Supplementary Information. Characteristics of Long Non-coding RNAs in the Brown Norway Rat and. Alterations in the Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rat
|
|
|
- Juliet Woods
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Information Characteristics of Long Non-coding RNAs in the Brown Norway Rat and Alterations in the Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rat Feng Wang 1,2,3,*, Liping Li 5,*, Haiming Xu 5, Yong Liu 2,3, Chun Yang 2, Allen W. Cowley, Jr. 2, Niansong Wang 1, Pengyuan Liu 2,3,4, Mingyu Liang 2,3 1 Department of Nephrology and Rheumatology, Shanghai Jiaotong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, Shanghai, China; 2 Department of Physiology, 3 Center of Systems Molecular Medicine, and 4 Cancer Center, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA; 5 Institute of Bioinformatics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang , China *Equal contribution Running title: Rat lncrnas Correspondence: Mingyu Liang, mliang@mcw.edu Pengyuan Liu, pliu@mcw.edu Niansong Wang, wangniansong2012@163.com 1
2 Supplementary Table S1. PCR Primers. Primers for qpcr verification of lncrna expression: Liver-enriched lncrna transcript_id:tcons_ : F: 5 CGTGCACTGgGGGATGG3 R: 5 AATTACCTACCTCGGTTTGAGTTCTC3 Cardiac left ventricle-enriched lncrna transcript_id:tcons_ : F: 5 AGAAAGaGTCAGCGTCACCACA3 R: 5 TGCAGCCTACAATCCATCCA3 Renal outer medulla-enriched lncrna transcript_id:tcons_ : F: 5 ATGGGGCAAAACTGGAAaAATA3 R: 5 TGAAGACGATGCAGGGATGAC3 Renal cortex-enriched lncrna transcript_id:tcons_ : F: 5 AAAgGGACAGGAGGACCACAC3 R: 5 TGCACCACAAGCCCACATT3 Hypothalamus-enriched lncrna transcript_id:tcons_ : F: 5 ATCGAGGGACAAGCAACAAAGA3 R: 5 CAGGGAAGGACTCAGACTCAAGATA3 Adrenal gland-enriched lncrna transcript_id:tcons_ : F: 5 GCACTGCCAGCGGACATC3 R: 5 GTCATTGTGGGATCtTGGCTGTA3 lncrna identified in SS and SS.13 BN26, transcript_id:tcons_ : Primers for transcript_id:tcons_ : 2
3 F: 5 GTTTTGGCTTGGCTACACATTCTA3 R: 5 CCTCCGGCTTTCCATACAGTT3 lncrna identified in SS and SS.13 BN26, transcript_id:tcons_ : F: 5 GGAGCGGGTATAGGGAGGAG3 R: 5 TGGGTCTTTCGGAGCATACAAT3 Primers for genomic DNA segments pulled out by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Rat GAPDH promotor region: F: 5'AGCTCCCCTCCCCCTCTC3' R: 5'GACCCGCCTCGTTTTTGAA3' Rat myglobin exon 2 region: F: 5 CTTGGTGGCGTGGGACTG3 R: 5 AGGGACAACATGCTGCTGAGA3 Promoter region of liver-enriched lncrna transcript_id:tcons_ : F: 5 ATACATGCCTCAGAGAAATCAATCA3 R: 5 AGGGCGCCAGAGAAAACAC3 Promoter region of cardiac left ventricle-enriched lncrna transcript_id: TCONS_ : F: 5 TGTGAAATGTAATGCAAATAAAAATCTG3 R: 5 TGTATATGACCTAAGCAAGTGAGTAAGC3 Promoter region of renal outer medulla-enriched lncrna transcript_id: TCONS_ : 3
4 F: 5 ATTGTTTCATGCTCTTCTCTATTTTTG3 R: 5 GGTTGCCATCCCACAGTCA3 Promoter region of renal cortex-enriched lncrna transcript_id:tcons_ : F: 5 GTGTCACTCTCCATCCCGTCTT3 R: 5 CTCGCACCAGCCCTTGTTT3 Promoter region of hypothalamus-enriched lncrna transcript_id:tcons_ F: 5 GAAAAATCATCAGCGACCACAG3 R: 5 CAGCAAAGAACGAAGGGAGAA3 Promoter region of adrenal gland-enriched lncrna transcript_id:tcons_ : F: 5 CTTCTTTCCCCATCCTTTATTCAG3 R: 5 CCTTCCCAGCAGAGCACTTG3 4
5 Supplementary Table S2. Yield and quality of RNA-seq. B, hypothalamus; C, renal cortex; G, adrenal gland; Li, liver; LV, cardiac left ventricle; M, renal outer medulla. Each sample was a pool of two Brown Norway rats. Sample ID Yield (Mbases) # Reads % of >= Q30 Bases (PF) Mean Quality Score (PF) % of mapping rate 1B 4,500 47,239, B 4,839 54,386, C 5,060 53,183, C 5,266 58,404, G 4,799 50,706, G 4,851 55,411, Li 7,577 79,940, Li 10, ,499, LV 5,257 54,702, LV 4,709 54,427, M 4,885 51,591, M 5,125 57,171,
6 Supplementary Table S3. Renal outer medullary lncrnas differentially expressed between SS and SS.13 BN26 rats. LS, 0.4% salt; HS, 4% salt for 7 days; L26, SS.13 BN26. SSLS vs. SSHS test_id gene_id locus sample_1 sample_2 value_1 value_2 log2(fold_change) test_stat p_value q_value TCONS_ XLOC_ chr11: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr3: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr6: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr17: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr11: L26LS vs. L26HS SSLS SSHS E E 02 SSLS SSHS E E 02 SSLS SSHS E E 02 SSLS SSHS E E 02 SSLS SSHS E E 02 test_id gene_id locus sample_1 sample_2 value_1 value_2 log2(fold_change) test_stat p_value q_value TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr11: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr12: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr13: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr15: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr16: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr17: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr18: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr19: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr19: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr19: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr20: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr3: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr4: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr7: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr8: L26LS L26HS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr8: L26LS L26HS E E 03 6
7 TCONS_ XLOC_ chr9: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr9: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr4: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr6: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr8: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr8: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr3: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr16: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr19: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr7: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr12: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr2: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: SSHS vs. L26HS L26LS L26HS E E 03 L26LS L26HS E E 03 L26LS L26HS E E 03 L26LS L26HS E E 03 L26LS L26HS E E 03 L26LS L26HS E E 03 L26LS L26HS E E 03 L26LS L26HS E E 02 L26LS L26HS E E 02 L26LS L26HS E E 02 L26LS L26HS E E 02 L26LS L26HS E E 02 L26LS L26HS E E 02 L26LS L26HS E E 02 L26LS L26HS E E 02 L26LS L26HS E E 02 L26LS L26HS E E 02 test_id gene_id locus sample_1 sample_2 value_1 value_2 log2(fold_change) test_stat p_value q_value TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr10: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr11: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr11: L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 7
8 TCONS_ XLOC_ chr14: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr15: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr15: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr15: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr16: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr16: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr16: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr17: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr17: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr18: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr19: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr19: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr19: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr2: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr2: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr2: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr20: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr3: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr3: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr4: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr4: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr4: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr5: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr5: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr6: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr6: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr6: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr7: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr8: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr8: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr8: L26HS SSHS E E TCONS_ XLOC_ chr9: L26HS SSHS E E 03 8
9 TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr13: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr18: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr5: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr5: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr10: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr7: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr5: TCONS_ XLOC_ chrx: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr3: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr11: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr4: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr8: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr1: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr7: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr3: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr16: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr16: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr9: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr2: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr4: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr16: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr3: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr3: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr20: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr8: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr13: TCONS_ XLOC_ chr5: L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 03 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 L26HS SSHS E E 02 9
10 Supplementary Table S4. Sequence variants between the Brown Norway (BN) and SS rat genomes in the genes encoding lncrnas TCONS_ and TCONS_ Variants in TCONS_ Chr Pos Reference Nucleotide (BN) SS/JrHsdMcwi (SS) C T A G T C A G C T T C Upstream T C A G G A C T C T T C A G G A T C Variants in TCONS_ Chr Pos Reference Nucleotide (BN) SS/JrHsdMcwi (SS) C T A C A G G A A G A C T A T G T C G A A G A G G T T C C A A G 10
11 T C C T C G T C G A A G T C C T G A C T T C A G G A C T T C G A A C T C C G T C T C C T A G G A G A C T C T T C A T T C C T A G A G C T C T G A G T G A A C C T T C T C G A 11
12 C T C T A T G C A T G C G C G C C T C T C T A C G A G A A G A T T C G A G A G A A C A G A C G A A G C G T C T C A G T G G C T C T C A G A G C T A C C T A T G A T C T C T C 12
13 T G G A T C C T A C C T T C T C T C C T A G A G G A T A G A C T A G G C T C T A G A C T G A A C A G G A G A G A G A A G C T C T A G T C G T A G T G T C C G A G C T A C A G 13
14 C A A G A G C T C G C T A G T C A G G A A G A G T C T G T A G C A G T C G A C G C T C G T C G A C T C T T C C G C T T C T G T C C G T A A G T C G A C T A G T C C T G A G C 14
15 T C A G C T C T C A T C C T T C C A C T G T A G A G T C C A A T C A A G G A G T G T G A T A C T G A C T G A G A T A T C C A G A G A G A C A C T G C G T A T T C G A C T C T 15
16 G A Upstream A G T G C T C T C T T C A C T A A G T C C T 16
17 Supplementary Figure S1. Analytical procedures and criteria for identifying lncrnas in rats. CBL, complete branch length; ORF, open reading frame; CDS, (protein) coding DNA sequence; FPKM, Fragments Per Kilobase of gene model per Million fragments mapped. 17
18 Supplementary Figure S2. Number of lncrnas expressed in one or more tissues. A. Overall summary. B, C, D, E showed number of lncrnas expressed in 5, 4, 3, and 2 of the 6 tissues examined. Each bar represents a tissue. The bars with the same color indicate these tissues share common lncrnas. See Supplementary Table S2 for abbreviations for tissue names. A. Number of lncrnas expressed in one or more tissues 18
19 B. Number of lncrnas expressed in 5 of the 6 tissues 19
20 C. Number of lncrnas expressed in 4 of the 6 tissues 20
21 D. Number of lncrnas expressed in 3 of the 6 tissues 21
22 E. Number of lncrnas expressed in 2 of the 6 tissues 22
23 Supplementary Figure S3. Abundance of rat lncrnas compared to mrna. (A) For each lncrna or mrna, the maximum FPKM among the six tissues examined were chosen for plotting the histogram. (B) Median of FPKM among six tissues was presented. (C-H) Each tissue was presented separately. See Supplementary Table S2 for abbreviations for tissue names. (A). Maximum expression among 6 tissues 23
24 (B) Median of FPKM among tissues 24
25 (C) Liver 25
26 (D) Cardiac left ventricle 26
27 (E) Renal cortex 27
28 (F) Renal outer medulla 28
29 (G) Hypothalamus 29
30 (H) Adrenal gland 30
31 Supplemental Figure S4. lncrnas enriched in the renal outer medulla of BN rats had higher abundance in the renal outer medulla of SS and SS.13BN26 rats than lncrnas enriched in the renal cortex of BN rats. BN, Brown Norway rat; SS, Dahl salt-sensitive rat; L26, congenic SS.13 BN26 rat; M, renal outer medulla; C, renal cortex. 31
32 Supplementary Figure S5. Number of lncrnas differentially expressed between SS and SS.13 BN26 rats on 0.4% or 4% salt diet. 32
33 Supplementary Dataset. Rat lncrnas identified in six tissue regions or organs in Brown Norway rats. Li, liver; LV, cardiac left ventricle; C, renal cortex; M, renal outer medulla; H, hypothalamus; A, adrenal gland. The dataset is in a separate Excel file. 33
Web-based Supplementary Materials for BM-Map: Bayesian Mapping of Multireads for Next-Generation Sequencing Data
 Web-based Supplementary Materials for BM-Map: Bayesian Mapping of Multireads for Next-Generation Sequencing Data Yuan Ji 1,, Yanxun Xu 2, Qiong Zhang 3, Kam-Wah Tsui 3, Yuan Yuan 4, Clift Norris 1, Shoudan
Web-based Supplementary Materials for BM-Map: Bayesian Mapping of Multireads for Next-Generation Sequencing Data Yuan Ji 1,, Yanxun Xu 2, Qiong Zhang 3, Kam-Wah Tsui 3, Yuan Yuan 4, Clift Norris 1, Shoudan
Inferring disease-associated lncrnas using expression data and disease-associated protein coding genes
 Inferring disease-associated lncrnas using expression data and disease-associated protein coding genes Xiaoyong Pan Center for non-coding RNA in Technology and Health, Department of Clinical Veterinary
Inferring disease-associated lncrnas using expression data and disease-associated protein coding genes Xiaoyong Pan Center for non-coding RNA in Technology and Health, Department of Clinical Veterinary
Genome Assembly. Sequencing Output. High Throughput Sequencing
 Genome High Throughput Sequencing Sequencing Output Example applications: Sequencing a genome (DNA) Sequencing a transcriptome and gene expression studies (RNA) ChIP (chromatin immunoprecipitation) Example
Genome High Throughput Sequencing Sequencing Output Example applications: Sequencing a genome (DNA) Sequencing a transcriptome and gene expression studies (RNA) ChIP (chromatin immunoprecipitation) Example
Supplemental Data. Hou et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Hou et al. (216). Plant Cell 1.115/tpc.16.295 A Distance to 1 st nt of start codon Distance to 1 st nt of stop codon B Normalized PARE abundance 8 14 nt 17 nt Frame1 Arabidopsis inflorescence
Supplemental Data. Hou et al. (216). Plant Cell 1.115/tpc.16.295 A Distance to 1 st nt of start codon Distance to 1 st nt of stop codon B Normalized PARE abundance 8 14 nt 17 nt Frame1 Arabidopsis inflorescence
BIOINFORMATICS LAB AP BIOLOGY
 BIOINFORMATICS LAB AP BIOLOGY Bioinformatics is the science of collecting and analyzing complex biological data. Bioinformatics combines computer science, statistics and biology to allow scientists to
BIOINFORMATICS LAB AP BIOLOGY Bioinformatics is the science of collecting and analyzing complex biological data. Bioinformatics combines computer science, statistics and biology to allow scientists to
Comparative RNA-seq analysis of transcriptome dynamics during petal development in Rosa chinensis
 Title Comparative RNA-seq analysis of transcriptome dynamics during petal development in Rosa chinensis Author list Yu Han 1, Huihua Wan 1, Tangren Cheng 1, Jia Wang 1, Weiru Yang 1, Huitang Pan 1* & Qixiang
Title Comparative RNA-seq analysis of transcriptome dynamics during petal development in Rosa chinensis Author list Yu Han 1, Huihua Wan 1, Tangren Cheng 1, Jia Wang 1, Weiru Yang 1, Huitang Pan 1* & Qixiang
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3848
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
The Research Plan. Functional Genomics Research Stream. Transcription Factors. Tuning In Is A Good Idea
 Functional Genomics Research Stream The Research Plan Tuning In Is A Good Idea Research Meeting: March 23, 2010 The Road to Publication Transcription Factors Protein that binds specific DNA sequences controlling
Functional Genomics Research Stream The Research Plan Tuning In Is A Good Idea Research Meeting: March 23, 2010 The Road to Publication Transcription Factors Protein that binds specific DNA sequences controlling
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems
 Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Genomics and bioinformatics summary. Finding genes -- computer searches
 Genomics and bioinformatics summary 1. Gene finding: computer searches, cdnas, ESTs, 2. Microarrays 3. Use BLAST to find homologous sequences 4. Multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) 5. Trees quantify sequence
Genomics and bioinformatics summary 1. Gene finding: computer searches, cdnas, ESTs, 2. Microarrays 3. Use BLAST to find homologous sequences 4. Multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) 5. Trees quantify sequence
Statistical Inferences for Isoform Expression in RNA-Seq
 Statistical Inferences for Isoform Expression in RNA-Seq Hui Jiang and Wing Hung Wong February 25, 2009 Abstract The development of RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) makes it possible for us to measure transcription
Statistical Inferences for Isoform Expression in RNA-Seq Hui Jiang and Wing Hung Wong February 25, 2009 Abstract The development of RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) makes it possible for us to measure transcription
DEGseq: an R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data
 DEGseq: an R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data Likun Wang Zhixing Feng i Wang iaowo Wang * and uegong Zhang * MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinformatics and Bioinformatics
DEGseq: an R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data Likun Wang Zhixing Feng i Wang iaowo Wang * and uegong Zhang * MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinformatics and Bioinformatics
The Developmental Transcriptome of the Mosquito Aedes aegypti, an invasive species and major arbovirus vector.
 The Developmental Transcriptome of the Mosquito Aedes aegypti, an invasive species and major arbovirus vector. Omar S. Akbari*, Igor Antoshechkin*, Henry Amrhein, Brian Williams, Race Diloreto, Jeremy
The Developmental Transcriptome of the Mosquito Aedes aegypti, an invasive species and major arbovirus vector. Omar S. Akbari*, Igor Antoshechkin*, Henry Amrhein, Brian Williams, Race Diloreto, Jeremy
Supplementary Information. Drought response transcriptomics are altered in poplar with reduced tonoplast sucrose transporter expression
 Supplementary Information Drought response transcriptomics are altered in poplar with reduced tonoplast sucrose transporter expression Liang Jiao Xue, Christopher J. Frost, Chung Jui Tsai, Scott A. Harding
Supplementary Information Drought response transcriptomics are altered in poplar with reduced tonoplast sucrose transporter expression Liang Jiao Xue, Christopher J. Frost, Chung Jui Tsai, Scott A. Harding
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Supplemental Data. Perrella et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Small RNA in rice genome
 Vol. 45 No. 5 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series C) October 2002 Small RNA in rice genome WANG Kai ( 1, ZHU Xiaopeng ( 2, ZHONG Lan ( 1,3 & CHEN Runsheng ( 1,2 1. Beijing Genomics Institute/Center of Genomics and
Vol. 45 No. 5 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series C) October 2002 Small RNA in rice genome WANG Kai ( 1, ZHU Xiaopeng ( 2, ZHONG Lan ( 1,3 & CHEN Runsheng ( 1,2 1. Beijing Genomics Institute/Center of Genomics and
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 26. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 26 Fruit fly chromosome 12-5 Gene Regulation Mouse chromosomes Fruit fly embryo Mouse embryo Adult fruit fly Adult mouse 2 of 26 Gene Regulation: An Example Gene Regulation: An Example
Biology Biology 1 of 26 Fruit fly chromosome 12-5 Gene Regulation Mouse chromosomes Fruit fly embryo Mouse embryo Adult fruit fly Adult mouse 2 of 26 Gene Regulation: An Example Gene Regulation: An Example
ChIP-seq analysis M. Defrance, C. Herrmann, S. Le Gras, D. Puthier, M. Thomas.Chollier
 ChIP-seq analysis M. Defrance, C. Herrmann, S. Le Gras, D. Puthier, M. Thomas.Chollier Data visualization, quality control, normalization & peak calling Peak annotation Presentation () Practical session
ChIP-seq analysis M. Defrance, C. Herrmann, S. Le Gras, D. Puthier, M. Thomas.Chollier Data visualization, quality control, normalization & peak calling Peak annotation Presentation () Practical session
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control
 BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control Lecture 24 Unregulated Gene Expression Model Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 The genetic material inside a cell, encoded in its DNA, governs the response of a cell to various
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control Lecture 24 Unregulated Gene Expression Model Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 The genetic material inside a cell, encoded in its DNA, governs the response of a cell to various
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles
 Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
TRANSCRIPTOMICS. (or the analysis of the transcriptome) Mario Cáceres. Main objectives of genomics. Determine the entire DNA sequence of an organism
 TRANSCRIPTOMICS (or the analysis of the transcriptome) Mario Cáceres Main objectives of genomics Determine the entire DNA sequence of an organism Identify and annotate the complete set of genes encoded
TRANSCRIPTOMICS (or the analysis of the transcriptome) Mario Cáceres Main objectives of genomics Determine the entire DNA sequence of an organism Identify and annotate the complete set of genes encoded
Next Generation Science Standards Life Science Performance Expectations
 A Correlation of Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 12 th Edition, 2018 To the Life Science Performance Expectations HS-LS1 From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes HS-LS1-1. Construct
A Correlation of Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 12 th Edition, 2018 To the Life Science Performance Expectations HS-LS1 From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes HS-LS1-1. Construct
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Breker et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201301120/dc1 Figure S1. Single-cell proteomics of stress responses. (a) Using
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Breker et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201301120/dc1 Figure S1. Single-cell proteomics of stress responses. (a) Using
RNASeq Differential Expression
 12/06/2014 RNASeq Differential Expression Le Corguillé v1.01 1 Introduction RNASeq No previous genomic sequence information is needed In RNA-seq the expression signal of a transcript is limited by the
12/06/2014 RNASeq Differential Expression Le Corguillé v1.01 1 Introduction RNASeq No previous genomic sequence information is needed In RNA-seq the expression signal of a transcript is limited by the
Transcription Regulation and Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS08 Pharmacenter/Biocenter Auditorium 1 Wednesdays 16h15-18h00.
 Transcription Regulation and Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS08 Pharmacenter/Biocenter Auditorium 1 Wednesdays 16h15-18h00. Promoters and Enhancers Systematic discovery of transcriptional regulatory motifs
Transcription Regulation and Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS08 Pharmacenter/Biocenter Auditorium 1 Wednesdays 16h15-18h00. Promoters and Enhancers Systematic discovery of transcriptional regulatory motifs
Going Beyond SNPs with Next Genera5on Sequencing Technology Personalized Medicine: Understanding Your Own Genome Fall 2014
 Going Beyond SNPs with Next Genera5on Sequencing Technology 02-223 Personalized Medicine: Understanding Your Own Genome Fall 2014 Next Genera5on Sequencing Technology (NGS) NGS technology Discover more
Going Beyond SNPs with Next Genera5on Sequencing Technology 02-223 Personalized Medicine: Understanding Your Own Genome Fall 2014 Next Genera5on Sequencing Technology (NGS) NGS technology Discover more
Motifs and Logos. Six Introduction to Bioinformatics. Importance and Abundance of Motifs. Getting the CDS. From DNA to Protein 6.1.
 Motifs and Logos Six Discovering Genomics, Proteomics, and Bioinformatics by A. Malcolm Campbell and Laurie J. Heyer Chapter 2 Genome Sequence Acquisition and Analysis Sami Khuri Department of Computer
Motifs and Logos Six Discovering Genomics, Proteomics, and Bioinformatics by A. Malcolm Campbell and Laurie J. Heyer Chapter 2 Genome Sequence Acquisition and Analysis Sami Khuri Department of Computer
BIOINFORMATICS ORIGINAL PAPER
 BIOINFORMATICS ORIGINAL PAPER Vol. 25 no. 8 29, pages 126 132 doi:1.193/bioinformatics/btp113 Gene expression Statistical inferences for isoform expression in RNA-Seq Hui Jiang 1 and Wing Hung Wong 2,
BIOINFORMATICS ORIGINAL PAPER Vol. 25 no. 8 29, pages 126 132 doi:1.193/bioinformatics/btp113 Gene expression Statistical inferences for isoform expression in RNA-Seq Hui Jiang 1 and Wing Hung Wong 2,
The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression. The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression. A. The Eukaryotic Genome. Lecture Series 11
 The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression Lecture Series 11 The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression A. The Eukaryotic Genome B. Repetitive Sequences (rem: teleomeres) C. The Structures of Protein-Coding
The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression Lecture Series 11 The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression A. The Eukaryotic Genome B. Repetitive Sequences (rem: teleomeres) C. The Structures of Protein-Coding
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A versatile genome-scale PCR-based pipeline for high-definition DNA FISH Magda Bienko,, Nicola Crosetto,, Leonid Teytelman, Sandy Klemm, Shalev Itzkovitz & Alexander van Oudenaarden,,
Supplementary Information A versatile genome-scale PCR-based pipeline for high-definition DNA FISH Magda Bienko,, Nicola Crosetto,, Leonid Teytelman, Sandy Klemm, Shalev Itzkovitz & Alexander van Oudenaarden,,
Statistics for Differential Expression in Sequencing Studies. Naomi Altman
 Statistics for Differential Expression in Sequencing Studies Naomi Altman naomi@stat.psu.edu Outline Preliminaries what you need to do before the DE analysis Stat Background what you need to know to understand
Statistics for Differential Expression in Sequencing Studies Naomi Altman naomi@stat.psu.edu Outline Preliminaries what you need to do before the DE analysis Stat Background what you need to know to understand
ChIP seq peak calling. Statistical integration between ChIP seq and RNA seq
 Institute for Computational Biomedicine ChIP seq peak calling Statistical integration between ChIP seq and RNA seq Olivier Elemento, PhD ChIP-seq to map where transcription factors bind DNA Transcription
Institute for Computational Biomedicine ChIP seq peak calling Statistical integration between ChIP seq and RNA seq Olivier Elemento, PhD ChIP-seq to map where transcription factors bind DNA Transcription
Geert Geeven. April 14, 2010
 iction of Gene Regulatory Interactions NDNS+ Workshop April 14, 2010 Today s talk - Outline Outline Biological Background Construction of Predictors The main aim of my project is to better understand the
iction of Gene Regulatory Interactions NDNS+ Workshop April 14, 2010 Today s talk - Outline Outline Biological Background Construction of Predictors The main aim of my project is to better understand the
itraq and RNA-Seq analyses provide new insights of Dendrobium officinale seeds (Orchidaceae)
 Page S-1 Supporting Information (SI) itraq and RNA-Seq analyses provide new insights into regulation mechanism of symbiotic germination of Dendrobium officinale seeds (Orchidaceae) Juan Chen 1, Si Si Liu
Page S-1 Supporting Information (SI) itraq and RNA-Seq analyses provide new insights into regulation mechanism of symbiotic germination of Dendrobium officinale seeds (Orchidaceae) Juan Chen 1, Si Si Liu
Introduction to Bioinformatics. Shifra Ben-Dor Irit Orr
 Introduction to Bioinformatics Shifra Ben-Dor Irit Orr Lecture Outline: Technical Course Items Introduction to Bioinformatics Introduction to Databases This week and next week What is bioinformatics? A
Introduction to Bioinformatics Shifra Ben-Dor Irit Orr Lecture Outline: Technical Course Items Introduction to Bioinformatics Introduction to Databases This week and next week What is bioinformatics? A
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression
 Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Resveratrol Serves as a Protein-Substrate Interaction Stabilizer in Human SIRT1 Activation Xuben Hou,, David Rooklin, Hao Fang *,,, Yingkai Zhang Department of Medicinal Chemistry
Supplementary Information Resveratrol Serves as a Protein-Substrate Interaction Stabilizer in Human SIRT1 Activation Xuben Hou,, David Rooklin, Hao Fang *,,, Yingkai Zhang Department of Medicinal Chemistry
Dynamic modular architecture of protein-protein interaction networks beyond the dichotomy of date and party hubs
 Dynamic modular architecture of protein-protein interaction networks beyond the dichotomy of date and party hubs Xiao Chang 1,#, Tao Xu 2,#, Yun Li 3, Kai Wang 1,4,5,* 1 Zilkha Neurogenetic Institute,
Dynamic modular architecture of protein-protein interaction networks beyond the dichotomy of date and party hubs Xiao Chang 1,#, Tao Xu 2,#, Yun Li 3, Kai Wang 1,4,5,* 1 Zilkha Neurogenetic Institute,
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
Whole-genome analysis of GCN4 binding in S.cerevisiae
 Whole-genome analysis of GCN4 binding in S.cerevisiae Lillian Dai Alex Mallet Gcn4/DNA diagram (CREB symmetric site and AP-1 asymmetric site: Song Tan, 1999) removed for copyright reasons. What is GCN4?
Whole-genome analysis of GCN4 binding in S.cerevisiae Lillian Dai Alex Mallet Gcn4/DNA diagram (CREB symmetric site and AP-1 asymmetric site: Song Tan, 1999) removed for copyright reasons. What is GCN4?
Technologie w skali genomowej 2/ Algorytmiczne i statystyczne aspekty sekwencjonowania DNA
 Technologie w skali genomowej 2/ Algorytmiczne i statystyczne aspekty sekwencjonowania DNA Expression analysis for RNA-seq data Ewa Szczurek Instytut Informatyki Uniwersytet Warszawski 1/35 The problem
Technologie w skali genomowej 2/ Algorytmiczne i statystyczne aspekty sekwencjonowania DNA Expression analysis for RNA-seq data Ewa Szczurek Instytut Informatyki Uniwersytet Warszawski 1/35 The problem
ChIP-seq analysis M. Defrance, C. Herrmann, S. Le Gras, D. Puthier, M. Thomas.Chollier
 ChIP-seq analysis M. Defrance, C. Herrmann, S. Le Gras, D. Puthier, M. Thomas.Chollier Visualization, quality, normalization & peak-calling Presentation (Carl Herrmann) Practical session Peak annotation
ChIP-seq analysis M. Defrance, C. Herrmann, S. Le Gras, D. Puthier, M. Thomas.Chollier Visualization, quality, normalization & peak-calling Presentation (Carl Herrmann) Practical session Peak annotation
Title: A novel mechanism of protein thermostability: a unique N-terminal domain confers
 1 2 Title: A novel mechanism of protein thermostability: a unique N-terminal domain confers heat resistance to Fe/Mn-SODs 3 4 Running Title: Thermostability-improving peptide for SODs 5 6 7 8 Authors Wei
1 2 Title: A novel mechanism of protein thermostability: a unique N-terminal domain confers heat resistance to Fe/Mn-SODs 3 4 Running Title: Thermostability-improving peptide for SODs 5 6 7 8 Authors Wei
GS Analysis of Microarray Data
 GS01 0163 Analysis of Microarray Data Keith Baggerly and Bradley Broom Department of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology UT M. D. Anderson Cancer Center kabagg@mdanderson.org bmbroom@mdanderson.org
GS01 0163 Analysis of Microarray Data Keith Baggerly and Bradley Broom Department of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology UT M. D. Anderson Cancer Center kabagg@mdanderson.org bmbroom@mdanderson.org
Systematic comparison of lncrnas with protein coding mrnas in population expression and their response to environmental change
 Xu et al. BMC Plant Biology (2017) 17:42 DOI 10.1186/s12870-017-0984-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Systematic comparison of lncrnas with protein coding mrnas in population expression and their response
Xu et al. BMC Plant Biology (2017) 17:42 DOI 10.1186/s12870-017-0984-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Systematic comparison of lncrnas with protein coding mrnas in population expression and their response
Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans, two fruit fly species that are nearly
 Comparative Genomics: Human versus chimpanzee 1. Introduction The chimpanzee is the closest living relative to humans. The two species are nearly identical in DNA sequence (>98% identity), yet vastly different
Comparative Genomics: Human versus chimpanzee 1. Introduction The chimpanzee is the closest living relative to humans. The two species are nearly identical in DNA sequence (>98% identity), yet vastly different
Bioinformatics and BLAST
 Bioinformatics and BLAST Overview Recap of last time Similarity discussion Algorithms: Needleman-Wunsch Smith-Waterman BLAST Implementation issues and current research Recap from Last Time Genome consists
Bioinformatics and BLAST Overview Recap of last time Similarity discussion Algorithms: Needleman-Wunsch Smith-Waterman BLAST Implementation issues and current research Recap from Last Time Genome consists
GS Analysis of Microarray Data
 GS01 0163 Analysis of Microarray Data Keith Baggerly and Kevin Coombes Section of Bioinformatics Department of Biostatistics and Applied Mathematics UT M. D. Anderson Cancer Center kabagg@mdanderson.org
GS01 0163 Analysis of Microarray Data Keith Baggerly and Kevin Coombes Section of Bioinformatics Department of Biostatistics and Applied Mathematics UT M. D. Anderson Cancer Center kabagg@mdanderson.org
BLAST. Varieties of BLAST
 BLAST Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (1990) Altschul, Gish, Miller, Myers, & Lipman Uses short-cuts or heuristics to improve search speed Like speed-reading, does not examine every nucleotide of database
BLAST Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (1990) Altschul, Gish, Miller, Myers, & Lipman Uses short-cuts or heuristics to improve search speed Like speed-reading, does not examine every nucleotide of database
GS Analysis of Microarray Data
 GS01 0163 Analysis of Microarray Data Keith Baggerly and Kevin Coombes Section of Bioinformatics Department of Biostatistics and Applied Mathematics UT M. D. Anderson Cancer Center kabagg@mdanderson.org
GS01 0163 Analysis of Microarray Data Keith Baggerly and Kevin Coombes Section of Bioinformatics Department of Biostatistics and Applied Mathematics UT M. D. Anderson Cancer Center kabagg@mdanderson.org
Complete all warm up questions Focus on operon functioning we will be creating operon models on Monday
 Complete all warm up questions Focus on operon functioning we will be creating operon models on Monday 1. What is the Central Dogma? 2. How does prokaryotic DNA compare to eukaryotic DNA? 3. How is DNA
Complete all warm up questions Focus on operon functioning we will be creating operon models on Monday 1. What is the Central Dogma? 2. How does prokaryotic DNA compare to eukaryotic DNA? 3. How is DNA
REVIEW SESSION. Wednesday, September 15 5:30 PM SHANTZ 242 E
 REVIEW SESSION Wednesday, September 15 5:30 PM SHANTZ 242 E Gene Regulation Gene Regulation Gene expression can be turned on, turned off, turned up or turned down! For example, as test time approaches,
REVIEW SESSION Wednesday, September 15 5:30 PM SHANTZ 242 E Gene Regulation Gene Regulation Gene expression can be turned on, turned off, turned up or turned down! For example, as test time approaches,
GFP GAL bp 3964 bp
 Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary information S1 (box). Supplementary Methods description. Prokaryotic Genome Database Archaeal and bacterial genome sequences were downloaded from the NCBI FTP site (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/)
Supplementary information S1 (box). Supplementary Methods description. Prokaryotic Genome Database Archaeal and bacterial genome sequences were downloaded from the NCBI FTP site (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/)
Computational Systems Biology
 Computational Systems Biology Vasant Honavar Artificial Intelligence Research Laboratory Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Graduate Program Center for Computational Intelligence, Learning, & Discovery
Computational Systems Biology Vasant Honavar Artificial Intelligence Research Laboratory Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Graduate Program Center for Computational Intelligence, Learning, & Discovery
Package NarrowPeaks. September 24, 2012
 Package NarrowPeaks September 24, 2012 Version 1.0.1 Date 2012-03-15 Type Package Title Functional Principal Component Analysis to Narrow Down Transcription Factor Binding Site Candidates Author Pedro
Package NarrowPeaks September 24, 2012 Version 1.0.1 Date 2012-03-15 Type Package Title Functional Principal Component Analysis to Narrow Down Transcription Factor Binding Site Candidates Author Pedro
Exhaustive search. CS 466 Saurabh Sinha
 Exhaustive search CS 466 Saurabh Sinha Agenda Two different problems Restriction mapping Motif finding Common theme: exhaustive search of solution space Reading: Chapter 4. Restriction Mapping Restriction
Exhaustive search CS 466 Saurabh Sinha Agenda Two different problems Restriction mapping Motif finding Common theme: exhaustive search of solution space Reading: Chapter 4. Restriction Mapping Restriction
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material Protocol S1 The PromPredict algorithm considers the average free energy over a 100nt window and compares it with the the average free energy over a downstream 100nt window separated
Supplemental Material Protocol S1 The PromPredict algorithm considers the average free energy over a 100nt window and compares it with the the average free energy over a downstream 100nt window separated
RNA Synthesis and Processing
 RNA Synthesis and Processing Introduction Regulation of gene expression allows cells to adapt to environmental changes and is responsible for the distinct activities of the differentiated cell types that
RNA Synthesis and Processing Introduction Regulation of gene expression allows cells to adapt to environmental changes and is responsible for the distinct activities of the differentiated cell types that
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic pipeline for single-cell genome assembly, cleaning and annotation. a. The assembly process was optimized to account for multiple cells putatively
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic pipeline for single-cell genome assembly, cleaning and annotation. a. The assembly process was optimized to account for multiple cells putatively
Grundlagen der Bioinformatik Summer semester Lecturer: Prof. Daniel Huson
 Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 12, 2010 1 1 Introduction Grundlagen der Bioinformatik Summer semester 2010 Lecturer: Prof. Daniel Huson Office hours: Thursdays 17-18h (Sand 14, C310a)
Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 12, 2010 1 1 Introduction Grundlagen der Bioinformatik Summer semester 2010 Lecturer: Prof. Daniel Huson Office hours: Thursdays 17-18h (Sand 14, C310a)
Genomes and Their Evolution
 Chapter 21 Genomes and Their Evolution PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 21 Genomes and Their Evolution PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Genomic insights into the taxonomic status of the Bacillus cereus group. Laboratory of Marine Genetic Resources, Third Institute of Oceanography,
 1 2 3 Genomic insights into the taxonomic status of the Bacillus cereus group Yang Liu 1, Qiliang Lai 1, Markus Göker 2, Jan P. Meier-Kolthoff 2, Meng Wang 3, Yamin Sun 3, Lei Wang 3 and Zongze Shao 1*
1 2 3 Genomic insights into the taxonomic status of the Bacillus cereus group Yang Liu 1, Qiliang Lai 1, Markus Göker 2, Jan P. Meier-Kolthoff 2, Meng Wang 3, Yamin Sun 3, Lei Wang 3 and Zongze Shao 1*
Network Biology-part II
 Network Biology-part II Jun Zhu, Ph. D. Professor of Genomics and Genetic Sciences Icahn Institute of Genomics and Multi-scale Biology The Tisch Cancer Institute Icahn Medical School at Mount Sinai New
Network Biology-part II Jun Zhu, Ph. D. Professor of Genomics and Genetic Sciences Icahn Institute of Genomics and Multi-scale Biology The Tisch Cancer Institute Icahn Medical School at Mount Sinai New
Statistical analysis of genomic binding sites using high-throughput ChIP-seq data
 Statistical analysis of genomic binding sites using high-throughput ChIP-seq data Ibrahim Ali H Nafisah Department of Statistics University of Leeds Submitted in accordance with the requirments for the
Statistical analysis of genomic binding sites using high-throughput ChIP-seq data Ibrahim Ali H Nafisah Department of Statistics University of Leeds Submitted in accordance with the requirments for the
Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall
 Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall Review session 5pm Thursday, Dec. 11 GPB100 Fig. 1.13 RNA-seq Expression effects of cancer AAAAA AAAAA AAAAA Solexa sequencing counts
Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall Review session 5pm Thursday, Dec. 11 GPB100 Fig. 1.13 RNA-seq Expression effects of cancer AAAAA AAAAA AAAAA Solexa sequencing counts
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 reverse 3175 3175 F L C 318 318 3185 3185 319 319 3195 3195 315 8 1 315 3155 315 317 Supplementary Figure 3. Stability of expression of the GFP sensor constructs return to warm conditions. Semi-quantitative
reverse 3175 3175 F L C 318 318 3185 3185 319 319 3195 3195 315 8 1 315 3155 315 317 Supplementary Figure 3. Stability of expression of the GFP sensor constructs return to warm conditions. Semi-quantitative
Bioinformatics 2 - Lecture 4
 Bioinformatics 2 - Lecture 4 Guido Sanguinetti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh February 14, 2011 Sequences Many data types are ordered, i.e. you can naturally say what is before and what
Bioinformatics 2 - Lecture 4 Guido Sanguinetti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh February 14, 2011 Sequences Many data types are ordered, i.e. you can naturally say what is before and what
Supplemental Information. Inferring Cell-State Transition. Dynamics from Lineage Trees. and Endpoint Single-Cell Measurements
 Cell Systems, Volume 3 Supplemental Information Inferring Cell-State Transition Dynamics from Lineage Trees and Endpoint Single-Cell Measurements Sahand Hormoz, Zakary S. Singer, James M. Linton, Yaron
Cell Systems, Volume 3 Supplemental Information Inferring Cell-State Transition Dynamics from Lineage Trees and Endpoint Single-Cell Measurements Sahand Hormoz, Zakary S. Singer, James M. Linton, Yaron
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1
 Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR
Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR
A Brief Overview of Biochemistry. And I mean BRIEF!
 A Brief Overview of Biochemistry And I mean BRIEF! Introduction A. Chemistry deals with the composition of substances and how they change. B. A knowledge of chemistry is necessary for the understanding
A Brief Overview of Biochemistry And I mean BRIEF! Introduction A. Chemistry deals with the composition of substances and how they change. B. A knowledge of chemistry is necessary for the understanding
Isoform discovery and quantification from RNA-Seq data
 Isoform discovery and quantification from RNA-Seq data C. Toffano-Nioche, T. Dayris, Y. Boursin, M. Deloger November 2016 C. Toffano-Nioche, T. Dayris, Y. Boursin, M. Isoform Deloger discovery and quantification
Isoform discovery and quantification from RNA-Seq data C. Toffano-Nioche, T. Dayris, Y. Boursin, M. Deloger November 2016 C. Toffano-Nioche, T. Dayris, Y. Boursin, M. Isoform Deloger discovery and quantification
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice Supplementary Figure 2.
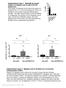 Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Department of Forensic Psychiatry, School of Medicine & Forensics, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China;
 Title: Evaluation of genetic susceptibility of common variants in CACNA1D with schizophrenia in Han Chinese Author names and affiliations: Fanglin Guan a,e, Lu Li b, Chuchu Qiao b, Gang Chen b, Tinglin
Title: Evaluation of genetic susceptibility of common variants in CACNA1D with schizophrenia in Han Chinese Author names and affiliations: Fanglin Guan a,e, Lu Li b, Chuchu Qiao b, Gang Chen b, Tinglin
3.B.1 Gene Regulation. Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization.
 3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula
 Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula Maheshi Dassanayake 1,9, Dong-Ha Oh 1,9, Jeffrey S. Haas 1,2, Alvaro Hernandez 3, Hyewon Hong 1,4, Shahjahan
Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula Maheshi Dassanayake 1,9, Dong-Ha Oh 1,9, Jeffrey S. Haas 1,2, Alvaro Hernandez 3, Hyewon Hong 1,4, Shahjahan
University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley U.C. Berkeley Division of Biostatistics Working Paper Series Year 2004 Paper 147 Multiple Testing Methods For ChIP-Chip High Density Oligonucleotide Array Data Sunduz
University of California, Berkeley U.C. Berkeley Division of Biostatistics Working Paper Series Year 2004 Paper 147 Multiple Testing Methods For ChIP-Chip High Density Oligonucleotide Array Data Sunduz
RiboTALE: A modular, inducible system for accurate gene expression control
 8 9 10 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 18 19 0 1 RiboTALE: A modular, inducible system for accurate gene expression control Navneet Rai, 1 Aura Ferreiro, Alexander Neckelmann, Amy Soon, Andrew Yao, 1, Justin Siegel, 1,,
8 9 10 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 18 19 0 1 RiboTALE: A modular, inducible system for accurate gene expression control Navneet Rai, 1 Aura Ferreiro, Alexander Neckelmann, Amy Soon, Andrew Yao, 1, Justin Siegel, 1,,
Supplemental Information. Anti-Inflammatory Chromatinscape. Suggests Alternative Mechanisms. of Glucocorticoid Receptor Action
 Immunity, Voume 7 Suppementa Information nti-infammatory Chromatinscape Suggests ternative Mechanisms of Gucocorticoid Receptor ction Kyu-Seon Oh, Heta Pate, Rache. Gottschak, Wai Shing Lee, Songjoon aek,
Immunity, Voume 7 Suppementa Information nti-infammatory Chromatinscape Suggests ternative Mechanisms of Gucocorticoid Receptor ction Kyu-Seon Oh, Heta Pate, Rache. Gottschak, Wai Shing Lee, Songjoon aek,
Bioinformatics. Transcriptome
 Bioinformatics Transcriptome Jacques.van.Helden@ulb.ac.be Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgique Laboratoire de Bioinformatique des Génomes et des Réseaux (BiGRe) http://www.bigre.ulb.ac.be/ Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics Transcriptome Jacques.van.Helden@ulb.ac.be Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgique Laboratoire de Bioinformatique des Génomes et des Réseaux (BiGRe) http://www.bigre.ulb.ac.be/ Bioinformatics
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.1 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HISTORY OF GENETICS The earliest use of genetics was through of plants and animals (8000-1000 B.C.) Selective breeding (artificial selection) is the process of breeding organisms
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HISTORY OF GENETICS The earliest use of genetics was through of plants and animals (8000-1000 B.C.) Selective breeding (artificial selection) is the process of breeding organisms
Lesson 11. Functional Genomics I: Microarray Analysis
 Lesson 11 Functional Genomics I: Microarray Analysis Transcription of DNA and translation of RNA vary with biological conditions 3 kinds of microarray platforms Spotted Array - 2 color - Pat Brown (Stanford)
Lesson 11 Functional Genomics I: Microarray Analysis Transcription of DNA and translation of RNA vary with biological conditions 3 kinds of microarray platforms Spotted Array - 2 color - Pat Brown (Stanford)
RNAseq Applications in Genome Studies. Alexander Kanapin, PhD Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford
 RNAseq Applications in Genome Studies Alexander Kanapin, PhD Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford RNAseq Protocols } Next generation sequencing protocol } cdna, not RNA sequencing
RNAseq Applications in Genome Studies Alexander Kanapin, PhD Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford RNAseq Protocols } Next generation sequencing protocol } cdna, not RNA sequencing
Fast and simple fluorescent RNA quality assessment
 Fast and simple fluorescent RNA quality assessment Chris Vonnegut Presented at ASHG Laboratory CoLab Session October, The world leader in serving science RNA Quality and Quantity RNA Sample Isolation Cells
Fast and simple fluorescent RNA quality assessment Chris Vonnegut Presented at ASHG Laboratory CoLab Session October, The world leader in serving science RNA Quality and Quantity RNA Sample Isolation Cells
COMPARING DNA SEQUENCES TO UNDERSTAND EVOLUTIONARY RELATIONSHIPS WITH BLAST
 Big Idea 1 Evolution INVESTIGATION 3 COMPARING DNA SEQUENCES TO UNDERSTAND EVOLUTIONARY RELATIONSHIPS WITH BLAST How can bioinformatics be used as a tool to determine evolutionary relationships and to
Big Idea 1 Evolution INVESTIGATION 3 COMPARING DNA SEQUENCES TO UNDERSTAND EVOLUTIONARY RELATIONSHIPS WITH BLAST How can bioinformatics be used as a tool to determine evolutionary relationships and to
Newly made RNA is called primary transcript and is modified in three ways before leaving the nucleus:
 m Eukaryotic mrna processing Newly made RNA is called primary transcript and is modified in three ways before leaving the nucleus: Cap structure a modified guanine base is added to the 5 end. Poly-A tail
m Eukaryotic mrna processing Newly made RNA is called primary transcript and is modified in three ways before leaving the nucleus: Cap structure a modified guanine base is added to the 5 end. Poly-A tail
Extensive Divergence of Transcription Factor Binding in Drosophila Embryos with Highly Conserved Gene Expression
 Extensive Divergence of Transcription Factor Binding in Drosophila Embryos with Highly Conserved Gene Expression Mathilde Paris 1 *, Tommy Kaplan 1,2, Xiao Yong Li 1,3, Jacqueline E. Villalta 2, Susan
Extensive Divergence of Transcription Factor Binding in Drosophila Embryos with Highly Conserved Gene Expression Mathilde Paris 1 *, Tommy Kaplan 1,2, Xiao Yong Li 1,3, Jacqueline E. Villalta 2, Susan
PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 11 Chapter 26 Activity #15 NAME DATE PERIOD PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS PHYLOGENY Evolutionary history of species or group of related species SYSTEMATICS Study
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 11 Chapter 26 Activity #15 NAME DATE PERIOD PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS PHYLOGENY Evolutionary history of species or group of related species SYSTEMATICS Study
DNA, Chromosomes, and Genes
 N, hromosomes, and Genes 1 You have most likely already learned about deoxyribonucleic acid (N), chromosomes, and genes. You have learned that all three of these substances have something to do with heredity
N, hromosomes, and Genes 1 You have most likely already learned about deoxyribonucleic acid (N), chromosomes, and genes. You have learned that all three of these substances have something to do with heredity
Supplemental Materials
 JOURNAL OF MICROBIOLOGY & BIOLOGY EDUCATION, May 2013, p. 107-109 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v14i1.496 Supplemental Materials for Engaging Students in a Bioinformatics Activity to Introduce Gene
JOURNAL OF MICROBIOLOGY & BIOLOGY EDUCATION, May 2013, p. 107-109 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v14i1.496 Supplemental Materials for Engaging Students in a Bioinformatics Activity to Introduce Gene
Chapter 18 Active Reading Guide Genomes and Their Evolution
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 18 Active Reading Guide Genomes and Their Evolution Most AP Biology teachers think this chapter involves an advanced topic. The questions posed here will help you understand
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 18 Active Reading Guide Genomes and Their Evolution Most AP Biology teachers think this chapter involves an advanced topic. The questions posed here will help you understand
Supplementary materials Quantitative assessment of ribosome drop-off in E. coli
 Supplementary materials Quantitative assessment of ribosome drop-off in E. coli Celine Sin, Davide Chiarugi, Angelo Valleriani 1 Downstream Analysis Supplementary Figure 1: Illustration of the core steps
Supplementary materials Quantitative assessment of ribosome drop-off in E. coli Celine Sin, Davide Chiarugi, Angelo Valleriani 1 Downstream Analysis Supplementary Figure 1: Illustration of the core steps
Tiffany Samaroo MB&B 452a December 8, Take Home Final. Topic 1
 Tiffany Samaroo MB&B 452a December 8, 2003 Take Home Final Topic 1 Prior to 1970, protein and DNA sequence alignment was limited to visual comparison. This was a very tedious process; even proteins with
Tiffany Samaroo MB&B 452a December 8, 2003 Take Home Final Topic 1 Prior to 1970, protein and DNA sequence alignment was limited to visual comparison. This was a very tedious process; even proteins with
Research Article Sample Size Calculation for Controlling False Discovery Proportion
 Probability and Statistics Volume 2012, Article ID 817948, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2012/817948 Research Article Sample Size Calculation for Controlling False Discovery Proportion Shulian Shang, 1 Qianhe Zhou,
Probability and Statistics Volume 2012, Article ID 817948, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2012/817948 Research Article Sample Size Calculation for Controlling False Discovery Proportion Shulian Shang, 1 Qianhe Zhou,
Annotation of Drosophila grimashawi Contig12
 Annotation of Drosophila grimashawi Contig12 Marshall Strother April 27, 2009 Contents 1 Overview 3 2 Genes 3 2.1 Genscan Feature 12.4............................................. 3 2.1.1 Genome Browser:
Annotation of Drosophila grimashawi Contig12 Marshall Strother April 27, 2009 Contents 1 Overview 3 2 Genes 3 2.1 Genscan Feature 12.4............................................. 3 2.1.1 Genome Browser:
Eukaryotic Gene Expression
 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Lectures 22-23 Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes From Mechanisms in Bacteria 123 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes
Eukaryotic Gene Expression Lectures 22-23 Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes From Mechanisms in Bacteria 123 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes
Course Syllabus. Biochemistry 107
 Course Syllabus Biochemistry 107 Spring/Summer 2007 University Health Science Antigua On-line 7 May - 6 August UHSA Bioch107 Course description Biochemistry and chemistry of biological materials: water,
Course Syllabus Biochemistry 107 Spring/Summer 2007 University Health Science Antigua On-line 7 May - 6 August UHSA Bioch107 Course description Biochemistry and chemistry of biological materials: water,
New RNA-seq workflows. Charlotte Soneson University of Zurich Brixen 2016
 New RNA-seq workflows Charlotte Soneson University of Zurich Brixen 2016 Wikipedia The traditional workflow ALIGNMENT COUNTING ANALYSIS Gene A Gene B... Gene X 7... 13............... The traditional workflow
New RNA-seq workflows Charlotte Soneson University of Zurich Brixen 2016 Wikipedia The traditional workflow ALIGNMENT COUNTING ANALYSIS Gene A Gene B... Gene X 7... 13............... The traditional workflow
