- Specialists in Science and Maths Education
|
|
|
- Shanon Arnold
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RADLEY COLLEGE Entrance Scholarships SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY I Monday 21 st February 2005 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer all questions. Write the answers to each section on a separate sheet of paper.
2 Biology Read the following passage: The oak's acorns, so rich in nutriment, provide meals for another whole range of diners. There is a lot for them to feed on, for a mature oak may produce 90,000 acorns a year - several million in its lifetime. Since only one acorn from each tree need grow to maturity each century to maintain the oak population, there is a vast surplus. Animals of all kinds make sure that it is not wasted. Rooks and jays rip the acorns from the branches as they mature. Wood pigeons are particularly gluttonous. One of them can hold seventy in its crop at any one time and consume a hundred and twenty in a day. Weevils bore holes into them with their long snouts and lay their eggs there. And when those acorns that survive this toll fall to the ground, they are greedily collected by mice, squirrels, deer and, in mainland Europe, by wild pig. The consumers of the oak's tissues, in their turn, serve as food for another set of animals. Wasps, spiders and ladybird larvae hunt for the caterpillars. Native birds are now beginning to nest and the females need to feed intensively in order to produce their eggs. Spotted woodpeckers and tree creepers clamber over the oak's bark, picking out insects hidden in the crevices. Great tits time the production of their families to coincide with that when the caterpillars are most abundant on the oak leaves and a parent bird, with nestlings to feed, may collect at least three hundred caterpillars a day. Many migrants including warblers and nightingales fly to share in the feast. And these small birds themselves become the food of bigger birds - magpies and jays - which take not only eggs and nestlings but the adults of smaller species. As the oak ages and holes develop in its trunk, owls and bats may take up residence inside it; and down among its gnarled interlacing roots, badgers and foxes burrow out their homes. Oaks are indeed the lords of the forest, and in the proper traditions of reigning monarchs, they provide a livelihood for a multitude of the smaller inhabitants of their kingdom. (Adapted from: ThePrivate Life of Plants. David Attenborough)
3 Using information in the passage and your own knowledge, answer the following questions. 1. What is meant in the passage by the words indicated in bold as follows: (i) gluttonous (ii) crop (iii) toll (iv) larvae (v) migrants (vi) gnarled [6] Give an example from the passage of each of the following: (i) a producer (ii) a secondary consumer (iii) a tertiary consumer (iv) a parasite [2] 2. Why does the oak tree need to produce so many acorns? [2] 3. Are weevils herbivores, carnivores or omnivores? [1] 4. To which Kingdom do oaks belong? [1] 5. To which Phylum do tree creepers belong? [1] 6. Give two distinguishing features of arachnids. [2] 7. To which Phylum do bats belong? [1] 8 Give three distinguishing features of mammals. [3] 9. How does the behaviour of the great tit benefit its young? [3] 10. Draw a food web using some of the organisms named in the passage. [3]
4 Chemistry 1. Some marble chips are reacted with hydrochloric acid in a divided flask connected to a gas syringe (Figure 1). To start the reaction, the flask is tipped up so the acid enters the side of the flask containing the marble chips. This is when the stopwatch is started and the volume of gas is recorded every 60 seconds for 10 minutes. Time (mins) Volume (cm 3 ) a) What is the formula of hydrochloric acid? [1] b) What is the chemical name of marble (CaCO 3 )? [1] c) Write a word equation for the reaction [2] d) Write a balanced symbol (formula) equation for the reaction [2] e) Describe what you would observe during the reaction [1] f) How would you test for the gas given off in the reaction? [1] g) On a piece of graph paper plot the results as a line graph [5] Hint: gas volume (y axis) & time (x axis)
5 h) When was the reaction fastest? [1] i) What was the rate (in cm 3 /min) of the reaction in part (h)? [2] j) When did the reaction stop? [1] k) How much gas was produced? [1] l) Why was the flask divided? [1] m) Why was the gas syringe connected before the reaction started? [1] n) Give two uses for the gas made in this reaction [2] o) Where in the human body would you find the acid used in this reaction? [1] p) Name the two elements which can be used to make the acid [2]
6 Physics Data (Approximate Values): Radius of Earth 6, 400 km Height of Sky Satellite 40,000 km Height of Moon 360,000 km Distance to Sun 150 million km Fast Walking Speed 3 m/s Fast Driving Speed 30 m/s Speed of Sound 300 m/s Speed of Light 300 million m/s Density of Air 1 kg/m 3 Density of Water 1000 kg /m 3 Density of Rock 5000 kg/m 3 1. Calculate how long it would take a beam of light to go from the Sun to the Earth. [1] 2. Calculate how long it would take a radio signal to go from the Earth to the Sky Satellite. [2] 3. Using your previous answer and no calculator, write down roughly how long it will take a radio signal to get to the Moon, stating your reasoning. [2] 4. If a string were stretched to the Sky Satellite from the Earth, then this length of string wrapped around the Earth, roughly how many times round would it go? [3] 5. What do you think the radius of the Moon might be? Explain your answer. [3]
7 6. How fast can you cycle? Explain your answer. [2] 7a. Estimate the volume of water in a reasonably deep bath. Show your working. [2] 7b. So, what would the mass of water in that bath be? [2] 8. Estimate the density of wood? Explain your answer. [2] 9. Estimate the density of Lead? Explain your answer. [2] 10. Rugby regulation 12 on shoulder pads states that no part of the pads may have a density of more than 45 kg/m 3. Write a detailed method to describe how you would test some shoulder pads to see if they are legal. [4]
8 Design & Technology 1. Using words from the list below, pick out the most appropriate word for each sentence. Tensile strength, compressive strength, density, brittleness, and conductivity a) Mercury is heavy because of its high b) Steel cable is used to pull heavy boats because of its excellent c) Copper is used in household electricity cables because of its excellent d) Concrete is used in columns that support bridges because of its excellent e) Great care has to be taken when transporting fine china because of its [5] 2. Structures play a very important part in our every day life and the life of the world around us. a) Give three everyday examples of natural structures. [1] b) Give three everyday examples of man-made structures. [1]
9 3. Name the four mechanical components shown in the drawings below. [4] Component A Component B Component C Component D 4. There are four basic types of motion, one example being rotary motion. a) What are the other three types of motion? [3] b) An example of rotary motion would be a spinning bicycle wheel. Give examples of the other three forms of motion. [3] c) Explain the major problem which prevents us from achieving perpetual motion in a machine. [2] 5. The diagram below shows a design for a steady hand game. The object of the game is to manoeuvre a ring along a bent wire without bringing the two in contact. If the ring touches the wire it creates a circuit which activates a buzzer. Suggest suitable materials for three of the labelled components. [6] B A C D E
What is wrong with deer on Haida Gwaii?
 What is wrong with deer on Haida Gwaii? A school curriculum by the Research Group on Introduced Species 2007 Forests of Haida Gwaii Haida Gwaii is an archipelago. It consists of a great number of islands,
What is wrong with deer on Haida Gwaii? A school curriculum by the Research Group on Introduced Species 2007 Forests of Haida Gwaii Haida Gwaii is an archipelago. It consists of a great number of islands,
Grade
 www.abubakrshalaby.com 5 Grade Ecology is the scientific study of the relation of living organisms to each other and their surroundings. Ecology includes the study of plant and animal populations, plant
www.abubakrshalaby.com 5 Grade Ecology is the scientific study of the relation of living organisms to each other and their surroundings. Ecology includes the study of plant and animal populations, plant
3 Types of Interactions
 CHAPTER 18 3 Types of Interactions SECTION Interactions of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What determines an area s carrying capacity?
CHAPTER 18 3 Types of Interactions SECTION Interactions of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What determines an area s carrying capacity?
5 th Grade Ecosystems Mini Assessment Name # Date. Name # Date
 An ecosystem is a community of organisms and their interaction with their environment. (abiotic, biotic, niche, habitat, population, community)- 1. Which effect does a decrease in sunlight have on a pond
An ecosystem is a community of organisms and their interaction with their environment. (abiotic, biotic, niche, habitat, population, community)- 1. Which effect does a decrease in sunlight have on a pond
Honors Biology Ecology Concept List
 1. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. a. mutualism and commensalism b. parasitism and predation c. species richness and species diversity d. primary succession and secondary
1. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. a. mutualism and commensalism b. parasitism and predation c. species richness and species diversity d. primary succession and secondary
Essential Characteristics of Scientists
 SELBY ABBEY CE (VC) PRIMARY SCHOOL SCIENCE CURRICULUM 2018-2019 Essential Characteristics of Scientists The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge
SELBY ABBEY CE (VC) PRIMARY SCHOOL SCIENCE CURRICULUM 2018-2019 Essential Characteristics of Scientists The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge
RADLEY COLLEGE Entrance Scholarships SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY. March Write the answers to each section on a separate sheet of paper.
 RADLEY COLLEGE Entrance Scholarships SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY March 2008 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer all questions. Write the answers to each section on a separate sheet of paper. Biology [25 marks] For
RADLEY COLLEGE Entrance Scholarships SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY March 2008 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer all questions. Write the answers to each section on a separate sheet of paper. Biology [25 marks] For
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision sheets
 Academic Year 2015-2016 Second Term Science Revision sheets Name: Date: Grade:3/ Q1 : Choose the letter of the choice that best answer the questions 1. Which of these is what a plant does that makes more
Academic Year 2015-2016 Second Term Science Revision sheets Name: Date: Grade:3/ Q1 : Choose the letter of the choice that best answer the questions 1. Which of these is what a plant does that makes more
National Curriculum 2014: Progression in Science
 Evaluating Concluding Working Scientifically Measuring and Recording Asking Questions Year 1/2 Year 3/4 Year 5/6 ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways ask relevant
Evaluating Concluding Working Scientifically Measuring and Recording Asking Questions Year 1/2 Year 3/4 Year 5/6 ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways ask relevant
Year 1 Science overview
 Year 1 Science overview asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways observing closely, using simple equipment performing simple tests identifying and classifying
Year 1 Science overview asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways observing closely, using simple equipment performing simple tests identifying and classifying
Nursery Reception Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 N/A N/A N/A
 Non Negotiables Science Plants Biology Nursery Reception Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Know some names of plants Begin to say how they are different from each other Start to describe the features
Non Negotiables Science Plants Biology Nursery Reception Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Know some names of plants Begin to say how they are different from each other Start to describe the features
Fairlawn Primary School Science Curriculum
 Materials Plants Animals and Humans At Fairlawn, we follow the curriculum set out in the Science Bug resource Year 1 SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE Identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians,
Materials Plants Animals and Humans At Fairlawn, we follow the curriculum set out in the Science Bug resource Year 1 SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE Identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians,
Mapping progression across KS1 to KS2. Science. Adapted from Mapping Progression in the Primary Science Curriculum written by Sue Atkinson CYC
 Mapping progression across KS1 to KS2 Science Adapted from Mapping Progression in the Primary Science Curriculum written by Sue Atkinson CYC Sc1 Working Scientifically Asking simple questions and recognising
Mapping progression across KS1 to KS2 Science Adapted from Mapping Progression in the Primary Science Curriculum written by Sue Atkinson CYC Sc1 Working Scientifically Asking simple questions and recognising
PAKISTAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, RIYADH 1ST Semester Revision Worksheet Subject: Science Grade: III Short Answers Answer these Questions:
 PAKISTAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, RIYADH 1ST Semester 2017-2018 Revision Worksheet Subject: Science Grade: III Short Answers Answer these Questions: Q-1 What two important functions do the ears perform? Q-2
PAKISTAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, RIYADH 1ST Semester 2017-2018 Revision Worksheet Subject: Science Grade: III Short Answers Answer these Questions: Q-1 What two important functions do the ears perform? Q-2
a. They get energy directly from sunlight c. They make their own food
 1) In which food chain is the most energy lost from the ecosystem? a. algae snail crane osprey b. algage zooplankton sunfish c. algae zooplankton sunfish tuna humans d. algae zooplankton sunfish heron
1) In which food chain is the most energy lost from the ecosystem? a. algae snail crane osprey b. algage zooplankton sunfish c. algae zooplankton sunfish tuna humans d. algae zooplankton sunfish heron
Primary Science Curriculum Pupil Assessment Record
 Year 1 Plants Can identify and name a variety of common plants, including garden plants, wild plants and trees, and those classified as deciduous and evergreen. Can describe the basic structure of a variety
Year 1 Plants Can identify and name a variety of common plants, including garden plants, wild plants and trees, and those classified as deciduous and evergreen. Can describe the basic structure of a variety
HfL Science Topic Maps for Years 1-6. Herts for Learning Ltd.
 HfL Science Topic Maps for Years 1-6 Year 1 Science Map Working scientifically Everyday materials Different animals asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways distinguish
HfL Science Topic Maps for Years 1-6 Year 1 Science Map Working scientifically Everyday materials Different animals asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways distinguish
Science Curriculum Overview
 YEAR 1 Seasonal changes Seasonal changes Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies observe changes across
YEAR 1 Seasonal changes Seasonal changes Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies observe changes across
Science subject progression and skills
 Science subject progression and skills Year 1 : Identify and name a variety of common animals that are birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles and mammals Identify and name a variety of common animals that are
Science subject progression and skills Year 1 : Identify and name a variety of common animals that are birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles and mammals Identify and name a variety of common animals that are
Science Curriculum Map Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2
 The objectvies in this curriculum map have been outlined by the National Curriculum and include additonal skill and knowledge based learning objectives grouped by units of work, taken from Hamilton Trust,
The objectvies in this curriculum map have been outlined by the National Curriculum and include additonal skill and knowledge based learning objectives grouped by units of work, taken from Hamilton Trust,
Exploring Matthaei s Ecosystems
 Name: Exploring Matthaei s Ecosystems As you walk on the trails, look for evidence of each of the following components of an ecosystem. Draw and describe what you observed and where you found it. Component
Name: Exploring Matthaei s Ecosystems As you walk on the trails, look for evidence of each of the following components of an ecosystem. Draw and describe what you observed and where you found it. Component
Science Curriculum Overview
 YEAR 1 Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe
YEAR 1 Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe
Band 1 - Science All. Working Scientifically Animals Including Humans Materials. Plants. Seasonal Changes
 Band 1 - Science All Working Scientifically Materials Ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways (Year 1 focus). I can ask questions and know they can be answered in
Band 1 - Science All Working Scientifically Materials Ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways (Year 1 focus). I can ask questions and know they can be answered in
Gathering and recording data to help in answering questions.
 Topic/Step Environmental Review Action Plan Monitoring and Evaluation Biodiversity Healthy Living Marine School Grounds Waste Science Year one Curriculum Link and Ideas Asking simple questions and recognising
Topic/Step Environmental Review Action Plan Monitoring and Evaluation Biodiversity Healthy Living Marine School Grounds Waste Science Year one Curriculum Link and Ideas Asking simple questions and recognising
Science Curriculum Map: KS1 & KS
 Subject In KS1 pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills through the teaching of the programme content of study content: Key stage Asking simple questions
Subject In KS1 pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills through the teaching of the programme content of study content: Key stage Asking simple questions
Mowbray School Long Term Science Plan KS1. Two Year rolling programme KS1
 Mowbray School Long Term Science Plan KS1 Two Year rolling programme KS1 Pupils should be taught to; Ø develop scientific knowledge and conceptual understanding through the specific disciplines of biology,
Mowbray School Long Term Science Plan KS1 Two Year rolling programme KS1 Pupils should be taught to; Ø develop scientific knowledge and conceptual understanding through the specific disciplines of biology,
National Curriculum 2014 Science Coverage
 National Curriculum 2014 Science Coverage Aims: The national curriculum for science aims to ensure that all pupils: FCCE Primary School - National Curriculum 2014 develop scientific knowledge and conceptual
National Curriculum 2014 Science Coverage Aims: The national curriculum for science aims to ensure that all pupils: FCCE Primary School - National Curriculum 2014 develop scientific knowledge and conceptual
Year/Cycle Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Y1 Animals, inc humans
 Science - Whole School Coverage of the National Curriculum 2018-19 Year/Cycle Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Y1 Animals, inc Everyday Plants identify and name a animals including
Science - Whole School Coverage of the National Curriculum 2018-19 Year/Cycle Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Y1 Animals, inc Everyday Plants identify and name a animals including
DOSTHILL PRIMARY SCHOOL I am working towards Building Block A1 in Science
 I am working towards Building Block A1 in Science 1 I can observe things closely using some simple equipment 2 I can carry out investigations 3 With some help, I can test out some ideas suggested to me
I am working towards Building Block A1 in Science 1 I can observe things closely using some simple equipment 2 I can carry out investigations 3 With some help, I can test out some ideas suggested to me
biotic factors camouflage carnivore chloroplast
 non-living parts of an organism's environment Eg air currents, temperature, moisture, light, and soil type special features about an organism that help it survive and reproduce living things that is different
non-living parts of an organism's environment Eg air currents, temperature, moisture, light, and soil type special features about an organism that help it survive and reproduce living things that is different
Stamford Green Primary School Science Progression Document. September 2014
 Stamford Green Primary School Science Progression Document September 2014 Early Years Early Learning Goals Area of EYFS curriculum Early Learning Goals The World Children know about the similarities and
Stamford Green Primary School Science Progression Document September 2014 Early Years Early Learning Goals Area of EYFS curriculum Early Learning Goals The World Children know about the similarities and
Question: What is the most common plant found on a heathland? Question: What is ancient woodland?
 Question: What is ancient woodland? Answer: Woodland that is at least 400 years old orwere present before 1600AD Question: What is the most common plant found on a heathland? Answer: Heather Question:
Question: What is ancient woodland? Answer: Woodland that is at least 400 years old orwere present before 1600AD Question: What is the most common plant found on a heathland? Answer: Heather Question:
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit # 6 Assessment
 Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit # 6 Assessment 1. Which of the following types of organisms mostly likely occupies the location marked X in the food web below? A. Primary consumer
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit # 6 Assessment 1. Which of the following types of organisms mostly likely occupies the location marked X in the food web below? A. Primary consumer
ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST
 4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK SPRING 2006 GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST WRITTEN TEST Student Name School Name Print your name and the name of your school on the lines above. The test
4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK SPRING 2006 GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST WRITTEN TEST Student Name School Name Print your name and the name of your school on the lines above. The test
Willow Pond Introduction
 Name: Willow Pond Introduction Pond Ecosystems An ecosystem is made up of both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components. Biotic elements include plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. Some
Name: Willow Pond Introduction Pond Ecosystems An ecosystem is made up of both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components. Biotic elements include plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. Some
Food Web and Ecological Relationships Quiz
 Biology II Ms. Chen Name: Food Web and Ecological Relationships Quiz Date: Multiple Choice (2 pts each) Directions: Circle the best answer. 1. The loss of the producers in an ecosystem would most likely
Biology II Ms. Chen Name: Food Web and Ecological Relationships Quiz Date: Multiple Choice (2 pts each) Directions: Circle the best answer. 1. The loss of the producers in an ecosystem would most likely
PARATAXONOMIST GUTPELA SAVE TEST PART 1 YOUR NAME:.. 1. Write names of all body parts you know for the following insect drawings: A
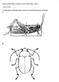 1 PARATAXONOMIST GUTPELA SAVE TEST 2006 - PART 1 YOUR NAME:.. 1. Write names of all body parts you know for the following insect drawings: A B 2 C D 2. These are chewing mouthparts. Name their parts (=
1 PARATAXONOMIST GUTPELA SAVE TEST 2006 - PART 1 YOUR NAME:.. 1. Write names of all body parts you know for the following insect drawings: A B 2 C D 2. These are chewing mouthparts. Name their parts (=
Parkstone Primary School Science Long Term Plan Updated January 2017
 Year 1 of cycle Key Stage 1 Autumn Term Spring Term Summer Term Investigation Seasonal Changes (1) Observing over time observe changes across the four seasons observe and describe weather associated with
Year 1 of cycle Key Stage 1 Autumn Term Spring Term Summer Term Investigation Seasonal Changes (1) Observing over time observe changes across the four seasons observe and describe weather associated with
1. What makes plants different than animals?
 1. What makes plants different than animals? tiger lily tiger 1. Plants are producers, which means they make their own food (through photosynthesis). 2. While plants can move certain structures, they cannot
1. What makes plants different than animals? tiger lily tiger 1. Plants are producers, which means they make their own food (through photosynthesis). 2. While plants can move certain structures, they cannot
Science Programme of study Key Stage 1
 Pupils will be taught to Working scientifically Science Programme of study Key Stage 1 During years 1 and 2, pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills
Pupils will be taught to Working scientifically Science Programme of study Key Stage 1 During years 1 and 2, pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills
Grade Level Suggestion: Grades 4 th to 8 th. Time Frame: minutes.
 I Have, Who Has? An Interactive Vocabulary Game Prairie Ecosystem Study Vocabulary Grades 4 th -8th Introduction: Below is a collection of cards that connect to the Prairie Study Vocabulary for 4 th -
I Have, Who Has? An Interactive Vocabulary Game Prairie Ecosystem Study Vocabulary Grades 4 th -8th Introduction: Below is a collection of cards that connect to the Prairie Study Vocabulary for 4 th -
Celebrate Spring! Vernal Equinox
 Celebrate Spring! Vernal Equinox In temperate climates that is, climates which have varying temperatures and seasons spring brings lots of changes to our world. The official first day of spring is called
Celebrate Spring! Vernal Equinox In temperate climates that is, climates which have varying temperatures and seasons spring brings lots of changes to our world. The official first day of spring is called
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 9477-1 - Page 1 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) The ecological niche of an organism refers to the A) relation of the organism to humans B) biosphere in which the organism lives C) position of the organism in a food
Name: 9477-1 - Page 1 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) The ecological niche of an organism refers to the A) relation of the organism to humans B) biosphere in which the organism lives C) position of the organism in a food
Chapter 6 Reading Questions
 Chapter 6 Reading Questions 1. Fill in 5 key events in the re-establishment of the New England forest in the Opening Story: 1. Farmers begin leaving 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Broadleaf forest reestablished 2.
Chapter 6 Reading Questions 1. Fill in 5 key events in the re-establishment of the New England forest in the Opening Story: 1. Farmers begin leaving 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Broadleaf forest reestablished 2.
UNIT 5. ECOSYSTEMS. Biocenosis Biotope Biotic factors Abiotic factors
 UNIT 5. ECOSYSTEMS 1. Define: ecosystem, biocenosis, biotope, abiotic factor, biotic factor 2. Complete using this word: ecosphere, biosphere, ecology, ecosystem a) The is all of the living thing on Earth.
UNIT 5. ECOSYSTEMS 1. Define: ecosystem, biocenosis, biotope, abiotic factor, biotic factor 2. Complete using this word: ecosphere, biosphere, ecology, ecosystem a) The is all of the living thing on Earth.
Aut1 Aut 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Kings and Queens Rocks
 Curriculum Overview Science Years 3/4 Cycle A 2016/17 Aut1 Aut 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Rocks living Identify and describe the together different things can be grouped functions of different
Curriculum Overview Science Years 3/4 Cycle A 2016/17 Aut1 Aut 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Rocks living Identify and describe the together different things can be grouped functions of different
HA Biology: Practice Quiz 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 HA Biology: Practice Quiz 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about the properties of life is false?
HA Biology: Practice Quiz 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about the properties of life is false?
Relationships in Ecosystems. Chapter 1 Lesson 2 page 38 WB pages 6-7
 Relationships in Ecosystems Chapter 1 Lesson 2 page 38 WB pages 6-7 Chapter 1 Lesson 2 Vocabulary 1. population- all the members of one species in an area 2. community- all the living things in an ecosystem
Relationships in Ecosystems Chapter 1 Lesson 2 page 38 WB pages 6-7 Chapter 1 Lesson 2 Vocabulary 1. population- all the members of one species in an area 2. community- all the living things in an ecosystem
Characteristics of Life
 Name Date Claas Score Characteristics of Life READ AND HILITE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living thing from a nonliving
Name Date Claas Score Characteristics of Life READ AND HILITE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living thing from a nonliving
Lesson 4: Insect Life Cycles
 Life Cycles -> 4: Insect Life Cycles Lesson 4: Insect Life Cycles Getting Started? Big Ideas P P P How are the life cycles of plants and animals similar and different? Where can cycles be found in nature?
Life Cycles -> 4: Insect Life Cycles Lesson 4: Insect Life Cycles Getting Started? Big Ideas P P P How are the life cycles of plants and animals similar and different? Where can cycles be found in nature?
A population is a group of individuals of the same species, living in a shared space at a specific point in time.
 A population is a group of individuals of the same species, living in a shared space at a specific point in time. A population size refers to the number of individuals in a population. Increase Decrease
A population is a group of individuals of the same species, living in a shared space at a specific point in time. A population size refers to the number of individuals in a population. Increase Decrease
2 nd Grade Science Cards. 1. Which of these is NOT a basic need for an animal? 2. Why do animals need air to live?
 nd Grade Science Cards 1. Which of these is NOT a basic need for an animal? A. sunlight B. water C. air D. food. Why do animals need air to live? A. to eat B. to breathe C. to run D. to sleep 3. Which
nd Grade Science Cards 1. Which of these is NOT a basic need for an animal? A. sunlight B. water C. air D. food. Why do animals need air to live? A. to eat B. to breathe C. to run D. to sleep 3. Which
Characteristics of Life
 Name Date Characteristics of Life Most people feel confident that they could identify a living thing from a nonliving thing, but sometimes it s not so easy. Scientists have argued for centuries over the
Name Date Characteristics of Life Most people feel confident that they could identify a living thing from a nonliving thing, but sometimes it s not so easy. Scientists have argued for centuries over the
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission 2015. S26 JUNIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2015 SCIENCE HIGHER LEVEL THURSDAY, 11 JUNE MORNING, 9.30 to 11.30 INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your examination
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission 2015. S26 JUNIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2015 SCIENCE HIGHER LEVEL THURSDAY, 11 JUNE MORNING, 9.30 to 11.30 INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your examination
7 FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I &
 7 FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I & Name :... Rank Time : 30 min. Class :... Section :... Roll No. :... Marks Subject : SCIENCE 1st Class Marks : 20 I. Answer any four of the following questions. 4 2 = 8 1. What
7 FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I & Name :... Rank Time : 30 min. Class :... Section :... Roll No. :... Marks Subject : SCIENCE 1st Class Marks : 20 I. Answer any four of the following questions. 4 2 = 8 1. What
INTERACTIONS IN AN ENVIRONMENT
 reflect Earth is full of living things. Our planet has many kinds of organisms including bacteria, fungi (like mushrooms), plants, and animals. In some ways, living things are alike. Almost all living
reflect Earth is full of living things. Our planet has many kinds of organisms including bacteria, fungi (like mushrooms), plants, and animals. In some ways, living things are alike. Almost all living
Unpack the Standard: Students will categorize relationships between organisms that are competitive or mutually beneficial.
 Unpack the Standard: Students will categorize relationships between organisms that are competitive or mutually beneficial. Competition Among Organisms Competition occurs when organisms of the same or different
Unpack the Standard: Students will categorize relationships between organisms that are competitive or mutually beneficial. Competition Among Organisms Competition occurs when organisms of the same or different
HW/CW #5 CHAPTER 3 PRACTICE
 HW/CW #5 CHAPTER 3 PRACTICE 1. The portion of Earth in which all life exists is known as A) the climax stage B) the biosphere C) a population D) a biotic community 2. The study of the interactions between
HW/CW #5 CHAPTER 3 PRACTICE 1. The portion of Earth in which all life exists is known as A) the climax stage B) the biosphere C) a population D) a biotic community 2. The study of the interactions between
BOOK 3 OUR PLANET SECTION 2 WORLD OF LIFE
 BOOK 3 OUR PLANET SECTION 2 WORLD OF LIFE ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS There are two general types of cell - the animal cell and the plant cell. The animal cell is the most basic with the fewest parts. The plant
BOOK 3 OUR PLANET SECTION 2 WORLD OF LIFE ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS There are two general types of cell - the animal cell and the plant cell. The animal cell is the most basic with the fewest parts. The plant
Organism Species Population Community Ecosystem
 Name: Date: Period: Ecosystems and Their Interactions S8.B.3.1 Getting the idea The environment is everything that surrounds an organism. Organisms cooperate and compete with each other to get everything
Name: Date: Period: Ecosystems and Their Interactions S8.B.3.1 Getting the idea The environment is everything that surrounds an organism. Organisms cooperate and compete with each other to get everything
6. Which of the following is not a basic need of all animals a. food b. friends c. water d. protection from predators
 NAME SOL 4.5 Habitats, Niches and Adaptations POPULATION A group of the same species living in the same place at the same time. COMMUNITY-- All of the populations that live in the same area 6. Which of
NAME SOL 4.5 Habitats, Niches and Adaptations POPULATION A group of the same species living in the same place at the same time. COMMUNITY-- All of the populations that live in the same area 6. Which of
SPRING Print Student Name. Science GRADE PRACTICE TEST
 Print Student Name SPRING 2018 PRACTICE TEST GRADE 4 DIRECTIONS Read each question carefully. For each multiple-choice question, decide which is the best answer. For each question that asks you to explain
Print Student Name SPRING 2018 PRACTICE TEST GRADE 4 DIRECTIONS Read each question carefully. For each multiple-choice question, decide which is the best answer. For each question that asks you to explain
Materials: 3 sets of cards, a teacher key, vocabulary list or glossary ((Vocabulary list is also available online below the corresponding program))
 I Have, Who Has? An Interactive Vocabulary Game Woodland Ecosystem Study Vocabulary Grades 4 th -8th Introduction: Below is a collection of cards that connect to the Woodland Ecosystem Study Vocabulary
I Have, Who Has? An Interactive Vocabulary Game Woodland Ecosystem Study Vocabulary Grades 4 th -8th Introduction: Below is a collection of cards that connect to the Woodland Ecosystem Study Vocabulary
All species evolve characteristics, features or behaviours that allow them to survive in a certain habitat (or environment)
 What is adaptation? All species evolve characteristics, features or behaviours that allow them to survive in a certain habitat (or environment) o Animals and plants living in different habitats need different
What is adaptation? All species evolve characteristics, features or behaviours that allow them to survive in a certain habitat (or environment) o Animals and plants living in different habitats need different
Grade 8 Science Practice Test
 Grade 8 Science Practice Test Nebraska Department of Education 2012 Directions: On the following pages of your test booklet are multiple-choice questions for Session 1 of the Grade 8 Nebraska State Accountability
Grade 8 Science Practice Test Nebraska Department of Education 2012 Directions: On the following pages of your test booklet are multiple-choice questions for Session 1 of the Grade 8 Nebraska State Accountability
1 29 g, 18% Potato chips 32 g, 23% 2 30 g, 18% Sugar cookies 35 g, 30% 3 28 g, 19% Mouse food 27 g, 18%
 1. When testing the benefits of a new fertilizer on the growth of tomato plants, the control group should include which of the following? A Tomato plants grown in soil with no fertilizer B Tomato plants
1. When testing the benefits of a new fertilizer on the growth of tomato plants, the control group should include which of the following? A Tomato plants grown in soil with no fertilizer B Tomato plants
Plant Picture. Date. Observations
 Plant Picture Date Observations Investigation 1: Grass and Grain Seeds No. 1 Notebook Master What Do Plants Need? Review Questions 1. What are the basic needs of plants? 2. What part of a plant takes up
Plant Picture Date Observations Investigation 1: Grass and Grain Seeds No. 1 Notebook Master What Do Plants Need? Review Questions 1. What are the basic needs of plants? 2. What part of a plant takes up
The Eco Pyramid By Michael Stahl
 The Eco Pyramid The Eco Pyramid By Michael Stahl An ecosystem is a community of living organisms interacting with one another as well as with nonliving things. One very important aspect of an ecosystem
The Eco Pyramid The Eco Pyramid By Michael Stahl An ecosystem is a community of living organisms interacting with one another as well as with nonliving things. One very important aspect of an ecosystem
California Content Standards Grade 4
 Grade 4 Standard Set 2. Life Sciences 2. All organisms need energy and matter to live and grow. Notes to Teacher Students have now had experience with energy flow through an ecosystem as depicted by food
Grade 4 Standard Set 2. Life Sciences 2. All organisms need energy and matter to live and grow. Notes to Teacher Students have now had experience with energy flow through an ecosystem as depicted by food
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Unit test 2 / revision questions /class1 Evs / ch.20,21 /
 Unit test 2 / revision questions /class1 Evs / ch.20,21 / 2018-19 Q.1 Fill in the blanks. (a) Some plants are small and. (b) creepers grow along the ground. (c) All the have two legs and a beak. (d) Animals
Unit test 2 / revision questions /class1 Evs / ch.20,21 / 2018-19 Q.1 Fill in the blanks. (a) Some plants are small and. (b) creepers grow along the ground. (c) All the have two legs and a beak. (d) Animals
Grade Level Suggestion: Grades 4 th to 5 th. Time Frame: minutes.
 I Have, Who Has? An Interactive Vocabulary Game Woodland Ecosystem Study Vocabulary Grades 4 th -8th Introduction: Below is a collection of cards that connect to the Woodland Ecosystem Study Vocabulary
I Have, Who Has? An Interactive Vocabulary Game Woodland Ecosystem Study Vocabulary Grades 4 th -8th Introduction: Below is a collection of cards that connect to the Woodland Ecosystem Study Vocabulary
Populations and Communities
 CHAPTER 21 Populations and Communities LESSON 3 Communities What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
CHAPTER 21 Populations and Communities LESSON 3 Communities What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
BIOLOGY Unit 2: Ecology Review Guide
 BIOLOGY 621 - Unit 2: Ecology Review Guide Worksheets to look over: BLUE notes packets on: o "Unit Two: Ecology" o "Feeding Relationships" o "Succession & Growth" Do Now's on: o "Food Web & Food Chains"
BIOLOGY 621 - Unit 2: Ecology Review Guide Worksheets to look over: BLUE notes packets on: o "Unit Two: Ecology" o "Feeding Relationships" o "Succession & Growth" Do Now's on: o "Food Web & Food Chains"
Round One All play. Each question = 1 point
 Ecology Unit Review Round One All play Each question = 1 point Leaf cells are one type of tree cell. Which process occurs in a live leaf cell? a. Evolution b. Adaptation c. sugar production d. sexual reproduction
Ecology Unit Review Round One All play Each question = 1 point Leaf cells are one type of tree cell. Which process occurs in a live leaf cell? a. Evolution b. Adaptation c. sugar production d. sexual reproduction
1 Vocabulary. Chapter 5 Ecology. Lesson. Carnivore an organism that only eats meat or flesh. Niche an organism s role in the habitat
 1 Vocabulary Carnivore an organism that only eats meat or flesh Niche an organism s role in the habitat Community all the populations in one place that interact with each other Decomposer digests the waste
1 Vocabulary Carnivore an organism that only eats meat or flesh Niche an organism s role in the habitat Community all the populations in one place that interact with each other Decomposer digests the waste
Define Ecology. study of the interactions that take place among organisms and their environment
 Ecology Define Ecology Define Ecology study of the interactions that take place among organisms and their environment Describe each of the following terms: Biosphere Biotic Abiotic Describe each of the
Ecology Define Ecology Define Ecology study of the interactions that take place among organisms and their environment Describe each of the following terms: Biosphere Biotic Abiotic Describe each of the
Decomposers recycle nutrients (matter) but ENERGY IS ALWAYS LOST
 Decomposers recycle nutrients (matter) but ENERGY IS ALWAYS LOST What does this mean to us Stable ecosystems have a continual input of energy And more producers than consumers It takes less energy to produce
Decomposers recycle nutrients (matter) but ENERGY IS ALWAYS LOST What does this mean to us Stable ecosystems have a continual input of energy And more producers than consumers It takes less energy to produce
Interactions of life
 Interactions of life Objectives Describe how organisms obtain energy for life. Explain how organisms interact. Recognize that every organism occupies a niche. Energy Living organisms need a constant supply
Interactions of life Objectives Describe how organisms obtain energy for life. Explain how organisms interact. Recognize that every organism occupies a niche. Energy Living organisms need a constant supply
Which of the following is NOT an abiotic factor? A) Rocks B) Soil C) Mountains D) Decomposers
 Which of the following is NOT an abiotic factor? A) Rocks B) Soil C) Mountains D) Decomposers Which of the following leads to stability in an ecosystem A) Low amount of biodiversity B) Low amount of biotic
Which of the following is NOT an abiotic factor? A) Rocks B) Soil C) Mountains D) Decomposers Which of the following leads to stability in an ecosystem A) Low amount of biodiversity B) Low amount of biotic
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: London City. Assessment: 07 Science Science Test 4. Description: Life Science Final 1.
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: London City Assessment: 07 Science Science Test 4 Description: Life Science Final 1 Form: 301 1. A food chain is shown. Sunlight Grass Rabbit Snake What is the abiotic
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: London City Assessment: 07 Science Science Test 4 Description: Life Science Final 1 Form: 301 1. A food chain is shown. Sunlight Grass Rabbit Snake What is the abiotic
Grade 5 Part 2.
 Part 2 2011 5Grade www.abubakrshalaby.com P a g e 1 Contents Chapter Lesson Page 1. Ecology 3 2. The basic animals' needs 4 1. living things 3. Ecosystem interact 4 4. Habitats and Niches 7 2. Animal Adaptations
Part 2 2011 5Grade www.abubakrshalaby.com P a g e 1 Contents Chapter Lesson Page 1. Ecology 3 2. The basic animals' needs 4 1. living things 3. Ecosystem interact 4 4. Habitats and Niches 7 2. Animal Adaptations
EGYPTIAN AMERICAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL
 EGYPTIAN AMERICAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Science Department Semester 1 GRADE 4 Revision 2 Name: Date: Class: A. Choose the correct answer: 1. What is the main source of energy for the food web shown? A.
EGYPTIAN AMERICAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Science Department Semester 1 GRADE 4 Revision 2 Name: Date: Class: A. Choose the correct answer: 1. What is the main source of energy for the food web shown? A.
water cycle evaporation condensation the process where water vapor the cycle in which Earth's water moves through the environment
 cycle a series of events that happen over and over water cycle evaporation the cycle in which Earth's water moves through the environment process when the heat of the sun changes water on Earth s surface
cycle a series of events that happen over and over water cycle evaporation the cycle in which Earth's water moves through the environment process when the heat of the sun changes water on Earth s surface
Ecology Student Edition. A. Sparrows breathe air. B. Sparrows drink water. C. Sparrows use the sun for food. D. Sparrows use plants for shelter.
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following does not give an example of how sparrows use resources in their environment to survive? A. Sparrows breathe air. B. Sparrows drink water. C. Sparrows use the sun for
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following does not give an example of how sparrows use resources in their environment to survive? A. Sparrows breathe air. B. Sparrows drink water. C. Sparrows use the sun for
1) Which of the following describes the mammals, fish, birds, and plants that live in an environment? a) Abiotic c) biome b) population d) biotic
 CH.16 practice TEST -6th grade Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following describes the mammals, fish, birds, and plants that
CH.16 practice TEST -6th grade Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following describes the mammals, fish, birds, and plants that
Principles of Ecology
 Principles of Ecology What is Ecology? Ecology is the study of interactions that occur between organisms and their environment Biosphere Recall that the biosphere includes all living things In order to
Principles of Ecology What is Ecology? Ecology is the study of interactions that occur between organisms and their environment Biosphere Recall that the biosphere includes all living things In order to
Organisms & Environments Task Cards
 Organisms & Environments Task Cards Organisms & Environments Task Cards Thank you so much for purchasing this product. I am truly appreciative of your business and I will happily respond to any of your
Organisms & Environments Task Cards Organisms & Environments Task Cards Thank you so much for purchasing this product. I am truly appreciative of your business and I will happily respond to any of your
Sample. Test Booklet. Subject: SC, Grade: 08 MEA Released 2009 Science Items Grade 8. - signup at to remove - Student name:
 Test Booklet Subject: SC, Grade: 08 MEA Released 2009 Science Items Grade 8 Student name: Author: Maine District: Maine Released Tests Printed: Monday October 08, 2012 1 What effect does gravity have on
Test Booklet Subject: SC, Grade: 08 MEA Released 2009 Science Items Grade 8 Student name: Author: Maine District: Maine Released Tests Printed: Monday October 08, 2012 1 What effect does gravity have on
The factors together:
 Biotic Interactions 8.11A DESCRIBE PRODUCER/CONSUMER, PREDATOR/PREY AND PARASITE/HOST RELATIONSHIPS AS THEY OCCUR IN FOOD WEBS WITHIN MARINE, FRESHWATER AND TERRESTRIAL ECOSYSTEMS Biotic These are the
Biotic Interactions 8.11A DESCRIBE PRODUCER/CONSUMER, PREDATOR/PREY AND PARASITE/HOST RELATIONSHIPS AS THEY OCCUR IN FOOD WEBS WITHIN MARINE, FRESHWATER AND TERRESTRIAL ECOSYSTEMS Biotic These are the
B2 Revision Questions Part 1
 B2 Revision Questions Part 1 Higher only questions are underlined Question 1 What are the two different ways that things can be classified? Answer 1 Artificially and naturally Question 2 What is natural
B2 Revision Questions Part 1 Higher only questions are underlined Question 1 What are the two different ways that things can be classified? Answer 1 Artificially and naturally Question 2 What is natural
TOTAL SCIENCE KEY STAGE LEVELS TEST B. Borderline check TEST B. First Name. Last Name. School
 SCIENCE KEY STAGE 2 2003 TEST B LEVELS 3 5 PAGE 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 TOTAL Borderline check MARKS TEST B First Name Last Name School INSTRUCTIONS Read this carefully. Answers This shows where you will
SCIENCE KEY STAGE 2 2003 TEST B LEVELS 3 5 PAGE 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 TOTAL Borderline check MARKS TEST B First Name Last Name School INSTRUCTIONS Read this carefully. Answers This shows where you will
Science Review- CBA #1- Life Science Test: Wednesday, October 12, 2016
 Science Review- CBA #1- Life Science Test: Wednesday, October 12, 2016 Interactions within an Ecosystem: Organisms perform a variety of roles in an ecosystem. Populations of organisms can be categorized
Science Review- CBA #1- Life Science Test: Wednesday, October 12, 2016 Interactions within an Ecosystem: Organisms perform a variety of roles in an ecosystem. Populations of organisms can be categorized
The Ron Clapp Nature Trail Activity Book
 The Ron Clapp Nature Trail Activity Book By The 2008 Adventurers Ron Clapp Memorial Trail Animal Signs Scavenger Hunt As you walk through the trails look closely to see if you can find the items listed
The Ron Clapp Nature Trail Activity Book By The 2008 Adventurers Ron Clapp Memorial Trail Animal Signs Scavenger Hunt As you walk through the trails look closely to see if you can find the items listed
Chapter Niches and Community Interactions
 Chapter 4 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions Key Questions: 1) What is a niche? 2) How does competition shape communities? 3) How do predation and herbivory shape communites? 4) What are three primary
Chapter 4 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions Key Questions: 1) What is a niche? 2) How does competition shape communities? 3) How do predation and herbivory shape communites? 4) What are three primary
SCIENCE. Year 9 Examination 2011
 NAME: SCIENCE TEACHER: (circle code) 2011 9A 9A SCIENCE Year 9 Examination 2011 9A 40 marks Make sure that you have answered all the questions in paper 9B before you start this paper Time allowed for both
NAME: SCIENCE TEACHER: (circle code) 2011 9A 9A SCIENCE Year 9 Examination 2011 9A 40 marks Make sure that you have answered all the questions in paper 9B before you start this paper Time allowed for both
5 th Grade Science TCAP Review Test. Name
 Name 5 th Grade Science TCAP Review Test Chapter 4 1. The center part of the Earth is called the. 2. The thick layer of solid and molten rock that lies under the crust is known as the. 3. The is the thin
Name 5 th Grade Science TCAP Review Test Chapter 4 1. The center part of the Earth is called the. 2. The thick layer of solid and molten rock that lies under the crust is known as the. 3. The is the thin
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS FOR: Grade
 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS FOR: Date 4/25/18 Wednesday Teacher Ms. Weger Subject/Grade Science 7 th Grade In-Class: REVIEW FOR CH. 22 TEST Go over the 22-3 Think Questions Look at the data from the Oh Deer!
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS FOR: Date 4/25/18 Wednesday Teacher Ms. Weger Subject/Grade Science 7 th Grade In-Class: REVIEW FOR CH. 22 TEST Go over the 22-3 Think Questions Look at the data from the Oh Deer!
A. Choose the correct answer:
 EGYPTIAN AMERICAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Science Department Semester 1 GRADE 4 Revision 2 A. Choose the correct answer: 1. What is the main source of energy for the food web shown? A. hawk B. rabbit C. plants
EGYPTIAN AMERICAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Science Department Semester 1 GRADE 4 Revision 2 A. Choose the correct answer: 1. What is the main source of energy for the food web shown? A. hawk B. rabbit C. plants
Ladybug- 7A-2. By the end of today, you will know a lot about these amazingly diverse insects. They come in all shapes, sizes, and colors.
 Ladybug- 7A-2 My grasshopper friend tells me that he asked you to guess the largest group of insects on Earth. Did anyone guess flies? Perhaps you guessed ants. Both ants and flies are good guesses. You
Ladybug- 7A-2 My grasshopper friend tells me that he asked you to guess the largest group of insects on Earth. Did anyone guess flies? Perhaps you guessed ants. Both ants and flies are good guesses. You
