Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology
|
|
|
- Randell Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye is. a. anatomy c. biology b. physiology d. pathology Anatomy is the study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye and how the body parts are organized. It is the science of the structure of organisms or of their parts. PTS: 1 REF: p. 144 OBJ: LO: 6.1 Define and explain the importance of anatomy, physiology, and histology to the barbering profession. 2. The study of the functions and activities performed by the body s structures is. a. anatomy c. biology b. physiology d. pathology Physiology is the study of the functions and activities performed by the body s structures. PTS: 1 REF: p. 144 OBJ: LO: 6.1 Define and explain the importance of anatomy, physiology, and histology to the barbering profession. 3. The study of tiny structures found in living tissues is called. a. histology c. gross anatomy b. physiology d. biology Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy, is the study of tiny structures found in living tissues. PTS: 1 REF: p. 145 OBJ: LO: 6.1 Define and explain the importance of anatomy, physiology, and histology to the barbering profession. 4. Cells. a. can be easily seen with the naked eye b. make up our organs but not our bones c. are responsible for carrying on all life processes d. are non-living Cells are responsible for carrying on all life processes. PTS: 1 REF: p. 145 OBJ: LO: 6.2 Describe cells, their structure, and their reproduction. 5. The part of the cell that contains material for the cell to grow, reproduce, and self-repair is the. a. nucleus c. protoplasm b. cytoplasm d. Golgi apparatus
2 The cytoplasm is the watery fluid that surrounds the nucleus of the cell and is needed for growth, reproduction, and self-repair. PTS: 1 REF: p. 145 OBJ: LO: 6.2 Describe cells, their structure, and their reproduction. 6. The cell membrane. a. allows soluble substances to enter and leave the cell b. is the center of the cell c. is the food source for the cell d. is impermeable to soluble substances The cell membrane is the cell wall that encloses the protoplasm and permits soluble substances to enter and leave the cell. PTS: 1 REF: p. 146 OBJ: LO: 6.2 Describe cells, their structure, and their reproduction. 7. Which cell structure can be visualized as the yolk in the middle of a raw egg? a. Cell membrane. c. Nucleus. b. Cytoplasm. d. Protoplasm. You can visualize the nucleus as the yolk in the middle of a raw egg. PTS: 1 REF: p. 145 OBJ: LO: 6.2 Describe cells, their structure, and their reproduction. 8. Mitosis is the process of cell. a. digestion c. reproduction b. mating d. death Mitosis is the usual process of cell reproduction of human tissues that occurs when the cell divides into two identical cells called daughter cells. PTS: 1 REF: p. 146 OBJ: LO: 6.2 Describe cells, their structure, and their reproduction. 9. What is an unfavorable condition for cell growth? a. Suitable temperatures. b. Presence of toxins. c. Supply of food. d. Ability to eliminate waste products. Unfavorable conditions for cell growth and reproduction are toxins (poisons), disease, and injury. PTS: 1 REF: p. 146 OBJ: LO: 6.2 Describe cells, their structure, and their reproduction. 10. Which type of tissues bind together, protect, and support the various parts of the body? a. Epithelial tissue. c. Nerve tissue.
3 b. Muscle tissue. d. Connective tissue. Connective tissue is fibrous tissue that binds together, protects, and supports the various parts of the body. PTS: 1 REF: p. 147 OBJ: LO: 6.3 Identify and define the types of tissues found in the body. 11. Bones and ligaments are examples of tissue. a. connective c. nerve b. mucous d. lymph Examples of connective tissue are bone, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, blood, lymph, and adipose tissue. PTS: 1 REF: p. 147 OBJ: LO: 6.3 Identify and define the types of tissues found in the body. 12. Which type of tissue offers a protective covering on body surfaces? a. Epithelial tissue. c. Nerve tissue. b. Muscle tissue. d. Connective tissue. Epithelial tissue is a protective covering on body surfaces, such as skin, mucous membranes, the tissue inside the mouth, the lining of the heart, digestive and respiratory organs, and the glands. PTS: 1 REF: p. 147 OBJ: LO: 6.3 Identify and define the types of tissues found in the body. 13. Organs are structures containing. a. general groups of tissues b. specialized tissues designed to perform specific functions c. a single cell d. non-living matter Organs are structures composed of specialized tissues designed to perform specific functions in plants and animals. PTS: 1 REF: p. 147 OBJ: LO: 6.4 Define organs and body systems. 14. What is a group of body organs acting together to perform one or more functions? a. Body tissues. c. Body systems. b. Body organization. d. Histology. Body systems, also known as systems, are groups of body organs acting together to perform one or more functions. PTS: 1 REF: p. 147 OBJ: LO: 6.4 Define organs and body systems. 15. Osteology is the study of the anatomy, structure, and function of the. a. blood c. bones
4 b. lungs d. skin Osteology is the study of the anatomy, structure, and function of the bones. PTS: 1 REF: p Red and white blood cells are produced by the system. a. skeletal c. lymph b. cardiovascular d. blood Red and white blood cells are produced by the skeletal system. PTS: 1 REF: p A joint is the connection between. a. two or more bones of the skeleton c. a bone and the skin b. a bone and a ligament d. a bone and an organ A joint is the connection between two or more bones of the skeleton. PTS: 1 REF: p There are facial bones and 8 cranial bones in the skull. a. 6 c. 10 b. 8 d. 14 There are 14 facial bones and 8 cranial bones in the skull. PTS: 1 REF: p The parietal bones form the of the cranium. a. sides c. sides and top b. top d. back The parietal bones form the sides and top of the cranium. PTS: 1 REF: p The sphenoid bone. a. joins all of the bones of the cranium together b. is found in the forehead c. forms part of the nasal cavities d. is another name for the lower jaw The sphenoid bone joins all of the bone of the cranium together.
5 PTS: 1 REF: p There are temporal bones that form the sides of the head in the ear region. a. two c. four b. three d. six There are two temporal bones that form the sides of the head in the ear region. PTS: 1 REF: p The nasal bones form. a. the bottom of the nose c. the nostrils b. the bridge of the nose d. the brow ridge The nasal bones form the bridge of the nose. PTS: 1 REF: p The mandible is the bone of the face. a. topmost c. smallest b. weakest d. largest The mandible bone is the largest and strongest bone of the face. PTS: 1 REF: p The hyoid bone is located at the base of the tongue and has a(n) shape. a. T c. V b. U d. O The hyoid bone is a u-shaped bone at the base of the tongue. It supports the tongue and its muscles. PTS: 1 REF: p What is the largest bone in the arm? a. Humerus. c. Radius. b. Ulna. d. Phalanges. The humerus is the largest bone of the arm and extends from the shoulder to the elbow. 26. The muscular system is responsible for.
6 a. circulating blood and lymph b. producing movement within the body c. breathing oxygen d. producing red and white blood cells The muscular system covers, shapes, and supports the skeleton, and its function is to help produce movement within the body to 50 percent of the body s weight is contributed by. a. bones c. muscles b. water d. blood The muscular system consists of over 600 large and small muscles that comprise 40 to 50 percent of the body s weight. 28. A(n) muscle that is not duplicated anywhere else in the body is the cardiac muscle. a. smooth c. involuntary b. striated d. nonstriated An involuntary muscle that is not duplicated anywhere else in the body is the cardiac muscle, or the heart. 29. The muscles found in the internal organs of the body are. a. controlled by will c. attached to the bones b. nonstriated muscles d. voluntary muscles The muscles found in the internal organs of the body, such as the stomach and intestines, are nonstriated (smooth) or involuntary muscles. 30. The part of the muscle that does not move and is attached closest to the skeleton is called the. a. origin c. internal attachment b. point d. belly The origin is the part of the muscle that does not move and is attached closest to the skeleton.
7 31. The is the part of a muscle that moves and is farthest from the skeleton. a. origin c. insertion b. belly d. None of the answers are correct. The insertion is the part of the muscle that moves and is farthest from the skeleton. 32. Muscular tissue may be stimulated by. a. salts c. moist heat b. light rays d. All answers are correct. Muscular tissue may be stimulated by any of the following methods: massage, electric current, light rays, salts, heat rays, moist heat, nerve impulses, and chemicals. PTS: 1 REF: p The frontalis muscle. a. controls chewing c. draws the scalp backward b. controls the smile d. draws the scalp forward The frontalis muscle of the scalp raises the eyebrows, draws the scalp forward, and causes wrinkles across the forehead. PTS: 1 REF: p The muscle that draws the scalp backward is the. a. epicranius c. corrugator b. occipitalis d. aponeurosis The occipitalis muscle draws the scalp backward. PTS: 1 REF: p The muscles called auricularis superior, posterior, and anterior control the. a. eye c. nose b. ear d. chin The three muscles of the ear are the auricularis superior, anterior, and posterior. PTS: 1 REF: p The masseter and temporalis muscles are also known as the. a. chewing muscles c. wrinkle makers b. seeing muscles d. smell generators
8 The masseter and temporalis are the main muscles of mastication and are also known as the chewing muscles. PTS: 1 REF: p The orbicularis oculi muscle surrounds the. a. forehead c. eye socket b. mouth d. ear The orbicularis oculi muscle surrounds the eye socket. PTS: 1 REF: p The depressor labii inferioris surrounds the. a. lower lip c. nose b. upper lip d. eye socket The depressor labii inferioris muscle surrounds the lower lip and can lower the lip and draw it to one side. PTS: 1 REF: p The muscle that pulls down the corner of the mouth is the. a. orbicularis oris c. zygomaticus b. mentalis d. triangularis The triangularis muscle extends alongside the chin and pulls down the corner of the mouth. PTS: 1 REF: p The are muscles found in the hands. a. trapezius and platysma c. orbicularis and mentalis b. abductors and adductors d. masseter and temporalis The abductors and adductors are muscles found in the hands. PTS: 1 REF: p Neurology is the study of the structure, function, and pathology of the system. a. endocrine c. nervous b. skin d. immune Neurology is the study of the structure, function, and pathology of the nervous system.
9 PTS: 1 REF: p The principal components of the nervous system are the. a. nerves c. spinal cord b. brain d. All answers are correct. The principal components of the nervous system are the brain, spinal cord, and the nerves themselves. PTS: 1 REF: p The brain controls the. a. ability to think and feel b. circulation of blood c. breathing motion d. connection between two or more bones The brain controls sensation, muscles, activity of glands, and the power to think, sense, and feel. PTS: 1 REF: p pairs of spinal nerves extending from the spinal cord are distributed to the muscles and skin of the trunk and limbs. a. Twelve c. Thirty-one b. Twenty-one d. Forty Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves extending from the spinal cord are distributed to the muscles and skin of the trunk and limbs. PTS: 1 REF: p Dendrites are treelike branchings that carry impulses toward and receive impulses from neurons. a. the lungs c. the cell b. the brain d. the heart Dendrites are treelike branchings of nerve fibers extending from the nerve cell that carry impulses toward the cell and receive impulses from other neurons. PTS: 1 REF: p Motor nerves carry impulses from the brain to the. a. muscles c. digestive system b. skin d. lungs Motor nerves carry impulses from the brain to the muscles or glands.
10 PTS: 1 REF: p A reflex is a(n) nerve reaction to a stimulus. a. efferent c. motor b. sensory d. automatic A reflex is an automatic reaction to a stimulus that involves the movement of an impulse from a sensory receptor along the sensory nerve to the spinal cord. PTS: 1 REF: p The fifth cranial nerve is the chief nerve of the face. a. motor c. mixed b. sensory d. facial The fifth cranial nerve is the chief sensory nerve of the face and serves as the motor never of the muscles that control chewing. PTS: 1 REF: p The three branches of the trifacial nerve are the ophthalmic,, and maxillary. a. cervical c. mandibular b. mental d. greater occipital The three branches of the trifacial nerve are the ophthalmic, mandibular, and maxillary. PTS: 1 REF: p The branches of the cranial nerve affected by massage include the supraorbital nerve, zygomatic nerve, and infraorbital nerve. a. first c. fifth b. third d. seventh The branches of the fifth cranial nerve that are affected by massage include the supraorbital nerve, zygomatic nerve, and infraorbital nerve. In addition the auriculotemporal nerve, infratrochlear nerve, mental nerve, nasal nerve, and supratrochlear nerve are affected by massage. PTS: 1 REF: p The seventh cranial nerve is the chief nerve of the face. a. motor c. spinal b. sensory d. cranial The seventh cranial nerve is the chief motor nerve of the face.
11 PTS: 1 REF: p The smaller occipital nerve is located. a. on top of the head c. at the base of the skull b. by the eye d. in the neck The smaller (lesser) occipital nerve is located at the base of the skull and affects the scalp and muscles of this region. PTS: 1 REF: p Another name for the cardiovascular system is the system. a. lymph c. circulatory b. blood d. nervous The cardiovascular system is also known as the circulatory system or vascular system. PTS: 1 REF: p The circulatory system consists of the. a. heart c. capillaries b. veins d. All answers are correct. The circulatory system consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries that distribute blood throughout the body. PTS: 1 REF: p What body structure is known as the body s pump? a. The heart. c. The lungs. b. The brain. d. The liver. The heart is a muscular, cone-shaped organ that keeps the blood moving within the circulatory system. It is often referred to as the body s pump. PTS: 1 REF: p The circulation system takes deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation and waste removal and then returns that blood to the heart so oxygen-rich blood can be delivered to the body. a. basic c. systemic b. general d. pulmonary The pulmonary circulation system takes deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation and waste removal and then returns that blood to the heart so oxygen-rich blood can be delivered to the body.
12 PTS: 1 REF: p The function of the is to carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the arterioles. a. veins c. arteries b. capillaries d. venules The function of the arteries is to carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the arterioles. PTS: 1 REF: p The blood vessels that connect the smaller to venules are the capillaries. a. nerves c. vesicles b. arteries d. lacteals The blood vessels that connect the smaller arteries to venules are the capillaries. PTS: 1 REF: p Blood carries away and waste products to be eliminated through the lungs, skin, kidneys, and large intestines. a. oxygen c. carbon dioxide b. white blood cells d. lymph Blood carries away carbon dioxide and waste products to be eliminated through the lungs, skin, kidneys, and large intestines. PTS: 1 REF: p Which artery supplies blood to the brain, eyes, eyelids, forehead, nose, and internal ear? a. External carotid artery. c. Superior labial artery. b. Internal carotid artery. d. Inferior labial artery. The internal carotid artery supplies blood to the brain, eyes, eyelids, forehead, nose, and internal ear. PTS: 1 REF: p Blood is supplied to the by the facial artery. a. scalp b. neck and shoulders c. forehead and eyes d. lower region of the face, mouth, and nose The facial artery, also known as the external maxillary artery, supplies blood to the lower region of the face, mouth, and nose.
13 PTS: 1 REF: p Lymph appears. a. as a thick yellow fluid c. mixed with blood b. as a clear watery fluid d. only in the lungs Lymph is a clear liquid that circulates in the lymph spaces of the body. PTS: 1 REF: p Which body system serves as a protective covering and helps regulate the body s temperature? a. Skeletal system. c. Integumentary system. b. Lymphatic system. d. Circulatory system. The integumentary system serves as a protective covering and helps regulate the body s temperature. PTS: 1 REF: p The are examples of endocrine glands. a. thyroid and pituitary glands c. sweat and oil glands b. follicles d. hairs The thyroid and pituitary glands are examples of endocrine glands. PTS: 1 REF: p The of the skin are examples of exocrine glands. a. thyroid and pituitary glands c. sweat and oil glands b. follicles d. hairs The sweat and oil glands of the skin are examples of exocrine glands. PTS: 1 REF: p Which system performs the function of producing offspring and passing on the genetic code from one generation to another? a. Muscular system. c. Circulatory system. b. Lymphatic system. d. Reproductive system. The reproductive system performs the function of producing offspring and passing on the genetic code from one generation to another. PTS: 1 REF: p. 167
Physiology. Organization of the Body. Assumptions in Physiology. Chapter 1. Physiology is the study of how living organisms function
 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis Chapter 1 Physiology Physiology is the study of how living organisms function On the street explanations are in terms of meeting a bodily need Physiologic explanations
Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis Chapter 1 Physiology Physiology is the study of how living organisms function On the street explanations are in terms of meeting a bodily need Physiologic explanations
Cells to systems. 1) Chemical Level All matter is a combination of atoms: - Oxygen - Carbon - Nitrogen - Hydrogen Make up 96% of total body chemistry
 Cells to systems Organisation of the Human body: 1. Chemical level 2. Cellular level 3. Tissue level 4. Organ level 5. Body system level 6. Organism level 1) Chemical Level All matter is a combination
Cells to systems Organisation of the Human body: 1. Chemical level 2. Cellular level 3. Tissue level 4. Organ level 5. Body system level 6. Organism level 1) Chemical Level All matter is a combination
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
SNC2D BIOLOGY 4/1/2013. TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Animal & Plant Tissues (P.42-45) Animal Tissues. Animal Tissues
 SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Animal & Plant Tissues (P.42-45) Animal Tissues As you already know, groups of cells that work together to perform a task are called tissues. For example, muscle
SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Animal & Plant Tissues (P.42-45) Animal Tissues As you already know, groups of cells that work together to perform a task are called tissues. For example, muscle
Chapter 1. The Human Organism 1-1
 Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization MADE UP OF CELLS REPRO- DUCE 5 CHARACH- TERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO CHANGES GROW AND DEVELOP USE ENERGY cells the basic units of structure and function of all living
Levels of Organization MADE UP OF CELLS REPRO- DUCE 5 CHARACH- TERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO CHANGES GROW AND DEVELOP USE ENERGY cells the basic units of structure and function of all living
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION. Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes
 Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
18. Which body system is needed for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide? A. Respiratory B. Integumentary C. Digestive D. Urinary 19.
 1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125
 Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog ANAT 125 Human Anatomy 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog ANAT 125 Human Anatomy 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill
 Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
VOCABULARY. Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System
 CELLS VOCABULARY Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System THE IMPORTANCE OF CELLS Cells are the smallest unit of life in all living things They are organized structures
CELLS VOCABULARY Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System THE IMPORTANCE OF CELLS Cells are the smallest unit of life in all living things They are organized structures
Name Period Date Science 7R - Marking Period 3 Review SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. What are the steps of the scientific method?
 Name Period Date Science 7R - Marking Period 3 Review SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. What are the steps of the scientific method? 2. What is meant by State the Problem? 3. What is a hypothesis? 4. In which step
Name Period Date Science 7R - Marking Period 3 Review SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. What are the steps of the scientific method? 2. What is meant by State the Problem? 3. What is a hypothesis? 4. In which step
Introduction Chpt 1. Study Slides
 Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Anatomy and Physiology. Science Curriculum Framework
 Anatomy and Physiology Science Curriculum Framework Revised 005 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology should develop an understanding of the organization of the human body through studies of body
Anatomy and Physiology Science Curriculum Framework Revised 005 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology should develop an understanding of the organization of the human body through studies of body
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS
 SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: BIOL 132 Department: Biological Sciences Course Title: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ 1. Recognize
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: BIOL 132 Department: Biological Sciences Course Title: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ 1. Recognize
Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards. Anatomical terms. Homeostatic mechanisms. Characteristics of Life. Requirements for life
 Honors Anatomy & Physiology 2012 Michael Harshaw, Melissa Castone Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards Month Introduction September- 1.5 weeks How do Anatomy and Physiology relate to
Honors Anatomy & Physiology 2012 Michael Harshaw, Melissa Castone Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards Month Introduction September- 1.5 weeks How do Anatomy and Physiology relate to
Form and Function. Physical Laws and Form. Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function. AP Biology Fig Figs & 40.
 Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function AP Biology 2013 1 Form and Function Comparative studies show that form and function are closely related Natural selection can fit the form (anatomy)
Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function AP Biology 2013 1 Form and Function Comparative studies show that form and function are closely related Natural selection can fit the form (anatomy)
Broken Arrow Public Schools Physiology Objectives
 1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
Levels of Organization. Monday, December 5, 16
 Levels of Organization The human body is structured into systems. Cells are the smallest unit of life. Calls similar in shape and function work together as tissues. Different types of tissues form organs
Levels of Organization The human body is structured into systems. Cells are the smallest unit of life. Calls similar in shape and function work together as tissues. Different types of tissues form organs
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE. Cells, Tissues, and Membranes
 NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition
 Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue.
 Plant Tissues Class- IX Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. PLANT TISSUES ANIMAL TISSUES 1. Most of the plant tissues are Most of the tissues
Plant Tissues Class- IX Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. PLANT TISSUES ANIMAL TISSUES 1. Most of the plant tissues are Most of the tissues
Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline
 Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned. B. Primitive people certainly suffered
Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned. B. Primitive people certainly suffered
Organization of Vertebrate Body. Organization of Vertebrate Body
 The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology. I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
INTRODUCTION Veterinary Physiology I Odd Semester 2015/2016. Division of Physiology Department of Anatomy, Physiology and Pharmacology FVM BAU
 INTRODUCTION Veterinary Physiology I Odd Semester 2015/2016 Division of Physiology Department of Anatomy, Physiology and Pharmacology FVM BAU 1 Main references: Cunningham, JG. 2002. Textbook of Veterinary
INTRODUCTION Veterinary Physiology I Odd Semester 2015/2016 Division of Physiology Department of Anatomy, Physiology and Pharmacology FVM BAU 1 Main references: Cunningham, JG. 2002. Textbook of Veterinary
East Poinsett County School District Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Guide Revised August 2011
 East Poinsett County School District Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Guide Revised August 0 Ongoing Strand: Nature of Science Standard 6: Students shall demonstrate an understanding that science is a
East Poinsett County School District Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Guide Revised August 0 Ongoing Strand: Nature of Science Standard 6: Students shall demonstrate an understanding that science is a
A) Collection of changing/dynamic information dealing with measurable phenomena. 2) study of matter and the energy changes that matter undergoes
 Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Introduction Part I Science and the Scientific Method A) Collection of changing/dynamic information dealing with measurable phenomena B) Disciplines of Science 1) study
Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Introduction Part I Science and the Scientific Method A) Collection of changing/dynamic information dealing with measurable phenomena B) Disciplines of Science 1) study
28.1. Levels of Organization. > Virginia standards
 28.1 Levels of Organization vocabulary determination differentiation tissue organ organ system > Virginia standards BIO.4 The student will investigate and understand life functions of Archaea, Bacteria
28.1 Levels of Organization vocabulary determination differentiation tissue organ organ system > Virginia standards BIO.4 The student will investigate and understand life functions of Archaea, Bacteria
adaptation a structure, feature, or behavior that helps an organism survive and/or reproduce (IG)
 FOSS Living Systems Module Glossary 3 rd Edition 2012 adaptation a structure, feature, or behavior that helps an organism survive and/or reproduce (IG) algae a large plantlike group of water organisms
FOSS Living Systems Module Glossary 3 rd Edition 2012 adaptation a structure, feature, or behavior that helps an organism survive and/or reproduce (IG) algae a large plantlike group of water organisms
ORGANISATION IN THE LIVING THINGS
 2 ORGANISATION IN THE LIVING THINGS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. A group of similar cells which perform a particular function is called (a) organism (b) tissue (c) organelle
2 ORGANISATION IN THE LIVING THINGS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. A group of similar cells which perform a particular function is called (a) organism (b) tissue (c) organelle
Slide 1 / Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system.
 Slide 1 / 64 1 Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system. Slide 2 / 64 2 List the four major groups of tissues in animals. Slide 3 /
Slide 1 / 64 1 Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system. Slide 2 / 64 2 List the four major groups of tissues in animals. Slide 3 /
Norwich City Schools Science 5
 12-23-03 Topic: Electromagnetism Transferable Concepts: forces, interaction 1:,, M.21 M.31 S.1-S.3 S2.1-S2.3 S3.1-S3.4 Engineering Design T1.1-T1.5 4: The Physical 5.2a-b Systems Thinking Enduring Understanding:
12-23-03 Topic: Electromagnetism Transferable Concepts: forces, interaction 1:,, M.21 M.31 S.1-S.3 S2.1-S2.3 S3.1-S3.4 Engineering Design T1.1-T1.5 4: The Physical 5.2a-b Systems Thinking Enduring Understanding:
JEFFERSON COLLEGE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms. Gene Families
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Gene Families In metazoans,
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Gene Families In metazoans,
Chapter 6: Tissues. KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept]
![Chapter 6: Tissues. KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] Chapter 6: Tissues. KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept]](/thumbs/78/78538656.jpg) Chapter 6: Tissues KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] CONCEPTS RATING Meristems in plants ** Permanent tissues in plants **** Animal tissues ***** 1. Tissue is a group of cells
Chapter 6: Tissues KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] CONCEPTS RATING Meristems in plants ** Permanent tissues in plants **** Animal tissues ***** 1. Tissue is a group of cells
Specialized Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems. Chap 2, p. 67 Chap 9, p. 295 Chap 14, p
 Specialized Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems Chap 2, p. 67 Chap 9, p. 295 Chap 14, p. 468-471 2. I. Cell (Review) basic unit of structure and function in a living thing. They carry out the processes
Specialized Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems Chap 2, p. 67 Chap 9, p. 295 Chap 14, p. 468-471 2. I. Cell (Review) basic unit of structure and function in a living thing. They carry out the processes
Unit 1: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
 Unit 1: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems Big Ideas The cell is the basic scientific unit of all living things. Cells must interact with the external environment to meet their basic needs. Your health
Unit 1: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems Big Ideas The cell is the basic scientific unit of all living things. Cells must interact with the external environment to meet their basic needs. Your health
HUMAN BODY THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS REM 653 A TEACHING RESOURCE FROM...
 THE HUMAN BODY SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS A TEACHING RESOURCE FROM... REM 653 AUTHOR Melba Callender 1987, 2001 Copyright by Remedia Publications, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. The
THE HUMAN BODY SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS A TEACHING RESOURCE FROM... REM 653 AUTHOR Melba Callender 1987, 2001 Copyright by Remedia Publications, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. The
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition
 Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
Skeletal 2 - joints. Puzzle 1 bones
 Puzzle 1 bones Listed below are the names of some of the bones that make up your skeletal system. But the names have been encrypted using a secret code. Can you decipher this code to find out what they
Puzzle 1 bones Listed below are the names of some of the bones that make up your skeletal system. But the names have been encrypted using a secret code. Can you decipher this code to find out what they
CURRICULUM MAP. TIME CONTENT PAGE REF. SKILLS ASSESSMENT/ACTIVITIES Day 1-3
 CURRICULUM MAP COURSE TITLE: Anatomy and Physiology DESCRIPTION TEXTBOOK Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology OF COURSE: 8 th ed: Elaine Marieb Integrated approach to human anatomy. Performance and lab
CURRICULUM MAP COURSE TITLE: Anatomy and Physiology DESCRIPTION TEXTBOOK Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology OF COURSE: 8 th ed: Elaine Marieb Integrated approach to human anatomy. Performance and lab
1. Why Dissect. Why are frogs a good model to use when studying the digestive system (as well as other systems)?
 Name: Date: Period: Frog Dissection Virtual Lab Use the frog Dissection link that follows to answer the questions. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/bl_16/bl_16.html Introduction 1. Why Dissect.
Name: Date: Period: Frog Dissection Virtual Lab Use the frog Dissection link that follows to answer the questions. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/bl_16/bl_16.html Introduction 1. Why Dissect.
BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. When a body is in the anatomical position, it is A. Standing erect,
BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. When a body is in the anatomical position, it is A. Standing erect,
Biology Test Review Science 8
 Biology Test Review Science 8 Introduction to Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems 304-7 Explain structural and functional relationships between and among cells, tissues, organs and systems in the human
Biology Test Review Science 8 Introduction to Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems 304-7 Explain structural and functional relationships between and among cells, tissues, organs and systems in the human
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment
 Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true.
 Unit 4 Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. A stimulus is anything that threatens the
Unit 4 Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. A stimulus is anything that threatens the
Anatomy & Physiology Curriculum Map Date Content/Topics Objectives Activities/Assessments Aug. 7th- 21st
 Anatomy & Physiology Curriculum Map 2012-13 Date Content/Topics Objectives Activities/Assessments Aug. 7th- 21st Chapter 1 Body Regions/Cavities Directional Terms Homeostasis System Basics with introduction
Anatomy & Physiology Curriculum Map 2012-13 Date Content/Topics Objectives Activities/Assessments Aug. 7th- 21st Chapter 1 Body Regions/Cavities Directional Terms Homeostasis System Basics with introduction
Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function. Chapter 40
 Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function Chapter 40 Form and Function Anatomy- biological form of an organism. Physiology- biological function. Size and Shape Development of body plan and shape is
Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function Chapter 40 Form and Function Anatomy- biological form of an organism. Physiology- biological function. Size and Shape Development of body plan and shape is
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
tissues are made of cells that work together, organs are )
 Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Anatomy and Physiology GRADE 12 Course Curriculum Prepared by Lou Pompilii ABINGTON SCHOOL DISTRICT Abington, Pennsylvania 2010
 Anatomy and Physiology GRADE 12 Course Curriculum Prepared by Lou Pompilii ABINGTON SCHOOL DISTRICT Abington, Pennsylvania 2010 Anatomy & Physiology A Course of Study Table of Contents Contents: Page:
Anatomy and Physiology GRADE 12 Course Curriculum Prepared by Lou Pompilii ABINGTON SCHOOL DISTRICT Abington, Pennsylvania 2010 Anatomy & Physiology A Course of Study Table of Contents Contents: Page:
Plant Tissues. Parenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, NOIDA CLASS-IX BIOLOGY TOPIC- TISSUES BY: UMESH VERMA Defination- A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. Also this group od
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, NOIDA CLASS-IX BIOLOGY TOPIC- TISSUES BY: UMESH VERMA Defination- A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. Also this group od
What is the structure of DNA?
 NAME Biology Final Review Sem. II Genetics 1. Define: a. allele b. phenotype c. genotype d. recessive e. dominant f. heterozygous g. homozygous h. autosomes i. sex chromosomes j. Punnett square k. pedigree
NAME Biology Final Review Sem. II Genetics 1. Define: a. allele b. phenotype c. genotype d. recessive e. dominant f. heterozygous g. homozygous h. autosomes i. sex chromosomes j. Punnett square k. pedigree
Nerve cells have many branches that help them send signals throughout the body.
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
PUBLIC SCHOOLS OF EDISON TOWNSHIP OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Length of Course: Student Eligibility: Grades 11, 12
 PUBLIC SCHOOLS OF EDISON TOWNSHIP OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Length of Course: Elective/Required: School: Term Elective High Schools Student Eligibility: Grades 11, 12
PUBLIC SCHOOLS OF EDISON TOWNSHIP OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Length of Course: Elective/Required: School: Term Elective High Schools Student Eligibility: Grades 11, 12
BIOL Anatomy and Physiology I ( version L )
 BIOL 2113 - Anatomy and Physiology I ( version 213L ) Course Title Course Development Learning Support Anatomy and Physiology I Standard No Course Description Introduces the anatomy and physiology of the
BIOL 2113 - Anatomy and Physiology I ( version 213L ) Course Title Course Development Learning Support Anatomy and Physiology I Standard No Course Description Introduces the anatomy and physiology of the
Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis. Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis
 Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis 1 Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis 2 Biological Explanations Proximate Proximate causation: an explanation of an animal's behavior based on
Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis 1 Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis 2 Biological Explanations Proximate Proximate causation: an explanation of an animal's behavior based on
CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES
 NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
STUDENT PACKET #1 Student Exploration: Cell Structure
 STUDENT PACKET #1 Student Exploration: Cell Structure Big Idea 14: Organization and Development of Living Organisms SC.6.L.14.1 Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of organisms
STUDENT PACKET #1 Student Exploration: Cell Structure Big Idea 14: Organization and Development of Living Organisms SC.6.L.14.1 Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of organisms
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Prepared by Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar
The Human Body: An Orientation Prepared by Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar
CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE Subject: Anatomy & Physiology Grade: 11-12
 Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: 8 weeks Topic(s): Introduction, Tissues, Integumentary System Describe the major components and functions of physiological systems, including skeletal, muscle,
Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: 8 weeks Topic(s): Introduction, Tissues, Integumentary System Describe the major components and functions of physiological systems, including skeletal, muscle,
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE 30
 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE 30 Description This second-year course in biology emphasizes the workings of the human body. The course is offered in the fall semester and meets six (6) periods per
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE 30 Description This second-year course in biology emphasizes the workings of the human body. The course is offered in the fall semester and meets six (6) periods per
D.C.H.S BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT
 D.C.H.S BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT NAT 5 Homework Booklet Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms 1 HOMEWORK 1- Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. (a) Multicellular organisms are composed of different types of cells which are
D.C.H.S BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT NAT 5 Homework Booklet Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms 1 HOMEWORK 1- Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. (a) Multicellular organisms are composed of different types of cells which are
Introduction. Cells under the Light Microscope. Activity 1
 Introduction If you look at a thin slice taken from any plant or animal under a microscope, you can see it is made up of small boxes called cells. Most cells are too small to see with the naked eye, so
Introduction If you look at a thin slice taken from any plant or animal under a microscope, you can see it is made up of small boxes called cells. Most cells are too small to see with the naked eye, so
7 th Grade PSI. Slide 1 / 116. Slide 2 / 116. Slide 3 / 116. Structure and Function & Information Processing. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 116 Slide 2 / 116 7 th Grade PSI Structure and Function & Information Processing 2015-11-07 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 116 Click on the topic to go to that section Cells: the Fundamental
Slide 1 / 116 Slide 2 / 116 7 th Grade PSI Structure and Function & Information Processing 2015-11-07 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 116 Click on the topic to go to that section Cells: the Fundamental
KRSN BIO 2030 Anatomy and Physiology - 8 credit hours KRSN BIO 2031 Anatomy and Physiology KRSN BIO 2032 Anatomy and Physiology Lab
 KRSN BIO 2030 Anatomy and Physiology - 8 credit hours KRSN BIO 2031 Anatomy and Physiology KRSN BIO 2032 Anatomy and Physiology Lab For institutional specific information, visit the University & College
KRSN BIO 2030 Anatomy and Physiology - 8 credit hours KRSN BIO 2031 Anatomy and Physiology KRSN BIO 2032 Anatomy and Physiology Lab For institutional specific information, visit the University & College
Architectural Pattern of an animal. Chapter 9
 Architectural Pattern of an animal Chapter 9 What is an animal? Levels of organization and organismal complexity 5 major levels of complexity Unicellular Metazoan? Tissue Organ Organ systems Levels of
Architectural Pattern of an animal Chapter 9 What is an animal? Levels of organization and organismal complexity 5 major levels of complexity Unicellular Metazoan? Tissue Organ Organ systems Levels of
human cell Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function.
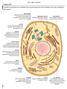 human cell CELL AND TISSUES Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function. Golgi apparatus Organelle composed of a series
human cell CELL AND TISSUES Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function. Golgi apparatus Organelle composed of a series
THE CELL THEORY (R+R+R+E+G+N+T+S) 3).
 CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
REVISION BOOKLET MIDTERM EXAM FIRST SEMESTER 2018 SCIENCE 6
 REVISION BOOKLET MIDTERM EXAM FIRST SEMESTER 2018 SCIENCE 6 Name: Grade: Date: QA: Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: adaptation biosphere red blood cells species single cytoplasm
REVISION BOOKLET MIDTERM EXAM FIRST SEMESTER 2018 SCIENCE 6 Name: Grade: Date: QA: Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: adaptation biosphere red blood cells species single cytoplasm
1. Anatomy is. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy involves the study of organs that function together?
 1 of 19 1 Student: 1. Anatomy is A. the study of function. B. a branch of physiology. C. the study of structure. D. the study of living organisms. E. the study of homeostasis. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy
1 of 19 1 Student: 1. Anatomy is A. the study of function. B. a branch of physiology. C. the study of structure. D. the study of living organisms. E. the study of homeostasis. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy
Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure
 The embryo is a Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure WEEK 4 EMBRYO General features Primordia of the brain Somites Primordia of the heart Branchial arches Primordia
The embryo is a Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure WEEK 4 EMBRYO General features Primordia of the brain Somites Primordia of the heart Branchial arches Primordia
Review. Watch the following video How Stuff Works - Cells video
 Types of Cells Review Watch the following video How Stuff Works - Cells video Multi-cellular Organisms Living things can be as simple as single-celled organisms such as a Paramecium or an Amoeba that lives
Types of Cells Review Watch the following video How Stuff Works - Cells video Multi-cellular Organisms Living things can be as simple as single-celled organisms such as a Paramecium or an Amoeba that lives
UNIT 6 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 UNIT 6 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM I. Functions of Muscular System A. Produces Movement Internal vs. External «locomotion & manipulation «circulate blood & maintain blood pressure «move fluids, food, baby B. Maintaining
UNIT 6 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM I. Functions of Muscular System A. Produces Movement Internal vs. External «locomotion & manipulation «circulate blood & maintain blood pressure «move fluids, food, baby B. Maintaining
NOTE: LOOK ON MY WEBSITE FOR THE MUSCLE LABELING POWER POINT/PDF Part I. Identify the parts of the neuron that are labeled below.
 Anatomy & Physiology Nervous System Part I 2/26/16 NOTE: LOOK ON MY WEBSITE FOR THE MUSCLE LABELING POWER POINT/PDF Part I. Identify the parts of the neuron that are labeled below. 1. 2. 3. 5. 4. 6. Part
Anatomy & Physiology Nervous System Part I 2/26/16 NOTE: LOOK ON MY WEBSITE FOR THE MUSCLE LABELING POWER POINT/PDF Part I. Identify the parts of the neuron that are labeled below. 1. 2. 3. 5. 4. 6. Part
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY, lecture and lab
 LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
Introduction. The study of animal form and function is integrated by the common set of problems that all animals must solve.
 Introduction The study of animal form and function is integrated by the common set of problems that all animals must solve. These include how to extract oxygen from the environment, how to nourish themselves,
Introduction The study of animal form and function is integrated by the common set of problems that all animals must solve. These include how to extract oxygen from the environment, how to nourish themselves,
Academic Anatomy Pacing Guide
 Academic Anatomy Pacing Guide Course Description: This course provides the student with a general study of the structure of EOC VOCATS the human body and the detailed study of the functions of the body
Academic Anatomy Pacing Guide Course Description: This course provides the student with a general study of the structure of EOC VOCATS the human body and the detailed study of the functions of the body
BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I
 South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 80 Types of Instruction Instruction Type Anatomy and Physiology
South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 80 Types of Instruction Instruction Type Anatomy and Physiology
Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum. Draft Units
 Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum Draft Units Human Anatomy and Physiology - Blood, Guts, Senses, and Defenses 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Blood, Guts, Senses, and Defenses: Description
Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum Draft Units Human Anatomy and Physiology - Blood, Guts, Senses, and Defenses 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Blood, Guts, Senses, and Defenses: Description
Class IX Chapter 6 Tissues Science
 Question 1: What is a tissue? Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform a specific task. Question 2: What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular
Question 1: What is a tissue? Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform a specific task. Question 2: What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular
Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora
 Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) Which term describes the study of the functions of body structures? a) anatomy
Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) Which term describes the study of the functions of body structures? a) anatomy
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 120 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Deborah Allen. Revised date: July, 2014
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 120 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Division Chair, Math, Science & Business Ms.
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 120 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Division Chair, Math, Science & Business Ms.
GENERAL INFORMATION. Number of One credit (1)
 GENERAL INFORMATION Course 2000350 Number: Course Path: Section: Basic and Adult Education» Grade Group: Secondary Grades 9-12» Subject: Science» SubSubject: Biological Sciences» Course Title: Anatomy
GENERAL INFORMATION Course 2000350 Number: Course Path: Section: Basic and Adult Education» Grade Group: Secondary Grades 9-12» Subject: Science» SubSubject: Biological Sciences» Course Title: Anatomy
The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY
 The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY The topography of organs and organ systems 1. The organs are: a. clusters of identical tissues; b. different tissue groups; c. morphological units that fulfill the function
The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY The topography of organs and organ systems 1. The organs are: a. clusters of identical tissues; b. different tissue groups; c. morphological units that fulfill the function
adaptation a structure, feature, or behavior that helps an organism survive and/or reproduce (IG)
 FOSS Living Systems Module Glossary NGSS Edition 2019 adaptation a structure, feature, or behavior that helps an organism survive and/or reproduce (IG) algae a large plantlike group of water organisms
FOSS Living Systems Module Glossary NGSS Edition 2019 adaptation a structure, feature, or behavior that helps an organism survive and/or reproduce (IG) algae a large plantlike group of water organisms
What is a Skeleton? SKELETONS: Museum of Osteology Lesson Curriculum K 5 th Grade 55 Minute Program
 Kindergarten: SC.K.N.1.2 Make observations of the natural world and know that they are descriptors collected using the five senses. SC.K.N.1.4 Observe and create a visual representation of an object which
Kindergarten: SC.K.N.1.2 Make observations of the natural world and know that they are descriptors collected using the five senses. SC.K.N.1.4 Observe and create a visual representation of an object which
Multicellular Organisms. Calderglen High School National 5 Biology Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms
 Calderglen High School National 5 Biology Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms 1 Sub topic: Producing new cells Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of the cell and carry coded instructions called genes from
Calderglen High School National 5 Biology Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms 1 Sub topic: Producing new cells Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of the cell and carry coded instructions called genes from
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE
 AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms Worksheet
 Name Date Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms Worksheet Instructions for VIVED Science 1. Open the Plant Cell Structures and Animal (Human) Cell Structures sessions and follow the instructions. 2.
Name Date Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms Worksheet Instructions for VIVED Science 1. Open the Plant Cell Structures and Animal (Human) Cell Structures sessions and follow the instructions. 2.
Advanced Anatomy and Physiology
 Lakeshore Technical College 10806179 Advanced Anatomy and Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Alternate Title Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 90 Adv Anatomy & Physiology Advanced
Lakeshore Technical College 10806179 Advanced Anatomy and Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Alternate Title Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 90 Adv Anatomy & Physiology Advanced
Head and Face Development
 Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
UNIT 2- BODY ORGANIZATION AND HOMEOSTASIS M E L A N I E L O U L O U S I S
 UNIT 2- BODY ORGANIZATION AND HOMEOSTASIS M E L A N I E L O U L O U S I S ANCHORING PHENOMENON- DIABETES MELLITUS What is Diabetes mellitus Questions: UNIT 2.1 DRIVING QUESTION- HOW ARE LIVING THINGS ORGANIZED?
UNIT 2- BODY ORGANIZATION AND HOMEOSTASIS M E L A N I E L O U L O U S I S ANCHORING PHENOMENON- DIABETES MELLITUS What is Diabetes mellitus Questions: UNIT 2.1 DRIVING QUESTION- HOW ARE LIVING THINGS ORGANIZED?
4. Which of the following organelles digests waste using hydrolytic enzymes:
 Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable
Pacing: August June These benchmarks serve as common threads to be integrated throughout the units of study Teacher Notes:
 Anatomy and Honors and Non-Honors Curriculum Map al Focus Calendar 1 Body of Knowledge :Practice of Science Standard:SC.912.N.1.1 Essential Questions Pacing: August June These benchmarks serve as common
Anatomy and Honors and Non-Honors Curriculum Map al Focus Calendar 1 Body of Knowledge :Practice of Science Standard:SC.912.N.1.1 Essential Questions Pacing: August June These benchmarks serve as common
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction
 East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Human Anatomy/Physiology, College Preparatory Course(s): CP Human Anatomy/Physiology Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Human Anatomy/Physiology, College Preparatory Course(s): CP Human Anatomy/Physiology Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period
