5. What is not typically considered to be a cause of natural error when using EDM devices?
|
|
|
- Cassandra Knight
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Student ID: Exam: RR - Introduction to Surveying and Measurement When you have completed your exam and reviewed your answers, click Submit Exam. Answers will not be recorded until you hit Submit Exam. If you need to exit before completing the exam, click Cancel Exam. Questions 1 to 20: Select the best answer to each question. Note that a question and its answers may be split across a page break, so be sure that you have seen the entire question and all the answers before choosing an answer. 1. Determine the standard deviation for the following series of repeated measurements: , , , , A..067 B C D If a steel tape is marked in 1/10-foot increments and a taping crew uses that tape to obtain a measurement of feet, how many of the figures in their result would be considered significant? A. 3 B. 4 C. 2 D A taping team is taking measurements on a hot, sunny summer day using a 100-foot steel tape. The temperature of the tape is determined to be 106 F. Which of the following corrections should be made to the measurements? A. Subtract.024 feet B. Add.024 feet C. Subtract.024 inches D. Add.024 inches 4. Two surveyors are discussing EDM setup. Surveyor A says that plumb bobs are the best choice for centering reflectors over the end point of a line. Surveyor B says that weather conditions have no bearing on measurements taken with an EDM system. Which of the following statements is correct? A. Only Surveyor A is correct. B. Both surveyors are correct. C. Neither surveyor is correct. D. Only Surveyor B is correct. 5. What is not typically considered to be a cause of natural error when using EDM devices? A. Humidity variation B. Temperature variation
2 C. Time variation D. Pressure variation 6. Two surveyors measure a slope distance using an EDM and obtain a result of feet after atmospheric and instrumental corrections. The difference in elevation between the two points of measurement is feet and the heights of the EDM and its reflectors are equal. Surveyor A says that the horizontal distance is if you use the slope correctional formula. Surveyor B says that the horizontal distance is using the Pythagorean theorem. Which of the following statements is correct? A. Only Surveyor B is correct. B. Neither surveyor is correct. C. Both surveyors are correct. D. Only Surveyor A is correct. 7. Two surveyors are discussing calibration of steel tapes. Surveyor A says that the NGS has hundreds of base lines across the country where you can calibrate a tape yourself. Surveyor B says that the NIST will determine the true length of your tape at a specific tension. Which of the following statements is correct? A. Only Surveyor B is correct. B. Neither surveyor is correct. C. Both surveyors are correct. D. Only Surveyor A is correct. 8. A device that contains leveling screws, an optical plummet, and a bull's-eye level used to set EDMs over a definite point is called a(n) A. reflector. B. tribrach. C. plumb bob. D. instrument constant. 9. A measurement of feet was made using a 100-foot steel tape. The steel tape is later standardized and found to have an actual length of feet. Which of the following options is an accurate corrected value for the measurement in feet? A B C D The right triangle in the figure provided has a hypotenuse of feet and an adjacent side measuring feet. What is the angle opposite the adjacent side expressed as degrees, minutes and rounded to the nearest second?
3 A '47" B. 47 9'41" C '19" D. 42 8'43" 11. A survey team makes a measurement of feet using a steel tape along smooth pavement on a road with a slope having a vertical angle of 5 36'. What is the horizontal distance (in feet) for the measurement? A B C D Which of the following types of measurement equipment would not typically be needed by a taping crew? A. Plumb bob B. Range pole C. Tripod D. Hand level 13. A taping team is making a measurement using a 100-foot "add" tape. The rear tapeman holds the 56- foot mark of the tape on his taping pin, and the head tapeman calls out a dimension of 33 hundredths. What is the total measured distance? A feet B feet C feet D feet 14. How many chaining pins are typically in a set assigned to a taping party? A. 50 B. 11
4 C. 25 D Which of the following statements about EDMs is false? A. New users can learn to use EDMs quickly. B. More costly EDMs generally have less instrument error. C. EDMs can measure a wide range of distances over all types of terrain. D. EDMs can be calibrated less often than mechanical theodolites. 16. What is the equivalent decimal value for an angle of 48 27' 49"? A B C D What measurement tool is attached to a wheel to count the revolutions that can be used for a quick check of a distance, but is not precise enough for most formal results? A. Stadia B. Pedometer C. Odometer D. Traverse 18. Which of the following types of surveys is used to measure relief, roughness, or three-dimensional variations of a surface? A. Land B. Hydrographic C. Construction D. Topographic 19. What do you call the two-man process used to measure along a slope where measurements start and stop at points where the tape can be held horizontally, verified with a plumb bob? A. Breaking tape B. Plumbing C. Cut and add D. Slope taping 20. What type of error is introduced into a project if a 100' steel measuring tape actually measures 100' 0.10" and is used to make 25 measurements? A. Random B. Accidental C. Systematic D. Personal
5 End of exam
6 4. What are the bearings for line DC in the figure provided? Student ID: Exam: RR - Leveling, Angles, and Calculating Land area When you have completed your exam and reviewed your answers, click Submit Exam. Answers will not be recorded until you hit Submit Exam. If you need to exit before completing the exam, click Cancel Exam. Questions 1 to 20: Select the best answer to each question. Note that a question and its answers may be split across a page break, so be sure that you have seen the entire question and all the answers before choosing an answer. 1. Which of the following types of levels uses a compensator to complete the finished leveling and uses a bar code on the level rod to determine rod readings and distances? A. Wye level B. Dumpy level C. Electronic digital level D. Tilting level 2. Using the information in the figure provided, determine the departure of side CD. A. W B. W C. E D. E An angle expressed as 48 22'48" would have been measured using the system. A. sexagesimal B. centesimal C. radian D. mil
7 A. N63 26'E B. N79 01'E C. N5 17'E D. N5 17'W 5. Which of the following levels would be considered the most precise? A. 1.0" bubble B. 10" bubble C..10" bubble D..25" bubble 6. Determine the most probable elevation, in feet, for the following series of route lengths and measured elevations for BM 2 : (a) route 2 miles, elevation at BM feet, (b) route 4 miles, elevation at BM feet, (c) route 5 miles, elevation at BM feet, (d) route 8 miles, elevation at BM feet. A B C D At a given point, the magnetic bearing of a line is N28 35'E. If the magnetic declination is 3 18'W, what is the astronomic bearing of the line? A. N31 53'E B. N31 53'W C. N25 17'E D. N25 17'W 8. The vertical distance between contour lines is called the A. scale. B. contour interval.
8 C. hachures. D. index contour. 9. Using the information in the figure provided, determine the bearing of side DA. A. N70 29'41"E B. N80 53'01"E C. N80 31'48"E D. N9 29'41"E 10. A line AD has a north azimuth of '. What are the bearings for this line? A. N47 14'W B. S62 23'W C. S27 14'W D. N43 17'W 11. Which of the following statements about traversing is false? A. Forward and back measurements should be made for all distances in an open traverse. B. An open traverse should be verified using simple arithmetic checks. C. A closed traverse begins and ends at the same point. D. A closed traverse is preferred over an open traverse because the verification process is easier. 12. The forward azimuth of a line AB is 30. What is its back azimuth? A. 210 B. 150 C. 330 D What is the deflection angle at B for the figure provided?
9 A ' B ' C ' D ' 14. A line AB has a bearing of S42 27' E. What is this bearing's north azimuth? A ' B ' C ' D ' 15. Which of the following abbreviations is used to designate a sight taken to the level rod on a known elevation to determine the height of the surveying instrument? A. FS B. HI C. BS D. BM 16. On a survey drawing, a series of straight lines connected together to show the outline of a plot of land would be called a(n) traverse. A. closed B. interior C. exterior D. open 17. Name the most common type of level rod. (It is made in two sections and uses alternating black and white spaces to indicate hundredths of feet.) A. San Francisco rod B. Philadelphia rod C. Florida rod D. Chicago rod
10 18. If a survey team determines the meridian reference for their data using a compass, they are using a(n) meridian. A. grid B. magnetic C. assumed D. astronomic 19. Two surveyors are discussing the development of typographic surveys. Surveyor A says that a photogrammetric survey is best for small areas in poor weather conditions. Surveyor B says that a 10-acre topographic survey would most likely be completed using a total station. Which of the following statements is correct? A. Neither surveyor is correct. B. Only Surveyor B is correct. C. Only Surveyor A is correct. D. Both surveyors are correct. 20. What is the interior angle at A for the figure provided? A ' B ' C ' D ' End of exam
11 Student ID: Exam: RR - GPS, GIS, and Construction Surveying When you have completed your exam and reviewed your answers, click Submit Exam. Answers will not be recorded until you hit Submit Exam. If you need to exit before completing the exam, click Cancel Exam. Questions 1 to 20: Select the best answer to each question. Note that a question and its answers may be split across a page break, so be sure that you have seen the entire question and all the answers before choosing an answer. 1. is a term that describes a set of carefully located monuments and their related measurements placed throughout large project sites. A. Spatial marking B. Control surveying C. Thematic layering D. Vertical datum 2. Two surveyors are discussing earthwork. Surveyor A says that a slope of 3:1 will rise 3 feet for every 1 foot you move out horizontally. Surveyor B says that slope stakes are used to indicate the point at which a cut or fill meets the existing ground line. Which of the following statements is correct? A. Both surveyors are correct. B. Only Surveyor A is correct. C. Neither surveyor is correct. D. Only Surveyor B is correct. 3. How much cut material is needed if the required fill material for a construction site is 1856 yd 3 with an assumed shrinkage factor of 12 percent? A yd 3 B yd 3 C yd 3 D yd 3 4. Which of the following is not considered an essential element of a GIS? A. Geographic location data B. Data correlation C. Software D. Hardware 5. Two surveyors are discussing network adjustments for GPS systems. Surveyor A says that a triple differencing is costly because three receivers must be used to obtain the measurements. Surveyor B says that the most precise GPS survey results are obtained by combining differencing techniques with carrier phase measurements. Which of the following statements is correct?
12 9. The figure for this question contains the cross section dimensions for stations 25 and 26 of a roadway. If the road bed is 35 feet and the distance between the stations is 100 feet, calculate the volume of excavation using the prismoidal formula. A. Both surveyors are correct. B. Neither surveyor is correct. C. Only Surveyor A is correct. D. Only Surveyor B is correct. 6. Which of the following types of surveys is completed after a construction project is completed? A. Site B. As-built C. Boundary D. Construction 7. The value generated by a GPS measurement system to indicate the accuracy of a measurement based on the effects of satellite geometry is called A. TDOP. B. HDOP. C. VDOP. D. GDOP. 8. The figure for this question shows an area of land laid out in 50-foot squares, with ground elevations as indicated. How many cubic yards of cut will be required to grade the area level to elevation 40.0? Ignore the shrinkage factor. A. 2,704 B. 4,226 C. 4,822 D. 5,127
13 14. You have obtained a measurement using a GPS device. The PDOP vale at the time of the measurement is 3.0. In addition, the following errors are anticipated: atmospheric error 10', clock bias error A yd 3 B yd 3 C yd 3 D yd What term refers to intentional errors created in the satellite system by the military in order to maintain a wartime advantage for the use of GPS systems? A. Multipath error B. Differential correction C. Clock bias D. Selective availability 11. The is a method for projecting curved areas on flat maps where plane or grid coordinates are provided at control stations in each state. A. Lambert projection B. raster system C. Universal Transverse Mercator projection D. state plane coordinate system 12. What is the name of a surveying tool that's used to measure vertical angles from a proposed measurement point to the top of obstacles to set up GPS systems for clear access to satellite signals? A. Compass B. Optical plummet C. Clinometer D. Sextant 13. Which of the following is not a type of survey required for the completion of a construction project? A. As-built survey B. Site survey C. Municipal survey D. Construction survey
14 20. The figure for this question contains the cross section dimensions for stations 25 and 26 of a roadway. If the road bed is 35 feet, and the distance between the stations is 100 feet, calculate the volume of excavation using the average-end-area and correct the value using the prismoidal correction formula. 3', multipath error 2', receiver error 3', and an orbit error of 8'. What is your best estimate of the total error of the reading? A. 27'17" B. 27'47" C. 10'12" D. 13'38" 15. A network of thousands of survey stations available across the United States that are referenced to NAD 83 is known as A. CORS. B. WAAS. C. OPUS. D. HARN. 16. What is the name given to the integration of population data related to geographic locations with the spatial data for that same region? A. GPS B. OPUS C. GIS D. HARN 17. A reference figure that approximates the shape of the earth referenced to MSL is called a(n) A. Cartesian coordinate. B. geodesy. C. geoid. D. ellipsoid. 18. The components of building layout formed using wooden frames that support string lines that indicate the position of building lines and foundation walls are called A. batter boards. B. base lines. C. height poles. D. grade stakes. 19. A point near an excavation site where crews can obtain earth in order to form new embankments is called a(n) A. stockpile. B. cut and fill. C. earthwork. D. borrow pit.
15 A yd 3 B yd 3 C. 784 yd 3 D yd 3 End of exam
16 Student ID: Exam: RR - Land Surveying, Curves, and Professional Practices When you have completed your exam and reviewed your answers, click Submit Exam. Answers will not be recorded until you hit Submit Exam. If you need to exit before completing the exam, click Cancel Exam. Questions 1 to 20: Select the best answer to each question. Note that a question and its answers may be split across a page break, so be sure that you have seen the entire question and all the answers before choosing an answer. 1. A horizontal curve is determined to have a degree of curvature of 4 30'. What is the curve's radius of curvature (on the arc basis), in feet? A B. 24, C. 25, D Two surveyors are staking procedures for curves. Surveyor A says that when staking out a curve the process begins by locating P.I. by extending the tangents and establishing P.C. and P.T. Surveyor B says that laying out half the stations of the curve from the P.C. and half from the P.T. allows for easier adjustment for errors in the middle of the curve. Which of the following statements is correct? A. Only Surveyor A is correct. B. Both surveyors are correct. C. Only Surveyor B is correct. D. Neither surveyor is correct. 3. In the public lands survey system, what is the name given to a row of townships that are arranged north and south? A. Section B. Guide meridian C. Tier D. Range 4. The point on a circular curve where the back tangent and forward tangent meet is called the A. P.I. B. P.C. C. P.T. D. P.O.T 5. A 600-foot vertical curve joins a + 4.5% grade line and a 3.6% grade line at grade station The elevation of the grade lines at P.V.I. is feet. What is the elevation of the curve, in feet, at P.V.I.? A B
17 C D Which of the following surveying terms does not apply specifically to property along a body of water? A. Reliction B. Adverse possession C. Accretion D. Riparian rights 7. is the term for the corner of a property that the surveyor is unable to access. A. Witness corner B. Lost corner C. Fence corner D. Obliterated corner 8. A horizontal curve with a radius of feet will join two roadway tangents. If the chord length is feet and the intersection angle is 64 17'21", what is the external distance (E) to the point of intersection of the curve, in feet? A B C D A horizontal curve is determined to have a radius of curvature of feet. What is the curve's degree of curvature to the closest minute? A. 3 42' B ' C. 3 70' D ' 10. You're staking out a horizontal circular curve. The P.I. is at station , the degree of curvature is 4 30', and the intersection angle is 21 30'. At what station will you locate the P.T.? A B C D You're staking out a horizontal circular curve. The P.I. is at station , the degree of curvature is 4 30', and the intersection angle is 21 30'. What is the length of the tangent for this curve? A ft B ft C ft D ft
18 12. A 30-foot wide roadway has a 9% banked curve. If the elevation at the inside edge of the curve is 42.5 feet, what is the elevation at the outside edge of the curve? A ft B ft C ft D ft 13. Two surveyors are discussing surveying ethics. Surveyor A says that it's okay to conduct one free survey for a large contractor as a way to develop a client base. Surveyor B says that an ethical source of income is to evaluate the work of other surveyors for their employers during the course of their assignment. Which of the following statements is correct? A. Neither surveyor is correct. B. Only Surveyor A is correct. C. Only Surveyor B is correct. D. Both surveyors are correct. 14. A 600-foot vertical curve joins a +4.5% grade line and a 3.6% grade line at grade station The elevation of the grade lines at P.V.I. is feet. What is the tangent offset at station , in feet? A..675 B C..380 D You're staking out a horizontal circular curve. The P.I. is at station , the degree of curvature is 4 30', and the intersection angle is 21 30'. How much should the deflection angle increase at each full 50-ft station throughout the curve? A. 1 16'43" B. 1 10'0" C. 2 20'0" D. 1 00'00" 16. Two surveyors are discussing licensing and registration for surveyors. Surveyor A says that in most states to be fully licensed you need to pass three examinations and have worked under the supervision of a licensed surveyor. Surveyor B says that a license is almost always required in order to conduct construction surveys. Which of the following statements is correct? A. Only Surveyor A is correct. B. Neither surveyor is correct. C. Both surveyors are correct. D. Only Surveyor B is correct. 17. A horizontal curve with a radius of feet will join two roadway tangents. If the chord length is feet and the intersection angle is 64 17'21", what is the outside length (L) of the curve, in feet? A B
19 C D A 600-foot vertical curve joins a +4.5% grade line and a 3.6% grade line at grade station The elevation of the grade lines at P.V.I. is feet. What is the elevation of the P.V.C., in feet? A B C D Which of the following statements is false regarding tree blazing? A. A tree on a boundary is called a line tree. B. Tree blazing is currently the most common method used to indicate surveying monuments. C. A corner monument would be marked with an X and three hacks. D. The height of the hacks above the ground can indicate distance to a property corner. 20. Two surveyors are discussing resurveying. Surveyor A says that making the survey match the original land description is more important than resetting the old lines and corners. Surveyor B says that surveyors are legally required to establish boundaries during a resurvey if the original boundary cannot be located. Which of the following statements is correct? A. Neither surveyor is correct. B. Only Surveyor A is correct. C. Only Surveyor B is correct. D. Both surveyors are correct. End of exam
Leveling. 3.1 Definitions
 Leveling 3.1 Definitions Leveling is the procedure used to determine differences in elevation between points that are remote from each other. Elevation is a vertical distance above or below a reference
Leveling 3.1 Definitions Leveling is the procedure used to determine differences in elevation between points that are remote from each other. Elevation is a vertical distance above or below a reference
NCEES FS Practice Exam
 NCEES FS Practice Exam Terrametra Resources Lynn Patten 1. One corner of a 60-ft. 120-ft. lot, otherwise rectangular, is a curve with a radius of 20 ft. and a central angle of 90. The area (ft. 2 ) of
NCEES FS Practice Exam Terrametra Resources Lynn Patten 1. One corner of a 60-ft. 120-ft. lot, otherwise rectangular, is a curve with a radius of 20 ft. and a central angle of 90. The area (ft. 2 ) of
CE 271 Spring Survey Camp
 PART IV LEVELING A. Importance of Leveling The determination of elevations with a surveying instrument, which is known as leveling, is a relatively simple but extraordinarily important process. B. Definitions
PART IV LEVELING A. Importance of Leveling The determination of elevations with a surveying instrument, which is known as leveling, is a relatively simple but extraordinarily important process. B. Definitions
VT State Plane. Daniel J. Martin National Geodetic Survey VT Geodetic Advisor. VSLS Conference Rutland VT April 11, 2008
 VT State Plane Daniel J. Martin National Geodetic Survey VT Geodetic Advisor VSLS Conference Rutland VT April 11, 2008 Today s Outline Define the problem Review of VT State Plane System Relationship
VT State Plane Daniel J. Martin National Geodetic Survey VT Geodetic Advisor VSLS Conference Rutland VT April 11, 2008 Today s Outline Define the problem Review of VT State Plane System Relationship
Cleveland State University
 CVE 212 - Surveying Lab #6 MEASURING ISTANCES USING STAIA METHOS EQUIPMENT Transit or theodolite with stadia hairs and tripod Philadelphia leveling rod Field book No. 3 drafting pencil INTROUCTION When
CVE 212 - Surveying Lab #6 MEASURING ISTANCES USING STAIA METHOS EQUIPMENT Transit or theodolite with stadia hairs and tripod Philadelphia leveling rod Field book No. 3 drafting pencil INTROUCTION When
Objective questions for Practical Examination (CBCS scheme) Introduction to Surveying CE-112
 Objective questions for Practical Examination (CBCS scheme) Introduction to Surveying CE-112 1. The curvature of the earth s surface, is taken into account only if the extent of survey is more than i)
Objective questions for Practical Examination (CBCS scheme) Introduction to Surveying CE-112 1. The curvature of the earth s surface, is taken into account only if the extent of survey is more than i)
Surveying FE Review. Fall CIVL 4197 FE Surveying Review 1/9
 CIVL 4197 FE Surveying Review 1/9 Surveying FE Review Fall 017 Problem 18.01: Two sides of a triangular-shaped parcel are 80 ft. and 100 ft. with a 60 angle between them. The length of the third side of
CIVL 4197 FE Surveying Review 1/9 Surveying FE Review Fall 017 Problem 18.01: Two sides of a triangular-shaped parcel are 80 ft. and 100 ft. with a 60 angle between them. The length of the third side of
Butte County Fire Department
 Butte County Fire Department Basic Land Navigation Verification Sheet I verify that Print Supervisor s name has completed the Print Employee s name Basic Land Navigation self study guide on. Date Attached
Butte County Fire Department Basic Land Navigation Verification Sheet I verify that Print Supervisor s name has completed the Print Employee s name Basic Land Navigation self study guide on. Date Attached
Sub. Code:
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Model Answer: Summer 08 Code: 05 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Model Answer: Summer 08 Code: 05 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
CE 311. Elementary & Higher Surveying
 CE 311 Elementary & Higher Surveying Surveying Concept What do surveyors do? What do surveyors measure? What distances do surveyors measure? What angles do surveyors measure? What positions do surveyors
CE 311 Elementary & Higher Surveying Surveying Concept What do surveyors do? What do surveyors measure? What distances do surveyors measure? What angles do surveyors measure? What positions do surveyors
Site Surveying Procedures for Construction and the Built Environment
 Unit 27: Site Surveying Procedures for Construction and the Built Environment Unit code: R/601/1291 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit develops an understanding of the principles of site surveying
Unit 27: Site Surveying Procedures for Construction and the Built Environment Unit code: R/601/1291 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit develops an understanding of the principles of site surveying
Basic Field Instruments Field Orientation, Basic Navigation ESRM 304
 Basic Field Instruments Field Orientation, Basic Navigation ESRM 304 Three Basic Navigation Measurements Direction Distance Elevation (or change in it) 2 Compass for Direction Looking from point to point,
Basic Field Instruments Field Orientation, Basic Navigation ESRM 304 Three Basic Navigation Measurements Direction Distance Elevation (or change in it) 2 Compass for Direction Looking from point to point,
Butte County Fire Department
 Butte County Fire Department Basic Land Navigation Verification Sheet I verify that Print Supervisor's name Print Employee's name has completed the Basic Land Navigation self study guide on Date Attached
Butte County Fire Department Basic Land Navigation Verification Sheet I verify that Print Supervisor's name Print Employee's name has completed the Basic Land Navigation self study guide on Date Attached
Package No.-36(Surveyor) Annexure -III
 Package No.-36(Surveyor) Annexure -III Reference- Clause-8 of DTCN S.L.No Item Quantity 1 Abney level.tube is 5 1/8 in. long, Radius arc of 1 1/8 in. graduated in degrees in both directions,vernier reading
Package No.-36(Surveyor) Annexure -III Reference- Clause-8 of DTCN S.L.No Item Quantity 1 Abney level.tube is 5 1/8 in. long, Radius arc of 1 1/8 in. graduated in degrees in both directions,vernier reading
Measurement of Horizontal Distances. the distance between two points means the horizontal distance
 Measurement of Horizontal Distances the distance between two points means the horizontal distance Pacing Mechanical Devices Taping * Tachymetric Photogrammetric * Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM)
Measurement of Horizontal Distances the distance between two points means the horizontal distance Pacing Mechanical Devices Taping * Tachymetric Photogrammetric * Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM)
71- Laxmi Nagar (South), Niwaru Road, Jhotwara, Jaipur ,India. Phone: Mob. : /
 www.aarekh.com 71- Laxmi Nagar (South), Niwaru Road, Jhotwara, Jaipur 302 012,India. Phone: 0141-2348647 Mob. : +91-9799435640 / 9166936207 1. An invar tape made of an alloy of: A. Copper and steel. B.
www.aarekh.com 71- Laxmi Nagar (South), Niwaru Road, Jhotwara, Jaipur 302 012,India. Phone: 0141-2348647 Mob. : +91-9799435640 / 9166936207 1. An invar tape made of an alloy of: A. Copper and steel. B.
AU-5029 GURU GHASIDAS VISHWAVIDYALAYA, BILASPUR (C.G.) INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING B.TECH
 AU-5029 GURU GHASIDAS VISHWAVIDYALAYA, BILASPUR (C.G.) INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING B.TECH 2 nd YEAR, III rd SEMESTER SUBJECT: SURVEYING-I COURSE CODE: 21CE02T Max Marks: 60
AU-5029 GURU GHASIDAS VISHWAVIDYALAYA, BILASPUR (C.G.) INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING B.TECH 2 nd YEAR, III rd SEMESTER SUBJECT: SURVEYING-I COURSE CODE: 21CE02T Max Marks: 60
Applied Geomorphology. Pocket Transit Survey Methods
 Applied Geomorphology Pocket Transit Survey Methods The Pocket Transit (Brunton) Used to measure compass directions Allows for magnetic declination correction Can measure vertical angles with clinometer.
Applied Geomorphology Pocket Transit Survey Methods The Pocket Transit (Brunton) Used to measure compass directions Allows for magnetic declination correction Can measure vertical angles with clinometer.
GEOMATICS ENGINEERING / SURVEYING
 1 GEOMATICS ENGINEERING / SURVEYING CHAPTER 1 Dr. Muhammad Ashraf Javid Assistant Professor Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Email: muhammad.javid@unizwa.edu.om 2 Geomatics Engineering
1 GEOMATICS ENGINEERING / SURVEYING CHAPTER 1 Dr. Muhammad Ashraf Javid Assistant Professor Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Email: muhammad.javid@unizwa.edu.om 2 Geomatics Engineering
-I g in y e SURVEYING-I rv u S
 SURVEYING-I Modern Surveying Chains & other Equipment Measuring Distance The historical method measuring distance is surveying chain. for the One of the first chains used in the U.S. was the Gunter s chain.
SURVEYING-I Modern Surveying Chains & other Equipment Measuring Distance The historical method measuring distance is surveying chain. for the One of the first chains used in the U.S. was the Gunter s chain.
GE 100: General Surveying I
 : General I INTRODUCTION TO SURVEYING Lecture No. Caraga State University College of Engineering and Information Technology SURVEYING It is the art and science of determining angular and linear measurements
: General I INTRODUCTION TO SURVEYING Lecture No. Caraga State University College of Engineering and Information Technology SURVEYING It is the art and science of determining angular and linear measurements
CE 316 GEOMATICS COURSE NOTES DR. MOIR D HAUG, C.L.S., P. ENG. JANUARY 2012
 CE 316 GEOMATICS COURSE NOTES DR. MOIR D HAUG, C.L.S., P. ENG. JANUARY 2012 0 COURSE INFORMATION Dr Moir D Haug, P. Eng University Office 2B25 Engineering 966 5355 moir.haug@usask.ca MDH Engineered Solutions
CE 316 GEOMATICS COURSE NOTES DR. MOIR D HAUG, C.L.S., P. ENG. JANUARY 2012 0 COURSE INFORMATION Dr Moir D Haug, P. Eng University Office 2B25 Engineering 966 5355 moir.haug@usask.ca MDH Engineered Solutions
DRAFT MARINE ARTILLERY SURVEY
 MARINE ARTILLERY SURVEY Table of Contents Chapter 1: Mission, Organization, and Duties Section I: Mission PARA TITLE PAGE 1-1 Common Grid 1-1 1-2 Components of a Common Grid 1-1 1-3 Fundamentals of Survey
MARINE ARTILLERY SURVEY Table of Contents Chapter 1: Mission, Organization, and Duties Section I: Mission PARA TITLE PAGE 1-1 Common Grid 1-1 1-2 Components of a Common Grid 1-1 1-3 Fundamentals of Survey
Only for Reference Page 1 of 11
 Only for Reference www.civilpddc2013.weebly.com Page 1 of 11 Seat No.: Enrolment No. PDDC - SEMESTER II EXAMINATION WINTER 2013 Subject Code: X20601 Date: 20-12-2013 Subject Name: Advance Surveying Time:
Only for Reference www.civilpddc2013.weebly.com Page 1 of 11 Seat No.: Enrolment No. PDDC - SEMESTER II EXAMINATION WINTER 2013 Subject Code: X20601 Date: 20-12-2013 Subject Name: Advance Surveying Time:
AGE 303 AGRICULTURAL LAND SURVEYING INTRODUCTION Land Surveying: It has to do with the determination of relative spatial location of points on or
 AGE 303 AGRICULTURAL LAND SURVEYING INTRODUCTION Land Surveying: It has to do with the determination of relative spatial location of points on or near the surface of the earth. It is the art of measuring
AGE 303 AGRICULTURAL LAND SURVEYING INTRODUCTION Land Surveying: It has to do with the determination of relative spatial location of points on or near the surface of the earth. It is the art of measuring
King County Explorer Search and Rescue. Course B Map & Compass
 King County Explorer Search and Rescue Course B Map & Compass Disclaimer The intent of this presentation is to provide a basic overview of maps, compasses, and location finding. It is not meant to be a
King County Explorer Search and Rescue Course B Map & Compass Disclaimer The intent of this presentation is to provide a basic overview of maps, compasses, and location finding. It is not meant to be a
The 3-D Global Spatial Data Model: Geometrical Foundation of the Global Spatial Data Infrastructure
 The 3-D Global Spatial Data Model: Geometrical Foundation of the Global Spatial Data Infrastructure Earl F. Burkholder, PS, PE Annotated Table of Contents July 8,2006 I. The Global Spatial Data Model (GSDM)
The 3-D Global Spatial Data Model: Geometrical Foundation of the Global Spatial Data Infrastructure Earl F. Burkholder, PS, PE Annotated Table of Contents July 8,2006 I. The Global Spatial Data Model (GSDM)
*1731* e) Define local attraction. State two causes of local attraction. f) State two principles of plane table survey. g) Define horizontal l
 *1731* 1731 21415 3 Hours/1 Marks S e a t o. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Answer each next main question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary.
*1731* 1731 21415 3 Hours/1 Marks S e a t o. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Answer each next main question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary.
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE Department of Civil Engineering CE6304 SURVEYING I Questions Bank UNIT-I FUNDAMENTALS AND CHAIN SURVEYING Part A 1) Define surveying. 2) What are the types of surveying?
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE Department of Civil Engineering CE6304 SURVEYING I Questions Bank UNIT-I FUNDAMENTALS AND CHAIN SURVEYING Part A 1) Define surveying. 2) What are the types of surveying?
Compass Basics. Quick Map Basics Review For Compass Use
 Compass Basics Quick Map Basics Review For Compass Use A topographic map tells you where things are and how to get to them, whether you're hiking, biking, hunting, fishing, or just interested in the world
Compass Basics Quick Map Basics Review For Compass Use A topographic map tells you where things are and how to get to them, whether you're hiking, biking, hunting, fishing, or just interested in the world
USING THE MILITARY LENSATIC COMPASS
 USING THE MILITARY LENSATIC COMPASS WARNING This presentation is intended as a quick summary, and not a comprehensive resource. If you want to learn Land Navigation in detail, either buy a book; or get
USING THE MILITARY LENSATIC COMPASS WARNING This presentation is intended as a quick summary, and not a comprehensive resource. If you want to learn Land Navigation in detail, either buy a book; or get
College of Engineering Tutorial Note 3: Chapter 7
 1 King Saud University CE 431: Highway Engineering College of Engineering Tutorial Note 3: Chapter 7 Civil Engineering Department 7.1 Given Δ = 35, R = 1,350 ft, and the PI station 75 + 8.10, compute the
1 King Saud University CE 431: Highway Engineering College of Engineering Tutorial Note 3: Chapter 7 Civil Engineering Department 7.1 Given Δ = 35, R = 1,350 ft, and the PI station 75 + 8.10, compute the
UNIT 1- CONTROL SURVEYING PART A
 QUESTION BANK (As per Anna University 2013 Regulation) UNIT 1- CONTROL SURVEYING Horizontal and vertical control Methods specifications triangulation- baseline instruments and accessories corrections satellite
QUESTION BANK (As per Anna University 2013 Regulation) UNIT 1- CONTROL SURVEYING Horizontal and vertical control Methods specifications triangulation- baseline instruments and accessories corrections satellite
GPS Measurement Protocol
 GPS Measurement Protocol Purpose To determine the latitude, longitude, and elevation of your school and of all your GLOBE sites Overview The GPS receiver will be used to determine the latitude, longitude
GPS Measurement Protocol Purpose To determine the latitude, longitude, and elevation of your school and of all your GLOBE sites Overview The GPS receiver will be used to determine the latitude, longitude
Low Distortion Projections Part 2 Ground versus Grid
 Blue Marble Geographic Calculator provides an incredible variety of tools for working with an infinite combination of datums and projections. Shown here, I ve entered the parameters for a Low Distortion
Blue Marble Geographic Calculator provides an incredible variety of tools for working with an infinite combination of datums and projections. Shown here, I ve entered the parameters for a Low Distortion
ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
 ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK 10CV34 SURVEYING-I UNIT -01 INTRODUCTION 1. Explain plane surveying and geodetic surveying. 2. Write a note on precision and accuracy
ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK 10CV34 SURVEYING-I UNIT -01 INTRODUCTION 1. Explain plane surveying and geodetic surveying. 2. Write a note on precision and accuracy
1 Line Length I Bearing
 being 6 15'W. Calculate the true bearing of the line also error of closure and relative error of closure. 1 Line Length I Bearing AB 470m 343 52' BC 635 m 87 50' CD 430 m 172 40' DA 563 m 265 12' 9. (a)
being 6 15'W. Calculate the true bearing of the line also error of closure and relative error of closure. 1 Line Length I Bearing AB 470m 343 52' BC 635 m 87 50' CD 430 m 172 40' DA 563 m 265 12' 9. (a)
APPENDIX A GLOSSARY. Appendix A.1
 APPENDIX A GLOSSARY Appendix A.1 Appendix A.2 Back Bearing A back bearing is measured from the object to your position. It is the exact opposite of a direct bearing. Base Line An imaginary line on the
APPENDIX A GLOSSARY Appendix A.1 Appendix A.2 Back Bearing A back bearing is measured from the object to your position. It is the exact opposite of a direct bearing. Base Line An imaginary line on the
Why do we need measurements?
 Why do we need measurements? Some of the earliest surviving measuring devices include gold scales recovered in present-day Greece from the tombs of Mycenaean kings. The tombs of Egyptian pharaohs the pyramids
Why do we need measurements? Some of the earliest surviving measuring devices include gold scales recovered in present-day Greece from the tombs of Mycenaean kings. The tombs of Egyptian pharaohs the pyramids
Measurement of Distance and Elevation Equipment and Procedures
 AMRC 2012 MODULE 2 Measurement of Distance and Elevation Equipment and Procedures CONTENTS Overview... 2-1 Objectives... 2-1 Procedures... 2-1 2.1 Introduction to Methods of Distance Measurement... 2-3
AMRC 2012 MODULE 2 Measurement of Distance and Elevation Equipment and Procedures CONTENTS Overview... 2-1 Objectives... 2-1 Procedures... 2-1 2.1 Introduction to Methods of Distance Measurement... 2-3
T.4 Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry
 424 section T4 T.4 Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry Solving Right Triangles Geometry of right triangles has many applications in the real world. It is often used by carpenters, surveyors, engineers,
424 section T4 T.4 Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry Solving Right Triangles Geometry of right triangles has many applications in the real world. It is often used by carpenters, surveyors, engineers,
Cleveland State University
 CVE 212 - Surveying Lab #1 MEASURING ANGLES & DISTANCES WITH A TOTAL STATION EQUIPMENT EDMI and Tripod Single prism mounted on a prism pole Field book Pencil 2 Walkie Talkies INTRODUCTION Recent developments
CVE 212 - Surveying Lab #1 MEASURING ANGLES & DISTANCES WITH A TOTAL STATION EQUIPMENT EDMI and Tripod Single prism mounted on a prism pole Field book Pencil 2 Walkie Talkies INTRODUCTION Recent developments
DOWNLOAD PDF PLANE AND GEODETIC SURVEYING FOR ENGINEERS
 Chapter 1 : Difference Between Plane Surveying and Geodetic Surveying Geodetic surveying. Effect of the curvature of the earth surface is ignored. The earth surface is assumed to be plane, i.e. two dimensional.
Chapter 1 : Difference Between Plane Surveying and Geodetic Surveying Geodetic surveying. Effect of the curvature of the earth surface is ignored. The earth surface is assumed to be plane, i.e. two dimensional.
Control Surveys and Coordinate Systems
 Control Surveys and Coordinate Systems The Earth is Round Basic Shape of the Earth: Oblate Spheroid of Revolution The length of the equatorial axis is approximately 27 miles greater than the polar axis.
Control Surveys and Coordinate Systems The Earth is Round Basic Shape of the Earth: Oblate Spheroid of Revolution The length of the equatorial axis is approximately 27 miles greater than the polar axis.
Map Reading & Compass Use
 Spring 2013 Kestrel Land Trust Page 2 / 10 Contents Map Basics... 3 Map Types... 3 Terrain Association... 4 Estimating Distance: Pacing... 4 Contour Lines... 5 Navigating with a Compass... 6 Compass Types...
Spring 2013 Kestrel Land Trust Page 2 / 10 Contents Map Basics... 3 Map Types... 3 Terrain Association... 4 Estimating Distance: Pacing... 4 Contour Lines... 5 Navigating with a Compass... 6 Compass Types...
Total station LEICA TPS
 Total station LEICA TPS405 200 The perfect solution for all sites Rugged, adaptable total station with accurate angle measurements, dual-axis compensator, powerful EDM, data output in any format, and application
Total station LEICA TPS405 200 The perfect solution for all sites Rugged, adaptable total station with accurate angle measurements, dual-axis compensator, powerful EDM, data output in any format, and application
Final Exam Review Packet
 Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the length of the missing side. The triangle is not drawn to scale. 6 8 a.
Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the length of the missing side. The triangle is not drawn to scale. 6 8 a.
Last Time. GY 301: Geomorphology. Today s Agenda. Vertical Exaggeration UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA. Another Simple day; Topographic Profiles
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 301: Geomorphology Lecture 5: Alidade & Plane Table Methods Last Time Another Simple day; Topographic profiles Drawing topographic profiles Vertical exaggeration Topographic
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 301: Geomorphology Lecture 5: Alidade & Plane Table Methods Last Time Another Simple day; Topographic profiles Drawing topographic profiles Vertical exaggeration Topographic
USING THE MILITARY LENSATIC COMPASS
 USING THE MILITARY LENSATIC COMPASS WARNING This presentation is intended as a quick summary, and not a comprehensive resource. If you want to learn Land Navigation in detail, either buy a book; or get
USING THE MILITARY LENSATIC COMPASS WARNING This presentation is intended as a quick summary, and not a comprehensive resource. If you want to learn Land Navigation in detail, either buy a book; or get
DETERMINATION OF AREA OF POLYGON BY CHAIN AND CROSS STAFF SURVEY 1. AIM:
 Expt. No: 2 Date: DETERMINATION OF AREA OF POLYGON BY CHAIN AND CROSS STAFF SURVEY 1. AIM: To determine the area of a given field with define boundary by conducting cross staff survey. 2. INSTRUMENTS REQUIRED:
Expt. No: 2 Date: DETERMINATION OF AREA OF POLYGON BY CHAIN AND CROSS STAFF SURVEY 1. AIM: To determine the area of a given field with define boundary by conducting cross staff survey. 2. INSTRUMENTS REQUIRED:
Preventing Coordinate- System Confusion (maybe?)
 Preventing Coordinate- System Confusion (maybe?) Montana Association of Registered Land Surveyors 2008 Convention Bozeman, Montana 07 & 08 February 2008 Glenn Borkenhagen Inland GPS Inc. - Cody, Wyoming
Preventing Coordinate- System Confusion (maybe?) Montana Association of Registered Land Surveyors 2008 Convention Bozeman, Montana 07 & 08 February 2008 Glenn Borkenhagen Inland GPS Inc. - Cody, Wyoming
Basic Principles of Surveying and Mathematics
 AMRC 2012 MODULE 1 Basic Principles of Surveying and Mathematics CONTENTS Overview... 1-1 Objectives... 1-1 Procedures... 1-1 1.1 Surveying Defined... 1-3 1.2 Types of Surveys... 1-5 1.3 Precision and
AMRC 2012 MODULE 1 Basic Principles of Surveying and Mathematics CONTENTS Overview... 1-1 Objectives... 1-1 Procedures... 1-1 1.1 Surveying Defined... 1-3 1.2 Types of Surveys... 1-5 1.3 Precision and
West Virginia University Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Course Syllabus
 West Virginia University Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Course Syllabus Course: CE 305 - Introduction to Geomatics Semester: Summer 2012 (6 weeks) May 21 June 29 Course Format And Credit
West Virginia University Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Course Syllabus Course: CE 305 - Introduction to Geomatics Semester: Summer 2012 (6 weeks) May 21 June 29 Course Format And Credit
Day 6: Angles of Depression and Elevation. Unit 5: Trigonometric Functions
 + Day 6: Angles of Depression and Elevation Unit 5: Trigonometric Functions Warm Up + n Find the missing side length 1) 2) n Find the missing angle 10 minutes 3) 4) End + Homework Check + Today s Objective
+ Day 6: Angles of Depression and Elevation Unit 5: Trigonometric Functions Warm Up + n Find the missing side length 1) 2) n Find the missing angle 10 minutes 3) 4) End + Homework Check + Today s Objective
Introduction to Land Measurement (Field Surveying and Navigation)
 Introduction to Land Measurement (Field Surveying and Navigation) ESRM 304 Peter Schiess / Eric Turnblom 1 of 37 Overview Overview of surveying Survey mathematics Collecting and recording data Correcting
Introduction to Land Measurement (Field Surveying and Navigation) ESRM 304 Peter Schiess / Eric Turnblom 1 of 37 Overview Overview of surveying Survey mathematics Collecting and recording data Correcting
ch02.pdf chap2.pdf chap02.pdf
 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
Projections & GIS Data Collection: An Overview
 Projections & GIS Data Collection: An Overview Projections Primary data capture Secondary data capture Data transfer Capturing attribute data Managing a data capture project Geodesy Basics for Geospatial
Projections & GIS Data Collection: An Overview Projections Primary data capture Secondary data capture Data transfer Capturing attribute data Managing a data capture project Geodesy Basics for Geospatial
In such cases, direction may be used for the location of a point by any of the following methods:
 COMPASS SURVEYING Surveying is concerned with the relative location of points on, above or below the surface of the earth. It therefore becomes necessary to start from known points on a line. If the location
COMPASS SURVEYING Surveying is concerned with the relative location of points on, above or below the surface of the earth. It therefore becomes necessary to start from known points on a line. If the location
HORIZONTAL PROJECTION PARAMETERS: DANE COUNTY COORDINATES
 Recommended RTK GPS Configuration Parameters for the City of Madison, WI Base Station Compiled by: Dan Rodman RLS, City of Madison (608)266-6674 drodman@cityofmadison.com For base station information see
Recommended RTK GPS Configuration Parameters for the City of Madison, WI Base Station Compiled by: Dan Rodman RLS, City of Madison (608)266-6674 drodman@cityofmadison.com For base station information see
CHENDU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SUB CODE & SUB NAME : CE6404 SURVEYING II
 CHENDU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SUB CODE & SUB NAME : CE6404 SURVEYING II UNIT I CONTROL SURVEYING PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What is the main principle involved in
CHENDU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SUB CODE & SUB NAME : CE6404 SURVEYING II UNIT I CONTROL SURVEYING PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What is the main principle involved in
What you learned. Lecture 27: Class Summary. Maps and geodesy. How you learned it
 What you learned Geography 12: Maps and Spatial Reasoning Lecture 27: Class Summary Professor Keith Clarke Map geometry, construction and content Practical map use, reading and navigation Map representation
What you learned Geography 12: Maps and Spatial Reasoning Lecture 27: Class Summary Professor Keith Clarke Map geometry, construction and content Practical map use, reading and navigation Map representation
Chapter-2 Direct Measurement Indirect Measurement Method of linear measurement Taping corrections Optical measurement Tachometry EDM Measurement
 Chapter-2 Direct Measurement Indirect Measurement Method of linear measurement Taping corrections Optical measurement Tachometry EDM Measurement 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Methods There are 3 methods of making linear
Chapter-2 Direct Measurement Indirect Measurement Method of linear measurement Taping corrections Optical measurement Tachometry EDM Measurement 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Methods There are 3 methods of making linear
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 INTRODUCTION We currently live in what is often termed the information age. Aided by new and emerging technologies, data are being collected at unprecedented rates in all walks
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 INTRODUCTION We currently live in what is often termed the information age. Aided by new and emerging technologies, data are being collected at unprecedented rates in all walks
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections
 NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
D) sin A = D) tan A = D) cos B =
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function requested. Write your answer as a fraction in lowest terms. 1) 1) Find sin A.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function requested. Write your answer as a fraction in lowest terms. 1) 1) Find sin A.
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems.
 Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
GEOMATICS ENGINEERING
 GEOMATICS ENGINEERING CHAPTER 2 Direct and Indirect Distance Measurement Methods Distance Measurement Methods Equipment Classification Usage Fieldwork procedure Booking system Adjustment and plotting Introduction
GEOMATICS ENGINEERING CHAPTER 2 Direct and Indirect Distance Measurement Methods Distance Measurement Methods Equipment Classification Usage Fieldwork procedure Booking system Adjustment and plotting Introduction
MAHATMA GANDHI MISSION S JAWAHARLAL NEHRU ENGINEERING COLLEGE, AURANGABAD. (M.S.)
 MAHATMA GANDHI MISSION S JAWAHARLAL NEHRU ENGINEERING COLLEGE, AURANGABAD. (M.S.) DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SURVEYING - II LAB MANUAL Prof.R.V.Wanjule Approved By Lab Incharge Dr. S. B. Shinde H.O.D.
MAHATMA GANDHI MISSION S JAWAHARLAL NEHRU ENGINEERING COLLEGE, AURANGABAD. (M.S.) DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SURVEYING - II LAB MANUAL Prof.R.V.Wanjule Approved By Lab Incharge Dr. S. B. Shinde H.O.D.
22X Builder s Transit Level Model No Instruction Manual
 2595H 7/29/09 10:15 AM Page 1 22X Builder s Transit Level Model No. 40-6910 Instruction Manual Congratulations on your choice of this 22X Builder s Transit Level. We suggest you read this instruction manual
2595H 7/29/09 10:15 AM Page 1 22X Builder s Transit Level Model No. 40-6910 Instruction Manual Congratulations on your choice of this 22X Builder s Transit Level. We suggest you read this instruction manual
Using Map and Compass Together
 Using Map and Compass Together In situations where you foresee a potential evacuation on foot, where there are no roads, and no indication as to the direction of travel (i.e., road signs), it is recommended
Using Map and Compass Together In situations where you foresee a potential evacuation on foot, where there are no roads, and no indication as to the direction of travel (i.e., road signs), it is recommended
Old Math 120 Exams. David M. McClendon. Department of Mathematics Ferris State University
 Old Math 10 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University 1 Contents Contents Contents 1 General comments on these exams 3 Exams from Fall 016 4.1 Fall 016 Exam 1...............................
Old Math 10 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University 1 Contents Contents Contents 1 General comments on these exams 3 Exams from Fall 016 4.1 Fall 016 Exam 1...............................
Meeting the ODOT Survey & Mapping Specifications
 Meeting the ODOT Survey & Mapping Specifications A Simple Solution Presented by Ray Foos, P.S, ODOT CADD & Mapping Services & Jon Keller, P.S., ODOT District 3 Phases of an ODOT Survey Project Research
Meeting the ODOT Survey & Mapping Specifications A Simple Solution Presented by Ray Foos, P.S, ODOT CADD & Mapping Services & Jon Keller, P.S., ODOT District 3 Phases of an ODOT Survey Project Research
Physics 101. Hour Exam I Spring Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name:
 Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators may not be shared. Please keep your calculator on your own desk.
Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators may not be shared. Please keep your calculator on your own desk.
Trigonometry Unit 5. Reflect previous TEST mark, Overall mark now. Looking back, what can you improve upon?
 1 U n i t 5 11C Date: Name: Tentative TEST date Trigonometry Unit 5 Reflect previous TEST mark, Overall mark now. Looking back, what can you improve upon? Learning Goals/Success Criteria Use the following
1 U n i t 5 11C Date: Name: Tentative TEST date Trigonometry Unit 5 Reflect previous TEST mark, Overall mark now. Looking back, what can you improve upon? Learning Goals/Success Criteria Use the following
Test Bank Chapter 2: Representations of Earth
 Multiple Choice Test Bank Chapter 2: Representations of Earth 1. A rhumb line on a Mercator projection is a line of. a. true size b. true shape c. true compass bearing d. true location 2. Maximum longitude
Multiple Choice Test Bank Chapter 2: Representations of Earth 1. A rhumb line on a Mercator projection is a line of. a. true size b. true shape c. true compass bearing d. true location 2. Maximum longitude
BUILDING AN ACCURATE GIS
 BUILDING AN ACCURATE GIS 2006 GIS in the Rockies Denver, Colorado September 13, 2006 William E. Linzey United States Department of Commerce National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration National Geodetic
BUILDING AN ACCURATE GIS 2006 GIS in the Rockies Denver, Colorado September 13, 2006 William E. Linzey United States Department of Commerce National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration National Geodetic
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts. -Coordinate Systems -Datum
 Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Surveying Prof. Bharat Lohani Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Module 5 Lecture 1
 Surveying Prof. Bharat Lohani Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur (Refer Slide Time: 00:20) Module 5 Lecture 1 Welcome to this another lecture on basic surveying. Today we are going to start a new module.
Surveying Prof. Bharat Lohani Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur (Refer Slide Time: 00:20) Module 5 Lecture 1 Welcome to this another lecture on basic surveying. Today we are going to start a new module.
PRIMARY CONTROL SURVEYS
 STATE CONTROL SURVEY SPECIFICATIONS FOR PRIMARY CONTROL SURVEYS Now Obsolete Caution: This document has been prepared by scanning the original Specifications for Primary Control Surveys - 1984 and using
STATE CONTROL SURVEY SPECIFICATIONS FOR PRIMARY CONTROL SURVEYS Now Obsolete Caution: This document has been prepared by scanning the original Specifications for Primary Control Surveys - 1984 and using
1. The horizontal beam represented in Examination Figure 6 carries three loads P 1. and R 2
 Student ID: 52573847 Exam: 286037RR - Engineering Mechanics, Part 2 When you have completed your exam and reviewed your answers, click Submit Exam. Answers will not be recorded until you hit Submit Exam.
Student ID: 52573847 Exam: 286037RR - Engineering Mechanics, Part 2 When you have completed your exam and reviewed your answers, click Submit Exam. Answers will not be recorded until you hit Submit Exam.
Unit 3 Right Triangle Trigonometry - Classwork
 Unit 3 Right Triangle Trigonometry - Classwork We have spent time learning the definitions of trig functions and finding the trig functions of both quadrant and special angles. But what about other angles?
Unit 3 Right Triangle Trigonometry - Classwork We have spent time learning the definitions of trig functions and finding the trig functions of both quadrant and special angles. But what about other angles?
Practice Questions - Revision
 Practice Questions - Revision Question 1: (a) The data from a survey, are shown below. Use either the Rise and Fall method or the Height of Plane of Collimation (HPC) method to reduce the data. Use arithmetic
Practice Questions - Revision Question 1: (a) The data from a survey, are shown below. Use either the Rise and Fall method or the Height of Plane of Collimation (HPC) method to reduce the data. Use arithmetic
UNIT What is basic principle on which Surveying has been classified? And explain them?
 Short Answer Type Questions: UNIT-1 1. State the Objectives of Surveying? 2. What is basic principle on which Surveying has been classified? And explain them? 3. Differentiate between Plane Surveying &
Short Answer Type Questions: UNIT-1 1. State the Objectives of Surveying? 2. What is basic principle on which Surveying has been classified? And explain them? 3. Differentiate between Plane Surveying &
Introduction to Measurements. Introduction to Measurements. Introduction to Measurements. Introduction to Measurements. Introduction to Measurements
 CIVL 1112 Surveying - Precision and 1/8 Typically, we are accustomed to counting but not measuring. Engineers are concerned with distances, elevations, volumes, direction, and weights. Fundamental principle
CIVL 1112 Surveying - Precision and 1/8 Typically, we are accustomed to counting but not measuring. Engineers are concerned with distances, elevations, volumes, direction, and weights. Fundamental principle
4 Survey Datums. 4.1 Horizontal Datum Policy SURVEY DATUMS SEPTEMBER 2006
 4 Survey Datums Today s multi-organizational Project Development efforts require the use of common, accurate horizontal and vertical survey datums and consistent, precise control-survey procedures to ensure
4 Survey Datums Today s multi-organizational Project Development efforts require the use of common, accurate horizontal and vertical survey datums and consistent, precise control-survey procedures to ensure
This week s topics. Week 6. FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications. Week 6
 FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 6 Week 6 Last week Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS databases Chapter 11 Overlay processes Questions? Next week
FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 6 Week 6 Last week Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS databases Chapter 11 Overlay processes Questions? Next week
Surveying I. Unit - I. Different methods and instruments are being used to facilitate the work of
 Surveying I Unit - I Definition of Survey Surveying is the art of determining the relative positions of different objects on the surface of the earth by measuring the horizontal distances between them,
Surveying I Unit - I Definition of Survey Surveying is the art of determining the relative positions of different objects on the surface of the earth by measuring the horizontal distances between them,
SURVEYING 1 CE 215 CHAPTER -3- LEVEL AND LEVELING
 Civil Engineering Department SURVEYING 1 CE 215 CHAPTER -3- LEVEL AND LEVELING 1 CHAPTER -3- LEVEL AND LEVELING 2 1 CONTENTS 1. Level instrument 2. Bubble 3. Tripod 4. Leveling staff 5. Definitions 6.
Civil Engineering Department SURVEYING 1 CE 215 CHAPTER -3- LEVEL AND LEVELING 1 CHAPTER -3- LEVEL AND LEVELING 2 1 CONTENTS 1. Level instrument 2. Bubble 3. Tripod 4. Leveling staff 5. Definitions 6.
FORCE TABLE INTRODUCTION
 FORCE TABLE INTRODUCTION All measurable quantities can be classified as either a scalar 1 or a vector 2. A scalar has only magnitude while a vector has both magnitude and direction. Examples of scalar
FORCE TABLE INTRODUCTION All measurable quantities can be classified as either a scalar 1 or a vector 2. A scalar has only magnitude while a vector has both magnitude and direction. Examples of scalar
FOR 274 Assignment 3 [20 points] This assignment should be completed and handed at the start of lecture on Friday 16th September.
![FOR 274 Assignment 3 [20 points] This assignment should be completed and handed at the start of lecture on Friday 16th September. FOR 274 Assignment 3 [20 points] This assignment should be completed and handed at the start of lecture on Friday 16th September.](/thumbs/90/101578770.jpg) FOR 274 Assignment 3 [20 points] Name: This assignment should be completed and handed at the start of lecture on Friday 16th September. 1. Convert the following bearings to azimuths: a. N35 W b. S22 E
FOR 274 Assignment 3 [20 points] Name: This assignment should be completed and handed at the start of lecture on Friday 16th September. 1. Convert the following bearings to azimuths: a. N35 W b. S22 E
Find the perimeter of the figure named and shown. Express the perimeter in the same unit of measure that appears on the given side or sides.
 Mth101 Chapter 8 HW Name Find the perimeter of the figure named and shown. Express the perimeter in the same unit of measure that appears on the given side or sides. 1) 1) Rectangle 6 in. 12 in. 12 in.
Mth101 Chapter 8 HW Name Find the perimeter of the figure named and shown. Express the perimeter in the same unit of measure that appears on the given side or sides. 1) 1) Rectangle 6 in. 12 in. 12 in.
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems
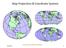 Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/7/2017 1 Why? Laying the Earth Flat Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveying instruments measure
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/7/2017 1 Why? Laying the Earth Flat Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveying instruments measure
B. Topographic maps are also called. contour maps
 Topographic Maps Introduction A. Topographic maps are essential tools in geologic and engineering studies because they show the configuration of Earth's surface in remarkable detail and permit one to measure
Topographic Maps Introduction A. Topographic maps are essential tools in geologic and engineering studies because they show the configuration of Earth's surface in remarkable detail and permit one to measure
Geographic coordinate systems
 1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
Trigonometry Project Student Package
 Trigonometry Project Student Package AWM11 Name: Date: What I can do in this unit 4-1a Label a right triangle with Opposite, Adjacent, and Hypotenuse. Level 4-1b Solve for side lengths of right triangles
Trigonometry Project Student Package AWM11 Name: Date: What I can do in this unit 4-1a Label a right triangle with Opposite, Adjacent, and Hypotenuse. Level 4-1b Solve for side lengths of right triangles
Geographers Perspectives on the World
 What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
Measuring Trees Activity
 What is a Clinometer? Measuring Trees Activity It is an instrument for measuring slope angle of a line of sight. It is included in some compasses. How to make a Clinometer? Materials Needed: piece of cardboard
What is a Clinometer? Measuring Trees Activity It is an instrument for measuring slope angle of a line of sight. It is included in some compasses. How to make a Clinometer? Materials Needed: piece of cardboard
Lecture 4. Coordinate Systems & Projections
 Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
How to Use a Compass with a USGS Topographic Map
 How to Use a Compass with a USGS Topographic Map METHOD #1: (these directions assume your orienting arrow lines up with the North indicator on your compass dial, meaning the compass has not been adjusted
How to Use a Compass with a USGS Topographic Map METHOD #1: (these directions assume your orienting arrow lines up with the North indicator on your compass dial, meaning the compass has not been adjusted
To convert a speed to a velocity. V = Velocity in feet per seconds (ft/sec) S = Speed in miles per hour (mph) = Mathematical Constant
 To convert a speed to a velocity V S ( 1.466) V Velocity in feet per seconds (ft/sec) S Speed in miles per hour (mph) 1.466 Mathematical Constant Example Your driver just had a rear-end accident and says
To convert a speed to a velocity V S ( 1.466) V Velocity in feet per seconds (ft/sec) S Speed in miles per hour (mph) 1.466 Mathematical Constant Example Your driver just had a rear-end accident and says
