/ 21 Time stealing: An adventure in tropical land Marianne Johnson Manchester, 16th November 2010 2/ 21 Time stealing: An adventure in tropical land For Dave on the occasion of his 60th Birthday (with
A Temperature-aware Synthesis Approach for Simultaneous Delay and Leakage Optimization
 A Temperature-aware Synthesis Approach for Simultaneous Delay and Leakage Optimization Nathaniel A. Conos and Miodrag Potkonjak Computer Science Department University of California, Los Angeles {conos,
A Temperature-aware Synthesis Approach for Simultaneous Delay and Leakage Optimization Nathaniel A. Conos and Miodrag Potkonjak Computer Science Department University of California, Los Angeles {conos,
The Separation Problem for Binary Decision Diagrams
 The Separation Problem for Binary Decision Diagrams J. N. Hooker Joint work with André Ciré Carnegie Mellon University ISAIM 2014 Separation Problem in Optimization Given a relaxation of an optimization
The Separation Problem for Binary Decision Diagrams J. N. Hooker Joint work with André Ciré Carnegie Mellon University ISAIM 2014 Separation Problem in Optimization Given a relaxation of an optimization
Timing-Aware Decoupling Capacitance Allocation in Power Distribution Networks
 Timing-Aware Decoupling Capacitance Allocation in Power Distribution Networks Sanjay Pant, David Blaauw Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Michigan 1/22 Power supply integrity issues
Timing-Aware Decoupling Capacitance Allocation in Power Distribution Networks Sanjay Pant, David Blaauw Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Michigan 1/22 Power supply integrity issues
Latch/Register Scheduling For Process Variation
 Latch/Register Scheduling For Process Variation Aaron P. Hurst Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720 ahurst@eecs.berkeley.edu Abstract
Latch/Register Scheduling For Process Variation Aaron P. Hurst Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720 ahurst@eecs.berkeley.edu Abstract
NP Completeness and Approximation Algorithms
 Chapter 10 NP Completeness and Approximation Algorithms Let C() be a class of problems defined by some property. We are interested in characterizing the hardest problems in the class, so that if we can
Chapter 10 NP Completeness and Approximation Algorithms Let C() be a class of problems defined by some property. We are interested in characterizing the hardest problems in the class, so that if we can
EE382 Processor Design Winter 1999 Chapter 2 Lectures Clocking and Pipelining
 Slide 1 EE382 Processor Design Winter 1999 Chapter 2 Lectures Clocking and Pipelining Slide 2 Topics Clocking Clock Parameters Latch Types Requirements for reliable clocking Pipelining Optimal pipelining
Slide 1 EE382 Processor Design Winter 1999 Chapter 2 Lectures Clocking and Pipelining Slide 2 Topics Clocking Clock Parameters Latch Types Requirements for reliable clocking Pipelining Optimal pipelining
Shift Register Counters
 Shift Register Counters Shift register counter: a shift register with the serial output connected back to the serial input. They are classified as counters because they give a specified sequence of states.
Shift Register Counters Shift register counter: a shift register with the serial output connected back to the serial input. They are classified as counters because they give a specified sequence of states.
EEE2135 Digital Logic Design
 EEE2135 Digital Logic Design Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Design 서강대학교 전자공학과 1. Model of Sequential Circuits 1) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits a. Sequential circuits: Outputs depend on both the
EEE2135 Digital Logic Design Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Design 서강대학교 전자공학과 1. Model of Sequential Circuits 1) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits a. Sequential circuits: Outputs depend on both the
More Approximation Algorithms
 CS 473: Algorithms, Spring 2018 More Approximation Algorithms Lecture 25 April 26, 2018 Most slides are courtesy Prof. Chekuri Ruta (UIUC) CS473 1 Spring 2018 1 / 28 Formal definition of approximation
CS 473: Algorithms, Spring 2018 More Approximation Algorithms Lecture 25 April 26, 2018 Most slides are courtesy Prof. Chekuri Ruta (UIUC) CS473 1 Spring 2018 1 / 28 Formal definition of approximation
Micro-architecture Pipelining Optimization with Throughput- Aware Floorplanning
 Micro-architecture Pipelining Optimization with Throughput- Aware Floorplanning Yuchun Ma* Zhuoyuan Li* Jason Cong Xianlong Hong Glenn Reinman Sheqin Dong* Qiang Zhou *Department of Computer Science &
Micro-architecture Pipelining Optimization with Throughput- Aware Floorplanning Yuchun Ma* Zhuoyuan Li* Jason Cong Xianlong Hong Glenn Reinman Sheqin Dong* Qiang Zhou *Department of Computer Science &
Logic Synthesis and Verification
 Logic Synthesis and Verification Jie-Hong Roland Jiang 江介宏 Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Fall Timing Analysis & Optimization Reading: Logic Synthesis in a Nutshell Sections
Logic Synthesis and Verification Jie-Hong Roland Jiang 江介宏 Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Fall Timing Analysis & Optimization Reading: Logic Synthesis in a Nutshell Sections
Problem Set 9 Solutions
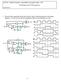 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
Dynamic Adaptation for Resilient Integrated Circuits and Systems
 Dynamic Adaptation for Resilient Integrated Circuits and Systems Krishnendu Chakrabarty Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University Durham, NC 27708, USA Department of Computer and
Dynamic Adaptation for Resilient Integrated Circuits and Systems Krishnendu Chakrabarty Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University Durham, NC 27708, USA Department of Computer and
Branch-and-Bound. Leo Liberti. LIX, École Polytechnique, France. INF , Lecture p. 1
 Branch-and-Bound Leo Liberti LIX, École Polytechnique, France INF431 2011, Lecture p. 1 Reminders INF431 2011, Lecture p. 2 Problems Decision problem: a question admitting a YES/NO answer Example HAMILTONIAN
Branch-and-Bound Leo Liberti LIX, École Polytechnique, France INF431 2011, Lecture p. 1 Reminders INF431 2011, Lecture p. 2 Problems Decision problem: a question admitting a YES/NO answer Example HAMILTONIAN
A Robustness Optimization of SRAM Dynamic Stability by Sensitivity-based Reachability Analysis
 ASP-DAC 2014 A Robustness Optimization of SRAM Dynamic Stability by Sensitivity-based Reachability Analysis Yang Song, Sai Manoj P. D. and Hao Yu School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang
ASP-DAC 2014 A Robustness Optimization of SRAM Dynamic Stability by Sensitivity-based Reachability Analysis Yang Song, Sai Manoj P. D. and Hao Yu School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang
SAT-Solving: From Davis- Putnam to Zchaff and Beyond Day 3: Recent Developments. Lintao Zhang
 SAT-Solving: From Davis- Putnam to Zchaff and Beyond Day 3: Recent Developments Requirements for SAT solvers in the Real World Fast & Robust Given a problem instance, we want to solve it quickly Reliable
SAT-Solving: From Davis- Putnam to Zchaff and Beyond Day 3: Recent Developments Requirements for SAT solvers in the Real World Fast & Robust Given a problem instance, we want to solve it quickly Reliable
Efficient Reluctance Extraction for Large-Scale Power Grid with High- Frequency Consideration
 Efficient Reluctance Extraction for Large-Scale Power Grid with High- Frequency Consideration Shan Zeng, Wenjian Yu, Jin Shi, Xianlong Hong Dept. Computer Science & Technology, Tsinghua University, Beijing
Efficient Reluctance Extraction for Large-Scale Power Grid with High- Frequency Consideration Shan Zeng, Wenjian Yu, Jin Shi, Xianlong Hong Dept. Computer Science & Technology, Tsinghua University, Beijing
Computer Systems on the CERN LHC: How do we measure how well they re doing?
 Computer Systems on the CERN LHC: How do we measure how well they re doing? Joshua Dawes PhD Student affiliated with CERN & Manchester My research pages: http://cern.ch/go/ggh8 Purpose of this talk Principally
Computer Systems on the CERN LHC: How do we measure how well they re doing? Joshua Dawes PhD Student affiliated with CERN & Manchester My research pages: http://cern.ch/go/ggh8 Purpose of this talk Principally
Static Timing Analysis Considering Power Supply Variations
 Static Timing Analysis Considering Power Supply Variations Sanay Pant, David Blaauw University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Abstract Power supply integrity verification has become a key concern in high performance
Static Timing Analysis Considering Power Supply Variations Sanay Pant, David Blaauw University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Abstract Power supply integrity verification has become a key concern in high performance
Thermal-reliable 3D Clock-tree Synthesis Considering Nonlinear Electrical-thermal-coupled TSV Model
 Thermal-reliable 3D Clock-tree Synthesis Considering Nonlinear Electrical-thermal-coupled TSV Model Yang Shang 1, Chun Zhang 1, Hao Yu 1, Chuan Seng Tan 1, Xin Zhao 2, Sung Kyu Lim 2 1 School of Electrical
Thermal-reliable 3D Clock-tree Synthesis Considering Nonlinear Electrical-thermal-coupled TSV Model Yang Shang 1, Chun Zhang 1, Hao Yu 1, Chuan Seng Tan 1, Xin Zhao 2, Sung Kyu Lim 2 1 School of Electrical
Segment-Fixed Priority Scheduling for Self-Suspending Real-Time Tasks
 Segment-Fixed Priority Scheduling for Self-Suspending Real-Time Tasks Junsung Kim, Björn Andersson, Dionisio de Niz, and Raj Rajkumar Carnegie Mellon University 2/31 Motion Planning on Self-driving Parallel
Segment-Fixed Priority Scheduling for Self-Suspending Real-Time Tasks Junsung Kim, Björn Andersson, Dionisio de Niz, and Raj Rajkumar Carnegie Mellon University 2/31 Motion Planning on Self-driving Parallel
P,NP, NP-Hard and NP-Complete
 P,NP, NP-Hard and NP-Complete We can categorize the problem space into two parts Solvable Problems Unsolvable problems 7/11/2011 1 Halting Problem Given a description of a program and a finite input, decide
P,NP, NP-Hard and NP-Complete We can categorize the problem space into two parts Solvable Problems Unsolvable problems 7/11/2011 1 Halting Problem Given a description of a program and a finite input, decide
Fault Modeling. 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee. Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan. VLSI Testing Class
 Fault Modeling 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Fault Modeling Some Definitions Why Modeling Faults Various Fault Models Fault Detection
Fault Modeling 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Fault Modeling Some Definitions Why Modeling Faults Various Fault Models Fault Detection
VIII. NP-completeness
 VIII. NP-completeness 1 / 15 NP-Completeness Overview 1. Introduction 2. P and NP 3. NP-complete (NPC): formal definition 4. How to prove a problem is NPC 5. How to solve a NPC problem: approximate algorithms
VIII. NP-completeness 1 / 15 NP-Completeness Overview 1. Introduction 2. P and NP 3. NP-complete (NPC): formal definition 4. How to prove a problem is NPC 5. How to solve a NPC problem: approximate algorithms
APTAS for Bin Packing
 APTAS for Bin Packing Bin Packing has an asymptotic PTAS (APTAS) [de la Vega and Leuker, 1980] For every fixed ε > 0 algorithm outputs a solution of size (1+ε)OPT + 1 in time polynomial in n APTAS for
APTAS for Bin Packing Bin Packing has an asymptotic PTAS (APTAS) [de la Vega and Leuker, 1980] For every fixed ε > 0 algorithm outputs a solution of size (1+ε)OPT + 1 in time polynomial in n APTAS for
Models for representing sequential circuits
 Sequential Circuits Models for representing sequential circuits Finite-state machines (Moore and Mealy) Representation of memory (states) Changes in state (transitions) Design procedure State diagrams
Sequential Circuits Models for representing sequential circuits Finite-state machines (Moore and Mealy) Representation of memory (states) Changes in state (transitions) Design procedure State diagrams
EECS 141: SPRING 09 MIDTERM 2
 University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences J. Rabaey WeFr 2-3:30pm We, April 22, 2:00-3:30pm EECS 141: SPRING 09 MIDTERM 2 NAME Last First
University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences J. Rabaey WeFr 2-3:30pm We, April 22, 2:00-3:30pm EECS 141: SPRING 09 MIDTERM 2 NAME Last First
DKDT: A Performance Aware Dual Dielectric Assignment for Tunneling Current Reduction
 DKDT: A Performance Aware Dual Dielectric Assignment for Tunneling Current Reduction Saraju P. Mohanty Dept of Computer Science and Engineering University of North Texas smohanty@cs.unt.edu http://www.cs.unt.edu/~smohanty/
DKDT: A Performance Aware Dual Dielectric Assignment for Tunneling Current Reduction Saraju P. Mohanty Dept of Computer Science and Engineering University of North Texas smohanty@cs.unt.edu http://www.cs.unt.edu/~smohanty/
On Greedy Algorithms and Approximate Matroids
 On Greedy Algorithms and Approximate Matroids a riff on Paul Milgrom s Prices and Auctions in Markets with Complex Constraints Tim Roughgarden (Stanford University) 1 A 50-Year-Old Puzzle Persistent mystery:
On Greedy Algorithms and Approximate Matroids a riff on Paul Milgrom s Prices and Auctions in Markets with Complex Constraints Tim Roughgarden (Stanford University) 1 A 50-Year-Old Puzzle Persistent mystery:
The P versus NP Problem. Ker-I Ko. Stony Brook, New York
 The P versus NP Problem Ker-I Ko Stony Brook, New York ? P = NP One of the seven Millenium Problems The youngest one A folklore question? Has hundreds of equivalent forms Informal Definitions P : Computational
The P versus NP Problem Ker-I Ko Stony Brook, New York ? P = NP One of the seven Millenium Problems The youngest one A folklore question? Has hundreds of equivalent forms Informal Definitions P : Computational
A An Overview of Complexity Theory for the Algorithm Designer
 A An Overview of Complexity Theory for the Algorithm Designer A.1 Certificates and the class NP A decision problem is one whose answer is either yes or no. Two examples are: SAT: Given a Boolean formula
A An Overview of Complexity Theory for the Algorithm Designer A.1 Certificates and the class NP A decision problem is one whose answer is either yes or no. Two examples are: SAT: Given a Boolean formula
Interconnect Power and Delay Optimization by Dynamic Programming in Gridded Design Rules
 Interconnect Power and Delay Optimization by Dynamic Programming in Gridded Design Rules Konstantin Moiseev, Avinoam Kolodny EE Dept. Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Shmuel Wimer Eng. School,
Interconnect Power and Delay Optimization by Dynamic Programming in Gridded Design Rules Konstantin Moiseev, Avinoam Kolodny EE Dept. Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Shmuel Wimer Eng. School,
ECS122A Handout on NP-Completeness March 12, 2018
 ECS122A Handout on NP-Completeness March 12, 2018 Contents: I. Introduction II. P and NP III. NP-complete IV. How to prove a problem is NP-complete V. How to solve a NP-complete problem: approximate algorithms
ECS122A Handout on NP-Completeness March 12, 2018 Contents: I. Introduction II. P and NP III. NP-complete IV. How to prove a problem is NP-complete V. How to solve a NP-complete problem: approximate algorithms
Buffered Clock Tree Sizing for Skew Minimization under Power and Thermal Budgets
 Buffered Clock Tree Sizing for Skew Minimization under Power and Thermal Budgets Krit Athikulwongse, Xin Zhao, and Sung Kyu Lim School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology
Buffered Clock Tree Sizing for Skew Minimization under Power and Thermal Budgets Krit Athikulwongse, Xin Zhao, and Sung Kyu Lim School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology
Switching Activity Estimation Based on Conditional Independence
 Switching Activity Estimation Based on Conditional Independence Radu Marculescu, Diana Marculescu and Massoud Pedram CENG Technical Report 95-04 Department of Electrical Engineering - Systems University
Switching Activity Estimation Based on Conditional Independence Radu Marculescu, Diana Marculescu and Massoud Pedram CENG Technical Report 95-04 Department of Electrical Engineering - Systems University
THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN. Faster Static Timing Analysis via Bus Compression
 Faster Static Timing Analysis via Bus Compression by David Van Campenhout and Trevor Mudge CSE-TR-285-96 THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN Computer Science and Engineering Division Department of Electrical Engineering
Faster Static Timing Analysis via Bus Compression by David Van Campenhout and Trevor Mudge CSE-TR-285-96 THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN Computer Science and Engineering Division Department of Electrical Engineering
Introduction to Digital Logic
 Introduction to Digital Logic Lecture 7: Design Goals (Metrics) 2-Level Logic Negative Logic Warmup Consider F(w,x,y,z). Show the algebraic form of m4 and M4? Use Boolean algebra to find the minimal SOP
Introduction to Digital Logic Lecture 7: Design Goals (Metrics) 2-Level Logic Negative Logic Warmup Consider F(w,x,y,z). Show the algebraic form of m4 and M4? Use Boolean algebra to find the minimal SOP
Statistical Timing Analysis using Kernel Smoothing
 Statistical Timing Analysis using Kernel Smoothing Jennifer L. Wong, Vishwal Khandelwal, Ankur Srivastava, Miodrag Potkonjak Computer Science Department, University of California, Los Angeles, {jwong,miodrag}@cs.ucla.edu
Statistical Timing Analysis using Kernel Smoothing Jennifer L. Wong, Vishwal Khandelwal, Ankur Srivastava, Miodrag Potkonjak Computer Science Department, University of California, Los Angeles, {jwong,miodrag}@cs.ucla.edu
Inferring positional homologs with common intervals of sequences
 Outline Introduction Our approach Results Conclusion Inferring positional homologs with common intervals of sequences Guillaume Blin, Annie Chateau, Cedric Chauve, Yannick Gingras CGL - Université du Québec
Outline Introduction Our approach Results Conclusion Inferring positional homologs with common intervals of sequences Guillaume Blin, Annie Chateau, Cedric Chauve, Yannick Gingras CGL - Université du Québec
Aside: Golden Ratio. Golden Ratio: A universal law. Golden ratio φ = lim n = 1+ b n = a n 1. a n+1 = a n + b n, a n+b n a n
 Aside: Golden Ratio Golden Ratio: A universal law. Golden ratio φ = lim n a n+b n a n = 1+ 5 2 a n+1 = a n + b n, b n = a n 1 Ruta (UIUC) CS473 1 Spring 2018 1 / 41 CS 473: Algorithms, Spring 2018 Dynamic
Aside: Golden Ratio Golden Ratio: A universal law. Golden ratio φ = lim n a n+b n a n = 1+ 5 2 a n+1 = a n + b n, b n = a n 1 Ruta (UIUC) CS473 1 Spring 2018 1 / 41 CS 473: Algorithms, Spring 2018 Dynamic
Introduction to VLSI Testing
 Introduction to 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Problems to Think How are you going to test A 32 bit adder A 32 bit counter A 32Mb
Introduction to 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Problems to Think How are you going to test A 32 bit adder A 32 bit counter A 32Mb
Some Algebra Problems (Algorithmic) CSE 417 Introduction to Algorithms Winter Some Problems. A Brief History of Ideas
 Some Algebra Problems (Algorithmic) CSE 417 Introduction to Algorithms Winter 2006 NP-Completeness (Chapter 8) Given positive integers a, b, c Question 1: does there exist a positive integer x such that
Some Algebra Problems (Algorithmic) CSE 417 Introduction to Algorithms Winter 2006 NP-Completeness (Chapter 8) Given positive integers a, b, c Question 1: does there exist a positive integer x such that
Lecture Note: Rounding From pseudo-polynomial to FPTAS
 Lecture Note: Rounding From pseudo-polynomial to FPTAS for Approximation Algorithms course in CCU Bang Ye Wu CSIE, Chung Cheng University, Taiwan Rounding Rounding is a kind of techniques used to design
Lecture Note: Rounding From pseudo-polynomial to FPTAS for Approximation Algorithms course in CCU Bang Ye Wu CSIE, Chung Cheng University, Taiwan Rounding Rounding is a kind of techniques used to design
Digital electronics form a class of circuitry where the ability of the electronics to process data is the primary focus.
 Chapter 2 Digital Electronics Objectives 1. Understand the operation of basic digital electronic devices. 2. Understand how to describe circuits which can process digital data. 3. Understand how to design
Chapter 2 Digital Electronics Objectives 1. Understand the operation of basic digital electronic devices. 2. Understand how to describe circuits which can process digital data. 3. Understand how to design
quantum information technology Tad Hogg HP Labs
 quantum information technology Tad Hogg HP Labs Hype or reality? possible in principle difficult in practice quantum states are fragile limited progress so far, e.g., factoring: 15 = 3x5 search: 3-variable
quantum information technology Tad Hogg HP Labs Hype or reality? possible in principle difficult in practice quantum states are fragile limited progress so far, e.g., factoring: 15 = 3x5 search: 3-variable
NP-Completeness. Until now we have been designing algorithms for specific problems
 NP-Completeness 1 Introduction Until now we have been designing algorithms for specific problems We have seen running times O(log n), O(n), O(n log n), O(n 2 ), O(n 3 )... We have also discussed lower
NP-Completeness 1 Introduction Until now we have been designing algorithms for specific problems We have seen running times O(log n), O(n), O(n log n), O(n 2 ), O(n 3 )... We have also discussed lower
Econ Slides from Lecture 10
 Econ 205 Sobel Econ 205 - Slides from Lecture 10 Joel Sobel September 2, 2010 Example Find the tangent plane to {x x 1 x 2 x 2 3 = 6} R3 at x = (2, 5, 2). If you let f (x) = x 1 x 2 x3 2, then this is
Econ 205 Sobel Econ 205 - Slides from Lecture 10 Joel Sobel September 2, 2010 Example Find the tangent plane to {x x 1 x 2 x 2 3 = 6} R3 at x = (2, 5, 2). If you let f (x) = x 1 x 2 x3 2, then this is
4. How to prove a problem is NPC
 The reducibility relation T is transitive, i.e, A T B and B T C imply A T C Therefore, to prove that a problem A is NPC: (1) show that A NP (2) choose some known NPC problem B define a polynomial transformation
The reducibility relation T is transitive, i.e, A T B and B T C imply A T C Therefore, to prove that a problem A is NPC: (1) show that A NP (2) choose some known NPC problem B define a polynomial transformation
Outline Fault Simulation
 K.T. Tim Cheng, 4_fault_sim, v. Outline Fault Simulation Applications of fault simulation Fault coverage vs product quality Fault simulation scenarios Fault simulation algorithms Fault sampling K.T. Tim
K.T. Tim Cheng, 4_fault_sim, v. Outline Fault Simulation Applications of fault simulation Fault coverage vs product quality Fault simulation scenarios Fault simulation algorithms Fault sampling K.T. Tim
Where Does Power Go in CMOS?
 Power Dissipation Where Does Power Go in CMOS? Dynamic Power Consumption Charging and Discharging Capacitors Short Circuit Currents Short Circuit Path between Supply Rails during Switching Leakage Leaking
Power Dissipation Where Does Power Go in CMOS? Dynamic Power Consumption Charging and Discharging Capacitors Short Circuit Currents Short Circuit Path between Supply Rails during Switching Leakage Leaking
EE371 - Advanced VLSI Circuit Design
 EE371 - Advanced VLSI Circuit Design Midterm Examination May 7, 2002 Name: No. Points Score 1. 18 2. 22 3. 30 TOTAL / 70 In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University Honor Code, I certify
EE371 - Advanced VLSI Circuit Design Midterm Examination May 7, 2002 Name: No. Points Score 1. 18 2. 22 3. 30 TOTAL / 70 In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University Honor Code, I certify
CS151 Complexity Theory. Lecture 1 April 3, 2017
 CS151 Complexity Theory Lecture 1 April 3, 2017 Complexity Theory Classify problems according to the computational resources required running time storage space parallelism randomness rounds of interaction,
CS151 Complexity Theory Lecture 1 April 3, 2017 Complexity Theory Classify problems according to the computational resources required running time storage space parallelism randomness rounds of interaction,
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 23: April 17, 2018 I/O Circuits, Inductive Noise, CLK Generation Lecture Outline! Packaging! Variation and Testing! I/O Circuits! Inductive
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 23: April 17, 2018 I/O Circuits, Inductive Noise, CLK Generation Lecture Outline! Packaging! Variation and Testing! I/O Circuits! Inductive
Probabilistic Databases
 Probabilistic Databases Amol Deshpande University of Maryland Goal Introduction to probabilistic databases Focus on an overview of: Different possible representations Challenges in using them Probabilistic
Probabilistic Databases Amol Deshpande University of Maryland Goal Introduction to probabilistic databases Focus on an overview of: Different possible representations Challenges in using them Probabilistic
Limitations of Algorithm Power
 Limitations of Algorithm Power Objectives We now move into the third and final major theme for this course. 1. Tools for analyzing algorithms. 2. Design strategies for designing algorithms. 3. Identifying
Limitations of Algorithm Power Objectives We now move into the third and final major theme for this course. 1. Tools for analyzing algorithms. 2. Design strategies for designing algorithms. 3. Identifying
Computer Sciences Department
 Computer Sciences Department 1 Reference Book: INTRODUCTION TO THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION, SECOND EDITION, by: MICHAEL SIPSER Computer Sciences Department 3 ADVANCED TOPICS IN C O M P U T A B I L I T Y
Computer Sciences Department 1 Reference Book: INTRODUCTION TO THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION, SECOND EDITION, by: MICHAEL SIPSER Computer Sciences Department 3 ADVANCED TOPICS IN C O M P U T A B I L I T Y
/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Matroids and Greedy Algorithms Date: 10/31/16
 60.433/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Matroids and Greedy Algorithms Date: 0/3/6 6. Introduction We talked a lot the last lecture about greedy algorithms. While both Prim
60.433/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Matroids and Greedy Algorithms Date: 0/3/6 6. Introduction We talked a lot the last lecture about greedy algorithms. While both Prim
Variation-Resistant Dynamic Power Optimization for VLSI Circuits
 Process-Variation Variation-Resistant Dynamic Power Optimization for VLSI Circuits Fei Hu Department of ECE Auburn University, AL 36849 Ph.D. Dissertation Committee: Dr. Vishwani D. Agrawal Dr. Foster
Process-Variation Variation-Resistant Dynamic Power Optimization for VLSI Circuits Fei Hu Department of ECE Auburn University, AL 36849 Ph.D. Dissertation Committee: Dr. Vishwani D. Agrawal Dr. Foster
Design for Manufacturability and Power Estimation. Physical issues verification (DSM)
 Design for Manufacturability and Power Estimation Lecture 25 Alessandra Nardi Thanks to Prof. Jan Rabaey and Prof. K. Keutzer Physical issues verification (DSM) Interconnects Signal Integrity P/G integrity
Design for Manufacturability and Power Estimation Lecture 25 Alessandra Nardi Thanks to Prof. Jan Rabaey and Prof. K. Keutzer Physical issues verification (DSM) Interconnects Signal Integrity P/G integrity
Nanolithography and Design- Technology Co-optimization Beyond 22nm
 Nanolithography and Design- Technology Co-optimization Beyond 22nm David Z. Pan Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin http://www.cerc.utexas.edu/utda 1 50+ Years
Nanolithography and Design- Technology Co-optimization Beyond 22nm David Z. Pan Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin http://www.cerc.utexas.edu/utda 1 50+ Years
Q520: Answers to the Homework on Hopfield Networks. 1. For each of the following, answer true or false with an explanation:
 Q50: Answers to the Homework on Hopfield Networks 1. For each of the following, answer true or false with an explanation: a. Fix a Hopfield net. If o and o are neighboring observation patterns then Φ(
Q50: Answers to the Homework on Hopfield Networks 1. For each of the following, answer true or false with an explanation: a. Fix a Hopfield net. If o and o are neighboring observation patterns then Φ(
Reduction of Detected Acceptable Faults for Yield Improvement via Error-Tolerance
 Reduction of Detected Acceptable Faults for Yield Improvement via Error-Tolerance Tong-Yu Hsieh and Kuen-Jong Lee Department of Electrical Engineering National Cheng Kung University Tainan, Taiwan 70101
Reduction of Detected Acceptable Faults for Yield Improvement via Error-Tolerance Tong-Yu Hsieh and Kuen-Jong Lee Department of Electrical Engineering National Cheng Kung University Tainan, Taiwan 70101
Computational Complexity and Intractability: An Introduction to the Theory of NP. Chapter 9
 1 Computational Complexity and Intractability: An Introduction to the Theory of NP Chapter 9 2 Objectives Classify problems as tractable or intractable Define decision problems Define the class P Define
1 Computational Complexity and Intractability: An Introduction to the Theory of NP Chapter 9 2 Objectives Classify problems as tractable or intractable Define decision problems Define the class P Define
Definition: A "system" of equations is a set or collection of equations that you deal with all together at once.
 System of Equations Definition: A "system" of equations is a set or collection of equations that you deal with all together at once. There is both an x and y value that needs to be solved for Systems
System of Equations Definition: A "system" of equations is a set or collection of equations that you deal with all together at once. There is both an x and y value that needs to be solved for Systems
This means that we can assume each list ) is
 This means that we can assume each list ) is of the form ),, ( )with < and Since the sizes of the items are integers, there are at most +1pairs in each list Furthermore, if we let = be the maximum possible
This means that we can assume each list ) is of the form ),, ( )with < and Since the sizes of the items are integers, there are at most +1pairs in each list Furthermore, if we let = be the maximum possible
Mark A. Horowitz, Metha Jeeradit, Frances Lau, Sabrina Liao, ByongChan Lim, James Mao Electrical Engineering, Stanford University.
 Digital Analog Design Mark A. Horowitz, Metha Jeeradit, Frances Lau, Sabrina Liao, ByongChan Lim, James Mao Electrical Engineering, Stanford University Jaeha Kim Seoul National University My Overall Goal:
Digital Analog Design Mark A. Horowitz, Metha Jeeradit, Frances Lau, Sabrina Liao, ByongChan Lim, James Mao Electrical Engineering, Stanford University Jaeha Kim Seoul National University My Overall Goal:
Introduction to Algorithms
 Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401J/SMA5503 Lecture 18 Prof. Erik Demaine Negative-weight cycles Recall: If a graph G = (V, E) contains a negativeweight cycle, then some shortest paths may not exist.
Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401J/SMA5503 Lecture 18 Prof. Erik Demaine Negative-weight cycles Recall: If a graph G = (V, E) contains a negativeweight cycle, then some shortest paths may not exist.
Improved Direct Product Theorems for Randomized Query Complexity
 Improved Direct Product Theorems for Randomized Query Complexity Andrew Drucker Nov. 16, 2010 Andrew Drucker, Improved Direct Product Theorems for Randomized Query Complexity 1/28 Big picture Usually,
Improved Direct Product Theorems for Randomized Query Complexity Andrew Drucker Nov. 16, 2010 Andrew Drucker, Improved Direct Product Theorems for Randomized Query Complexity 1/28 Big picture Usually,
Structural Delay Testing Under Restricted Scan of Latch-based Pipelines with Time Borrowing
 Structural Delay Testing Under Restricted Scan of Latch-based Pipelines with Borrowing Kun Young Chung and Sandeep K. Gupta University of Southern California, EE Systems Abstract High-speed circuits use
Structural Delay Testing Under Restricted Scan of Latch-based Pipelines with Borrowing Kun Young Chung and Sandeep K. Gupta University of Southern California, EE Systems Abstract High-speed circuits use
A Geometric Programming-based Worst-Case Gate Sizing Method Incorporating Spatial Correlation
 A Geometric Programming-based Worst-Case Gate Sizing Method Incorporating Spatial Correlation Jaskirat Singh Vidyasagar Nookala Zhi-Quan Luo Sachin S. Sapatnekar Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
A Geometric Programming-based Worst-Case Gate Sizing Method Incorporating Spatial Correlation Jaskirat Singh Vidyasagar Nookala Zhi-Quan Luo Sachin S. Sapatnekar Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
