Chapter 7 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth
|
|
|
- Dwain Paul Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 7 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth Building Your Knowledge I) What is the process by which organisms acquire nutrients from the environment? 2) How do essential nutrients differ fro m nonessential nutrients? 3) Differentiate between micronutrients and macronutrients. Category Quantities Used Use in Bacterial Cell Examples Macronutrients Micronutrients 4) What is the difference between heterotrophs and autotrophs? Autotrophs get carbon from Heterotrophs get carbon from 5) How do photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs differ in how ihey get energy? Photoautotrophs get energy Chemoautotrophs get energy 6) Photosynthetic algae get carbon and energy from 7) Humans and most bacteria are (autotrophs or heterotrophs). 8) What is the difference between saprobes and parasites/pathogens? 9) Can obligate parasites be cultured using solid, synthetic media? 10) All viruses and some bacteria are obligate intracellular parasites. Name one bacterial species and one virus that is an obligate intracellular parasite. a. b
2 11) Without the addition of energy, do molecules move from high concentrations to low concentrations or from low concentrations to high concentrations? Explain your answer. 12) Draw a cell in hypertonic, isotonic and hypotonic solutions. Use x' s to indicate solute molecules. Which cells shrink? Which swell? Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic What does a bacterial cell wall protect against? 13) How are faci litated diffusion and active transport similar? How are they different? Do both require energy? 14) When is active transport necessary? What advantage does group translocation have over simple pumps? 15) What are the three cardinal temperatures of microbial growth? 16)00 all microbes have similar temperature ranges? Explain
3 17) What are psychrophiles, mesophiles, and thermophiles? Which are of concern to food microbiologists? Which are most commonly pathogenic? 18) How do the oxygen requirements of obligate aerobes, facultative anaerobes, microaerophiles and obligate anaerobes differ? 19) How would each grow in thioglycolate broth? Draw each test tube. Obligate aerobe Microaerophile Obligate Anaerobe Facultati ve Anaerobe 20) Halophiles live in extreme conditions. 21) Barophiles live in extreme conditions. 22) How do bacteria reproduce? Draw the process of binary fission below. 23) If you place 100 bacterial cells in media and their doubling time is 30 minutes, how many cells are in the media at the end of 5 hours?
4 24) Do all bacteria reproduce at the same rate? Explain and give examples. 25) Draw a growth curve of bacteria in batch culture, labeling lag phase, log phase, stationary phase and death phase. Time 26) Which stage has the fastest-growing bacteria? 27) Why do cultures move from log phase to stationary phase? 28) Why do cultures move from stationary to death phase? 29) How may we count bacteria? (list 3 ways) Which methods count live cells only?
5 Organizing Your Knowledge Type of Bacteria Psycbrophile Living Conditions Preferred Acidic ph Obligate anaerobe Small amounts of oxygen Alkalinophile Extreme salt conditions Osmophile Moderate temperatures Barophile Extreme heat Obligate Aerobe Can grow with or without oxygen Micronutrient Use in Bacterial Cells Potassium Sodium Calcium Magnesium Iron
6 Macronutrient Use in Bacterial Cells Source or Environmental Reservoir Carbon Autotrophs Heterotrophs Nitrogen Oxygen Phosphorus Sulfur Relationship Interaction (+/+, +/-, +/0, etc.) Symbiotic (yes/no?) Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Synergism Antagonism Stage of Growth What's Happening? Growth Speed Live/dead cell ratio Curve (fast/slow/level) Lag phase Exponential phase Stationary phase Death phase
7 Practicing Your Knowledge I. If placed in a hypertonic solution, most bacterial cells will - - a. burst if they lack a cell wall b. remain unchanged c. shrink and die d. change color 2. Bacteria preferring low temperatures for optimum growth are called. a. barophiles b. halophiles c. thermophiles d. psychrophiles 3. Macronutrients are required by cells in quantities and are used to _. a. small: boost enzyme function b. large: boost enzyme function c. small: form cell structures d. large: form cell structures 4. Which of the following methods measures live bacterial cells only? a. turbidity b. plate counts c. cytometer d. Coulter counter 5. Which of the following transport processes requires energy? a. diffusion b. osmosis c. facilitated diffusion d. group translocation 6. Which of the following microbial associations is NOT symbiotic? a. mutualism b. commensalism c. synergism d. parasitism 7. Which phase of the growth curve sees an equal rate of bacterial death and reproduction? a. lag phase b. stationary phase c. exponential phase d. death phase 8. Strict halophiles are commonly human pathogens. a. True b. False 9. Photosynthetic bacteria are considered _. a. nonexistent- bacteria don't have chloroplasts b. heterotrophs because they feed off dead things c. autotrophs because they get their carbon from carbon dioxide d. saprobes because they feed off dead things 10. As a bacterial culture grows, the media a. gets thicker because of all the bacteria b. gets cloudier because of all the bacteria c. gets wanner because of the heat generated by bacterial cells d. gets clearer because the bacteria consume all the nutrients I I. What is the correct order for a growth curve progression, with bacterial cells in batch culture? a. lag phase - exponential - stationary b. stationary - lag phase - exponential c. exponential - stationary - lag phase d. lag phase - stationary - exponential 12. Bacteria lacking superoxide dismutase and catalase are a. strict aerobes b. strict anaerobes c. facultative anaerobes d. strict acidophiles 13. What are the three cardinal temperatures for microbial growth? a. hypertonic, isotonic and hypotonic b. minimul11, maximum and optimum c. aerobic, anaerobic and microaerobic d. halophile, barophile, osl11ophile
8 14. Active transport mechanisms are req u ired to _ a. move nutrients from high to low concentrations b. move any nutrient across a plasma membrane c. complete facilitated diffusion d. move molecules from low to high concentrations 15. Most human pathogens are a. mesophiles b. psychrophiles c. thermophiles d. psychrotrophs
Chapter 6 Microbial Growth With a focus on Bacteria
 Chapter 6 Microbial Growth With a focus on Bacteria Temperature Minimum growth temperature Optimum growth temperature Maximum growth temperature Usually within a 30-40 degree range Microbial growth = increase
Chapter 6 Microbial Growth With a focus on Bacteria Temperature Minimum growth temperature Optimum growth temperature Maximum growth temperature Usually within a 30-40 degree range Microbial growth = increase
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria
 Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
What is measuring bacterial growth? Define all the techniques below, when you would use them, if they give an accurate count.
 NAS 161 Exam 3 Study Guide Define bacterial growth. What are the 2 methods of bacterial growth? What are the 4 phases of bacterial growth, what happens during each? Lag Log Stationary Decline Synchronous
NAS 161 Exam 3 Study Guide Define bacterial growth. What are the 2 methods of bacterial growth? What are the 4 phases of bacterial growth, what happens during each? Lag Log Stationary Decline Synchronous
The Prokaryotic World
 The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
KINGDOM MONERA. Bacterial Cell Shape 8/22/2010. The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
Outline. Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea. Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea
 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Classifying Prokaryotes: Eubacteria Plasma Membrane. Ribosomes. Plasmid (DNA) Capsule. Cytoplasm. Outer Membrane DNA. Flagellum.
 Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Organic Molecules: (All contain carbon) Inorganic Molecules: (Do NOT contain carbon)
 Organic Molecules: (All contain carbon) 1.) Carbohydrates: Quick source of energy 2.) Lipids: Long-term energy storage 3.) Proteins: Raw materials and enzyme action (catalysts) Inorganic Molecules: (Do
Organic Molecules: (All contain carbon) 1.) Carbohydrates: Quick source of energy 2.) Lipids: Long-term energy storage 3.) Proteins: Raw materials and enzyme action (catalysts) Inorganic Molecules: (Do
Biology I Midterm 2018 Study Guide
 Biology I Midterm 2018 Study Guide These questions are designed to get you thinking about all the concepts we have discussed from Chapters 1-11. However, you will be responsible for knowing ALL the information
Biology I Midterm 2018 Study Guide These questions are designed to get you thinking about all the concepts we have discussed from Chapters 1-11. However, you will be responsible for knowing ALL the information
Notes - Microbiology Monera
 Notes - Microbiology Monera Part 1 Classification - Kingdom moneran is more commonly known as bacteria. This is the largest kingdom with inhabitants covering almost every square metre of the planet! -
Notes - Microbiology Monera Part 1 Classification - Kingdom moneran is more commonly known as bacteria. This is the largest kingdom with inhabitants covering almost every square metre of the planet! -
COLLEGE OF THE NORTH ATLANTIC BIOLOGY Practice Final Exam
 COLLEGE OF THE NORTH ATLANTIC BIOLOGY 1170 Practice Final Exam Students please take note: This exam has been produced and distributed solely as a practice exam. The questions are similar to questions that
COLLEGE OF THE NORTH ATLANTIC BIOLOGY 1170 Practice Final Exam Students please take note: This exam has been produced and distributed solely as a practice exam. The questions are similar to questions that
Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes
 The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
9/8/2017. Bacteria and Archaea. Three domain system: The present tree of life. Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success
 5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
Untitled Document Eco Photo Cell resp Use the information below to answer the following question(s).
 Untitled Document Eco Photo Cell resp 25 1. Use the information below to answer the following question(s). The drawing below shows a field habitat. 3. An increase in which atmospheric gas would most likely
Untitled Document Eco Photo Cell resp 25 1. Use the information below to answer the following question(s). The drawing below shows a field habitat. 3. An increase in which atmospheric gas would most likely
MICROBIAL GROUPS CE 421/521
 MICROBIAL GROUPS CE 421/521 Chapter 10 in Vaccari et.al. www.ibuf.coartuja.csic.es www.environmentaleverage.com www.astrosurf.com www.lbl.gov www.library.thinkquest.org www.ecosys.uni-erlangen.de erlangen.de
MICROBIAL GROUPS CE 421/521 Chapter 10 in Vaccari et.al. www.ibuf.coartuja.csic.es www.environmentaleverage.com www.astrosurf.com www.lbl.gov www.library.thinkquest.org www.ecosys.uni-erlangen.de erlangen.de
Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria
 Unit: 3.1 Name: Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: None New Information: Bacteria Notes Basic Bacteria Facts Classification of Bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
Unit: 3.1 Name: Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: None New Information: Bacteria Notes Basic Bacteria Facts Classification of Bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
Microbial Nutrition and Growth
 Microbial Nutrition and Growth Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College Some of the information relating to microbial nutrition and growth has been presented in previous
Microbial Nutrition and Growth Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College Some of the information relating to microbial nutrition and growth has been presented in previous
Chapter 1. Basics of Microbiology
 Chapter 1 Basics of Microbiology Objectives How microorganisms are classified (taxonomy) What they look like (morphology) The major divisions among microorganisms based upon their function in the environment
Chapter 1 Basics of Microbiology Objectives How microorganisms are classified (taxonomy) What they look like (morphology) The major divisions among microorganisms based upon their function in the environment
Know Your Microbes Introduction to food microbiology Factors affecting microbial growth Temperature Time
 Know Your Microbes Know Your Microbes Introduction to food microbiology Factors affecting microbial growth Temperature Time ph Water activity (Aw) Nutrient availability Atmosphere Hurdle technology Foodborne
Know Your Microbes Know Your Microbes Introduction to food microbiology Factors affecting microbial growth Temperature Time ph Water activity (Aw) Nutrient availability Atmosphere Hurdle technology Foodborne
Unit 5. Organisms C H A P T E R 1 5. Bacteria: Unicellular R E A D P
 Unit 5 Bacteria: Unicellular Organisms C H A P T E R 1 5 R E A D P. 2 9 3-305 Bacterial Cell Structure: Prokaryotic Single cellular no membrane bound organelles primitive Parts of Bacteria 1. Cell membrane
Unit 5 Bacteria: Unicellular Organisms C H A P T E R 1 5 R E A D P. 2 9 3-305 Bacterial Cell Structure: Prokaryotic Single cellular no membrane bound organelles primitive Parts of Bacteria 1. Cell membrane
Game plan Lecture Lab Prelabs
 Game plan Lecture Binary fission Growth curves Physical requirements for growth Chemical requirements for growth Lab Lab Exam Prelabs Growth Curve Bring books and APO-3 for next class Microbial growth
Game plan Lecture Binary fission Growth curves Physical requirements for growth Chemical requirements for growth Lab Lab Exam Prelabs Growth Curve Bring books and APO-3 for next class Microbial growth
Characteristics. Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome
 Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are of immense importance because of their rapid growth, reproduction, and mutation rates, as well as, their ability to exist under adverse conditions. The oldest
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are of immense importance because of their rapid growth, reproduction, and mutation rates, as well as, their ability to exist under adverse conditions. The oldest
General concepts, history. Microscopy and staining. Review Questions-1
 Review Questions-1 General concepts, history What was the technique that Carl Woese used to identify another domain to classify m/o in? How did Pasteur help resolve the debate on spontaneous generation?
Review Questions-1 General concepts, history What was the technique that Carl Woese used to identify another domain to classify m/o in? How did Pasteur help resolve the debate on spontaneous generation?
The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms
 Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & Eubacteria)
 Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Announcements KEY CONCEPTS
 What do these things have in common? Announcements Lab this week: bring textbook and photo atlas. Relevant reading BEFORE lab: Ch. 30 http://i.cnn.net/cnn/specials/2001/trade.center/images/anthrax.jpg
What do these things have in common? Announcements Lab this week: bring textbook and photo atlas. Relevant reading BEFORE lab: Ch. 30 http://i.cnn.net/cnn/specials/2001/trade.center/images/anthrax.jpg
TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING
 BACTERIA! TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING PROKARYOTES KINGDOM EUBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA CHARACTERISTICS: 1. NO NUCLEUS 2. NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES 4. MOST ARE SMALLER THAN EUKARYOTES 5. ARE SINGLE-CELLED
BACTERIA! TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING PROKARYOTES KINGDOM EUBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA CHARACTERISTICS: 1. NO NUCLEUS 2. NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES 4. MOST ARE SMALLER THAN EUKARYOTES 5. ARE SINGLE-CELLED
Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea
 Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Plant Function. KEB no office hour on Monday 23 March. Chs 38, 39 (parts), March 2009 ECOL 182R UofA K. E. Bonine
 Plant Function Chs 38, 39 (parts), 40 KEB no office hour on Monday 23 March 10 March 2009 ECOL 182R UofA K. E. Bonine Videos: 39.3, 34.3, 39.1, 34.1 Web Browser Open 1 Video 39.3 Pollination of a night-blooming
Plant Function Chs 38, 39 (parts), 40 KEB no office hour on Monday 23 March 10 March 2009 ECOL 182R UofA K. E. Bonine Videos: 39.3, 34.3, 39.1, 34.1 Web Browser Open 1 Video 39.3 Pollination of a night-blooming
Biology Fall Semester Exam Review. Unit 1: Scientific method, characteristics of life What are the characteristics of life (pg. 6)
 Biology Fall Semester Exam Review Unit 1: Scientific method, characteristics of life What are the characteristics of life (pg. 6) Define the following terms: biology observation hypothesis dependent variable
Biology Fall Semester Exam Review Unit 1: Scientific method, characteristics of life What are the characteristics of life (pg. 6) Define the following terms: biology observation hypothesis dependent variable
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 DIRECTED READING Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 5-1: Energy and Living Things Energy Flows Between Organisms in Living Systems In the space provided, write the
Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 DIRECTED READING Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 5-1: Energy and Living Things Energy Flows Between Organisms in Living Systems In the space provided, write the
Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages )
 Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour
 MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour STATION A: MICROSCOPY 1. A microscope has an 10 objective and oculars of 4X, 10X, 40X and 100X. What is the range of magnification for this microscope.
MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour STATION A: MICROSCOPY 1. A microscope has an 10 objective and oculars of 4X, 10X, 40X and 100X. What is the range of magnification for this microscope.
Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle
 Chapter 8 Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle In your textbook, read about osmosis: diffusion of water. Reinforcement and Study Guide Section 8.1 Cellular Transport Complete the table by checking the
Chapter 8 Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle In your textbook, read about osmosis: diffusion of water. Reinforcement and Study Guide Section 8.1 Cellular Transport Complete the table by checking the
Answer Key- Biology Review for Fall Benchmark
 Name Class Answer Key- Biology Review for Fall Benchmark Definitions You should know what every word on this page means. Look through the entire review sheet and highlight any words you do not recognize.
Name Class Answer Key- Biology Review for Fall Benchmark Definitions You should know what every word on this page means. Look through the entire review sheet and highlight any words you do not recognize.
Classification. Old 5 Kingdom system. New 3 Domain system. reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence
 Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Biology Midterm Test Review
 Biology Midterm Test Review Levels of Organization 1. Put these levels of organization in order from simplest to most complex (smallest to largest): cell, community, atom, organism, biosphere, organ system,
Biology Midterm Test Review Levels of Organization 1. Put these levels of organization in order from simplest to most complex (smallest to largest): cell, community, atom, organism, biosphere, organ system,
Biology Test 2 BIO.2c-d: Metabolic Processes. For questions 1 16, choose the best answer. Indicate your answer on the Scantron and on the test.
 Name Block Date Biology Test 2 BIO.2c-d: Metabolic Processes For questions 1 16, choose the best answer. Indicate your answer on the Scantron and on the test. 1. Scientists hypothesize that oxygen began
Name Block Date Biology Test 2 BIO.2c-d: Metabolic Processes For questions 1 16, choose the best answer. Indicate your answer on the Scantron and on the test. 1. Scientists hypothesize that oxygen began
Name: Characteristics of Life and Ecology Guided Notes (PAP)
 Name: Characteristics of Life and Ecology Guided Notes (PAP) I. What is Biology? a. Biology is the study of II. The Eight Characteristics of Life a. Organization & the presence of or more cells b. Response
Name: Characteristics of Life and Ecology Guided Notes (PAP) I. What is Biology? a. Biology is the study of II. The Eight Characteristics of Life a. Organization & the presence of or more cells b. Response
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 (p471-477) 2 of 40 Microorganisms = Microbes Microbiology is the study of living creatures too small to see with the unaided eye including : bacteria protozoa fungi algae viruses other
Biology 1 of 40 (p471-477) 2 of 40 Microorganisms = Microbes Microbiology is the study of living creatures too small to see with the unaided eye including : bacteria protozoa fungi algae viruses other
(A) Exotoxin (B) Endotoxin (C) Cilia (D) Flagella (E) Capsule. A. Incorrect! Only gram-positive bacteria secrete exotoxin.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 13: Prokaryots and Protists Question No. 1 of 10 1. Gram-negative bacteria can cause disease in humans by release of what substance? Question #01 (A) Exotoxin (B) Endotoxin
College Biology - Problem Drill 13: Prokaryots and Protists Question No. 1 of 10 1. Gram-negative bacteria can cause disease in humans by release of what substance? Question #01 (A) Exotoxin (B) Endotoxin
Cells & Bacteria Notes
 Cells & Bacteria Notes 4 Major Macromolecules Macromolecules are large molecules. The four groups of macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of a cell. Group Building Block Large Molecule
Cells & Bacteria Notes 4 Major Macromolecules Macromolecules are large molecules. The four groups of macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of a cell. Group Building Block Large Molecule
Plant Function Chs 38, 39 (parts), 40
 Plant Function Chs 38, 39 (parts), 40 KEB no office hour on Monday 23 March 10 March 2009 ECOL 182R UofA K. E. Bonine Videos: 39.3, 34.3, 39.1, 34.1 Web Browser Open 1 Video 39.3 Pollination of a night-blooming
Plant Function Chs 38, 39 (parts), 40 KEB no office hour on Monday 23 March 10 March 2009 ECOL 182R UofA K. E. Bonine Videos: 39.3, 34.3, 39.1, 34.1 Web Browser Open 1 Video 39.3 Pollination of a night-blooming
Cell Structure and Function Unit 4
 Cell Structure and Function Unit 4 Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. RECALL... Levels of Organization! Why do we call them cells? In 1665, Robert
Cell Structure and Function Unit 4 Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. RECALL... Levels of Organization! Why do we call them cells? In 1665, Robert
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 4.2 - Plant Nutrition Photosynthesis You need to know the definition of photosynthesis as: the fundamental process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 4.2 - Plant Nutrition Photosynthesis You need to know the definition of photosynthesis as: the fundamental process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates
Chapter 7. Cell Structure & Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function Scientists & Discoveries Early 1600 s (Holland): 1st microscope was constructed Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600 s) used single lens as a microscope to study and very carefully
Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function Scientists & Discoveries Early 1600 s (Holland): 1st microscope was constructed Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600 s) used single lens as a microscope to study and very carefully
PROPERTY OF: BIOLOGY UNIT 3 CHAPTER 19 NOTES THE HISTORY OF LIFE
 PROPERTY OF: BIOLOGY UNIT 3 CHAPTER 19 NOTES THE HISTORY OF LIFE Spontaneous Generation - theory that life arises from non-life (early-mid 1700 s) EX: rotting meat became covered with flies and maggots
PROPERTY OF: BIOLOGY UNIT 3 CHAPTER 19 NOTES THE HISTORY OF LIFE Spontaneous Generation - theory that life arises from non-life (early-mid 1700 s) EX: rotting meat became covered with flies and maggots
13. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
There are 5 kingdoms: Animalia multicellular animals, heterotrophic (eat other things), evolved 700,000,000 years ago (1,000,000 2,000,000 species)
 Classification The modern system of naming gives each living thing 7 names. Each name is a little more specific than the one before it. The categories are (in order from least to most specific): Kingdom
Classification The modern system of naming gives each living thing 7 names. Each name is a little more specific than the one before it. The categories are (in order from least to most specific): Kingdom
THE FANTASTIC, FESTIVE FALL FINAL FREVIEW
 Lab Safety & General Bio 1. Things that are flammable should not come in contact with. 2. In the lab, if you are uncertain of what to do, you should always (because she s really cool and you probably want
Lab Safety & General Bio 1. Things that are flammable should not come in contact with. 2. In the lab, if you are uncertain of what to do, you should always (because she s really cool and you probably want
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 TEST PREP PRETEST Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each
Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 TEST PREP PRETEST Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each
Kingdom Monera Bacteria
 Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
quarterly 2 practice test
 Name: Date: 1. The picture below shows an ocean bay food chain. Sea otters move into the ocean bay. They eat all the sea urchins. This change will cause the 3. Ecosystems are composed of all living and
Name: Date: 1. The picture below shows an ocean bay food chain. Sea otters move into the ocean bay. They eat all the sea urchins. This change will cause the 3. Ecosystems are composed of all living and
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION NOTES
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION NOTES Cell Theory 1. All living things 2. Cells are the. 3. Cells are produced All Living things have cells a. Unicellular b. Multicellular Types of Cells a. Prokaryote: i.
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION NOTES Cell Theory 1. All living things 2. Cells are the. 3. Cells are produced All Living things have cells a. Unicellular b. Multicellular Types of Cells a. Prokaryote: i.
You learned a tremendous amount about science over the last five months. Think of the semester final as a way for you to show how much you know!
 Scientific Method, Metrics, Graphing, Characteristics of Life, Chemistry, Cells, Microscopes, Cell Reproduction, Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis, DNA Structure, Replication, Translation and Transcription
Scientific Method, Metrics, Graphing, Characteristics of Life, Chemistry, Cells, Microscopes, Cell Reproduction, Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis, DNA Structure, Replication, Translation and Transcription
Decomposers recycle nutrients (matter) but ENERGY IS ALWAYS LOST
 Decomposers recycle nutrients (matter) but ENERGY IS ALWAYS LOST What does this mean to us Stable ecosystems have a continual input of energy And more producers than consumers It takes less energy to produce
Decomposers recycle nutrients (matter) but ENERGY IS ALWAYS LOST What does this mean to us Stable ecosystems have a continual input of energy And more producers than consumers It takes less energy to produce
Bacteria and Viruses. 1 Bacteria CHAPTER 18. MAINIDEA Bacteria are prokaryotic cells.
 CHAPTER 18 Bacteria and Viruses 1 Bacteria 7(F), 8(B), 8(C), 11(C), 12(A) Before You Read When you hear the word bacteria, what comes to mind? On the lines below, describe places you think bacteria might
CHAPTER 18 Bacteria and Viruses 1 Bacteria 7(F), 8(B), 8(C), 11(C), 12(A) Before You Read When you hear the word bacteria, what comes to mind? On the lines below, describe places you think bacteria might
Define: Alleles. Define: Chromosome. In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways.
 Alleles Chromosome In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways. How do the bases A, C, G, T, and U match up in DNA? How about RNA? Summarize the cell process called protein synthesis!
Alleles Chromosome In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways. How do the bases A, C, G, T, and U match up in DNA? How about RNA? Summarize the cell process called protein synthesis!
EOC MILESTONE REVIEW
 Introduction 1. What does the term biology mean? EOC MILESTONE REVIEW 2. What is homeostasis and why is it important to living things? Content Domain: Cells (SB1) 1. Define eukaryote: List 3 examples of
Introduction 1. What does the term biology mean? EOC MILESTONE REVIEW 2. What is homeostasis and why is it important to living things? Content Domain: Cells (SB1) 1. Define eukaryote: List 3 examples of
Biology EOCT Review. Milton High School
 Biology EOCT Review Milton High School Cell Organelles Nucleus holds DNA Cell membrane what comes in and goes out Mitochondria powerhouse of the cell Ribosomes protein synthesis Lysosomes digestion Cell
Biology EOCT Review Milton High School Cell Organelles Nucleus holds DNA Cell membrane what comes in and goes out Mitochondria powerhouse of the cell Ribosomes protein synthesis Lysosomes digestion Cell
Summer vacation Home work
 Biology Class Xth 1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation 6) holozoic nutrition 2. Distinguish between: 1) breathing and respiration
Biology Class Xth 1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation 6) holozoic nutrition 2. Distinguish between: 1) breathing and respiration
Biology. Chapter 26. Plant Nutrition and Transport. Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr. Cengage Learning 2015
 Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 26 Plant Nutrition and Transport 26.1 Where Do Plants Get the Nutrients They Require? A plant needs sixteen elements to survive and grow Macronutrients:
Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 26 Plant Nutrition and Transport 26.1 Where Do Plants Get the Nutrients They Require? A plant needs sixteen elements to survive and grow Macronutrients:
Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria
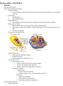 Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion
Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion
Semester Biology FINAL EXAM
 Semester 1 2012 Biology FINAL EXAM There are 50 questions on your final exam, all of which are found below in no particular order. In addition, I have included 10 more questions to help you prepare. Go
Semester 1 2012 Biology FINAL EXAM There are 50 questions on your final exam, all of which are found below in no particular order. In addition, I have included 10 more questions to help you prepare. Go
MAJOR EPISODES IN THE HISTORY OF LIFE
 MAJOR EPISODES IN THE HISTORY OF LIFE All the major phyla of animals evolved by the end of the Cambrian explosion, which began about 540 million years ago and lasted about 10 million years. Plants and
MAJOR EPISODES IN THE HISTORY OF LIFE All the major phyla of animals evolved by the end of the Cambrian explosion, which began about 540 million years ago and lasted about 10 million years. Plants and
9 Week Review Biology. Magnolia High School 2015
 9 Week Review Biology Magnolia High School 2015 What is the cellular process shown below? Phagocytosis The BEST choice to complete this concept map! Animal Cell or Plant Cell? PLANT Cell What is the function
9 Week Review Biology Magnolia High School 2015 What is the cellular process shown below? Phagocytosis The BEST choice to complete this concept map! Animal Cell or Plant Cell? PLANT Cell What is the function
Honors Biology Midterm Review
 Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
Principles of Cellular Biology
 Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
Write the events about the origins of life on Earth in order from oldest to youngest
 Write the events about the origins of life on Earth in order from oldest to youngest 1. Earth forms 2. First organic molecules (such as amino acids) appear 3. First anaerobic prokaryotic cells appear 4.
Write the events about the origins of life on Earth in order from oldest to youngest 1. Earth forms 2. First organic molecules (such as amino acids) appear 3. First anaerobic prokaryotic cells appear 4.
Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words)
 Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Biology Spring Final Exam Study Guide
 Name: Hour: Basic Biology Skills Graphing Know the keys to creating a graph Know how to interpret a graph Independent variable Dependent variable Biology Spring Final Exam Study Guide Levels of Organization
Name: Hour: Basic Biology Skills Graphing Know the keys to creating a graph Know how to interpret a graph Independent variable Dependent variable Biology Spring Final Exam Study Guide Levels of Organization
Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide
 Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Information: Exam has 100 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencils and a four-function calculator on the day of the test. Review ALL vocabulary,
Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Information: Exam has 100 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencils and a four-function calculator on the day of the test. Review ALL vocabulary,
Chapter Outline. The Living Cell. The Cell Theory. The Nature and Variety of Cells. Cell theory. Observing Cells: The Microscope
 Chapter Outline The Living Cell Chapter 21 The Nature and Variety of Cells How Does a Cell Work? Metabolism: Energy and Life Cell Division Great Idea: Life is based on chemistry, and chemistry takes place
Chapter Outline The Living Cell Chapter 21 The Nature and Variety of Cells How Does a Cell Work? Metabolism: Energy and Life Cell Division Great Idea: Life is based on chemistry, and chemistry takes place
NOTES: FLOW OF ENERGY
 NOTES: FLOW OF ENERGY Chapter 2 Principles of Ecology 2.2 Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem Energy in an Ecosystem Autotrophs (Producers) Organisms that use energy from sunlight or chemicals to produce food.
NOTES: FLOW OF ENERGY Chapter 2 Principles of Ecology 2.2 Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem Energy in an Ecosystem Autotrophs (Producers) Organisms that use energy from sunlight or chemicals to produce food.
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA 10/15/2012
 BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
Prokaryotes (Domains Bacteria & Archaea) KEY POINTS
 Prokaryotes (Domains Bacteria & Archaea) KEY POINTS 1. Decomposers: recycle organic and inorganic molecules in environment; makes them available to other organisms. 2. Essential components of symbioses.
Prokaryotes (Domains Bacteria & Archaea) KEY POINTS 1. Decomposers: recycle organic and inorganic molecules in environment; makes them available to other organisms. 2. Essential components of symbioses.
Prokaryotes. Chapter 27. PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition. Lectures by Chris Romero. Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 27 Prokaryotes PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: They re (Almost) Everywhere! Most prokaryotes are microscopic But
Chapter 27 Prokaryotes PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: They re (Almost) Everywhere! Most prokaryotes are microscopic But
Introduction to Microbiology. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 Introduction to Microbiology CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Microbiology Micro- means very small (that needs a microscope to see). Microbiology is the study of very small living organisms.
Introduction to Microbiology CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Microbiology Micro- means very small (that needs a microscope to see). Microbiology is the study of very small living organisms.
Assessment Schedule 2016 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to micro-organisms (90927)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90927) 2016 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2016 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to micro-organisms (90927) Evidence Statement Question One No response
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90927) 2016 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2016 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to micro-organisms (90927) Evidence Statement Question One No response
ET Life #17. Today: Reminders: Energy of Life. Paper Proposal Due Friday First Mid-term Next Monday
 ET Life #17 Today: Energy of Life Reminders: Paper Proposal Due Friday First Mid-term Next Monday Origin of Life: Summary 1. Early Organic Molecules 2. Complex organics developed (mineral templates?).
ET Life #17 Today: Energy of Life Reminders: Paper Proposal Due Friday First Mid-term Next Monday Origin of Life: Summary 1. Early Organic Molecules 2. Complex organics developed (mineral templates?).
1- What are rod-shaped bacteria called? A. cocci B. bacilli C. spirilla D. halophiles
 Question 1: Multiple Choice (20 Marks) 1- What are rod-shaped bacteria called? A. cocci B. bacilli C. spirilla D. halophiles 2- The eukaryotic nucleus houses all of the following except the A. RNA B. DNA
Question 1: Multiple Choice (20 Marks) 1- What are rod-shaped bacteria called? A. cocci B. bacilli C. spirilla D. halophiles 2- The eukaryotic nucleus houses all of the following except the A. RNA B. DNA
Bacteria. The Three Types of Important Heterotrophic Bacteria
 Bacteria Kingdom Monera Prokaryote (their genetic material is not bound with a membrane) Classified according to shape - Spherical (cocci) - Spiral - Rod Shaped -TWO TYPES: Heterotrophic (organism that
Bacteria Kingdom Monera Prokaryote (their genetic material is not bound with a membrane) Classified according to shape - Spherical (cocci) - Spiral - Rod Shaped -TWO TYPES: Heterotrophic (organism that
Early History and Primitive Life. Unit 2: How do cells support life? Chapter: What are the origins of life? What are the simplest forms of life?
 Early History and Primitive Life Unit 2: How do cells support life? Chapter: What are the origins of life? What are the simplest forms of life? Chapter 17-2 EARTH S EARLY HISTORY Evidence for Early Life
Early History and Primitive Life Unit 2: How do cells support life? Chapter: What are the origins of life? What are the simplest forms of life? Chapter 17-2 EARTH S EARLY HISTORY Evidence for Early Life
Name Date Period Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life?
 Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life? Eukaryotic cell parts you should be able a. to identify and label: Nucleus b. Nucleolus c. Rough/smooth ER Ribosomes d. Golgi
Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life? Eukaryotic cell parts you should be able a. to identify and label: Nucleus b. Nucleolus c. Rough/smooth ER Ribosomes d. Golgi
11/15/2011. Outline. Prokaryotes. Why care about the small stuff. Bacteria in our bodies. I. Categories of life. II.
 Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea Outline I. Categories of life A. Domains B. Eukaryote vs Prokaryote II. Domain Bacteria A. cell walls, structure B. Bacterial reproduction C. Nitrogen fixation D. Pathogenic
Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea Outline I. Categories of life A. Domains B. Eukaryote vs Prokaryote II. Domain Bacteria A. cell walls, structure B. Bacterial reproduction C. Nitrogen fixation D. Pathogenic
Plant Nutrition and Transport. Chapter 29
 Plant Nutrition and Transport Chapter 29 Overview: Underground Plants The success of plants depends on their ability to gather and conserve resources from their environment. The transport of materials
Plant Nutrition and Transport Chapter 29 Overview: Underground Plants The success of plants depends on their ability to gather and conserve resources from their environment. The transport of materials
Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago.
 Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago. Two theories: 1. Infolding theory 2. Endosymbiotic theory The infolding of the prokaryotic plasma
Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago. Two theories: 1. Infolding theory 2. Endosymbiotic theory The infolding of the prokaryotic plasma
MICROBIOLOGY TEST 1 - SPRING 2007
 MICROBIOLOGY TEST 1 - SPRING 2007 Name Part One: Short Answers. Answer 5 of the following 6 questions in the space that has been provided. Each question is worth 15 points. Question 1: Name and briefly
MICROBIOLOGY TEST 1 - SPRING 2007 Name Part One: Short Answers. Answer 5 of the following 6 questions in the space that has been provided. Each question is worth 15 points. Question 1: Name and briefly
Biology Unit 3 Exam DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Unit 3 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) solution. a. osmotic c. hypotonic b. hypertonic
Biology Unit 3 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) solution. a. osmotic c. hypotonic b. hypertonic
REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION. A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned:
 Name AP Biology REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes No internal membranes vs. membrane-bound organelles
Name AP Biology REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes No internal membranes vs. membrane-bound organelles
DNA Technology, Bacteria, Virus and Meiosis Test REVIEW
 Be prepared to turn in a completed test review before your test. In addition to the questions below you should be able to make and analyze a plasmid map. Prokaryotic Gene Regulation 1. What is meant by
Be prepared to turn in a completed test review before your test. In addition to the questions below you should be able to make and analyze a plasmid map. Prokaryotic Gene Regulation 1. What is meant by
Name Date Block. Biology EOCT Review
 Name Date Block Biology EOCT Review Section 1: Nature of Science 1. Bobby thinks that eating fish for breakfast will make people smarter. He gets 10 of his friends and divides them into 2 groups. Group
Name Date Block Biology EOCT Review Section 1: Nature of Science 1. Bobby thinks that eating fish for breakfast will make people smarter. He gets 10 of his friends and divides them into 2 groups. Group
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists
 Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
Which row in the chart correctly identifies the functions of structures A, B, and C? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a cell wall 2. Which statement is
1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a cell wall 2. Which statement is
Review for Biology Benchmark #2
 1. For each lab tool, give the function: balance - measures mass, graduated cylinder - measures volume, ruler - measures length, pipet - (some measure) add small amounts of liquid, scapel - cut specimens.
1. For each lab tool, give the function: balance - measures mass, graduated cylinder - measures volume, ruler - measures length, pipet - (some measure) add small amounts of liquid, scapel - cut specimens.
Chapter 17B. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains. Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
 Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity Section 3 Complex Multicellularity The Six Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into six kingdoms and
Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity Section 3 Complex Multicellularity The Six Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into six kingdoms and
Principles of Ecology
 Principles of Ecology Ecology is the scientific study of interactions between 1. organisms and other organisms 2. organisms and their environment. Biotic vs. Abiotic Factors Biotic Factors: All of the
Principles of Ecology Ecology is the scientific study of interactions between 1. organisms and other organisms 2. organisms and their environment. Biotic vs. Abiotic Factors Biotic Factors: All of the
Photosynthesis (Chapter 7 Outline) A. For life based on organic compounds, two questions can be raised:
 Photosynthesis (Chapter 7 Outline) Sun, Rain, and Survival A. For life based on organic compounds, two questions can be raised: 1. Where does the carbon come from? 2. Where does the energy come from to
Photosynthesis (Chapter 7 Outline) Sun, Rain, and Survival A. For life based on organic compounds, two questions can be raised: 1. Where does the carbon come from? 2. Where does the energy come from to
Endosymbiotic Theory
 Endosymbiotic Theory Evolution of Prokaryotes The oldest known fossils are 3.5 bya = stromatolites which are rock like layers of bacteria and sediment. Earliest life forms may have emerged as early as
Endosymbiotic Theory Evolution of Prokaryotes The oldest known fossils are 3.5 bya = stromatolites which are rock like layers of bacteria and sediment. Earliest life forms may have emerged as early as
