Problem Set 6 Solutions
|
|
|
- Lucas Perkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS/EE 260 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design Problem Set 6 Solutions Jon Turner Quiz on 2/21/02 1. The logic diagram at left below shows a 5 bit ripple-carry decrement circuit. Draw a logic diagram for a 5 bit borrow-lookahead decrement circuit. You may use gates with more than 2 inputs. What is the worst-case propagation delay for your circuit, if all gates with 1 input have a delay of 1 ns, all gates with 2 inputs have a delay of 2 ns, all gates with 3 or 4 inputs have a delay of 4 ns and all gates with 5 to 8 inputs have a delay of 6 ns? The max delay is from the DECR input through the 5 input OR gate to Q4. This delay is 1+6+2=9ns
2 2. An n bit comparator takes two n bit input values x and y and has two outputs L and G. If the value of x is numerically smaller than y, then L is high and G is low. If the value of x is greater than y, then G is high and L is low. Otherwise, both L and G are low. An n bit comparator can be implemented using n 1 bit comparators. Show how to implement a 4 bit comparator in this way. (Note that the outcome of the comparison is determined entirely by the most significant bit position in which the value of x differs from y.) The two outputs L and G of a 1 bit comparator are defined by the logic equations L=x y and G=xy. For a 2 bit comparator, the corresponding equations are L = x 1 y 1 + (x 1y 1 ) (x 0 y 0) and G = x 1y 1 + (x 1 y 1) (x 0y 0 ). This leads to a circuit that looks like this. x 1 x 0 G L y 1 y 0 The portion of the circuit highlighted by the dashed lines can be cascaded to produce an n bit comparator. So, for example, using 4 copies of this circuit, we can get the 4 bit comparator shown below. x 3 x 2 x 1 x 0 1 bit comparator 1 bit comparator 1 bit comparator 1 bit comparator G L y 3 y 2 y 1 y 0-2 -
3 If every gate has a worst-case delay of 1 ns, what is the longest possible delay in your 4 bit circuit from the time the input values change to the time the output values finish changing? What is the worst-case delay for an n bit version of your circuit? Show how to build a faster lookahead version of your circuit, using only simple gates. The longest path from an input to an output is from input x n-1 to output L, which must go through n+2 gates. So, with a 1 ns delay per gate, the longest possible delay is 6 ns and for an n bit comparator, the worst-case delay is n+2 ns. We can build a lookahead version of the circuit we first need to derive the appropriate logic equations. Let L i = x i y i and G i=x iy i. Then, for the 4 bit comparator, we can write L = L 3+G 3 L 2 + G 3 G 2 L 1 + G 3 G 2 G 1 L 0 and G = G 3+L 3 G 2 + L 3 L 2 G 1 + L 3 L 2 L 1 G 0. A circuit implementing these equations appears below. This can be converted to a circuit using simple gates by replacing each of the k input gates (for k>2) with a balanced tree of k-1 simple gates. This circuit has a worst-case delay of 7 ns, which is actually worse than the earlier circuit, but an for larger n it will be faster. The n bit version of the circuit has a worst-case delay of 3 + 2log 2n for any n that is a power of
4 There is an alternative design for a lookahead comparator that requires fewer gates than the n bit version of the design shown above, which requires about n 2 simple gates. This one is based on a different way of writing the logic equations. Define L(i,j) to be true if the number formed from bits x i+j-1...x i is less than the number formed from bits y i+j-1...y i. Define G(i,j) similarly. Then for an n bit comparator, the final outputs L = L(0,n) and G = G(0,n). Now if n is a power of 2, we can write L(0,n) = L(n/2,n/2) + G(n/2,n/2) L(0,n/2) and G(0,n) = G(n/2,n/2) + L(n/2,n/2) G(0,n/2). Similarly, L(0,n/2) = L(n/4,n/4) + G(n/4,n/4) L(0,n/4) and L(0,n/2) = L(n/4,n/4) + G(n/4,n/4) L(0,n/4) and in general L(i,j) = L(i+j/2,j/2) + G(i+j//2,j/2) L(i,j/2) and G(i,j) = G(i+j/2,j/2) + L(i+j//2,j/2) G(i,j/2). A 4 bit version of the circuit obtained using these equations is shown below. The n bit version has a worst-case delay of log 2n which is not quite as good as the first lookahead circuit, but this circuit has a gate count of 8n 5, which is a huge improvement
5 3. Write a VHDL module (entity and architecture) that implements a 2 4 decoder with an enable input. Your decoder should have three inputs (including the enable) and four outputs. The outputs should all be low when the enable is low. This can be written using a single conditional signal assignment statement. library IEEE; entity dec24 is A: in std_logic_vector(1 downto 0 en: in std_logic; X: out std_logic_vector(3 downto 0) end dec24; architecture dec24arch of dec24 is X <= 0001 when en = 1 and A = 00 else 0010 when en = 1 and A = 01 else 0100 when en = 1 and A = 10 else 1000 when en = 1 and A = 11 else 0000 ; end dec24arch; Now, write a VHDL module that implements a 3 8 decoder using two copies of the 2 4 decoder, that are wired together using component statements with port maps. library IEEE; entity dec38 is A: in std_logic_vector(2 downto 0 X: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) end dec38; architecture dec38arch of dec38 is signal Z: std_logic; component dec24 A: in std_logic_vector(1 downto 0 en: in std_logic; X: out std_logic_vector(3 downto 0) end component; Z <= not A(2 lo: dec24 port map(a(1 downto 0),Z,X(3 downto 0) hi: dec24 port map(a(1 downto 0),A(2),X(7 downto 4) end dec38arch; - 5 -
6 4. Draw logic diagrams for combinational circuits that are equivalent to each of the VHDL modules shown below. Use simple gates only in your circuits. (a) library IEEE; entity parta is A, B, C, D: in std_logic; X, Y: out std_logic end parta; architecture partaarch of parta is signal Z: std_logic; Z <= (A and B) or C; X <= (not D) xor Z; Y <= (A or (not B)) and Z; end partaarch; A BC D Z X Y - 6 -
7 (b) library IEEE; entity partb is A, B, C, D: in std_logic; X, Y: out std_logic end partb; architecture partbarch of partb is X <= (not D) xor (A or C Y <= 0 when (A = 1 and B = 0 ) or (C = 1 and D = 1 ) or (A = 0 and B = 1 ) else 1 ; end partbarch; A C D B X Y - 7 -
8 5. Write two different VHDL modules that implement the logic unit in problem 1 of design problem 2. In the first version, write logic equations for each output signal that correspond directly to the schematic in the solution set provided on the web site. Pattern the second version, after the arithmetic unit design on page 3-36 of the lecture notes. library IEEE; entity version1 is A, B: in std_logic_vector(3 downto 0 S: in std_logic_vector(1 downto 0 R: out std_logic_vector(3 downto 0) end version1; architecture v1arch of version1 is R(0) <=(S(1) and not S(0) and not A(0)) or (not S(1) and A(0) and B(0)) or (S(0) and A(0) xor B(0) R(1) <=(S(1) and not S(0) and not A(1)) or (not S(1) and A(1) and B(1)) or (S(0) and A(1) xor B(1) R(2) <=(S(1) and not S(0) and not A(2)) or (not S(1) and A(2) and B(2)) or (S(0) and A(2) xor B(2) R(3) <=(S(1) and not S(0) and not A(3)) or (not S(1) and A(3) and B(3)) or (S(0) and A(3) xor B(3) end v1arch; library IEEE; entity version2 is A, B: in std_logic_vector(3 downto 0 S: in std_logic_vector(1 downto 0 R: out std_logic_vector(3 downto 0) end version2; architecture v2arch of version2 is R <= A and B when S = 00 else A or B when S = 01 else not A when S = 10 else A xor B when S = 11 ; end v2arch; - 8 -
9 6. Draw a logic diagram using simple gates and a 4:1 multiplexor that is equivalent to the VHDL code shown below. Be sure to label all the inputs of your multiplexor correctly. library IEEE; entity foo is curve, slider, wild: in std_logic; sign: in std_logic_vector (1 downto 0 strike, run: out std_logic end foo; architecture bar of foo is strike <= (curve or slider) and not wild; run <= (curve xor slider) when sign = 00 else wild when sign = 01 else slider and wild; end bar; curve slider wild strike :1 Mux run s 1 s 0-9 -
10 7. Page 4-7 and 4-8 of the lecture notes discuss a serial parity generator. During what time period must the D input be stable if the gate delays can vary from.8 to 2.5 ns. During what period must the EN input be stable in this case? Draw a diagram like the one on page 4-8, showing the time periods during which the inputs must be stable. Input D must be stable from 7 ns before the clock changes to.6 ns before the clock changes. Input EN must be stable from 4.5 ns before the clock changes to.2 ns after the clock changes. The timing diagram appears below. C D EN
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Introductory Digital Systems Lab (6.111) Quiz #1 - Spring 2003 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan and Prof. Don
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Introductory Digital Systems Lab (6.111) Quiz #1 - Spring 2003 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan and Prof. Don
Assignment # 3 - CSI 2111(Solutions)
 Assignment # 3 - CSI 2111(Solutions) Q1. Realize, using a suitable PLA, the following functions : [10 marks] f 1 (x,y,z) = Σm(0,1,5,7) f 2 (x,y,z) = Σm(2,5,6) f 3 (x,y,z) = Σm(1,4,5,7) f 4 (x,y,z) = Σm(0,3,6)
Assignment # 3 - CSI 2111(Solutions) Q1. Realize, using a suitable PLA, the following functions : [10 marks] f 1 (x,y,z) = Σm(0,1,5,7) f 2 (x,y,z) = Σm(2,5,6) f 3 (x,y,z) = Σm(1,4,5,7) f 4 (x,y,z) = Σm(0,3,6)
Chapter 5. Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition. David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris. Chapter 5 <1>
 Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Acknowledgment. DLD Lab. This set of slides on VHDL are due to Brown and Vranesic.
 Acknowledgment DLD Lab Thi et o lide on VHDL are due to Brown and Vraneic. Introduction to VHDL (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Hardware Decription Language) 2 3 A imple logic unction and correponding
Acknowledgment DLD Lab Thi et o lide on VHDL are due to Brown and Vraneic. Introduction to VHDL (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Hardware Decription Language) 2 3 A imple logic unction and correponding
Experiment 4 Decoder Encoder Design using VHDL
 Objective: Experiment 4 Decoder Encoder Design using VHDL To learn how to write VHDL code To Learn how to do functional simulation To do study of the synthesis done by VHDL and the theoretical desin obtained
Objective: Experiment 4 Decoder Encoder Design using VHDL To learn how to write VHDL code To Learn how to do functional simulation To do study of the synthesis done by VHDL and the theoretical desin obtained
Written exam for IE1204/5 Digital Design with solutions Thursday 29/
 Written exam for IE4/5 Digital Design with solutions Thursday 9/ 5 9.-. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 8-794487 Exam text does not have to be returned when
Written exam for IE4/5 Digital Design with solutions Thursday 9/ 5 9.-. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 8-794487 Exam text does not have to be returned when
Chapter 5 Arithmetic Circuits
 Chapter 5 Arithmetic Circuits SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} February 11, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Iterative Designs 2 Adders 3 High-Speed
Chapter 5 Arithmetic Circuits SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} February 11, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Iterative Designs 2 Adders 3 High-Speed
CMSC 313 Lecture 18 Midterm Exam returned Assign Homework 3 Circuits for Addition Digital Logic Components Programmable Logic Arrays
 CMSC 33 Lecture 8 Midterm Exam returned ssign Homework 3 Circuits for ddition Digital Logic Components Programmable Logic rrays UMC, CMSC33, Richard Chang Half dder Inputs: and Outputs:
CMSC 33 Lecture 8 Midterm Exam returned ssign Homework 3 Circuits for ddition Digital Logic Components Programmable Logic rrays UMC, CMSC33, Richard Chang Half dder Inputs: and Outputs:
Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006
 COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Fall 2006 Page 1 Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006 Instructions: This examination paper includes 12 pages and 20 multiple-choice questions starting
COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Fall 2006 Page 1 Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006 Instructions: This examination paper includes 12 pages and 20 multiple-choice questions starting
CHAPTER * 2-2.* Pearson Education Limited Problem Solutions, Global Edition Chapter 2. Verification of DeMorgan s Theorem
 HPTER 2 2-.* a) XYZ = X + Y + Z Verification of DeMorgan s Theorem Pearson Education Limited 206. X Y Z XYZ XYZ X + Y + Z 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 b) X + YZ = ( X + Y) ( X + Z) The Second
HPTER 2 2-.* a) XYZ = X + Y + Z Verification of DeMorgan s Theorem Pearson Education Limited 206. X Y Z XYZ XYZ X + Y + Z 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 b) X + YZ = ( X + Y) ( X + Z) The Second
Digital Electronics II Mike Brookes Please pick up: Notes from the front desk
 NOTATION.PPT(10/8/2010) 1.1 Digital Electronics II Mike Brookes Please pick up: Notes from the front desk 1. What does Digital mean? 2. Where is it used? 3. Why is it used? 4. What are the important features
NOTATION.PPT(10/8/2010) 1.1 Digital Electronics II Mike Brookes Please pick up: Notes from the front desk 1. What does Digital mean? 2. Where is it used? 3. Why is it used? 4. What are the important features
ECE 448 Lecture 6. Finite State Machines. State Diagrams, State Tables, Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts, and VHDL Code. George Mason University
 ECE 448 Lecture 6 Finite State Machines State Diagrams, State Tables, Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts, and VHDL Code George Mason University Required reading P. Chu, FPGA Prototyping by VHDL Examples
ECE 448 Lecture 6 Finite State Machines State Diagrams, State Tables, Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts, and VHDL Code George Mason University Required reading P. Chu, FPGA Prototyping by VHDL Examples
7 Multipliers and their VHDL representation
 7 Multipliers and their VHDL representation 7.1 Introduction to arithmetic algorithms If a is a number, then a vector of digits A n 1:0 = [a n 1... a 1 a 0 ] is a numeral representing the number in the
7 Multipliers and their VHDL representation 7.1 Introduction to arithmetic algorithms If a is a number, then a vector of digits A n 1:0 = [a n 1... a 1 a 0 ] is a numeral representing the number in the
Sequential Logic Worksheet
 Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Written reexam with solutions for IE1204/5 Digital Design Monday 14/
 Written reexam with solutions for IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 4/3 206 4.-8. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 08-7904487 Exam text does not have to be returned
Written reexam with solutions for IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 4/3 206 4.-8. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 08-7904487 Exam text does not have to be returned
Problem Set 9 Solutions
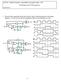 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
Shannon decomposition
 Shannon decomposition Claude Shannon mathematician / electrical engineer 96 William Sandqvist illiam@kth.se E 8.6 Sho ho a 4-to- multipleer can e used as a "function generator" for eample to generate the
Shannon decomposition Claude Shannon mathematician / electrical engineer 96 William Sandqvist illiam@kth.se E 8.6 Sho ho a 4-to- multipleer can e used as a "function generator" for eample to generate the
Design of Sequential Circuits
 Design of Sequential Circuits Seven Steps: Construct a state diagram (showing contents of flip flop and inputs with next state) Assign letter variables to each flip flop and each input and output variable
Design of Sequential Circuits Seven Steps: Construct a state diagram (showing contents of flip flop and inputs with next state) Assign letter variables to each flip flop and each input and output variable
LECTURE 2: Delay models, std_ulogic and. EECS 316 CAD Computer Aided Design. with-select-when. Chris Papachristou Case Western Reserve University
 CAD Computer Aided Design LECTURE 2: Delay models, std_ulogic and with-select-when Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Chris Papachristou Case Western Reserve University Review: Full Adder:
CAD Computer Aided Design LECTURE 2: Delay models, std_ulogic and with-select-when Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Chris Papachristou Case Western Reserve University Review: Full Adder:
Shannon decomposition
 Shannon decomposition Claude Shannon mathematician / electrical engineer 96 William Sandqvist illiam@kth.se E 8.6 Sho ho a 4-to- multipleer can e used as a "function generator" for eample to generate the
Shannon decomposition Claude Shannon mathematician / electrical engineer 96 William Sandqvist illiam@kth.se E 8.6 Sho ho a 4-to- multipleer can e used as a "function generator" for eample to generate the
Overview. Arithmetic circuits. Binary half adder. Binary full adder. Last lecture PLDs ROMs Tristates Design examples
 Overview rithmetic circuits Last lecture PLDs ROMs Tristates Design examples Today dders Ripple-carry Carry-lookahead Carry-select The conclusion of combinational logic!!! General-purpose building blocks
Overview rithmetic circuits Last lecture PLDs ROMs Tristates Design examples Today dders Ripple-carry Carry-lookahead Carry-select The conclusion of combinational logic!!! General-purpose building blocks
Computer Architecture 10. Fast Adders
 Computer Architecture 10 Fast s Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 1 Carry Problem Addition is primary mechanism in implementing arithmetic operations Slow addition directly affects the total performance
Computer Architecture 10 Fast s Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 1 Carry Problem Addition is primary mechanism in implementing arithmetic operations Slow addition directly affects the total performance
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, RIVERSIDE
 Final Page of UNIVERITY OF CLIFORNI, RIVERIDE Computer cience Department and Electrical Engineering Department C/EE20 Logic Design Final December, 2000 50 Name: olution Key tudent ID#: Please print legibly
Final Page of UNIVERITY OF CLIFORNI, RIVERIDE Computer cience Department and Electrical Engineering Department C/EE20 Logic Design Final December, 2000 50 Name: olution Key tudent ID#: Please print legibly
COE 328 Final Exam 2008
 COE 328 Final Exam 2008 1. Design a comparator that compares a 4 bit number A to a 4 bit number B and gives an Output F=1 if A is not equal B. You must use 2 input LUTs only. 2. Given the following logic
COE 328 Final Exam 2008 1. Design a comparator that compares a 4 bit number A to a 4 bit number B and gives an Output F=1 if A is not equal B. You must use 2 input LUTs only. 2. Given the following logic
CS 140 Lecture 14 Standard Combinational Modules
 CS 14 Lecture 14 Standard Combinational Modules Professor CK Cheng CSE Dept. UC San Diego Some slides from Harris and Harris 1 Part III. Standard Modules A. Interconnect B. Operators. Adders Multiplier
CS 14 Lecture 14 Standard Combinational Modules Professor CK Cheng CSE Dept. UC San Diego Some slides from Harris and Harris 1 Part III. Standard Modules A. Interconnect B. Operators. Adders Multiplier
ECE223. R eouven Elbaz Office room: DC3576
 ECE223 R eouven Elz reouven@uwterloo.c Office room: DC3576 Outline Decoders Decoders with Enle VHDL Exmple Multiplexers Multiplexers with Enle VHDL Exmple From Decoder to Multiplexer 3-stte Gtes Multiplexers
ECE223 R eouven Elz reouven@uwterloo.c Office room: DC3576 Outline Decoders Decoders with Enle VHDL Exmple Multiplexers Multiplexers with Enle VHDL Exmple From Decoder to Multiplexer 3-stte Gtes Multiplexers
CMSC 313 Lecture 17. Focus Groups. Announcement: in-class lab Thu 10/30 Homework 3 Questions Circuits for Addition Midterm Exam returned
 Focus Groups CMSC 33 Lecture 7 Need good sample of all types of CS students Mon /7 & Thu /2, 2:3p-2:p & 6:p-7:3p Announcement: in-class lab Thu /3 Homework 3 Questions Circuits for Addition Midterm Exam
Focus Groups CMSC 33 Lecture 7 Need good sample of all types of CS students Mon /7 & Thu /2, 2:3p-2:p & 6:p-7:3p Announcement: in-class lab Thu /3 Homework 3 Questions Circuits for Addition Midterm Exam
Chapter 4. Combinational: Circuits with logic gates whose outputs depend on the present combination of the inputs. elements. Dr.
 Chapter 4 Dr. Panos Nasiopoulos Combinational: Circuits with logic gates whose outputs depend on the present combination of the inputs. Sequential: In addition, they include storage elements Combinational
Chapter 4 Dr. Panos Nasiopoulos Combinational: Circuits with logic gates whose outputs depend on the present combination of the inputs. Sequential: In addition, they include storage elements Combinational
Floating Point Representation and Digital Logic. Lecture 11 CS301
 Floating Point Representation and Digital Logic Lecture 11 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (10/4) at 8am Lab #3 due Friday (9/7) 1:29pm HW #5 assigned w Due Monday 10/8
Floating Point Representation and Digital Logic Lecture 11 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (10/4) at 8am Lab #3 due Friday (9/7) 1:29pm HW #5 assigned w Due Monday 10/8
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 24 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 2 + Shifters
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 24 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 2 + Shifters April 15, 2010 John Wawrzynek 1 Multiplication a 3 a 2 a 1 a 0 Multiplicand b 3 b 2 b 1 b 0 Multiplier X a 3 b 0 a 2 b 0 a 1 b
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 24 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 2 + Shifters April 15, 2010 John Wawrzynek 1 Multiplication a 3 a 2 a 1 a 0 Multiplicand b 3 b 2 b 1 b 0 Multiplier X a 3 b 0 a 2 b 0 a 1 b
CSE 140 Spring 2017: Final Solutions (Total 50 Points)
 CSE 140 Spring 2017: Final Solutions (Total 50 Points) 1. (Boolean Algebra) Prove the following Boolean theorem using Boolean laws only, i.e. no theorem is allowed for the proof. State the name of the
CSE 140 Spring 2017: Final Solutions (Total 50 Points) 1. (Boolean Algebra) Prove the following Boolean theorem using Boolean laws only, i.e. no theorem is allowed for the proof. State the name of the
CprE 281: Digital Logic
 CprE 28: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Decoders and Encoders CprE 28: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames, IA Copyright Alexander Stoytchev
CprE 28: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Decoders and Encoders CprE 28: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames, IA Copyright Alexander Stoytchev
Written exam with solutions IE Digital Design Friday 21/
 Written exam with solutions IE204-5 Digital Design Friday 2/0 206 09.00-3.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist tel 08-7904487, Elena Dubrova phone 08-790 4 4 Exam
Written exam with solutions IE204-5 Digital Design Friday 2/0 206 09.00-3.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist tel 08-7904487, Elena Dubrova phone 08-790 4 4 Exam
Module 2. Basic Digital Building Blocks. Binary Arithmetic & Arithmetic Circuits Comparators, Decoders, Encoders, Multiplexors Flip-Flops
 Module 2 asic Digital uilding locks Lecturer: Dr. Yongsheng Gao Office: Tech 3.25 Email: Web: Structure: Textbook: yongsheng.gao@griffith.edu.au maxwell.me.gu.edu.au 6 lecturers 1 tutorial 1 laboratory
Module 2 asic Digital uilding locks Lecturer: Dr. Yongsheng Gao Office: Tech 3.25 Email: Web: Structure: Textbook: yongsheng.gao@griffith.edu.au maxwell.me.gu.edu.au 6 lecturers 1 tutorial 1 laboratory
CMSC 313 Lecture 18 Midterm Exam returned Assign Homework 3 Circuits for Addition Digital Logic Components Programmable Logic Arrays
 MS 33 Lecture 8 Midterm Exam returned Assign Homework 3 ircuits for Addition Digital Logic omponents Programmable Logic Arrays UMB, MS33, Richard hang MS 33, omputer Organization & Assembly
MS 33 Lecture 8 Midterm Exam returned Assign Homework 3 ircuits for Addition Digital Logic omponents Programmable Logic Arrays UMB, MS33, Richard hang MS 33, omputer Organization & Assembly
A COMBINED 16-BIT BINARY AND DUAL GALOIS FIELD MULTIPLIER. Jesus Garcia and Michael J. Schulte
 A COMBINED 16-BIT BINARY AND DUAL GALOIS FIELD MULTIPLIER Jesus Garcia and Michael J. Schulte Lehigh University Department of Computer Science and Engineering Bethlehem, PA 15 ABSTRACT Galois field arithmetic
A COMBINED 16-BIT BINARY AND DUAL GALOIS FIELD MULTIPLIER Jesus Garcia and Michael J. Schulte Lehigh University Department of Computer Science and Engineering Bethlehem, PA 15 ABSTRACT Galois field arithmetic
Preparation of Examination Questions and Exercises: Solutions
 Questions Preparation of Examination Questions and Exercises: Solutions. -bit Subtraction: DIF = B - BI B BI BO DIF 2 DIF: B BI 4 6 BI 5 BO: BI BI 4 5 7 3 2 6 7 3 B B B B B DIF = B BI ; B = ( B) BI ( B),
Questions Preparation of Examination Questions and Exercises: Solutions. -bit Subtraction: DIF = B - BI B BI BO DIF 2 DIF: B BI 4 6 BI 5 BO: BI BI 4 5 7 3 2 6 7 3 B B B B B DIF = B BI ; B = ( B) BI ( B),
Problem Set 4 Solutions
 SE 26 igital omputers: Organization and Logical esign Jon Turner Problem Set 4 Solutions 1. Find a minimal logic expression for the NN/NOR circuit shown below. The circuit implements the expression ((()
SE 26 igital omputers: Organization and Logical esign Jon Turner Problem Set 4 Solutions 1. Find a minimal logic expression for the NN/NOR circuit shown below. The circuit implements the expression ((()
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture
 Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 6 - Combinational Logic Introduction A combinational circuit consists of input variables, logic gates, and output variables. The logic gates accept
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 6 - Combinational Logic Introduction A combinational circuit consists of input variables, logic gates, and output variables. The logic gates accept
CSE 140 Midterm 3 version A Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2015
 CSE 140 Midterm 3 version A Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2015 Name of the person on your left : Name of the person on your right: 1. 20 points 2. 20 points 3. 20 points 4. 15 points 5. 15 points 6. 10
CSE 140 Midterm 3 version A Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2015 Name of the person on your left : Name of the person on your right: 1. 20 points 2. 20 points 3. 20 points 4. 15 points 5. 15 points 6. 10
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals. Chapter 5 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 5 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits Arithmetic functions Operate on binary vectors Use the same subfunction in each bit position Can design functional block
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 5 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits Arithmetic functions Operate on binary vectors Use the same subfunction in each bit position Can design functional block
Combinational Logic. Lan-Da Van ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C.
 Combinational Logic ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2017 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Combinational Circuits
Combinational Logic ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2017 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Combinational Circuits
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Final Examination
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Final Examination ECE 24S - Digital Systems Examiner: Belinda Wang, Jianwen Zhu 2: - 4:3pm, April 26th, 24 Duration: 5 minutes (2.5 hours)
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Final Examination ECE 24S - Digital Systems Examiner: Belinda Wang, Jianwen Zhu 2: - 4:3pm, April 26th, 24 Duration: 5 minutes (2.5 hours)
L8/9: Arithmetic Structures
 L8/9: Arithmetic Structures Acknowledgements: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following sources and are used with permission. Rex Min Kevin Atkinson Prof. Randy Katz (Unified Microelectronics
L8/9: Arithmetic Structures Acknowledgements: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following sources and are used with permission. Rex Min Kevin Atkinson Prof. Randy Katz (Unified Microelectronics
Digital System Design Combinational Logic. Assoc. Prof. Pradondet Nilagupta
 Digital System Design Combinational Logic Assoc. Prof. Pradondet Nilagupta pom@ku.ac.th Acknowledgement This lecture note is modified from Engin112: Digital Design by Prof. Maciej Ciesielski, Prof. Tilman
Digital System Design Combinational Logic Assoc. Prof. Pradondet Nilagupta pom@ku.ac.th Acknowledgement This lecture note is modified from Engin112: Digital Design by Prof. Maciej Ciesielski, Prof. Tilman
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 DEPARTMENT: EEE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE: EE55 SEMESTER IV UNIT : Design of Synchronous Sequential Circuits PART
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 DEPARTMENT: EEE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE: EE55 SEMESTER IV UNIT : Design of Synchronous Sequential Circuits PART
Luleå Tekniska Universitet Kurskod SMD098 Tentamensdatum
 Luleå Tekniska Universitet Kurskod SMD098 Tentamensdatum 991215 Skrivtid 4 timmar Tentamen i Beräkningsstrukturer Antal uppgifter: 6 Max poäng: 30 Betygsgränser: >20 poäng 4 >25 poäng 5 Betygsgränser kan
Luleå Tekniska Universitet Kurskod SMD098 Tentamensdatum 991215 Skrivtid 4 timmar Tentamen i Beräkningsstrukturer Antal uppgifter: 6 Max poäng: 30 Betygsgränser: >20 poäng 4 >25 poäng 5 Betygsgränser kan
Combinational Logic. Mantıksal Tasarım BBM231. section instructor: Ufuk Çelikcan
 Combinational Logic Mantıksal Tasarım BBM23 section instructor: Ufuk Çelikcan Classification. Combinational no memory outputs depends on only the present inputs expressed by Boolean functions 2. Sequential
Combinational Logic Mantıksal Tasarım BBM23 section instructor: Ufuk Çelikcan Classification. Combinational no memory outputs depends on only the present inputs expressed by Boolean functions 2. Sequential
Slide Set 6. for ENEL 353 Fall Steve Norman, PhD, PEng. Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary
 Slide Set 6 for ENEL 353 Fall 2017 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Fall Term, 2017 SN s ENEL 353 Fall 2017 Slide Set 6 slide
Slide Set 6 for ENEL 353 Fall 2017 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Fall Term, 2017 SN s ENEL 353 Fall 2017 Slide Set 6 slide
ECE 341. Lecture # 3
 ECE 341 Lecture # 3 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@ece.pdx.edu October 7, 2013 Portland State University Lecture Topics Counters Finite State Machines Decoders Multiplexers Reference: Appendix A of
ECE 341 Lecture # 3 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@ece.pdx.edu October 7, 2013 Portland State University Lecture Topics Counters Finite State Machines Decoders Multiplexers Reference: Appendix A of
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 21 - Design Blocks
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 21 - Design Blocks April 3, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec21-db3 Page 1 Fixed Shifters / Rotators fixed shifters hardwire the shift amount into the circuit.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 21 - Design Blocks April 3, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec21-db3 Page 1 Fixed Shifters / Rotators fixed shifters hardwire the shift amount into the circuit.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 25 Shifters and Counters. Recap
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 25 Shifters and Counters Nov. 21, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 25 Shifters and Counters Nov. 21, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John
Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic
 Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic E-mail: shimada@is.naist.jp Already optimized circuits There are many optimized circuits which are well used You can reduce your design workload
Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic E-mail: shimada@is.naist.jp Already optimized circuits There are many optimized circuits which are well used You can reduce your design workload
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Logic minimization algorithm summary. Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Logic minimization algorithm summary Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing & Dr.Pietro Mercati Definition
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Logic minimization algorithm summary Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing & Dr.Pietro Mercati Definition
Laboratory Exercise #10 An Introduction to High-Speed Addition
 Laboratory Exercise #10 An Introduction to High-Speed Addition ECEN 248: Introduction to Digital Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University 2 Laboratory Exercise #10
Laboratory Exercise #10 An Introduction to High-Speed Addition ECEN 248: Introduction to Digital Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University 2 Laboratory Exercise #10
Combinational Logic. By : Ali Mustafa
 Combinational Logic By : Ali Mustafa Contents Adder Subtractor Multiplier Comparator Decoder Encoder Multiplexer How to Analyze any combinational circuit like this? Analysis Procedure To obtain the output
Combinational Logic By : Ali Mustafa Contents Adder Subtractor Multiplier Comparator Decoder Encoder Multiplexer How to Analyze any combinational circuit like this? Analysis Procedure To obtain the output
Lecture 8: Sequential Multipliers
 Lecture 8: Sequential Multipliers ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic 3/25/08 ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic Lecture Roadmap Sequential Multipliers Unsigned Signed Radix-2 Booth Recoding High-Radix Multiplication
Lecture 8: Sequential Multipliers ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic 3/25/08 ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic Lecture Roadmap Sequential Multipliers Unsigned Signed Radix-2 Booth Recoding High-Radix Multiplication
University of Florida EEL 3701 Summer 2015 Dr. Eric. M. Schwartz Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Tuesday, 30 June 2015
 University of Florida EEL 3701 Summer 2015 Dr Eric M Schwartz Page 1/13 Exam 1 May the Schwartz be with you! Instructions: Turn off all cell phones and other noise making devices Show all work on the front
University of Florida EEL 3701 Summer 2015 Dr Eric M Schwartz Page 1/13 Exam 1 May the Schwartz be with you! Instructions: Turn off all cell phones and other noise making devices Show all work on the front
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Decoders, adders, comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements. Tajana Simunic Rosing
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Decoders, adders, comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Tajana Simunic Rosing Mux, Demux Encoder, Decoder 2 Transmission Gate: Mux/Tristate
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Decoders, adders, comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Tajana Simunic Rosing Mux, Demux Encoder, Decoder 2 Transmission Gate: Mux/Tristate
Table of Content. Chapter 11 Dedicated Microprocessors Page 1 of 25
 Chapter 11 Dedicated Microprocessors Page 1 of 25 Table of Content Table of Content... 1 11 Dedicated Microprocessors... 2 11.1 Manual Construction of a Dedicated Microprocessor... 3 11.2 FSM + D Model
Chapter 11 Dedicated Microprocessors Page 1 of 25 Table of Content Table of Content... 1 11 Dedicated Microprocessors... 2 11.1 Manual Construction of a Dedicated Microprocessor... 3 11.2 FSM + D Model
Slides for Lecture 19
 Slides for Lecture 19 ENEL 353: Digital Circuits Fall 2013 Term Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary 23 October, 2013 ENEL 353
Slides for Lecture 19 ENEL 353: Digital Circuits Fall 2013 Term Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary 23 October, 2013 ENEL 353
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
Written exam with solutions IE1204/5 Digital Design Monday 23/
 Written exam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 23/0 207 4.00-8.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist Exam text has to be returned when you hand in your
Written exam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 23/0 207 4.00-8.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist Exam text has to be returned when you hand in your
Digital Circuits. 1. Inputs & Outputs are quantized at two levels. 2. Binary arithmetic, only digits are 0 & 1. Position indicates power of 2.
 Digital Circuits 1. Inputs & Outputs are quantized at two levels. 2. inary arithmetic, only digits are 0 & 1. Position indicates power of 2. 11001 = 2 4 + 2 3 + 0 + 0 +2 0 16 + 8 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 25 Digital
Digital Circuits 1. Inputs & Outputs are quantized at two levels. 2. inary arithmetic, only digits are 0 & 1. Position indicates power of 2. 11001 = 2 4 + 2 3 + 0 + 0 +2 0 16 + 8 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 25 Digital
ECE 3401 Lecture 23. Pipeline Design. State Table for 2-Cycle Instructions. Control Unit. ISA: Instruction Specifications (for reference)
 ECE 3401 Lecture 23 Pipeline Design Control State Register Combinational Control Logic New/ Modified Control Word ISA: Instruction Specifications (for reference) P C P C + 1 I N F I R M [ P C ] E X 0 PC
ECE 3401 Lecture 23 Pipeline Design Control State Register Combinational Control Logic New/ Modified Control Word ISA: Instruction Specifications (for reference) P C P C + 1 I N F I R M [ P C ] E X 0 PC
Number representation
 Number representation A number can be represented in binary in many ways. The most common number types to be represented are: Integers, positive integers one-complement, two-complement, sign-magnitude
Number representation A number can be represented in binary in many ways. The most common number types to be represented are: Integers, positive integers one-complement, two-complement, sign-magnitude
ECE 545 Digital System Design with VHDL Lecture 1. Digital Logic Refresher Part A Combinational Logic Building Blocks
 ECE 545 Digital System Design with VHDL Lecture Digital Logic Refresher Part A Combinational Logic Building Blocks Lecture Roadmap Combinational Logic Basic Logic Review Basic Gates De Morgan s Law Combinational
ECE 545 Digital System Design with VHDL Lecture Digital Logic Refresher Part A Combinational Logic Building Blocks Lecture Roadmap Combinational Logic Basic Logic Review Basic Gates De Morgan s Law Combinational
Chapter 9. Counters and Shift Registers. Counters and Shift Registers
 Chapter 9 Counters and Shift Registers Counters and Shift Registers Counter: A Sequential Circuit that counts pulses. Used for Event Counting, Frequency Division, Timing, and Control Operations. Shift
Chapter 9 Counters and Shift Registers Counters and Shift Registers Counter: A Sequential Circuit that counts pulses. Used for Event Counting, Frequency Division, Timing, and Control Operations. Shift
Introduction to the Xilinx Spartan-3E
 Introduction to the Xilinx Spartan-3E Nash Kaminski Instructor: Dr. Jafar Saniie ECE597 Illinois Institute of Technology Acknowledgment: I acknowledge that all of the work (including figures and code)
Introduction to the Xilinx Spartan-3E Nash Kaminski Instructor: Dr. Jafar Saniie ECE597 Illinois Institute of Technology Acknowledgment: I acknowledge that all of the work (including figures and code)
Exam for Physics 4051, October 31, 2008
 Exam for Physics 45, October, 8 5 points - closed book - calculators allowed - show your work Problem : (6 Points) The 4 bit shift register circuit shown in Figure has been initialized to contain the following
Exam for Physics 45, October, 8 5 points - closed book - calculators allowed - show your work Problem : (6 Points) The 4 bit shift register circuit shown in Figure has been initialized to contain the following
Homework 4 due today Quiz #4 today In class (80min) final exam on April 29 Project reports due on May 4. Project presentations May 5, 1-4pm
 EE241 - Spring 2010 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 25: Digital Arithmetic Adders Announcements Homework 4 due today Quiz #4 today In class (80min) final exam on April 29 Project reports due
EE241 - Spring 2010 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 25: Digital Arithmetic Adders Announcements Homework 4 due today Quiz #4 today In class (80min) final exam on April 29 Project reports due
Logic. Combinational. inputs. outputs. the result. system can
 Digital Electronics Combinational Logic Functions Digital logic circuits can be classified as either combinational or sequential circuits. A combinational circuit is one where the output at any time depends
Digital Electronics Combinational Logic Functions Digital logic circuits can be classified as either combinational or sequential circuits. A combinational circuit is one where the output at any time depends
EECS 427 Lecture 8: Adders Readings: EECS 427 F09 Lecture 8 1. Reminders. HW3 project initial proposal: due Wednesday 10/7
 EECS 427 Lecture 8: dders Readings: 11.1-11.3.3 3 EECS 427 F09 Lecture 8 1 Reminders HW3 project initial proposal: due Wednesday 10/7 You can schedule a half-hour hour appointment with me to discuss your
EECS 427 Lecture 8: dders Readings: 11.1-11.3.3 3 EECS 427 F09 Lecture 8 1 Reminders HW3 project initial proposal: due Wednesday 10/7 You can schedule a half-hour hour appointment with me to discuss your
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 22 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 1
 EECS150 - igital esign Lecture 22 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 1 April 10, 2011 John Wawrzynek Spring 2011 EECS150 - Lec23-arith1 Page 1 Each cell: r i = a i XOR b i XOR c in Carry-ripple Adder Revisited
EECS150 - igital esign Lecture 22 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 1 April 10, 2011 John Wawrzynek Spring 2011 EECS150 - Lec23-arith1 Page 1 Each cell: r i = a i XOR b i XOR c in Carry-ripple Adder Revisited
CMPUT 329. Circuits for binary addition
 CMPUT 329 Parallel Adder with Carry Lookahead and ALU Ioanis Nikolaidis (Katz & Borriello) rcuits for binary addition Full adder (carry-in to cascade for multi-bit adders) Sum = xor A xor B Cout = B +
CMPUT 329 Parallel Adder with Carry Lookahead and ALU Ioanis Nikolaidis (Katz & Borriello) rcuits for binary addition Full adder (carry-in to cascade for multi-bit adders) Sum = xor A xor B Cout = B +
Lecture 10: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design
 Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
ENGG 1203 Tutorial_9 - Review. Boolean Algebra. Simplifying Logic Circuits. Combinational Logic. 1. Combinational & Sequential Logic
 ENGG 1203 Tutorial_9 - Review Boolean Algebra 1. Combinational & Sequential Logic 2. Computer Systems 3. Electronic Circuits 4. Signals, Systems, and Control Remark : Multiple Choice Questions : ** Check
ENGG 1203 Tutorial_9 - Review Boolean Algebra 1. Combinational & Sequential Logic 2. Computer Systems 3. Electronic Circuits 4. Signals, Systems, and Control Remark : Multiple Choice Questions : ** Check
Parity Checker Example. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9 - Finite State Machines 1. Formal Design Process. Formal Design Process
 Parity Checker Example A string of bits has even parity if the number of 1 s in the string is even. Design a circuit that accepts a bit-serial stream of bits and outputs a 0 if the parity thus far is even
Parity Checker Example A string of bits has even parity if the number of 1 s in the string is even. Design a circuit that accepts a bit-serial stream of bits and outputs a 0 if the parity thus far is even
ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals. Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals
 University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall 2001 Lecture 5 Registers & Counters Part 2 Charles Kime Counters Counters are sequential circuits
University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall 2001 Lecture 5 Registers & Counters Part 2 Charles Kime Counters Counters are sequential circuits
Review for Test 1 : Ch1 5
 Review for Test 1 : Ch1 5 October 5, 2006 Typeset by FoilTEX Positional Numbers 527.46 10 = (5 10 2 )+(2 10 1 )+(7 10 0 )+(4 10 1 )+(6 10 2 ) 527.46 8 = (5 8 2 ) + (2 8 1 ) + (7 8 0 ) + (4 8 1 ) + (6 8
Review for Test 1 : Ch1 5 October 5, 2006 Typeset by FoilTEX Positional Numbers 527.46 10 = (5 10 2 )+(2 10 1 )+(7 10 0 )+(4 10 1 )+(6 10 2 ) 527.46 8 = (5 8 2 ) + (2 8 1 ) + (7 8 0 ) + (4 8 1 ) + (6 8
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Analysis and Design of Digital Integrated Circuits (6.374) - Fall 2003 Quiz #2 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Analysis and Design of Digital Integrated Circuits (6.374) - Fall 2003 Quiz #2 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan
Lecture 4. Adders. Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University
 Lecture 4 Adders Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University horowitz@stanford.edu Copyright 2006 Mark Horowitz Some figures from High-Performance Microprocessor Design IEEE 1 Overview Readings Today
Lecture 4 Adders Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University horowitz@stanford.edu Copyright 2006 Mark Horowitz Some figures from High-Performance Microprocessor Design IEEE 1 Overview Readings Today
ECE 545 Digital System Design with VHDL Lecture 1A. Digital Logic Refresher Part A Combinational Logic Building Blocks
 ECE 545 Digital System Design with VHDL Lecture A Digital Logic Refresher Part A Combinational Logic Building Blocks Lecture Roadmap Combinational Logic Basic Logic Review Basic Gates De Morgan s Laws
ECE 545 Digital System Design with VHDL Lecture A Digital Logic Refresher Part A Combinational Logic Building Blocks Lecture Roadmap Combinational Logic Basic Logic Review Basic Gates De Morgan s Laws
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS151/251A V. Stojanovic, J. Wawrzynek Fall 2015 10/13/15 Midterm Exam Name: ID
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS151/251A V. Stojanovic, J. Wawrzynek Fall 2015 10/13/15 Midterm Exam Name: ID
Solutions for Appendix C Exercises
 C Solutions for Appix C Exercises 1 Solutions for Appix C Exercises C.1 A B A B A + B A B A B A + B 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 C.2 Here is the first equation: E = ((
C Solutions for Appix C Exercises 1 Solutions for Appix C Exercises C.1 A B A B A + B A B A B A + B 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 C.2 Here is the first equation: E = ((
3. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Use binary numbers with a sign bit and 7 bits for the value
 EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
3. Combinational Circuit Design
 CSEE 3827: Fundamentals of Computer Systems, Spring 2 3. Combinational Circuit Design Prof. Martha Kim (martha@cs.columbia.edu) Web: http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~martha/courses/3827/sp/ Outline (H&H 2.8,
CSEE 3827: Fundamentals of Computer Systems, Spring 2 3. Combinational Circuit Design Prof. Martha Kim (martha@cs.columbia.edu) Web: http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~martha/courses/3827/sp/ Outline (H&H 2.8,
Sample Test Paper - I
 Scheme G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Marks : 25 Hours: 1 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any THREE: 09 Marks a) Define i) Propagation delay ii) Fan-in iii) Fan-out b) Convert the following:
Scheme G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Marks : 25 Hours: 1 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any THREE: 09 Marks a) Define i) Propagation delay ii) Fan-in iii) Fan-out b) Convert the following:
Pin Details of Digital Logic Gates:
 (1) (2) Pin Details of Digital Logic Gates: (3) Postulates and Theorems of Boolean algebra: S. No Postulate/Theorem Duality Remarks 1. X + 0 = X X.1 = X - 2. X + X = 1 X.X = 0-3. X + X = X X.X = X - 4.
(1) (2) Pin Details of Digital Logic Gates: (3) Postulates and Theorems of Boolean algebra: S. No Postulate/Theorem Duality Remarks 1. X + 0 = X X.1 = X - 2. X + X = 1 X.X = 0-3. X + X = X X.X = X - 4.
DIGITAL TECHNICS. Dr. Bálint Pődör. Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute
 DIGITAL TECHNICS Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DESIGN: ARITHMETICS (THROUGH EXAMPLES) 2016/2017 COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DESIGN:
DIGITAL TECHNICS Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DESIGN: ARITHMETICS (THROUGH EXAMPLES) 2016/2017 COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DESIGN:
Introduction EE 224: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER DESIGN. Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 5/9/2010
 EE 224: INTROUCTION TO IGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER ESIGN Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 05/10/2010 Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohio.edu Introduction 2 A Flip-Flop stores one bit of information
EE 224: INTROUCTION TO IGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER ESIGN Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 05/10/2010 Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohio.edu Introduction 2 A Flip-Flop stores one bit of information
Combinational Logic. Lan-Da Van ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C.
 Combinational Logic ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2010 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Combinational Circuits
Combinational Logic ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2010 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Combinational Circuits
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FSMs & Counters
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FSMs & Counters April 8, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec22-counters Page 1 One-hot encoding of states. One FF per state. State Encoding Why one-hot encoding?
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FSMs & Counters April 8, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec22-counters Page 1 One-hot encoding of states. One FF per state. State Encoding Why one-hot encoding?
CprE 281: Digital Logic
 CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Fast Adders CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames, IA Copyright Alexander Stoytchev HW5
CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Fast Adders CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames, IA Copyright Alexander Stoytchev HW5
COSC 243. Introduction to Logic And Combinatorial Logic. Lecture 4 - Introduction to Logic and Combinatorial Logic. COSC 243 (Computer Architecture)
 COSC 243 Introduction to Logic And Combinatorial Logic 1 Overview This Lecture Introduction to Digital Logic Gates Boolean algebra Combinatorial Logic Source: Chapter 11 (10 th edition) Source: J.R. Gregg,
COSC 243 Introduction to Logic And Combinatorial Logic 1 Overview This Lecture Introduction to Digital Logic Gates Boolean algebra Combinatorial Logic Source: Chapter 11 (10 th edition) Source: J.R. Gregg,
ARITHMETIC COMBINATIONAL MODULES AND NETWORKS
 ARITHMETIC COMBINATIONAL MODULES AND NETWORKS 1 SPECIFICATION OF ADDER MODULES FOR POSITIVE INTEGERS HALF-ADDER AND FULL-ADDER MODULES CARRY-RIPPLE AND CARRY-LOOKAHEAD ADDER MODULES NETWORKS OF ADDER MODULES
ARITHMETIC COMBINATIONAL MODULES AND NETWORKS 1 SPECIFICATION OF ADDER MODULES FOR POSITIVE INTEGERS HALF-ADDER AND FULL-ADDER MODULES CARRY-RIPPLE AND CARRY-LOOKAHEAD ADDER MODULES NETWORKS OF ADDER MODULES
GALOP : A Generalized VLSI Architecture for Ultrafast Carry Originate-Propagate adders
 GALOP : A Generalized VLSI Architecture for Ultrafast Carry Originate-Propagate adders Dhananjay S. Phatak Electrical Engineering Department State University of New York, Binghamton, NY 13902-6000 Israel
GALOP : A Generalized VLSI Architecture for Ultrafast Carry Originate-Propagate adders Dhananjay S. Phatak Electrical Engineering Department State University of New York, Binghamton, NY 13902-6000 Israel
Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: Ph:
 Serial : S_CS_C_Digital Logic_588 Delhi Noida hopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune hubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: -56 CLASS TEST 8-9 COMPUTER SCIENCE & IT Subject : Digital
Serial : S_CS_C_Digital Logic_588 Delhi Noida hopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune hubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: -56 CLASS TEST 8-9 COMPUTER SCIENCE & IT Subject : Digital
Midterm Exam Two is scheduled on April 8 in class. On March 27 I will help you prepare Midterm Exam Two.
 Announcements Midterm Exam Two is scheduled on April 8 in class. On March 27 I will help you prepare Midterm Exam Two. Chapter 5 1 Chapter 3: Part 3 Arithmetic Functions Iterative combinational circuits
Announcements Midterm Exam Two is scheduled on April 8 in class. On March 27 I will help you prepare Midterm Exam Two. Chapter 5 1 Chapter 3: Part 3 Arithmetic Functions Iterative combinational circuits
