VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
|
|
|
- Gabriella Alexia Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6502 -INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION I Regulation 2013 Academic Year Prepared by Ms. M. Shanthi, Assistant Professor / EIE Mr. B. Parameswaran, Assistant Professor / EIE Mr. G. Shiva, Assistant Professor / EIE
2 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EI6502 INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION-I SEM / YEAR : V/III UNIT I - MEASUREMENT OF FORCE, TORQUE AND SPEED Electric balance - Different types of load cells - Hydraulic, Pneumatic, strain gauge - Magneto elastic and Piezoelectric load cells - Different methods of torque measurement:- Strain gauge - Relative angular twist-speed measurement:- Capacitive tacho - Drag cup type tacho - D.C and A.C tachogenerators Stroboscope. PART A Q.No Question BT Competence Level 1. What is meant by Strobotron? BTL1 Remember 2. What are the properties of materials used for Piezo electric transducers? 3. Define gauge factor for strain gauge. 4. What is magneto-elastic effect? 5. What are the merits of stroboscope? 6. Define force and write its units. 7. What do you mean by Load Cell? Give the types of load cell. 8. What is the principle of drag cup type Tachometer? 9. Give the different types of strain gauge load cell. 10. Discuss how the torque is measured using strain gauge? 11. What are the classifications of Tachometer? BTL 3 Apply 12. Illustrate the principle of DC Tacho generator. BTL 3 Apply 13. Show how Elastic materials are used for force measurement. BTL 3 Apply 14. Why are dummy gauges used? In what way they affect the output of a strain gauge bridge? BTL 4 Analyze 15. Point out the measurement procedure for force using load cell. BTL 4 Analyze 16. Identify the factors affecting the accuracy of force measurement. BTL 4 Analyze 17. Justify the effect of Temperature in strain gauge bridge circuitry? How it is to be compensated? 18. Summarize the applications of load cell. 19. Prepare a bridge circuit for any measuring instrument and justify its need. BTL 6 Create 20. Propose a suitable signal conditioning circuit for LVDT based force measurement system of your own. BTL 6 Create PART B 1. i.) Explain the principle and working of a strain gauge. Derive the relationship between gauge factor and (8) poison s ratio for a given strain gauge. ii.) A strain gauge has a gauge factor of 4. If the strain (5) gauge is attached to a metal bar, that stretches from 0.25m to 0.258m when strained. What is the
3 percentage of chain in resistance? If the unstrained value of the gauge is 120 ohm, what is the resistance value of the gauge after it is strained? 2. Explain the principle and construction of : i) Hydraulic load cell. (7) ii) Drag cup DC tachogenerator. (6) 3. Describe about Magneto Elastic and Piezo Electric Load (13) cell with a neat diagram. 4. Draw the diagram and describe the working, construction of: i) Inductive torque transducer. (7) ii) Electric balance. (6) 5. Discuss the construction and working of DC and AC (13) Tachogenerator with diagram and mention its advantages and disadvantages. 6. Briefly describe the working of different speed (13) measurement methods. 7. i) With necessary diagram, describe how speed can (7) be measured using Revolution counter. ii) With relevant diagram, describe how proximity (6) sensor can be used for torque measurement. 8. i) Illustrate the basic means of force measurement. (7) ii) Illustrate with neat sketches, the working of (6) pneumatic load cell. 9. With neat diagram explain,the construction and working of i) Strain gauge load cell (7) ii) Stroboscope. (6) 10. i) Illustrate the construction, working of optical (7) torsion meter. ii) Describe the torque measurement principle (6) involving relative angular twist. 11. Explain the following methods of measurement of torque: i) Capacitive torque transducer. (7) ii) Magneto strictive methods (6) 12. i) Illustrate the working of Strobotron. (7) ii) Mention the advantages and disadvantages of (6) stroboscope measurement technique? 13. Propose a method for strain gauge torsion meter. Discuss (13) the construction, working and advantage of the same. 14. Explain any two types of torque measurement with neat (13) sketch. PART C 1. i) Draw and explain the equivalent circuit for (8) piezoelectric transducer. ii) Draw and explain pulse response of piezoelectric (7) transducer. 2. i) A rotating disc has five equispaced radial lines (8) marked on it. When a stroboscope is directed at the disc a true pattern is observed at the highest flash BTL 4 BTL 1 BTL 1 BTL 1 BTL 3 BTL 4 BTL 4 BTL 3 BTL 6 BTL 1 BTL 5 BTL 5 Analyze Remember Remember Remember Apply Analyze Analyze Apply Create Remember Evaluate Evaluate
4 frequency equal to 3000 flashes per seconds. What will be the other flash frequencies which produce a 5 line pattern and 10 line pattern? ii) While measuring the speed of a steam turbine with stroboscope single line images were observed for stroboscope setting of 3000, 4000 and 5230 rpm. Evaluate the speed of turbine. 3. Design a Torsion bar dynamometer for torque measurement. Discuss about the various methods force measurement. 4. Design a Bonded strain gauge transducer for measuring compressive force and explain with bridge circuit. (7) (15) BTL 6 Create (15) BTL 6 Create UNIT II -MEASUREMENT OF ACCELERATION, VIBRATION AND DENSITY Accelerometers :- LVDT, Piezoelectric, Strain gauge and Variable reluctance type accelerometers - Mechanical type vibration instruments - Seismic instruments as accelerometer - Vibration sensor - Calibration of vibration pickups - Units of density and specific gravity - Baume scale and API scale - Pressure type densitometers - Float type densitometers - Ultrasonic densitometer gas densitometer. PART A Q.No Question BT Level Competence 1. What is a seismic instrument? State the function of seismic transducer. 2. List the properties of spring employed seismic type of instrument for measurement of vibration and acceleration. 3. State the principle of operation of Ultrasonic densitometer. 4. Give any two features of piezo-electric accelerometer. 5. Give the methods of calibration of vibration pickup. 6. Define specific weight and density. 7. Give the units of density used in industries. 8. Summarize the different ways to measure density. 9. Specify the applications of bridge type gas densitometer. 10. What is the basic principle of strain gauge accelerometer? 11. Examine the quantities required in a vibration measurement system. BTL 3 Apply 12. Show the advantages of mechanical type vibration measuring instruments. BTL 3 Apply 13. An accelerometer has a seismic mass of 0.05kg and a spring constant of 3000 N/m. Maximum mass displacement is +/ BTL 3 Apply m. Calculate the natural frequency. 14. Differentiate relative and absolute Acceleration measurement. BTL 4 Analyze 15. Explain how Ultrasonic densitometer used to measure the flow rate of mixture. BTL 4 Analyze 16. Differentiate the two modes of operation of accelerometer. BTL 4 Analyze 17. Compare the terms specific weight and specific gravity. 18. Criticize how a seismic instrument acts as accelerometer. 19. Formulate the expression for sinusoidal vibration. BTL 6 Create
5 20. Draw the setup of Gas densitometer. BTL 6 Create PART B 1. i.) Give a detailed explanation about working of LVDT (8) type and Piezo electric type accelerometers used for measurement of acceleration. ii.) Write their advantages and disadvantages. (5) 2. Discriminate the seismic instruments as a vibrometer and (13) accelerometer. Justify with your answer. 3. Discuss about the quantities involved in vibration (13) measurement. Explain the operation of seismic transducer in different modes of operation. 4. Investigate how relative motion is measured using seismic instruments. (13) BTL 6 Create 5. i) What is a vibrational pick up? Explain about the (8) Measurements? nature of vibration. ii) What are the quantities involved in Vibration (5) 6. i) Describe about the basic of Vibration (8) exposure to vibration. Measurement System. ii) Describe the different methods of Controlling (5) 7. i) Explain in detail about Variable reluctance (8) accelerometer with a neat sketch. BTL 4 Analyze ii) Explain in detail about strain gauge accelerometer. (5) 8. Draw the schematic diagram of Pressure head type (13) densitometer and explain its working and construction. BTL 4 Analyze 9. Explain the following with a neat sketch i) Float type densitometer (6) ii) Electromagnetic suspension type gas densitometer. (7) 10. i) Briefly describe about the construction and (8) working principle of Ultrasonic densitometer. ii) Write short notes on Hydrostatic type (5) densitometer. 11. Explain the working and construction of (13) displacement-type densitometers. 12. Mention in detail about the API scale and Baume scale. (13) BTL 3 Apply 13. Explain the working and construction of Thermal gas (13) BTL 4 Analyze densitometer. 14. Illustrate in detail about the calibration of vibration (13) BTL 3 Apply pickup. PART C 1. Analyze three stages of measuring system for seismic (15) mass accelerometer with the help of neat sketch. 2. Propose method to measure a vibration using Laser (15) BTL 6 Create Doppler technique and discuss above meter in detail. 3. Design an ultrasonic slurry densitometer. Discuss about (15) the attenuation of sonic or ultrasonic pulses increases as the sludge density rises. BTL 6 Create
6 4. Deduce a displacer type densitometer with Torque-Tube. (15) UNIT III - PRESSURE MEASUREMENT Units of pressure - Manometers, different types, Elastic type pressure gauges, Bourdon tube, bellows and diaphragms - Electrical methods:- Elastic elements with LVDT and strain gauges - Capacitive type pressure gauge - Piezo resistive pressure sensor-resonator pressure sensor - Measurement of vacuum-mcleod gauge-thermal conductivity gauge-ionization gauges Cold cathode type and hot cathode type - calibration of pressure gauges - Dead weight tester. PART A Q.No Question BT Competence Level 1. List the transducer used for measuring low pressure. 2. List the applications of piezo resistive pressure sensor. 3. What is a dead weight tester? 4. State the principle of McLeod gauge. 5. Mention any three elastic type pressure gauges. 6. Name the pressure gauges used to measure Vacuum pressure. 7. Illustrate the working principle of thermal conductivity gauge. 8. Give the relationship between pressure and its measuring devices. 9. Express the different units of pressure. 10. Write down the expression for pressure in friction gauge. 11. Classify the types of Diaphragms. BTL 3 Apply 12. What do you infer from the limitations of McLeod gauge? BTL 3 Apply 13. Classify the pressure based on the type of measurement. BTL 3 Apply 14. Categorize the different application of dead weight tester. BTL 4 Analyze 15. Compare the materials used for Diaphragm design. BTL 4 Analyze 16. How is differential pressure measured in multiple fluid column? BTL 4 Analyze 17. Assess the working principle of capacitive transducer for pressure measurement. 18. Why elastic element type gauges are recommended and preferred to liquid column manometers in industry? 19. Develop an arrangement used for calibration of pressure gauge. BTL 6 Create 20. Formulate the expression for pressure in hot cathode type ionization gauge. BTL 6 Create PART B 1. Describe the methods of measurement of pressure using (13) thermal conductivity gauges and ionization gauge. 2. Describe the pressure measurement process using the following: i) Bourdon tubes (4) ii) Bellows (4) iii) Diaphragms (5) 3. With neat sketch describe the method of measurement (13) differential pressure using Capacitive differential pressure sensor. Mention its advantages and disadvantages. 4. Describe the methods of pressure measurement using (13) resistive type pressure transducers 5. Describe the methods of pressure measurement using (13)
7 resistive type pressure transducers. 6. i) What are the different types of electrical pressure transducers commonly used in industries? Discuss. (8) ii) Describe with a neat sketch, the construction and working principles of different types of manometer used for pressure measurement. (5) 7. i) Classify the pressure transducer based on range of measurement and type of measurement. (8) ii) Explain with a neat sketch, the construction and working principles of well type and inclined type manometer used for pressure measurement. (5) BTL 4 Analyze 8. Illustrate, the pressure measurement methods by using the following with neat diagram: i) Capacitance Pressure Transducer (7) BTL 3 Apply ii) Potentiometric Pressure Transducer (6) 9. Demonstrate how a Dead weight tester is used to (13) calibrate Pressure measuring device and mention the factors affecting the accuracy of Dead weight Tester. BTL 3 Apply 10. i) What is meant by pressure? Write short notes on its (8) classification based on Reference pressure. ii) Outline the working cold cathode type ionization (5) gauge. BTL 4 Analyze 11. i) How LVDT is used for process pressure (8) measurement? Explain ii) A pressure gauge in the range of 0 to 100kg/cm 2 is (5) to be calibrated with the help of Deadweight tester. Calibration is used to be checked in the steps of 10kg/cm 2. Recommend the standard weights required if the average area of piston and cylinder is 1cm 2. Assume that the friction and other effects are negligible. 12. Describe the working of all types of bourdon tube (13) pressure gauges with a neat schematic. 13. Explain how McLeod gauge used for low pressure (13) BTL 4 Analyze measurement. Justify this with your answer. 14. Propose a setup to measure vacuum pressure. Explain (13) BTL 6 Create the mechanism behind it. PART C 1. Design a gauge using bellow to measure gauge pressure (15) BTL 6 Create and differential pressure. 2. Prepare a detail notes on various types of diaphragm and bourdon tubes. (15) BTL 6 Create 3. i) A McLeod gauge has volume of bulb capillary and (8) tube down to its opening equal to 90 cm 3 and a capillary diameter of 1 mm. Evaluate the pressure indicated by a reading of 3 cm. ii) Explain about the manometer dynamics. (7) 4. Explain about the testing and obtaining error of pressure (15) gauges by a suitable calibration technique.
8 UNIT-IV TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT-I Definitions and standards - Primary and secondary fixed points - Calibration of thermometers - Different types of filled in system thermometers - Sources of errors in - filled in systems and their compensation - Bimetallic thermometers - RTD - characteristics and signal conditioning - 3 lead and 4 lead RTDs - Thermistors. PART A Q.No Question BT Competence Level 1. Mention the sources of error in filled in system thermometer. 2. Show the relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit. 3. What are the primary standards for temperature measuring calibration? 4. Define boiling point, freezing point and triple point. 5. Enumerate the differences between RTD and thermistor. 6. List out the materials used in thermistors. 7. Differentiate between 3-wire RTD and 4-wire RTD. 8. Express the V-I characteristics of Thermistor with a neat diagram. 9. Illustrate the working principle of bimetallic thermometer. 10. Classify the different temperature measurement types using change in physical properties. 11. Draw the response curve for different bimetallic elements. BTL 3 Apply 12. Draw the different compensation types in filled in system BTL 3 Apply thermometers. 13. Sketch the response curves for resistance thermometers in air BTL 3 Apply and water. 14. Infer the general classes of filled system thermometers. BTL 4 Analyze 15. A bimetal element formed with stainless steel and invar at BTL 4 Analyze C is raised to C. Each strip has a thickness of cm. calculate ρ. 16. Write down the classification of Expansion thermometers. BTL 4 Analyze 17. Predict for what application thermistor is preferred as temperature sensor. 18. Frame the pressure temperature relationship for filled in system thermometer under constant volume condition. 19. Propose the sources of error is occurring in filled system BTL 6 Create thermometer 20. Write the features of liquid in glass thermometer. BTL 6 Create PART B 1. i) What is calibration? Prepare a notes on thermometer (8) should be Calibrated. ii) Prepare short notes on Definitions and Standards of (5) temperature scale. BTL 6 Create 2. i) Describe the different types of thermistor with (8) sketch. ii) Give the merits and demerits of thermistor. (5) 3. i) Demonstrate the applications of bimetallic (8) BTL 3 Apply
9 thermometer in detail. ii) Mention the merits and demerits of bimetallic thermometer. 4. What are the possible sources of errors in filled-in thermometers and how are they compensated? 5. Discuss the features of RTD and explain the working of RTD in 3 wire configuration. 6. Differentiate thermistor and RTD. Discuss about the characteristics of materials used for resistance thermometers. 7. Explain briefly about (5) (13) (13) (13) BTL 4 Analyze i) Primary fixed points (8) BTL 4 Analyze ii) Secondary fixed points. (5) 8. Explain with sketches, Where bimetallic elements are used as i) Temperature sensors. (8) BTL 4 Analyze ii) Compensating elements. (5) 9. Draw the neat sketch and explain the construction and (13) Apply BTL 3 working principle of vapour pressure thermometer. 10. Explain in detail the RTD signal conditioning and their (13) characteristics. 11. With neat sketch, describe the construction and working (13) principle of gas expansion type thermometer. 12. With neat sketch, describe the construction and working (13) principle of Fluid expansion type thermometer. 13. Discuss the features of RTD and explain the construction and working of RTD in 4-wire configuration. (13) 14. Explain the constructional details, principle, (13) characteristics and applications of bimetallic thermometers. PART C 1. Develop RTD 4 wire configuration arrangement and (15) BTL 6 Create compare with the 3 wire configuration. 2. Summarize the notes on installation of Resistance (15) temperature detector. 3. i) A platinum thermometer has a resistance of 100 ohm at 25 0 C. (a) Evaluate its resistance at 65 0 C if the platinum has a resistance temperature co-efficient of (8) / 0 C. (b) If the thermometer has a resistance of 150 ohm. Calculate the temperature. ii) Explain about the compensation technique s used in (7) thermometers. 4. Prepare a detail notes on helix and spiral Bimetallic (15) BTL 6 Create thermometer.
10 UNIT V - TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT II Thermocouples - Laws of thermocouple - Fabrication of industrial thermocouples Signal conditioning for thermocouple - isothermal block reference junctions - Commercial circuits for cold junction compensation - Response of thermocouple - Special techniques for measuring high temperature using thermocouple - Radiation fundamentals - Radiation methods of temperature measurement - Total radiation pyrometers - Optical pyrometers - Two color radiation pyrometers - Fiber optic sensor for temperature measurement. PART A Q.No Question BT Competence Level 1. State the selective radiation pyrometer principle. 2. Define Stefan Boltzman Law. 3. Recall See back effect. 4. List any four types of Thermocouples with composition and temperature range. 5. What is pyrometer? 6. List the uses of Radiation pyrometer. 7. Give few types of Thermocouple with composition and temperature range. 8. Illustrate the need of protective sheath in Thermocouple. 9. Illustrate the need for cold junction compensation. 10. Sketch the thermoelectric characteristics of thermocouple. 11. Draw the transmission characteristics of various Optical BTL 3 Apply materials. 12. Draw the response characteristics of different types of radiation BTL 3 Apply detectors. 13. Classify the types of pyrometers? BTL 3 Apply 14. Point out the factors that affect the response of Thermocouple. BTL 4 Analyze 15. What are the advantages of fiber optic based temperature BTL 4 Analyze measuring instruments? 16. Point out the operation of optical pyrometer. BTL 4 Analyze 17. Discriminate the various images of filament and target. Used in optical pyrometer with neat diagram. 18. Summarize the different response criteria in which radiation detector depends on. 19. Construct the mounting diagram of thermocouple. BTL 6 Create 20. Write down the demerits of optical pyrometer. BTL 6 Create PART B 1. Describe the special techniques adopted for measuring high temperature using thermocouples. (13) BTL 1 Remember 2. i) Describe the construction of Thermocouple. (4) ii) State the laws of thermocouple. (4) iii) What are the common materials used for (5) thermocouple? 3. i) Name different types of Pyrometer and Recall the (5) radiation pyrometers. basic working principle of Pyrometer. ii) Describe the working principle of two color (8) 4. i) Describe the factors to be considered for the (8)
11 selection of thermocouple. ii) Describe the advantages and disadvantages of thermocouple? (5) 5. i) Elaborate how the fiber optic temperature (8) measurement is advantageous than other methods. ii) Explain in detail about the cold junction (5) BTL 4 compensation used in thermocouple. 6. Explain about the construction and working of different (13) types of radiation pyrometer with neat sketch. BTL 4 7. i) Summarize the advantages and disadvantages of (8) radiation pyrometer. ii) Summarize the applications of radiation pyrometer. (5) 8. Draw and explain the signal conditioning circuit diagram (13) BTL 4 of thermocouple. 9. i) Generalize laws of intermediate temperatures and (8) metals. BTL 6 ii) Compare and contrast different types of pyrometers. (5) 10. Explain about Isothermal block reference junctions in (13) thermocouple. BTL i) Describe the advantages and disadvantages of optical (8) pyrometer. ii) Describe the applications of optical pyrometer in (5) detail. 12. Interpret the working principle of i) Total radiation pyrometer. (8) ii) Optical pyrometer. (5) 13. Demonstrate the different types of thermocouple with (13) necessary specification. BTL i) Illustrate the fabrication of industrial thermocouple. (8) ii) How do we relate Thermocouple and Thermopile? (5) BTL 3 Write short notes on thermopile. PART C 1. Explain in detail about the dynamic response of (15) thermocouple. BTL 5 2. Suggest a suitable measuring system to measure the (15) inside temperature of nuclear reactor and explain the BTL 6 method with block diagram. 3. i) Evaluate the thermoelectric sensitivity of a device (8) using bismuth and tellurium as the dissimilar metals. Estimate the maximum output voltage for a C temperature difference at room temperature using one junction. The sensitivity of bismuth is -72 microvolt/ 0 C and that of tellurium 500 microvolt/ 0 C. ii) A copper constantan thermocouple was found to have (7) BTL 5 linear calibration between 0 0 C and C with at maximum temperature (reference junction temperature 0 0 C) equal to 20.68mV. (a) Evaluate the correction what must be made to the indicated emf if the junction temperature is 25 0 C. (b) If the indicated Analyze Analyze Analyze Create Evaluate Apply Apply Evaluate Create Evaluate
12 emf is 8.92 mv in the thermocouple circuit with reference junction at 25 0 C. Determine the temperature of the hot junction. 4. Prepare a short note on installation and protection of thermocouple. (15) BTL 6 Create
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS Code : A70343 Class : IV B. Tech
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS Code : A70343 Class : IV B. Tech
 Set No. 1 1. (a) Differentiate among Desired, Modifying and Interfering inputs. (b) How do you eliminate the effects of interfering and modifying inputs? Explain 2. (a) Define the term Transducer and explain
Set No. 1 1. (a) Differentiate among Desired, Modifying and Interfering inputs. (b) How do you eliminate the effects of interfering and modifying inputs? Explain 2. (a) Define the term Transducer and explain
III B.Tech. II Semester Regular Examinations, April/May INSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL SYSTEMS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 75
 R10 Set No: 1 1. (a) Distinguish between accuracy and Precision. Which of these is more desirable during the act of measurement and why? (b) Discuss the necessity and importance of dynamic performance
R10 Set No: 1 1. (a) Distinguish between accuracy and Precision. Which of these is more desirable during the act of measurement and why? (b) Discuss the necessity and importance of dynamic performance
Siddharth Institute of Engineering & Technology
 SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi & Affiliated to JNTUA, Anantapuramu) (Accredited by NBA & Accredited by NAAC with A Grade) (An ISO 9001:2008
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi & Affiliated to JNTUA, Anantapuramu) (Accredited by NBA & Accredited by NAAC with A Grade) (An ISO 9001:2008
ANAND INSTITUTE OF HIGHER TECHNOLOGY, Kazhipattur, Chennai DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING
 ANAND INSTITUTE OF HIGHER TECHNOLOGY, Kazhipattur, Chennai-603 103 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING 2 Marks and 16 Marks QUESTION BANK Course code / Course Name: EI2251 / INDUSTRIAL
ANAND INSTITUTE OF HIGHER TECHNOLOGY, Kazhipattur, Chennai-603 103 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING 2 Marks and 16 Marks QUESTION BANK Course code / Course Name: EI2251 / INDUSTRIAL
Control Engineering BDA30703
 Control Engineering BDA30703 Lecture 4: Transducers Prepared by: Ramhuzaini bin Abd. Rahman Expected Outcomes At the end of this lecture, students should be able to; 1) Explain a basic measurement system.
Control Engineering BDA30703 Lecture 4: Transducers Prepared by: Ramhuzaini bin Abd. Rahman Expected Outcomes At the end of this lecture, students should be able to; 1) Explain a basic measurement system.
Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control. The General Control System
 WALJAT COLLEGES OF APPLIED SCIENCES In academic partnership with BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Question Bank Course: Biotechnology Session: 005-006 Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control Semester:
WALJAT COLLEGES OF APPLIED SCIENCES In academic partnership with BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Question Bank Course: Biotechnology Session: 005-006 Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control Semester:
Roll No. :... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (EIE)/SEM-5/EI-501/ INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION II
 Name : Roll No. :.... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (EIE)/SEM-5/EI-501/2011-12 2011 INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION II Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full
Name : Roll No. :.... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (EIE)/SEM-5/EI-501/2011-12 2011 INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION II Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full
2. (a) Differentiate between rare metal thermocouples and base metal thermocouples.
 Code No: R05410304 Set No. 1 1. (a) Distinguish between direct and indirect methods of measurement with suitable examples. (b) What are desired, modifying and interfering inputs for an instrumentation
Code No: R05410304 Set No. 1 1. (a) Distinguish between direct and indirect methods of measurement with suitable examples. (b) What are desired, modifying and interfering inputs for an instrumentation
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6501 Analytical Instruments Regulation 2013 Academic
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6501 Analytical Instruments Regulation 2013 Academic
Transducers. EEE355 Industrial Electronics
 Transducers EEE355 Industrial Electronics 1 Terminology Transducers convert one form of energy into another Sensors/Actuators are input/output transducers Sensors can be passive (e.g. change in resistance)
Transducers EEE355 Industrial Electronics 1 Terminology Transducers convert one form of energy into another Sensors/Actuators are input/output transducers Sensors can be passive (e.g. change in resistance)
1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16]
![1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16] 1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16]](/thumbs/96/127822274.jpg) Code No: RR320204 Set No. 1 1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16] 2. Distinguish between deterministic signals and
Code No: RR320204 Set No. 1 1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16] 2. Distinguish between deterministic signals and
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE
 I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
Preface... (vii) Acknowledgement... (ix)
 Preface... (vii) Acknowledgement... (ix) Chapter 1 Measurement Systems An Overview and Basic Concepts 1 1.1 Introduction 4 1.2 The Process of Measurement 4 1.3 Scope of Instrumentation 7 1.4 Jargon of
Preface... (vii) Acknowledgement... (ix) Chapter 1 Measurement Systems An Overview and Basic Concepts 1 1.1 Introduction 4 1.2 The Process of Measurement 4 1.3 Scope of Instrumentation 7 1.4 Jargon of
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements
 Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements Third Edition Richard S. Figliola Clemson University Donald E. Beasley Clemson University John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York / Chichester / Weinheim / Brisbane
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements Third Edition Richard S. Figliola Clemson University Donald E. Beasley Clemson University John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York / Chichester / Weinheim / Brisbane
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS
 Electrical Measurements International Program Department of Electrical Engineering UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANDRITTO ABDUL GHAFFAR ANDHIKA ADIEL INSANI Lecturer : Ir. Chairul Hudaya, ST, M.Eng., Ph.D., IPM
Electrical Measurements International Program Department of Electrical Engineering UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANDRITTO ABDUL GHAFFAR ANDHIKA ADIEL INSANI Lecturer : Ir. Chairul Hudaya, ST, M.Eng., Ph.D., IPM
Temperature Scales. Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties. Temperature. Temperature Scale
 Temperature Scales The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales: Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties Physics Enhancement Programme Dr. M.H. CHAN, HKBU 9 T F T 5 T T
Temperature Scales The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales: Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties Physics Enhancement Programme Dr. M.H. CHAN, HKBU 9 T F T 5 T T
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) Subject Code : Page No: 1/
 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code : 17434 Page No: 1/ Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code : 17434 Page No: 1/ Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester. Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE
 INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE Detailed Contents Objectives Sensors and transducer Classification of transducers Temperature transducers Resistance
INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE Detailed Contents Objectives Sensors and transducer Classification of transducers Temperature transducers Resistance
LABORATORY MANUAL MEASUREMENTS & INSTRUMENTATION (ME- 318-F)
 LABORATORY MANUAL MEASUREMENTS & INSTRUMENTATION (ME- 318-F) LIST OF THE EXPERIMENT S. NO. NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT PAGE NO FROM TO 1. To measure stress and strain using strain gauge mounted on a cantilever
LABORATORY MANUAL MEASUREMENTS & INSTRUMENTATION (ME- 318-F) LIST OF THE EXPERIMENT S. NO. NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT PAGE NO FROM TO 1. To measure stress and strain using strain gauge mounted on a cantilever
Part 2. Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour)
 Part 2 Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour) At the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the definition of sensor and transducer Determine the specification of control
Part 2 Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour) At the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the definition of sensor and transducer Determine the specification of control
MODEL ANSWER WINTER 17 EXAMINATION
 MODEL ANSWER WINTER 17 EXAMINATION 17434 Subject Title: Industrial Measurements Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
MODEL ANSWER WINTER 17 EXAMINATION 17434 Subject Title: Industrial Measurements Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
Unit 57: Mechatronic System
 Unit 57: Mechatronic System Unit code: F/60/46 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 5 OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 2 - SENSOR TECHNOLOGIES 2 Understand electro-mechanical models and components in mechatronic systems and products
Unit 57: Mechatronic System Unit code: F/60/46 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 5 OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 2 - SENSOR TECHNOLOGIES 2 Understand electro-mechanical models and components in mechatronic systems and products
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING. (Dr.VPR Nagar, Manimangalam, Tambaram) Chennai
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (Dr.VPR Nagar, Manimangalam, Tambaram) Chennai - 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING III YEAR V SEMESTER ME6504 ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (Dr.VPR Nagar, Manimangalam, Tambaram) Chennai - 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING III YEAR V SEMESTER ME6504 ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION
= A x (t) + B utt), by d{ _-=-=-
 M.Tech. [ 24 103 ] Degree Examination ndustrial Process nstrumentation First Semester COMPUTER CONTROL OF PROCESSES (Effective from the Admitted Batch of2003-2004) Time: 3 Hours Maximum marks: 100 Answer
M.Tech. [ 24 103 ] Degree Examination ndustrial Process nstrumentation First Semester COMPUTER CONTROL OF PROCESSES (Effective from the Admitted Batch of2003-2004) Time: 3 Hours Maximum marks: 100 Answer
: INSTRUMENTATION AND PROCESS CONTROL COURSE CODE : 6071 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : INSTRUMENTATION AND PROCESS CONTROL COURSE CODE : 6071 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Measuring Instruments
COURSE TITLE : INSTRUMENTATION AND PROCESS CONTROL COURSE CODE : 6071 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Measuring Instruments
Experimentation. Third Edition. Wheeler. Ahmad R. Ganji. School of Engineering. With Third Edition contributions by. V. V. Krishnan. Brian S.
 Introduction to Engineering Experimentation Third Edition Anthony J. Ahmad R. Wheeler Ganji School of Engineering San Francisco State University With Third Edition contributions by V. V. Krishnan San Francisco
Introduction to Engineering Experimentation Third Edition Anthony J. Ahmad R. Wheeler Ganji School of Engineering San Francisco State University With Third Edition contributions by V. V. Krishnan San Francisco
Sensors and transducers
 Sensors and transducers Measurement is an important subsystem of a mechatronics system. Its main function is to collect the information on system status and to feed it to the micro-processor(s) for controlling
Sensors and transducers Measurement is an important subsystem of a mechatronics system. Its main function is to collect the information on system status and to feed it to the micro-processor(s) for controlling
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER BE8255 BASIC ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONICS AND MEASUREMENT ENGINEERING
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER BE8255 BASIC ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONICS AND MEASUREMENT ENGINEERING
12. A signal established as a standard of comparison for a feed back control system by virtue of its
 INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS 2 MID ONLINE BITS www.uandistar.org 1. "A function of the controlled output, which is compared with the reference input to obtain the actuating signal" is called as
INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS 2 MID ONLINE BITS www.uandistar.org 1. "A function of the controlled output, which is compared with the reference input to obtain the actuating signal" is called as
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad DEPARTMENT OF ECE QUESTION BANK. : G.Lakshminarayana, Asst.
 ` INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 DEPARTMENT OF ECE QUESTION BANK Name Code Class Branch P a g e : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation : A504 : III - B. Tech
` INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 DEPARTMENT OF ECE QUESTION BANK Name Code Class Branch P a g e : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation : A504 : III - B. Tech
1. Mark the correct statement(s)
 1. Mark the correct statement(s) Figure to the right shows a mass measurement scale using a spring. 1.1 The span of the scale is a) 16 kg b) 21 kg c) 11 kg d) 5-16 kg 1.2 The range of the scale is a) 16
1. Mark the correct statement(s) Figure to the right shows a mass measurement scale using a spring. 1.1 The span of the scale is a) 16 kg b) 21 kg c) 11 kg d) 5-16 kg 1.2 The range of the scale is a) 16
Chapter 6 Temperature Measurement (Revision 2.0, 1/12/2009)
 Chapter 6 emperature Measurement (Revision 2.0, /2/2009). Introduction his Chapter looks that various methods of temperature measurement. Historically, there are two temperature measurement scales: he
Chapter 6 emperature Measurement (Revision 2.0, /2/2009). Introduction his Chapter looks that various methods of temperature measurement. Historically, there are two temperature measurement scales: he
Unit 3 Transducers. Lecture_3.1 Introduction to Transducers
 Unit 3 Transducers Lecture_3.1 Introduction to Transducers Introduction to transducers A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy to other form. It converts the measurand to a usable electrical
Unit 3 Transducers Lecture_3.1 Introduction to Transducers Introduction to transducers A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy to other form. It converts the measurand to a usable electrical
PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6404-MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION
 PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6404-MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION ACADEMIC YEAR: 2015-2016 (EVEN SEMESTER) Branch: EEE QUESTION BANK
PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6404-MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION ACADEMIC YEAR: 2015-2016 (EVEN SEMESTER) Branch: EEE QUESTION BANK
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Name : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Code : A50422 Class : III -
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Name : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Code : A50422 Class : III -
14CH406. Chemical Engineering Scheme of Valuation Process Instrumentation Maximum : 60 Marks (1X12 = 12 Marks) Answer ONE question from each unit.
 April, 2018 Fourth Semester Time: Three Hours Answer Question No.1 compulsorily. II/IV B.Tech. (Regular/Supplementary) DEGREE EXAMINATION 14CH406 Chemical Engineering Scheme of Valuation Process Instrumentation
April, 2018 Fourth Semester Time: Three Hours Answer Question No.1 compulsorily. II/IV B.Tech. (Regular/Supplementary) DEGREE EXAMINATION 14CH406 Chemical Engineering Scheme of Valuation Process Instrumentation
Transducer. A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity. Transducer. (Input) Sensor.
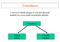 Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ
 BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ Year/Sem : III/V Sub.Code/Title: ME6504- METROLOGY & MEASUREMENTS UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT PART-A 1. Define
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ Year/Sem : III/V Sub.Code/Title: ME6504- METROLOGY & MEASUREMENTS UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT PART-A 1. Define
Section 7. Temperature Measurement
 Section 7 Temperature Measurement 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 1 Working Definition Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules that make of a substance. After time,
Section 7 Temperature Measurement 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 1 Working Definition Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules that make of a substance. After time,
Measurements & Instrumentation. Module 3: Temperature Sensors
 Measurements & Instrumentation PREPARED BY Academic Services Unit August 2013 Institute of Applied Technology, 2013 Module Objectives Upon successful completion of this module, students should be able
Measurements & Instrumentation PREPARED BY Academic Services Unit August 2013 Institute of Applied Technology, 2013 Module Objectives Upon successful completion of this module, students should be able
Scheme & Solutions of 14EI 505 (OCT-2018)
 Scheme & Solutions of 14EI 505 (OCT-2018) Prepared By: P. Vinodh Babu Associate Professor Department of EIE Bapatla Engineering College Bapatla-522102 Phone numbers: 9490126829, 7386014802 Hall Ticket
Scheme & Solutions of 14EI 505 (OCT-2018) Prepared By: P. Vinodh Babu Associate Professor Department of EIE Bapatla Engineering College Bapatla-522102 Phone numbers: 9490126829, 7386014802 Hall Ticket
(Refer Slide Time 03:12)
 Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module -2 Lecture - 20 Pressure Measurement So this will be lecture
Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module -2 Lecture - 20 Pressure Measurement So this will be lecture
THERMOCOUPLE CHARACTERISTICS TRAINER
 THERMOCOUPLE CHARACTERISTICS TRAINER (Model No : ) User Manual Version 2.0 Technical Clarification /Suggestion : / Technical Support Division, Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd., Plot No :75,Electronics Estate,
THERMOCOUPLE CHARACTERISTICS TRAINER (Model No : ) User Manual Version 2.0 Technical Clarification /Suggestion : / Technical Support Division, Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd., Plot No :75,Electronics Estate,
INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL
 INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL This tutorial provides minimal engineering science necessary to complete the rest of the tutorials. Greater depth of the individual topics can be found on the web site. It is
INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL This tutorial provides minimal engineering science necessary to complete the rest of the tutorials. Greater depth of the individual topics can be found on the web site. It is
US06CPHY06 Instrumentation and Sensors UNIT 2 Part 2 Pressure Measurements
 US06CPHY06 Instrumentation and Sensors UNIT 2 Part 2 Pressure Measurements Pressure Measurements What is Pressure? Pressure: Force exerted by a fluid on unit surface area of a container i.e. P = F/A. Units
US06CPHY06 Instrumentation and Sensors UNIT 2 Part 2 Pressure Measurements Pressure Measurements What is Pressure? Pressure: Force exerted by a fluid on unit surface area of a container i.e. P = F/A. Units
Course Name: Sensor and Transducer Course Code: EE 802B Credit: 3
 Course Name: Sensor and Transducer Course Code: EE 802B Credit: 3 Prerequisites: Sl. No. Subject Description Level of Study 01 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering 02 Electrical & Electronics Measurement
Course Name: Sensor and Transducer Course Code: EE 802B Credit: 3 Prerequisites: Sl. No. Subject Description Level of Study 01 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering 02 Electrical & Electronics Measurement
Temperature Measurement
 MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Temperature Measurement Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Introduction Temperature is one of the most
MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Temperature Measurement Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Introduction Temperature is one of the most
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING UNIT I - INTRODUCTION SYLLABUS
 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING YEAR/SEM NAME OF THE SUBJECT NAME OF THE FACULTY : II / IV : EE6404 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION : K.M.S.MUTHUKUMARA RAJAGURU, AP/EEE
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING YEAR/SEM NAME OF THE SUBJECT NAME OF THE FACULTY : II / IV : EE6404 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION : K.M.S.MUTHUKUMARA RAJAGURU, AP/EEE
ME 515 Mechatronics. Overview of Computer based Control System
 ME 515 Mechatronics Introduction to Sensors I Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Faculty of Engineering University of Peradeniya Tel: 081239 (3627) Email: asangar@pdn.ac.lk Overview of Computer based Control
ME 515 Mechatronics Introduction to Sensors I Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Faculty of Engineering University of Peradeniya Tel: 081239 (3627) Email: asangar@pdn.ac.lk Overview of Computer based Control
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Course Name : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Course Code : A50422
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Course Name : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Course Code : A50422
UNIT 2 STRAIN MEASURMENTS, FORCE MEASUREMENTS. Therefore, resistance strain gauges are also known as piezo-resistive gauges.
 UNIT 2 STRAIN MEASURMENTS, FORCE MEASUREMENTS STRAIN MEASURMENTS Introduction: When a metal conductor is stretched or compressed, its resistance changes an account of the fact that both length and diameter
UNIT 2 STRAIN MEASURMENTS, FORCE MEASUREMENTS STRAIN MEASURMENTS Introduction: When a metal conductor is stretched or compressed, its resistance changes an account of the fact that both length and diameter
1 Attempt any FIVE of the following: 20. a) What is measurement? Explain its significance. 4M. ANS: (Definition 01 M and significance 03M)
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8.
 Question Sheet Page 1 of 5 Instructions for the student: Question 1 is compulsory [40 marks] Attempt any two other questions [30 marks per question] The following must be made available during the examination:
Question Sheet Page 1 of 5 Instructions for the student: Question 1 is compulsory [40 marks] Attempt any two other questions [30 marks per question] The following must be made available during the examination:
Introduction. Measurement of temperature is generally considered to be one of the simplest and most accurate measurements performed in engineering.
 Slide Nr. 0 of 15 Slides Introduction Measurement of temperature is generally considered to be one of the simplest and most accurate measurements performed in engineering. Some important considerations
Slide Nr. 0 of 15 Slides Introduction Measurement of temperature is generally considered to be one of the simplest and most accurate measurements performed in engineering. Some important considerations
Industrial Instrumentation Prof. A. Barua Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Kharagpur
 Industrial Instrumentation Prof. A. Barua Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Kharagpur Lecture - 19 Low Pressure Measurement Welcome to the lesson 19 of Industrial Instrumentation.
Industrial Instrumentation Prof. A. Barua Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Kharagpur Lecture - 19 Low Pressure Measurement Welcome to the lesson 19 of Industrial Instrumentation.
Force and Displacement Measurement
 Force and Displacement Measurement Prof. R.G. Longoria Updated Fall 20 Simple ways to measure a force http://scienceblogs.com/dotphysics/200/02/diy_force_probe.php Example: Key Force/Deflection measure
Force and Displacement Measurement Prof. R.G. Longoria Updated Fall 20 Simple ways to measure a force http://scienceblogs.com/dotphysics/200/02/diy_force_probe.php Example: Key Force/Deflection measure
PHYS 352 Assignment #1 Solutions
 PHYS 352 Assignment #1 Solutions 1. Steinhart-Hart Equation for a thermistor In[1]:= a : 0.00128 In[2]:= b : 0.000236 In[3]:= In[4]:= d : 9.27 10^ 8 t r_ : a b Log r d Log r ^3 ^ 1 Note: Mathematica Log
PHYS 352 Assignment #1 Solutions 1. Steinhart-Hart Equation for a thermistor In[1]:= a : 0.00128 In[2]:= b : 0.000236 In[3]:= In[4]:= d : 9.27 10^ 8 t r_ : a b Log r d Log r ^3 ^ 1 Note: Mathematica Log
CHAPTER 9: TEMPERATURE, PRESSURE, STRAIN AND MOTION MEASUREMENTS
 CHAPTER 9: TEMPERATURE, PRESSURE, STRAIN AND MOTION MEASUREMENTS I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE 1. Introduction In industrial-process control, temperature is the most frequently controlled and measured
CHAPTER 9: TEMPERATURE, PRESSURE, STRAIN AND MOTION MEASUREMENTS I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE 1. Introduction In industrial-process control, temperature is the most frequently controlled and measured
Lecture 20. Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature MECH 373. Instrumentation and Measurements
 MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 20 Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature 1 Measuring Acceleration and Vibration Accelerometers using
MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 20 Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature 1 Measuring Acceleration and Vibration Accelerometers using
Cryogenic Instrumentation I Thermometry OUTLINE Thermometry Pt (pure metal) Temperature Ranges of Thermometer Application Typical Resistive Thermal
 Cryogenic Instrumentation I 1. Thermometry 2. anges of Application 3. Constant Volume 4. Thermocouples 5. Time esponse Data 6. 4 Terminal esistance Measurement OUTLINE 8. Pt (pure metal) 9. Typical esistive
Cryogenic Instrumentation I 1. Thermometry 2. anges of Application 3. Constant Volume 4. Thermocouples 5. Time esponse Data 6. 4 Terminal esistance Measurement OUTLINE 8. Pt (pure metal) 9. Typical esistive
COURSE TEMPLATE. The Course content covers the following broad topics: 1. Experimental Analysis:
 COURSE TEMPLATE 1. Department centre Proposing the course Applied Mechanics. Course Title Experimental Methods 3. L-T-P Structure 3-0- 4. Credits 4 5. Course Number AML 130 6. Status ( Category for Program)
COURSE TEMPLATE 1. Department centre Proposing the course Applied Mechanics. Course Title Experimental Methods 3. L-T-P Structure 3-0- 4. Credits 4 5. Course Number AML 130 6. Status ( Category for Program)
Strain, Force, and Pressure
 10-1 10-1 Strain, Force, and Pressure Force is that which results in acceleration (when forces don t cancel). Strain is the change in shape of an object...... usually due to some force. (Force is usually
10-1 10-1 Strain, Force, and Pressure Force is that which results in acceleration (when forces don t cancel). Strain is the change in shape of an object...... usually due to some force. (Force is usually
Week-7 Assignment-1. The due date for submitting this assignment has passed. (1/273.15)th of the normal freezing point of water
 X reviewer2@nptel.iitm.ac.in Courses» Chemical Process Instrumentation Unit 8 - Week 7 Announcements Course Ask a Question Progress Mentor Course outline How to access the portal Week-7 Assignment-1 The
X reviewer2@nptel.iitm.ac.in Courses» Chemical Process Instrumentation Unit 8 - Week 7 Announcements Course Ask a Question Progress Mentor Course outline How to access the portal Week-7 Assignment-1 The
Total Marks Q.1 Attempt any Six of following Measured in kilogram per square of centimeter(kg/cm 2 ).
 Model wer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by keywords and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Model wer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by keywords and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Lecture 36: Temperatue Measurements
 Lecture 36: Temperatue Measurements Contents Principle of thermocouples Materials for themocouples Cold junction compensation Compensating wires Selection of thermocouples Illustration of gas temperature
Lecture 36: Temperatue Measurements Contents Principle of thermocouples Materials for themocouples Cold junction compensation Compensating wires Selection of thermocouples Illustration of gas temperature
BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE B.Sc. PHYSICS DEGREE COURSE (Colleges) Course Title
 Part Ins. hrs / Week Dur.Hr CIA Marks Total Marks Credit Page 1 of 6 BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE-641 046 B.Sc. PHYSICS DEGREE COURSE (Colleges) REVISED SCHEME OF EXAMINATIONS (CBCS PATTERN) (For
Part Ins. hrs / Week Dur.Hr CIA Marks Total Marks Credit Page 1 of 6 BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE-641 046 B.Sc. PHYSICS DEGREE COURSE (Colleges) REVISED SCHEME OF EXAMINATIONS (CBCS PATTERN) (For
The secondary winding have equal no. of turns. The secondary windings are placed identically on either side of the primary winding.
 UNIT 4 DISPLACEMENT MEASURMENT Electrical comparator Working principle of Electrical comparators: These instruments are based on the theory of Wheatstone A.C. Bridge. When the bridge is electrically balanced,
UNIT 4 DISPLACEMENT MEASURMENT Electrical comparator Working principle of Electrical comparators: These instruments are based on the theory of Wheatstone A.C. Bridge. When the bridge is electrically balanced,
Thermometry. History. History 1/21/18. The art or science of temperature observation
 Thermometry The art or science of temperature observation History No one person credited with the invention of the thermometer; developed over time Avicenna used this principal to show that hotness and
Thermometry The art or science of temperature observation History No one person credited with the invention of the thermometer; developed over time Avicenna used this principal to show that hotness and
MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
 Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering g Department MEASURING INSTRUMENTS AND CALIBRATION Lecture (7) Temperature measurement By: Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical
Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering g Department MEASURING INSTRUMENTS AND CALIBRATION Lecture (7) Temperature measurement By: Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical
Slide 1. Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic Fields Strain Pressure Displacement and Rotation Acceleration Electronic Sensors
 Slide 1 Electronic Sensors Electronic sensors can be designed to detect a variety of quantitative aspects of a given physical system. Such quantities include: Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic
Slide 1 Electronic Sensors Electronic sensors can be designed to detect a variety of quantitative aspects of a given physical system. Such quantities include: Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic
Earlier Lecture. In the earlier lecture, we have seen non metallic sensors like Silicon diode, Cernox and Ruthenium Oxide.
 41 1 Earlier Lecture In the earlier lecture, we have seen non metallic sensors like Silicon diode, Cernox and Ruthenium Oxide. Silicon diodes have negligible i 2 R losses. Cernox RTDs offer high response
41 1 Earlier Lecture In the earlier lecture, we have seen non metallic sensors like Silicon diode, Cernox and Ruthenium Oxide. Silicon diodes have negligible i 2 R losses. Cernox RTDs offer high response
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Sub Code/Name: ME 1304/Engineering Metrology & Measurements Year/Sem :III/ V UNIT-I
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code/Name: ME 1304/Engineering Metrology & Measurements Year/Sem :III/ V UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT Part- A (2 Marks) 1. Differentiate between
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code/Name: ME 1304/Engineering Metrology & Measurements Year/Sem :III/ V UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT Part- A (2 Marks) 1. Differentiate between
APPLICATIONS OF VIBRATION TRANSDUCERS
 APPLICATIONS OF VIBRATION TRANSDUCERS 1) Measurements on Structures or Machinery Casings: Accelerometers and Velocity Sensors Used in gas turbines, axial compressors, small and mid-size pumps. These sensors
APPLICATIONS OF VIBRATION TRANSDUCERS 1) Measurements on Structures or Machinery Casings: Accelerometers and Velocity Sensors Used in gas turbines, axial compressors, small and mid-size pumps. These sensors
Instrumentation & Measurement AAiT. Chapter 3. Transducers and Their Response
 3.1 Transducer Chapter 3 Transducers and Their Response Instrument Society of America defines a sensor or transducer as a device which provides a usable output in response to a specified measured. Here
3.1 Transducer Chapter 3 Transducers and Their Response Instrument Society of America defines a sensor or transducer as a device which provides a usable output in response to a specified measured. Here
Chapter 3. Lecture 3 Chapter 3 Basic Principles of Transducers. Chapter 3 - Definitions. Chapter 3. Chapter 3 7/28/2010. Chapter 3 - Definitions.
 Lecture 3 Basic Principles of ransducers By Hung Nguyen Maritime Engineering and Hydrodynamics Learning Outcomes: p. 3-3 Contents of : resistance transducers capacitance transducers inductance transducers
Lecture 3 Basic Principles of ransducers By Hung Nguyen Maritime Engineering and Hydrodynamics Learning Outcomes: p. 3-3 Contents of : resistance transducers capacitance transducers inductance transducers
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME (CAD/CAM) QUESTION BANK
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME (CAD/CAM) QUESTION BANK III SEMESTER CC 7007 METROLOGY AND NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING Regulation 2013
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME (CAD/CAM) QUESTION BANK III SEMESTER CC 7007 METROLOGY AND NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING Regulation 2013
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer. Week 1
 Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 1 This Lecture Course Organization Introduction Basic Modes of Heat Transfer Application Areas Instructor Information Professor Chang-Da Wen 温昌達» Office: 91713
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 1 This Lecture Course Organization Introduction Basic Modes of Heat Transfer Application Areas Instructor Information Professor Chang-Da Wen 温昌達» Office: 91713
Solution for Mechanical Measurement & Control
 Solution for Mechanical Measurement & Control December-2015 Index Q.1) a). 2-3 b).3-4 c). 5 d). 6 Q.2) a). 7 b). 7 to 9 c). 10-11 Q.3) a). 11-12 b). 12-13 c). 13 Q.4) a). 14-15 b). 15 (N.A.) Q.5) a). 15
Solution for Mechanical Measurement & Control December-2015 Index Q.1) a). 2-3 b).3-4 c). 5 d). 6 Q.2) a). 7 b). 7 to 9 c). 10-11 Q.3) a). 11-12 b). 12-13 c). 13 Q.4) a). 14-15 b). 15 (N.A.) Q.5) a). 15
INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS LAB
 INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS LAB INDEX S.No. Name of the Experiment Page No. 1 Linear Variable Differential Transformer (L.V.D.T) 2 Speed Measurement Module 3 Capacitive Pickup 4 Thermister Module
INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS LAB INDEX S.No. Name of the Experiment Page No. 1 Linear Variable Differential Transformer (L.V.D.T) 2 Speed Measurement Module 3 Capacitive Pickup 4 Thermister Module
ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS
 EE 326 (RR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02 III/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 2017 Second Semester ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS Time: Three Hours Answer
EE 326 (RR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02 III/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 2017 Second Semester ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS Time: Three Hours Answer
Sensors and Actuators Sensors Physics
 Sensors and ctuators Sensors Physics Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC SENSORS (Chapter 3.9, 16.4) 3 Thermoelectric effect thermoelectric
Sensors and ctuators Sensors Physics Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC SENSORS (Chapter 3.9, 16.4) 3 Thermoelectric effect thermoelectric
Objective Type Questions Instrumentation System & Devices (IDS)
 1. A balance beam scale uses which of the following units? a. grams b.pounds c. ounces d. kilograms 2. Which of the following would be about the height of the average doorway? a. 2 meters b. 2 centimeters
1. A balance beam scale uses which of the following units? a. grams b.pounds c. ounces d. kilograms 2. Which of the following would be about the height of the average doorway? a. 2 meters b. 2 centimeters
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR-603203 EI 2302 ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS QUESTION BANK UNIT I COLORIMETRY AND SPECTROPHOTOMETRY Part A 1. State Lambert
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR-603203 EI 2302 ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS QUESTION BANK UNIT I COLORIMETRY AND SPECTROPHOTOMETRY Part A 1. State Lambert
e453.eps 1 Change (or the absolute value) in the measured physical variable 2 Change in the sensor property is translated into low-power-level
 3 Basic Phenomenon in Effect in Sensor Operation Sensors Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of
3 Basic Phenomenon in Effect in Sensor Operation Sensors Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of
Temperature Measurement
 Temperature Measurement Temperature is one of the most common measurements What is Temperature? Intuitively understood as sensation of hot/cold Early Researchers: Galileo (1564-1642) Newton (1642-1727)
Temperature Measurement Temperature is one of the most common measurements What is Temperature? Intuitively understood as sensation of hot/cold Early Researchers: Galileo (1564-1642) Newton (1642-1727)
UNIT I - INTRODUCTION SYLLABUS
 SEM / YEAR: VII/IV QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EE670 HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING UNIT I - INTRODUCTION SYLLABUS Causes of over voltages and its effects on power system Lightning, switching surges and temporary
SEM / YEAR: VII/IV QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EE670 HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING UNIT I - INTRODUCTION SYLLABUS Causes of over voltages and its effects on power system Lightning, switching surges and temporary
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17322 21314 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
17322 21314 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER PH8252 - PHYSICS FOR INFORMATION SCIENCE (Common to CSE & IT) Regulation 2017 Academic Year
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER PH8252 - PHYSICS FOR INFORMATION SCIENCE (Common to CSE & IT) Regulation 2017 Academic Year
ME332 FLUID MECHANICS LABORATORY (PART II)
 ME332 FLUID MECHANICS LABORATORY (PART II) Mihir Sen Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556 Version: April 2, 2002 Contents Unit 5: Momentum transfer
ME332 FLUID MECHANICS LABORATORY (PART II) Mihir Sen Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556 Version: April 2, 2002 Contents Unit 5: Momentum transfer
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING
 INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
Process Control & Design
 458.308 Process Control & Design Lecture 5: Feedback Control System Jong Min Lee Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Seoul National University 1 / 29 Feedback Control Scheme: The Continuous Blending Process.1
458.308 Process Control & Design Lecture 5: Feedback Control System Jong Min Lee Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Seoul National University 1 / 29 Feedback Control Scheme: The Continuous Blending Process.1
Sensors: a) Gyroscope. Micro Electro-Mechanical (MEM) Gyroscopes: (MEM) Gyroscopes. Needs:
 Sensors: Needs: Data redundancy Data for both situations: eclipse and sun Question of sampling frequency Location and size/weight Ability to resist to environment Low consumption Low price a) Gyroscope
Sensors: Needs: Data redundancy Data for both situations: eclipse and sun Question of sampling frequency Location and size/weight Ability to resist to environment Low consumption Low price a) Gyroscope
Estimate, for this water, the specific heat capacity, specific heat capacity =... J kg 1 K 1. the specific latent heat of vaporisation.
 1 A kettle is rated as 2.3 kw. A mass of 750 g of water at 20 C is poured into the kettle. When the kettle is switched on, it takes 2.0 minutes for the water to start boiling. In a further 7.0 minutes,
1 A kettle is rated as 2.3 kw. A mass of 750 g of water at 20 C is poured into the kettle. When the kettle is switched on, it takes 2.0 minutes for the water to start boiling. In a further 7.0 minutes,
15. Compare the result with the value you have taken above Compare the calculated pressure value with the actual pressure value that you have
 105) to convert it to. 15. Compare the result with the value you have taken above. 17. 16. Compare the calculated pressure value with the actual pressure value that you have taken from the, is it the same?
105) to convert it to. 15. Compare the result with the value you have taken above. 17. 16. Compare the calculated pressure value with the actual pressure value that you have taken from the, is it the same?
Overview. Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples
 Intro to Sensors Overview Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples Sensors? American National Standards Institute A device
Intro to Sensors Overview Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples Sensors? American National Standards Institute A device
Sensors and Transducers. mywbut.com
 Sensors and Transducers 1 Objectives At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: describe the principle of operation of various sensors and transducers; namely.. Resistive Position Transducers.
Sensors and Transducers 1 Objectives At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: describe the principle of operation of various sensors and transducers; namely.. Resistive Position Transducers.
Solved Problems. Electric Circuits & Components. 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown.
 Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Mechanical Sensors 1.
 DR. GYURCSEK ISTVÁN Mechanical Sensors 1. Sources and additional materials (recommended) Lambert Miklós: Szenzorok elmélet (ISBN 978-963-874001-1-3) Bp. 2009 Jacob Fraden: Handbook of Modern Sensors (ISBN
DR. GYURCSEK ISTVÁN Mechanical Sensors 1. Sources and additional materials (recommended) Lambert Miklós: Szenzorok elmélet (ISBN 978-963-874001-1-3) Bp. 2009 Jacob Fraden: Handbook of Modern Sensors (ISBN
Detection range and accuracy specs.
 Example Detection range and accuracy specs. Calculate accuracy and relative error for I = 2.458 ma in all possible ranges. Select the best range and answer why is the best? Write the display indication
Example Detection range and accuracy specs. Calculate accuracy and relative error for I = 2.458 ma in all possible ranges. Select the best range and answer why is the best? Write the display indication
