FINE STRUCTURE OF MYCOTA
|
|
|
- Willis Rich
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FINE STRUCTURE OF MYCOTA XI. OCCURRENCE OF THE GOLGI DICTYOSOME IN THE HETEROBASIDIOMYCETE P UCCINIA POD OPHYLLI ROYALL T. MOORE Electron Microscope Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, California Received for publication 24 June 1963 ABSTRACT MOORE, ROYALL T. (University of California, Berkeley). Fine structure of mycota. XI. Occurrence of the Golgi dictyosome in the heterobasidiomycete Puccinia podophylli. J. Bacteriol. 86: The Golgi dictyosome is reported for the first time in the subclass Heterobasidiomycetidae in the rust Puccinia podophylli Schw. It is observed that the dictyosome appears to be limited to primordial cells, particularly those nearest the host, and does not occur in the aeciospores. In comparison with the Golgi systems of plant and animal cells, the Golgi complex of P. podophylli is found to be more similar to those of the latter. Also discussed is the distribution of the Golgi complex in fungi described in published reports and the need for more such reports so that the range of its variation and distribution may be established. The Golgi dictyosome has only recently been demonstrated in the fungi. First described in the Ascomycete Neobulgaria pura (Moore and Mc- Alear, 1962, 1963), it has most recently been described in Peronospora rmnshurica (Peyton and Bowen, in press) and Pythium debaryanum (Hawker, 1963), both biflagellate Phycomycetes, and in the Homobasidiomycete Armillaria mellea (Roskin, Snyder, and McAlear, in preparation). The following communication relates the occurrence of what is believed to be an example of the Golgi system in the Heterobasidiomycete Puccinia podophylli, a representative of the other Basidiomycete subclass. MATERIALS AND METHODS Young aecia of P. podophylli Schw. were excised from the lower stem of Podophyllum peltatum L. (Berberidaceae) collected from the field. (Reference material from the same specimen 866 has been deposited in the Cornell University Plant Pathology Herbarium, CUP ) These were prefixed for about 10 min in 2% aqueous unbuffered KMnO4, then fixed in buffered OS04 for 3 to 5 hr, dehydrated in an ethanol series, and embedded in a methacrylate mixture (Moore, 1962). Sections cut with a diamond knife were examined in a Siemens Elmiskop I electron microscope. RESULTS Figure 1 shows a cell of the aecial primordium contiguous with a thick-walled epidermal cell (E, E) of the host. A Golgi dictyosome (G) with numerous marginal vesicles (X) is prominent near the fungal nucleus (N). Above this are what appear to be two smaller complexes. Figure 2 is a similar plane of section at a higher magnification. The dictyosome membranes display frequent swellings at their margins (arrows), and adjacent vesicle aggregations (X) are conspicuous. Figure 3 presents a somewhat tangential section of a Golgi complex proximate to a nucleus (N). The fungal wall (W) is identified. Figure 4 is interpreted as a section cut approximately perpendicular to the vertical stack of saucer-shaped sacs that form the dictyosome. The three dictyosome membrane aggregates (G) are believed all to belong to one complex. The great accumulation of Golgi vesicles (X) spacially is probably at the inner region of the complex (similar to those in Fig. 1 and 3). DISCUSSION The Golgi system, thought classically to occur only in animal cells, owes its present delimitations to the early studies of zoological fine structure. These established the following criteria: (i) stacks of flattened sacs-the "fingerprint" of the dictyosome; (ii) propinquity of the dictyosome to the
2 lz FIG. 1. Contiguity of fungal and host epidermal (E, E) cells. A Golgi dicytosome (G) and vesicles (X) are prominent near the nucleus (N). Scale line = 1,; X 20,
3 FIG. 2. Dictyosome lamellae showing blebbing (arrows) and adjacent vesicle clusters (X). Scale line = 1 /A; X 50,
4 FIG. 3. Tangential section through a Golgi complex near a nucleus (N). W', the fungal cell wall. Scale line = 1 IA; X 60,
5 FIG. 4. Section through the Golgi apparatus approximately perpendicular to the plane of stacking; G, dictyosome; X, vesicles. Scale line = 1 p; X 30,
6 VOL. 86, 1963 GOLGI DICTYOSOME IN P. PODOPHYLLI 8371 nucleus; (iii) the apparent blebbing off of small vesicles from the margin of the dictyosome; (iv) membranes that are smooth, i.e., ribosome-free. Criteria i and iv appear to be invariable: the dictyosome is, ipso facto, the defining attribute of the Golgi complex, and in no examples of osmium-fixed material have ribosomes been reported on Golgi membranes. An exception to criterion iii was reported by imoore and McAlear (1963) in the fungus Neobulgaria in which marginal vesicles were not observed. Plant cells tend to be exceptions to criterion ii. In these cells, the dictyosomes generally appear to be rather scattered in the cytoplasm. Also, the dictyosomes as most frequently observed are more compact and more numerous, and the quantity of marginal vesicles is sparser than is generally characteristic of the dictyosomes of animal cells. From the numerous electron microscopic studies of plant tissues during the past several years, it now is quite evident that the Golgi system is as widely occurring in plant cells as in animal cells. The same is not yet true for the fungi. The Golgi dictyosome for these organisms was first reported from the monotypic discomycete N. pura (MIoore and MIcAlear, 1963). This still remains our only example from the Ascomycetes. However, as mentioned above, there are now several reports of the Golgi apparatus from the Phycomycetes. All of these, curiously enough, are from the biflagellate series, a series uniquely characterized by cellulose in the hyphal walls (J. M. Aronson, personal communication) and a series which Bessey (1942) believed to be phylogenetically linked with the Vaucheriaceae of the yellow-green algae. The first report of the Golgi dictyosome in the Basidiomycetes was made by Roskin et al. (in preparation) from A. mellea. The present report is believed to be the second for this class. The thallus of P. podophylli is composed of disarticulated cells (Moore, in press), and the Golgi formation is observed most frequently in the several layers of cells nearest the host. At the outer face of the aecium, aesciospores are produced. These are dikaryotic, filled with storage vesicles, and bounded by a thick, warty wall. No Golgi-like membranes have been observed in them, and their appearance is quite similar to the aeciospores of Uromyces caladii (Moore and McAlear 1961). The observed membrane complex in P. podophylli complies with the first three criteria. (Information on the fourth criterion is precluded by the permanganate fixation.) Its micromorphology appears most similar, broadly speaking, to the dictyosomes observed in animal cells; that is, the lamellae forming the dictyosome are quite broad, the number of marginal vesicles is large, and the complex occupies the perinuclear region. Further, there is seldom more than one fully developed complex per cell. From this r6sum6 of all the reports of the occurrence of the Golgi dictyosome in the fungi, it is quite evident that it is still rather a novelty in the Eumycota. It is, therefore, important that as examples of the Golgi system are encountered in these organisms they be reported so that the range of the micromorphology and the distribution of the organelle may be established. From an accumulation of such information, there may perhaps be derived in the future a clearer understanding of the phylogenetic position of the fungi. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The technical assistance of Lloyd Thibodeau and Philip Spencer of our Laboratory is gratefully acknowledged. This investigation was supported by Postdoctoral Fellowships and 2 F2 AI from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, U.S. Public Health Service; James H. McAlear, sponsor. LITERATURE CITED BESSEY, E. A Some problems in fungus phylogeny. Mycologia 34: HAWKER, L. E Fine structure of Pythium de bar yanum Hesse and its probable significance. Nature 197:619. MIOORE, R. T Fine structure of mycota. 1. Electron microscopy of the discomycete Ascodesmis. Nova Hedwigia 5: MOORE, R. T., AND J. H. MCALEAR Fine structure of mycota. 8. On the aecidial stage of Uromyces caladii. Phytopathol. Z. 42: MOORE, R. T., ANI) J. H. McALEAR Characterization of the Golgi dictyosome of the fungus Neobulgaria pura. Intern. Conf. Electron Microscopy, 5th 2:UU-7. MOORE, R. T., AND J. H. McALEAR Fine structure of mycota. 4. The occurrence of the Golgi dictyosome in the fungus Neobulgaria pura (Fr.) Petrak. J. Cell Biol. 16:
Discovery of the Cell
 Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Parenchyma Cell. Magnification 2375X
 Parenchyma Cell The large size of parenchyma cells is due in part to their relatively large vacuole (V) and in part also to the large number of chloroplasts (Cp) they contain. From a crimson clover, Trifolium
Parenchyma Cell The large size of parenchyma cells is due in part to their relatively large vacuole (V) and in part also to the large number of chloroplasts (Cp) they contain. From a crimson clover, Trifolium
Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6. Microscopes pp Microscopes. Microscopes. Microscopes. Microscopes
 Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6 -All life is composed of cells and all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. pp.105-107 - The development of the microscope was the key to understanding that all living
Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6 -All life is composed of cells and all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. pp.105-107 - The development of the microscope was the key to understanding that all living
Magnification 200. (a) Give the letter that correctly identifies the plant tissues shown in the photograph above. (2)
 1 The photograph below shows a cross-section through part of the stem of a sunflower (Helianthus annuus) as seen using a microscope. D Magnification 200 (a) Give the letter that correctly identifies the
1 The photograph below shows a cross-section through part of the stem of a sunflower (Helianthus annuus) as seen using a microscope. D Magnification 200 (a) Give the letter that correctly identifies the
AN ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PYTHIUM ULTfMUM
 New Phytol. (1968) 67, 167-171. AN ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PYTHIUM ULTfMUM BY R. MARCHANT Department of Botany, University College, London (Received 12 May 1967) SUMMARY The original
New Phytol. (1968) 67, 167-171. AN ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PYTHIUM ULTfMUM BY R. MARCHANT Department of Botany, University College, London (Received 12 May 1967) SUMMARY The original
ANUMBER of electron microscope studies have been made on Amoeba
 An Electron Microscope Study of a Small Free-living Amoeba (Hartmanella astronyxis) By K. DEUTSCH and M. M. SWANN (From the Department of Zoology, University of Edinburgh) With two plates (figs. I and
An Electron Microscope Study of a Small Free-living Amoeba (Hartmanella astronyxis) By K. DEUTSCH and M. M. SWANN (From the Department of Zoology, University of Edinburgh) With two plates (figs. I and
Cells and Their Organelles
 Cells and Their Organelles The cell is the basic unit of life. The following is a glossary of animal cell terms. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing
Cells and Their Organelles The cell is the basic unit of life. The following is a glossary of animal cell terms. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing
Module 2: Foundations in biology
 alevelbiology.co.uk Module 2: Foundations in biology SPECIFICATION 2.1.1 Cell structure Learners should be able to demonstrate and apply their knowledge and understanding of: (a) The use of microscopy
alevelbiology.co.uk Module 2: Foundations in biology SPECIFICATION 2.1.1 Cell structure Learners should be able to demonstrate and apply their knowledge and understanding of: (a) The use of microscopy
Cell Structure. Chapter 4
 Cell Structure Chapter 4 Cell Theory Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke. Early studies of cells were conducted by - Mathias Schleiden (1838) - Theodor Schwann (1839) Schleiden and Schwann proposed
Cell Structure Chapter 4 Cell Theory Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke. Early studies of cells were conducted by - Mathias Schleiden (1838) - Theodor Schwann (1839) Schleiden and Schwann proposed
CELLS STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 CELLS STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Jhia Anjela D. Rivera Department of Biological Sciences School of Science and Technology Centro Escolar University DISCOVERY OF CELLS Robert Hooke (1665): Observed a thin slice
CELLS STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Jhia Anjela D. Rivera Department of Biological Sciences School of Science and Technology Centro Escolar University DISCOVERY OF CELLS Robert Hooke (1665): Observed a thin slice
Name: Date: Hour:
 Name: Date: Hour: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Comprehension Questions 1. At what level of organization does life begin? 2. What surrounds all cells? 3. What is meant by semipermeable? 4. What 2 things make up the cell
Name: Date: Hour: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Comprehension Questions 1. At what level of organization does life begin? 2. What surrounds all cells? 3. What is meant by semipermeable? 4. What 2 things make up the cell
The Discovery of Cells
 The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
Warm-Up Pairs Discuss the diagram What Where Which Why
 Warm-Up In Pairs Discuss the diagram What is it? Where does it come from? Which parts can you label? (in pencil) Why do you think you will learn about it? 5 m Eukaryote: Organelles, Structure and Function
Warm-Up In Pairs Discuss the diagram What is it? Where does it come from? Which parts can you label? (in pencil) Why do you think you will learn about it? 5 m Eukaryote: Organelles, Structure and Function
Discovery of the Cell
 Cells Chapter 4 Discovery of the Cell 1665 Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a piece of cork. He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells. 1673 Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first person
Cells Chapter 4 Discovery of the Cell 1665 Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a piece of cork. He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells. 1673 Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first person
Cells and Their Organelles
 Mr. Ulrich Regents Biology Name:.. Cells and Their Organelles The cell is the basic unit of life. The following is a glossary of animal cell terms. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. The cell
Mr. Ulrich Regents Biology Name:.. Cells and Their Organelles The cell is the basic unit of life. The following is a glossary of animal cell terms. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. The cell
Cell Structure. Chapter 4. Cell Theory. Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke.
 Cell Structure Chapter 4 Cell Theory Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke. Early studies of cells were conducted by - Mathias Schleiden (1838) - Theodor Schwann (1839) Schleiden and Schwann proposed
Cell Structure Chapter 4 Cell Theory Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke. Early studies of cells were conducted by - Mathias Schleiden (1838) - Theodor Schwann (1839) Schleiden and Schwann proposed
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell The cell is the basic unit of life Although cells differ substantially from one another, they all share certain characteristics that reflect a common ancestry and remind us
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell The cell is the basic unit of life Although cells differ substantially from one another, they all share certain characteristics that reflect a common ancestry and remind us
Cell Organelles. 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism Cells tissues organ organ system organism
 Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Cell Theory. Cell Structure. Chapter 4. Cell is basic unit of life. Cells discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke
 Cell Structure Chapter 4 Cell is basic unit of life Cell Theory Cells discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke Early cell studies conducted by - Mathias Schleiden (1838) - Theodor Schwann (1839) Schleiden &
Cell Structure Chapter 4 Cell is basic unit of life Cell Theory Cells discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke Early cell studies conducted by - Mathias Schleiden (1838) - Theodor Schwann (1839) Schleiden &
8/25/ Opening Questions: Are all living things made of cells? What are at least five things you know about cells?
 Chapter 3 The Cell: Module Hyperlinks 3.1 Cells are the fundamental units of life 3.2 Plant vs. animal cells 3.3 Membranes: structure 3.4 Membranes: function 3.5 The nucleus 3.6 Organelles in protein production
Chapter 3 The Cell: Module Hyperlinks 3.1 Cells are the fundamental units of life 3.2 Plant vs. animal cells 3.3 Membranes: structure 3.4 Membranes: function 3.5 The nucleus 3.6 Organelles in protein production
Introduction to Cells. Intro to Cells. Scientists who contributed to cell theory. Cell Theory. There are 2 types of cells: All Cells:
 Intro to Cells Key Concept: Cells are the basic unit of life. Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: 1 Animal Cell
Intro to Cells Key Concept: Cells are the basic unit of life. Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: 1 Animal Cell
II. Eukaryotic Cell Structure A. Boundaries 1. plasma membrane a. serves as a boundary b/w the cell and its environment b. controls movement of
 I. History of the cell theory A. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600s) - dutch lens maker could see things with his lenses that were invisible to the naked eye - developed the simple microscope B. Robert Hooke
I. History of the cell theory A. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600s) - dutch lens maker could see things with his lenses that were invisible to the naked eye - developed the simple microscope B. Robert Hooke
Cellular basis of life History of cell Biology Year Name of the scientist Importance
 Cellular basis of life History of cell Biology Year Name of the scientist Importance 1590 Jansen 1650 Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1665 Robert Hooke 1831 Matthias Schleiden 1831 Theodore Schwann 1855 Rudolf Virchow
Cellular basis of life History of cell Biology Year Name of the scientist Importance 1590 Jansen 1650 Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1665 Robert Hooke 1831 Matthias Schleiden 1831 Theodore Schwann 1855 Rudolf Virchow
7-1 Life Is Cellular. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
Biology Teach Yourself Series Topic 2: Cells
 Biology Teach Yourself Series Topic 2: Cells A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au TSSM 2013 Page 1 of 14 Contents Cells... 3 Prokaryotic
Biology Teach Yourself Series Topic 2: Cells A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au TSSM 2013 Page 1 of 14 Contents Cells... 3 Prokaryotic
7 Characteristics of Life
 7 Characteristics of Life 1. Interdependence 2. Metabolism 3. Homeostasis 4. Cellular Structure and Function 5. Reproduction 6. Heredity 7. Evolution The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one
7 Characteristics of Life 1. Interdependence 2. Metabolism 3. Homeostasis 4. Cellular Structure and Function 5. Reproduction 6. Heredity 7. Evolution The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one
Cell Structure. Lab Exercise 6. Contents. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise Cell Structure Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Cellular Structures 2 Activity.2 Matching Exercise 2 Activity.3 Identify Organelles 2 Resutls Section 3 Objectives - Identify
Lab Exercise Cell Structure Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Cellular Structures 2 Activity.2 Matching Exercise 2 Activity.3 Identify Organelles 2 Resutls Section 3 Objectives - Identify
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 1 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 1 2 Number
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10
 Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University September 23, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10 September 23, 2013 1 / 20 Outline 1 Questions and answers
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University September 23, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10 September 23, 2013 1 / 20 Outline 1 Questions and answers
Ask yourself. Chapter 3 Cell Structure and Function. Examples of Cells. A is cell the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions.
 Chapter 3 Cell Structure and Function Ask yourself If you were a scientist living in the 1500s, what kind of questions would you ask yourself if you were the one to discover cells? Let me think. Cell Video
Chapter 3 Cell Structure and Function Ask yourself If you were a scientist living in the 1500s, what kind of questions would you ask yourself if you were the one to discover cells? Let me think. Cell Video
Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology
 Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
10/1/2014. Chapter Explain why the cell is considered to be the basic unit of life.
 Chapter 4 PSAT $ by October by October 11 Test 3- Tuesday October 14 over Chapter 4 and 5 DFA- Monday October 20 over everything covered so far (Chapters 1-5) Review on Thursday and Friday before 1. Explain
Chapter 4 PSAT $ by October by October 11 Test 3- Tuesday October 14 over Chapter 4 and 5 DFA- Monday October 20 over everything covered so far (Chapters 1-5) Review on Thursday and Friday before 1. Explain
Function and Illustration. Nucleus. Nucleolus. Cell membrane. Cell wall. Capsule. Mitochondrion
 Intro to Organelles Name: Block: Organelles are small structures inside cells. They are often covered in membranes. Each organelle has a job to do in the cell. Their name means little organ. Just like
Intro to Organelles Name: Block: Organelles are small structures inside cells. They are often covered in membranes. Each organelle has a job to do in the cell. Their name means little organ. Just like
The Cell. What is a cell?
 The Cell What is a cell? The Cell What is a cell? Structure which makes up living organisms. The Cell Theory l All living things are composed of cells. l Cells are the basic unit of life. l Cells come
The Cell What is a cell? The Cell What is a cell? Structure which makes up living organisms. The Cell Theory l All living things are composed of cells. l Cells are the basic unit of life. l Cells come
Chapter 7.2. Cell Structure
 Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Class IX: Biology Chapter 5: The fundamental unit of life. Chapter Notes. 1) In 1665, Robert Hooke first discovered and named the cells.
 Class IX: Biology Chapter 5: The fundamental unit of life. Key learnings: Chapter Notes 1) In 1665, Robert Hooke first discovered and named the cells. 2) Cell is the structural and functional unit of all
Class IX: Biology Chapter 5: The fundamental unit of life. Key learnings: Chapter Notes 1) In 1665, Robert Hooke first discovered and named the cells. 2) Cell is the structural and functional unit of all
2.1 CELL STRUCTURE. The cell is the smallest unit of living organisms that shows the characteristics of life.
 2.1.1 Microscopy The cell is the smallest unit of living organisms that shows the characteristics of life. A general introduction to the microscope. The light microscope All cells are microscopic which
2.1.1 Microscopy The cell is the smallest unit of living organisms that shows the characteristics of life. A general introduction to the microscope. The light microscope All cells are microscopic which
Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards
 Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students
Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students
Complete the table by stating the function associated with each organelle. contains the genetic material.... lysosome ribosome... Table 6.
 1 (a) Table 6.1 gives the functions of certain organelles in a eukaryotic cell. Complete the table by stating the function associated with each organelle. The first row has been completed for you. Organelle
1 (a) Table 6.1 gives the functions of certain organelles in a eukaryotic cell. Complete the table by stating the function associated with each organelle. The first row has been completed for you. Organelle
1. Cell Theory Organelle containing the genetic information of the cell.
 GLOSSARY MATCHING GAME The words and definitions are all mixed up. Cut out each word and definition and glue the correct matches into your workbook. Word Definition 1. Cell Theory Organelle containing
GLOSSARY MATCHING GAME The words and definitions are all mixed up. Cut out each word and definition and glue the correct matches into your workbook. Word Definition 1. Cell Theory Organelle containing
and their organelles
 and their organelles Discovery Video: Cells REVIEW!!!! The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest
and their organelles Discovery Video: Cells REVIEW!!!! The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest
NCERT solution for Fundamental Unit of Life
 1 NCERT solution for Fundamental Unit of Life Question 1 Who discovered cells and how? An English Botanist, Robert Hooke discovered cells. In 1665, he used self-designed microscope to observe cells in
1 NCERT solution for Fundamental Unit of Life Question 1 Who discovered cells and how? An English Botanist, Robert Hooke discovered cells. In 1665, he used self-designed microscope to observe cells in
Chapter 5: The Fundamental Unit of Life Science
 Chapter 5: The Fundamental Unit of Life Science 1 Who discovered cells and how? An English Botanist, Robert Hooke discovered cells In 1665, he used self-designed microscope to observe cells in a cork slice
Chapter 5: The Fundamental Unit of Life Science 1 Who discovered cells and how? An English Botanist, Robert Hooke discovered cells In 1665, he used self-designed microscope to observe cells in a cork slice
Today s materials: Cell Structure and Function. 1. Prokaryote and Eukaryote 2. DNA as a blue print of life Prokaryote and Eukaryote. What is a cell?
 Today s materials: 1. Prokaryote and Eukaryote 2. DNA as a blue print of life Prokaryote and Eukaryote Achadiah Rachmawati What is a cell? Cell Structure and Function All living things are made of cells
Today s materials: 1. Prokaryote and Eukaryote 2. DNA as a blue print of life Prokaryote and Eukaryote Achadiah Rachmawati What is a cell? Cell Structure and Function All living things are made of cells
Day 1. What You ll Learn. 1. Organisms are living things. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells.
 What You ll Learn Day 1 1. Organisms are living things. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 3. There are two main types of cells: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic A cell is the basic unit and structure
What You ll Learn Day 1 1. Organisms are living things. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 3. There are two main types of cells: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic A cell is the basic unit and structure
What in the Cell is Going On?
 What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
Van Leeuwenhoek. 1 st crude microscope made by the Dutchman
 The Cell History of Cells In 1665, English scientist Robert Hooke used the first compound light microscope to see plant tissues He viewed several thin slices of cork He called the small chambers within
The Cell History of Cells In 1665, English scientist Robert Hooke used the first compound light microscope to see plant tissues He viewed several thin slices of cork He called the small chambers within
CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL. I. Discovery of the Cell. Kennedy biol. 1ab
 CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES Kennedy biol. 1ab STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL I. Discovery of the Cell Cells were discovered by scientists before electricity was in every home and horses were still the
CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES Kennedy biol. 1ab STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL I. Discovery of the Cell Cells were discovered by scientists before electricity was in every home and horses were still the
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 3
 Introduction to Botany. Lecture 3 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University August 30th, 2010 Taxonomic pyramid Monday test Name at least one function of proteins in plasma membrane Monday test What will
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 3 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University August 30th, 2010 Taxonomic pyramid Monday test Name at least one function of proteins in plasma membrane Monday test What will
Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification
 Table of Contents Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification Section 1: Living Things 1- What is an organism? Any living thing is called an organism. Organisms vary in size: 1)one-celled or unicellular
Table of Contents Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification Section 1: Living Things 1- What is an organism? Any living thing is called an organism. Organisms vary in size: 1)one-celled or unicellular
The Cell: The smallest unit in living things that shows the characteristics of life; the basic building blocks of life.
 The Cell: The smallest unit in living things that shows the characteristics of life; the basic building blocks of life. What is a cell s function? Each cell contains information (DNA) that is used as instructions
The Cell: The smallest unit in living things that shows the characteristics of life; the basic building blocks of life. What is a cell s function? Each cell contains information (DNA) that is used as instructions
Pre-lab Homework Lab 4: The Cell
 Lab Section: Name: Pre-lab Homework After reading over the lab and the cell chapter in your textbook, answer these questions to be turned in at the beginning of the lab! 1. Define organelle : Two examples
Lab Section: Name: Pre-lab Homework After reading over the lab and the cell chapter in your textbook, answer these questions to be turned in at the beginning of the lab! 1. Define organelle : Two examples
To help you complete this review activity and to help you study for your test, you should read SC State Standards B
 Name: Test Date: PAGE: Biology I: Unit 3 Cell Structure Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through your notes, worksheets,
Name: Test Date: PAGE: Biology I: Unit 3 Cell Structure Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through your notes, worksheets,
Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 1: Cell Structure
 Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 1: Cell Structure Lesson 1.1.1 I will know I am successful if I can: 1. Label all parts of plant and animal cells and state their functions 2. State the differences between plant
Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 1: Cell Structure Lesson 1.1.1 I will know I am successful if I can: 1. Label all parts of plant and animal cells and state their functions 2. State the differences between plant
Biology: Life on Earth
 Teresa Audesirk Gerald Audesirk Bruce E. Byers Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 What
Teresa Audesirk Gerald Audesirk Bruce E. Byers Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 What
THE CELL THEORY (R+R+R+E+G+N+T+S) 3).
 CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
Introduction to Botany
 Introduction to Botany Alexey Shipunov Minot State University Lecture 13 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany Lecture 13 1 / 27 Outline 1 Questions and answers Quiz 2 Plant cell Cell boundaries Protein
Introduction to Botany Alexey Shipunov Minot State University Lecture 13 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany Lecture 13 1 / 27 Outline 1 Questions and answers Quiz 2 Plant cell Cell boundaries Protein
Cell Organelles. a review of structure and function
 Cell Organelles a review of structure and function TEKS and Student Expectations (SE s) B.4 Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized
Cell Organelles a review of structure and function TEKS and Student Expectations (SE s) B.4 Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized
Tissues, cells and molecular studies
 1 Module 1 Tissues, cells and molecular studies In this module you will be able to integrate your knowledge of the use of the light microscope with an understanding of cell structure. The difference between
1 Module 1 Tissues, cells and molecular studies In this module you will be able to integrate your knowledge of the use of the light microscope with an understanding of cell structure. The difference between
prokaryotic eukaryotic
 Cell Basics Two Basic Cell Types All cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cells a.k.a. Bacteria Prokaryotes, which includes all bacteria. They are the simplest cellular organisms. They
Cell Basics Two Basic Cell Types All cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cells a.k.a. Bacteria Prokaryotes, which includes all bacteria. They are the simplest cellular organisms. They
The Basic Unit of Life Copyright Amy Brown Science Stuff
 Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life Copyright Amy Brown Science Stuff The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under the microscope. Named it a
Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life Copyright Amy Brown Science Stuff The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under the microscope. Named it a
Cell Structure, Function & Ultrastructure
 Cell Structure, Function & Ultrastructure Learning Objectives 2.1.2 Components of the cell as seen under the light microscope and their functions. Cell Structure and Function 1. Plant cells: cell wall,
Cell Structure, Function & Ultrastructure Learning Objectives 2.1.2 Components of the cell as seen under the light microscope and their functions. Cell Structure and Function 1. Plant cells: cell wall,
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab
 Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
1 Woese was the scientist who proposed a classification of organisms into three domains called the Archaea, Bacteria and Eukaryota (Eucarya).
 1 Woese was the scientist who proposed a classification of organisms into three domains called the rchaea, acteria and Eukaryota (Eucarya). (a) The table below shows some of the characteristics of the
1 Woese was the scientist who proposed a classification of organisms into three domains called the rchaea, acteria and Eukaryota (Eucarya). (a) The table below shows some of the characteristics of the
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10
 Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University September 21, 2015 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10 September 21, 2015 1 / 33 Outline 1 Questions and answers
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University September 21, 2015 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10 September 21, 2015 1 / 33 Outline 1 Questions and answers
Cell Organelles. Wednesday, October 22, 14
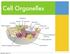 Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
THE FREQUENCY OF HETEROCYSTS IN THE NOSTOC PHYCOBIONT OF THE LICHEN PELTIGERA CANINA WILLD.
 New Phytol. (1972) 71, 11-13. THE FREQUENCY OF HETEROCYSTS IN THE NOSTOC PHYCOBIONT OF THE LICHEN PELTIGERA CANINA WILLD. BY H. BRONWEN GRIFFITHS, A. D. GREENWOOD AND J. W. MILLBANK Department of Botany,
New Phytol. (1972) 71, 11-13. THE FREQUENCY OF HETEROCYSTS IN THE NOSTOC PHYCOBIONT OF THE LICHEN PELTIGERA CANINA WILLD. BY H. BRONWEN GRIFFITHS, A. D. GREENWOOD AND J. W. MILLBANK Department of Botany,
It helps scientists understand the workings of the human body and of other animals and plants
 Science 8 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 Cells Online resources: Click on Chapter 1 at the site below. http://www.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe8/student/weblinks.html Chapter 1.1 1. Organism is another word used
Science 8 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 Cells Online resources: Click on Chapter 1 at the site below. http://www.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe8/student/weblinks.html Chapter 1.1 1. Organism is another word used
Eukaryotic Cells: The Inside Story. Day 1
 Eukaryotic Cells: The Inside Story Day 1 Objective 1. I will describe each part of a eukaryotic. 2. I will explain the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell. 3. I will describe the difference between
Eukaryotic Cells: The Inside Story Day 1 Objective 1. I will describe each part of a eukaryotic. 2. I will explain the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell. 3. I will describe the difference between
Unicellular Marine Organisms. Chapter 4
 Unicellular Marine Organisms Chapter 4 The Cellular Structure of Life: Review Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists;
Unicellular Marine Organisms Chapter 4 The Cellular Structure of Life: Review Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists;
3.2.1 Cell structure Structure of eukaryotic cells
 alevelbiology.co.uk 3.2.1 Cell structure 3.2.1.1 Structure of eukaryotic cells SPECIFICATION The structure of eukaryotic cells, restricted to the structure and function of: cell-surface membrane nucleus
alevelbiology.co.uk 3.2.1 Cell structure 3.2.1.1 Structure of eukaryotic cells SPECIFICATION The structure of eukaryotic cells, restricted to the structure and function of: cell-surface membrane nucleus
Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function
 Name: Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function a. Define the word cell: 1. I know the history of the cell: b. Who discovered the cell? What did he observe? 2. I can list the three parts of
Name: Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function a. Define the word cell: 1. I know the history of the cell: b. Who discovered the cell? What did he observe? 2. I can list the three parts of
Cell Types. Prokaryotes
 Cell Types Prokaryotes before nucleus no membrane-bound nucleus only organelle present is the ribosome all other reactions occur in the cytoplasm not very efficient Ex.: bacteria 1 Cell Types Eukaryotes
Cell Types Prokaryotes before nucleus no membrane-bound nucleus only organelle present is the ribosome all other reactions occur in the cytoplasm not very efficient Ex.: bacteria 1 Cell Types Eukaryotes
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE ORGANIZATION OF LIFE CELL THEORY TIMELINE
 CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE 1. composed of cells either uni/multi 2. reproduce sexual and/or asexual 3. contain DNA in cells 4. grow and develop 5. use material/energy in metabolic reactions 6. respond to
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE 1. composed of cells either uni/multi 2. reproduce sexual and/or asexual 3. contain DNA in cells 4. grow and develop 5. use material/energy in metabolic reactions 6. respond to
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when Robert Hooke first looked at dead cells from an oak tree.
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when Robert Hooke first looked at dead cells from an oak tree.
The formation of zymogen granules in the pancreas of the mouse By S. K. MALHOTRA
 The formation of zymogen granules in the pancreas of the mouse By S. K. MALHOTRA (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, Oxford) With 3 plates (figs, i to 3) Summary Electron-dense, granular
The formation of zymogen granules in the pancreas of the mouse By S. K. MALHOTRA (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, Oxford) With 3 plates (figs, i to 3) Summary Electron-dense, granular
UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure
 UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure Page CP: CHAPTER 3, Sections 1-3; HN: CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-2 Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their
UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure Page CP: CHAPTER 3, Sections 1-3; HN: CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-2 Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
 Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan &Talaro Chapter 5 Eucaryotic cells and microorganisms Chapter 5 2 3 Eucaryotic cells 3 Flagella 4 Cilia similar in overall structure to flagella, but
Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan &Talaro Chapter 5 Eucaryotic cells and microorganisms Chapter 5 2 3 Eucaryotic cells 3 Flagella 4 Cilia similar in overall structure to flagella, but
Cell Structure: What cells are made of. Can you pick out the cells from this picture?
 Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
Chapter 3: Cells. Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College
 Chapter 3: Cells Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College Learning Objectives Be able to describe: what a cell is & two main classes of cells. structure & functions of cell membranes. how
Chapter 3: Cells Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College Learning Objectives Be able to describe: what a cell is & two main classes of cells. structure & functions of cell membranes. how
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus Archaea & Eubacteria One circular chromosome Extremely small Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus!!! Membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, &
Basic Structure of a Cell Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus Archaea & Eubacteria One circular chromosome Extremely small Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus!!! Membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, &
Cell Theory. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century!
 Cell Notes Cell Theory All living organisms are made of. cells The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century! In 1665,
Cell Notes Cell Theory All living organisms are made of. cells The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century! In 1665,
TUBULAR ELEMENTS-A NEW STRUCTURE IN BLUE-GREEN ALGAL CELLS
 J. Cell Sci. 38, 303-308 (i977) 303 Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited TUBULAR ELEMENTS-A NEW STRUCTURE IN BLUE-GREEN ALGAL CELLS Z. N. TAHMIDA KHAN AND M. B. E. GODWARD Department
J. Cell Sci. 38, 303-308 (i977) 303 Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited TUBULAR ELEMENTS-A NEW STRUCTURE IN BLUE-GREEN ALGAL CELLS Z. N. TAHMIDA KHAN AND M. B. E. GODWARD Department
Chapter 4 Active Reading Guide A Tour of the Cell
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 4 Active Reading Guide A Tour of the Cell Section 1 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 4 Active Reading Guide A Tour of the Cell Section 1 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when
Anatomy of Plants Student Notes
 Directions: Fill in the blanks. Anatomy of Plants Student Notes Plant Cell Biology Segment 1. Plants Plants are organisms are incapable of movement produce food through 2. Animals Animals are multicellular
Directions: Fill in the blanks. Anatomy of Plants Student Notes Plant Cell Biology Segment 1. Plants Plants are organisms are incapable of movement produce food through 2. Animals Animals are multicellular
National Cell structure Pupil notes. Cell Biology. Sub-topic (1.1) Cell Structure. On completion of this topic I will be able to state that:
 Cell Biology Sub-topic (1.1) Cell Structure On completion of this topic I will be able to state that: Cells differ in structure as to whether they are animal, plant, fungi or bacterial cells. The detail
Cell Biology Sub-topic (1.1) Cell Structure On completion of this topic I will be able to state that: Cells differ in structure as to whether they are animal, plant, fungi or bacterial cells. The detail
Biology Slide 1 of 31
 Biology 1 of 31 2 of 31 The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of the Cell Because there were no instruments to make cells visible, the existence of cells was unknown for most of human history. This changed
Biology 1 of 31 2 of 31 The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of the Cell Because there were no instruments to make cells visible, the existence of cells was unknown for most of human history. This changed
Organelles & Cells Student Edition. A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole
 Name: Date: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains DNA? A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole 2. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure
Name: Date: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains DNA? A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole 2. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure
Unit 4: Cells. Biology 309/310. Name: Review Guide
 Unit 4: Cells Review Guide LEARNING TARGETS Place a checkmark next to the learning targets you feel confident on. Then go back and focus on the learning targets that are not checked. Identify the parts
Unit 4: Cells Review Guide LEARNING TARGETS Place a checkmark next to the learning targets you feel confident on. Then go back and focus on the learning targets that are not checked. Identify the parts
CELL STRUCTURE. What are the basic units of life? What are the structures within a cell and what are they capable of? How and why do cells divide?
 CELL STRUCTURE What are the basic units of life? What are the structures within a cell and what are they capable of? How and why do cells divide? YEAR 8 BODY SYSTEMS Cells alive! Cells are the smallest
CELL STRUCTURE What are the basic units of life? What are the structures within a cell and what are they capable of? How and why do cells divide? YEAR 8 BODY SYSTEMS Cells alive! Cells are the smallest
General Fungus Anatomy: Yeast: single cell fungi that reproduces by fission or budding
 Make-Up Assignment: Using the notes below as a guide, look up the organisms you are required to draw on the internet or in a book. Draw the organism in the circles provided and write a description of the
Make-Up Assignment: Using the notes below as a guide, look up the organisms you are required to draw on the internet or in a book. Draw the organism in the circles provided and write a description of the
Cell structure and functions
 Cell structure and functions Cells: The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. All living organisms are made up of cells. Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make organ systems
Cell structure and functions Cells: The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. All living organisms are made up of cells. Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make organ systems
UNIT 1: WELLNESS & HOMEOSTASIS. Biology notes 1 Mr.Yeung
 UNIT 1: WELLNESS & HOMEOSTASIS Biology notes 1 Mr.Yeung WHAT IS UNIT 1 ABOUT? Wellness & Homeostasis 0. Wellness (Reading labels/homeostasis/ serving size) 1. Cell Biology (Ch.3) Cell organelles Cell types
UNIT 1: WELLNESS & HOMEOSTASIS Biology notes 1 Mr.Yeung WHAT IS UNIT 1 ABOUT? Wellness & Homeostasis 0. Wellness (Reading labels/homeostasis/ serving size) 1. Cell Biology (Ch.3) Cell organelles Cell types
BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES
 BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES A1 A1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms 2. Compare cellular structures and their function
BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES A1 A1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms 2. Compare cellular structures and their function
COMPARISON OF PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS SIMILARITIES IN PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS
 COMPARISON OF PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Cells vary widely in structure and function, even within the same organism. The human body, for example, has more than 200 different types of cells, each with a specialized
COMPARISON OF PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Cells vary widely in structure and function, even within the same organism. The human body, for example, has more than 200 different types of cells, each with a specialized
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location ALL CELLS DNA Common in Animals Uncommon in Plants Lysosome
 CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
2. Cell surface proteins or receptors, that help cells communicate, are embedded within the cell membrane s phospholipid bilayer.
 UNIT 3 TEST BIOLOGY: 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.1.3 Cells, Cell Structures, Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic, Bacteria & Protists, Microscopes, Cell Communication, & Stem Cells True/False Indicate whether the statement
UNIT 3 TEST BIOLOGY: 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.1.3 Cells, Cell Structures, Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic, Bacteria & Protists, Microscopes, Cell Communication, & Stem Cells True/False Indicate whether the statement
Class XI Chapter 8 Cell The Unit of Life Biology
 Question 1: Which of the following is not correct? (a) Robert Brown discovered the cell. (b) Schleiden and Schwann formulated the cell theory. (c) Virchow explained that cells are formed from pre-existing
Question 1: Which of the following is not correct? (a) Robert Brown discovered the cell. (b) Schleiden and Schwann formulated the cell theory. (c) Virchow explained that cells are formed from pre-existing
Chapter 1 Lesson 1 page 26
 Chapter 1 Lesson 1 page 26 1. organism- any living thing that can carry out its life on its own 2. unicellular-one-celled organism 3. multicellular- many-celled organism Chapter 1 Lesson 1 Cells Vocab
Chapter 1 Lesson 1 page 26 1. organism- any living thing that can carry out its life on its own 2. unicellular-one-celled organism 3. multicellular- many-celled organism Chapter 1 Lesson 1 Cells Vocab
PARTICLES AND MICROTUBULES IN VASCULAR CELLS OF PINUS STROBUS L. DURING CELL WALL FORMATION
 Neu'Phytol (1971) 70, 1089-1093. PARTICLES AND MICROTUBULES IN VASCULAR CELLS OF PINUS STROBUS L. DURING CELL WALL FORMATION BY LIDIJA MURMANIS Forest Products Laboratory, * Forest Service, U.S. Department
Neu'Phytol (1971) 70, 1089-1093. PARTICLES AND MICROTUBULES IN VASCULAR CELLS OF PINUS STROBUS L. DURING CELL WALL FORMATION BY LIDIJA MURMANIS Forest Products Laboratory, * Forest Service, U.S. Department
