Process Control & Design
|
|
|
- Edward Hunt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Process Control & Design Lecture 5: Feedback Control System Jong Min Lee Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Seoul National University 1 / 29
2 Feedback Control Scheme: The Continuous Blending Process.1 Sensor (AT) measures the controlled variable: x..2 Controller (AC) calculates the manipulated input: w 2 in terms of an electronic signal..3 Current-to-pressure (I/P) converts it to an equivalent pneumatic signal. 2 / 29
3 Simplified Control Block Diagram d(s) y sp (s) Controller u(s) + Process y(s) + Negative feedback: self-stabilizing property with positive process gain e = y sp y Positive feedback: makes a process unstable with positive process gain in general e = y sp + y Used for describing complex systems (i.e., biological system) 3 / 29
4 Block Diagram dt dt = w i Q ρvc Vρ (T i T) + τ dt dt = (T i T) + Q Cw See lecture 2 for mass, energy balance eqns. w i = w: No need for mass balance y = T T, u = Q Q, d = T i T i Y (s) = 1 ( U ) (s) τs + 1 Cw + D (s) 4 / 29
5 Equivalent Representations U (s) 1 wc D (s) τs+1 Process Y (s) D (s) Process 1 τs+1 U (s) 1/wC τs Y (s) D (s) Process U (s) wc + + 1/wC τs+1 Y (s) 5 / 29
6 Proportional Control. Adjustment proportional to the current error..p(t) = p + K c (y sp (t) y m (t)) p (t) = K c e(t) Static control, memory-less control Proportional Band (PB) = 100 K c % (Foxboro, etc.) Reverse acting vs. Direct acting (Read section in the textbook.) Reverse acting: sensor output (y m ) Controller output K c > 0 Direct acting: sensor output (y m ) Controller output K c < 0 6 / 29
7 Level Controller (LC): Reverse-Acting or Direct-Acting? h LT LC q Level transmitter (LT): designed to be direct-acting (most transmitters are direct-acting) Its output signal increases as the level increases. Air-to-Open Valve: direct-acting Air-to-Close Valve: reverse-acting 7 / 29
8 P-Controller: Advantages and Disadvantages Advantage: simplicity Disadvantage Leaves offset with a set-point change or a sustained disturbance. Note: p is a equilibrium point (input) for the ``previous" set point or disturbance. 8 / 29
9 Proportional Integral (PI) Control. Adjustment proportional to the current error + accumulated error. ( p(t) = p + K c e(t) + 1 t ) e(t )dt τ I. τ I : Integral time or Reset time ( =P-control) Integral control action: reset control, floating control Some variations ( ) t Honeywell: p(t) = p + K c e(t) + τ R 0 e(t )dt ) Foxboro: p(t) = p t0 PB (e(t) + τ R e(t )dt τ R : reset rate 0 9 / 29
10 PI-Controller: Advantages and Disadvantages Advantage: eliminates offset (regardless of size of K c ) Disadvantage One more parameter to tune Easier to induce oscillation or instability 10 / 29
11 Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) Control. Adjustment proportional to the current error + accumulated error + current rate of change in the error. ( p(t) = p + K c e(t) + 1 t τ I. τ D: Derivative time constant 0 e(t )dt + τ D de dt Pure differentiation in real-time is not possible since evaluation of de/dt at time t requires error information beyond time t. But it can be approximated very closely. ) 11 / 29
12 PID-Controller: Advantages and Disadvantages Advantages Quick action to a change in the error -- effective prevention of runaway (e.g., in an auto-catalytic reactor) Decrease settling time for processes with slow dynamics and fast disturbances Decrease oscillation (stabilizing factor for integral mode, etc.) Disadvantage Yet one more parameter to tune Amplifies measurement noise effect (not suitable in flow control) 12 / 29
13 Typical PID Controller Display SP PV CO A D L CO SP M R R 167% PB 7.5min TI 1.5min TD PV, SP, CO: Process variable, Set point, Control output (normalized %) Local/Remote Switch: source of set point signal Auto/Manual Switch: Auto Manual (Bumpless transfer) Direct/Reverse Switch 13 / 29
14 Digital PID Controller Analog: Digital: ( p(t) = p + K c e(t) + 1 t τ I p(t k ) = p + K c ( e(t k ) + t τ I t: sampling period (interval) k i=0 e(t k ): error at the k th sample time 0 ) e(t )dt de + τ D dt p(t k ): controller output at the k th sample time ) e(t k ) e(t k 1 ) e(t i ) + τ D t 14 / 29
15 Removing ``Kicks" Sudden set point change (a step change) de/dt will be very large, giving a sudden jump in the valve position (undesirable in most cases) Apply the derivative action only on the output signal, not set point signal de dt = d dt (y sp(t) y m (t)) dy m dt Similar phenomenon can show up for the P-mode, though not as severe as the D-mode 15 / 29
16 Windup and Anti-Windup Windup When a constant error persists for a long time (such as when the valve ``saturates"), the integral term can be wound up to a very large term Consequence When the reason for the constant error (e.g., un-realizable set point change or too large a disturbance to reject completely) goes away, the integral term must unwind before the valve position returns to the normal value and control resumes. Large error in the opposite direction will result. 16 / 29
17 What do we need? Sensor (e.g., thermocouple) Transmitter (e.g., signal converter/amplifier/conditioner) Transmission Line (e.g., electrical line, air tube, data line) Controller (e.g., computer) Actuator (e.g., control valve) 17 / 29
18 Typical Setup Disturbance Process input (MV) Process Process output (CV) Actuator Sensor + Transmitter Controller output (4-20mA or 3-15 psig) Controller Controller input (4-20mA or 3-15 psig) 4-20mA Calibration Set point 18 / 29
19 Exemplary Control Loop: Temperature Control Actuator F 1 F 2 T 1 T psig Air I/P 4-20 ma D/A Sensor Thermowell T Thermocouple millivolt signal Operator Console DCS Control Computer A/D 4-20mA Transmitter 19 / 29
20 Implementation Modes Digital Transmission: either analog signal (which gets converted to digital signal just before entering the controller) or digital signal (sequence of 0-1 binary pulses) A/D: converts analog signal to digital signal D/A: converts digital signal to analog signal Controller: digital computer High flexibility and easy reconfiguration Easy access of remote data and past data 20 / 29
21 Sensors Physical properties signals appropriate for electric and mechanical processing Common sensors Temperature: thermocouple, resistance temperature detector (RTD) Pressure: bellows, bourdon tube, diaphragm Differential pressure: same as above Flow rate: orifice, venturi, vane, magnetic flow meter Liquid level: free float, fixed float, differential pressure ph: ph meter (electrode) Viscosity: differential pressure under constant flowrate Chemical composition: gas chromatograhy See Table 8.1 (p. 143) in the textbook. 21 / 29
22 Thermocouple Two metal junctions at different temperatures generating a voltage that is proportional to the temperature. Chromel-alumel (K-type): most popularly used Iron-constantan (J-type): higher emf Copper-constantan (T-type): cryogenic temperature 13% Rh.Pt-Pt (R-type): high temperature (>900 C) A Th Tc C i Th A Ice point o Tc = 0 C C V + - Th A Electronic ice point o C C 22 / 29
23 Resistance Thermometer Detector (RTD) Resistance of certain metals depends strongly upon their temperature Platinum and nickel are typical choices More accurate and repeatable but more expensive and less rugged than TCs Used for important temperature control points (reactors, distillation columns) R w 1 ma R Pt V 23 / 29
24 Pressure Measurement DP Cells Displacement to current low pressure diaphragm high pressure Strain guages High pressure measurements Stretched wire (elastic) Increased resistance 24 / 29
25 Level Measurement: Closed Tank low pressure h high pressure Differential Pressure Transmitter condensate drain P = ρgh 25 / 29
26 Transmitter Sensor signal (typically in mv) signal that can be transmitted and accepted by the controller (e.g., 4--20mA) Example 50 C 150 C 4mA -- 20mA Gain of the transmitter = 16mA/100 C = 0.16 ma/ C Zero of the transmitter = value when the output is at the minimum (4mA) = 50 C Why make the minimum output 4mA instead of 0mA? 26 / 29
27 Actuators Convert controller output signal (4--20 ma or psig) to physical adjustment in the process input variables (MVs). For process control, the most common type of actuator is the control valve. Others include Variable speed pumps Hydraulic actuators 27 / 29
28 Air-to-Open vs. Air-to-Close Air-to-Open (A-O) or Fail-Close (FC) More air larger opening No air valve closes Air-to-Close (A-C) or Fail-Open (FO) More air smaller opening No air valve opens completely Proper type to use is determined from safety considerations Air-to-Close: Coolant valve in an exothermic reactor or in a condenser of a distillation column Air-to-Open: Steam valve in a reactor, inlet flow valve to a tank Control Valve Dynamics U(s) P(s) = G v(s) = K v τ v s / 29
29 Specifying and Sizing Control Valves Basic valve equation q(l) = C v f(l) P v g s 0 l 1 l: valve lift, g s : specific gravity of the fluid (water = 1) Valve size: determines C v (valve coefficient) Valve trim type (valve characteristic) Linear: f(l) = l Square-root (Quick opening): f(l) = l Equal percentage: f(l) = R l 1, R / 29
Chapter 8. Feedback Controllers. Figure 8.1 Schematic diagram for a stirred-tank blending system.
 Feedback Controllers Figure 8.1 Schematic diagram for a stirred-tank blending system. 1 Basic Control Modes Next we consider the three basic control modes starting with the simplest mode, proportional
Feedback Controllers Figure 8.1 Schematic diagram for a stirred-tank blending system. 1 Basic Control Modes Next we consider the three basic control modes starting with the simplest mode, proportional
Process Control J.P. CORRIOU. Reaction and Process Engineering Laboratory University of Lorraine-CNRS, Nancy (France) Zhejiang University 2016
 Process Control J.P. CORRIOU Reaction and Process Engineering Laboratory University of Lorraine-CNRS, Nancy (France) Zhejiang University 206 J.P. Corriou (LRGP) Process Control Zhejiang University 206
Process Control J.P. CORRIOU Reaction and Process Engineering Laboratory University of Lorraine-CNRS, Nancy (France) Zhejiang University 206 J.P. Corriou (LRGP) Process Control Zhejiang University 206
SIMULATION SUITE CHEMCAD SOFTWARE PROCESS CONTROL SYSTEMS PROCESS CONTROL SYSTEMS COURSE WITH CHEMCAD MODELS. Application > Design > Adjustment
 COURSE WITH CHEMCAD MODELS PROCESS CONTROL SYSTEMS Application > Design > Adjustment Based on F.G. Shinskey s 1967 Edition Presenter John Edwards P & I Design Ltd, UK Contact: jee@pidesign.co.uk COURSE
COURSE WITH CHEMCAD MODELS PROCESS CONTROL SYSTEMS Application > Design > Adjustment Based on F.G. Shinskey s 1967 Edition Presenter John Edwards P & I Design Ltd, UK Contact: jee@pidesign.co.uk COURSE
CPC Engineering Training Brochure
 Training Brochure Module 1: Field Instrumentation for the Process Industry None Understanding of measurement principles Understanding of development of instrument specification Understanding criteria for
Training Brochure Module 1: Field Instrumentation for the Process Industry None Understanding of measurement principles Understanding of development of instrument specification Understanding criteria for
Control Engineering BDA30703
 Control Engineering BDA30703 Lecture 4: Transducers Prepared by: Ramhuzaini bin Abd. Rahman Expected Outcomes At the end of this lecture, students should be able to; 1) Explain a basic measurement system.
Control Engineering BDA30703 Lecture 4: Transducers Prepared by: Ramhuzaini bin Abd. Rahman Expected Outcomes At the end of this lecture, students should be able to; 1) Explain a basic measurement system.
Temperature Scales. Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties. Temperature. Temperature Scale
 Temperature Scales The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales: Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties Physics Enhancement Programme Dr. M.H. CHAN, HKBU 9 T F T 5 T T
Temperature Scales The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales: Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties Physics Enhancement Programme Dr. M.H. CHAN, HKBU 9 T F T 5 T T
Solutions for Tutorial 10 Stability Analysis
 Solutions for Tutorial 1 Stability Analysis 1.1 In this question, you will analyze the series of three isothermal CSTR s show in Figure 1.1. The model for each reactor is the same at presented in Textbook
Solutions for Tutorial 1 Stability Analysis 1.1 In this question, you will analyze the series of three isothermal CSTR s show in Figure 1.1. The model for each reactor is the same at presented in Textbook
TS02 - Pre-Instructional Survey
 TS02 - Pre-Instructional Survey 1. Which type of drawing provides detailed piping and process information, including wire terminations? a. Loop Wiring Diagrams b. Piping and Instrument Diagrams (P&IDs)
TS02 - Pre-Instructional Survey 1. Which type of drawing provides detailed piping and process information, including wire terminations? a. Loop Wiring Diagrams b. Piping and Instrument Diagrams (P&IDs)
CHAPTER 10: STABILITY &TUNING
 When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Determine the stability of a process without control Determine the stability of a closed-loop feedback control system Use these approaches
When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Determine the stability of a process without control Determine the stability of a closed-loop feedback control system Use these approaches
: INSTRUMENTATION AND PROCESS CONTROL COURSE CODE : 6071 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : INSTRUMENTATION AND PROCESS CONTROL COURSE CODE : 6071 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Measuring Instruments
COURSE TITLE : INSTRUMENTATION AND PROCESS CONTROL COURSE CODE : 6071 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Measuring Instruments
Fundamental Principles of Process Control
 Fundamental Principles of Process Control Motivation for Process Control Safety First: people, environment, equipment The Profit Motive: meeting final product specs minimizing waste production minimizing
Fundamental Principles of Process Control Motivation for Process Control Safety First: people, environment, equipment The Profit Motive: meeting final product specs minimizing waste production minimizing
Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control. The General Control System
 WALJAT COLLEGES OF APPLIED SCIENCES In academic partnership with BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Question Bank Course: Biotechnology Session: 005-006 Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control Semester:
WALJAT COLLEGES OF APPLIED SCIENCES In academic partnership with BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Question Bank Course: Biotechnology Session: 005-006 Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control Semester:
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 5
 Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 5 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 12 March 2014 This assignment is due on Wednesday, 12 March 2014. Late hand-ins are not allowed. Since it is posted mainly
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 5 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 12 March 2014 This assignment is due on Wednesday, 12 March 2014. Late hand-ins are not allowed. Since it is posted mainly
B1-1. Closed-loop control. Chapter 1. Fundamentals of closed-loop control technology. Festo Didactic Process Control System
 B1-1 Chapter 1 Fundamentals of closed-loop control technology B1-2 This chapter outlines the differences between closed-loop and openloop control and gives an introduction to closed-loop control technology.
B1-1 Chapter 1 Fundamentals of closed-loop control technology B1-2 This chapter outlines the differences between closed-loop and openloop control and gives an introduction to closed-loop control technology.
Roll No. :... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (EIE)/SEM-5/EI-501/ INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION II
 Name : Roll No. :.... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (EIE)/SEM-5/EI-501/2011-12 2011 INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION II Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full
Name : Roll No. :.... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (EIE)/SEM-5/EI-501/2011-12 2011 INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION II Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full
Lecture 11 Temperature Sensing. ECE 5900/6900 Fundamentals of Sensor Design
 EE 4900: Fundamentals of Sensor Design Lecture 11 Temperature Sensing 1 Temperature Sensing Q: What are we measuring? A: Temperature 2 SI Units: Celcius ( C), Kelvin (K) British Units: Fahrenheit ( F)
EE 4900: Fundamentals of Sensor Design Lecture 11 Temperature Sensing 1 Temperature Sensing Q: What are we measuring? A: Temperature 2 SI Units: Celcius ( C), Kelvin (K) British Units: Fahrenheit ( F)
Solutions for Tutorial 3 Modelling of Dynamic Systems
 Solutions for Tutorial 3 Modelling of Dynamic Systems 3.1 Mixer: Dynamic model of a CSTR is derived in textbook Example 3.1. From the model, we know that the outlet concentration of, C, can be affected
Solutions for Tutorial 3 Modelling of Dynamic Systems 3.1 Mixer: Dynamic model of a CSTR is derived in textbook Example 3.1. From the model, we know that the outlet concentration of, C, can be affected
CHAPTER 13: FEEDBACK PERFORMANCE
 When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Apply two methods for evaluating control performance: simulation and frequency response Apply general guidelines for the effect of -
When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Apply two methods for evaluating control performance: simulation and frequency response Apply general guidelines for the effect of -
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS
 Electrical Measurements International Program Department of Electrical Engineering UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANDRITTO ABDUL GHAFFAR ANDHIKA ADIEL INSANI Lecturer : Ir. Chairul Hudaya, ST, M.Eng., Ph.D., IPM
Electrical Measurements International Program Department of Electrical Engineering UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANDRITTO ABDUL GHAFFAR ANDHIKA ADIEL INSANI Lecturer : Ir. Chairul Hudaya, ST, M.Eng., Ph.D., IPM
CHBE320 LECTURE XI CONTROLLER DESIGN AND PID CONTOLLER TUNING. Professor Dae Ryook Yang
 CHBE320 LECTURE XI CONTROLLER DESIGN AND PID CONTOLLER TUNING Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 11-1 Road Map of the Lecture XI Controller Design and PID
CHBE320 LECTURE XI CONTROLLER DESIGN AND PID CONTOLLER TUNING Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 11-1 Road Map of the Lecture XI Controller Design and PID
Safety Barriers Series 9001, 9002 Standard Applications
 Standard s Analog input with transmitter Smart 9001/51-80-091-141 09949E0 Load of transmitter U N = + 0 V... 35 V I N = 3.6 ma... ma R L ( 350 O U min (I N= 0 ma) U N - 9.5 V 14 V U N ( 3.5 V > 3.5 V Maximum
Standard s Analog input with transmitter Smart 9001/51-80-091-141 09949E0 Load of transmitter U N = + 0 V... 35 V I N = 3.6 ma... ma R L ( 350 O U min (I N= 0 ma) U N - 9.5 V 14 V U N ( 3.5 V > 3.5 V Maximum
Chapter 2 Linear Feedback Control
 Chapter 2 Linear Feedback Control The by far most used control method in industry is the proportional-integralderivative or PID controller. It is currently claimed that 90 to 95% of industrial problems
Chapter 2 Linear Feedback Control The by far most used control method in industry is the proportional-integralderivative or PID controller. It is currently claimed that 90 to 95% of industrial problems
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6502 -INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION I Regulation 2013
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6502 -INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION I Regulation 2013
CONTROL OF MULTIVARIABLE PROCESSES
 Process plants ( or complex experiments) have many variables that must be controlled. The engineer must. Provide the needed sensors 2. Provide adequate manipulated variables 3. Decide how the CVs and MVs
Process plants ( or complex experiments) have many variables that must be controlled. The engineer must. Provide the needed sensors 2. Provide adequate manipulated variables 3. Decide how the CVs and MVs
Index. INDEX_p /15/02 3:08 PM Page 765
 INDEX_p.765-770 11/15/02 3:08 PM Page 765 Index N A Adaptive control, 144 Adiabatic reactors, 465 Algorithm, control, 5 All-pass factorization, 257 All-pass, frequency response, 225 Amplitude, 216 Amplitude
INDEX_p.765-770 11/15/02 3:08 PM Page 765 Index N A Adaptive control, 144 Adiabatic reactors, 465 Algorithm, control, 5 All-pass factorization, 257 All-pass, frequency response, 225 Amplitude, 216 Amplitude
Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies Chapter 16
 Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies Chapter 16 1. Cascade control 2. Time-delay compensation 3. Inferential control 4. Selective and override control 5. Nonlinear control 6. Adaptive control 1 Chapter
Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies Chapter 16 1. Cascade control 2. Time-delay compensation 3. Inferential control 4. Selective and override control 5. Nonlinear control 6. Adaptive control 1 Chapter
Analyzing Control Problems and Improving Control Loop Performance
 OptiControls Inc. Houston, TX Ph: 713-459-6291 www.opticontrols.com info@opticontrols.com Analyzing Control s and Improving Control Loop Performance -by Jacques F. Smuts Page: 1 Presenter Principal Consultant
OptiControls Inc. Houston, TX Ph: 713-459-6291 www.opticontrols.com info@opticontrols.com Analyzing Control s and Improving Control Loop Performance -by Jacques F. Smuts Page: 1 Presenter Principal Consultant
THERMOCOUPLE CHARACTERISTICS TRAINER
 THERMOCOUPLE CHARACTERISTICS TRAINER (Model No : ) User Manual Version 2.0 Technical Clarification /Suggestion : / Technical Support Division, Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd., Plot No :75,Electronics Estate,
THERMOCOUPLE CHARACTERISTICS TRAINER (Model No : ) User Manual Version 2.0 Technical Clarification /Suggestion : / Technical Support Division, Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd., Plot No :75,Electronics Estate,
Transducers. EEE355 Industrial Electronics
 Transducers EEE355 Industrial Electronics 1 Terminology Transducers convert one form of energy into another Sensors/Actuators are input/output transducers Sensors can be passive (e.g. change in resistance)
Transducers EEE355 Industrial Electronics 1 Terminology Transducers convert one form of energy into another Sensors/Actuators are input/output transducers Sensors can be passive (e.g. change in resistance)
Sensors and transducers
 Sensors and transducers Measurement is an important subsystem of a mechatronics system. Its main function is to collect the information on system status and to feed it to the micro-processor(s) for controlling
Sensors and transducers Measurement is an important subsystem of a mechatronics system. Its main function is to collect the information on system status and to feed it to the micro-processor(s) for controlling
NE 418 Exam # 2 Spring 2013
 NE 418 Exam # Spring 13 1 (4% The piping system shown below is equipped with pressure and temperature measuring sensors. Temperature is measured by thermocouples and pressure is measured by strain gauges.
NE 418 Exam # Spring 13 1 (4% The piping system shown below is equipped with pressure and temperature measuring sensors. Temperature is measured by thermocouples and pressure is measured by strain gauges.
Class 27: Block Diagrams
 Class 7: Block Diagrams Dynamic Behavior and Stability of Closed-Loop Control Systems We no ant to consider the dynamic behavior of processes that are operated using feedback control. The combination of
Class 7: Block Diagrams Dynamic Behavior and Stability of Closed-Loop Control Systems We no ant to consider the dynamic behavior of processes that are operated using feedback control. The combination of
15. Compare the result with the value you have taken above Compare the calculated pressure value with the actual pressure value that you have
 105) to convert it to. 15. Compare the result with the value you have taken above. 17. 16. Compare the calculated pressure value with the actual pressure value that you have taken from the, is it the same?
105) to convert it to. 15. Compare the result with the value you have taken above. 17. 16. Compare the calculated pressure value with the actual pressure value that you have taken from the, is it the same?
Feedforward Control Feedforward Compensation
 Feedforward Control Feedforward Compensation Compensation Feedforward Control Feedforward Control of a Heat Exchanger Implementation Issues Comments Nomenclature The inherent limitation of feedback control
Feedforward Control Feedforward Compensation Compensation Feedforward Control Feedforward Control of a Heat Exchanger Implementation Issues Comments Nomenclature The inherent limitation of feedback control
Temperature Measurement
 MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Temperature Measurement Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Introduction Temperature is one of the most
MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Temperature Measurement Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Introduction Temperature is one of the most
Subject: Introduction to Process Control. Week 01, Lectures 01 02, Spring Content
 v CHEG 461 : Process Dynamics and Control Subject: Introduction to Process Control Week 01, Lectures 01 02, Spring 2014 Dr. Costas Kiparissides Content 1. Introduction to Process Dynamics and Control 2.
v CHEG 461 : Process Dynamics and Control Subject: Introduction to Process Control Week 01, Lectures 01 02, Spring 2014 Dr. Costas Kiparissides Content 1. Introduction to Process Dynamics and Control 2.
Measurements & Instrumentation. Module 3: Temperature Sensors
 Measurements & Instrumentation PREPARED BY Academic Services Unit August 2013 Institute of Applied Technology, 2013 Module Objectives Upon successful completion of this module, students should be able
Measurements & Instrumentation PREPARED BY Academic Services Unit August 2013 Institute of Applied Technology, 2013 Module Objectives Upon successful completion of this module, students should be able
Index Accumulation, 53 Accuracy: numerical integration, sensor, 383, Adaptive tuning: expert system, 528 gain scheduling, 518, 529, 709,
 Accumulation, 53 Accuracy: numerical integration, 83-84 sensor, 383, 772-773 Adaptive tuning: expert system, 528 gain scheduling, 518, 529, 709, 715 input conversion, 519 reasons for, 512-517 relay auto-tuning,
Accumulation, 53 Accuracy: numerical integration, 83-84 sensor, 383, 772-773 Adaptive tuning: expert system, 528 gain scheduling, 518, 529, 709, 715 input conversion, 519 reasons for, 512-517 relay auto-tuning,
YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department
 YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture of Special Laboratory of Machine Theory, System Dynamics and Control Division Coupled Tank 1 Level Control with using Feedforward PI Controller Lab Date: Lab
YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture of Special Laboratory of Machine Theory, System Dynamics and Control Division Coupled Tank 1 Level Control with using Feedforward PI Controller Lab Date: Lab
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6
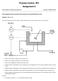 Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
I m. R s. Digital. R x. OhmmetersxSeries Shunt Digital. R m
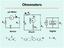 µa Meter I I s I m s E Digital x I Voltmeter x x E µa Meter m Is OhmmetersxSeries Shunt Digital EIx= = ()E sm x mxvi= x Shunt Ohmmeter Shunt s x E µa Meter I m I m V m E ) ( v I E ) ( E v E v E I When
µa Meter I I s I m s E Digital x I Voltmeter x x E µa Meter m Is OhmmetersxSeries Shunt Digital EIx= = ()E sm x mxvi= x Shunt Ohmmeter Shunt s x E µa Meter I m I m V m E ) ( v I E ) ( E v E v E I When
Dynamics and PID control. Process dynamics
 Dynamics and PID control Sigurd Skogestad Process dynamics Things take time Step response (response of output y to step in input u): k = Δy( )/ Δu process gain - process time constant (63%) - process time
Dynamics and PID control Sigurd Skogestad Process dynamics Things take time Step response (response of output y to step in input u): k = Δy( )/ Δu process gain - process time constant (63%) - process time
Transducer. A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity. Transducer. (Input) Sensor.
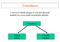 Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
(Refer Slide Time: 1:42)
 Control Engineering Prof. Madan Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 21 Basic Principles of Feedback Control (Contd..) Friends, let me get started
Control Engineering Prof. Madan Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 21 Basic Principles of Feedback Control (Contd..) Friends, let me get started
Slide 1. Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic Fields Strain Pressure Displacement and Rotation Acceleration Electronic Sensors
 Slide 1 Electronic Sensors Electronic sensors can be designed to detect a variety of quantitative aspects of a given physical system. Such quantities include: Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic
Slide 1 Electronic Sensors Electronic sensors can be designed to detect a variety of quantitative aspects of a given physical system. Such quantities include: Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic
Process Control and Instrumentation Prof. D. Sarkar Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Process Control and Instrumentation Prof. D. Sarkar Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 35 Instrumentation: General Principles of Measurement Systems
Process Control and Instrumentation Prof. D. Sarkar Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 35 Instrumentation: General Principles of Measurement Systems
CHAPTER 2 CONTINUOUS STIRRED TANK REACTOR PROCESS DESCRIPTION
 11 CHAPTER 2 CONTINUOUS STIRRED TANK REACTOR PROCESS DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter deals with the process description and analysis of CSTR. The process inputs, states and outputs are identified
11 CHAPTER 2 CONTINUOUS STIRRED TANK REACTOR PROCESS DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter deals with the process description and analysis of CSTR. The process inputs, states and outputs are identified
Feedback Control of Linear SISO systems. Process Dynamics and Control
 Feedback Control of Linear SISO systems Process Dynamics and Control 1 Open-Loop Process The study of dynamics was limited to open-loop systems Observe process behavior as a result of specific input signals
Feedback Control of Linear SISO systems Process Dynamics and Control 1 Open-Loop Process The study of dynamics was limited to open-loop systems Observe process behavior as a result of specific input signals
CHAPTER 19: Single-Loop IMC Control
 When I coplete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Recognize that other feedback algoriths are possible Understand the IMC structure and how it provides the essential control features
When I coplete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Recognize that other feedback algoriths are possible Understand the IMC structure and how it provides the essential control features
Innovative Solutions from the Process Control Professionals
 Control Station Innovative Solutions from the Process Control Professionals Software For Process Control Analysis, Tuning & Training Control Station Software For Process Control Analysis, Tuning & Training
Control Station Innovative Solutions from the Process Control Professionals Software For Process Control Analysis, Tuning & Training Control Station Software For Process Control Analysis, Tuning & Training
Multi-Input Multi-output (MIMO) Processes CBE495 LECTURE III CONTROL OF MULTI INPUT MULTI OUTPUT PROCESSES. Professor Dae Ryook Yang
 Multi-Input Multi-output (MIMO) Processes CBE495 LECTURE III CONTROL OF MULTI INPUT MULTI OUTPUT PROCESSES Professor Dae Ryook Yang Fall 2013 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering Korea University
Multi-Input Multi-output (MIMO) Processes CBE495 LECTURE III CONTROL OF MULTI INPUT MULTI OUTPUT PROCESSES Professor Dae Ryook Yang Fall 2013 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering Korea University
Sensors and Actuators Sensors Physics
 Sensors and ctuators Sensors Physics Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC SENSORS (Chapter 3.9, 16.4) 3 Thermoelectric effect thermoelectric
Sensors and ctuators Sensors Physics Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC SENSORS (Chapter 3.9, 16.4) 3 Thermoelectric effect thermoelectric
CM 3310 Process Control, Spring Lecture 21
 CM 331 Process Control, Spring 217 Instructor: Dr. om Co Lecture 21 (Back to Process Control opics ) General Control Configurations and Schemes. a) Basic Single-Input/Single-Output (SISO) Feedback Figure
CM 331 Process Control, Spring 217 Instructor: Dr. om Co Lecture 21 (Back to Process Control opics ) General Control Configurations and Schemes. a) Basic Single-Input/Single-Output (SISO) Feedback Figure
Section 7. Temperature Measurement
 Section 7 Temperature Measurement 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 1 Working Definition Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules that make of a substance. After time,
Section 7 Temperature Measurement 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 1 Working Definition Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules that make of a substance. After time,
Cryogenic Engineering
 2017 Fall Semester Cryogenic Engineering 2017 Fall Semester Kim, Min Soo Chapter 6. Measurement Systems for Low Temperatures 6.1 Theoretical plate calculations for columns Temperature measurement from
2017 Fall Semester Cryogenic Engineering 2017 Fall Semester Kim, Min Soo Chapter 6. Measurement Systems for Low Temperatures 6.1 Theoretical plate calculations for columns Temperature measurement from
Systems Engineering/Process Control L1
 Systems Engineering/Process Control L1 What is Systems Engineering/Process Control? Graphical system representations Fundamental control principles Reading: Systems Engineering and Process Control: 1.1
Systems Engineering/Process Control L1 What is Systems Engineering/Process Control? Graphical system representations Fundamental control principles Reading: Systems Engineering and Process Control: 1.1
DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8.
 Question Sheet Page 1 of 5 Instructions for the student: Question 1 is compulsory [40 marks] Attempt any two other questions [30 marks per question] The following must be made available during the examination:
Question Sheet Page 1 of 5 Instructions for the student: Question 1 is compulsory [40 marks] Attempt any two other questions [30 marks per question] The following must be made available during the examination:
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements
 Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements Third Edition Richard S. Figliola Clemson University Donald E. Beasley Clemson University John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York / Chichester / Weinheim / Brisbane
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements Third Edition Richard S. Figliola Clemson University Donald E. Beasley Clemson University John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York / Chichester / Weinheim / Brisbane
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE
 I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
Process Solutions. Process Dynamics. The Fundamental Principle of Process Control. APC Techniques Dynamics 2-1. Page 2-1
 Process Dynamics The Fundamental Principle of Process Control APC Techniques Dynamics 2-1 Page 2-1 Process Dynamics (1) All Processes are dynamic i.e. they change with time. If a plant were totally static
Process Dynamics The Fundamental Principle of Process Control APC Techniques Dynamics 2-1 Page 2-1 Process Dynamics (1) All Processes are dynamic i.e. they change with time. If a plant were totally static
FLOW MEASUREMENT. INC 102 Fundamental of Instrumentation and Process Control 2/2560
 FLOW MEASUREMENT INC 102 Fundamental of Instrumentation and Process Control 2/2560 TABLE OF CONTENTS A. INTRODUCTION B. LOCAL FLOW MEASUREMENT B.1 Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) B.2 Laser doppler anemometry
FLOW MEASUREMENT INC 102 Fundamental of Instrumentation and Process Control 2/2560 TABLE OF CONTENTS A. INTRODUCTION B. LOCAL FLOW MEASUREMENT B.1 Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) B.2 Laser doppler anemometry
Using a Mercury itc with thermocouples
 Technical Note Mercury Support Using a Mercury itc with thermocouples Abstract and content description This technical note describes how to make accurate and reliable temperature measurements using an
Technical Note Mercury Support Using a Mercury itc with thermocouples Abstract and content description This technical note describes how to make accurate and reliable temperature measurements using an
Lecture 36: Temperatue Measurements
 Lecture 36: Temperatue Measurements Contents Principle of thermocouples Materials for themocouples Cold junction compensation Compensating wires Selection of thermocouples Illustration of gas temperature
Lecture 36: Temperatue Measurements Contents Principle of thermocouples Materials for themocouples Cold junction compensation Compensating wires Selection of thermocouples Illustration of gas temperature
Cryogenic Instrumentation I Thermometry OUTLINE Thermometry Pt (pure metal) Temperature Ranges of Thermometer Application Typical Resistive Thermal
 Cryogenic Instrumentation I 1. Thermometry 2. anges of Application 3. Constant Volume 4. Thermocouples 5. Time esponse Data 6. 4 Terminal esistance Measurement OUTLINE 8. Pt (pure metal) 9. Typical esistive
Cryogenic Instrumentation I 1. Thermometry 2. anges of Application 3. Constant Volume 4. Thermocouples 5. Time esponse Data 6. 4 Terminal esistance Measurement OUTLINE 8. Pt (pure metal) 9. Typical esistive
Control Lab. Thermal Plant. Chriss Grimholt
 Control Lab Thermal Plant Chriss Grimholt Process System Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering Norwegian University of Science and Technology October 3, 23 C. Grimholt (NTNU) Thermal Plant October
Control Lab Thermal Plant Chriss Grimholt Process System Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering Norwegian University of Science and Technology October 3, 23 C. Grimholt (NTNU) Thermal Plant October
PROCESS CONTROL (IT62) SEMESTER: VI BRANCH: INSTRUMENTATION TECHNOLOGY
 PROCESS CONTROL (IT62) SEMESTER: VI BRANCH: INSTRUMENTATION TECHNOLOGY by, Dr. Mallikarjun S. Holi Professor & Head Department of Biomedical Engineering Bapuji Institute of Engineering & Technology Davangere-577004
PROCESS CONTROL (IT62) SEMESTER: VI BRANCH: INSTRUMENTATION TECHNOLOGY by, Dr. Mallikarjun S. Holi Professor & Head Department of Biomedical Engineering Bapuji Institute of Engineering & Technology Davangere-577004
(Refer Slide Time: 01:16)
 Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 4 Lecture - 50 Case Studies This will be lecture 50 in
Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 4 Lecture - 50 Case Studies This will be lecture 50 in
Part 2. Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour)
 Part 2 Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour) At the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the definition of sensor and transducer Determine the specification of control
Part 2 Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour) At the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the definition of sensor and transducer Determine the specification of control
Objective Type Questions Instrumentation System & Devices (IDS)
 1. A balance beam scale uses which of the following units? a. grams b.pounds c. ounces d. kilograms 2. Which of the following would be about the height of the average doorway? a. 2 meters b. 2 centimeters
1. A balance beam scale uses which of the following units? a. grams b.pounds c. ounces d. kilograms 2. Which of the following would be about the height of the average doorway? a. 2 meters b. 2 centimeters
Principles and Practice of Automatic Process Control
 Principles and Practice of Automatic Process Control Third Edition Carlos A. Smith, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Chemical Engineering University of South Florida Armando B. Corripio, Ph.D., P.E. Gordon A.
Principles and Practice of Automatic Process Control Third Edition Carlos A. Smith, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Chemical Engineering University of South Florida Armando B. Corripio, Ph.D., P.E. Gordon A.
is to accounting. Arithmetic provides the notation
 221. 20-5 Mathematics - Course 221 THE DERIVATIVE IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY I Some Common Differential Equations CalculUs is to modern science and technology as arithmetic is to accounting. Arithmetic
221. 20-5 Mathematics - Course 221 THE DERIVATIVE IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY I Some Common Differential Equations CalculUs is to modern science and technology as arithmetic is to accounting. Arithmetic
MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
 Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering g Department MEASURING INSTRUMENTS AND CALIBRATION Lecture (7) Temperature measurement By: Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical
Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering g Department MEASURING INSTRUMENTS AND CALIBRATION Lecture (7) Temperature measurement By: Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical
YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department
 YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture of Special Laboratory of Machine Theory, System Dynamics and Control Division Coupled Tank 1 Level Control with using Feedforward PI Controller Lab Report
YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture of Special Laboratory of Machine Theory, System Dynamics and Control Division Coupled Tank 1 Level Control with using Feedforward PI Controller Lab Report
FEEDBACK CONTROL SYSTEMS
 FEEDBAC CONTROL SYSTEMS. Control System Design. Open and Closed-Loop Control Systems 3. Why Closed-Loop Control? 4. Case Study --- Speed Control of a DC Motor 5. Steady-State Errors in Unity Feedback Control
FEEDBAC CONTROL SYSTEMS. Control System Design. Open and Closed-Loop Control Systems 3. Why Closed-Loop Control? 4. Case Study --- Speed Control of a DC Motor 5. Steady-State Errors in Unity Feedback Control
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 5 FIRST ORDER SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION APPLIED TO TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS
 ME 365 EXPERIMENT 5 FIRST ORDER SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION APPLIED TO TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS Objectives: In this two week experiment, we will gain familiarity with first order systems by using two
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 5 FIRST ORDER SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION APPLIED TO TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS Objectives: In this two week experiment, we will gain familiarity with first order systems by using two
PROCESS INSTRUMENTATION I. Module Code: EIPIN1 PREVIOUS EVALUATION AND ASSESSMENT VUT. Vaal University of Technology 2/10
 PROCESS INSTRUMENTATION I Module Code: EIPIN1 PREVIOUS EVALUATION AND ASSESSMENT VUT Vaal University of Technology 2/10 Process Instrumentation I EIPIN1 Unit 1 First assessment March 2005 Page 1 Question
PROCESS INSTRUMENTATION I Module Code: EIPIN1 PREVIOUS EVALUATION AND ASSESSMENT VUT Vaal University of Technology 2/10 Process Instrumentation I EIPIN1 Unit 1 First assessment March 2005 Page 1 Question
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
A Tuning of the Nonlinear PI Controller and Its Experimental Application
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 18(4), 451-455 (2001) A Tuning of the Nonlinear PI Controller and Its Experimental Application Doe Gyoon Koo*, Jietae Lee*, Dong Kwon Lee**, Chonghun Han**, Lyu Sung Gyu, Jae Hak
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 18(4), 451-455 (2001) A Tuning of the Nonlinear PI Controller and Its Experimental Application Doe Gyoon Koo*, Jietae Lee*, Dong Kwon Lee**, Chonghun Han**, Lyu Sung Gyu, Jae Hak
CBE495 LECTURE IV MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROL
 What is Model Predictive Control (MPC)? CBE495 LECTURE IV MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROL Professor Dae Ryook Yang Fall 2013 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering Korea University * Some parts are from
What is Model Predictive Control (MPC)? CBE495 LECTURE IV MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROL Professor Dae Ryook Yang Fall 2013 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering Korea University * Some parts are from
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Theoretical Models of Chemical Processes
 Theoretical Models of Chemical Processes Dr. M. A. A. Shoukat Choudhury 1 Rationale for Dynamic Models 1. Improve understanding of the process 2. Train Plant operating personnel 3. Develop control strategy
Theoretical Models of Chemical Processes Dr. M. A. A. Shoukat Choudhury 1 Rationale for Dynamic Models 1. Improve understanding of the process 2. Train Plant operating personnel 3. Develop control strategy
Open Loop Tuning Rules
 Open Loop Tuning Rules Based on approximate process models Process Reaction Curve: The process reaction curve is an approximate model of the process, assuming the process behaves as a first order plus
Open Loop Tuning Rules Based on approximate process models Process Reaction Curve: The process reaction curve is an approximate model of the process, assuming the process behaves as a first order plus
Solutions for Tutorial 4 Modelling of Non-Linear Systems
 Solutions for Tutorial 4 Modelling of Non-Linear Systems 4.1 Isothermal CSTR: The chemical reactor shown in textbook igure 3.1 and repeated in the following is considered in this question. The reaction
Solutions for Tutorial 4 Modelling of Non-Linear Systems 4.1 Isothermal CSTR: The chemical reactor shown in textbook igure 3.1 and repeated in the following is considered in this question. The reaction
Systems Engineering/Process Control L1
 Systems Engineering/Process Control L1 What is Systems Engineering/Process Control? Graphical system representations Fundamental control principles Reading: Systems Engineering and Process Control: 1.1
Systems Engineering/Process Control L1 What is Systems Engineering/Process Control? Graphical system representations Fundamental control principles Reading: Systems Engineering and Process Control: 1.1
Chapter 7 Control. Part Classical Control. Mobile Robotics - Prof Alonzo Kelly, CMU RI
 Chapter 7 Control 7.1 Classical Control Part 1 1 7.1 Classical Control Outline 7.1.1 Introduction 7.1.2 Virtual Spring Damper 7.1.3 Feedback Control 7.1.4 Model Referenced and Feedforward Control Summary
Chapter 7 Control 7.1 Classical Control Part 1 1 7.1 Classical Control Outline 7.1.1 Introduction 7.1.2 Virtual Spring Damper 7.1.3 Feedback Control 7.1.4 Model Referenced and Feedforward Control Summary
Index. Index. More information. in this web service Cambridge University Press
 A-type elements, 4 7, 18, 31, 168, 198, 202, 219, 220, 222, 225 A-type variables. See Across variable ac current, 172, 251 ac induction motor, 251 Acceleration rotational, 30 translational, 16 Accumulator,
A-type elements, 4 7, 18, 31, 168, 198, 202, 219, 220, 222, 225 A-type variables. See Across variable ac current, 172, 251 ac induction motor, 251 Acceleration rotational, 30 translational, 16 Accumulator,
LYOPHILIZATION. First of Four Lectures. Introduction to Freeze-Drying. Introduction to Freeze-Drying. J. Jeff Schwegman, Ph.D. AB BioTechnologies
 LYOPHILIZATION Introduction to Freeze-Drying First of Four Lectures Introduction to Freeze-Drying J. Jeff Schwegman, Ph.D. AB BioTechnologies P.O. Box 1430 Bloomington, Indiana, 47402 812-327-6898 jjschwegman@ab-biotech.com
LYOPHILIZATION Introduction to Freeze-Drying First of Four Lectures Introduction to Freeze-Drying J. Jeff Schwegman, Ph.D. AB BioTechnologies P.O. Box 1430 Bloomington, Indiana, 47402 812-327-6898 jjschwegman@ab-biotech.com
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) Subject Code : Page No: 1/
 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code : 17434 Page No: 1/ Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code : 17434 Page No: 1/ Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
Sensing, Computing, Actuating
 Sensing, Computing, ctuating Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC EFFECT (Chapter 5.11) 3 Thermocouple cylinder head temperature (thermocouple)
Sensing, Computing, ctuating Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC EFFECT (Chapter 5.11) 3 Thermocouple cylinder head temperature (thermocouple)
Overview of Control System Design
 Overview of Control System Design General Requirements 1. Safety. It is imperative that industrial plants operate safely so as to promote the well-being of people and equipment within the plant and in
Overview of Control System Design General Requirements 1. Safety. It is imperative that industrial plants operate safely so as to promote the well-being of people and equipment within the plant and in
405 Compact Orifice Series and 1595 Conditioning Orifice Plate Flow Test Data Book and Flow Handbook
 Reference Manual 405 Compact Orifice Series and 1595 Conditioning Orifice Plate Flow Test Book and Flow Handbook www.rosemount.com Reference Manual 405 and 1595 405 Compact Orifice Series and 1595 Conditioning
Reference Manual 405 Compact Orifice Series and 1595 Conditioning Orifice Plate Flow Test Book and Flow Handbook www.rosemount.com Reference Manual 405 and 1595 405 Compact Orifice Series and 1595 Conditioning
1. Mark the correct statement(s)
 1. Mark the correct statement(s) Figure to the right shows a mass measurement scale using a spring. 1.1 The span of the scale is a) 16 kg b) 21 kg c) 11 kg d) 5-16 kg 1.2 The range of the scale is a) 16
1. Mark the correct statement(s) Figure to the right shows a mass measurement scale using a spring. 1.1 The span of the scale is a) 16 kg b) 21 kg c) 11 kg d) 5-16 kg 1.2 The range of the scale is a) 16
Welcome. Functionality and application of RTD Temperature Probes and Thermocouples. Dipl.-Ing. Manfred Schleicher
 Welcome Functionality and application of RTD Temperature Probes and Thermocouples Dipl.-Ing. Manfred Schleicher This presentation informs about the basics of RTD Temperature Probes and thermocouples Functionality
Welcome Functionality and application of RTD Temperature Probes and Thermocouples Dipl.-Ing. Manfred Schleicher This presentation informs about the basics of RTD Temperature Probes and thermocouples Functionality
Analysis and Design of Control Systems in the Time Domain
 Chapter 6 Analysis and Design of Control Systems in the Time Domain 6. Concepts of feedback control Given a system, we can classify it as an open loop or a closed loop depends on the usage of the feedback.
Chapter 6 Analysis and Design of Control Systems in the Time Domain 6. Concepts of feedback control Given a system, we can classify it as an open loop or a closed loop depends on the usage of the feedback.
By-Pass. This voltage is proportional to the liquid level (threewire potentiometer circuit). The resistance reading can
 " " ' " ' / The magnetic field which is in the ball or cylindrical floats actuates very small reed contacts through the wall of a guide tube and these pick up an uninterrupted measuring-circuit voltage
" " ' " ' / The magnetic field which is in the ball or cylindrical floats actuates very small reed contacts through the wall of a guide tube and these pick up an uninterrupted measuring-circuit voltage
Unit 57: Mechatronic System
 Unit 57: Mechatronic System Unit code: F/60/46 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 5 OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 2 - SENSOR TECHNOLOGIES 2 Understand electro-mechanical models and components in mechatronic systems and products
Unit 57: Mechatronic System Unit code: F/60/46 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 5 OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 2 - SENSOR TECHNOLOGIES 2 Understand electro-mechanical models and components in mechatronic systems and products
REPORT ON TRANSDUCERS TRANSDUCERS
 REPORT ON TRANSDUCERS TRANSDUCERS DEFINITIONS: TRANSDUCER A transducer is a device, usually electrical, electronic, electro-mechanical, electromagnetic, photonic, or photovoltaic that converts one type
REPORT ON TRANSDUCERS TRANSDUCERS DEFINITIONS: TRANSDUCER A transducer is a device, usually electrical, electronic, electro-mechanical, electromagnetic, photonic, or photovoltaic that converts one type
Overview of Control System Design
 Overview of Control System Design Introduction Degrees of Freedom for Process Control Selection of Controlled, Manipulated, and Measured Variables Process Safety and Process Control 1 General Requirements
Overview of Control System Design Introduction Degrees of Freedom for Process Control Selection of Controlled, Manipulated, and Measured Variables Process Safety and Process Control 1 General Requirements
( ) ( = ) = ( ) ( ) ( )
 ( ) Vρ C st s T t 0 wc Ti s T s Q s (8) K T ( s) Q ( s) + Ti ( s) (0) τs+ τs+ V ρ K and τ wc w T (s)g (s)q (s) + G (s)t(s) i G and G are transfer functions and independent of the inputs, Q and T i. Note
( ) Vρ C st s T t 0 wc Ti s T s Q s (8) K T ( s) Q ( s) + Ti ( s) (0) τs+ τs+ V ρ K and τ wc w T (s)g (s)q (s) + G (s)t(s) i G and G are transfer functions and independent of the inputs, Q and T i. Note
Accurate Flow Measurements in Changing Process Conditions
 Instruments, Valves, and Controls Thank You for Attending Today s Webinar: Accurate Flow Measurements in Changing Process Conditions Your Host Mike DeLacluyse President Lesman Instrument Co miked@lesman.com
Instruments, Valves, and Controls Thank You for Attending Today s Webinar: Accurate Flow Measurements in Changing Process Conditions Your Host Mike DeLacluyse President Lesman Instrument Co miked@lesman.com
