Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Mass Balance
|
|
|
- Oswin Boyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Mass Balance 1. The mass balance equation for the system is: = m This yields, m = 5 kg 2. The mass balance equation for the system is: = m This yields, m = 5 kg/s 3. We have 1 mass balance equation for each sub-system, yielding a total of 2 equations. First sub-system: = m Second sub-system: = 2 + m 2 Solving, we get: m = 1 kg/s, m = 6 kg/s 4. In this system, we have 2 equations and 2 unknowns. However, the mass balance equation in the first sub-system does not give us any information except that the problem is well-posed. Thus, we are left with one mass balance equation for sub-system #2 and 2 unknowns in that equation. Thus, we can not solve for m 1 and m 2 in this problem. All that we can say is that: 4 + m = 2 + m. 5. The Overall Mass Balance (OMB) equation is: = m The solids balance equation is: 0.3 (2) + x (1) = 0.4 (m) This yields, m = 3 kg/s, x = OMB: = m Sugar: 0.2 (5) (1) = x 1 (m) Starch: 0.6 (5) (1) = x 2 (m) Solving, we get: m = 6 kg/s, x = 0.22, x = OMB for first sub-system: = m Solids balance for first sub-system: 0.6 (10) (2) = x 1 (m 1) (9) OMB for second sub-system: 9 = m Solids balance for second sub-system: 0.7 (9) = x (m ) (6) (2) 2 2 Solving, we get: m 1 = 3 kg/s, x 1 = 0.18, m 2 = 1 kg/s, x 2 = There are four components (sugar, starch, oil, and water) in each sub-system and hence there are four mass balance equations in each sub-system, yielding a total of 8 equations. OMB in first sub-system: = m 1 Starch balance in first sub-system: 0.3 (10) = x 4 (2) + x 1 (m 1) (5) Sugar balance in first sub-system: 0.06 (10) + x 2 (3) = 0.4 (m 1) Oil balance in first sub-system: x (3) = 0.3 (2) 3
2 OMB in second sub-system: m m 2 = Starch balance in second sub-system: x 1 (m 1) = 0 Sugar balance in second sub-system: 0.4 (m 1) + x 6 (m 2) (2) = x 2 (3) (9) Oil balance in second sub-system: x (m ) = x (3) Solving, we get: m 1 = 6 kg/s, m 2 = 4 kg/s, x 1 = 0, x 2 = 0.6, x 3 = 0.2, x 4 = 0.5, x 5 = 0.15, x 6 = There are four components (sugar, starch, oil, and water) in each sub-system and hence there are four mass balance equations in each sub-system, yielding a total of 8 equations. OMB in first sub-system: = 8 + m 1 Starch balance in first sub-system: 0.4 (10) = x 1 (m 1) Sugar balance in first sub-system: 0.5 (10) (2) = 0.7 (8) Oil balance in first sub-system: 0 = x (m ) 2 1 OMB in second sub-system: m 1 + m 2 = Starch balance in second sub-system: x 1 (m 1) (m 2) = x 5 (5) Sugar balance in second sub-system: 0 = x 3 (5) + x 6 (5) Oil balance in second sub-system: x (m ) (m ) = x (5) (5) 2 4 Solving, we get: m 1 = 4 kg/s, m 2 = 6 kg/s, x 1 = 1.0, x 2 = 0, x 3 = 0, x 4 = 0.4, x 5 = 0.92, x 6 = Since there are 5 components in this system, there are 5 equations. OMB: = 8 + m Sugar: 0.2 (6) = x 3 (8) Starch: x 1 (6) (4) = 0.3 (8) (m) Oil: x 6 (4) = 0.2 (m) Protein: 0 = x (8) + x (m) 2 5 In order to determine x 4, we note that the sum of the fractions of the individual components of the product exiting from the top of the system at 8 kg/s must add up to 1.0. i.e., x + x + x = Solving, we get: m = 2 kg/s, x 1 = 0.4, x 2 = 0, x 3 = 0.15, x 4 = 0.55, x 5 = 0, x 6 = Since there are 4 components in each of the 3 sub-systems, we have a total of 12 equations. Overall mass balance equation: 10 + m 1 = m2 Total Fat balance equation: 10 (x 2) + m 1 (x 3) = m 2 (0.8) Total Protein balance equation: 10 (x 1) + m 1 (0.25) = 3 (1.0) + m 2 (x 8) + 5 (0.02) Total Vitamin balance equation: 10 (0.35) = 5 (0.64) + m (x ) 2 9
3 Overall mass balance equation: = m 1 + m3 Total Fat balance equation: 2 (x 5) = m 1 (x 3) Total Protein balance equation: 5 (0.02) + 2 (x 6) + 1 (0.3) = m 1 (0.25) Total Vitamin balance equation: 5 (0.64) + 2 (x ) + 1 (x ) = m (1.0) For the third sub-system: Overall mass balance equation: m 2 = Total Fat balance equation: m 2 (0.8) = 4 (1.0) + 2 (x 5) Total Protein balance equation: m 2 (x 8) = 2 (x 6) Total Vitamin balance equation: m (x ) = 2 (x ) Solving, we get: m 1 = 4 kg/s, m 2 = 6 kg/s, m 3 = 4 kg/s, x 1 = 0.27, x 2 = 0.4, x 3 = 0.2, x 4 = 0.5, x 5 = 0.4, x = 0.3, x = 0.15, x = 0.1, x = Since there are 3 components in each of the sub-systems, we have a total of 6 equations. Overall mass balance equation: = 2 + m 1 Protein balance equation: 0.5 (5) = 0.3 (2) + x 1 (m 1) Fat balance equation: 0.3 (3) = 0.2 (2) + x (m ) Overall mass balance equation: m 1 = m Protein balance equation: x 1 (m 1) = x 3 (2) Fat balance equation: x (m ) = x (m ) Solving, we get: m 1 = 6 kg/s, m 2 = 2 kg/s, x 1 = 0.317, x 2 = 0.083, x 3 = 0.95, x 4 = Since there are 3 components in each of the 3 sub-systems, we have a total of 9 equations. Overall mass balance equation: 10 + m = Total Sugar balance equation: 0.3 (10) + x 2 (m 1) (2) = 0.1 (3) + x 1 (13) Total Starch balance equation: x (m ) = Overall mass balance equation: = m Total Sugar balance equation: x 5 (13) (2) = x 5 (m 2) (2) Total Starch balance equation: 0.05 (2) = 0.02 (5) + x (m ) 4 2 For the third sub-system: Overall mass balance equation: 5 = m 1 + m3 Total Sugar balance equation: 0 = x 7 (m 3) + x 2 (m 1) Total Starch balance equation: 0.02 (5) = x (m ) + x (m ) Solving, we get: m = 4 kg/s, m = 8 kg/s, m = 1 kg/s, x = 0.3, x = 0, x = 0, x = 0, x = 0.35, x = 0.1, x =
4 14. The system diagram for the problem is as shown below: We have 5 equations and 5 unknowns in this problem. Overall mass balance in first sub-system: 20 = m 1 + m2 Sugar balance in first sub-system: 0.15 (20) = x 1 (m 2) Overall mass balance in second sub-system: m 2 + m 3 = m Sugar balance in second sub-system: x 1 (m 2) = 0.3 (m 4) Starch balance in second sub-system: m = 0.4 (m ) 3 4 Solving, we get: m 1 = 9 kg/hr, m 2 = 11 kg/hr, m 3 = 4 kg/hr, m 4 = 10 kg/hr, x 1 = The mass flow rate (m) and moisture content on wet basis (x) are the two unknowns in the system shown below: Mass balance: 20 = 15 + m Solids balance: 0.1 (20) = x (m) m = 5 kg/hr and x = 0.4 Thus, the product consists of 2 kg/hr of solids and 3 kg/hr of water. Thus, (mc) = 3/2 = 1.5 = 150 % db
5 16. First sub-system Overall mass balance: 5 + m 1 = 3 + m 2 => 2 + m 1 = m2 Protein balance: 0.2 (5) (m 1) = 0.4 (3) + x 2 (m 2) => (m 1) = x 2 (m 2) Fat balance: 0.2 (5) (m 1) = x 1 (3) + x 3 (m 2) => (m 1) = x 1 (3) + x 3 (m 2) Carbohydrates balance: 0.3 (m ) = 0.2 (3) + x (m ) => 0.3 (m ) = x (m ) Second sub-system Overall mass balance: m = 5 + m 3 => m = m3 Protein balance: x 2 (m 2) (10) = 0.4 (5) => x 2 (m 2) = 0 Fat balance: x 3 (m 2) (10) = 0.6 (5) => x 3 (m 2) = 0 Carbohydrates balance: x (m ) + x (10) = 0.4 (m ) => x (m ) + 10 x = 0.4 (m ) Substituting x 2 (m 2) = 0 into the protein balance equation for the first sub-system, we get: (m 1) = 1.2 This yields: m = 2 kg/s 1 Substituting this value in the overall mass balance equation for the first sub-system, we get: m = 4 kg/s 2 Since m 2 0, and x 2 (m 2) = x 3 (m 2) = 0, we get: x 2 = x 3 = 0 Substituting these values of m 1 and m 2 in the fat balance equation for the first sub-system, and noting that x (m ) = 0, we get: x = Solving for the remaining variables, we get: m 3 = 9 kg/s, x 4 = 0, x 5 = 0.36
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Psychrometrics
 Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 21) Solutions to Example Problems on Psychrometrics 1. We begin by identifying the conditions of the two streams on the psychrometric chart as follows.
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 21) Solutions to Example Problems on Psychrometrics 1. We begin by identifying the conditions of the two streams on the psychrometric chart as follows.
Warm-Up. Describe what happens to an enzyme placed at high temperatures.
 Warm-Up Describe what happens to an enzyme placed at high temperatures. Food (carbohydrates, lipids and proteins) is essentially many carbon atoms bound together. Food (carbohydrates, lipids and proteins)
Warm-Up Describe what happens to an enzyme placed at high temperatures. Food (carbohydrates, lipids and proteins) is essentially many carbon atoms bound together. Food (carbohydrates, lipids and proteins)
Chemistry Basics. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass Energy the ability to do work. Chemical Electrical Mechanical Radiant. Slide 2.
 Chemistry Basics Matter anything that occupies space and has mass Energy the ability to do work Chemical Electrical Mechanical Radiant Slide 2.1 Composition of Matter Elements Fundamental units of matter
Chemistry Basics Matter anything that occupies space and has mass Energy the ability to do work Chemical Electrical Mechanical Radiant Slide 2.1 Composition of Matter Elements Fundamental units of matter
Biogeochemical Review
 Biogeochemical Review Name KEY LT 1 1. Name and define 5 processes in the water cycle. Precipitation moisture falls back to the earth as rain, snow, sleet, or hail. Evaporation liquid water changes into
Biogeochemical Review Name KEY LT 1 1. Name and define 5 processes in the water cycle. Precipitation moisture falls back to the earth as rain, snow, sleet, or hail. Evaporation liquid water changes into
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 2 FLASHCARDS
 LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 2 FLASHCARDS Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all organisms share? A. ability to taste and smell B. ability to grow and develop C. ability to use energy D. ability
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 2 FLASHCARDS Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all organisms share? A. ability to taste and smell B. ability to grow and develop C. ability to use energy D. ability
Analysis of Cocoa Butter Using the SpectraStar 2400 NIR Spectrometer
 Application Note: F04 Analysis of Cocoa Butter Using the SpectraStar 2400 NIR Spectrometer Introduction Near-infrared (NIR) technology has been used in the food, feed, and agriculture industries for over
Application Note: F04 Analysis of Cocoa Butter Using the SpectraStar 2400 NIR Spectrometer Introduction Near-infrared (NIR) technology has been used in the food, feed, and agriculture industries for over
M1. (a) light is trapped / absorbed / used extra answers cancel mark ignore solar / sunshine 1
 M. (a) light is trapped / absorbed / used extra answers cancel mark ignore solar / sunshine by chlorophyll / chloroplasts if no other marks awarded, allow mark for photosynthesis / equation for photosynthesis
M. (a) light is trapped / absorbed / used extra answers cancel mark ignore solar / sunshine by chlorophyll / chloroplasts if no other marks awarded, allow mark for photosynthesis / equation for photosynthesis
Course Title: Consumer Chemistry Topic/Concept: Measuring the properties of matter Time Allotment: 21 days Unit Sequence: 1
 Course Title: Consumer Chemistry Topic/Concept: Measuring the properties of matter Time Allotment: 21 days Unit Sequence: 1 1. Scientific method 2. Measurement 3. Physical and Chemical properties 4. Phases
Course Title: Consumer Chemistry Topic/Concept: Measuring the properties of matter Time Allotment: 21 days Unit Sequence: 1 1. Scientific method 2. Measurement 3. Physical and Chemical properties 4. Phases
Biology. Chapter 2 Notes
 Biology Chapter 2 Notes Section 1: Nature of Matter Objectives: 1) Differentiate between atoms and elements 2) Analyze how compounds are formed 3) Distinguish between covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds and
Biology Chapter 2 Notes Section 1: Nature of Matter Objectives: 1) Differentiate between atoms and elements 2) Analyze how compounds are formed 3) Distinguish between covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds and
What are the building blocks of life?
 Why? What are the building blocks of life? From the smallest single-celled organism to the tallest tree, all life depends on the properties and reactions of four classes of organic (carbon-based) compounds
Why? What are the building blocks of life? From the smallest single-celled organism to the tallest tree, all life depends on the properties and reactions of four classes of organic (carbon-based) compounds
Study Guide: Basic Chemistry, Water, Life Compounds and Enzymes
 Study Guide: Basic Chemistry, Water, Life Compounds and Enzymes 1. Lipids are good energy-storage molecules because a) the can absorb a large amount of energy while maintaining a constant temperature b)
Study Guide: Basic Chemistry, Water, Life Compounds and Enzymes 1. Lipids are good energy-storage molecules because a) the can absorb a large amount of energy while maintaining a constant temperature b)
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Problems on Heat Transfer
 Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 1) Problems on Heat Transfer 1. What is the thermal conductivity of a material 8 cm thick if the temperature at one end of the product is 0 C and the temperature
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 1) Problems on Heat Transfer 1. What is the thermal conductivity of a material 8 cm thick if the temperature at one end of the product is 0 C and the temperature
The Science of Biology
 The Science of Biology Biology Key aspect of Biology Organisms = Living things How do we know that something is a living thing? Characteristics of Living Things Have a cellular organization Contain similar
The Science of Biology Biology Key aspect of Biology Organisms = Living things How do we know that something is a living thing? Characteristics of Living Things Have a cellular organization Contain similar
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms. Section 1: Building Blocks of Life
 Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 1: 30 Essential Question:What is matter and how does it change? Notes - Blocks of Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Atomic theory Molecule Compound
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 1: 30 Essential Question:What is matter and how does it change? Notes - Blocks of Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Atomic theory Molecule Compound
UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY
 UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 1: Biochemistry Chapter 6.1: Chemistry of Life I. Atoms, Ions, and Molecules A. Living things consist of atoms of different elements 1. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter
UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 1: Biochemistry Chapter 6.1: Chemistry of Life I. Atoms, Ions, and Molecules A. Living things consist of atoms of different elements 1. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter
Specific heat below freezing point:
 Specific heat below freezing point: Only the difference due to water is taken into consideration. Other than water, the specific heats of the other contituents of food do not change with the temperature
Specific heat below freezing point: Only the difference due to water is taken into consideration. Other than water, the specific heats of the other contituents of food do not change with the temperature
Chapter Test A. It s Alive!! Or Is It? MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Assessment Chapter Test A It s Alive!! Or Is It? MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all organisms share?
Assessment Chapter Test A It s Alive!! Or Is It? MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all organisms share?
Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review
 Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life macromolecules - The four types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins Types of Macromolecules
Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life macromolecules - The four types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins Types of Macromolecules
Name: Date: Period: Biology Notes: Biochemistry Directions: Fill this out as we cover the following topics in class
 Name: Date: Period: Biology Notes: Biochemistry Directions: Fill this out as we cover the following topics in class Part I. Water Water Basics Polar: part of a molecule is slightly, while another part
Name: Date: Period: Biology Notes: Biochemistry Directions: Fill this out as we cover the following topics in class Part I. Water Water Basics Polar: part of a molecule is slightly, while another part
Unit 2: The Properties of Water, Organic Macromolecules, Enzymes, Digestion (questions)
 Table 1: ph Values of Common Substances 1. Observe Table 1, which substance has the highest concentration of H+ ions? a. Water b. Baking soda solution c. Lemon juice d. Sodium hydroxide solution 2. Which
Table 1: ph Values of Common Substances 1. Observe Table 1, which substance has the highest concentration of H+ ions? a. Water b. Baking soda solution c. Lemon juice d. Sodium hydroxide solution 2. Which
Chapter 6 Chemistry in Biology
 Section 1: Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Section 2: Chemical Reactions Section 3: Water and Solutions Section 4: The Building Blocks of Life Click on a lesson name to select. 6.1 Atoms, Elements, and
Section 1: Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Section 2: Chemical Reactions Section 3: Water and Solutions Section 4: The Building Blocks of Life Click on a lesson name to select. 6.1 Atoms, Elements, and
Do Now. What is a catalyst? PASS UP LABS!
 Do Now What is a catalyst? PASS UP LABS! Do Now What is a compound? Give an example Name 3 elements found in our body. What are the 3 parts of an atom and where are they located? Do Now What are carbohydrates
Do Now What is a catalyst? PASS UP LABS! Do Now What is a compound? Give an example Name 3 elements found in our body. What are the 3 parts of an atom and where are they located? Do Now What are carbohydrates
Matter and Substances Section 3-1
 Matter and Substances Section 3-1 Key Idea: All matter is made up of atoms. An atom has a positively charges core surrounded by a negatively charged region. An atom is the smallest unit of matter that
Matter and Substances Section 3-1 Key Idea: All matter is made up of atoms. An atom has a positively charges core surrounded by a negatively charged region. An atom is the smallest unit of matter that
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Evaporation
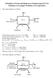 Princiles of Food and Biorocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Examle Problems on Eaoration 1. The system diagram is as follows: Solids balance equation: 0.1 (m f) = 0.5 (1,000) Thus, m f = 5,000 kg/hr
Princiles of Food and Biorocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Examle Problems on Eaoration 1. The system diagram is as follows: Solids balance equation: 0.1 (m f) = 0.5 (1,000) Thus, m f = 5,000 kg/hr
Y7 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Keywords
 Y7 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Biology Cells. Cells as the fundamental unit of living organisms, including how to observe cell structure using a light microscope. The functions of the cell wall,
Y7 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Biology Cells. Cells as the fundamental unit of living organisms, including how to observe cell structure using a light microscope. The functions of the cell wall,
Chapter 6 The Chemistry of Life
 Chapter 6 The Chemistry of Life Atoms: The Building Blocks of Life Both living and non-living things have atoms Everything, living and non, is made of Atoms. An elements is something you can break down
Chapter 6 The Chemistry of Life Atoms: The Building Blocks of Life Both living and non-living things have atoms Everything, living and non, is made of Atoms. An elements is something you can break down
2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules. 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules. 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules. 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
 All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. Living things consist of atoms of different elements. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. An element is one type of atom. ydrogen
All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. Living things consist of atoms of different elements. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. An element is one type of atom. ydrogen
the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together Chemical structure Covalent bond Ionic bond
 Chemical structure the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together Covalent bond bond formed by the sharing of valence electrons between atoms Ionic bond
Chemical structure the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together Covalent bond bond formed by the sharing of valence electrons between atoms Ionic bond
Lab: Using indicator dyes to examine macromolecules in food.
 Lab: Using indicator dyes to examine macromolecules in food. Chemistry deals with the study of matter. Matter: Anything that takes up space and has mass (rock, bug, human). Atoms are the fundamental units
Lab: Using indicator dyes to examine macromolecules in food. Chemistry deals with the study of matter. Matter: Anything that takes up space and has mass (rock, bug, human). Atoms are the fundamental units
Guided Notes Unit 1: Biochemistry
 Name: Date: Block: Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life I. Concept 2.1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules a. Atoms Guided Notes Unit 1: Biochemistry i. Atom: _ ii. (They are SUPER small! It would take 3 million carbon
Name: Date: Block: Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life I. Concept 2.1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules a. Atoms Guided Notes Unit 1: Biochemistry i. Atom: _ ii. (They are SUPER small! It would take 3 million carbon
Photosynthesis. Synthesizing food from light
 Photosynthesis Synthesizing food from light 7.5A recognize that radiant energy from the Sun is transformed into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis Consider a Hamburger.. It contains
Photosynthesis Synthesizing food from light 7.5A recognize that radiant energy from the Sun is transformed into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis Consider a Hamburger.. It contains
Living Things. perform a specific job in the body. Skin and lining of organs. Blood, bones, cartilage, fat. Brain and nerves
 Living Things Structure & Function BIG IDEA : All living things are made of cells A. Unicellular Organisms 1. Made of only one cell. 2. Examples paramecia, amoebas, bacteria B. Multicellular Organisms
Living Things Structure & Function BIG IDEA : All living things are made of cells A. Unicellular Organisms 1. Made of only one cell. 2. Examples paramecia, amoebas, bacteria B. Multicellular Organisms
Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher
 Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Section 1: Nature of Matter Objectives: Differentiate between atoms and elements. Analyze how compounds are formed. Distinguish between covalent bonds, hydrogen
Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Section 1: Nature of Matter Objectives: Differentiate between atoms and elements. Analyze how compounds are formed. Distinguish between covalent bonds, hydrogen
2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Living things consist of atoms of different elements. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. An element is one type of atom. 6 elements make up 99% of all living things
2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Living things consist of atoms of different elements. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. An element is one type of atom. 6 elements make up 99% of all living things
Unit 2: Basic Chemistry
 Unit 2: Basic Chemistry I. Matter and Energy A. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass (weight) B. Energy the ability to do work 1. Chemical 2. Electrical 3. Mechanical 4. Radiant C. Composition
Unit 2: Basic Chemistry I. Matter and Energy A. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass (weight) B. Energy the ability to do work 1. Chemical 2. Electrical 3. Mechanical 4. Radiant C. Composition
1. The drawings below show three healthy young plants. A B C. The drawings below show the three plants after two weeks.
 1. The drawings below show three healthy young plants. A B C The drawings below show the three plants after two weeks. A C B (a) (i) Plant B did not have enough light. How can you tell this from the drawing?....
1. The drawings below show three healthy young plants. A B C The drawings below show the three plants after two weeks. A C B (a) (i) Plant B did not have enough light. How can you tell this from the drawing?....
What to do about the world s most deadly compound DIHYDROGEN MONOXIDE (DHMO)
 What to do about the world s most deadly compound DIHYDROGEN MONOXIDE (DHMO) Unit 2 Bio-molecules and Biochemistry The Chemistry of Life It all starts with Water Life depends on water! Why do you think
What to do about the world s most deadly compound DIHYDROGEN MONOXIDE (DHMO) Unit 2 Bio-molecules and Biochemistry The Chemistry of Life It all starts with Water Life depends on water! Why do you think
Which of the following are autotrophs?
 Which of the following are autotrophs? 1. Impalas 2. Plants 3. Leopards 4. mushrooms 82% 15% 3% 0% Impalas Plants Leopards mushrooms One of the principal chemical compounds that living things use for 1.
Which of the following are autotrophs? 1. Impalas 2. Plants 3. Leopards 4. mushrooms 82% 15% 3% 0% Impalas Plants Leopards mushrooms One of the principal chemical compounds that living things use for 1.
Photosynthesis and Life
 7-1 Chapter 7 Photosynthesis and Life During photosynthesis Organisms use the energy of light to build highenergy organic molecules. Plants, algae, and some bacteria can do this. Can make their own food
7-1 Chapter 7 Photosynthesis and Life During photosynthesis Organisms use the energy of light to build highenergy organic molecules. Plants, algae, and some bacteria can do this. Can make their own food
Nature of matter. Chemical bond is a force that joins atoms
 Nature of matter Atom the smallest unit of matter that cannot be broken down by chemical means The subatomic particles of an atom consist of protons, neutrons and electrons Element is a pure substance
Nature of matter Atom the smallest unit of matter that cannot be broken down by chemical means The subatomic particles of an atom consist of protons, neutrons and electrons Element is a pure substance
Cell Energetics - Practice Test
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Cell Energetics - Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the source of energy used
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Cell Energetics - Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the source of energy used
Elements and Isotopes
 Section 2-1 Notes Atoms Life depends on chemistry. The basic unit of matter is the atom. Atoms are incredibly small The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Parts
Section 2-1 Notes Atoms Life depends on chemistry. The basic unit of matter is the atom. Atoms are incredibly small The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Parts
Photosynthesis Prep Test 2
 Photosynthesis Prep Test 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Energy is released from ATP when a. a phosphate group is added. b. adenine bonds
Photosynthesis Prep Test 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Energy is released from ATP when a. a phosphate group is added. b. adenine bonds
2015 Biology Unit #3 Quiz 1 Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Week of November
 Name: Class: Date: 2015 Biology Unit #3 Quiz 1 Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Week of 02-09 November 1 Which of the following statements is true for all cells? a They use solar energy
Name: Class: Date: 2015 Biology Unit #3 Quiz 1 Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Week of 02-09 November 1 Which of the following statements is true for all cells? a They use solar energy
1.Matter and Organic Compounds Matter =
 The Chemistry of Life Notes Unit 2 1.Matter and Organic Compounds Matter = All things are made of matter Name Matter is made up of substances Chemical substance = definite composition throughout Either
The Chemistry of Life Notes Unit 2 1.Matter and Organic Compounds Matter = All things are made of matter Name Matter is made up of substances Chemical substance = definite composition throughout Either
Lab 8. Lab-tray dryer
 BAEN/CHEN-474 page 1 of 6 Student s Name: Factors influencing the drying rates in Objectives: 1.) To become familiar with the operation of a tray dryer 2.) To determine the psychrometric properties of
BAEN/CHEN-474 page 1 of 6 Student s Name: Factors influencing the drying rates in Objectives: 1.) To become familiar with the operation of a tray dryer 2.) To determine the psychrometric properties of
Do we need plants to survive?
 Please write a short answer response (3-4 sentences) to the following question on half a sheet of paper. Do we need plants to survive? 1 of 20 General Sherman, a Giant Sequoia, is the world s tallest tree,
Please write a short answer response (3-4 sentences) to the following question on half a sheet of paper. Do we need plants to survive? 1 of 20 General Sherman, a Giant Sequoia, is the world s tallest tree,
AP BIOLOGY BIOCHEMISTRY MULTIPLE CHOICE EXAM (RAVEN CHAPTERS 2, 3)
 Period Date AP BIOLOGY BIOCHEMISTRY MULTIPLE CHOICE EXAM (RAVEN CHAPTERS 2, 3) 1. Which of the following is an example of a hydrogen bond? (90:09) A. The peptide bond between amino acids in a protein B.
Period Date AP BIOLOGY BIOCHEMISTRY MULTIPLE CHOICE EXAM (RAVEN CHAPTERS 2, 3) 1. Which of the following is an example of a hydrogen bond? (90:09) A. The peptide bond between amino acids in a protein B.
Chapter 2 Chemical Aspects of Life
 Chapter 2 Chemical Aspects of Life Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that has weight and occupies space can be described as A. an atom. B. matter. C. a compound. D. a molecule. #1 Learning Outcome:
Chapter 2 Chemical Aspects of Life Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that has weight and occupies space can be described as A. an atom. B. matter. C. a compound. D. a molecule. #1 Learning Outcome:
Photosynthesis in Detail
 4.3 Photosynthesis in Detail KEY CONCEPT Photosynthesis requires a series of chemical reactions. MAIN IDEAS The first stage of photosynthesis captures and transfers energy. The second stage of photosynthesis
4.3 Photosynthesis in Detail KEY CONCEPT Photosynthesis requires a series of chemical reactions. MAIN IDEAS The first stage of photosynthesis captures and transfers energy. The second stage of photosynthesis
CELLS. Structure and Function
 CELLS Structure and Function Cell Structure All plant and animal tissue consist of cells. Cells are microscopic in size. In general, each cell performs all the characteristics of life and, though in reality
CELLS Structure and Function Cell Structure All plant and animal tissue consist of cells. Cells are microscopic in size. In general, each cell performs all the characteristics of life and, though in reality
Combinatorial Optimization: AMS Amitabh Basu. Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, Johns Hopkins U.
 Combinatorial Optimization: AMS 550.766 Amitabh Basu Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, Johns Hopkins U., Spring 2018 1 / 7 Two types of optimization problems Type I n Items: weights w 1,...,
Combinatorial Optimization: AMS 550.766 Amitabh Basu Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, Johns Hopkins U., Spring 2018 1 / 7 Two types of optimization problems Type I n Items: weights w 1,...,
Energy Flow in Ecosystems
 http://media-2.web.britannica.com/eb-media/22/94122-034-4cfcfcc7.jpg Energy Flow in Ecosystems The Sun All living things require a source of energy in order to survive. Radiant energy from the sun sustains
http://media-2.web.britannica.com/eb-media/22/94122-034-4cfcfcc7.jpg Energy Flow in Ecosystems The Sun All living things require a source of energy in order to survive. Radiant energy from the sun sustains
Bio110 Lab 3: Basic Chemistry A. Carranza
 NAME Basic Chemistry The following chart lists the important elements found in cytoplasm by weight. On the chart, fill in the symbol and the number of electrons found in each element Use the periodic table
NAME Basic Chemistry The following chart lists the important elements found in cytoplasm by weight. On the chart, fill in the symbol and the number of electrons found in each element Use the periodic table
SCIENCE. Year 10 Examination B 80 marks. Make sure you have answered all the questions in this paper before you start 10A or 10C
 NAME: SCIENCE TEACHER: (circle code) 10B SCIENCE Year 10 Examination 2013 10B 80 marks Make sure you have answered all the questions in this paper before you start 10A or 10C Time allowed for both examinations:
NAME: SCIENCE TEACHER: (circle code) 10B SCIENCE Year 10 Examination 2013 10B 80 marks Make sure you have answered all the questions in this paper before you start 10A or 10C Time allowed for both examinations:
Elements, Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet
 Elements, Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet Part 1: Read the following information on elements, compounds and mixtures. Fill in the blanks where necessary. Elements: A pure substance containing only one kind
Elements, Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet Part 1: Read the following information on elements, compounds and mixtures. Fill in the blanks where necessary. Elements: A pure substance containing only one kind
4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP. KEY CONCEPT All cells need chemical energy.
 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP KEY CONCEPT All cells need chemical energy. 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP The chemical energy used for most cell processes is carried by ATP. Molecules in food store chemical
4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP KEY CONCEPT All cells need chemical energy. 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP The chemical energy used for most cell processes is carried by ATP. Molecules in food store chemical
Roots, Shoots & Leaves
 Name Test Date Hour Plant Structure & Function #2 - Notebook Roots, Shoots & Leaves LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the functions of roots I can explain the nitrogen fixing process and why it is needed.
Name Test Date Hour Plant Structure & Function #2 - Notebook Roots, Shoots & Leaves LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the functions of roots I can explain the nitrogen fixing process and why it is needed.
SAMPLE CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS MIXTURE OF UNIT 3 & 4 MATERIALS
 SAMPLE CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS MIXTURE OF UNIT 3 & 4 MATERIALS QUESTION 1 The equation describing the production of butyl ethanoate is given below. Catalyst C4H 9OH CH 3COOH CH 3COOC 4H 9 H 2O( l ) 0.0500
SAMPLE CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS MIXTURE OF UNIT 3 & 4 MATERIALS QUESTION 1 The equation describing the production of butyl ethanoate is given below. Catalyst C4H 9OH CH 3COOH CH 3COOC 4H 9 H 2O( l ) 0.0500
2/18/2013 CHEMISTRY OF CELLS. Carbon Structural Formations. 4 Classes of Organic Compounds (biomolecules)
 CHEMISTRY OF CELLS 11 elements make up all organisms C, O, N, H: 96% weight of human body ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic compounds: contain C Inorganic compounds: no C Bonding and Structural Formulas H and
CHEMISTRY OF CELLS 11 elements make up all organisms C, O, N, H: 96% weight of human body ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic compounds: contain C Inorganic compounds: no C Bonding and Structural Formulas H and
Chapter 3.1 Chemistry of Life
 Life Science Chapter 3: Cell Processes 1. Chemistry of Life 2. Moving Cellular Materials 3. Energy for Life http://www.connecticutvalleybiological.com/cell processes vhs p 14026.html Chapter 3.1 Chemistry
Life Science Chapter 3: Cell Processes 1. Chemistry of Life 2. Moving Cellular Materials 3. Energy for Life http://www.connecticutvalleybiological.com/cell processes vhs p 14026.html Chapter 3.1 Chemistry
COMMON ENTRANCE EXAMINATION AT 13+ SCIENCE LEVEL 2 BIOLOGY MARK SCHEME. Specimen Paper. (for first examination in Autumn 2017)
 COMMON ENTRANCE EXAMINATION AT 3+ SCIENCE LEVEL 2 BIOLOGY MARK SCHEME Specimen Paper (for first examination in Autumn 207) This is a suggested, not a prescriptive, mark scheme. 2835SM29 Independent Schools
COMMON ENTRANCE EXAMINATION AT 3+ SCIENCE LEVEL 2 BIOLOGY MARK SCHEME Specimen Paper (for first examination in Autumn 207) This is a suggested, not a prescriptive, mark scheme. 2835SM29 Independent Schools
Water in Food 3 rd International Workshop. Water Analysis of Food Products with at-line and on-line FT-NIR Spectroscopy. Dr.
 Water in Food 3 rd International Workshop Water Analysis of Food Products with at-line and on-line FT-NIR Spectroscopy Dr. Andreas Niemöller Lausanne 29th 30th March 2004 Bruker Group Company Technology
Water in Food 3 rd International Workshop Water Analysis of Food Products with at-line and on-line FT-NIR Spectroscopy Dr. Andreas Niemöller Lausanne 29th 30th March 2004 Bruker Group Company Technology
Chapter 02. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 02 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 02 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
B DAYS BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT GUIDE Due 9/13/16 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 8/22 - A 8/23 - B
 B DAYS BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT GUIDE Due 9/13/16 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 8/22 - A 8/23 - B 8/24 - A 8/25 - B 8/26 - A 8/29 - B *Hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis *Macromolecule active reading
B DAYS BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT GUIDE Due 9/13/16 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 8/22 - A 8/23 - B 8/24 - A 8/25 - B 8/26 - A 8/29 - B *Hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis *Macromolecule active reading
Key Stage 3 Subject: Science Autumn term
 Key Stage 3 Subject: Science Autumn term Year: Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Term: Autumn Spring Summer Topic/Module: Introductory safety and skills Unit Half Term: 1st half 2nd half Description of lessons:biology,
Key Stage 3 Subject: Science Autumn term Year: Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Term: Autumn Spring Summer Topic/Module: Introductory safety and skills Unit Half Term: 1st half 2nd half Description of lessons:biology,
Chapter 02 Chemical Composition of the Body
 Chapter 02 Chemical Composition of the Body 1. In an atom, the number of Student: A. Protons always equals the number of neutrons B. Of protons always equals the number of electrons C. Of neutrons always
Chapter 02 Chemical Composition of the Body 1. In an atom, the number of Student: A. Protons always equals the number of neutrons B. Of protons always equals the number of electrons C. Of neutrons always
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Biology. Dr. Ramos BIO 370
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Biology Dr. Ramos BIO 370 2 Atoms, Bonds, and Molecules Matter - all materials that occupy space and have mass Matter is composed of atoms. Atom simplest form of matter not divisible
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Biology Dr. Ramos BIO 370 2 Atoms, Bonds, and Molecules Matter - all materials that occupy space and have mass Matter is composed of atoms. Atom simplest form of matter not divisible
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Name Period Date Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Biology A - STUDY GUIDE 1. Know the parts of the process. (MTS_LT1 ) a. The site (organelle) in a plant cell where photosynthesis takes place: b.
Name Period Date Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Biology A - STUDY GUIDE 1. Know the parts of the process. (MTS_LT1 ) a. The site (organelle) in a plant cell where photosynthesis takes place: b.
`1AP Biology Study Guide Chapter 2 v Atomic structure is the basis of life s chemistry Ø Living and non- living things are composed of atoms Ø
 `1AP Biology Study Guide Chapter 2 v Atomic structure is the basis of life s chemistry Ø Living and non- living things are composed of atoms Ø Element pure substance only one kind of atom Ø Living things
`1AP Biology Study Guide Chapter 2 v Atomic structure is the basis of life s chemistry Ø Living and non- living things are composed of atoms Ø Element pure substance only one kind of atom Ø Living things
Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process of harnessing the energy of sunlight to make carbohydrates (sugars).
 Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process of harnessing the energy of sunlight to make carbohydrates (sugars). Plants do photosynthesis to make their own food (sugars) and are called, photoautotrophs.
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process of harnessing the energy of sunlight to make carbohydrates (sugars). Plants do photosynthesis to make their own food (sugars) and are called, photoautotrophs.
Lecture 3: DESIGN CONSIDERATION OF DRIERS
 Lecture 3: DESIGN CONSIDERATION OF DRIERS 8. DESIGN OF DRYER Design of a rotary dryer only on the basis of fundamental principle is very difficult. Few of correlations that are available for design may
Lecture 3: DESIGN CONSIDERATION OF DRIERS 8. DESIGN OF DRYER Design of a rotary dryer only on the basis of fundamental principle is very difficult. Few of correlations that are available for design may
Ch. 10 Photosynthesis: The Calvin Cycle Life from Air
 Ch. 10 Photosynthesis: The Calvin Cycle Life from Air 2007-2008 Whoops! Wrong Calvin The Calvin Cycle 1950s 1961 Remember what it means to be a plant Need to produce all organic molecules necessary for
Ch. 10 Photosynthesis: The Calvin Cycle Life from Air 2007-2008 Whoops! Wrong Calvin The Calvin Cycle 1950s 1961 Remember what it means to be a plant Need to produce all organic molecules necessary for
The Chemistry of Biology
 The Chemistry of Biology Life depends on chemistry. Living things are composed of chemical compounds. If order to understand biology, one must first understand the chemistry of life. I. The Nature of Matter
The Chemistry of Biology Life depends on chemistry. Living things are composed of chemical compounds. If order to understand biology, one must first understand the chemistry of life. I. The Nature of Matter
How do we get the energy, building blocks, and important molecules out of our food?
 Why do we need to eat food? To get a source of energy To get building blocks (raw materials) for growth/repair/maintenance/ energy storage To get the homeostasis molecules needed to keep our body "machinery"
Why do we need to eat food? To get a source of energy To get building blocks (raw materials) for growth/repair/maintenance/ energy storage To get the homeostasis molecules needed to keep our body "machinery"
Biochemistry. The Chemistry of Life
 Biochemistry The Chemistry of Life Biochemistry The life processes (Chapter 1) are chemical in nature. Chemical reactions occur in life. Living things are made of chemical compounds. The Atom- The Basic
Biochemistry The Chemistry of Life Biochemistry The life processes (Chapter 1) are chemical in nature. Chemical reactions occur in life. Living things are made of chemical compounds. The Atom- The Basic
McPherson College Football Nutrition
 McPherson College Football Nutrition McPherson College Football 10 RULES OF PROPER NUTRITION 1. CONSUME 5-6 MEALS EVERY DAY (3 SQUARE MEALS / 3 SNACKS). 2. EVERY MEAL YOU CONSUME SHOULD CONTAIN THE FOLLOWING:
McPherson College Football Nutrition McPherson College Football 10 RULES OF PROPER NUTRITION 1. CONSUME 5-6 MEALS EVERY DAY (3 SQUARE MEALS / 3 SNACKS). 2. EVERY MEAL YOU CONSUME SHOULD CONTAIN THE FOLLOWING:
1 Nutrition in Plants
 1 Nutrition in Plants Quick Peek 1. All living organisms perform some basic functions to keep themselves alive. These basic functions are called life processes. 2. All organisms require food to get energy
1 Nutrition in Plants Quick Peek 1. All living organisms perform some basic functions to keep themselves alive. These basic functions are called life processes. 2. All organisms require food to get energy
LIFE OF CELL. Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1. BS Biology Graduate, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2
 LIFE OF CELL Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1 BS Biology Graduate, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2 MS Biology Student, Graduate School, Centro Escolar
LIFE OF CELL Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1 BS Biology Graduate, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2 MS Biology Student, Graduate School, Centro Escolar
Military High School AL- Ain. Grade 10 &11. Biology Sample Questions. Student Name: Computer #:
 Military High School AL- Ain Grade 10 &11 Biology Sample Questions Student Name: Computer #: Chapter 1: Cells In all multiple choice questions, more than answer could be correct Section : 1 What Is a Cell?
Military High School AL- Ain Grade 10 &11 Biology Sample Questions Student Name: Computer #: Chapter 1: Cells In all multiple choice questions, more than answer could be correct Section : 1 What Is a Cell?
1. Matter is anything that has mass and volume. 2. What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical change?
 Name Chemistry: Matter, Water, Acids & Bases, and Macromolecules Study Guide This study guide is a good representation of what you will need to know for your test. You are responsible for completing the
Name Chemistry: Matter, Water, Acids & Bases, and Macromolecules Study Guide This study guide is a good representation of what you will need to know for your test. You are responsible for completing the
4.3. Photosynthesis in Detail. The first stage of photosynthesis captures and transfers energy.
 4.3 Photosynthesis in Detail VOCABULARY photosystem electron transport chain ATP synthase Calvin cycle Key Concept Photosynthesis requires a series of chemical reactions. MAIN IDEAS The first stage of
4.3 Photosynthesis in Detail VOCABULARY photosystem electron transport chain ATP synthase Calvin cycle Key Concept Photosynthesis requires a series of chemical reactions. MAIN IDEAS The first stage of
Name: Photosynthesis. Class: Date: 76 minutes. Time: 76 marks. Marks: level 1, 2 and 3. Increasing demand. Comments:
 Photosynthesis Name: Class: Date: Time: 76 minutes Marks: 76 marks Comments: level, 2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Complete the word equation for photosynthesis. carbon dioxide + water energy glucose +
Photosynthesis Name: Class: Date: Time: 76 minutes Marks: 76 marks Comments: level, 2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Complete the word equation for photosynthesis. carbon dioxide + water energy glucose +
Chemistry of Life 10/1/2010. What makes up the chemistry of life?
 A. Students will be able to identify and define the parts of an atom. Chemistry of Life At the Completion of this Unit, Students will be able to: A. Identify and define the parts of an atom. B. Demonstrate
A. Students will be able to identify and define the parts of an atom. Chemistry of Life At the Completion of this Unit, Students will be able to: A. Identify and define the parts of an atom. B. Demonstrate
UNIT 3: Cell Energy What is energy? energy is a property of objects which can be transferred to other objects or converted into different forms.
 UNIT 3: Cell Energy What is energy? energy is a property of objects which can be transferred to other objects or converted into different forms. Energy can be found in a number of different forms. 1 Law
UNIT 3: Cell Energy What is energy? energy is a property of objects which can be transferred to other objects or converted into different forms. Energy can be found in a number of different forms. 1 Law
Fifth Grade: FOSS Life Science - Living Systems
 Fifth Grade: FOSS Life Science - Living Systems Investigation Title and Synopsis Concepts Assessments and TE Page Numbers 1. Living Cells Students study four related human/body transport systems that provide
Fifth Grade: FOSS Life Science - Living Systems Investigation Title and Synopsis Concepts Assessments and TE Page Numbers 1. Living Cells Students study four related human/body transport systems that provide
Downloaded from
 Nutrition in Plants 1.If the pitcher plant is green and carries out photosynthesis then why does it feed on insects? 2.Which of the following part/s of a desert plant perform the function of photosynthesis?
Nutrition in Plants 1.If the pitcher plant is green and carries out photosynthesis then why does it feed on insects? 2.Which of the following part/s of a desert plant perform the function of photosynthesis?
Ch 7: Cell Structure and Functions. AP Biology
 Ch 7: Cell Structure and Functions AP Biology The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. New cells come from existing cells. 3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of living
Ch 7: Cell Structure and Functions AP Biology The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. New cells come from existing cells. 3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of living
Teacher Instructions
 Teacher Instructions To print handouts for students Go to File print, change Print what: to handouts, change # per page if desired to enlarge slides on page Change Print range to slides and type in slide
Teacher Instructions To print handouts for students Go to File print, change Print what: to handouts, change # per page if desired to enlarge slides on page Change Print range to slides and type in slide
DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF CEREALS AT MICROWAVE FREQUENCY AND THEIR BIO CHEMICAL ESTIMATION
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol., No 3, 013, 369 374 ISSN 78-3687 (O) DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF CEREALS AT MICROWAVE FREQUENCY AND THEIR BIO CHEMICAL ESTIMATION *Nidhi
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol., No 3, 013, 369 374 ISSN 78-3687 (O) DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF CEREALS AT MICROWAVE FREQUENCY AND THEIR BIO CHEMICAL ESTIMATION *Nidhi
Which row in the chart below identifies the lettered substances in this process?
 1. A biological process that occurs in both plants and animals is shown below. Which row in the chart below identifies the lettered substances in this process? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 2. All life depends on
1. A biological process that occurs in both plants and animals is shown below. Which row in the chart below identifies the lettered substances in this process? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 2. All life depends on
The Chemistry and Energy of Life
 2 The Chemistry and Energy of Life Chapter 2 The Chemistry and Energy of Life Key Concepts 2.1 Atomic Structure Is the Basis for Life s Chemistry 2.2 Atoms Interact and Form Molecules 2.3 Carbohydrates
2 The Chemistry and Energy of Life Chapter 2 The Chemistry and Energy of Life Key Concepts 2.1 Atomic Structure Is the Basis for Life s Chemistry 2.2 Atoms Interact and Form Molecules 2.3 Carbohydrates
Main Topic Sub-topics Students should be able to R O G
 Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
Catalyst/Bellringer: Because of our shortened class period today, please follow these instructions in order to start Part III of our SOL review:
 SOL REVIEW DAYSHEET 75: SOL Review Part IV: Biochemistry Biology I Name: Date: Catalyst/Bellringer:Becauseofourshortenedclassperiodtoday,pleasefollowthese instructionsinordertostartpartiiiofoursolreview:
SOL REVIEW DAYSHEET 75: SOL Review Part IV: Biochemistry Biology I Name: Date: Catalyst/Bellringer:Becauseofourshortenedclassperiodtoday,pleasefollowthese instructionsinordertostartpartiiiofoursolreview:
Part I: Short answer (25 points)
 Part I: Short answer (25 points) Part II: / 75 1. Recently, researchers published a five-year study involving 2,687 subjects with a disorder called sleep apnea. The subjects were between the ages of 45
Part I: Short answer (25 points) Part II: / 75 1. Recently, researchers published a five-year study involving 2,687 subjects with a disorder called sleep apnea. The subjects were between the ages of 45
Biology. Slide 1 of 28. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 28 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview 2 of 28 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview The key cellular process identified with energy production is photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process in which
Biology 1 of 28 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview 2 of 28 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview The key cellular process identified with energy production is photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process in which
8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview. 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview
 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview The key cellular process identified with energy production is photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process in which green plants use the energy of sunlight to convert water
8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview The key cellular process identified with energy production is photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process in which green plants use the energy of sunlight to convert water
Effect of Baking Powder in Wheat Flour Dough on Its Thermal Conduction during
 Food Sci. Technol. Res., 5 (), 7, 009 Effect of Baking Powder in Wheat Flour Dough on Its Thermal Conduction during Heating Tamako mizu and Keiko nagao * Tokyo Kasei University, Faculty of Home Economics,
Food Sci. Technol. Res., 5 (), 7, 009 Effect of Baking Powder in Wheat Flour Dough on Its Thermal Conduction during Heating Tamako mizu and Keiko nagao * Tokyo Kasei University, Faculty of Home Economics,
2.1 Matter and Organic Compounds
 2.1 Matter and Organic Compounds Lesson 2.1: True or False Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false. 1. An atom is smaller than an element. 2. Organic compounds are found
2.1 Matter and Organic Compounds Lesson 2.1: True or False Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false. 1. An atom is smaller than an element. 2. Organic compounds are found
Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air
 Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air 2006-2007 Energy needs of life All life needs a constant input of energy get their energy from eating others eat food = other organisms = make energy through get
Photosynthesis: Life from Light and Air 2006-2007 Energy needs of life All life needs a constant input of energy get their energy from eating others eat food = other organisms = make energy through get
