EXAMINATION in Hardware Description and Verification
|
|
|
- George Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of VT09 Computer Science and Engineering TDA956/DIT780 Chalmers and Gothenburg University EXAMINATION in Hardware Description and Verification DAY : TIME : 14:00-18:00 ROOM : Väg och Vatten Responsible for course : Thomas Hallgren, tel Result : To be available at the latest 12/06-09 Permitted in the exam : Paper and pen. No books, PDAs etc. Minimum points for each grade : CTH: 3 : 24, 4 : 36, 5 : 48 out of 60 : GU: G : 24, VG : 48 out of 60 PLEASE NOTE THE FOLLOWING Start each new question on a new page. Write your personal number (or date of birth) and name on each page. Write on only one side of each page. Attempt all questions. Read through all the questions first. Questions that look long may need short answers! 1
2 Questions 1-4 Consider the following circuit: NOR x AND OR 1 1 z y This small circuit has one input x and one output y, and contains two d-type flip-flops that output 1 in the first clock cycle. Here is an VHDL entity declaration for the circuit: library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; entity circuit2 is port (clk,x : in std_logic; y : out std_logic); end circuit2; Question 1 (8 points) 1. Write a behavioural architecture for circuit2. Use Gaisler s two-process method. (5 points) 2. Write a test bench that connects circuit2 to a 500MHz clock and an input signal that is high for 5 clock cycles, then goes low. Question 2 (8 points) 1. A property that holds of circuit2 is that if the input x is always high, then the output y is always high. Express this property as a PSL assertion. 2. Is the above property a safety property? If not, write a safety property in PSL that captures the same intention as closely as possible. Also explain in words what your PSL property means. 2
3 3. Another property that holds of circuit2 is that zeros in the output y always occur in pairs: whenever the output goes low, it stays low for exactly two cycles, then it goes high. Write two PSL assertions that both verify this property: one that uses SEREs (Sequential Extended Regular Expressions) and one that does not use SEREs. Question 3 (10 points) 1. Write down the state transition system of circuit2, in the following form: (x, y, z) (x, y, z ) where. In this description, x corresponds to the input, and y and z to the outputs of the two flip-flops. You should replace the dots with equations that define the correct values for x, y, and z that are enforced by the circuit. Read (x, y, z) as the current state, and (x, y, z ) as the next state. 2. Draw the state transition diagram of this system. Hint: One way to organise the diagram is shown below: Calculate the set of states for which the CTL formula EG y holds, i.e., the set of states in which it is possible for the output y to remain high forever. Show all the steps of your calculation carefully. Hint: use the following model checking formulas: H(EG f) = Gfp U. H(f) Prev(R, U) Prev(R, U) = {s ( t)srt t U} 3
4 Question 4 (11 points) 1. In Lava, define the circuit circuit2 considered in the previous questions. Use the delay element (delay) for the flip-flops, and the built in gates and2, or2 and nor2. 2. In Lava, write the code for an observer circuit check that checks the property defined in question 2.3. Show how you would use the observer (and Lava and SMV) to formally verify that circuit2 has the property. check (x,y) = ok where... (Hint: your observer will need to make use of the delay element.) 3. In Lava, define a circuit that computes the dot product of two vectors, [x 1, x 2,...,x n ] [y 1, y 2,...,y n ] = x 1 y 1 + x 2 y x n y n Numbers are represented as lists of bits, as usual, and vectors are represented as lists of numbers: type Bit = Signal Bool type Binary = [Bit] type Vector = [Binary] Your definition can start like this: dotproduct :: (Vector,Vector) -> Binary dotproduct (xs,ys) =... The following and other circuits from the Lava library and tutorial are available: adder :: (Bit,(Binary,Binary)) -> (Binary,Bit) multi :: (Binary,Binary) -> Binary bintree :: ((a,a)->a) -> ([a] -> a) The carry output form the adders can be ignored, so for example, the dot product of two vectors of 16-bit numbers will be a 32-bit number. 4
5 Question 5 (10 points) 1. It is possible to use a Boolean formula to represent a set of states. Assume that each state comprises three bits (a, b, c). Give a formula that represents the state set {(0, 1, 0), (1, 0, 0), (1, 1, 0)}. 2. Construct the Ordered Binary Decision Diagram for the formula above. Choose the variable ordering a, then b, then c. 3. A simple way to compare if two Boolean formulas are equivalent is to check if their truth tables are the same. How many entries does the truth table for a formula of n variables have? 4. Many Boolean formulas can be efficiently represented as BDDs, but how big can the BDD for a formula of n variables get in the worst case? Question 6 (7 points) 1. LTL has only two basic temporal operators, X p and p U q, and a small number of derived operators, particularly F p and G p. Explain in words what the two basic operators mean, and show how the two derived operators can be defined in terms of the basic operators. 2. Which temporal operators in PSL do the four LTL operators above correspond to? 3. Assuming a request is made by holding the Req line high for one clock cycle, and a request is acknowledged by holding the Ack line high in a subsequent clock cycle, how can the following requirement be expressed in PSL? Before a second request can be made, the first request must be acknowledged. Question 7 (6 points) 1. Four different parallel prefix networks that you may have encountered in the course are the ones by Sklansky, Brent Kung, Kogge Stone and Ladner Fischer. Pick two of them and give for each one an advantage that it has over the other. Consider properties like circuit depth, the number of operators and fanout. 2. Give a Lava definition for one of the above parallel prefix networks. 5
Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006
 COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Fall 2006 Page 1 Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006 Instructions: This examination paper includes 12 pages and 20 multiple-choice questions starting
COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Fall 2006 Page 1 Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006 Instructions: This examination paper includes 12 pages and 20 multiple-choice questions starting
Written reexam with solutions for IE1204/5 Digital Design Monday 14/
 Written reexam with solutions for IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 4/3 206 4.-8. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 08-7904487 Exam text does not have to be returned
Written reexam with solutions for IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 4/3 206 4.-8. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 08-7904487 Exam text does not have to be returned
Written exam for IE1204/5 Digital Design with solutions Thursday 29/
 Written exam for IE4/5 Digital Design with solutions Thursday 9/ 5 9.-. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 8-794487 Exam text does not have to be returned when
Written exam for IE4/5 Digital Design with solutions Thursday 9/ 5 9.-. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 8-794487 Exam text does not have to be returned when
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, RIVERSIDE
 Final Page of UNIVERITY OF CLIFORNI, RIVERIDE Computer cience Department and Electrical Engineering Department C/EE20 Logic Design Final December, 2000 50 Name: olution Key tudent ID#: Please print legibly
Final Page of UNIVERITY OF CLIFORNI, RIVERIDE Computer cience Department and Electrical Engineering Department C/EE20 Logic Design Final December, 2000 50 Name: olution Key tudent ID#: Please print legibly
Assignment # 3 - CSI 2111(Solutions)
 Assignment # 3 - CSI 2111(Solutions) Q1. Realize, using a suitable PLA, the following functions : [10 marks] f 1 (x,y,z) = Σm(0,1,5,7) f 2 (x,y,z) = Σm(2,5,6) f 3 (x,y,z) = Σm(1,4,5,7) f 4 (x,y,z) = Σm(0,3,6)
Assignment # 3 - CSI 2111(Solutions) Q1. Realize, using a suitable PLA, the following functions : [10 marks] f 1 (x,y,z) = Σm(0,1,5,7) f 2 (x,y,z) = Σm(2,5,6) f 3 (x,y,z) = Σm(1,4,5,7) f 4 (x,y,z) = Σm(0,3,6)
Written exam with solutions IE1204/5 Digital Design Friday 13/
 Written eam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Friday / 207 08.00-2.00 General Information Eaminer: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandqvist tel 08-7904487 Teacher: Valhallavägen, Ahmed Hemani
Written eam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Friday / 207 08.00-2.00 General Information Eaminer: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandqvist tel 08-7904487 Teacher: Valhallavägen, Ahmed Hemani
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Introductory Digital Systems Lab (6.111) Quiz #1 - Spring 2003 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan and Prof. Don
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Introductory Digital Systems Lab (6.111) Quiz #1 - Spring 2003 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan and Prof. Don
Exam for Physics 4051, October 31, 2008
 Exam for Physics 45, October, 8 5 points - closed book - calculators allowed - show your work Problem : (6 Points) The 4 bit shift register circuit shown in Figure has been initialized to contain the following
Exam for Physics 45, October, 8 5 points - closed book - calculators allowed - show your work Problem : (6 Points) The 4 bit shift register circuit shown in Figure has been initialized to contain the following
Written exam with solutions IE Digital Design Friday 21/
 Written exam with solutions IE204-5 Digital Design Friday 2/0 206 09.00-3.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist tel 08-7904487, Elena Dubrova phone 08-790 4 4 Exam
Written exam with solutions IE204-5 Digital Design Friday 2/0 206 09.00-3.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist tel 08-7904487, Elena Dubrova phone 08-790 4 4 Exam
Model Checking I. What are LTL and CTL? dack. and. dreq. and. q0bar
 Model Checking I What are LTL and CTL? q0 or and dack dreq q0bar and 1 View circuit as a transition system (dreq, q0, dack) (dreq, q0, dack ) q0 = dreq and dack = dreq & (q0 + ( q0 & dack)) q0 or and D
Model Checking I What are LTL and CTL? q0 or and dack dreq q0bar and 1 View circuit as a transition system (dreq, q0, dack) (dreq, q0, dack ) q0 = dreq and dack = dreq & (q0 + ( q0 & dack)) q0 or and D
Fundamentals of Digital Design
 Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
Model Checking I. What are LTL and CTL? dack. and. dreq. and. q0bar
 Model Checking I What are LTL and CTL? and dack q0 or D dreq D q0bar and 1 View circuit as a transition system (dreq, q0, dack) (dreq, q0, dack ) q0 = dreq dack = dreq and (q0 or (not q0 and dack)) q0
Model Checking I What are LTL and CTL? and dack q0 or D dreq D q0bar and 1 View circuit as a transition system (dreq, q0, dack) (dreq, q0, dack ) q0 = dreq dack = dreq and (q0 or (not q0 and dack)) q0
Computer Science Final Examination Friday December 14 th 2001
 Computer Science 03 60 265 Final Examination Friday December 14 th 2001 Dr. Robert D. Kent and Dr. Alioune Ngom Last Name: First Name: Student Number: INSTRUCTIONS EXAM DURATION IS 3 HOURs. CALCULATORS,
Computer Science 03 60 265 Final Examination Friday December 14 th 2001 Dr. Robert D. Kent and Dr. Alioune Ngom Last Name: First Name: Student Number: INSTRUCTIONS EXAM DURATION IS 3 HOURs. CALCULATORS,
Memory Elements I. CS31 Pascal Van Hentenryck. CS031 Lecture 6 Page 1
 Memory Elements I CS31 Pascal Van Hentenryck CS031 Lecture 6 Page 1 Memory Elements (I) Combinational devices are good for computing Boolean functions pocket calculator Computers also need to remember
Memory Elements I CS31 Pascal Van Hentenryck CS031 Lecture 6 Page 1 Memory Elements (I) Combinational devices are good for computing Boolean functions pocket calculator Computers also need to remember
And Inverter Graphs. and and nand. inverter or nor xor
 And Inverter Graphs and and nand inverter or nor xor And Inverter Graphs A B gate 1 u gate 4 X C w gate 3 v gate 2 gate 5 Y A u B X w Y C v And Inverter Graphs Can represent any Boolean function: v i+1
And Inverter Graphs and and nand inverter or nor xor And Inverter Graphs A B gate 1 u gate 4 X C w gate 3 v gate 2 gate 5 Y A u B X w Y C v And Inverter Graphs Can represent any Boolean function: v i+1
The Design Procedure. Output Equation Determination - Derive output equations from the state table
 The Design Procedure Specification Formulation - Obtain a state diagram or state table State Assignment - Assign binary codes to the states Flip-Flop Input Equation Determination - Select flipflop types
The Design Procedure Specification Formulation - Obtain a state diagram or state table State Assignment - Assign binary codes to the states Flip-Flop Input Equation Determination - Select flipflop types
XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL.
![XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL. XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL.](/thumbs/81/84726747.jpg) 2017-18 XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL HALF ADDER 1. The circuit that performs addition within the Arithmetic and Logic Unit of the CPU are called adders. 2. A unit that adds two
2017-18 XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL HALF ADDER 1. The circuit that performs addition within the Arithmetic and Logic Unit of the CPU are called adders. 2. A unit that adds two
Latches. October 13, 2003 Latches 1
 Latches The second part of CS231 focuses on sequential circuits, where we add memory to the hardware that we ve already seen. Our schedule will be very similar to before: We first show how primitive memory
Latches The second part of CS231 focuses on sequential circuits, where we add memory to the hardware that we ve already seen. Our schedule will be very similar to before: We first show how primitive memory
ECE 407 Computer Aided Design for Electronic Systems. Simulation. Instructor: Maria K. Michael. Overview
 407 Computer Aided Design for Electronic Systems Simulation Instructor: Maria K. Michael Overview What is simulation? Design verification Modeling Levels Modeling circuits for simulation True-value simulation
407 Computer Aided Design for Electronic Systems Simulation Instructor: Maria K. Michael Overview What is simulation? Design verification Modeling Levels Modeling circuits for simulation True-value simulation
CS/COE1541: Introduction to Computer Architecture. Logic Design Review. Sangyeun Cho. Computer Science Department University of Pittsburgh
 CS/COE54: Introduction to Computer Architecture Logic Design Review Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Logic design? Digital hardware is implemented by way of logic design Digital circuits process
CS/COE54: Introduction to Computer Architecture Logic Design Review Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Logic design? Digital hardware is implemented by way of logic design Digital circuits process
ECE 645: Lecture 3. Conditional-Sum Adders and Parallel Prefix Network Adders. FPGA Optimized Adders
 ECE 645: Lecture 3 Conditional-Sum Adders and Parallel Prefix Network Adders FPGA Optimized Adders Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 7.4, Conditional-Sum
ECE 645: Lecture 3 Conditional-Sum Adders and Parallel Prefix Network Adders FPGA Optimized Adders Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 7.4, Conditional-Sum
University of Guelph School of Engineering ENG 2410 Digital Design Fall There are 7 questions, answer all questions.
 Final Examination Instructor: Shawki M. Areibi Co-examiner: Medhat Moussa. Location: UOG Date: Wednesday, December 5th, 2007 Time: 8:30-10:30 AM Duration: 2 hours. Type: R Closed Book. Instructions: University
Final Examination Instructor: Shawki M. Areibi Co-examiner: Medhat Moussa. Location: UOG Date: Wednesday, December 5th, 2007 Time: 8:30-10:30 AM Duration: 2 hours. Type: R Closed Book. Instructions: University
Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
PAST EXAM PAPER & MEMO N3 ABOUT THE QUESTION PAPERS:
 EKURHULENI TECH COLLEGE. No. 3 Mogale Square, Krugersdorp. Website: www. ekurhulenitech.co.za Email: info@ekurhulenitech.co.za TEL: 011 040 7343 CELL: 073 770 3028/060 715 4529 PAST EXAM PAPER & MEMO N3
EKURHULENI TECH COLLEGE. No. 3 Mogale Square, Krugersdorp. Website: www. ekurhulenitech.co.za Email: info@ekurhulenitech.co.za TEL: 011 040 7343 CELL: 073 770 3028/060 715 4529 PAST EXAM PAPER & MEMO N3
Final Exam. ECE 25, Spring 2008 Thursday, June 12, Problem Points Score Total 90
 Final Exam ECE 25, Spring 2008 Thursday, June 12, 2008 Name: PID: Problem Points Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 Total 90 1) Number representation (10 pts) a) For each binary vector
Final Exam ECE 25, Spring 2008 Thursday, June 12, 2008 Name: PID: Problem Points Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 Total 90 1) Number representation (10 pts) a) For each binary vector
Logic design? Transistor as a switch. Layered design approach. CS/COE1541: Introduction to Computer Architecture. Logic Design Review.
 Logic design? CS/COE54: Introduction to Computer rchitecture Digital hardware is implemented by way of logic design Digital circuits process and produce two discrete values: and Example: -bit full adder
Logic design? CS/COE54: Introduction to Computer rchitecture Digital hardware is implemented by way of logic design Digital circuits process and produce two discrete values: and Example: -bit full adder
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number:
 Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, Second Semester: 2015/2016 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 08/06/2016
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, Second Semester: 2015/2016 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 08/06/2016
Written exam with solutions IE1204/5 Digital Design Monday 23/
 Written exam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 23/0 207 4.00-8.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist Exam text has to be returned when you hand in your
Written exam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 23/0 207 4.00-8.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist Exam text has to be returned when you hand in your
CSC9R6 Computer Design. Practical Digital Logic
 CSC9R6 Computer Design Practical Digital Logic 1 References (for this part of CSC9R6) Hamacher et al: Computer Organization App A. In library Floyd: Digital Fundamentals Ch 1, 3-6, 8-10 web page: www.prenhall.com/floyd/
CSC9R6 Computer Design Practical Digital Logic 1 References (for this part of CSC9R6) Hamacher et al: Computer Organization App A. In library Floyd: Digital Fundamentals Ch 1, 3-6, 8-10 web page: www.prenhall.com/floyd/
COE 328 Final Exam 2008
 COE 328 Final Exam 2008 1. Design a comparator that compares a 4 bit number A to a 4 bit number B and gives an Output F=1 if A is not equal B. You must use 2 input LUTs only. 2. Given the following logic
COE 328 Final Exam 2008 1. Design a comparator that compares a 4 bit number A to a 4 bit number B and gives an Output F=1 if A is not equal B. You must use 2 input LUTs only. 2. Given the following logic
control in out in out Figure 1. Binary switch: (a) opened or off; (b) closed or on.
 Chapter 2 Digital Circuits Page 1 of 18 2. Digital Circuits Our world is an analog world. Measurements that we make of the physical objects around us are never in discrete units but rather in a continuous
Chapter 2 Digital Circuits Page 1 of 18 2. Digital Circuits Our world is an analog world. Measurements that we make of the physical objects around us are never in discrete units but rather in a continuous
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems. Tutorial Note 9
 ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 9 Outline 1. Exercise(1) Sequential Circuit Analysis 2. Exercise (2) Sequential Circuit Analysis 3. Exercise (3) Sequential Circuit Analysis 4. Ref. Construction
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 9 Outline 1. Exercise(1) Sequential Circuit Analysis 2. Exercise (2) Sequential Circuit Analysis 3. Exercise (3) Sequential Circuit Analysis 4. Ref. Construction
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number:
 Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, First Semester: 2017/2018 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 29/01/2018
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, First Semester: 2017/2018 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 29/01/2018
Lecture 7: Logic design. Combinational logic circuits
 /24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
/24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
7 Multipliers and their VHDL representation
 7 Multipliers and their VHDL representation 7.1 Introduction to arithmetic algorithms If a is a number, then a vector of digits A n 1:0 = [a n 1... a 1 a 0 ] is a numeral representing the number in the
7 Multipliers and their VHDL representation 7.1 Introduction to arithmetic algorithms If a is a number, then a vector of digits A n 1:0 = [a n 1... a 1 a 0 ] is a numeral representing the number in the
Synchronous Sequential Circuit
 Synchronous Sequential Circuit The change of internal state occurs in response to the synchronized clock pulses. Data are read during the clock pulse (e.g. rising-edge triggered) It is supposed to wait
Synchronous Sequential Circuit The change of internal state occurs in response to the synchronized clock pulses. Data are read during the clock pulse (e.g. rising-edge triggered) It is supposed to wait
Lecture 4. Adders. Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University
 Lecture 4 Adders Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University horowitz@stanford.edu Copyright 2006 Mark Horowitz Some figures from High-Performance Microprocessor Design IEEE 1 Overview Readings Today
Lecture 4 Adders Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University horowitz@stanford.edu Copyright 2006 Mark Horowitz Some figures from High-Performance Microprocessor Design IEEE 1 Overview Readings Today
Chapter 4. Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 1 2 Chapter 4 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 1 2 Chapter 4 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of
Digital Systems. Validation, verification. R. Pacalet January 4, 2018
 Digital Systems Validation, verification R. Pacalet January 4, 2018 2/98 Simulation Extra design tasks Reference model Simulation environment A simulation cannot be exhaustive Can discover a bug Cannot
Digital Systems Validation, verification R. Pacalet January 4, 2018 2/98 Simulation Extra design tasks Reference model Simulation environment A simulation cannot be exhaustive Can discover a bug Cannot
For smaller NRE cost For faster time to market For smaller high-volume manufacturing cost For higher performance
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS5 J. Wawrzynek Spring 22 2/22/2. [2 pts] Short Answers. Midterm Exam I a) [2 pts]
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS5 J. Wawrzynek Spring 22 2/22/2. [2 pts] Short Answers. Midterm Exam I a) [2 pts]
Experiment 4 Decoder Encoder Design using VHDL
 Objective: Experiment 4 Decoder Encoder Design using VHDL To learn how to write VHDL code To Learn how to do functional simulation To do study of the synthesis done by VHDL and the theoretical desin obtained
Objective: Experiment 4 Decoder Encoder Design using VHDL To learn how to write VHDL code To Learn how to do functional simulation To do study of the synthesis done by VHDL and the theoretical desin obtained
CHAPTER * 2-2.* Pearson Education Limited Problem Solutions, Global Edition Chapter 2. Verification of DeMorgan s Theorem
 HPTER 2 2-.* a) XYZ = X + Y + Z Verification of DeMorgan s Theorem Pearson Education Limited 206. X Y Z XYZ XYZ X + Y + Z 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 b) X + YZ = ( X + Y) ( X + Z) The Second
HPTER 2 2-.* a) XYZ = X + Y + Z Verification of DeMorgan s Theorem Pearson Education Limited 206. X Y Z XYZ XYZ X + Y + Z 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 b) X + YZ = ( X + Y) ( X + Z) The Second
ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter. Lab 3. Lab 3 Gate Timing. Lab 3 Steps in designing a State Machine. Timing diagram of a DFF
 ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter Timing diagram of a DFF Lab 3 Gate Timing difference timing for difference kind of gate, cost dependence (1) Setup Time = t2-t1 (2) Propagation
ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter Timing diagram of a DFF Lab 3 Gate Timing difference timing for difference kind of gate, cost dependence (1) Setup Time = t2-t1 (2) Propagation
Table of Content. Chapter 11 Dedicated Microprocessors Page 1 of 25
 Chapter 11 Dedicated Microprocessors Page 1 of 25 Table of Content Table of Content... 1 11 Dedicated Microprocessors... 2 11.1 Manual Construction of a Dedicated Microprocessor... 3 11.2 FSM + D Model
Chapter 11 Dedicated Microprocessors Page 1 of 25 Table of Content Table of Content... 1 11 Dedicated Microprocessors... 2 11.1 Manual Construction of a Dedicated Microprocessor... 3 11.2 FSM + D Model
University of Florida EEL 3701 Fall 2014 Dr. Eric. M. Schwartz Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Wednesday, 15 October 2014
 Page 1/12 Exam 1 May the Schwartz Instructions: be with you! Turn off all cell phones and other noise making devices and put away all electronics Show all work on the front of the test papers Box each
Page 1/12 Exam 1 May the Schwartz Instructions: be with you! Turn off all cell phones and other noise making devices and put away all electronics Show all work on the front of the test papers Box each
Acknowledgment. DLD Lab. This set of slides on VHDL are due to Brown and Vranesic.
 Acknowledgment DLD Lab Thi et o lide on VHDL are due to Brown and Vraneic. Introduction to VHDL (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Hardware Decription Language) 2 3 A imple logic unction and correponding
Acknowledgment DLD Lab Thi et o lide on VHDL are due to Brown and Vraneic. Introduction to VHDL (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Hardware Decription Language) 2 3 A imple logic unction and correponding
Time Allowed 3:00 hrs. April, pages
 IGITAL ESIGN COEN 32 Prof. r. A. J. Al-Khalili Time Allowed 3: hrs. April, 998 2 pages Answer All uestions No materials are allowed uestion a) esign a half subtractor b) esign a full subtractor c) Using
IGITAL ESIGN COEN 32 Prof. r. A. J. Al-Khalili Time Allowed 3: hrs. April, 998 2 pages Answer All uestions No materials are allowed uestion a) esign a half subtractor b) esign a full subtractor c) Using
Problem Set 9 Solutions
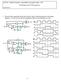 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Minsub Shin, Lisa Ossian, Sujith Surendran Midterm Examination 2 In Class (50 minutes) Friday,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Minsub Shin, Lisa Ossian, Sujith Surendran Midterm Examination 2 In Class (50 minutes) Friday,
Sequential Circuit Analysis
 Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
EE40 Lec 15. Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits
 EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS151/251A V. Stojanovic, J. Wawrzynek Fall 2015 10/13/15 Midterm Exam Name: ID
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS151/251A V. Stojanovic, J. Wawrzynek Fall 2015 10/13/15 Midterm Exam Name: ID
Lecture 10: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design
 Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
Synchronous Sequential Logic
 1 IT 201 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN MODULE4 NOTES Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits - A sequential circuit consists of a combinational circuit and a feedback through the storage elements in
1 IT 201 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN MODULE4 NOTES Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits - A sequential circuit consists of a combinational circuit and a feedback through the storage elements in
3. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Use binary numbers with a sign bit and 7 bits for the value
 EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 DEPARTMENT: EEE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE: EE55 SEMESTER IV UNIT : Design of Synchronous Sequential Circuits PART
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 DEPARTMENT: EEE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE: EE55 SEMESTER IV UNIT : Design of Synchronous Sequential Circuits PART
Pin Details of Digital Logic Gates:
 (1) (2) Pin Details of Digital Logic Gates: (3) Postulates and Theorems of Boolean algebra: S. No Postulate/Theorem Duality Remarks 1. X + 0 = X X.1 = X - 2. X + X = 1 X.X = 0-3. X + X = X X.X = X - 4.
(1) (2) Pin Details of Digital Logic Gates: (3) Postulates and Theorems of Boolean algebra: S. No Postulate/Theorem Duality Remarks 1. X + 0 = X X.1 = X - 2. X + X = 1 X.X = 0-3. X + X = X X.X = X - 4.
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization
 CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Logic Design Review Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science Logic design? Digital hardware is implemented by way of logic design Digital circuits
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Logic Design Review Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science Logic design? Digital hardware is implemented by way of logic design Digital circuits
Errata for Fundamentals of Logic Design, 5th ed, hardcover (1st printing)
 Errata for Fundamentals of Logic Design, 5th ed, hardcover (1st printing) Look on the back of the title page of the textbook (the copyright page) and you will find a line that reads either 3 4 5 6 7 06
Errata for Fundamentals of Logic Design, 5th ed, hardcover (1st printing) Look on the back of the title page of the textbook (the copyright page) and you will find a line that reads either 3 4 5 6 7 06
Lecture 17: Designing Sequential Systems Using Flip Flops
 EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 17: Designing Sequential Systems Using Flip Flops Prof. YingLi Tian April 11, 2019 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 17: Designing Sequential Systems Using Flip Flops Prof. YingLi Tian April 11, 2019 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
Design of Sequential Circuits
 Design of Sequential Circuits Seven Steps: Construct a state diagram (showing contents of flip flop and inputs with next state) Assign letter variables to each flip flop and each input and output variable
Design of Sequential Circuits Seven Steps: Construct a state diagram (showing contents of flip flop and inputs with next state) Assign letter variables to each flip flop and each input and output variable
Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis
 Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis Given the circuit diagram of a state machine: Analyze the combinational logic to determine flip-flop input (excitation) equations: D i = F i (Q, inputs) The input
Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis Given the circuit diagram of a state machine: Analyze the combinational logic to determine flip-flop input (excitation) equations: D i = F i (Q, inputs) The input
CMSC 313 Lecture 17. Focus Groups. Announcement: in-class lab Thu 10/30 Homework 3 Questions Circuits for Addition Midterm Exam returned
 Focus Groups CMSC 33 Lecture 7 Need good sample of all types of CS students Mon /7 & Thu /2, 2:3p-2:p & 6:p-7:3p Announcement: in-class lab Thu /3 Homework 3 Questions Circuits for Addition Midterm Exam
Focus Groups CMSC 33 Lecture 7 Need good sample of all types of CS students Mon /7 & Thu /2, 2:3p-2:p & 6:p-7:3p Announcement: in-class lab Thu /3 Homework 3 Questions Circuits for Addition Midterm Exam
Sample Test Paper - I
 Scheme G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Marks : 25 Hours: 1 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any THREE: 09 Marks a) Define i) Propagation delay ii) Fan-in iii) Fan-out b) Convert the following:
Scheme G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Marks : 25 Hours: 1 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any THREE: 09 Marks a) Define i) Propagation delay ii) Fan-in iii) Fan-out b) Convert the following:
Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates. Textbook Chapter 3
 Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates Textbook Chapter 3 Basic Logic Gates XOR CMPE12 Summer 2009 02-2 Truth Table The most basic representation of a logic function Lists the output for all possible
Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates Textbook Chapter 3 Basic Logic Gates XOR CMPE12 Summer 2009 02-2 Truth Table The most basic representation of a logic function Lists the output for all possible
WORKBOOK. Try Yourself Questions. Electrical Engineering Digital Electronics. Detailed Explanations of
 27 WORKBOOK Detailed Eplanations of Try Yourself Questions Electrical Engineering Digital Electronics Number Systems and Codes T : Solution Converting into decimal number system 2 + 3 + 5 + 8 2 + 4 8 +
27 WORKBOOK Detailed Eplanations of Try Yourself Questions Electrical Engineering Digital Electronics Number Systems and Codes T : Solution Converting into decimal number system 2 + 3 + 5 + 8 2 + 4 8 +
Vidyalankar. S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design. Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form
![Vidyalankar. S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design. Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form Vidyalankar. S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design. Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form](/thumbs/96/126594189.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form [5] (i) (42) 10 (ii) (17)
S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form [5] (i) (42) 10 (ii) (17)
10/12/2016. An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State. ECE 120: Introduction to Computing. Eventually, the States Form a Loop
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution](/thumbs/90/103673562.jpg) . (a) (i) ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H = (FFFF 698) H (ii) (2.3) 4 + (22.3) 4 2 2. 3 2. 3 2 3. 2 (2.3)
. (a) (i) ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H = (FFFF 698) H (ii) (2.3) 4 + (22.3) 4 2 2. 3 2. 3 2 3. 2 (2.3)
ECE321 Electronics I
 ECE321 Electronics I Lecture 1: Introduction to Digital Electronics Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: payman@ece.unm.edu Slide: 1 Textbook
ECE321 Electronics I Lecture 1: Introduction to Digital Electronics Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: payman@ece.unm.edu Slide: 1 Textbook
Week-5. Sequential Circuit Design. Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA.
 Week-5 Sequential Circuit Design Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA. Storing a value: SR = 00 What if S = 0 and R = 0? The equations on the
Week-5 Sequential Circuit Design Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA. Storing a value: SR = 00 What if S = 0 and R = 0? The equations on the
EECS 270 Midterm Exam 2 Fall 2009
 EECS 270 Midterm Exam 2 Fall 2009 Name: unique name: UMID: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: NOTES: Problem # Points 1&2
EECS 270 Midterm Exam 2 Fall 2009 Name: unique name: UMID: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: NOTES: Problem # Points 1&2
Dr. S. Shirani COE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov. 9, 2010
 Dr. S. Shirani COE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov. 9, 2010 Instructions: This examination paper includes 11 pages and 20 multiple-choice questions starting on page 3. You are responsible for ensuring that your
Dr. S. Shirani COE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov. 9, 2010 Instructions: This examination paper includes 11 pages and 20 multiple-choice questions starting on page 3. You are responsible for ensuring that your
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department
 King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page 1 of 13 COE 202: Digital Logic Design (3-0-3) Term 112 (Spring 2012) Final
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page 1 of 13 COE 202: Digital Logic Design (3-0-3) Term 112 (Spring 2012) Final
Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 2009, University of Colombo School of Computing
 IT 204 Section 3.0 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic Boolean Algebra 2 Logic Equations to Truth Tables X = A. B + A. B + AB A B X 0 0 0 0 3 Sum of Products The OR operation performed on the products of
IT 204 Section 3.0 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic Boolean Algebra 2 Logic Equations to Truth Tables X = A. B + A. B + AB A B X 0 0 0 0 3 Sum of Products The OR operation performed on the products of
DE58/DC58 LOGIC DESIGN DEC 2014
 Q.2 a. In a base-5 number system, 3 digit representations is used. Find out (i) Number of distinct quantities that can be represented.(ii) Representation of highest decimal number in base-5. Since, r=5
Q.2 a. In a base-5 number system, 3 digit representations is used. Find out (i) Number of distinct quantities that can be represented.(ii) Representation of highest decimal number in base-5. Since, r=5
Combinational Logic Design Combinational Functions and Circuits
 Combinational Logic Design Combinational Functions and Circuits Overview Combinational Circuits Design Procedure Generic Example Example with don t cares: BCD-to-SevenSegment converter Binary Decoders
Combinational Logic Design Combinational Functions and Circuits Overview Combinational Circuits Design Procedure Generic Example Example with don t cares: BCD-to-SevenSegment converter Binary Decoders
Number System. Decimal to binary Binary to Decimal Binary to octal Binary to hexadecimal Hexadecimal to binary Octal to binary
 Number System Decimal to binary Binary to Decimal Binary to octal Binary to hexadecimal Hexadecimal to binary Octal to binary BOOLEAN ALGEBRA BOOLEAN LOGIC OPERATIONS Logical AND Logical OR Logical COMPLEMENTATION
Number System Decimal to binary Binary to Decimal Binary to octal Binary to hexadecimal Hexadecimal to binary Octal to binary BOOLEAN ALGEBRA BOOLEAN LOGIC OPERATIONS Logical AND Logical OR Logical COMPLEMENTATION
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison. Fall Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 2014-2015 Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK Kewal K. Saluja
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 2014-2015 Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK Kewal K. Saluja
Building a Computer Adder
 Logic Gates are used to translate Boolean logic into circuits. In the abstract it is clear that we can build AND gates that perform the AND function and OR gates that perform the OR function and so on.
Logic Gates are used to translate Boolean logic into circuits. In the abstract it is clear that we can build AND gates that perform the AND function and OR gates that perform the OR function and so on.
COSC 243. Introduction to Logic And Combinatorial Logic. Lecture 4 - Introduction to Logic and Combinatorial Logic. COSC 243 (Computer Architecture)
 COSC 243 Introduction to Logic And Combinatorial Logic 1 Overview This Lecture Introduction to Digital Logic Gates Boolean algebra Combinatorial Logic Source: Chapter 11 (10 th edition) Source: J.R. Gregg,
COSC 243 Introduction to Logic And Combinatorial Logic 1 Overview This Lecture Introduction to Digital Logic Gates Boolean algebra Combinatorial Logic Source: Chapter 11 (10 th edition) Source: J.R. Gregg,
Review for Final Exam
 CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Review for Final Exam Mohsen Imani CAPE Please submit your evaluations!!!! RTL design Use the RTL design process to design a system that has
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Review for Final Exam Mohsen Imani CAPE Please submit your evaluations!!!! RTL design Use the RTL design process to design a system that has
Simplify the following Boolean expressions and minimize the number of literals:
 Boolean Algebra Task 1 Simplify the following Boolean expressions and minimize the number of literals: 1.1 1.2 1.3 Task 2 Convert the following expressions into sum of products and product of sums: 2.1
Boolean Algebra Task 1 Simplify the following Boolean expressions and minimize the number of literals: 1.1 1.2 1.3 Task 2 Convert the following expressions into sum of products and product of sums: 2.1
Faculty of Engineering. FINAL EXAMINATION FALL 2008 (December2008) ANSWER KEY
 1 McGill University Faculty of Engineering DIGITAL SYSTEM DESIGN ECSE-323 FINAL EXAMINATION FALL 2008 (December2008) ANSWER KEY STUDENT NAME McGILL I.D. NUMBER Examiner: Prof. J. Clark Signature: Associate
1 McGill University Faculty of Engineering DIGITAL SYSTEM DESIGN ECSE-323 FINAL EXAMINATION FALL 2008 (December2008) ANSWER KEY STUDENT NAME McGILL I.D. NUMBER Examiner: Prof. J. Clark Signature: Associate
Problem Set 6 Solutions
 CS/EE 260 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design Problem Set 6 Solutions Jon Turner Quiz on 2/21/02 1. The logic diagram at left below shows a 5 bit ripple-carry decrement circuit. Draw a logic
CS/EE 260 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design Problem Set 6 Solutions Jon Turner Quiz on 2/21/02 1. The logic diagram at left below shows a 5 bit ripple-carry decrement circuit. Draw a logic
ENGG 1203 Tutorial_9 - Review. Boolean Algebra. Simplifying Logic Circuits. Combinational Logic. 1. Combinational & Sequential Logic
 ENGG 1203 Tutorial_9 - Review Boolean Algebra 1. Combinational & Sequential Logic 2. Computer Systems 3. Electronic Circuits 4. Signals, Systems, and Control Remark : Multiple Choice Questions : ** Check
ENGG 1203 Tutorial_9 - Review Boolean Algebra 1. Combinational & Sequential Logic 2. Computer Systems 3. Electronic Circuits 4. Signals, Systems, and Control Remark : Multiple Choice Questions : ** Check
Digital Logic Design - Chapter 4
 Digital Logic Design - Chapter 4 1. Analyze the latch circuit shown below by obtaining timing diagram for the circuit; include propagation delays. Y This circuit has two external input and one feedback
Digital Logic Design - Chapter 4 1. Analyze the latch circuit shown below by obtaining timing diagram for the circuit; include propagation delays. Y This circuit has two external input and one feedback
ENEL Digital Circuit Design. Final Examination
 ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ENEL 353 - Digital Circuit Design Final Examination Friday, December 17, 1999 Red Gymnasium, 3:30PM - 6:30 PM Instructions: Time allowed is 3 hours. The examination
ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ENEL 353 - Digital Circuit Design Final Examination Friday, December 17, 1999 Red Gymnasium, 3:30PM - 6:30 PM Instructions: Time allowed is 3 hours. The examination
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization
 Logic design? CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Logic Design Review Digital hardware is implemented by way of logic design Digital circuits process and produce two discrete values:
Logic design? CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Logic Design Review Digital hardware is implemented by way of logic design Digital circuits process and produce two discrete values:
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON Prof. Mark D. Hill & Prof. Mikko Lipasti TAs Sanghamitra Roy, Eric Hill, Samuel Javner, Natalie
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON Prof. Mark D. Hill & Prof. Mikko Lipasti TAs Sanghamitra Roy, Eric Hill, Samuel Javner, Natalie
ECE 448 Lecture 6. Finite State Machines. State Diagrams, State Tables, Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts, and VHDL Code. George Mason University
 ECE 448 Lecture 6 Finite State Machines State Diagrams, State Tables, Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts, and VHDL Code George Mason University Required reading P. Chu, FPGA Prototyping by VHDL Examples
ECE 448 Lecture 6 Finite State Machines State Diagrams, State Tables, Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts, and VHDL Code George Mason University Required reading P. Chu, FPGA Prototyping by VHDL Examples
Luleå Tekniska Universitet Kurskod SMD098 Tentamensdatum
 Luleå Tekniska Universitet Kurskod SMD098 Tentamensdatum 991215 Skrivtid 4 timmar Tentamen i Beräkningsstrukturer Antal uppgifter: 6 Max poäng: 30 Betygsgränser: >20 poäng 4 >25 poäng 5 Betygsgränser kan
Luleå Tekniska Universitet Kurskod SMD098 Tentamensdatum 991215 Skrivtid 4 timmar Tentamen i Beräkningsstrukturer Antal uppgifter: 6 Max poäng: 30 Betygsgränser: >20 poäng 4 >25 poäng 5 Betygsgränser kan
Chapter 3 Combinational Logic Design
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 3 Combinational Logic Design Part 1- Implementation Technology and Logic Design Overview Part 1-Implementation Technology and Logic Design Design Concepts
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 3 Combinational Logic Design Part 1- Implementation Technology and Logic Design Overview Part 1-Implementation Technology and Logic Design Design Concepts
Appendix B. Review of Digital Logic. Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs
 Appendix B Review of Digital Logic Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Elect. & Comp. Eng. 2 DeMorgan Symbols NAND (A.B) = A +B NOR (A+B) = A.B AND A.B = A.B = (A +B ) OR
Appendix B Review of Digital Logic Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Elect. & Comp. Eng. 2 DeMorgan Symbols NAND (A.B) = A +B NOR (A+B) = A.B AND A.B = A.B = (A +B ) OR
Verification. Arijit Mondal. Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Patna
 IIT Patna 1 Verification Arijit Mondal Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Patna arijit@iitp.ac.in Introduction The goal of verification To ensure 100% correct in functionality
IIT Patna 1 Verification Arijit Mondal Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Patna arijit@iitp.ac.in Introduction The goal of verification To ensure 100% correct in functionality
Adders - Subtractors
 Adders - Subtractors Lesson Objectives: The objectives of this lesson are to learn about: 1. Half adder circuit. 2. Full adder circuit. 3. Binary parallel adder circuit. 4. Half subtractor circuit. 5.
Adders - Subtractors Lesson Objectives: The objectives of this lesson are to learn about: 1. Half adder circuit. 2. Full adder circuit. 3. Binary parallel adder circuit. 4. Half subtractor circuit. 5.
Finite-State Model Checking
 EECS 219C: Computer-Aided Verification Intro. to Model Checking: Models and Properties Sanjit A. Seshia EECS, UC Berkeley Finite-State Model Checking G(p X q) Temporal logic q p FSM Model Checker Yes,
EECS 219C: Computer-Aided Verification Intro. to Model Checking: Models and Properties Sanjit A. Seshia EECS, UC Berkeley Finite-State Model Checking G(p X q) Temporal logic q p FSM Model Checker Yes,
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Final Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Tuesday Dec 12 th 13:00-15:00 (1-3pm) 2 hour
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Final Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Tuesday Dec 12 th 13:00-15:00 (1-3pm) 2 hour
ECEN 651: Microprogrammed Control of Digital Systems Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University
 ECEN 651: Microprogrammed Control of Digital Systems Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Prof. Mi Lu TA: Ehsan Rohani Laboratory Exercise #2 Behavioral, Dataflow, and
ECEN 651: Microprogrammed Control of Digital Systems Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Prof. Mi Lu TA: Ehsan Rohani Laboratory Exercise #2 Behavioral, Dataflow, and
The University of Michigan Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. EECS 270 Fall Practice Final Exam.
 The University of Michigan Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 270 Fall 2003 Practice Final Exam Name: UM ID: For all questions, show all work that leads to your answer. Problem
The University of Michigan Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 270 Fall 2003 Practice Final Exam Name: UM ID: For all questions, show all work that leads to your answer. Problem
