Ministry of Public Health of Ukraine M. Gorky Donetsk National Medical University. SYLLABUS of histology, cytology and embryology
|
|
|
- Matthew Boyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Form Н-3.04 Ministry of Public Health of Ukraine M. Gorky Donetsk National Medical University "APPROVED The first Deputy Rector for Educational Procedure Professor A.N. Talalayenko. " " 2012 SYLLABUS of histology, cytology and embryology Area of training 121 Medicine Intended speciality «Clinical Sciences» International medical faculty 1st year 2 nd term, 2 nd year 3 rd term Donetsk 2012
2 2 SYLLABUS of histology, cytology and embryology for the students on area of training Medicine Intended speciality «Clinical Sciences» Developed by the Head of the Histology department professor Barinov E.F., Senior Staff of the histology Department reader Nikolenko O.I. The Syllabus was considered at the Department Staff`s Session of histology, cytology and embryology Protocol Head of the Department of Histology, Cytology and Embryology, DM, professor E.F. Barinov Approved by the Methodological Commission of DNMU on biomedical disciplines Protocol Head of the Methodological Commission of DNMU on biomedical disciplines Head of the pathomorphology department, DM, professor I.V. Vasilenko
3 3 Description of discipline Name of parameter Credit number 9,5 Modules 3. Content modules 7 Individual work - no General number of hours 285 Hours for this form of education: Classes 170; Students independent work area of knowledge, area of training, educationallyqualifying level area of knowledge Medicine area of training 121 Medicine Speciality (professional direction): «Clinical Sciences» specialist Description of educational discipline daily form of studies Normative Year 1st, 2nd Semester 2nd, 3rd Lectures 34 hours Practical, seminars 136 hours Independent work 115 hours Type of control: Tests. Note: Correlation of amount of hours of classes makes to independent work: 67,6 %.
4 4 1. Aim and task of educational discipline: Aim: Task: To interpret the microscopic and submicroscopic structure of cells. To interpret regularities of embryonic development of human. To determine the critical periods of embryonic development, defect of human development. To explain the features of tissue embryonic development (histogenesis) and organs (organogenesis). To explain basic principles of organization of different tissues, their interactions. To interpret the microscopic structure of different human organs in the aspect of tissue interactions inside in different age periods, and also in the conditions of physiological regeneration. To learn at microscopic and submicroscopic level structure of cells, tissues, organs and systems of organism according to the functional state, and to establish links with structural features and functions. To establish regularities of development of human cells, tissues and organs. To find out structural organization of processes of vital activity and possibilities of the target influencing on it. As a result of study of histology, cytology and embryology a student must To know: Microscopic and submicroscopic structure of cells and noncellular structures. Regularities of human development, critical periods of embryogenesis, defect of development. Features of embryonic development of tissues (histogenesis) and organs (organogenesis). Basic principles of organization of different tissues and their interactions. Microscopic and submicroscopic structure of different human organs in the aspect of tissue interactions inside in different age periods, and also in the conditions of physiological regeneration. To be able: To determine histological elements (cells, cellular structures, intercellular matrix, postcellular structures) at a light and electronic microscopy. To interpret regularities of human embryonic development, explain the features of embryonic development of tissues (histogenesis) and organs (organogenesis). To recognize and differentiate different tissues in histological specimens. To interpret histophysiology of cells, tissues and organs at microscopic and submicroscopic levels of image. To interpret the role of different organs in homeostasis maintenance by the different systems, to analyse the microscopic structure of different human organs in the aspect of tissue interactions inside in different age periods, and also in the conditions of physiological regeneration.
5 5 2. Program of educational discipline. MODULE 1. CYTOLOGY AND GENERAL EMBRYOLOGY. Content module 1 «Cytology and general embryology». Theme 1 Methods of microscopy. Histological technique. Cytology. Surface apparatus. Intercellular junctions. Cytoplasm. Hyaloplasm. Methods of histological, cytological and embryological investigations. Structure of the light microscope. Rules of LM using. Histological technique. The term of the cell as an elementary level of organisation of life - the main structural and functional unit of all eukaryotic organisms. Importance of cytology in medicine. The modern conception of cell theory. General structure of the eukaryotic cell. Shapes and sizes of cells in animal and human body. Noncellular structures of organism. Cell membrane (plasma membrane, plasmolemma). Glycocalyx and submembrane layer, their chemical, structural and functional characteristic. Membrane properties. Endo- and exocytosis. Membranous digestion. Receptor function of the plasma membrane. Transport of substances. Intercellular junctions, their types, structure and functions. Components of the cytoplasm - hyaloplasm, organelles, inclusions. Hyaloplasm - definition, cytozol and cytomatrix, properties and significance. Theme 2 Cytology. Organells of common and special meaning. Organelles - definition, classification. Organelles of common meaning. Membranous organelles (smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus/complex, lysosomes, peroxysomes and mitochondria). Unmembranous organelles (ribosomes, centrioles, microtubules and microfilaments). Organelles of special-meaning as transformations of commonmeaning organelles or others cells parts (microvilli, basal folds, cilia, tails, tonofibrillae, neurofibrillae, myofibrils). Theme 3 Cytology. Inclusions. Nucleus. Inclusions - definition, classification, importance. Structure and functions of nucleus main components: chromatin, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, nuclear matrix. Nucleus-cytoplasm interactions. Significance of the nucleus in cells life, saving, realisation and reproduction of the genetic information. Shape, size and amount of nuclei, nucleus-cytoplasmic index in different cell types. Nuclear envelope. Its structure and functions. Membranes of the nuclear envelope, perinuclear space, nuclear pores, lamina, nuclear matrix. Chromatin: its structure and chemical composition. Chromosomes of nucleus during interphase. Eu- and heterochromatin. Sex-chromatin. Cell morphology during cell division. Karyotype, chromosome set. Nucleolus as a part of chromosomes which includes nuclear organisator. Structure of the nucleolus and its role in ribosome synthesis. Relationship between nucleus and cytoplasm during protein synthesis. Theme 4 Cell cycle. Cell reproduction. Cell aging and death. Life cycle of cells, its periods. Cells with different cell cycles. Influence of different factors on the cell cycle. Growth factors, chalones. Mitosis, its biological significance. Phases of the mitosis. Cells transformation during each phase of mitosis. Endomitosis. Polyploid cells. Meiosis, its peculiarities and biological role. Amitosis, its significance in physiological and reparative regeneration. Intracellular regeneration: general morpho-functional characteristic and biological role. Synthesis in a cell. Interactions between different structural elements during proteins, lipids and carbohydrates synthesis. Cell reaction on injury. Morphological changes after damage. Restoration of the cells structures. Cells adaptation, its role in cell survivability upon environmental changes. Theme 5 Human embryology. Subject and tasks of the human embryology. Medical embryology. Relations between phylogenesis and ontogenesis. Progenesis. Periods of human embryogenesis. Gametes. Male and female gametes: their structure and functions, the main stages of their development. Fertilisation. Conditions to normal fertilisation. Terms: capacitation, acrosomal reaction, sperm penetration, formation of male pronucleus. The cortical reaction of oocyte. Term the extracorporal fertilisation, its medical and social significance. Zygote as unicellular organism. Cleavage of human embryo, its characteristic. Implantation, its mechanisms, stages, chronology, peculiarities in human. Gastrulation. The early gastrulation, its chronology and results. Theme 6 Human embryology. The late gastrulation. The germ layers formation. Neurulation and axial organs complex formation. Presomitic and somitic periods. Differentiation of germ layers and their derivatives. Differentiation of the germ layers and their derivatives. Extraembryonal organs: amnion, chorion, yolk sack, allantois, umbilical cord. Human placenta, its development and functions. Changes of endometrium during gestation. Maternal-fetal system. The crucial periods of embryogenesis and ontogenesis. Theme 7 Control of practical skills on Content Module 2 Cytology and general embryology Theme 8 Resulting control on Module 1 Cytology and general embryology MODULE 2. GENERAL HISTOLOGY.
6 6 Content module 2 The common meaning tissues. Theme 1 Tissues. Epithelial tissues. Simple epithelia. The term of the tissue as system of cells and their derivatives that is the levels of life organisation. Mechanisms of histogenesis. Cells populations. Stem cells, its features. Determination and differentiation, their molecular mechanisms. The term of the histogenetic lineage (differon), regeneration. Tissues classification. Types of the physiological regeneration. Reparative regeneration. Epithelial tissues. General morpho-functional characteristic of epithelium. Histogenesis of epithelial tissues. Structure of various epithelial tissues. Basal lamina. Current conception of its structure, chemical composition and functional significance. Covering epithelia. Types of simple epithelia. Horizontal anisomorphism. Polarity of the epithelial cells. Cytokeratines as markers of different epithelia. Theme 2 Epithelial tissues. Stratified epithelia. Glandular epithelium. Morphofunctional characteristic of the stratified epithelium. Differones, their content and principles of differentiation. Vertical anisomorphism. Peculiarities of physiological and reparative regeneration of epithelial tissues. Glandular epithelium. General characteristic. Glands. Classifications and their principles. End-peices and duct system. Secretory activity of cells. Phases of the secretory cycle. Their morphological characteristic. Types of secretion. Theme 3 Tissues of the internal environment. Blood. General characteristic of the tissues of the internal environment. Sources of development, structure and functions. Mesenchyme. Classification of tissues of the internal environment. Blood content (plasma and blood cells). Blood functions. Plasma. Structure and functions of erythrocytes and thrombocytes. Erythrocytes: size, amount, stricture and functions. Classification of leukocytes. Hemogram. Age related peculiarities. Theme 4 Blood. Lymph. Structure and functions of leukocytes. Leukocytes classification, amount. Granulocytes: structure, functions. Agranulocytes: structure, functions. Role of leukocytes in immune reactions of organism. Hemogramm and leukocytes formula, its ageing peculiarities. Characteristic of lymph. Physiological regeneration of blood and lymph. Theme 5 Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis in embryological periods. Postnatal hematopoiesis as physiological regeneration of blood. Myeloid and lymphoid tissues. Modern theory of hematopoiesis. Stem cell of blood, its properties and abilities. The term of the colony forming unit of hematopoiesis. Unipotent cells - is progenitors. Precursors which can be detected by morphological investigation. Maturated cells of different lineage. Mature blood cells. Different histogenetic lineages: erythropoiesis, granulocytopoiesis, monocytopoiesis, thrombocytopoiesis, lymphopoiesis. Embryonal hematopoiesis as development of blood as tissue. Stages of embryonal hematopoiesis (mesoblastic, hepato-thymo-splenic and bone marrow-thymolymphoid), their peculiarities. Theme 6 Connective tissues. Loose connective tissue. General characteristic. Classification. Loose and dense connective tissues. Characteristic of loose connective tissue, its cells (fibroblast, macrophage, plasmocyte, mast cell, adipocyte, pigment cell, adventitial cell, endotheliocyte), fibres (collagen, reticular and elastic) and ground substance. Macrophages and mononuclear phagocyte system in human organism. Cells interactions during inflammation. Theme 7 Loose connective tissue. Extracellular matrix. Extracellular matrix. Fibres (collagen, elastic and reticular) and ground substance. Chemical composition of each components of extracellular matrix, morphological features for diagnostic and functional significance. Stages of synthesis of the components of the extracellular matrix. Collagen fibers formation. Balance between production and elimination of the extracellular matrix. Regeneration of the connective tissue. Theme 8 Connective tissues. Dense connective tissues. Tissues with special properties. Dense connective tissue, its types: regular and irregular, their location, structure and functions. Structure of tendons. Connective tissues with special properties: reticular tissue, adipose tissue (white and brown), pigment tissue, mucous tissue, their location, structure and functions. Theme 9 Skeletal tissues. Cartilage. General structure and functions. Types of cartilage (hyaline, elastic cartilage and fibrocartilage). Cartilage formation. Cells of the cartilage (chondroblasts, chondrocytes). Isogenous groups of cells. Extracellular matrix, its histochemical peculiarities.perichondrium, its role in cartilage nutrition, growth and regeneration. Bone tissues. General structure and functions. Primary and secondary bone tissues. Cells of bone tissue (osteoblasts, osteocytes and osteoclasts). Extracellular matrix of bone tissue, its content (fibres and ground substance), chemical composition and physical properties. Osteon structure. Bone histogenesis. Intramembranous and enchondral ossification. Structure of bone as organ. Periosteum, its role in bone nutrition, growth and regeneration. Bone remodelling during organism growth. Influence of different factors on bone growth. Joints, classification. Joint structure, articular cartilage, capsule and synovial fluid.
7 7 Theme 10 Bone formation. Membranous bone formation. Bone formation by the cartilage remodeling. Bone remodeling during the organism growth. Factors which influence on the bone growth and remodeling. Theme 11 Control of practical skills on content Module 2: Common meaning tissues. Content module 3 Specialised tissues. Theme 1 Muscle tissues. General morpho-functional characteristic of muscular tissues, sources of development, classification. Smooth muscle tissue derived from mesenchyme. Histogenesis, structure and functions. Myocyte. Organisation of the contractile apparatus. Regeneration of the smooth muscle tissue. Smooth muscle tissue derived from ectoderm and neural crest. Striated muscle tissue. Skeletal (somatic) muscle tissue. Situation, histogenesis, functional properties. Muscle fibre (symplast) as structural unit of muscle tissue, its structure. Myofibril structure. Sarcomere. Molecular mechanisms of contraction. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. Transverse tubule system. Types of muscular fibres. Muscle as organ. Myon. Endomysium, perimysium, epimysium. Myosatellicytes. Regeneration of skeletal muscular tissue. Cardiac muscle tissue (celomic type). Histogenesis. Structural peculiarities of contractile and conducing cardiomyocytes. Regeneration of cardiac muscle tissue. Atrial natriuretic factor. Theme 2 Nerve tissue. Neurons, glial cells. General morpho-functional characteristic. Histogenesis. Neurons. Morphological and functional classification. Structure of nerve cell body (perikaryon), axon and dendrites. Common and special-meaning organelles of neurons, their significance. Substances transport in neuron. Neurotransmitters. Neurosecretory cells. Neuroglia. General characteristic, classification. Neuroglia in the central nervous system. Macroglia (ependymocytes, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes). Microglia. Gliocytes in peripheral nervous system. Theme 3 Nerve tissue. Nerve fibers. Nerve endings, synapses. Nerve fibres. General characteristic, classification. Myelinated and unmyelinated fibres. Myelin formation in the central and peripheral nervous system. Degeneration and regeneration of nerve fibres. Nerve endings. General morphofunctional characteristic. Sensory and efferent endings, classification and structure. Synapses, classification, structure and mediators. Mechanisms of nerve impulse transmission in synapses. Neuronal reflectory arch. Neuronal theory. Theme 4 Control of practical skills on Module 2 General histology. Theme 5 Resulting tests control on Module 2 General histology. MODULE 3. SPECIAL HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Content module 4 Histology of the circulatory, endocrine and immune systems. Theme 1 Circulatory system. Arteries. General characteristic. Embryonal sources and developmental mechanisms. Classification of vessels. Dependency of vessel structure on hemodynamic. Endothelium. Structural and functional characteristic. Age changes. Arteries. General structure of vessels wall. Types of arteries. Structural peculiarities of the elastic arteries. Relations between hemodynamic and structure of wall. Peculiarities of arteries structure. Theme 2 Circulatory system. Microcirculatory bed. Microvessels. General characteristic, classification. Arterioles: structure and functions. Capillaries. Types of capillaries, functional significance. Venules. Wall structure, types, functions. Arteriovenous anastomoses. Theme 3 Circulatory system. Veins. Lymphatic vessels. Veins. Comparative peculiarities of vein and artery structure. Vein classification. Valves of veins. Organs peculiarities of veins structure. Lymphatic vessels. Classification, structure and functions. Lymphatic capillaries, structural peculiarities, role. Theme 4 Circulatory system. Heart. Heart. Embryogenesis. Heart wall structure, layers, their tissue content. Endocardium. Heart valves. Myocardium. Structural and functional peculiarities of cardiac muscle tissue. Morphological and functional characteristic of the contractile, conducting and secretory cardiomyocytes. Conducting system of the heart. Cardiac regeneration. Epicardium structure. Theme 5 Endocrine system. Hypothalamo-pituitary system.
8 8 General morpho-functional characteristic. Notion of hormones and their role in organism. Notions of hormone receptors and target cells. Mechanisms of hormone action. Feed-back regulation. Neuroendocrine system in human organism. Endocrine glands. Classification. Central and peripheral endocrine glands. Hypothalamus. Nuclei of the anterior and mediobasal regions of hypothalamus as the central part of the endocrine system. Structure and functions of neurosecretory cells. Relationship between hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Neurohemal organs (neurohypophysis and medial eminentia). Liberines and statines. Hypophysis. Embryogenesis of adeno- and neurohypophysis. Structure, cell types of adenohypophysis. Morphofunctional characteristic of endocrine cells, their alterations upon endocrine disbalance. Vascular system of the adenohypophysis, its significance in hormone passing from anterior hypothalamus. Age-related dynamiс. Theme 6 Endocrine system. Pineal gland. Adrenal gland. Pineal gland. Structure, tissue and cellular content, relations with others endocrine glands. Pineal hormones, their role in human organism. Development Age-related changes. Adrenal glands. Embryogenesis, fetal and definitive adrenal cortex. Zonal structure of adrenal cortex, characteristic of different endocrinocytes, their hormones. Role of adrenal cortex hormones in adaptation and metabolism. Adrenal medulla. Structure, cell types, hormones and their role. Theme 7 Endocrine system. Thyroid and parathyroid glands. Thyroid gland. Development, structure, cells. Follicles. Types of endocrine cells in the follicle, produced hormones and effects. Peculiarities of the secretory cycle. Follicles structure at different functional activity. C-cells, their hormone, significance and regulation. Parathyroid glands. Structure, cells types, hormone and its significance. APUD-system - is a system of a single hormone-producing cells in non-endocrine organs. Types of cells, situation, hormones and their action in organism. Theme 8 Immune system and lymphoid organs. Red bone marrow. Thymus. General morpho-functional characteristic and classification. Red bone marrow. Situation, structure and function. Stroma and parenchyma. Blood vessels system. Yellow bone marrow. Age-related changes. Regeneration. Thymus as a central organ of lymphopoiesis. Lobules with cortex and medulla. Hassal`s corpuscle. Histophysiology of the organ. Age-related and accidental involution. Status thymico-lymphaticus. Theme 9 Immune system and lymphoid organs. Spleen. General characteristic of the peripheral organs of the immune system. Spleen. General plan of structure. Tissues content of stroma and parenchyma. Red and white pulp. Peculiarities of vascularization. Structure and functions of the venous sinuses. White pulp: zones and their functional significance. Red pulp: structural content, mechanisms of old erythrocytes and platelets elimination. Regeneration. Theme 10 Immune system and lymphoid organs. Lymph nodes. General characteristic of the peripheral organs of the immune system. Lymph node structure. Stroma and parenchyma. Cortex and medulla. T- and B-zones. Paracortical zone. Medullary cords. Their cellular content. Lymph filtration and clearance. Afferent lymphatic vessels. System of sinuses. Histophysiology of the lymph nodes. Regeneration. Hemolymphatic nodes. Functional and structural peculiarities. Common lymphoid system of the mucosae. Lymphatic follicles and aggregates in respiratory and digestive system mucosa. Immune reactions. Cells classification according to the role in immune reaction realisation. Theme 11 Control of the practical skills on Content Module 4 Histology of the сirculatory, endocrine and immune systems. Content Module 5 Histology of Nervous system and special senses. Theme 1 Nervous system. Peripheral nerves, spinal ganglia, spinal cord. General morpho-functional characteristic of nervous system. Embryogenesis. Classification (anatomical and functional). Peripheral nervous system. Sensory ganglia (spinal and cranial). Tissues content. Structure: capsule, neurons and glia. Ganglia place in reflector arc. Nerve endings. Structure and functions. Peripheral nerve. The central nervous system. White and grey matter. Nerve centres. Spinal cord. General morphofunctional characteristic. Structure of grey matter. Neuronal content. Nuclei. Anterior and posterior roots. White matter. Conducting tracts. Spinal ganglion. General plan of structure. Key morphological features. Type of neurons. Pseudounipolar neurons, their capsules. Function of the spinal ganglion. Theme 2 Nervous system. Brain stem. Cerebellum. Brain. General characteristic, development. Brain stem. Neuronal organisation of grey matter. Nuclei of different parts of brain stem. Reticular formation. Diencefalon. Thalamus, its nuclei. Hypothalamus. Main nuclei. Functions of the diencefalon. Medulla oblongata. Morphological organisation. Main nucleui. Functional significance. Cerebellum. Structure and functions. Grey and white matter. Cerebellar cortex, its layers, neurones. Interneuronal relations. Afferent fibers and efferent neurones. Glial cells. Theme 3 Nervous system. Cerebrum. Cerebral cortex. Meninges. Blood-brain barriers.
9 9 Cerebrum. Cerebral cortex. General morphofunctional characteristic. Peculiarities of embryogenesis. Role of glial cells in column formation. Cytoarchitecture. Layers of the cerebral cortex. Structural and functional unit of cerebral cortex. Myeloarchitecture. Glial cells. Motor and sensor cortex. Their cellular content and characteristic of layers. Meninges. Blood-brain barrier. Structure and functions. Choroid plexus. Production of the cerebro-spinal fluid. Theme 4 Nervous system. Autonomic nervous system. Autonomic nervous system. General morphofunctional characteristic. Sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Notion of methasympathetic nervous system. Central nuclei of the autonomic nervous system. Structure of autonomic ganglia. Preganglionar and postganglionar fibers. Theme 5 Special senses. General characteristic. Organ of vision. General characteristic of special senses. Sensor systems. Classification of special senses. Eye. General characteristic, development. General structure of eye globe. Layers of eye globe, their parts and tissues content. Functional apparatus of the eye. Histophysiology of the cornea, iris and ciliary body. Blood-aqueous barrier. Theme 6 Special senses. Organ of vision. Retina. Retina layer and cellular composition. Photoreceptor cells in the retina. Pigment epithelium structure and functions. Neurones and glial cells of the retina. Optic nerve. Yellow macula. Blood-ophthalmic barrier. Age-related changes. Theme 7 Special senses. Auditory system and vestibular apparatus. General morphofunctional characteristic of auditory and vestibular system. Outer, middle and inner ear. Bone and membranous labyrinths. Vestibular part of the membranous labyrinths: sackulus and utriculus, semicircular canals. Their receptor zones. Hair and supporting cells. Membranes with otolites, cupula. Cochlea part of membranous labyrinths. Organ of Corti. Types of cells. Heir cells. Tectorial membrane. Histophisiology of Corti organ. Age-related changes. Theme 8 Special senses. Organ of olfaction, taste and tough. Olfactory part of the nasal cavity mucosa. General characteristic. Development, location. Olfactory and supporting cells. Histophisiology of the olfactory epithelium. Vomero-nasal organ. Taste buds. General morphofunctional characteristic and embryogenesis. Cell content and histophysiology of taste buds. Theme 9 Control of practical skills on content module 5 Histology of Nervous system and special senses Content Module 6 Histology of systems which maintain homeostasis. Theme 1 Digestive system. Digestive system development. Oral cavity. Tongue. Tonsils. General characteristic of the digestive system, classification. Alimentary canal. General plan of structure. Mucosa. Embryogenesis of the digestive system. Origin of epithelium in different parts of the alimentary canal. Oral cavity. Oral mucosa. Lips, chits, palate, gingiva, tongue, tonsils: structural and functional peculiarities of mucosa. Tongue structure. Dorsal and ventral surfaces. Tongue papillae. Their classification, structure and functions. Tonsils. General characteristic. Classification. Structure of the pharyngeal tonsils. Theme 2 Digestive system. Teeth development and structure. Teeth. Tissues and parts. Enamel. Dentin, cementum - chemical composition, structure and functions. Pulp structure and functions. Periodontal ligament structure and functions. Teeth development. Primary and definitive teeth. Age-related changes. Theme 3 Digestive system. Salivary glands. Big salivary glands: development, structure and functions. Exocrine and endocrine functions of the salivary glands. Endpieces and duct system. Structure of different types of the end-pieces according to different chemical composition of the secret. Age-related changes. Regeneratory properties. Regulation. Theme 4 Digestive system. Morphofunctional characteristic of the alimentary canal. Pharynx. Esophagus. Alimentary canal. The structure of alimentary canal wall. Its layers: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa and serosa or adventitia. Tissue and cellular content of layers, zonal peculiarities. Innervation and blood supply of the digestive tract, its lymphoid apparatus. Pharynx. Esophagus. Structural peculiarities of mucosa. Esophageal glands, situation and structure. Esophageal wall structure at different parts of the organ. Age-related changes. Theme 5 Digestive system. Stomach. Stomach. Its wall structure, tissue content. Folds, area and pits. Covering epithelium. Gastric glands, types, cellular content, structural peculiarities in different parts of the stomach. Regeneration of the epithelium of the stomach. Histophysiology of the organ. Age-related changes. Theme 6 Digestive system. Small intestine.
10 10 Small intestine. Regions of small intestine. Layers and their tissues. Epithelium, lining the wall of small intestine and its cells. Structure and function of the duodenum, ileum and jejunum. Distribution of the blood vessels, lymphatic, and nerve plexuses in the small intestine. Theme 7 Digestive system. Large intestine. Mucosa of large intestine. Cell types in epithelium of intestine. Entero-endocrine cells. Epithelial cell death and renewal. Lymphoid tissue associated with intestine wall. Appendix. Structural peculiarities of the rectum. Theme 8 Digestive system. Liver. Liver. General morphofunctional characteristic. Classical lobule, a portal lobule, and a liver acinus. Functions of the liver. Hepatocyte. Structure and functional peculiarities. Hepatic sinusoid, its relationship to the space of Disse, its cells and functional significance. Blood flow in the liver. Liver histophysiology. Synthesis, concentration, and storage of bile. Gallbladder. Theme 9 Digestive system. Pancreas. General morphofucntional characteristic. Structure of the exocrine part. Acinus as structural and functional unit of the exocrine part of organ. Structural and functional peculiarities of the acinocytes. Centroacinar cells. Structure of duct system. Pancreatic islets. Cellular content, hormones, functional significance. Regulation of the exocrine and endocrine functions of the pancreas. Regeneration. Age-related changes. Theme 10 Respiratory system. Respiratory tract. General morphofunctional characteristic. Respiratory tract. Layers of its wall. Structure and functions of the respiratory mucosa. Nasal cavity. Respiratory epithelium, its cell types and their structure and functions. General structure of the larynx. Vocal and ventricular folds. Structure and function of the trachea. Branches of the bronchial tree (large, middle and small bronchi). Lymphoid tissue associated with bronchial tree? Its significance to organism. Theme 11 Respiratory system. Lungs. Respiratory part. Respiratory portions of the respiratory system. Lungs. General morphofunctional characteristic. Structural unit of the respiratory part - acinus. Alveoli. Structure of the alveolar wall. Cell types, their structure and functions. Air-blood barrier, surfactant producing cells, and distribution of connective tissue fibers. Blood flow through the lungs: bronchial and pulmonary parts. Pleura. Age-related changes. Theme 12 Skin. Skin: general morphofunctional characteristic. Thin and thick skin. Layers of the skin, their structure and functions. Epidermis, its stratums in different types of skin, cellular content. Differonum of keratinocytes. Intraepidermal macrophages. Melanocytes characteristic. Dermis: papillary and reticular layers. Tissue content. Functional significance. Thick and chin skin. Nerve endings as peripheral part of the tough analyzator. Skin glands. Sweat glands, their types, location, structure and functions. Sebaceous glands. Structural and functional peculiarities. Hair follicle. Development, structure and functions. Theme 13 Urinary system. Kidney. Organs of urinary system. Kidney. General morphofunctional characteristic. Embryogenesis. Renal cortex and medulla. Nephron as structural unit of the kidney. Types of nephrones. Parts of nephron. Structure of the renal corpuscle, its cellular components. Glomerulus structure and functions, filtrating barrier. Nephron tubules, their structure and functions. Medullary rays and cortical labyrinth. Histophysiology of the different nephron tubules. Relationship of the renal pyramid with the minor and major calyx. Blood circulation through the kidney. Theme 14 Urinary system. Renal endocrine apparatus. Urinary tract. Juxtaglomerular apparatus, its components and their localisation. Physiological and clinical significance of the reninangiotensine system. Interstitial cells of the kidney medulla. General morphofunctional characteristic of urinary passage organs. Structure of the ureter and urinary bladder wall. Regeneration of urinary system organs. Theme 15 Control of practical skills on content module 6 Histology of the systems which maintain the homeostasis. Content Module 7 Histology of the reproductive systems. Theme 1 Male reproductive system. General morphofunctional characteristic. Testis. Organs of the male reproductive system. General characteristic. Embryogenesis. Primary germ cells, source, migration into gonads. Testis structure and functions. Seminiferous tubule structure and function. Spermatogenesis. Endocrine interstitial cells, their function. Theme 2 Male reproductive system. Gonadal ducts. Accessory glands.
11 11 Organs of the genital tract. Intragonadal and extragonadal genital ducts. Epididymis structure and functions. Accessory male reproductive glands. Structure and functions of prostate gland. Age-related changes. Theme 3 Female reproductive system. Ovarium. Organs of the female reproductive system. General characteristic. Histological organisation of the ovaries. Cortex and medulla. Oogenesis and folliculogenesis. Ovarian follicle, corpus luteum and corpus albicans. Changes in the ovaries during ageing process. Hypothalamo-pituitary-ovarian axis and ovarian cycle. Ovogenesis and its morphological peculiarities. Theme 4 Female reproductive system. Genital tract. Menstrual cycle. Organs of the female reproductive system. General organisation, layers. Oviducts: structure of mucosa, epithelium transformation during menstrual cycle. Uterus wall structure (layers). Endometrium layers. Characteristic of basal and functional layers. Variations in the mucosa of the uterus at different phases of the menstrual cycle. Regulation of the menstrual cycle. Myometrium. Tissue content, layers. Structural changes during pregnancy and delivery. Vagina: structure and functions. Age-related changes. Theme 5 Female reproductive system. Placenta. Origin and development of the placenta. Placenta structure, development, function. Chorionic villi: classification, structural composition. Placental barrier. Endocrine function of the placenta. Relationship between maternal and fetal organisms. Theme 6 Mammary gland. Development of the mammary gland. Structure of mammary gland. Structure and functions of the alveoli and duct system. Variations in the structure of mammary gland at different age and station. Posl lactational involution, Age-related involution of the mammary gland. Theme 7 Control of practical skills on Content Module 7 Histology of the reproductive systems. Theme 8 Resulting control on Module 3 Special histology and embryology.
12 12 4. Structure of educational discipline Modules, Content modules, topics Total Hours/ credits Hours (credits) Classes Lectu Practical res classes selfinstruct ion MODULE 1. CYTOLOGY AND GENERAL EMBRYOLOGY. Content module 1 «Cytology and general embryology». 30/ Theme 1 Methods of microscopy. Histological technique. Cytology. Surface apparatus. Intercellular junctions. Cytoplasm. Hyaloplasm. Theme 2 Cytology. Organells of common and special meaning. 2 1,5 Theme 3 Cytology. Inclusions. Nucleus. 2 1,5 Theme 4 Cell cycle. Cell reproduction. Cell aging and death. 2 1 Theme 5 Human embryology. 2 1 Theme 6 Human embryology. 2 1, Theme 7 Control of practical skills on Content Module 2 Cytology and 2 1,5 general embryology. Theme 8 Resulting control on Module 1 Cytology and general 2 3 embryology. Total Hours 30/ MODULE 2. GENERAL HISTOLOGY. Content module 2 The common meaning tissues. Theme 1 Tissues. Epithelial tissues. Simple epithelia Theme 2 Epithelial tissues. Stratified epithelia. Glandular epithelium. 2 2 Theme 3 Tissues of the internal environment. Blood ,5 Theme 4 Blood. Lymph. 2 1,5 Theme 5 Hematopoiesis. 2 1,5 Theme 6 Connective tissues. Loose connective tissue ,5 Theme 7 Loose connective tissue. Extracellular matrix. 2 1,5 Theme 8 Connective tissues. Dense connective tissues. 2 1,5 Tissues with special properties. 2 2 Theme 9 Skeletal tissues. 2 2 Theme 10 Bone formation. 2 2 Theme 11 Control of practical skills on content Module 2 Common 2 2 meaning tissues. Content module 3 Specialised tissues. Theme 1 Muscle tissues ,5 Theme 2 Nerve tissue. Neurons, glial cells ,5 Theme 3 Nerve tissue. Nerve fibers. Nerve endings, synapses. 2 1,5 Theme 4 Control of practical skills on Module 2 General histology. 2 2 Theme 5 Resulting tests control on Module 2 General histology. 2 4 Total Hours 73/2, MODULE 3. SPECIAL HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Content module 4 Histology of the circulatory, endocrine and immune systems. Theme 1 Circulatory system. Arteries ,5 Theme 2 Circulatory system. Microcirculatory bed. 2 1,5 Theme 3 Circulatory system. Veins. Lymphatic vessels. 2 1,5 Theme 4 Circulatory system. Heart. 2 1,5 Theme 5 Endocrine system. Hypothalamo-pituitary system Theme 6 Endocrine system. Pineal gland. Adrenal gland. 2 1 Theme 7 Endocrine system. Thyroid and parathyroid glands. 2 1 Theme 8 Immune system and lymphoid organs. Red bone marrow Thymus. Theme 9 Immune system and lymphoid organs. Spleen. 2 1
13 13 Theme 10 Immune system and lymphoid organs. Lymph nodes. 2 2 Theme 11 Control of the practical skills on Content Module 4 Histology 2 2 of the сirculatory, endocrine and immune systems. Content Module 5 Histology of Nervous system and special senses. Theme 1 Nervous system. Peripheral nerves, spinal ganglia, spinal cord ,5 Theme 2 Nervous system. Brain stem. Cerebellum. 2 2 Theme 3 Nervous system. Cerebrum. Cerebral cortex. Meninges. Bloodbrain 2 2 barriers. Theme 4 Nervous system. Autonomic nervous system. 2 1,5 Theme 5 Special senses. General characteristic. Organ of vision. 2 2 Theme 6 Special senses. Organ of vision. Retina. 2 2 Theme 7 Special senses. Auditory system and vestibular apparatus. 2 2 Theme 8 Special senses. Organ of olfaction, taste and tough. 2 1 Theme 9 Control of practical skills on content module 5 Histology of 2 2 Nervous system and special senses Content Module 6 Histology of systems which maintain homeostasis. Theme 1 Digestive system. Digestive system development. Oral cavity. 2 1,5 Tongue. Tonsils. Theme 2 Digestive system. Teeth development and structure. 2 1,5 Theme 3 Digestive system. Salivary glands. 2 1,5 Theme 4 Digestive system. Morphofunctional characteristic of the 2 2 1,5 alimentary canal. Pharynx. Esophagus. Theme 5 Digestive system. Stomach. 2 1,5 Theme 6 Digestive system. Small intestine. 2 1,5 Theme 7 Digestive system. Large intestine. 2 1 Theme 8 Digestive system. Liver ,5 Theme 9 Digestive system. Pancreas. 2 1,5 Theme 10 Respiratory system. Respiratory tract Theme 11 Respiratory system. Lungs. Respiratory part. 2 2 Theme 12 Skin. 2 2 Theme 13 Urinary system. Kidney Theme 14 Urinary system. Renal endocrine apparatus. Urinary tract. 2 2 Theme 15 Control of practical skills on content module 6 Histology of the 2 2 systems which maintain the homeostasis. Content Module 7 Histology of the reproductive systems. Theme 1 Male reproductive system. General morphofunctional characteristic. Testis. Theme 2 Male reproductive system. Gonadal ducts. Accessory glands. 2 2 Theme 3 Female reproductive system. Ovarium Theme 4 Female reproductive system. Genital tract. Menstrual cycle Theme 5 Female reproductive system. Placenta. 2 2 Theme 6 Mammary gland. 2 2 Theme 7 Control of practical skills on Content Module 7 Histology of the 2 2 reproductive systems. Theme 8 Resulting control on Module 3 Special histology and 4 2 embryology. Total Hours 180/
14 14 THEMES OF LECTURES AND PRACTICAL CLASSES ON HISTOLOGY, CYTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY FOR 1-2 YESR STUDENTS OF MEDICAL FACULTY Calendar plan of lectures on module 1 Cytology and general embryology. Topic Hours 1. Introduction on the histology, cytology and embryology 2 Altogether 2 Calendar plan of practical classes on module 1 Cytology and general embryology. Topic Hours 1. Methods of microscopy. Histological technique. Cytology. Surface apparatus. 2 Intercellular junctions. Cytoplasm. Hyaloplasm. 2. Cytology. Organells of common and special meaning Cytology. Inclusions. Nucleus Cell cycle. Cell reproduction. Cell aging and death Human embryology (1) Human embryology (2) Control of practical skills on Content Module 2 Cytology and general embryology Resulting control on Module 1 Cytology and general embryology. 2 Altogether 16 Calendar plan of lectures on Module 2 General histology Topic hours 2. Tissues. Epithelial tissues 2 3. Tissues of the internal environment. Blood. Hematopoiesis Connective tissues Muscle tissues Nerve tissue. 2 Altogether 12 Calendar plan of practical classes on module 2 Topic 9. Tissues. Epithelial tissues. Simple epithelia Epithelial tissues. Stratified epithelia. Glandular epithelium Tissues of the internal environment. Blood Blood. Lymph Hematopoiesis Connective tissues. Loose connective tissue Loose connective tissue. Extracellular matrix Connective tissues. Dense connective tissues. Tissues with special properties Skeletal tissues Bone formation Control of practical skills on content Module 2 Common meaning tissues Muscle tissues Nerve tissue. Neurons, glial cells (1) Nerve tissue. Nerve fibers. Nerve endings, synapses (2) Control of practical skills on Module 2 General histology Resulting tests control on Module 2 General histology 2 Altogether 32 Hours
15 15 Calendar plan of lectures on Module 3 Special histology and embryology Topic 7. Circulatory system Endocrine system Immune system and lymphoid organs Nervous system Digestive system Digestive glands Respiratory system Urinary system Male reproductive system Female reproductive system. 4 Altogether 22 Hours Calendar plan of practical classes on module 3 Special histology and embryology Topic Hours 25. Circulatory system. Arteries Circulatory system. Microcirculatory bed Circulatory system. Veins. Lymphatic vessels Circulatory system. Heart Endocrine system. Hypothalamo-pituitary system Endocrine system. Pineal gland. Adrenal gland Endocrine system. Thyroid and parathyroid glands Immune system and lymphoid organs. Red bone marrow. Thymus Immune system and lymphoid organs. Spleen Immune system and lymphoid organs. Lymph nodes Control of the practical skills on Content Module 4 Histology of the сirculatory, endocrine 2 and immune systems 36. Nervous system. Peripheral nerves, spinal ganglia, spinal cord Nervous system. Brain stem. Cerebellum Nervous system. Cerebrum. Cerebral cortex. Meninges. Blood-brain barriers Nervous system. Autonomic nervous system Special senses. Eye Special senses. Ear. Vestibulocochlear apparatus Special senses. Taste, olfaction and touch Control of practical skills on content module 5 Histology of Nervous system and special 2 senses 44. Digestive system. Oral cavity Digestive system. Teeth Digestive system. Salivary glands Digestive system. Pharynx. Esophagus Digestive system. Stomach Digestive system. Small and large intestine Digestive system. Liver Digestive system. Pancreas Respiratory system. Respiratory tract Respiratory system. Lungs Skin Urinary system. Kidneys Urinary system. Renal endocrine apparatus. Urinary tract Control of practical skills on content module 6 Histology of the systems which maintain the 2 homeostasis 58. Male reproductive system (1) Male reproductive system (2) Female reproductive system (1). 2
16 61. Female reproductive system (2) Female reproductive system (3) Mammary gland Control of practical skills on Content Module 7 Histology of the reproductive systems RESULTING TEST CONTROL OF MODULE 3 Special histology and embryology. 4 Altogether 88 16
17 17 CALENDAR PLAN OF TOPICS FOR EXTRAAUDITORY INDEPENDENT STUDENTS WORK (ISW) ON HISTOLOGY, CYTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY FOR 1-2 YEAR STUDENTS OF MEDICAL FACULTY TOPIC Calendar plan of extraauditory ISW on Module 1 Cytology and general embryology. 1. Introduction to microscopy and its methods. Histological technic Cytology. General cell structure. Surface apparatus. Hyaloplasm Cytology. Cytoplasm. Organelles. Inclusions 1,5 4. Cytology. Cell nucleus. Interaction between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell 1,5 reproduction. 5. General Embryology. Birds and mammalian Embryology. 1,5 6. Human Embryology (1) Human Embryology (2). 1,5 8. RESULTING test CONTROL OF MODULE 1 Cytology and general embryology 3 Altogether 12 TOPIC Calendar plan of extraauditory ISW on Module 2 General histology Hours Hours 9. Tissues. Epithelial tissues (1) Epithelial tissues (2) Tissues of the internal environment. Blood (1). 1,5 12. Lymph. Blood(2). 1,5 13. Hematopoiesis Connective tissues. Loose connective tissue. (1). 1,5 15. Connective tissues. Loose connective tissue. (2). 1,5 16. Connective tissues. Dense connective tissues. Connective tissues with special 1,5 properties. 17. Skeletal tissues Bone tissues histogenesis SKILLS CONTROL ON CONTENT MODULE Muscle tissues. 2,5 21. Nerve tissue (1). 1,5 22. Nerve tissue (2). 1,5 23. SKILLS CONTROL ON CONTENT MODULE RESULTING TEST CONTROL OF MODULE 2 General histology. 4 All 31 Topic Calendar plan of extraauditory ISW on Module 3 Special histology and embryology 25. Circulatory system. Arteries. 1,5 26. Circulatory system. Microcirculatory band. Lymphatic vessels. 1,5 27. Circulatory system. Veins. 1,5 28. Circulatory system. Heart. 1,5 29. Endocrine system. Hypothalamohypophyseal system Endocrine system. Pineal gland. Adrenal glands. 1,5 31. Endocrine system. Thyroid glands. Parathyroid glands. 1,5 32. Immune system and lymphoid organs. Bone marrow. Thymus Immune system and lymphoid organs. Spleen Immune system and lymphoid organs. Lymph nodes SKILLS CONTROL ON CONTENT MODULE 4 2 Hours
18 36. Nervous system. Nerves. Dorsal root ganglia. Spinal cord.. 1,5 37. Nervous system. Brain stem. Cerebellum Nervous system. Cerebral cortex Nervous system. Autonomic nervous system. Structure and functions. Meninges. 1,5 40. Special senses. Eye Special senses. Ear. Vestibulocochlear apparatus Special senses. Taste, olfaction and touch SKILLS CONTROL ON CONTENT MODULE Digestive system. Oral cavity. 1,5 45. Digestive system. Teeth. 1,5 46. Digestive system. Salivary glands. 1,5 47. Digestive system. Pharynx. Esophagus. 1,5 48. Digestive system. Stomach. 1,5 49. Digestive system. Small and large intestine. 2,5 50. Digestive system. Liver. 1,5 51. Digestive system. Pancreas. 1,5 52. Respiratory system. Respiratory tract Respiratory system. Lungs Skin Urinary system. Kidneys Urinary system. Renal endocrine apparatus. Urinary tract SKILLS CONTROL ON CONTENT MODULE Male reproductive system (1). 1,5 59. Male reproductive system (2). 1,5 60. Female reproductive system (1) Female reproductive system (2). 1,5 62. Female reproductive system (3) Mammary gland. 1,5 64. SKILLS CONTROL ON CONTENT MODULE RESULTING TEST CONTROL OF MODULE 3 Special histology and 2 embryology. All Methods of studies The following didactics methods are used on the department of histology, cytology and embryology: Organization and realization of educational-cognitive activity. Lectures, discussions are the sources of educational information transfer. Lectures serve as basis of acquirement of new knowledges by students, explain the difficult questions of discipline. Discussions make possible to turn the students to activation of acquisition of knowledge with the skilfully formulated by a teacher questions. Evident methods are widely used such as illustration, demonstration of tables, slides, multimedia systems during the conduction of lectures, discussions on a department. Examining with students topic of lesson a teacher always uses an inductive method: from the particular to the general examining unity of structure and function. A deductive method is also used, it allows to develop abstract thinking at students more active, assists students in mastering of educational material. Mastering and fixing of educational material by students on a department takes place during the independent work: examination by the students of microscopic structure of cells, tissues and organs in the process of study of histological specimens. This independent work is conducted under the direction of teacher, as a result students comprehend new material and apply knowledge in practice, that assists training of practical skills. On a department also there is independent work of students beyond control of teacher - self-instruction, when students fill in the tables, which represent development, structure and functions of cells and their structures, tissues, organs, draw schemes, ultramicroscopy structure of cells, tissues, organs. The home tasks have a positive influence on mastering of material, assist in forming of abilities and skills.
QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY"
 QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY" 1. The structure of the Plasmolemma. 2. Characteristic of receptive and transport functions of the plasmolemma. 3. The structure of intercellular contacts: Simple contact,
QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY" 1. The structure of the Plasmolemma. 2. Characteristic of receptive and transport functions of the plasmolemma. 3. The structure of intercellular contacts: Simple contact,
Physiology. Organization of the Body. Assumptions in Physiology. Chapter 1. Physiology is the study of how living organisms function
 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis Chapter 1 Physiology Physiology is the study of how living organisms function On the street explanations are in terms of meeting a bodily need Physiologic explanations
Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis Chapter 1 Physiology Physiology is the study of how living organisms function On the street explanations are in terms of meeting a bodily need Physiologic explanations
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
University of Jordan School of Medicine MD Program Curriculum
 University of Jordan School of Medicine MD Program Curriculum Course Title: General Histology Course number: 0502111 Credit Hours: 2 credits Academic Year Level: 1st year, 2nd semester 2016/2017 Course
University of Jordan School of Medicine MD Program Curriculum Course Title: General Histology Course number: 0502111 Credit Hours: 2 credits Academic Year Level: 1st year, 2nd semester 2016/2017 Course
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE. Cells, Tissues, and Membranes
 NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE Subject: Anatomy & Physiology Grade: 11-12
 Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: 8 weeks Topic(s): Introduction, Tissues, Integumentary System Describe the major components and functions of physiological systems, including skeletal, muscle,
Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: 8 weeks Topic(s): Introduction, Tissues, Integumentary System Describe the major components and functions of physiological systems, including skeletal, muscle,
Course Outcome Summary
 Course Information: Description: Instruction Level: 11-12 Total Credits: Prerequisites: Textbooks: Course Content: (SCANAT) Advanced Anatomy & Physiology A basic understanding of the human body is essential
Course Information: Description: Instruction Level: 11-12 Total Credits: Prerequisites: Textbooks: Course Content: (SCANAT) Advanced Anatomy & Physiology A basic understanding of the human body is essential
Organization of Vertebrate Body. Organization of Vertebrate Body
 The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
JEFFERSON COLLEGE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms. Gene Families
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Gene Families In metazoans,
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Gene Families In metazoans,
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE
 AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
The University of Jordan. Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center. Histology 1 for dentistry. COURSE Syllabus
 The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus Histology 1 for dentistry 1 Course title Histology-1 2 Course number 0542226 Credit hours (theory, practical) 3 (2 theory,
The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus Histology 1 for dentistry 1 Course title Histology-1 2 Course number 0542226 Credit hours (theory, practical) 3 (2 theory,
BIOL Anatomy and Physiology I ( version L )
 BIOL 2113 - Anatomy and Physiology I ( version 213L ) Course Title Course Development Learning Support Anatomy and Physiology I Standard No Course Description Introduces the anatomy and physiology of the
BIOL 2113 - Anatomy and Physiology I ( version 213L ) Course Title Course Development Learning Support Anatomy and Physiology I Standard No Course Description Introduces the anatomy and physiology of the
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill
 Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy & Physiology Curriculum Map Date Content/Topics Objectives Activities/Assessments Aug. 7th- 21st
 Anatomy & Physiology Curriculum Map 2012-13 Date Content/Topics Objectives Activities/Assessments Aug. 7th- 21st Chapter 1 Body Regions/Cavities Directional Terms Homeostasis System Basics with introduction
Anatomy & Physiology Curriculum Map 2012-13 Date Content/Topics Objectives Activities/Assessments Aug. 7th- 21st Chapter 1 Body Regions/Cavities Directional Terms Homeostasis System Basics with introduction
Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue.
 Plant Tissues Class- IX Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. PLANT TISSUES ANIMAL TISSUES 1. Most of the plant tissues are Most of the tissues
Plant Tissues Class- IX Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. PLANT TISSUES ANIMAL TISSUES 1. Most of the plant tissues are Most of the tissues
INTRODUCTION Veterinary Physiology I Odd Semester 2015/2016. Division of Physiology Department of Anatomy, Physiology and Pharmacology FVM BAU
 INTRODUCTION Veterinary Physiology I Odd Semester 2015/2016 Division of Physiology Department of Anatomy, Physiology and Pharmacology FVM BAU 1 Main references: Cunningham, JG. 2002. Textbook of Veterinary
INTRODUCTION Veterinary Physiology I Odd Semester 2015/2016 Division of Physiology Department of Anatomy, Physiology and Pharmacology FVM BAU 1 Main references: Cunningham, JG. 2002. Textbook of Veterinary
CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES
 NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
Functions of the systems of the human body and their relation to homeostasis; includes disease prevention and cure, health, wellness, and nutrition.
 UNITED STATES INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCES COURSE SYLLABUS NSC 2205: HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY CREDIT 3 UNITS A. COURSE DESCRIPTION Functions of the systems of the human body and their relation
UNITED STATES INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCES COURSE SYLLABUS NSC 2205: HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY CREDIT 3 UNITS A. COURSE DESCRIPTION Functions of the systems of the human body and their relation
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction
 East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Human Anatomy/Physiology, College Preparatory Course(s): CP Human Anatomy/Physiology Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Human Anatomy/Physiology, College Preparatory Course(s): CP Human Anatomy/Physiology Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period
Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards. Anatomical terms. Homeostatic mechanisms. Characteristics of Life. Requirements for life
 Honors Anatomy & Physiology 2012 Michael Harshaw, Melissa Castone Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards Month Introduction September- 1.5 weeks How do Anatomy and Physiology relate to
Honors Anatomy & Physiology 2012 Michael Harshaw, Melissa Castone Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards Month Introduction September- 1.5 weeks How do Anatomy and Physiology relate to
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes
 Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
KRSN BIO 2030 Anatomy and Physiology - 8 credit hours KRSN BIO 2031 Anatomy and Physiology KRSN BIO 2032 Anatomy and Physiology Lab
 KRSN BIO 2030 Anatomy and Physiology - 8 credit hours KRSN BIO 2031 Anatomy and Physiology KRSN BIO 2032 Anatomy and Physiology Lab For institutional specific information, visit the University & College
KRSN BIO 2030 Anatomy and Physiology - 8 credit hours KRSN BIO 2031 Anatomy and Physiology KRSN BIO 2032 Anatomy and Physiology Lab For institutional specific information, visit the University & College
1. In regard to the characteristics of connective tissue, which of the following is TRUE?
 Anatomy and Physiology Fall 2017: Exam I Form A Name: 1. In regard to the characteristics of connective tissue, which of the following is TRUE? a. Once formed the ground substance found in areolar CT is
Anatomy and Physiology Fall 2017: Exam I Form A Name: 1. In regard to the characteristics of connective tissue, which of the following is TRUE? a. Once formed the ground substance found in areolar CT is
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY, lecture and lab
 LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR MDCA 1309 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR MEDICAL ASSISTANTS Semester Hours Credit: 3 Instructor: Office Hours:
 1 CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR MDCA 1309 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR MEDICAL ASSISTANTS Semester Hours Credit: 3 Instructor: I. INTRODUCTION Office Hours: A. Course Description: Emphasis on structure
1 CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR MDCA 1309 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR MEDICAL ASSISTANTS Semester Hours Credit: 3 Instructor: I. INTRODUCTION Office Hours: A. Course Description: Emphasis on structure
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125
 Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog ANAT 125 Human Anatomy 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog ANAT 125 Human Anatomy 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I
 South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 80 Types of Instruction Instruction Type Anatomy and Physiology
South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 80 Types of Instruction Instruction Type Anatomy and Physiology
Broken Arrow Public Schools Physiology Objectives
 1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record AP 150
 Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record AP 150 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2012-2013 catalog AP 150 Integrative Anatomy and Physiology 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record AP 150 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2012-2013 catalog AP 150 Integrative Anatomy and Physiology 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory
1 P a g e. Course Title. Course Number PN 111
 Date Course Title Credits Course Number PN 111 Human Anatomy & Physiology Pre-requisite (s) PN 110 Co-requisite (s) Hours 105 Hours Out of Class Work Assignment Hours Place and Time of Class Meeting 32
Date Course Title Credits Course Number PN 111 Human Anatomy & Physiology Pre-requisite (s) PN 110 Co-requisite (s) Hours 105 Hours Out of Class Work Assignment Hours Place and Time of Class Meeting 32
28.1. Levels of Organization. > Virginia standards
 28.1 Levels of Organization vocabulary determination differentiation tissue organ organ system > Virginia standards BIO.4 The student will investigate and understand life functions of Archaea, Bacteria
28.1 Levels of Organization vocabulary determination differentiation tissue organ organ system > Virginia standards BIO.4 The student will investigate and understand life functions of Archaea, Bacteria
Chapter 1. The Human Organism 1-1
 Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE 30
 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE 30 Description This second-year course in biology emphasizes the workings of the human body. The course is offered in the fall semester and meets six (6) periods per
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE 30 Description This second-year course in biology emphasizes the workings of the human body. The course is offered in the fall semester and meets six (6) periods per
Academic Anatomy Pacing Guide
 Academic Anatomy Pacing Guide Course Description: This course provides the student with a general study of the structure of EOC VOCATS the human body and the detailed study of the functions of the body
Academic Anatomy Pacing Guide Course Description: This course provides the student with a general study of the structure of EOC VOCATS the human body and the detailed study of the functions of the body
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 3. Cells and Tissues. Slides Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L.
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Slides 3.1 3.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Slides 3.1 3.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION. Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 120 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Deborah Allen. Revised date: July, 2014
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 120 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Division Chair, Math, Science & Business Ms.
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 120 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Division Chair, Math, Science & Business Ms.
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
SCIENCE: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 SCIENCE: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY END-OF-COURSE EXAM GRADE 9-12 YEAR 17 18 ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT Purpose Statement Anatomy and Physiology The Anatomy and Physiology End-of-Course (EOC) exam is intended to
SCIENCE: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY END-OF-COURSE EXAM GRADE 9-12 YEAR 17 18 ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT Purpose Statement Anatomy and Physiology The Anatomy and Physiology End-of-Course (EOC) exam is intended to
ESSENTIAL LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 ESSENTIAL LEARNING OUTCOMES: Upon satisfactory completion of BIO 2331 - Anatomy and Physiology I, the student should be able to perform the following outcomes and supporting objectives: Outcome: A. Critical/Creative
ESSENTIAL LEARNING OUTCOMES: Upon satisfactory completion of BIO 2331 - Anatomy and Physiology I, the student should be able to perform the following outcomes and supporting objectives: Outcome: A. Critical/Creative
Advanced Anatomy and Physiology
 Lakeshore Technical College 10806179 Advanced Anatomy and Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Alternate Title Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 90 Adv Anatomy & Physiology Advanced
Lakeshore Technical College 10806179 Advanced Anatomy and Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Alternate Title Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 90 Adv Anatomy & Physiology Advanced
Anatomy and Physiology. Science Curriculum Framework
 Anatomy and Physiology Science Curriculum Framework Revised 005 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology should develop an understanding of the organization of the human body through studies of body
Anatomy and Physiology Science Curriculum Framework Revised 005 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology should develop an understanding of the organization of the human body through studies of body
Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List Updated Edition
 Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List Updated Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1578421/ Section 1 Cells and Tissues (74 cards) 1 The Cell (11 cards) Plate 1-1 The Cell 1-1.1 Centrioles 1-1.2
Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List Updated Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1578421/ Section 1 Cells and Tissues (74 cards) 1 The Cell (11 cards) Plate 1-1 The Cell 1-1.1 Centrioles 1-1.2
Pacing: August June These benchmarks serve as common threads to be integrated throughout the units of study Teacher Notes:
 Anatomy and Honors and Non-Honors Curriculum Map al Focus Calendar 1 Body of Knowledge :Practice of Science Standard:SC.912.N.1.1 Essential Questions Pacing: August June These benchmarks serve as common
Anatomy and Honors and Non-Honors Curriculum Map al Focus Calendar 1 Body of Knowledge :Practice of Science Standard:SC.912.N.1.1 Essential Questions Pacing: August June These benchmarks serve as common
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY. 4 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Vivian Aubuchon. Revised date: May, 2014
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Vivian Aubuchon Revised date: May, 2014 Minor Revision or Update by: Fran Moore Per Curriculum Committee Process
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Vivian Aubuchon Revised date: May, 2014 Minor Revision or Update by: Fran Moore Per Curriculum Committee Process
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Anatomy and Physiology I
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Anatomy and Physiology I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 201 (SUN# BIO 2201) Title Human Anatomy and Physiology I Credits 4 Developed
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Anatomy and Physiology I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 201 (SUN# BIO 2201) Title Human Anatomy and Physiology I Credits 4 Developed
BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I
 South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Information Description Anatomy and Physiology I is an introduction to the structure and function of the human body under normal and abnormal
South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Information Description Anatomy and Physiology I is an introduction to the structure and function of the human body under normal and abnormal
Unit code: K/503/1682 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15
 Unit 10: Anatomy and Physiology Unit code: K/503/1682 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit aims to develop learner understanding of physical support and movement in animals, body transport systems,
Unit 10: Anatomy and Physiology Unit code: K/503/1682 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit aims to develop learner understanding of physical support and movement in animals, body transport systems,
Chapter 6: Tissues. KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept]
![Chapter 6: Tissues. KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] Chapter 6: Tissues. KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept]](/thumbs/78/78538656.jpg) Chapter 6: Tissues KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] CONCEPTS RATING Meristems in plants ** Permanent tissues in plants **** Animal tissues ***** 1. Tissue is a group of cells
Chapter 6: Tissues KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] CONCEPTS RATING Meristems in plants ** Permanent tissues in plants **** Animal tissues ***** 1. Tissue is a group of cells
Introduction to the Human Body. Cells. Body Functions. Tissues. Organs. Systems. Body Functions & Life Process
 complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
WHAT UNIVERSITY GENERAL EDUCATION OUTCOMES GUIDE STUDENT LEARNING IN COURSES THAT CARRY NATURAL SCIENCES CREDIT?
 Ralph Henry Contact: ralph.henry@uark.edu, 479-283-0154 A plan to assess student learning in a University General Education Core Curriculum course: BIOL2213/BIOL2211L Human Physiology/Human Physiology
Ralph Henry Contact: ralph.henry@uark.edu, 479-283-0154 A plan to assess student learning in a University General Education Core Curriculum course: BIOL2213/BIOL2211L Human Physiology/Human Physiology
3. Structure, Function, and Genetics of Plants and Animals
 3. Structure, Function, and Genetics of Plants and Animals 3.1 Structure of Plants 3.2 Plant Physiology and Reproduction 3.3 Structure and Function of Animal Tissues 3.4 Anatomy of Animal Systems, Part
3. Structure, Function, and Genetics of Plants and Animals 3.1 Structure of Plants 3.2 Plant Physiology and Reproduction 3.3 Structure and Function of Animal Tissues 3.4 Anatomy of Animal Systems, Part
The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY
 The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY The topography of organs and organ systems 1. The organs are: a. clusters of identical tissues; b. different tissue groups; c. morphological units that fulfill the function
The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY The topography of organs and organ systems 1. The organs are: a. clusters of identical tissues; b. different tissue groups; c. morphological units that fulfill the function
MIDDLE TOWNSHIP PUBLIC SCHOOLS CAPE MAY COURT HOUSE, NJ CURRICULUM GUIDE DISCIPLINE: Science: Anatomy and Physiology GRADE LEVEL: 10-12
 s DISCIPLINE: Science: Physiology GRADE LEVEL: 10-12 5.1.12 B 5.2.12A B.4 A.a A.1 A.b A.d A.5 A.6 A.a A.1 A.b A.2 Organizati on and General Plan of the Body Basic Chemistry How are locations within the
s DISCIPLINE: Science: Physiology GRADE LEVEL: 10-12 5.1.12 B 5.2.12A B.4 A.a A.1 A.b A.d A.5 A.6 A.a A.1 A.b A.2 Organizati on and General Plan of the Body Basic Chemistry How are locations within the
Detailed Learning Outcomes
 Detailed Learning Outcomes Following lectures, workshops and directed study activities, students should: 1. Understand the principles behind the study of bioscience in relation to the profession of SLT
Detailed Learning Outcomes Following lectures, workshops and directed study activities, students should: 1. Understand the principles behind the study of bioscience in relation to the profession of SLT
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS
 SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: BIOL 132 Department: Biological Sciences Course Title: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ 1. Recognize
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: BIOL 132 Department: Biological Sciences Course Title: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ 1. Recognize
STRANDS AND STANDARDS
 STRANDS AND STANDARDS ADVANCED HEALTH SCIENCE: TECHNOLOGY ENHANCED HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Course Description An Advanced Health Science course that is taught through Weber State University as a Concurrent
STRANDS AND STANDARDS ADVANCED HEALTH SCIENCE: TECHNOLOGY ENHANCED HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Course Description An Advanced Health Science course that is taught through Weber State University as a Concurrent
7. CONTROL AND COORDINATION
 7. CONTROL AND COORDINATION Multicellular animals, except sponges, have specialized cells called neurons, for responding to stimuli. A neuron or nerve cell is the structural and functional unit of the
7. CONTROL AND COORDINATION Multicellular animals, except sponges, have specialized cells called neurons, for responding to stimuli. A neuron or nerve cell is the structural and functional unit of the
Anatomy and Physiology GRADE 12 Course Curriculum Prepared by Lou Pompilii ABINGTON SCHOOL DISTRICT Abington, Pennsylvania 2010
 Anatomy and Physiology GRADE 12 Course Curriculum Prepared by Lou Pompilii ABINGTON SCHOOL DISTRICT Abington, Pennsylvania 2010 Anatomy & Physiology A Course of Study Table of Contents Contents: Page:
Anatomy and Physiology GRADE 12 Course Curriculum Prepared by Lou Pompilii ABINGTON SCHOOL DISTRICT Abington, Pennsylvania 2010 Anatomy & Physiology A Course of Study Table of Contents Contents: Page:
Developmental Zoology. Ectodermal derivatives (ZOO ) Developmental Stages. Developmental Stages
 Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
4. Which of the following organelles digests waste using hydrolytic enzymes:
 Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Form and Function. Physical Laws and Form. Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function. AP Biology Fig Figs & 40.
 Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function AP Biology 2013 1 Form and Function Comparative studies show that form and function are closely related Natural selection can fit the form (anatomy)
Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function AP Biology 2013 1 Form and Function Comparative studies show that form and function are closely related Natural selection can fit the form (anatomy)
ORGANISATION IN THE LIVING THINGS
 2 ORGANISATION IN THE LIVING THINGS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. A group of similar cells which perform a particular function is called (a) organism (b) tissue (c) organelle
2 ORGANISATION IN THE LIVING THINGS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. A group of similar cells which perform a particular function is called (a) organism (b) tissue (c) organelle
Passaic County Technical Institute. Wayne, NJ. Anatomy and Physiology II Curriculum. August 2015
 Passaic County Technical Institute Wayne, NJ Anatomy and Physiology II Curriculum August 2015 Anatomy and Physiology II Curriculum August 2015 I. Course Description Anatomy and Physiology II is a full
Passaic County Technical Institute Wayne, NJ Anatomy and Physiology II Curriculum August 2015 Anatomy and Physiology II Curriculum August 2015 I. Course Description Anatomy and Physiology II is a full
Cells. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Next Generation Science Standards Life Science Performance Expectations
 A Correlation of Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 12 th Edition, 2018 To the Life Science Performance Expectations HS-LS1 From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes HS-LS1-1. Construct
A Correlation of Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology 12 th Edition, 2018 To the Life Science Performance Expectations HS-LS1 From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes HS-LS1-1. Construct
Inferring disease-associated lncrnas using expression data and disease-associated protein coding genes
 Inferring disease-associated lncrnas using expression data and disease-associated protein coding genes Xiaoyong Pan Center for non-coding RNA in Technology and Health, Department of Clinical Veterinary
Inferring disease-associated lncrnas using expression data and disease-associated protein coding genes Xiaoyong Pan Center for non-coding RNA in Technology and Health, Department of Clinical Veterinary
CURRICULUM MAP. TIME CONTENT PAGE REF. SKILLS ASSESSMENT/ACTIVITIES Day 1-3
 CURRICULUM MAP COURSE TITLE: Anatomy and Physiology DESCRIPTION TEXTBOOK Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology OF COURSE: 8 th ed: Elaine Marieb Integrated approach to human anatomy. Performance and lab
CURRICULUM MAP COURSE TITLE: Anatomy and Physiology DESCRIPTION TEXTBOOK Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology OF COURSE: 8 th ed: Elaine Marieb Integrated approach to human anatomy. Performance and lab
Cells - Chapter 3. Transport into and out of cells. The Cell Theory. Hooke (1665) Leeuwenhoek ( ) Simple Cells Cell Tutorial
 Cells - Chapter 3 Cells Alive Intro Video Transport into and out of cells Organization/Review Simple Cells Cell Tutorial http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/framz.asp?objid=ap11604 Cell Death http://www.whfreeman.com/kuby/content/anm/kb04an01.htm
Cells - Chapter 3 Cells Alive Intro Video Transport into and out of cells Organization/Review Simple Cells Cell Tutorial http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/framz.asp?objid=ap11604 Cell Death http://www.whfreeman.com/kuby/content/anm/kb04an01.htm
18. Which body system is needed for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide? A. Respiratory B. Integumentary C. Digestive D. Urinary 19.
 1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
HSC HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Midterm Exam October 17, 2001 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology and Department of Physiology Time: 50 minutes 1.
 HSC 208.6 - HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Midterm Exam October 17, 2001 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology and Department of Physiology Time: 50 minutes 1. An organ: A. is the smallest independent unit of life
HSC 208.6 - HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Midterm Exam October 17, 2001 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology and Department of Physiology Time: 50 minutes 1. An organ: A. is the smallest independent unit of life
Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology
 Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
East Poinsett County School District Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Guide Revised August 2011
 East Poinsett County School District Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Guide Revised August 0 Ongoing Strand: Nature of Science Standard 6: Students shall demonstrate an understanding that science is a
East Poinsett County School District Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Guide Revised August 0 Ongoing Strand: Nature of Science Standard 6: Students shall demonstrate an understanding that science is a
Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: Anatomy Final Exam Review: This review is an overview, and does not represent a complete copy of the final exam, nor is it an exhaustive listing of topics from this year. Directions: Complete
Class: Date: Anatomy Final Exam Review: This review is an overview, and does not represent a complete copy of the final exam, nor is it an exhaustive listing of topics from this year. Directions: Complete
Foundation Year Programme
 Foundation Year Programme Entrance Tests BIOLOGY SPECIFICATION Standard ATS sample material 2 3 Biology 1. Living organisms 1.1. Characteristics of living organisms a. List and define the main characteristics
Foundation Year Programme Entrance Tests BIOLOGY SPECIFICATION Standard ATS sample material 2 3 Biology 1. Living organisms 1.1. Characteristics of living organisms a. List and define the main characteristics
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR BY 124 EXAM Distinguish between osmoregulators and osmoconformers. Give an example of each.
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR BY 124 EXAM 4 CHAPTER 44 1. Distinguish between osmoregulators and osmoconformers. Give an example of each. 2. Discuss the problems that marine organisms, freshwater organisms,
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR BY 124 EXAM 4 CHAPTER 44 1. Distinguish between osmoregulators and osmoconformers. Give an example of each. 2. Discuss the problems that marine organisms, freshwater organisms,
NOTE: LOOK ON MY WEBSITE FOR THE MUSCLE LABELING POWER POINT/PDF Part I. Identify the parts of the neuron that are labeled below.
 Anatomy & Physiology Nervous System Part I 2/26/16 NOTE: LOOK ON MY WEBSITE FOR THE MUSCLE LABELING POWER POINT/PDF Part I. Identify the parts of the neuron that are labeled below. 1. 2. 3. 5. 4. 6. Part
Anatomy & Physiology Nervous System Part I 2/26/16 NOTE: LOOK ON MY WEBSITE FOR THE MUSCLE LABELING POWER POINT/PDF Part I. Identify the parts of the neuron that are labeled below. 1. 2. 3. 5. 4. 6. Part
Active movement Cancer. Cell. Cell inclusion Cytoplasm Diffusion Organelle Osmosis Passive movement Plasma membrane. Cell
 CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Learning Objective At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: - Define Anatomy and Physiology - Explain Homeostasis - Describe levels
CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Learning Objective At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: - Define Anatomy and Physiology - Explain Homeostasis - Describe levels
Head and Face Development
 Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
PSYCHOSOMATICS COURSE PSYCHOSOMATICS MANUAL. Section E DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES WORK IN PROGRESS - DO NOT COPY - FOR CORE ENERGETICS TRAINING USE, ONLY!
 PSYCHOSOMATICS MANUAL Section E DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES 1 DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS TISSUE LAYERS, ENERGETIC BLUE PRINT and PSYCHOSOMATIC UNITY Understanding the basic function of the tissue
PSYCHOSOMATICS MANUAL Section E DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES 1 DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS TISSUE LAYERS, ENERGETIC BLUE PRINT and PSYCHOSOMATIC UNITY Understanding the basic function of the tissue
Plant Tissues. Parenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, NOIDA CLASS-IX BIOLOGY TOPIC- TISSUES BY: UMESH VERMA Defination- A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. Also this group od
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, NOIDA CLASS-IX BIOLOGY TOPIC- TISSUES BY: UMESH VERMA Defination- A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. Also this group od
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition
 Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic)
 Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic) Fates of Mesoderm Paraxial - Dermis of skin - Axial Skeleton - Axial and limb muscles/tendons
Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic) Fates of Mesoderm Paraxial - Dermis of skin - Axial Skeleton - Axial and limb muscles/tendons
human cell Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function.
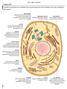 human cell CELL AND TISSUES Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function. Golgi apparatus Organelle composed of a series
human cell CELL AND TISSUES Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function. Golgi apparatus Organelle composed of a series
The Cell. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 2 The Cell PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
C h a p t e r 2 The Cell PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
Module A BODY PLAN & ORGANIZATION
 Module A BODY PLAN & ORGANIZATION Topic from Anatomical position Body planes & sections Body cavities & regions Directional terms Basic terminology Levels of organization Survey of body systems 1. Describe
Module A BODY PLAN & ORGANIZATION Topic from Anatomical position Body planes & sections Body cavities & regions Directional terms Basic terminology Levels of organization Survey of body systems 1. Describe
Slide 1 / Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system.
 Slide 1 / 64 1 Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system. Slide 2 / 64 2 List the four major groups of tissues in animals. Slide 3 /
Slide 1 / 64 1 Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system. Slide 2 / 64 2 List the four major groups of tissues in animals. Slide 3 /
Physiology 2 nd year. Neuroscience Optional Lecture
 Academic year 2018/2019 Physiology 2 nd year Semester 1 Curricula Nervous system physiology Blood physiology Acid-base equilibrium Bibliography: Boron & Boulpaep Medical Physiology, 3 rd edition Physiology
Academic year 2018/2019 Physiology 2 nd year Semester 1 Curricula Nervous system physiology Blood physiology Acid-base equilibrium Bibliography: Boron & Boulpaep Medical Physiology, 3 rd edition Physiology
Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye is. a. anatomy c. biology b. physiology d. pathology Anatomy is the
Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye is. a. anatomy c. biology b. physiology d. pathology Anatomy is the
Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p.
 Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p. 5 Signaling in Nerve Cells p. 9 Cellular and Molecular Biology of Neurons
Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p. 5 Signaling in Nerve Cells p. 9 Cellular and Molecular Biology of Neurons
Pre-requisites: Botany 11; Zoology 11; Zoology 12 and Chemistry 131
 CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Department of Biological Sciences Manila*Malolos*Makati SYLLABUS PRBS 115 Bio. Sci 115 General Physiology 5 3 hrs. lec; 6 hrs. lab Subject Code Subject Title Descriptive Title
CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Department of Biological Sciences Manila*Malolos*Makati SYLLABUS PRBS 115 Bio. Sci 115 General Physiology 5 3 hrs. lec; 6 hrs. lab Subject Code Subject Title Descriptive Title
4. Neural tube cells are specified by opposing dorsal-ventral gradients of a. Wnts and Nodal. b. FGF and Shh. c. BMPs and Wnts. d. BMPs and Shh.
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: August 1, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: August 1, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
SHEET. Name: Class: Date: the sentence: write highest, lowest, higher, lower. level of organization is the organism; the
 1 1 Label the levels of organization Then complete the sentence: write highest, lowest, higher, lower The level of organization is the organism; the level of organization is the cell Tissues are a organs,
1 1 Label the levels of organization Then complete the sentence: write highest, lowest, higher, lower The level of organization is the organism; the level of organization is the cell Tissues are a organs,
HS ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CURRICULUM
 Born On: August 2018 HS ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CURRICULUM Middle Township Public Schools 216 S. Main Street Cape May Court House, NJ 08210 1 Page Content Area: Anatomy and Physiology Grade(s) 10-12 Unit
Born On: August 2018 HS ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CURRICULUM Middle Township Public Schools 216 S. Main Street Cape May Court House, NJ 08210 1 Page Content Area: Anatomy and Physiology Grade(s) 10-12 Unit
Cell Organelles. 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism Cells tissues organ organ system organism
 Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Anatomy and Physiology Rev. 2010
 Anatomy and Physiology Rev. 2010 Course Description: The Anatomy and Physiology curriculum at Lee Academy is designed to provide students with advanced investigations and deepen student understanding of
Anatomy and Physiology Rev. 2010 Course Description: The Anatomy and Physiology curriculum at Lee Academy is designed to provide students with advanced investigations and deepen student understanding of
1. Which of the cellular components listed above are part of the endomembrane system and surrounded by a double membrane?
 Anatomy and Physiology 141 Fall 2014: Exam IA Name: Use the following list to answer Question 1. 1 Golgi apparatus 2 Nuclear membrane 3 Mitochondria 4 Rough ER 5 Smooth ER 1. Which of the cellular components
Anatomy and Physiology 141 Fall 2014: Exam IA Name: Use the following list to answer Question 1. 1 Golgi apparatus 2 Nuclear membrane 3 Mitochondria 4 Rough ER 5 Smooth ER 1. Which of the cellular components
