ECEN326: Electronic Circuits Fall 2017
|
|
|
- Austin Barrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECEN6: Electnic Cicuits Fall 07 Lectue : Diffeential Aplifies Sa Pale Anal & Mixed-Sinal Cente Texas A&M Uniesity
2 Annunceents Lab Use the updated Lab specs psted n the website Get the actual 6 lab kit f the MSC Bkste HW is psted n the website and due 0/4 eadin azai Chapte 0
3 Aenda Geneal cnsideatins Bipla diffeential pai MOS diffeential pai Cascde diffeential aplifies Cn-de ejectin Diffeential pai with actie lad
4 Audi Aplifie Exaple An audi aplifie is cnstucted abe that takes n a ectified AC ltae as its supply and aplifies an audi sinal f a icphne. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 4
5 Huin Nise in Audi Aplifie Exaple Undesied pwe supply nise cpnent Desied utput sinal in, DC in ut CC C C A in CC Hwee, CC cntains a ipple f ectificatin that leaks t the utput and is peceied as a huin nise by the use. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 5
6 Supply ipple ejectin X Y X A Y in A in Since bth nde X and Y cntain the ipple,, thei diffeence will be fee f ipple. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 6
7 ipple-fee Diffeential Output Since the sinal is taken as a diffeence between tw ndes, an aplifie that senses diffeential sinals is needed. Hw can we cnstuct this diffeential aplifie? CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 7
8 Cn nputs t Diffeential Aplifie X Y X A in A in 0 Y Sinals cannt be applied in phase t the inputs f a diffeential aplifie, since the utputs will als be in phase, pducin ze diffeential utput. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 8
9 Diffeential nputs t Diffeential Aplifie X A in Y A in X Y A in When the inputs ae applied diffeentially, the utputs ae 80 ut f phase; enhancin each the when sensed diffeentially. Pides twice the utput swin f the iinal aplifie CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 9
10 Diffeential Sinals A pai f diffeential sinals can be eneated, an the ways, by a tansfe. Diffeential sinals hae the ppety that they shae the sae aeae alue t und and ae equal in anitude but ppsite in phase. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 0
11 Sinle-ended s. Diffeential Sinals Sinle-Ended Sinals Measued with espect t the cn und eside n ne line nde Diffeential Sinals Measued between tw ndes eside n tw diffeential lines ndes ut sint CM sint CM sint CM sint CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies
12 Sinle-Ended & Diffeential Sinals A sinle-ended sinal is easued with espect t a fixed ptential (und) A diffeential sinal is easued between tw equal and ppsite sinals which swin aund a fixed ptential (cn-de leel) Yu can decpse diffeential sinals int a diffeential de (diffeence) and a cn-de (aeae) Sinle-Ended Sinal Diffeential Sinal DM ut ut CM ut ut
13 Sinle-Ended & Diffeential Aplifies Diffeential sinalin adantaes Cn-de nise ejectin Hihe (ideally duble) ptential utput swin Siple biasin ped lineaity Main disadantae is aea, which is uhly duble Althuh, t et the sae pefance in sinle-ended desins, we ften hae t incease the aea daatically DD Max Output Swin DD Max Output Swin GS Tn GS Tn
14 Cn-Mde Leel Sensitiity A desin which uses tw sinle-ended aplifies t ealize a diffeential aplifie is ey sensitie t the cn-de input leel The tansists bias cuent and tanscnductance can ay daatically with the cn-de input pacts sall-sinal ain Chanes the utput cn-de, which ipacts the axiu utput swin 4
15 Aenda Geneal cnsideatins Bipla diffeential pai MOS diffeential pai Cascde diffeential aplifies Cn-de ejectin Diffeential pai with actie lad 5
16 Diffeential Pai With the additin f a tail cuent, the cicuits abe peate as an eleant, yet bust diffeential pai. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 6
17 Cn-Mde espnse Assuin f siplicity EE EE BE C X C Y BE EE CC C EE CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 7
18 Cn-Mde ejectin Due t the fixed tail cuent suce, the input cn-de alue can ay withut chanin the utput cnde alue. Lwe liit f CM als ccus due t the equieent f a iniu cpliance ltae Assuin BC =0 f satuatin ( CE ~0.7) acss a eal cuent suce Often we allw f BC =0.4 CE ~0. and still cnside actie de peatin, althuh this is fally sft satuatin n any pbles, ll ake it clea what assuptins t use CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 8
19 Diffeential espnse Bi Diffeential nput Cutff EE ~. C C X Y 0 EE CC CC C EE CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 9
20 Diffeential espnse Bi Diffeential nput Cutff ~. EE C C Y X 0 EE CC CC C EE CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 0
21 Diffeential Pai Chaacteistics Tansist Cuents Output Cn Mde Output ltaes CC C EE Nne-ze diffeential input pduces aiatins in utput cuents and ltaes, wheeas cn-de input pduces n aiatins. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies
22 Sall-Sinal Analysis C C EE EE Since the input t Q and Q ises and falls by the sae aunt, and thei bases ae tied tethe, the ise in C has the sae anitude as the fall in C. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies
23 CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies itual Gund F sall chanes at inputs, the s ae the sae, and the espectie incease and decease f C and C ae the sae, nde P ust stay cnstant t accdate these chanes. Theefe, nde P can be iewed as AC und. C C P 0 Because C C P C P C
24 CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 4 Sall-Sinal Diffeential Gain Since the utput chanes by - C and input by, the sall sinal ain is C, siila t that f the CE stae. Hwee, t btain sae ain as the CE stae, pwe dissipatin is dubled. C C diff Y X A C Y C X C C
25 CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 5 Lae Sinal Analysis ln ln ln KL aund the input netwk Witin a. ln ln Usin. C C T S C T S C T BE BE in in BE in P BE in S C T BE S C T BE S C e T BE
26 Lae Sinal Analysis C. Witin a KCL at nde P C C exp EE C exp in in T T C 4. Cbinin peius KL equatin with the KCL in in exp EE in EE C T EE in 5. F cicuit syety exp exp EE in in T T in in CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 6
27 nput/output Chaacteistics C C EE exp exp exp in in EE in T T T in in in ut in in tanh CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 7 C EE ut f in - in 4 T = 04, the ajity f the cuent is steeed thuh Q T
28 Linea/Nnlinea eins The left clun peates in linea ein, wheeas the iht clun peates in nnlinea ein. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 8
29 Sall-Sinal Mdel We can use the itual GND cncept discussed in Slide 4 t siplify this CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 9
30 itual GND Pf 0 0 that which iplies and usin the abe KL, peatin F diffeential and F sall sinals 0 KCL at nde P. KL aund the input netwks. in P in in in in P in
31 Half Cicuits ut ut ut in ut ut ut in C C in in C Since P is unded, we can teat the diffeential pai as tw CE half cicuits, with half the utput swin n eithe side f the cicuit is syetical, we can just analyze the half-cicuit with a itual und t et the ain equatin CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies
32 Exaple: Diffeential Gain w/ finite ut in ut in O CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies
33 Extensin f itual Gund Syety Axis X 0 t can be shwn that if =, and pints A and B up and dwn by the sae aunt espectiely, X des nt e. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies
34 Half Cicuit Exaple A CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 4 O O
35 Half Cicuit Exaple A CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 5 O O
36 Half Cicuit Exaple assuin f siplicity A CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 6 E C
37 Half Cicuit Exaple assuin f siplicity A E CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 7 C
38 BJT Diffeential Pai nput esistance 8 n de t btain the diffeential input esistance, apply a test diffeential ltae X and find the deelped cuent i X i i i X X in X X X Diffeential
39 Aenda Geneal cnsideatins Bipla diffeential pai MOS diffeential pai Cascde diffeential aplifies Cn-de ejectin Diffeential pai with actie lad 9
40 MOS Diffeential Pai s Cn-Mde espnse SS SS X Y DD D SS Siila t its bipla cuntepat, MOS diffeential pai pduces ze diffeential utput as CM chanes. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 40
41 Equilibiu Oedie ltae Usin Satuatin D nc x W L GS TH SS SS GS TH equil C n SS x W L The equilibiu edie ltae is defined as the edie ltae seen by M and M when bth cay an SS / cuent Lae tail cuent salle W/L esults in a lae equilibiu edie ltae CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 4
42 Miniu Cn-de Output ltae DD D SS CM TH n de t aintain M and M in satuatin, the cnde utput ltae cannt fall belw the alue abe. This alue usually liits ltae ain. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 4
43 Diffeential espnse CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 4
44 Sall-Sinal espnse 0 A P D Siila t its bipla cuntepat, the MOS diffeential pai exhibits the sae itual und nde and sall sinal ain. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 44
45 Pwe and Gain Tadeff n de t btain the suce ain as a CS stae, a MOS diffeential pai ust dissipate twice the aunt f cuent (assuin the sae MOSFET edie ltae). This pwe and ain tadeff is als eched in its bipla cuntepat. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 45
46 MOS Diffeential Pai s Lae-Sinal espnse. Witin a in D Usin in in GS D in in in nc GS Squain bth sides KL aund the input netwk GS. Witin a KCL at the tail nde D SS x C n W L GS x W L GS D TH C n x D W L and GS D D D CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 46 TH D C n x n C W L D x W L SS D D
47 MOS Diffeential Pai s Lae-Sinal espnse Afte se alebaic anipulatins (see azai0..), can shw that D D D SS SS D in in nc 4 4 x in in W L C n C SS in n x x W L W L in 4 4 SS 4 n SS C C x n C W L n x CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 47 x W L W L in in in in in in *Nte, this equatin is nly alid f a cetain axiu input diffeential ltae in in
48 Maxiu Diffeential nput ltae ncx W 4 D D in in L W ncx L The abe equatin is nly alid when bth This stps when GS TH C n GS SS x SS W L TH and GS M in and M suppts a full in SS ae n. alue. Thee exists a finite diffeential input ltae that cpletely stees the tail cuent f ne tansist t the the. This alue is knwn as the axiu diffeential input ltae. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 48 in in ax GS TH equil C n SS x W L
49 Cntast Between MOS and Bipla Diffeential Pais MOS Bipla ut ut D nc x W L SS in in 4 C n x W L in in ut ut C EE in in tanh T n a MOS diffeential pai, thee exists a finite diffeential input ltae t cpletely switch the cuent f ne tansist t the the, wheeas, in a bipla pai that ltae is infinite. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 49
50 The effects f Dublin the Tail Cuent Since SS is dubled and W/L is unchaned, the equilibiu edie ltae f each tansist ust incease by t accdate this chane, thus in,ax inceases by as well. Mee, since SS is dubled, the diffeential utput swin will duble. Sall sinal ain als inceases by Linea input ane inceases, assuin D alue is sall enuh t keep tansists in satuatin CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 50
51 The effects f Dublin W/L Since W/L is dubled and the tail cuent eains unchaned, the equilibiu edie ltae will be lweed by t accdate this chane, thus in,ax will be lweed by as well. Mee, the diffeential utput swin will eain unchaned since neithe SS n D has chaned Sall sinal ain inceases by Linea input ane deceases CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 5
52 Sall-Sinal Analysis f MOS Diffeential Pai nc x W L D SS SS SS C in D in nc 4 C n x x W L W L in n in x W L 4 C n x W L in in in in in in When the input diffeential sinal is sall cpaed t 4 SS / n C x (W/L), the utput diffeential cuent is linealy pptinal t it, and sall-sinal del can be applied. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 5
53 itual Gund and Half Cicuit ut ut ut ut C C in in 0 A P C Applyin the sae analysis as the bipla case, we will aie at the sae cnclusin that nde P will nt e f sall input sinals and the cncept f half cicuit can be used t calculate the ain. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 5
54 Sall-Sinal pedance: Siple Cuent Suce (Finite ) ut 54
55 Sall-Sinal pedance: Dide Lad (Finite ) ut 55
56 Sall-Sinal pedance: Lkin nt Suce (Finite and b ) 56 b b ut b b i
57 Sall-Sinal pedance: Lkin nt Suce w/ D (Finite and b ) ut b D 57
58 CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 58 MOS Diffeential Pai Half Cicuit Exaple 0 O O A ut
59 MOS Diffeential Pai Half Cicuit Exaple A CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 59 0
60 MOS Diffeential Pai Half Cicuit Exaple A 0 CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 60 SS DD
61 Aenda Geneal cnsideatins Bipla diffeential pai MOS diffeential pai Cascde diffeential aplifies Cn-de ejectin Diffeential pai with actie lad 6
62 Maxiu Diffeential Aplifie Gain w/ finite ut in ut in O With ideal cuent suce lads, the diffeential ain is liited by the intinsic tansist ain ( ) Hw t incease the ain futhe? Use a tply which bsts the utput esistance 6
63 Bipla Cascde Tply 6 x x 0 KCL at the utput nde Witin a ut x x x i i i i i i The dinant te is the btt effectie esistance bsted by the ain f the tp tansist ( )
64 CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 64 Bipla Cascde Diffeential Pai ut Cascde Output esistance A Gain is uhly squaed elatie t the siple diffeential pai Tade-ff is educed utput ltae swin ane Sliht appxiatin hee. Me when we study Cascdes in detail.
65 CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 65 Bipla Telescpic Cascde A
66 CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 66 Exaple: Bipla Telescpic Paasitic esistance p O O O O O O O p A ) (
67 MOS Cascde Tply 67 0 KCL at the utput nde Witin a ut x x x i i i i i i The dinant te is the btt effectie esistance bsted by the ain f the tp tansist ( ) x x
68 CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 68 MOS Cascde Diffeential Pai A ut Cascde Output esistance Gain is uhly squaed elatie t the siple diffeential pai Tade-ff is educed utput ltae swin ane
69 MOS Telescpic Cascde A CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 69 ( 5 O5 7 O O O )
70 CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 70 Exaple: MOS Telescpic Paasitic esistance p A
71 Aenda Geneal cnsideatins Bipla diffeential pai MOS diffeential pai Cascde diffeential aplifies Cn-de ejectin Diffeential pai with actie lad 7
72 Effect f Finite Tail pedance C ut, CM in, CM Assuin = f the tail cuent suce is nt ideal, then when a input CM ltae is applied, the cuents in Q and Q and hence utput CM ltae will chane. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 7 EE C / /
73 nput CM Nise with deal Tail Cuent CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 7
74 nput CM Nise with Nn-ideal Tail Cuent Cn-de nise is nw tansfeed t the sinle-ended utputs Hwee, utput diffeential sinal is still ideally unaffected by cnde nise CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 74
75 Cpaisn As it can be seen, the diffeential utput ltaes f bth cases ae the sae. S f sall input CM nise, the diffeential pai is nt affected. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 75
76 CM t DM Cnesin, A CM-DM f finite tail ipedance and asyety ae bth pesent, then the diffeential utput sinal will cntain a ptin f input cn-de sinal. ut D Assuin hih CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 76 ut D CM CM ut ut D A net cuent f ut CM in the diff. pai tansists and D D will flw thuh GS D GS D SS D D D CM D SS CM SS SS D SS D GS D SS GS D D
77 CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 77 Exaple: A CM-DM A C ut C CM ut DM CM
78 CM C C CM C C EE A A CM DM C DM C C EE CM defines the ati f wanted aplified diffeential input sinal t unwanted cneted input cn-de nise that appeas at the utput. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 78
79 Aenda Geneal cnsideatins Bipla diffeential pai MOS diffeential pai Cascde diffeential aplifies Cn-de ejectin Diffeential pai with actie lad 79
80 Diffeential t Sinle-ended Cnesin Siple OpAp Many cicuits equie a diffeential t sinle-ended cnesin, hwee, the abe tply is nt ey d. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 80
81 Supply Nise Cuptin The st citical dawback f this tply is supply nise cuptin, since n cn-de cancellatin echanis exists. Als, we lse half f the sinal. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 8
82 Gain eductin in in in ut ut in in in C in in in in in C C The st citical dawback f this tply is supply nise cuptin, since n cn-de cancellatin echanis exists. Als, we lse half f the sinal. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 8
83 Bette Altenatie Cuent Mi Actie Lad This cicuit tply pefs diffeential t sinle-ended cnesin with n lss f ain. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 8
84 Actie Lad ~ EE With cuent i used as the lad, the sinal cuent pduced by the Q can be eplicated nt Q 4. This type f lad is diffeent f the cnentinal static lad and is knwn as an actie lad. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 84
85 Diffeential Pai with Actie Lad EE ut L The input diffeential pai deceases the cuent dawn f L by and the actie lad pushes an exta int L by cuent i actin; these effects enhance each the. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 85
86 Actie Lad s. Static Lad Actie Lad Static Lad The lad n the left espnds t the input sinal and enhances the sinle-ended utput, wheeas the lad n the iht des nt. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 86
87 MOS Diffeential Pai with Actie Lad ut L SS SS SS Siila t its bipla cuntepat, MOS diffeential pai can als use actie lad t enhance its sinle-ended utput. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 87
88 Asyetic Diffeential Pai Because f the astly diffeent esistance anitude at the dains f M and M, the ltae swins at these tw ndes ae diffeent and theefe nde P cannt be iewed as a itual und. CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 88
89 Theenin Equialent f the nput Pai T Find The The The N N CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 89 N ( ) in in
90 CH 0 Diffeential Aplifies 90 Siplified Diffeential Pai with Actie Lad ) ( OP ON N in in ut P N N in in ut P ut The ut The P P The ut The ut The The The The ut ut A The ut The A E A and and and since 0 0 KCL at the utput nde Witin a diided esin f can be iewed as a
91 Next Tie Cascde Staes & Cuent Mis azai Chapte 9 9
Exercises for Cascode Amplifiers. ECE 102, Fall 2012, F. Najmabadi
 Execises f Cascde plifies ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabadi F. Najabadi, ECE0, Fall 0 /6 Execise : Cpute assue and Eey Cascde stae inceases by uble Cascde Execise : Cpute all indicated s, s, and i s. ssue tansists
Execises f Cascde plifies ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabadi F. Najabadi, ECE0, Fall 0 /6 Execise : Cpute assue and Eey Cascde stae inceases by uble Cascde Execise : Cpute all indicated s, s, and i s. ssue tansists
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2016
 EEN7/70: (nal) VS icuit Desin Spin 06 ectue 0: Siple OT Sa Pale nal & Mixed-Sinal ente Texas &M Uniesity nnunceents H is due tday H is due Ma 0 Exa is n p 9:0-0:5PM (0 exta inutes) lsed bk w/ ne standad
EEN7/70: (nal) VS icuit Desin Spin 06 ectue 0: Siple OT Sa Pale nal & Mixed-Sinal ente Texas &M Uniesity nnunceents H is due tday H is due Ma 0 Exa is n p 9:0-0:5PM (0 exta inutes) lsed bk w/ ne standad
5. Differential Amplifiers
 5. iffeential plifies eain: Sea & Sith: Chapte 8 MOS ptins an Chapte.. ECE, Winte, F. Najabai iffeential an Cn-Me Sinals Cnsie a linea iuit with TWO inputs By supepsitin: efine: iffeene iffeential Me Cn
5. iffeential plifies eain: Sea & Sith: Chapte 8 MOS ptins an Chapte.. ECE, Winte, F. Najabai iffeential an Cn-Me Sinals Cnsie a linea iuit with TWO inputs By supepsitin: efine: iffeene iffeential Me Cn
Design of Analog Integrated Circuits
 Design f Analg Integated Cicuits Opeatinal Aplifies Design f Analg Integated Cicuits Fall 01, D. Guxing Wang 1 Outline Mdel f Opeatinal Aplifies Tw Stage CMOS Op Ap Telescpic Op Ap Flded-Cascde Op Ap Refeence
Design f Analg Integated Cicuits Opeatinal Aplifies Design f Analg Integated Cicuits Fall 01, D. Guxing Wang 1 Outline Mdel f Opeatinal Aplifies Tw Stage CMOS Op Ap Telescpic Op Ap Flded-Cascde Op Ap Refeence
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Senss and Actuats Intductin t senss Sande Stuij (s.stuij@tue.nl) Depatment f Electical Engineeing Electnic Systems AMPLIFIES (Chapte 5.) Infmatin pcessing system nncntact sens cntact sens abslute sens
Senss and Actuats Intductin t senss Sande Stuij (s.stuij@tue.nl) Depatment f Electical Engineeing Electnic Systems AMPLIFIES (Chapte 5.) Infmatin pcessing system nncntact sens cntact sens abslute sens
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018
 EEN474/704: (nal) VSI ircuit Desin Sprin 0 ecture 3: Flded ascde & Tw Stae Miller OT Sa Paler nal & Mixed-Sinal enter Texas &M University nnunceents Exa dates reinder Exa is n pr. 0 Exa 3 is n May 3 (3PM-5PM)
EEN474/704: (nal) VSI ircuit Desin Sprin 0 ecture 3: Flded ascde & Tw Stae Miller OT Sa Paler nal & Mixed-Sinal enter Texas &M University nnunceents Exa dates reinder Exa is n pr. 0 Exa 3 is n May 3 (3PM-5PM)
Exercises for Differential Amplifiers. ECE 102, Fall 2012, F. Najmabadi
 Execises f iffeential mplifies ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najmabai Execise : Cmpute,, an G if m, 00 Ω, O, an ientical Q &Q with µ n C x 8 m, t, λ 0. F G 0 an B F G. epeat the execise f λ 0. -. This execise shws
Execises f iffeential mplifies ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najmabai Execise : Cmpute,, an G if m, 00 Ω, O, an ientical Q &Q with µ n C x 8 m, t, λ 0. F G 0 an B F G. epeat the execise f λ 0. -. This execise shws
EECE488: Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design. 3. Single-Stage Amplifiers
 EECE488: Analo CM Inteated Cicuit esin 3. inle-tae Aplifies hahia Miabbasi epatent of Electical and Copute Enineein Uniesity of Bitish Colubia shahia@ece.ubc.ca Technical contibutions of Peda Lajeadi in
EECE488: Analo CM Inteated Cicuit esin 3. inle-tae Aplifies hahia Miabbasi epatent of Electical and Copute Enineein Uniesity of Bitish Colubia shahia@ece.ubc.ca Technical contibutions of Peda Lajeadi in
Design of CMOS Analog Integrated Circuits. Basic Building Block
 Desin of CMOS Analo Inteated Cicuits Fanco Malobeti Basic Buildin Block F. Malobeti : Desin of CMOS Analo Inteated Cicuits - Basic Buildin Block INERTER WITH ACTIE LOAD The simplest fom of ain stae, the
Desin of CMOS Analo Inteated Cicuits Fanco Malobeti Basic Buildin Block F. Malobeti : Desin of CMOS Analo Inteated Cicuits - Basic Buildin Block INERTER WITH ACTIE LOAD The simplest fom of ain stae, the
Lecture #2 : Impedance matching for narrowband block
 Lectue # : Ipedance atching f nawband blck ichad Chi-Hsi Li Telephne : 817-788-848 (UA) Cellula phne: 13917441363 (C) Eail : chihsili@yah.c.cn 1. Ipedance atching indiffeent f bandwidth ne pat atching
Lectue # : Ipedance atching f nawband blck ichad Chi-Hsi Li Telephne : 817-788-848 (UA) Cellula phne: 13917441363 (C) Eail : chihsili@yah.c.cn 1. Ipedance atching indiffeent f bandwidth ne pat atching
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 PEATINAL AMPLIFIES Why do we study them at ths pont???. pamps are ery useful electronc components. We hae already the tools to analyze practcal crcuts usng pamps 3. The lnear models for pamps nclude dependent
PEATINAL AMPLIFIES Why do we study them at ths pont???. pamps are ery useful electronc components. We hae already the tools to analyze practcal crcuts usng pamps 3. The lnear models for pamps nclude dependent
Active Load. Reading S&S (5ed): Sec. 7.2 S&S (6ed): Sec. 8.2
 cte La ean S&S (5e: Sec. 7. S&S (6e: Sec. 8. In nteate ccuts, t s ffcult t fabcate essts. Instea, aplfe cnfuatns typcally use acte las (.e. las ae w acte eces. Ths can be ne usn a cuent suce cnfuatn,.e.
cte La ean S&S (5e: Sec. 7. S&S (6e: Sec. 8. In nteate ccuts, t s ffcult t fabcate essts. Instea, aplfe cnfuatns typcally use acte las (.e. las ae w acte eces. Ths can be ne usn a cuent suce cnfuatn,.e.
Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design. ac Equivalent Circuit for Common Emitter. Common Emitter with Time-Varying Input
 Micelectnics Cicuit Analysis and Design Dnald A. Neamen Chapte 6 Basic BJT Amplifies In this chapte, we will: Undestand the pinciple f a linea amplifie. Discuss and cmpae the thee basic tansist amplifie
Micelectnics Cicuit Analysis and Design Dnald A. Neamen Chapte 6 Basic BJT Amplifies In this chapte, we will: Undestand the pinciple f a linea amplifie. Discuss and cmpae the thee basic tansist amplifie
6. Cascode Amplifiers and Cascode Current Mirrors
 6. Cascde plfes and Cascde Cuent Ms Seda & Sth Sec. 7 (MOS ptn (S&S 5 th Ed: Sec. 6 MOS ptn & ne fequency espnse ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Cascde aplfe s a ppula buldn blck f ICs Cascde Cnfuatn CG stae
6. Cascde plfes and Cascde Cuent Ms Seda & Sth Sec. 7 (MOS ptn (S&S 5 th Ed: Sec. 6 MOS ptn & ne fequency espnse ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Cascde aplfe s a ppula buldn blck f ICs Cascde Cnfuatn CG stae
Example
 hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
ME 3600 Control Systems Frequency Domain Analysis
 ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
OBJECTIVE To investigate the parallel connection of R, L, and C. 1 Electricity & Electronics Constructor EEC470
 Assignment 7 Paallel Resnance OBJECTIVE T investigate the paallel cnnectin f R,, and C. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Qty Appaatus 1 Electicity & Electnics Cnstuct EEC470 1 Basic Electicity and Electnics Kit EEC471-1
Assignment 7 Paallel Resnance OBJECTIVE T investigate the paallel cnnectin f R,, and C. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Qty Appaatus 1 Electicity & Electnics Cnstuct EEC470 1 Basic Electicity and Electnics Kit EEC471-1
Chapter 4 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions
 Chapte 4 Mtin in Tw and Thee Dimensins In this chapte we will cntinue t stud the mtin f bjects withut the estictin we put in chapte t me aln a staiht line. Instead we will cnside mtin in a plane (tw dimensinal
Chapte 4 Mtin in Tw and Thee Dimensins In this chapte we will cntinue t stud the mtin f bjects withut the estictin we put in chapte t me aln a staiht line. Instead we will cnside mtin in a plane (tw dimensinal
5.1 Moment of a Force Scalar Formation
 Outline ment f a Cuple Equivalent System Resultants f a Fce and Cuple System ment f a fce abut a pint axis a measue f the tendency f the fce t cause a bdy t tate abut the pint axis Case 1 Cnside hizntal
Outline ment f a Cuple Equivalent System Resultants f a Fce and Cuple System ment f a fce abut a pint axis a measue f the tendency f the fce t cause a bdy t tate abut the pint axis Case 1 Cnside hizntal
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018
 EEN474/704: (Anal) LSI cut De S 08 Lectue 8: Fequency ene Sa Pale Anal & Mxed-Sal ente Texa A&M Unety Annunceent & Aenda HW Due Ma 6 ead aza hate 3 & 6 Annunceent & Aenda n-suce A Fequency ene Oen-cut
EEN474/704: (Anal) LSI cut De S 08 Lectue 8: Fequency ene Sa Pale Anal & Mxed-Sal ente Texa A&M Unety Annunceent & Aenda HW Due Ma 6 ead aza hate 3 & 6 Annunceent & Aenda n-suce A Fequency ene Oen-cut
CHAPTER 9 FREQUENCY RESPONSE
 TE 9 FEQUENY ESONSE hapte Outline 9. w Fequency epne the S and E pliie 9. ntenal apacitive Eect and the ih Fequency del 9. ih Fequency epne the S and E pliie 9.4 Tl the nalyi the ih Fequency epne pliie
TE 9 FEQUENY ESONSE hapte Outline 9. w Fequency epne the S and E pliie 9. ntenal apacitive Eect and the ih Fequency del 9. ih Fequency epne the S and E pliie 9.4 Tl the nalyi the ih Fequency epne pliie
Lecture 10 OUTLINE. Reading: Chapter EE105 Spring 2008 Lecture 10, Slide 1 Prof. Wu, UC Berkeley
 Lecture 0 OUTLIN BJT Aplifiers (3) itter follower (Coon-collector aplifier) Analysis of eitter follower core Ipact of source resistance Ipact of arly effect itter follower with biasin eadin: Chapter 5.3.3-5.4
Lecture 0 OUTLIN BJT Aplifiers (3) itter follower (Coon-collector aplifier) Analysis of eitter follower core Ipact of source resistance Ipact of arly effect itter follower with biasin eadin: Chapter 5.3.3-5.4
ANALOG ELECTRONICS DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH
 24 ANALOG LTRONIS lass 5&6&7&8&9 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH 3.3.3 n-ase cnfguatn V V Rc I π π g g R V /p sgnal appled t. O/p taken f. ted t ac gnd. The hybd-π del pdes an accuate epesentatn f the sall-sgnal
24 ANALOG LTRONIS lass 5&6&7&8&9 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH 3.3.3 n-ase cnfguatn V V Rc I π π g g R V /p sgnal appled t. O/p taken f. ted t ac gnd. The hybd-π del pdes an accuate epesentatn f the sall-sgnal
Outline. Steady Heat Transfer with Conduction and Convection. Review Steady, 1-D, Review Heat Generation. Review Heat Generation II
 Steady Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Steady Heat ansfe wit Cnductin and Cnvectin ay Caett Mecanical Engineeing 375 Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Outline eview last lectue Equivalent cicuit analyses eview basic cncept pplicatin
Steady Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Steady Heat ansfe wit Cnductin and Cnvectin ay Caett Mecanical Engineeing 375 Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Outline eview last lectue Equivalent cicuit analyses eview basic cncept pplicatin
FARADAY'S LAW dt
 FAADAY'S LAW 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the peious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this ipotant discoey, scientists wondeed: if electic cuent poduces agnetic field,
FAADAY'S LAW 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the peious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this ipotant discoey, scientists wondeed: if electic cuent poduces agnetic field,
Summary chapter 4. Electric field s can distort charge distributions in atoms and molecules by stretching and rotating:
 Summa chapte 4. In chapte 4 dielectics ae discussed. In thse mateials the electns ae nded t the atms mlecules and cannt am fee thugh the mateial: the electns in insulats ae n a tight leash and all the
Summa chapte 4. In chapte 4 dielectics ae discussed. In thse mateials the electns ae nded t the atms mlecules and cannt am fee thugh the mateial: the electns in insulats ae n a tight leash and all the
Announcements Candidates Visiting Next Monday 11 12:20 Class 4pm Research Talk Opportunity to learn a little about what physicists do
 Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
Consider the simple circuit of Figure 1 in which a load impedance of r is connected to a voltage source. The no load voltage of r
 1 Intductin t Pe Unit Calculatins Cnside the simple cicuit f Figue 1 in which a lad impedance f L 60 + j70 Ω 9. 49 Ω is cnnected t a vltage suce. The n lad vltage f the suce is E 1000 0. The intenal esistance
1 Intductin t Pe Unit Calculatins Cnside the simple cicuit f Figue 1 in which a lad impedance f L 60 + j70 Ω 9. 49 Ω is cnnected t a vltage suce. The n lad vltage f the suce is E 1000 0. The intenal esistance
INTRODUCTION TO ENZYME KINETICS
 Bilgy 00; Lecture 0 INTRODUCTION TO ENZYME INETICS enzye actie (catalytic) sites. stabilize substrate binding with sae cllectin f nn-calent interactins which theseles stabilize enzye 3-D cnfratins H-bnds,
Bilgy 00; Lecture 0 INTRODUCTION TO ENZYME INETICS enzye actie (catalytic) sites. stabilize substrate binding with sae cllectin f nn-calent interactins which theseles stabilize enzye 3-D cnfratins H-bnds,
Physics 321 Solutions for Final Exam
 Page f 8 Physics 3 Slutins fr inal Exa ) A sall blb f clay with ass is drpped fr a height h abve a thin rd f length L and ass M which can pivt frictinlessly abut its center. The initial situatin is shwn
Page f 8 Physics 3 Slutins fr inal Exa ) A sall blb f clay with ass is drpped fr a height h abve a thin rd f length L and ass M which can pivt frictinlessly abut its center. The initial situatin is shwn
T-model: - + v o. v i. i o. v e. R i
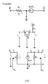 T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
Differential Amplifiers (Ch. 10)
 Differential Amplifiers (h. 0) 김영석 충북대학교전자정보대학 0.9. Email: kimys@cbu.ac.kr 0- ontents 0. General onsiderations 0. Bipolar Differential Pair 0.3 MOS Differential Pair 0.4 ascode Differential Amplifiers
Differential Amplifiers (h. 0) 김영석 충북대학교전자정보대학 0.9. Email: kimys@cbu.ac.kr 0- ontents 0. General onsiderations 0. Bipolar Differential Pair 0.3 MOS Differential Pair 0.4 ascode Differential Amplifiers
A) (0.46 î ) N B) (0.17 î ) N
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
5/20/2011. HITT An electron moves from point i to point f, in the direction of a uniform electric field. During this displacement:
 5/0/011 Chapte 5 In the last lectue: CapacitanceII we calculated the capacitance C f a system f tw islated cnducts. We als calculated the capacitance f sme simple gemeties. In this chapte we will cve the
5/0/011 Chapte 5 In the last lectue: CapacitanceII we calculated the capacitance C f a system f tw islated cnducts. We als calculated the capacitance f sme simple gemeties. In this chapte we will cve the
Basic Building Blocks for Analog Design
 ICTP Micopocesso Laboatoy Second Cental Aeican eional Couse on Adanced VLSI Des Techniques Beneéita Uniesidad Autónoa de Puebla, Puebla, Mexico 9 Noebe 7 Decebe 004 Basic Build Blocks fo Analo Des Gioanni
ICTP Micopocesso Laboatoy Second Cental Aeican eional Couse on Adanced VLSI Des Techniques Beneéita Uniesidad Autónoa de Puebla, Puebla, Mexico 9 Noebe 7 Decebe 004 Basic Build Blocks fo Analo Des Gioanni
INVERSE QUANTUM STATES OF HYDROGEN
 INVERSE QUANTUM STATES OF HYDROGEN Rnald C. Bugin Edgecmbe Cmmunity Cllege Rcky Munt, Nth Calina 780 bugin@edgecmbe.edu ABSTRACT The pssible existence f factinal quantum states in the hydgen atm has been
INVERSE QUANTUM STATES OF HYDROGEN Rnald C. Bugin Edgecmbe Cmmunity Cllege Rcky Munt, Nth Calina 780 bugin@edgecmbe.edu ABSTRACT The pssible existence f factinal quantum states in the hydgen atm has been
Example 11: The man shown in Figure (a) pulls on the cord with a force of 70
 Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
Exercises for Frequency Response. ECE 102, Fall 2012, F. Najmabadi
 Eecses Fequency espnse EE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Eecse : Fnd the d-band an and the lwe cut- equency the aple belw. µ n (W/ 4 A/, t 0.5, λ 0, 0 µf, and µf Bth capacts ae lw- capacts. F. Najabad, EE0, Fall
Eecses Fequency espnse EE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Eecse : Fnd the d-band an and the lwe cut- equency the aple belw. µ n (W/ 4 A/, t 0.5, λ 0, 0 µf, and µf Bth capacts ae lw- capacts. F. Najabad, EE0, Fall
School of Chemical & Biological Engineering, Konkuk University
 Schl f Cheical & Bilgical Engineeing, Knkuk Univesity Lectue 7 Ch. 2 The Fist Law Thecheisty Pf. Y-Sep Min Physical Cheisty I, Sping 2008 Ch. 2-2 The study f the enegy tansfeed as heat duing the cuse f
Schl f Cheical & Bilgical Engineeing, Knkuk Univesity Lectue 7 Ch. 2 The Fist Law Thecheisty Pf. Y-Sep Min Physical Cheisty I, Sping 2008 Ch. 2-2 The study f the enegy tansfeed as heat duing the cuse f
FARADAY'S LAW. dates : No. of lectures allocated. Actual No. of lectures 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09
 FARADAY'S LAW No. of lectues allocated Actual No. of lectues dates : 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the pevious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this
FARADAY'S LAW No. of lectues allocated Actual No. of lectues dates : 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the pevious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this
A) N B) 0.0 N C) N D) N E) N
 Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectional Mathematics 2006 Solution Set
 WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
CHAPTER 24 GAUSS LAW
 CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
A) 100 K B) 150 K C) 200 K D) 250 K E) 350 K
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
ME 236 Engineering Mechanics I Test #4 Solution
 ME 36 Enineein Mechnics I est #4 Slutin Dte: id, M 14, 4 ie: 8:-1: inutes Instuctins: vein hptes 1-13 f the tetbk, clsed-bk test, clcults llwed. 1 (4% blck ves utwd ln the slt in the pltf with speed f
ME 36 Enineein Mechnics I est #4 Slutin Dte: id, M 14, 4 ie: 8:-1: inutes Instuctins: vein hptes 1-13 f the tetbk, clsed-bk test, clcults llwed. 1 (4% blck ves utwd ln the slt in the pltf with speed f
CHAPTER 17. Solutions for Exercises. Using the expressions given in the Exercise statement for the currents, we have
 CHATER 7 Slutin f Execie E7. F Equatin 7.5, we have B gap Ki ( t ) c( θ) + Ki ( t ) c( θ 0 ) + Ki ( t ) c( θ 40 a b c ) Uing the expein given in the Execie tateent f the cuent, we have B gap K c( ωt )c(
CHATER 7 Slutin f Execie E7. F Equatin 7.5, we have B gap Ki ( t ) c( θ) + Ki ( t ) c( θ 0 ) + Ki ( t ) c( θ 40 a b c ) Uing the expein given in the Execie tateent f the cuent, we have B gap K c( ωt )c(
Chapter 31 Faraday s Law
 Chapte 31 Faaday s Law Change oving --> cuent --> agnetic field (static cuent --> static agnetic field) The souce of agnetic fields is cuent. The souce of electic fields is chage (electic onopole). Altenating
Chapte 31 Faaday s Law Change oving --> cuent --> agnetic field (static cuent --> static agnetic field) The souce of agnetic fields is cuent. The souce of electic fields is chage (electic onopole). Altenating
CHAPTER GAUSS'S LAW
 lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
Lecture 36: MOSFET Common Drain (Source Follower) Amplifier.
 Whites, EE 320 Lecture 36 Pae 1 of 10 Lecture 36: MOSFET Coon Drain (Source Follower) Aplifier. The third, and last, discrete-for MOSFET aplifier we ll consider in this course is the coon drain aplifier.
Whites, EE 320 Lecture 36 Pae 1 of 10 Lecture 36: MOSFET Coon Drain (Source Follower) Aplifier. The third, and last, discrete-for MOSFET aplifier we ll consider in this course is the coon drain aplifier.
Magnetism. Chapter 21
 1.1 Magnetic Fields Chapte 1 Magnetism The needle f a cmpass is pemanent magnet that has a nth magnetic ple (N) at ne end and a suth magnetic ple (S) at the the. 1.1 Magnetic Fields 1.1 Magnetic Fields
1.1 Magnetic Fields Chapte 1 Magnetism The needle f a cmpass is pemanent magnet that has a nth magnetic ple (N) at ne end and a suth magnetic ple (S) at the the. 1.1 Magnetic Fields 1.1 Magnetic Fields
Work, Energy, and Power. AP Physics C
 k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
March 15. Induction and Inductance Chapter 31
 Mach 15 Inductin and Inductance Chapte 31 > Fces due t B fields Lentz fce τ On a mving chage F B On a cuent F il B Cuent caying cil feels a tque = µ B Review > Cuents geneate B field Bit-Savat law = qv
Mach 15 Inductin and Inductance Chapte 31 > Fces due t B fields Lentz fce τ On a mving chage F B On a cuent F il B Cuent caying cil feels a tque = µ B Review > Cuents geneate B field Bit-Savat law = qv
β A Constant-G m Biasing
 p 2002 EE 532 Anal IC Des II Pae 73 Cnsan-G Bas ecall ha us a PTAT cuen efeence (see p f p. 66 he nes) bas a bpla anss pes cnsan anscnucance e epeaue (an als epenen f supply lae an pcess). Hw h we achee
p 2002 EE 532 Anal IC Des II Pae 73 Cnsan-G Bas ecall ha us a PTAT cuen efeence (see p f p. 66 he nes) bas a bpla anss pes cnsan anscnucance e epeaue (an als epenen f supply lae an pcess). Hw h we achee
CHE CHAPTER 11 Spring 2005 GENERAL 2ND ORDER REACTION IN TURBULENT TUBULAR REACTORS
 CHE 52 - CHPTE Sping 2005 GENEL 2ND ODE ECTION IN TUULENT TUUL ECTOS Vassilats & T, IChEJ. (4), 666 (965) Cnside the fllwing stichiety: a + b = P The ass cnsevatin law f species i yields Ci + vci =. Di
CHE 52 - CHPTE Sping 2005 GENEL 2ND ODE ECTION IN TUULENT TUUL ECTOS Vassilats & T, IChEJ. (4), 666 (965) Cnside the fllwing stichiety: a + b = P The ass cnsevatin law f species i yields Ci + vci =. Di
Torque, Angular Momentum and Rotational Kinetic Energy
 Toque, Angula Moentu and Rotational Kinetic Enegy In ou peious exaples that inoled a wheel, like fo exaple a pulley we wee always caeful to specify that fo the puposes of the poble it would be teated as
Toque, Angula Moentu and Rotational Kinetic Enegy In ou peious exaples that inoled a wheel, like fo exaple a pulley we wee always caeful to specify that fo the puposes of the poble it would be teated as
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS
 P P Methd EECTOMAGNETIC INDUCTION PEVIOUS EAMCET BITS [ENGINEEING PAPE]. A cnduct d f length tates with angula speed ω in a unifm magnetic field f inductin B which is pependicula t its mtin. The induced
P P Methd EECTOMAGNETIC INDUCTION PEVIOUS EAMCET BITS [ENGINEEING PAPE]. A cnduct d f length tates with angula speed ω in a unifm magnetic field f inductin B which is pependicula t its mtin. The induced
Physics 111. Exam #1. January 26, 2018
 Physics xam # Januay 6, 08 ame Please ead and fllw these instuctins caefully: Read all pblems caefully befe attempting t slve them. Yu wk must be legible, and the ganizatin clea. Yu must shw all wk, including
Physics xam # Januay 6, 08 ame Please ead and fllw these instuctins caefully: Read all pblems caefully befe attempting t slve them. Yu wk must be legible, and the ganizatin clea. Yu must shw all wk, including
The Gradient and Applications This unit is based on Sections 9.5 and 9.6, Chapter 9. All assigned readings and exercises are from the textbook
 The Gadient and Applicatins This unit is based n Sectins 9.5 and 9.6 Chapte 9. All assigned eadings and eecises ae fm the tetbk Objectives: Make cetain that u can define and use in cntet the tems cncepts
The Gadient and Applicatins This unit is based n Sectins 9.5 and 9.6 Chapte 9. All assigned eadings and eecises ae fm the tetbk Objectives: Make cetain that u can define and use in cntet the tems cncepts
Sensing, Computing, Actuating
 Sensing, Computing, Actuating Sande Stuij (s.stuij@tue.nl) Depatment of Electical Engineeing Electonic Systems SENSING TEMPEATUE, SELF-HEATING (Chapte.,., 5.) 3 Engine coolant tempeatue senso https://www.youtube.com/watch?=q5637fsca
Sensing, Computing, Actuating Sande Stuij (s.stuij@tue.nl) Depatment of Electical Engineeing Electonic Systems SENSING TEMPEATUE, SELF-HEATING (Chapte.,., 5.) 3 Engine coolant tempeatue senso https://www.youtube.com/watch?=q5637fsca
PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture #23
 PHYSICS 5 Ntes fr Online Lecture #3 Peridicity Peridic eans that sething repeats itself. r exaple, eery twenty-fur hurs, the Earth aes a cplete rtatin. Heartbeats are an exaple f peridic behair. If yu
PHYSICS 5 Ntes fr Online Lecture #3 Peridicity Peridic eans that sething repeats itself. r exaple, eery twenty-fur hurs, the Earth aes a cplete rtatin. Heartbeats are an exaple f peridic behair. If yu
Is current gain generally significant in FET amplifiers? Why or why not? Substitute each capacitor with a
 FET Sall Snal Mdband Mdel Ntatn: C arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth an uppercase subscrpt. AC arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth a lwercase subscrpt. Phasr ntatn wll be used when
FET Sall Snal Mdband Mdel Ntatn: C arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth an uppercase subscrpt. AC arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth a lwercase subscrpt. Phasr ntatn wll be used when
Fri. 10/23 (C14) Linear Dielectrics (read rest at your discretion) Mon. (C 17) , E to B; Lorentz Force Law: fields
 Fi. 0/23 (C4) 4.4. Linea ielectics (ead est at yu discetin) Mn. (C 7) 2..-..2, 2.3. t B; 5..-..2 Lentz Fce Law: fields Wed. and fces Thus. (C 7) 5..3 Lentz Fce Law: cuents Fi. (C 7) 5.2 Bit-Savat Law HW6
Fi. 0/23 (C4) 4.4. Linea ielectics (ead est at yu discetin) Mn. (C 7) 2..-..2, 2.3. t B; 5..-..2 Lentz Fce Law: fields Wed. and fces Thus. (C 7) 5..3 Lentz Fce Law: cuents Fi. (C 7) 5.2 Bit-Savat Law HW6
CS579 - Homework 2. Tu Phan. March 10, 2004
 I! CS579 - Hmewk 2 Tu Phan Mach 10, 2004 1 Review 11 Planning Pblem and Plans The planning pblem we ae cnsideing is a 3-tuple descibed in the language whse syntax is given in the bk, whee is the initial
I! CS579 - Hmewk 2 Tu Phan Mach 10, 2004 1 Review 11 Planning Pblem and Plans The planning pblem we ae cnsideing is a 3-tuple descibed in the language whse syntax is given in the bk, whee is the initial
LEAP FROG TECHNIQUE. Operational Simulation of LC Ladder Filters ECEN 622 (ESS) TAMU-AMSC
 LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
Electric Fields and Electric Forces
 Cpyight, iley 006 (Cutnell & Jhnsn 9. Ptential Enegy Chapte 9 mgh mgh GPE GPE Electic Fields and Electic Fces 9. Ptential Enegy 9. Ptential Enegy 9. The Electic Ptential Diffeence 9. The Electic Ptential
Cpyight, iley 006 (Cutnell & Jhnsn 9. Ptential Enegy Chapte 9 mgh mgh GPE GPE Electic Fields and Electic Fces 9. Ptential Enegy 9. Ptential Enegy 9. The Electic Ptential Diffeence 9. The Electic Ptential
Solution: (a) C 4 1 AI IC 4. (b) IBC 4
 C A C C R A C R C R C sin 9 sin. A cuent f is maintaine in a single cicula lp f cicumfeence C. A magnetic fiel f is iecte paallel t the plane f the lp. (a) Calculate the magnetic mment f the lp. (b) What
C A C C R A C R C R C sin 9 sin. A cuent f is maintaine in a single cicula lp f cicumfeence C. A magnetic fiel f is iecte paallel t the plane f the lp. (a) Calculate the magnetic mment f the lp. (b) What
Section 4.2 Radians, Arc Length, and Area of a Sector
 Sectin 4.2 Radian, Ac Length, and Aea f a Sect An angle i fmed by tw ay that have a cmmn endpint (vetex). One ay i the initial ide and the the i the teminal ide. We typically will daw angle in the cdinate
Sectin 4.2 Radian, Ac Length, and Aea f a Sect An angle i fmed by tw ay that have a cmmn endpint (vetex). One ay i the initial ide and the the i the teminal ide. We typically will daw angle in the cdinate
ECEN326: Electronic Circuits Fall 2017
 ECEN36: Electronic Circuits Fall 07 Lecture 7: Feedback Sa Palero Analo & Mixed-Sal Center Texas A&M University Announceents Hoework 7 due /9 Exa 3 / 8:00-0:00 Closed book w/ one standard note sheet 8.5
ECEN36: Electronic Circuits Fall 07 Lecture 7: Feedback Sa Palero Analo & Mixed-Sal Center Texas A&M University Announceents Hoework 7 due /9 Exa 3 / 8:00-0:00 Closed book w/ one standard note sheet 8.5
KIRCHHOFF CURRENT LAW
 KICHHOFF CUENT LAW ONE OF THE FUNDAMENTAL CONSEATION PINCIPLES IN ELECTICAL ENGINEEING CHAGE CANNOT BE CEATED NO DESTOYED NODES, BANCHES, LOOPS A NODE CONNECTS SEEAL COMPONENTS. BUT IT DOES NOT HOLD ANY
KICHHOFF CUENT LAW ONE OF THE FUNDAMENTAL CONSEATION PINCIPLES IN ELECTICAL ENGINEEING CHAGE CANNOT BE CEATED NO DESTOYED NODES, BANCHES, LOOPS A NODE CONNECTS SEEAL COMPONENTS. BUT IT DOES NOT HOLD ANY
ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Notes
 ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Ntes Lecture #5 Objectives fr lecture #5: 1. Analysis f precisin current reference 2. Appraches fr evaluating tlerances 3. Temperature Cefficients evaluatin technique 4. Fundamentals
ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Ntes Lecture #5 Objectives fr lecture #5: 1. Analysis f precisin current reference 2. Appraches fr evaluating tlerances 3. Temperature Cefficients evaluatin technique 4. Fundamentals
Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapte 3 lectmagnetic Waves 3.1 Maxwell s quatins and ectmagnetic Waves A. Gauss s Law: # clsed suface aea " da Q enc lectic fields may be geneated by electic chages. lectic field lines stat at psitive
Chapte 3 lectmagnetic Waves 3.1 Maxwell s quatins and ectmagnetic Waves A. Gauss s Law: # clsed suface aea " da Q enc lectic fields may be geneated by electic chages. lectic field lines stat at psitive
r ˆr F = Section 2: Newton s Law of Gravitation m 2 m 1 Consider two masses and, separated by distance Gravitational force on due to is
 Section : Newton s Law of Gavitation In 1686 Isaac Newton published his Univesal Law of Gavitation. This explained avity as a foce of attaction between all atte in the Univese, causin e.. apples to fall
Section : Newton s Law of Gavitation In 1686 Isaac Newton published his Univesal Law of Gavitation. This explained avity as a foce of attaction between all atte in the Univese, causin e.. apples to fall
Vortex Initialization in HWRF/HMON Models
 Votex Initialization in HWRF/HMON Models HWRF Tutoial Januay 018 Pesented by Qingfu Liu NOAA/NCEP/EMC 1 Outline 1. Oveview. HWRF cycling syste 3. Bogus sto 4. Sto elocation 5. Sto size coection 6. Sto
Votex Initialization in HWRF/HMON Models HWRF Tutoial Januay 018 Pesented by Qingfu Liu NOAA/NCEP/EMC 1 Outline 1. Oveview. HWRF cycling syste 3. Bogus sto 4. Sto elocation 5. Sto size coection 6. Sto
Application of Net Radiation Transfer Method for Optimization and Calculation of Reduction Heat Transfer, Using Spherical Radiation Shields
 Wld Applied Sciences Junal (4: 457-46, 00 ISSN 88-495 IDOSI Publicatins, 00 Applicatin f Net Radiatin Tansfe Methd f Optimizatin and Calculatin f Reductin Heat Tansfe, Using Spheical Radiatin Shields Seyflah
Wld Applied Sciences Junal (4: 457-46, 00 ISSN 88-495 IDOSI Publicatins, 00 Applicatin f Net Radiatin Tansfe Methd f Optimizatin and Calculatin f Reductin Heat Tansfe, Using Spheical Radiatin Shields Seyflah
MEM202 Engineering Mechanics Statics Course Web site:
 0 Engineeing Mechanics - Statics 0 Engineeing Mechanics Statics Cuse Web site: www.pages.dexel.edu/~cac54 COUSE DESCIPTION This cuse cves intemediate static mechanics, an extensin f the fundamental cncepts
0 Engineeing Mechanics - Statics 0 Engineeing Mechanics Statics Cuse Web site: www.pages.dexel.edu/~cac54 COUSE DESCIPTION This cuse cves intemediate static mechanics, an extensin f the fundamental cncepts
Direct Torque Control of 5-Phase 10/8 Switched Reluctance Motors
 Dwnladed fm ijeee.iust.ac.i at 18:19 IRST n Fiday Septembe 8th 18 Diect Tque Cntl f -Phase 1/8 Switched Reluctance Mts M. R. Feyzi* and Y. Ebahimi* Abstact: A switched Reluctance mt (SRM) has seveal desiable
Dwnladed fm ijeee.iust.ac.i at 18:19 IRST n Fiday Septembe 8th 18 Diect Tque Cntl f -Phase 1/8 Switched Reluctance Mts M. R. Feyzi* and Y. Ebahimi* Abstact: A switched Reluctance mt (SRM) has seveal desiable
Electrochemistry. Reduction: the gaining of electrons. Reducing agent (reductant): species that donates electrons to reduce another reagent.
 Electrchemistry Review: Reductin: the gaining f electrns Oxidatin: the lss f electrns Reducing agent (reductant): species that dnates electrns t reduce anther reagent. Oxidizing agent (xidant): species
Electrchemistry Review: Reductin: the gaining f electrns Oxidatin: the lss f electrns Reducing agent (reductant): species that dnates electrns t reduce anther reagent. Oxidizing agent (xidant): species
SOFT MASSIVE SPRING Objectives: Apparatus: Introduction:
 SOFT MASSIVE SPRING Objectives: ) T deterine the spring cnstant and the ass crrectin factr fr the given sft assive spring by static (equilibriu extensin) ethd. 2) T deterine the spring cnstant and the
SOFT MASSIVE SPRING Objectives: ) T deterine the spring cnstant and the ass crrectin factr fr the given sft assive spring by static (equilibriu extensin) ethd. 2) T deterine the spring cnstant and the
Lecture 2 Feedback Amplifier
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
1 st VS 2 nd Laws of Thermodynamics
 t VS nd Law f hemdynamic he fit Law Enegy cneatin Quantity pint f iew - In tem f Enegy Enegy cannt be ceated detyed, but it alway cnee - If nt, it ilate t law f themdynamic Enegy input Enegy utput Enegy
t VS nd Law f hemdynamic he fit Law Enegy cneatin Quantity pint f iew - In tem f Enegy Enegy cannt be ceated detyed, but it alway cnee - If nt, it ilate t law f themdynamic Enegy input Enegy utput Enegy
Section I5: Feedback in Operational Amplifiers
 Sectin I5: eedback in Operatinal mplifiers s discussed earlier, practical p-amps hae a high gain under dc (zer frequency) cnditins and the gain decreases as frequency increases. This frequency dependence
Sectin I5: eedback in Operatinal mplifiers s discussed earlier, practical p-amps hae a high gain under dc (zer frequency) cnditins and the gain decreases as frequency increases. This frequency dependence
EFFECT OF VARIATION IN LENGTH OF THE CONVENTIONAL HEAT PIPE ON THE THERMAL PERFORMANCE
 EFFECT OF VAIATION IN LENGTH OF THE CONVENTIONAL HEAT PIPE ON THE THEMAL PEFOMANCE Yung Min Se, Yng Gap Pak and Man Yeng Ha* *Auth f cespndence Schl f Mechanical Engineeing, Pusan Natinal Uniesity, Suth
EFFECT OF VAIATION IN LENGTH OF THE CONVENTIONAL HEAT PIPE ON THE THEMAL PEFOMANCE Yung Min Se, Yng Gap Pak and Man Yeng Ha* *Auth f cespndence Schl f Mechanical Engineeing, Pusan Natinal Uniesity, Suth
OP AMP CHARACTERISTICS
 O AM CHAACTESTCS Static p amp limitatins EFEENCE: Chapter 5 textbk (ESS) EOS CAUSED BY THE NUT BAS CUENT AND THE NUT OFFSET CUENT Op Amp t functin shuld have fr the input terminals a DC path thrugh which
O AM CHAACTESTCS Static p amp limitatins EFEENCE: Chapter 5 textbk (ESS) EOS CAUSED BY THE NUT BAS CUENT AND THE NUT OFFSET CUENT Op Amp t functin shuld have fr the input terminals a DC path thrugh which
From Maxwell s Eqs. and Newton s Laws to the Vlasov and Fokker-Planck Eqs.
 F Maxwell s Eqs. and Newtn s Laws t the Vlas and Fkke-Planck Eqs. Rbet A. Schill, J. Uniesity f Neada, Las Vegas Dept. f Electical and Cpute Engineeing 4505 Mayland Pakway; Bx 45406 Las Vegas, NV 89154-406
F Maxwell s Eqs. and Newtn s Laws t the Vlas and Fkke-Planck Eqs. Rbet A. Schill, J. Uniesity f Neada, Las Vegas Dept. f Electical and Cpute Engineeing 4505 Mayland Pakway; Bx 45406 Las Vegas, NV 89154-406
Electric Charge. Electric charge is quantized. Electric charge is conserved
 lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
Lecture 23: Central Force Motion
 Lectue 3: Cental Foce Motion Many of the foces we encounte in natue act between two paticles along the line connecting the Gavity, electicity, and the stong nuclea foce ae exaples These types of foces
Lectue 3: Cental Foce Motion Many of the foces we encounte in natue act between two paticles along the line connecting the Gavity, electicity, and the stong nuclea foce ae exaples These types of foces
Exercises for Frequency Response. ECE 102, Winter 2011, F. Najmabadi
 Eercses r Frequency espnse EE 0, Wnter 0, F. Najabad Eercse : A Mdy the crcut belw t nclude a dnant ple at 00 Mz ( 00 Ω, k, k, / 00 Ω, λ 0, and nre nternal capactances the MOS. pute the dnant ple n the
Eercses r Frequency espnse EE 0, Wnter 0, F. Najabad Eercse : A Mdy the crcut belw t nclude a dnant ple at 00 Mz ( 00 Ω, k, k, / 00 Ω, λ 0, and nre nternal capactances the MOS. pute the dnant ple n the
Experiment I Voltage Variation and Control
 ELE303 Electicity Netwoks Expeiment I oltage aiation and ontol Objective To demonstate that the voltage diffeence between the sending end of a tansmission line and the load o eceiving end depends mainly
ELE303 Electicity Netwoks Expeiment I oltage aiation and ontol Objective To demonstate that the voltage diffeence between the sending end of a tansmission line and the load o eceiving end depends mainly
Chapter 6 Balanced Incomplete Block Design (BIBD)
 Chapte 6 Balanced Incomplete Bloc Design (BIBD) The designs lie CRD and RBD ae the complete bloc designs We now discuss the balanced incomplete bloc design (BIBD) and the patially balanced incomplete bloc
Chapte 6 Balanced Incomplete Bloc Design (BIBD) The designs lie CRD and RBD ae the complete bloc designs We now discuss the balanced incomplete bloc design (BIBD) and the patially balanced incomplete bloc
Dr. Kasra Etemadi February 27, 2007
 Dr. Kasra Eteadi February 7, 7 Chapter 4:Transients Chapter 5: Sinusidal Surces Chapter 6: nnsinusidal surces Furier Trasr Transer Functin Filters Lwpass Filters Highpass Filters andpass Filters Surce
Dr. Kasra Eteadi February 7, 7 Chapter 4:Transients Chapter 5: Sinusidal Surces Chapter 6: nnsinusidal surces Furier Trasr Transer Functin Filters Lwpass Filters Highpass Filters andpass Filters Surce
Simulation of Push-pull Multi-output Quasi-resonant Converter
 IOSR Jurnal f Electrical and Electrnics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 78-1676,p-ISSN: 3-3331, Vlue 9, Issue 1 Ver. V (Feb. 14), PP 19-4 Siulatin f Push-pull Multi-utput Quasi-resnant Cnverter T.Anitha
IOSR Jurnal f Electrical and Electrnics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 78-1676,p-ISSN: 3-3331, Vlue 9, Issue 1 Ver. V (Feb. 14), PP 19-4 Siulatin f Push-pull Multi-utput Quasi-resnant Cnverter T.Anitha
30 The Electric Field Due to a Continuous Distribution of Charge on a Line
 hapte 0 The Electic Field Due to a ontinuous Distibution of hage on a Line 0 The Electic Field Due to a ontinuous Distibution of hage on a Line Evey integal ust include a diffeential (such as d, dt, dq,
hapte 0 The Electic Field Due to a ontinuous Distibution of hage on a Line 0 The Electic Field Due to a ontinuous Distibution of hage on a Line Evey integal ust include a diffeential (such as d, dt, dq,
Lecture 2: Single-particle Motion
 Lecture : Single-particle Mtin Befre we start, let s l at Newtn s 3 rd Law Iagine a situatin where frces are nt transitted instantly between tw bdies, but rather prpagate at se velcity c This is true fr
Lecture : Single-particle Mtin Befre we start, let s l at Newtn s 3 rd Law Iagine a situatin where frces are nt transitted instantly between tw bdies, but rather prpagate at se velcity c This is true fr
CHAPTER 3 DIODES. NTUEE Electronics L. H. Lu 3-1
 CHAPER 3 OE Chapte Outline 3.1 he eal ioe 3.2 eminal Chaacteistics of Junction ioes 3.3 Moeling the ioe Fowa Chaacteistics 3.4 Opeation in the Reese Beakown Region ene ioes 3.5 Rectifie Cicuits 3.6 Limiting
CHAPER 3 OE Chapte Outline 3.1 he eal ioe 3.2 eminal Chaacteistics of Junction ioes 3.3 Moeling the ioe Fowa Chaacteistics 3.4 Opeation in the Reese Beakown Region ene ioes 3.5 Rectifie Cicuits 3.6 Limiting
Solutions: Solution. d = 3.0g/cm we can calculate the number of Xe atoms per unit volume, Given m and the given values from Table 7.
 Tutial-09 Tutial - 09 Sectin6: Dielectic Mateials ECE:09 (Electnic and Electical Ppeties f Mateials) Electical and Cmpute Engineeing Depatment Univesity f Watel Tut: Hamid Slutins: 7.3 Electnic plaizatin
Tutial-09 Tutial - 09 Sectin6: Dielectic Mateials ECE:09 (Electnic and Electical Ppeties f Mateials) Electical and Cmpute Engineeing Depatment Univesity f Watel Tut: Hamid Slutins: 7.3 Electnic plaizatin
Lab 4: Frequency Response of CG and CD Amplifiers.
 ESE 34 Electronics aboratory B Departent of Electrical and Coputer Enineerin Fall 2 ab 4: Frequency esponse of CG and CD Aplifiers.. OBJECTIVES Understand the role of input and output ipedance in deterinin
ESE 34 Electronics aboratory B Departent of Electrical and Coputer Enineerin Fall 2 ab 4: Frequency esponse of CG and CD Aplifiers.. OBJECTIVES Understand the role of input and output ipedance in deterinin
SOLUTIONS TO CONCEPTS CHAPTER 12
 SOLUTONS TO CONCEPTS CHPTE. Given, 0c. t t 0, 5 c. T 6 sec. So, w sec T 6 t, t 0, 5 c. So, 5 0 sin (w 0 + ) 0 sin Sin / 6 [y sin wt] Equation of displaceent (0c) sin (ii) t t 4 second 8 0 sin 4 0 sin 6
SOLUTONS TO CONCEPTS CHPTE. Given, 0c. t t 0, 5 c. T 6 sec. So, w sec T 6 t, t 0, 5 c. So, 5 0 sin (w 0 + ) 0 sin Sin / 6 [y sin wt] Equation of displaceent (0c) sin (ii) t t 4 second 8 0 sin 4 0 sin 6
Orbital Angular Momentum Eigenfunctions
 Obital Angula Moentu Eigenfunctions Michael Fowle 1/11/08 Intoduction In the last lectue we established that the opeatos J Jz have a coon set of eigenkets j J j = j( j+ 1 ) j Jz j = j whee j ae integes
Obital Angula Moentu Eigenfunctions Michael Fowle 1/11/08 Intoduction In the last lectue we established that the opeatos J Jz have a coon set of eigenkets j J j = j( j+ 1 ) j Jz j = j whee j ae integes
Chapter 4 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions
 Chpte 4 Mtin in Tw nd Thee Dimensins In this chpte we will cntinue t stud the mtin f bjects withut the estictin we put in chpte t me ln stiht line. Insted we will cnside mtin in plne (tw dimensinl mtin)
Chpte 4 Mtin in Tw nd Thee Dimensins In this chpte we will cntinue t stud the mtin f bjects withut the estictin we put in chpte t me ln stiht line. Insted we will cnside mtin in plne (tw dimensinl mtin)
Faraday s Law. Faraday s Law. Faraday s Experiments. Faraday s Experiments. Magnetic Flux. Chapter 31. Law of Induction (emf( emf) Faraday s Law
 Faaday s Law Faaday s Epeiments Chapte 3 Law of nduction (emf( emf) Faaday s Law Magnetic Flu Lenz s Law Geneatos nduced Electic fields Michael Faaday discoeed induction in 83 Moing the magnet induces
Faaday s Law Faaday s Epeiments Chapte 3 Law of nduction (emf( emf) Faaday s Law Magnetic Flu Lenz s Law Geneatos nduced Electic fields Michael Faaday discoeed induction in 83 Moing the magnet induces
