Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies Chapter 16
|
|
|
- Brice Marsh
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies Chapter Cascade control 2. Time-delay compensation 3. Inferential control 4. Selective and override control 5. Nonlinear control 6. Adaptive control 1
2 Chapter 16 Example: Cascade Control 2
3 Chapter 16 3
4 Chapter 16 4
5 Cascade Control Chapter 16 Distinguishing features: 1. Two FB controllers but only a single control valve (or other final control element). 2. Output signal of the "master" controller is the set-point for slave" controller. 3. Two FB control loops are "nested" with the "slave" (or "secondary") control loop inside the "master" (or "primary") control loop. Terminology: slave vs. master secondary vs. primary inner vs. outer 5
6 Chapter 16 6
7 Y G 1 P1Gd2 = (16 5) D 1+ G G G G + G G G G G G 2 c2 v p2 m2 c1 c2 v p2 p1 m1 Chapter 16 Y Y 1 2 D D Y Y Y Y% 1 2 m1 m2 = hot oil temperature = fuel gas pressure = cold oil temperature (or cold oil flow rate) = supply pressure of gas fuel = measured value of hot oil temperature = measured value of fuel gas temperature = set point for sp1 1 = set point for Y Y sp2 2 7
8 Chapter 16 Example 16.1 Consider the block diagram in Fig with the following transfer functions: 5 4 Gv = Gp1= Gp2= 1 s+ 1 ( 4s+ 1)( 2s+ 1) 1 Gd2= 1 Gm1= 0.05 Gm2= 0.2 Gd1= 3s + 1 8
9 Chapter 16 9
10 Example 16.2 Compare the set-point responses for a second-order process with a time delay (min) and without the delay. The transfer function is G p ( s) = e θ s ( 5s+ 1)( 3s+ 1) ( 16 18) Chapter 16 Assume Gm= Gv= 1 and time constants in minutes. Use the following PI controllers. For θ = 0, K c = 3.02andτ1 = 6.5min, while for θ = 2 min the controller gain must be reduced to meet stability requirements K = 1.23, τ = 7.0min. ( c ) 1 10
11 Time Delay Compensation Chapter 16 ( ) ( ) E' = E Y% = Y Y% Y Y% 1 sp If the process model is perfect and the disturbance is zero, then Y % 2 = Y and sp ( ) E' = Y Y % For this ideal case the controller responds to the error signal that would occur if not time were present. Assuming there is no model error ( G% = G), the inner loop has the effective transfer function P G G' = = c E 1 + GG* 1 e θ c ( s ) ( 16 21) 11
12 Chapter 16 For no model error: G=G % G c Gc = 1+ GG 1 c θ ( e ) * s * θ s θ = G * e - s Y GGe c GG c = = Y θ 1+ GGe 1+ GG * s * sp c c By contrast, for conventional feedback control Y Y sp θ s GGe c * = θ s 1 + GGe * c ( 16 23) 12
13 Chapter 16 13
14 Chapter 16 14
15 Inferential Control Problem: Controlled variable cannot be measured or has large sampling period. Chapter 16 Possible solutions: 1. Control a related variable (e.g., temperature instead of composition). 2. Inferential control: Control is based on an estimate of the controlled variable. The estimate is based on available measurements. Examples: empirical relation, Kalman filter Modern term: soft sensor 15
16 Chapter 16 Inferential Control with Fast and Slow Measured Variables 16
17 Selective Control Systems & Overrides For every controlled variable, it is very desirable that there be at least one manipulated variable. Chapter 16 But for some applications, N C > N M where: N C = number of controlled variables N M = number of manipulated variables Solution: Use a selective control system or an override. Selective control is also referred as Auctioneering. 17
18 Low selector: Chapter 16 High selector: Median selector: The output, Z, is the median of an odd number of inputs 18
19 Chapter 16 Example: High Selector Control System multiple measurements one controller one final control element 19
20 Chapter 16 2 measurements, 2 controllers, 1 final control element 20
21 Chapter 16 Overrides An override is a special case of a selective control system One of the inputs is a numerical value, a limit. Used when it is desirable to limit the value of a signal (e.g., a controller output). Softer than ESD or SIS Example: - anti-reset wind-up - lower and upper heat input rate for distillation column for ensuring liquid inventory or preventing flooding of the column Split-range control 21
22 Chapter 16 22
23 Nonlinear Control Strategies Chapter 16 Most physical processes are nonlinear to some degree. Some are very nonlinear. Examples: ph, high purity distillation columns, chemical reactions with large heats of reaction. However, linear control strategies (e.g., PID) can be effective if: 1. The nonlinearities are rather mild. or, 2. A highly nonlinear process usually operates over a narrow range of conditions. For very nonlinear strategies, a nonlinear control strategy can provide significantly better control. Two general classes of nonlinear control: 1. Enhancements of conventional, linear, feedback control 2. Model-based control strategies Reference: Henson & Seborg (Ed.), 1997 book. 23
24 Enhancements of Conventional Feedback Control Chapter 16 We will consider three enhancements of conventional feedback control: 1. Nonlinear modifications of PID control 2. Nonlinear transformations of input or output variables 3. Controller parameter scheduling such as gain scheduling. Nonlinear Modifications of PID Control: One Example: nonlinear controller gain K = K (1 + a et ( ) ) (16-26) c c0 K c0 and a are constants, and e(t) is the error signal (e = y sp -y). Also called, error squared controller because controller output is proportional to e(t) e(t) Example: level control in surge vessels. 24
25 Nonlinear Transformations of Variables Chapter 16 Objective: Make the closed-loop system as linear as possible. (Why?) Typical approach: transform an input or an output. Example: logarithmic transformation of a product composition in a high purity distillation column. (cf. McCabe-Thiele diagram) x 1 x = log 1 x * D D Dsp where x* D denotes the transformed distillate composition. Related approach: Define u or y to be combinations of several variables, based on physical considerations. Example: Continuous ph neutralization CVs: ph and liquid level, h (16-27) MVs: acid and base flow rates, q A and q B Conventional approach: single-loop controllers for ph and h. Better approach: control ph by adjusting the ratio, q A / q B, and control h by adjusting their sum. Thus, u 1 = q A / q B and u 2 = q A / q B 25
26 Chapter 16 Gain Scheduling Objective: Make the closed-loop system as linear as possible. Basic Idea: Adjust the controller gain based on current measurements of a scheduling variable, e.g., u, y, or some other variable. Note: Requires knowledge about how the process gain changes with this measured variable. 26
27 Examples of Gain Scheduling Example 1. Titration curve for a strong acid-strong base neutralization. Example 2. Once through boiler The open-loop step response are shown in Fig for two different feedwater flow rates. Chapter 16 Fig Open-loop responses. Proposed control strategy: Vary controller setting with w, the fraction of full-scale (100%) flow. K = wk, τ = τ / w, τ = τ / w, (16-30) c c I I D D Compare with the IMC controller settings for Model H in Table 12.1: θ s Ke θ τ + 1 (), 2 θ τθ Model H : Gs = Kc =, τi = τ +, τd = τs + 1 K θ 2 2τ + θ τc
28 Adaptive Control A general control strategy for control problems where the process or operating conditions can change significantly and unpredictably. Chapter 16 Example: Catalyst decay, equipment fouling Many different types of adaptive control strategies have been proposed. Self-Tuning Control (STC): A very well-known strategy and probably the most widely used adaptive control strategy. Basic idea: STC is a model-based approach. As process conditions change, update the model parameters by using least squares estimation and recent u & y data. Note: For predictable or measurable changes, use gain scheduling instead of adaptive control Reason: Gain scheduling is much easier to implement and less trouble prone. 28
29 Chapter 16 Block Diagram for Self-Tuning Control 29
30 Bumpless Transfer When a control loop is turned on without bumpless transfer, the process can become unduly upset. With bumpless transfer, an internal setpoint is used for the controller and the internal setpoint is ramped at a slow rate from the initial conditions to the actual desired setpoint to order to provide a smooth startup of a control loop. 30
31 Comparison of True and Internal Setpoints True Setpoint Internal Setpoint Time 31
32 Control Performance With and Without Bumpless Transfer w/o bumpless transfer w/ bumpless transfer Time 32
33 Split Range Flow Control In certain applications, a single flow control loop cannot provide accurate flow metering over the full range of operation. Split range flow control uses two flow controllers (one with a small control valve and one with a large control valve) in parallel. At low flow rates, the large valve is closed and the small valve provides accurate flow control. At large flow rates, both valve are open. 33
34 Split Range Flow Controller FC FT FT FC 34
35 Coordination of Control Valves for Split Range Flow Control Signal to Control Valve (%) Smaller Control Valve Larger Control Valve Total Flow Rate 35
36 Example for Split Range Flow Control RSP FC FT Acid Wastewater FT NaOH Solution phc pht Effluent 36
37 Titration Curve for a Strong Acid-Strong Base System ph Base to Acid Ratio Therefore, for accurate ph control for a wide range of flow rates for acid wastewater, a split range flow controller for the NaOH is required. 37
38 Other Split-Range Flow Control Examples When the controlled flow rate has a turn down ratio greater than 9 See value sizing examples in Chapter 2 38
39 Split Range Temperature Control Cooling Water Split-Range Temperature Controller Steam TT RSP TT TC 39
40 Split Range Temperature Control 100 Signal to Control Valve (%) Cooling Water Steam Error from Setpoint for Jacket Temperature 40
41 Overview All controllers that employ integral action should have anti-reset windup applied. Bumpless transfer provides a means for smooth startup of a control loop. When accurate metering of a flow over a very wide flow rate range is called for, use split range flow control. 41
42 Bumpless Transfer When a control loop is turned on without bumpless transfer, the process can become unduly upset. With bumpless transfer, an internal setpoint is used for the controller and the internal setpoint is ramped at a slow rate from the initial conditions to the actual desired setpoint to order to provide a smooth startup of a control loop. 42
43 Comparison of True and Internal Setpoints True Setpoint Internal Setpoint Time 43
44 Control Performance With and Without Bumpless Transfer w/o bumpless transfer w/ bumpless transfer Time 44
45 Split Range Flow Control In certain applications, a single flow control loop cannot provide accurate flow metering over the full range of operation. Split range flow control uses two flow controllers (one with a small control valve and one with a large control valve) in parallel. At low flow rates, the large valve is closed and the small valve provides accurate flow control. At large flow rates, both valve are open. 45
46 Split Range Flow Controller FC FT FT FC 46
47 Coordination of Control Valves for Split Range Flow Control Signal to Control Valve (%) Smaller Control Valve Larger Control Valve Total Flow Rate 47
48 Example for Split Range Flow Control RSP FC FT Acid Wastewater FT NaOH Solution phc pht Effluent 48
49 Titration Curve for a Strong Acid-Strong Base System ph Base to Acid Ratio Therefore, for accurate ph control for a wide range of flow rates for acid wastewater, a split range flow controller for the NaOH is required. 49
50 Other Split-Range Flow Control Examples When the controlled flow rate has a turn down ratio greater than 9 See value sizing examples in Chapter 2 50
51 Split Range Temperature Control Cooling Water Split-Range Temperature Controller Steam TT RSP TT TC 51
52 Split Range Temperature Control 100 Signal to Control Valve (%) Cooling Water Steam Error from Setpoint for Jacket Temperature 52
53 Overview All controllers that employ integral action should have anti-reset windup applied. Bumpless transfer provides a means for smooth startup of a control loop. When accurate metering of a flow over a very wide flow rate range is called for, use split range flow control. 53
Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies (Advanced Control) Cascade Control Time-Delay Compensation Inferential Control Selective and Override Control
 Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies (Advanced Control) Cascade Control Time-Delay Compensation Inferential Control Selective and Override Control 1 Cascade Control A disadvantage of conventional feedback
Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies (Advanced Control) Cascade Control Time-Delay Compensation Inferential Control Selective and Override Control 1 Cascade Control A disadvantage of conventional feedback
CM 3310 Process Control, Spring Lecture 21
 CM 331 Process Control, Spring 217 Instructor: Dr. om Co Lecture 21 (Back to Process Control opics ) General Control Configurations and Schemes. a) Basic Single-Input/Single-Output (SISO) Feedback Figure
CM 331 Process Control, Spring 217 Instructor: Dr. om Co Lecture 21 (Back to Process Control opics ) General Control Configurations and Schemes. a) Basic Single-Input/Single-Output (SISO) Feedback Figure
Control Lab. Thermal Plant. Chriss Grimholt
 Control Lab Thermal Plant Chriss Grimholt Process System Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering Norwegian University of Science and Technology October 3, 23 C. Grimholt (NTNU) Thermal Plant October
Control Lab Thermal Plant Chriss Grimholt Process System Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering Norwegian University of Science and Technology October 3, 23 C. Grimholt (NTNU) Thermal Plant October
Fundamental Principles of Process Control
 Fundamental Principles of Process Control Motivation for Process Control Safety First: people, environment, equipment The Profit Motive: meeting final product specs minimizing waste production minimizing
Fundamental Principles of Process Control Motivation for Process Control Safety First: people, environment, equipment The Profit Motive: meeting final product specs minimizing waste production minimizing
Advanced control If single-loop feedback control (PID) alone is not good enough
 The decision hierarchy is based on time scale separation setpoints Advanced control (MPC) setpoints Fast regulatory control (PID) PROCESS Advanced control If single-loop feedback control (PID) alone is
The decision hierarchy is based on time scale separation setpoints Advanced control (MPC) setpoints Fast regulatory control (PID) PROCESS Advanced control If single-loop feedback control (PID) alone is
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6
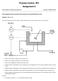 Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
Index Accumulation, 53 Accuracy: numerical integration, sensor, 383, Adaptive tuning: expert system, 528 gain scheduling, 518, 529, 709,
 Accumulation, 53 Accuracy: numerical integration, 83-84 sensor, 383, 772-773 Adaptive tuning: expert system, 528 gain scheduling, 518, 529, 709, 715 input conversion, 519 reasons for, 512-517 relay auto-tuning,
Accumulation, 53 Accuracy: numerical integration, 83-84 sensor, 383, 772-773 Adaptive tuning: expert system, 528 gain scheduling, 518, 529, 709, 715 input conversion, 519 reasons for, 512-517 relay auto-tuning,
Chapter 8. Feedback Controllers. Figure 8.1 Schematic diagram for a stirred-tank blending system.
 Feedback Controllers Figure 8.1 Schematic diagram for a stirred-tank blending system. 1 Basic Control Modes Next we consider the three basic control modes starting with the simplest mode, proportional
Feedback Controllers Figure 8.1 Schematic diagram for a stirred-tank blending system. 1 Basic Control Modes Next we consider the three basic control modes starting with the simplest mode, proportional
Solutions for Tutorial 10 Stability Analysis
 Solutions for Tutorial 1 Stability Analysis 1.1 In this question, you will analyze the series of three isothermal CSTR s show in Figure 1.1. The model for each reactor is the same at presented in Textbook
Solutions for Tutorial 1 Stability Analysis 1.1 In this question, you will analyze the series of three isothermal CSTR s show in Figure 1.1. The model for each reactor is the same at presented in Textbook
CHBE320 LECTURE XI CONTROLLER DESIGN AND PID CONTOLLER TUNING. Professor Dae Ryook Yang
 CHBE320 LECTURE XI CONTROLLER DESIGN AND PID CONTOLLER TUNING Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 11-1 Road Map of the Lecture XI Controller Design and PID
CHBE320 LECTURE XI CONTROLLER DESIGN AND PID CONTOLLER TUNING Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 11-1 Road Map of the Lecture XI Controller Design and PID
Control Introduction. Gustaf Olsson IEA Lund University.
 Control Introduction Gustaf Olsson IEA Lund University Gustaf.Olsson@iea.lth.se Lecture 3 Dec Nonlinear and linear systems Aeration, Growth rate, DO saturation Feedback control Cascade control Manipulated
Control Introduction Gustaf Olsson IEA Lund University Gustaf.Olsson@iea.lth.se Lecture 3 Dec Nonlinear and linear systems Aeration, Growth rate, DO saturation Feedback control Cascade control Manipulated
Dynamics and PID control. Process dynamics
 Dynamics and PID control Sigurd Skogestad Process dynamics Things take time Step response (response of output y to step in input u): k = Δy( )/ Δu process gain - process time constant (63%) - process time
Dynamics and PID control Sigurd Skogestad Process dynamics Things take time Step response (response of output y to step in input u): k = Δy( )/ Δu process gain - process time constant (63%) - process time
Feedforward Control Feedforward Compensation
 Feedforward Control Feedforward Compensation Compensation Feedforward Control Feedforward Control of a Heat Exchanger Implementation Issues Comments Nomenclature The inherent limitation of feedback control
Feedforward Control Feedforward Compensation Compensation Feedforward Control Feedforward Control of a Heat Exchanger Implementation Issues Comments Nomenclature The inherent limitation of feedback control
Principles and Practice of Automatic Process Control
 Principles and Practice of Automatic Process Control Third Edition Carlos A. Smith, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Chemical Engineering University of South Florida Armando B. Corripio, Ph.D., P.E. Gordon A.
Principles and Practice of Automatic Process Control Third Edition Carlos A. Smith, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Chemical Engineering University of South Florida Armando B. Corripio, Ph.D., P.E. Gordon A.
Ali Karimpour Associate Professor Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 CONTROL IN INSTRUMENTATION Ali Karimpour Associate Professor Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Reference: - Advanced PID Control by Karl j. Astrom and Tore Hagglund, ISA, 2006 مدلسازی و کنترل صنعتی تالیف
CONTROL IN INSTRUMENTATION Ali Karimpour Associate Professor Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Reference: - Advanced PID Control by Karl j. Astrom and Tore Hagglund, ISA, 2006 مدلسازی و کنترل صنعتی تالیف
Input-output Controllability Analysis
 Input-output Controllability Analysis Idea: Find out how well the process can be controlled - without having to design a specific controller Note: Some processes are impossible to control Reference: S.
Input-output Controllability Analysis Idea: Find out how well the process can be controlled - without having to design a specific controller Note: Some processes are impossible to control Reference: S.
Analyzing Control Problems and Improving Control Loop Performance
 OptiControls Inc. Houston, TX Ph: 713-459-6291 www.opticontrols.com info@opticontrols.com Analyzing Control s and Improving Control Loop Performance -by Jacques F. Smuts Page: 1 Presenter Principal Consultant
OptiControls Inc. Houston, TX Ph: 713-459-6291 www.opticontrols.com info@opticontrols.com Analyzing Control s and Improving Control Loop Performance -by Jacques F. Smuts Page: 1 Presenter Principal Consultant
Process Control & Design
 458.308 Process Control & Design Lecture 5: Feedback Control System Jong Min Lee Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Seoul National University 1 / 29 Feedback Control Scheme: The Continuous Blending Process.1
458.308 Process Control & Design Lecture 5: Feedback Control System Jong Min Lee Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Seoul National University 1 / 29 Feedback Control Scheme: The Continuous Blending Process.1
3.1 Overview 3.2 Process and control-loop interactions
 3. Multivariable 3.1 Overview 3.2 and control-loop interactions 3.2.1 Interaction analysis 3.2.2 Closed-loop stability 3.3 Decoupling control 3.3.1 Basic design principle 3.3.2 Complete decoupling 3.3.3
3. Multivariable 3.1 Overview 3.2 and control-loop interactions 3.2.1 Interaction analysis 3.2.2 Closed-loop stability 3.3 Decoupling control 3.3.1 Basic design principle 3.3.2 Complete decoupling 3.3.3
Process Control Exercise 2
 Process Control Exercise 2 1 Distillation Case Study Distillation is a method of separating liquid mixtures by means of partial evaporation. The volatility α of a compound determines how enriched the liquid
Process Control Exercise 2 1 Distillation Case Study Distillation is a method of separating liquid mixtures by means of partial evaporation. The volatility α of a compound determines how enriched the liquid
CONTROL OF MULTIVARIABLE PROCESSES
 Process plants ( or complex experiments) have many variables that must be controlled. The engineer must. Provide the needed sensors 2. Provide adequate manipulated variables 3. Decide how the CVs and MVs
Process plants ( or complex experiments) have many variables that must be controlled. The engineer must. Provide the needed sensors 2. Provide adequate manipulated variables 3. Decide how the CVs and MVs
Overview of Control System Design
 Overview of Control System Design Chapter 10 General Requirements 1. Safety. It is imperative that industrial plants operate safely so as to promote the well-being of people and equipment within the plant
Overview of Control System Design Chapter 10 General Requirements 1. Safety. It is imperative that industrial plants operate safely so as to promote the well-being of people and equipment within the plant
Subject: Introduction to Process Control. Week 01, Lectures 01 02, Spring Content
 v CHEG 461 : Process Dynamics and Control Subject: Introduction to Process Control Week 01, Lectures 01 02, Spring 2014 Dr. Costas Kiparissides Content 1. Introduction to Process Dynamics and Control 2.
v CHEG 461 : Process Dynamics and Control Subject: Introduction to Process Control Week 01, Lectures 01 02, Spring 2014 Dr. Costas Kiparissides Content 1. Introduction to Process Dynamics and Control 2.
CHAPTER 19: Single-Loop IMC Control
 When I coplete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Recognize that other feedback algoriths are possible Understand the IMC structure and how it provides the essential control features
When I coplete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Recognize that other feedback algoriths are possible Understand the IMC structure and how it provides the essential control features
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 5
 Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 5 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 12 March 2014 This assignment is due on Wednesday, 12 March 2014. Late hand-ins are not allowed. Since it is posted mainly
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 5 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 12 March 2014 This assignment is due on Wednesday, 12 March 2014. Late hand-ins are not allowed. Since it is posted mainly
DESIGN OF AN ON-LINE TITRATOR FOR NONLINEAR ph CONTROL
 DESIGN OF AN ON-LINE TITRATOR FOR NONLINEAR CONTROL Alex D. Kalafatis Liuping Wang William R. Cluett AspenTech, Toronto, Canada School of Electrical & Computer Engineering, RMIT University, Melbourne,
DESIGN OF AN ON-LINE TITRATOR FOR NONLINEAR CONTROL Alex D. Kalafatis Liuping Wang William R. Cluett AspenTech, Toronto, Canada School of Electrical & Computer Engineering, RMIT University, Melbourne,
BITS-Pilani Dubai, International Academic City, Dubai Second Semester. Academic Year
 BITS-Pilani Dubai, International Academic City, Dubai Second Semester. Academic Year 2007-2008 Evaluation Com anent: Com rehensive Examination Closed Book CHE UC441/11NSTR UC 45'1 PROCESS CONTROL Date:
BITS-Pilani Dubai, International Academic City, Dubai Second Semester. Academic Year 2007-2008 Evaluation Com anent: Com rehensive Examination Closed Book CHE UC441/11NSTR UC 45'1 PROCESS CONTROL Date:
Index. INDEX_p /15/02 3:08 PM Page 765
 INDEX_p.765-770 11/15/02 3:08 PM Page 765 Index N A Adaptive control, 144 Adiabatic reactors, 465 Algorithm, control, 5 All-pass factorization, 257 All-pass, frequency response, 225 Amplitude, 216 Amplitude
INDEX_p.765-770 11/15/02 3:08 PM Page 765 Index N A Adaptive control, 144 Adiabatic reactors, 465 Algorithm, control, 5 All-pass factorization, 257 All-pass, frequency response, 225 Amplitude, 216 Amplitude
Feedback Control of Linear SISO systems. Process Dynamics and Control
 Feedback Control of Linear SISO systems Process Dynamics and Control 1 Open-Loop Process The study of dynamics was limited to open-loop systems Observe process behavior as a result of specific input signals
Feedback Control of Linear SISO systems Process Dynamics and Control 1 Open-Loop Process The study of dynamics was limited to open-loop systems Observe process behavior as a result of specific input signals
Overview of Control System Design
 Overview of Control System Design General Requirements 1. Safety. It is imperative that industrial plants operate safely so as to promote the well-being of people and equipment within the plant and in
Overview of Control System Design General Requirements 1. Safety. It is imperative that industrial plants operate safely so as to promote the well-being of people and equipment within the plant and in
Process Unit Control System Design
 Process Unit Control System Design 1. Introduction 2. Influence of process design 3. Control degrees of freedom 4. Selection of control system variables 5. Process safety Introduction Control system requirements»
Process Unit Control System Design 1. Introduction 2. Influence of process design 3. Control degrees of freedom 4. Selection of control system variables 5. Process safety Introduction Control system requirements»
Process Solutions. Process Dynamics. The Fundamental Principle of Process Control. APC Techniques Dynamics 2-1. Page 2-1
 Process Dynamics The Fundamental Principle of Process Control APC Techniques Dynamics 2-1 Page 2-1 Process Dynamics (1) All Processes are dynamic i.e. they change with time. If a plant were totally static
Process Dynamics The Fundamental Principle of Process Control APC Techniques Dynamics 2-1 Page 2-1 Process Dynamics (1) All Processes are dynamic i.e. they change with time. If a plant were totally static
IMPROVED CONSTRAINED CASCADE CONTROL FOR PARALLEL PROCESSES. Richard Lestage, André Pomerleau and André Desbiens
 IMPROVED CONSTRAINED CASCADE CONTROL FOR PARALLEL PROCESSES Richard Lestage, André Pomerleau and André Desbiens Groupe de Recherche sur les Applications de l Informatique à l Industrie Minérale(GRAIIM),
IMPROVED CONSTRAINED CASCADE CONTROL FOR PARALLEL PROCESSES Richard Lestage, André Pomerleau and André Desbiens Groupe de Recherche sur les Applications de l Informatique à l Industrie Minérale(GRAIIM),
NonlinearControlofpHSystemforChangeOverTitrationCurve
 D. SWATI et al., Nonlinear Control of ph System for Change Over Titration Curve, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 19 (4) 341 349 (2005) 341 NonlinearControlofpHSystemforChangeOverTitrationCurve D. Swati, V. S. R.
D. SWATI et al., Nonlinear Control of ph System for Change Over Titration Curve, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 19 (4) 341 349 (2005) 341 NonlinearControlofpHSystemforChangeOverTitrationCurve D. Swati, V. S. R.
EXAMINATION INFORMATION PAGE Written examination
 EXAMINATION INFORMATION PAGE Written examination Course code: Course name: PEF3006 Process Control Examination date: 30 November 2018 Examination time from/to: 09:00-13:00 Total hours: 4 Responsible course
EXAMINATION INFORMATION PAGE Written examination Course code: Course name: PEF3006 Process Control Examination date: 30 November 2018 Examination time from/to: 09:00-13:00 Total hours: 4 Responsible course
CHAPTER 10: STABILITY &TUNING
 When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Determine the stability of a process without control Determine the stability of a closed-loop feedback control system Use these approaches
When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Determine the stability of a process without control Determine the stability of a closed-loop feedback control system Use these approaches
Twin-Screw Food Extruder: A Multivariable Case Study for a Process Control Course
 Twin-Screw Food Extruder: A Multivariable Case Study for a Process Control Course Process Control Course Overview Case Studies Realistic Industrial Problems Motivating to Students Integrate Techniques
Twin-Screw Food Extruder: A Multivariable Case Study for a Process Control Course Process Control Course Overview Case Studies Realistic Industrial Problems Motivating to Students Integrate Techniques
Lecture 5 Classical Control Overview III. Dr. Radhakant Padhi Asst. Professor Dept. of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Science - Bangalore
 Lecture 5 Classical Control Overview III Dr. Radhakant Padhi Asst. Professor Dept. of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Science - Bangalore A Fundamental Problem in Control Systems Poles of open
Lecture 5 Classical Control Overview III Dr. Radhakant Padhi Asst. Professor Dept. of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Science - Bangalore A Fundamental Problem in Control Systems Poles of open
SIMULATION SUITE CHEMCAD SOFTWARE PROCESS CONTROL SYSTEMS PROCESS CONTROL SYSTEMS COURSE WITH CHEMCAD MODELS. Application > Design > Adjustment
 COURSE WITH CHEMCAD MODELS PROCESS CONTROL SYSTEMS Application > Design > Adjustment Based on F.G. Shinskey s 1967 Edition Presenter John Edwards P & I Design Ltd, UK Contact: jee@pidesign.co.uk COURSE
COURSE WITH CHEMCAD MODELS PROCESS CONTROL SYSTEMS Application > Design > Adjustment Based on F.G. Shinskey s 1967 Edition Presenter John Edwards P & I Design Ltd, UK Contact: jee@pidesign.co.uk COURSE
Introduction to. Process Control. Ahmet Palazoglu. Second Edition. Jose A. Romagnoli. CRC Press. Taylor & Francis Group. Taylor & Francis Group,
 Introduction to Process Control Second Edition Jose A. Romagnoli Ahmet Palazoglu CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London NewYork CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa
Introduction to Process Control Second Edition Jose A. Romagnoli Ahmet Palazoglu CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London NewYork CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa
CHAPTER 13: FEEDBACK PERFORMANCE
 When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Apply two methods for evaluating control performance: simulation and frequency response Apply general guidelines for the effect of -
When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Apply two methods for evaluating control performance: simulation and frequency response Apply general guidelines for the effect of -
Control Systems II. ETH, MAVT, IDSC, Lecture 4 17/03/2017. G. Ducard
 Control Systems II ETH, MAVT, IDSC, Lecture 4 17/03/2017 Lecture plan: Control Systems II, IDSC, 2017 SISO Control Design 24.02 Lecture 1 Recalls, Introductory case study 03.03 Lecture 2 Cascaded Control
Control Systems II ETH, MAVT, IDSC, Lecture 4 17/03/2017 Lecture plan: Control Systems II, IDSC, 2017 SISO Control Design 24.02 Lecture 1 Recalls, Introductory case study 03.03 Lecture 2 Cascaded Control
Distributed Parameter Systems
 Distributed Parameter Systems Introduction All the apparatus dynamic experiments in the laboratory exhibit the effect known as "minimum phase dynamics". Process control loops are often based on simulations
Distributed Parameter Systems Introduction All the apparatus dynamic experiments in the laboratory exhibit the effect known as "minimum phase dynamics". Process control loops are often based on simulations
Solution to exam in PEF3006 Process Control at Telemark University College
 Solution to exam in PEF3006 Process Control at Telemark University College Exam date: 7. December 2015. Duration: 4 hours. Weight in final grade of the course: 100%. Teacher: Finn Aakre Haugen (finn.haugen@hit.no).
Solution to exam in PEF3006 Process Control at Telemark University College Exam date: 7. December 2015. Duration: 4 hours. Weight in final grade of the course: 100%. Teacher: Finn Aakre Haugen (finn.haugen@hit.no).
Process Control J.P. CORRIOU. Reaction and Process Engineering Laboratory University of Lorraine-CNRS, Nancy (France) Zhejiang University 2016
 Process Control J.P. CORRIOU Reaction and Process Engineering Laboratory University of Lorraine-CNRS, Nancy (France) Zhejiang University 206 J.P. Corriou (LRGP) Process Control Zhejiang University 206
Process Control J.P. CORRIOU Reaction and Process Engineering Laboratory University of Lorraine-CNRS, Nancy (France) Zhejiang University 206 J.P. Corriou (LRGP) Process Control Zhejiang University 206
ChE 6303 Advanced Process Control
 ChE 6303 Advanced Process Control Teacher: Dr. M. A. A. Shoukat Choudhury, Email: shoukat@buet.ac.bd Syllabus: 1. SISO control systems: Review of the concepts of process dynamics and control, process models,
ChE 6303 Advanced Process Control Teacher: Dr. M. A. A. Shoukat Choudhury, Email: shoukat@buet.ac.bd Syllabus: 1. SISO control systems: Review of the concepts of process dynamics and control, process models,
Model predictive control of industrial processes. Vitali Vansovitš
 Model predictive control of industrial processes Vitali Vansovitš Contents Industrial process (Iru Power Plant) Neural networ identification Process identification linear model Model predictive controller
Model predictive control of industrial processes Vitali Vansovitš Contents Industrial process (Iru Power Plant) Neural networ identification Process identification linear model Model predictive controller
Guide to Selected Process Examples :ili3g eil;]iil
![Guide to Selected Process Examples :ili3g eil;]iil Guide to Selected Process Examples :ili3g eil;]iil](/thumbs/85/91730677.jpg) Guide to Selected Process Examples :ili3g eil;]iil Because of the strong interplay between process dynamics and control perfor mance, examples should begin with process equipment and operating conditions.
Guide to Selected Process Examples :ili3g eil;]iil Because of the strong interplay between process dynamics and control perfor mance, examples should begin with process equipment and operating conditions.
Design and Comparative Analysis of Controller for Non Linear Tank System
 Design and Comparative Analysis of for Non Linear Tank System Janaki.M 1, Soniya.V 2, Arunkumar.E 3 12 Assistant professor, Department of EIE, Karpagam College of Engineering, Coimbatore, India 3 Associate
Design and Comparative Analysis of for Non Linear Tank System Janaki.M 1, Soniya.V 2, Arunkumar.E 3 12 Assistant professor, Department of EIE, Karpagam College of Engineering, Coimbatore, India 3 Associate
Control of MIMO processes. 1. Introduction. Control of MIMO processes. Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Processes
 Control of MIMO processes Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Processes Statistical Process Control Feedforward and ratio control Cascade control Split range and selective control Control
Control of MIMO processes Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Processes Statistical Process Control Feedforward and ratio control Cascade control Split range and selective control Control
Lecture 7: Anti-windup and friction compensation
 Lecture 7: Anti-windup and friction compensation Compensation for saturations (anti-windup) Friction models Friction compensation Material Lecture slides Course Outline Lecture 1-3 Lecture 2-6 Lecture
Lecture 7: Anti-windup and friction compensation Compensation for saturations (anti-windup) Friction models Friction compensation Material Lecture slides Course Outline Lecture 1-3 Lecture 2-6 Lecture
DYNAMIC SIMULATOR-BASED APC DESIGN FOR A NAPHTHA REDISTILLATION COLUMN
 HUNGARIAN JOURNAL OF INDUSTRY AND CHEMISTRY Vol. 45(1) pp. 17 22 (2017) hjic.mk.uni-pannon.hu DOI: 10.1515/hjic-2017-0004 DYNAMIC SIMULATOR-BASED APC DESIGN FOR A NAPHTHA REDISTILLATION COLUMN LÁSZLÓ SZABÓ,
HUNGARIAN JOURNAL OF INDUSTRY AND CHEMISTRY Vol. 45(1) pp. 17 22 (2017) hjic.mk.uni-pannon.hu DOI: 10.1515/hjic-2017-0004 DYNAMIC SIMULATOR-BASED APC DESIGN FOR A NAPHTHA REDISTILLATION COLUMN LÁSZLÓ SZABÓ,
Improved cascade control structure for enhanced performance
 Improved cascade control structure for enhanced performance Article (Unspecified) Kaya, İbrahim, Tan, Nusret and Atherton, Derek P. (7) Improved cascade control structure for enhanced performance. Journal
Improved cascade control structure for enhanced performance Article (Unspecified) Kaya, İbrahim, Tan, Nusret and Atherton, Derek P. (7) Improved cascade control structure for enhanced performance. Journal
Class 27: Block Diagrams
 Class 7: Block Diagrams Dynamic Behavior and Stability of Closed-Loop Control Systems We no ant to consider the dynamic behavior of processes that are operated using feedback control. The combination of
Class 7: Block Diagrams Dynamic Behavior and Stability of Closed-Loop Control Systems We no ant to consider the dynamic behavior of processes that are operated using feedback control. The combination of
Nonlinear ph Control Using a Three Parameter Model
 130 ICASE: The Institute of Control, Automation and Systems Engineers, KOREA Vol. 2, No. 2, June, 2000 Nonlinear ph Control Using a Three Parameter Model Jietae Lee and Ho-Cheol Park Abstract: A two parameter
130 ICASE: The Institute of Control, Automation and Systems Engineers, KOREA Vol. 2, No. 2, June, 2000 Nonlinear ph Control Using a Three Parameter Model Jietae Lee and Ho-Cheol Park Abstract: A two parameter
Overview of Control System Design
 Overview of Control System Design Introduction Degrees of Freedom for Process Control Selection of Controlled, Manipulated, and Measured Variables Process Safety and Process Control 1 General Requirements
Overview of Control System Design Introduction Degrees of Freedom for Process Control Selection of Controlled, Manipulated, and Measured Variables Process Safety and Process Control 1 General Requirements
B1-1. Closed-loop control. Chapter 1. Fundamentals of closed-loop control technology. Festo Didactic Process Control System
 B1-1 Chapter 1 Fundamentals of closed-loop control technology B1-2 This chapter outlines the differences between closed-loop and openloop control and gives an introduction to closed-loop control technology.
B1-1 Chapter 1 Fundamentals of closed-loop control technology B1-2 This chapter outlines the differences between closed-loop and openloop control and gives an introduction to closed-loop control technology.
Model based control design
 Model based control design Alf Isaksson September, 999 Supplied as supplement to course book in Automatic Control Basic course (Reglerteknik AK) Objective: To introduce some general approaches to model
Model based control design Alf Isaksson September, 999 Supplied as supplement to course book in Automatic Control Basic course (Reglerteknik AK) Objective: To introduce some general approaches to model
CHAPTER 2 PROCESS DESCRIPTION
 15 CHAPTER 2 PROCESS DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION A process havin only one input variable used for controllin one output variable is known as SISO process. The problem of desinin controller for SISO systems
15 CHAPTER 2 PROCESS DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION A process havin only one input variable used for controllin one output variable is known as SISO process. The problem of desinin controller for SISO systems
Analysis and Design of Control Systems in the Time Domain
 Chapter 6 Analysis and Design of Control Systems in the Time Domain 6. Concepts of feedback control Given a system, we can classify it as an open loop or a closed loop depends on the usage of the feedback.
Chapter 6 Analysis and Design of Control Systems in the Time Domain 6. Concepts of feedback control Given a system, we can classify it as an open loop or a closed loop depends on the usage of the feedback.
CHAPTER 15: FEEDFORWARD CONTROL
 CHAPER 5: EEDORWARD CONROL When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Identify situations for which feedforward is a good control enhancement Design feedforward control using
CHAPER 5: EEDORWARD CONROL When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Identify situations for which feedforward is a good control enhancement Design feedforward control using
Integrator Windup
 3.5.2. Integrator Windup 3.5.2.1. Definition So far we have mainly been concerned with linear behaviour, as is often the case with analysis and design of control systems. There is, however, one nonlinear
3.5.2. Integrator Windup 3.5.2.1. Definition So far we have mainly been concerned with linear behaviour, as is often the case with analysis and design of control systems. There is, however, one nonlinear
Multi-Input Multi-output (MIMO) Processes CBE495 LECTURE III CONTROL OF MULTI INPUT MULTI OUTPUT PROCESSES. Professor Dae Ryook Yang
 Multi-Input Multi-output (MIMO) Processes CBE495 LECTURE III CONTROL OF MULTI INPUT MULTI OUTPUT PROCESSES Professor Dae Ryook Yang Fall 2013 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering Korea University
Multi-Input Multi-output (MIMO) Processes CBE495 LECTURE III CONTROL OF MULTI INPUT MULTI OUTPUT PROCESSES Professor Dae Ryook Yang Fall 2013 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering Korea University
Control System Design
 ELEC ENG 4CL4: Control System Design Notes for Lecture #36 Dr. Ian C. Bruce Room: CRL-229 Phone ext.: 26984 Email: ibruce@mail.ece.mcmaster.ca Friday, April 4, 2003 3. Cascade Control Next we turn to an
ELEC ENG 4CL4: Control System Design Notes for Lecture #36 Dr. Ian C. Bruce Room: CRL-229 Phone ext.: 26984 Email: ibruce@mail.ece.mcmaster.ca Friday, April 4, 2003 3. Cascade Control Next we turn to an
Design and analysis of the prototype of boiler for steam pressure control
 Design and analysis of the prototype of boiler for steam pressure control Akanksha Bhoursae, 2 Jalpa Shah, 3 Nishith Bhatt Institute of Technology, Nirma University, SG highway, Ahmedabad-38248,India 3
Design and analysis of the prototype of boiler for steam pressure control Akanksha Bhoursae, 2 Jalpa Shah, 3 Nishith Bhatt Institute of Technology, Nirma University, SG highway, Ahmedabad-38248,India 3
Lynkurs Prosessregulering (Crash course process control) Sigurd Skogestad Institutt for kjemisk prosessteknologi Rom K4-211
 Lynkurs Prosessregulering (Crash course process control) Sigurd Skogestad Institutt for kjemisk prosessteknologi Rom K4-211 skoge@ntnu.no 1 Course for 3rd year students: Pensum (syllabus): Lectures/exercises
Lynkurs Prosessregulering (Crash course process control) Sigurd Skogestad Institutt for kjemisk prosessteknologi Rom K4-211 skoge@ntnu.no 1 Course for 3rd year students: Pensum (syllabus): Lectures/exercises
Systems Engineering/Process Control L1
 Systems Engineering/Process Control L1 What is Systems Engineering/Process Control? Graphical system representations Fundamental control principles Reading: Systems Engineering and Process Control: 1.1
Systems Engineering/Process Control L1 What is Systems Engineering/Process Control? Graphical system representations Fundamental control principles Reading: Systems Engineering and Process Control: 1.1
PROCESS CONTROL (IT62) SEMESTER: VI BRANCH: INSTRUMENTATION TECHNOLOGY
 PROCESS CONTROL (IT62) SEMESTER: VI BRANCH: INSTRUMENTATION TECHNOLOGY by, Dr. Mallikarjun S. Holi Professor & Head Department of Biomedical Engineering Bapuji Institute of Engineering & Technology Davangere-577004
PROCESS CONTROL (IT62) SEMESTER: VI BRANCH: INSTRUMENTATION TECHNOLOGY by, Dr. Mallikarjun S. Holi Professor & Head Department of Biomedical Engineering Bapuji Institute of Engineering & Technology Davangere-577004
Plantwide Control of Chemical Processes Prof. Nitin Kaistha Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Plantwide Control of Chemical Processes Prof. Nitin Kaistha Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 41 Cumene Process Plantwide Control (Refer Slide Time: 00:18)
Plantwide Control of Chemical Processes Prof. Nitin Kaistha Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 41 Cumene Process Plantwide Control (Refer Slide Time: 00:18)
SCALE-UP OF BATCH PROCESSES VIA DECENTRALIZED CONTROL. A. Marchetti, M. Amrhein, B. Chachuat and D. Bonvin
 SCALE-UP OF BATCH PROCESSES VIA DECENTRALIZED CONTROL A. Marchetti, M. Amrhein, B. Chachuat and D. Bonvin Laboratoire d Automatique Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) CH-1015 Lausanne, Switzerland
SCALE-UP OF BATCH PROCESSES VIA DECENTRALIZED CONTROL A. Marchetti, M. Amrhein, B. Chachuat and D. Bonvin Laboratoire d Automatique Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) CH-1015 Lausanne, Switzerland
Chapter 1 Basic Characteristics of Control Systems and their Representation Process and Instrument Diagrams
 Chapter 1 Basic Characteristics of Control Systems and their Representation Process and Instrument Diagrams We need ways to describe process control systems. We will learn several ways in this course.
Chapter 1 Basic Characteristics of Control Systems and their Representation Process and Instrument Diagrams We need ways to describe process control systems. We will learn several ways in this course.
CONTROL MODE SETTINGS. The quality of control obtained from a particular system depends largely on the adj ustments made to the various mode
 Instrumentation & Control - Course 136 CONTROL MODE SETTINGS The quality of control obtained from a particular system depends largely on the adj ustments made to the various mode settings. Many control
Instrumentation & Control - Course 136 CONTROL MODE SETTINGS The quality of control obtained from a particular system depends largely on the adj ustments made to the various mode settings. Many control
CPC Engineering Training Brochure
 Training Brochure Module 1: Field Instrumentation for the Process Industry None Understanding of measurement principles Understanding of development of instrument specification Understanding criteria for
Training Brochure Module 1: Field Instrumentation for the Process Industry None Understanding of measurement principles Understanding of development of instrument specification Understanding criteria for
MULTILOOP CONTROL APPLIED TO INTEGRATOR MIMO. PROCESSES. A Preliminary Study
 MULTILOOP CONTROL APPLIED TO INTEGRATOR MIMO PROCESSES. A Preliminary Study Eduardo J. Adam 1,2*, Carlos J. Valsecchi 2 1 Instituto de Desarrollo Tecnológico para la Industria Química (INTEC) (Universidad
MULTILOOP CONTROL APPLIED TO INTEGRATOR MIMO PROCESSES. A Preliminary Study Eduardo J. Adam 1,2*, Carlos J. Valsecchi 2 1 Instituto de Desarrollo Tecnológico para la Industria Química (INTEC) (Universidad
Systems Engineering/Process Control L1
 Systems Engineering/Process Control L1 What is Systems Engineering/Process Control? Graphical system representations Fundamental control principles Reading: Systems Engineering and Process Control: 1.1
Systems Engineering/Process Control L1 What is Systems Engineering/Process Control? Graphical system representations Fundamental control principles Reading: Systems Engineering and Process Control: 1.1
Chapter 5 The SIMC Method for Smooth PID Controller Tuning
 Chapter 5 The SIMC Method for Smooth PID Controller Tuning Sigurd Skogestad and Chriss Grimholt 5.1 Introduction Although the proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller has only three parameters,
Chapter 5 The SIMC Method for Smooth PID Controller Tuning Sigurd Skogestad and Chriss Grimholt 5.1 Introduction Although the proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller has only three parameters,
Goodwin, Graebe, Salgado, Prentice Hall Chapter 11. Chapter 11. Dealing with Constraints
 Chapter 11 Dealing with Constraints Topics to be covered An ubiquitous problem in control is that all real actuators have limited authority. This implies that they are constrained in amplitude and/or rate
Chapter 11 Dealing with Constraints Topics to be covered An ubiquitous problem in control is that all real actuators have limited authority. This implies that they are constrained in amplitude and/or rate
Time scale separation and the link between open-loop and closed-loop dynamics
 Time scale separation and the link between open-loop and closed-loop dynamics Antonio Araújo a Michael Baldea b Sigurd Skogestad a,1 Prodromos Daoutidis b a Department of Chemical Engineering Norwegian
Time scale separation and the link between open-loop and closed-loop dynamics Antonio Araújo a Michael Baldea b Sigurd Skogestad a,1 Prodromos Daoutidis b a Department of Chemical Engineering Norwegian
CHAPTER 3 TUNING METHODS OF CONTROLLER
 57 CHAPTER 3 TUNING METHODS OF CONTROLLER 3.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter deals with a simple method of designing PI and PID controllers for first order plus time delay with integrator systems (FOPTDI).
57 CHAPTER 3 TUNING METHODS OF CONTROLLER 3.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter deals with a simple method of designing PI and PID controllers for first order plus time delay with integrator systems (FOPTDI).
Control of Electromechanical Systems
 Control of Electromechanical Systems November 3, 27 Exercise Consider the feedback control scheme of the motor speed ω in Fig., where the torque actuation includes a time constant τ A =. s and a disturbance
Control of Electromechanical Systems November 3, 27 Exercise Consider the feedback control scheme of the motor speed ω in Fig., where the torque actuation includes a time constant τ A =. s and a disturbance
TS02 - Pre-Instructional Survey
 TS02 - Pre-Instructional Survey 1. Which type of drawing provides detailed piping and process information, including wire terminations? a. Loop Wiring Diagrams b. Piping and Instrument Diagrams (P&IDs)
TS02 - Pre-Instructional Survey 1. Which type of drawing provides detailed piping and process information, including wire terminations? a. Loop Wiring Diagrams b. Piping and Instrument Diagrams (P&IDs)
Improved PI control for a surge tank satisfying level constraints
 Integral-Derivative Control, Ghent, Belgium, May 9-, 28 FrBT4.6 Improved PI control for a surge tank satisfying level constraints Adriana Reyes-Lúa Christoph Josef Backi Sigurd Skogestad, Department of
Integral-Derivative Control, Ghent, Belgium, May 9-, 28 FrBT4.6 Improved PI control for a surge tank satisfying level constraints Adriana Reyes-Lúa Christoph Josef Backi Sigurd Skogestad, Department of
Multi-Loop Control. Department of Chemical Engineering,
 Interaction ti Analysis and Multi-Loop Control Sachin C. Patawardhan Department of Chemical Engineering, I.I.T. Bombay Outline Motivation Interactions in Multi-loop control Loop pairing using Relative
Interaction ti Analysis and Multi-Loop Control Sachin C. Patawardhan Department of Chemical Engineering, I.I.T. Bombay Outline Motivation Interactions in Multi-loop control Loop pairing using Relative
A unified double-loop multi-scale control strategy for NMP integrating-unstable systems
 Home Search Collections Journals About Contact us My IOPscience A unified double-loop multi-scale control strategy for NMP integrating-unstable systems This content has been downloaded from IOPscience.
Home Search Collections Journals About Contact us My IOPscience A unified double-loop multi-scale control strategy for NMP integrating-unstable systems This content has been downloaded from IOPscience.
Competences. The smart choice of Fluid Control Systems
 Competences The smart choice of Fluid Control Systems Contents 1. Open-loop and closed-loop control Page 4 1.1. Function and sequence of an open-loop control system Page 4 1.2. Function and sequence of
Competences The smart choice of Fluid Control Systems Contents 1. Open-loop and closed-loop control Page 4 1.1. Function and sequence of an open-loop control system Page 4 1.2. Function and sequence of
Chapter 7 Control. Part Classical Control. Mobile Robotics - Prof Alonzo Kelly, CMU RI
 Chapter 7 Control 7.1 Classical Control Part 1 1 7.1 Classical Control Outline 7.1.1 Introduction 7.1.2 Virtual Spring Damper 7.1.3 Feedback Control 7.1.4 Model Referenced and Feedforward Control Summary
Chapter 7 Control 7.1 Classical Control Part 1 1 7.1 Classical Control Outline 7.1.1 Introduction 7.1.2 Virtual Spring Damper 7.1.3 Feedback Control 7.1.4 Model Referenced and Feedforward Control Summary
CHAPTER 2 CONTINUOUS STIRRED TANK REACTOR PROCESS DESCRIPTION
 11 CHAPTER 2 CONTINUOUS STIRRED TANK REACTOR PROCESS DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter deals with the process description and analysis of CSTR. The process inputs, states and outputs are identified
11 CHAPTER 2 CONTINUOUS STIRRED TANK REACTOR PROCESS DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter deals with the process description and analysis of CSTR. The process inputs, states and outputs are identified
Practical Process Control for Engineers and Technicians
 Practical Process Control for Engineers and Technicians Dedication This book is dedicated to Wolfgang who fought a courageous battle against motor neurone disease and continued teaching until the very
Practical Process Control for Engineers and Technicians Dedication This book is dedicated to Wolfgang who fought a courageous battle against motor neurone disease and continued teaching until the very
Design of Decentralised PI Controller using Model Reference Adaptive Control for Quadruple Tank Process
 Design of Decentralised PI Controller using Model Reference Adaptive Control for Quadruple Tank Process D.Angeline Vijula #, Dr.N.Devarajan * # Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Sri Ramakrishna
Design of Decentralised PI Controller using Model Reference Adaptive Control for Quadruple Tank Process D.Angeline Vijula #, Dr.N.Devarajan * # Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Sri Ramakrishna
Acceleration Feedback
 Acceleration Feedback Mechanical Engineer Modeling & Simulation Electro- Mechanics Electrical- Electronics Engineer Sensors Actuators Computer Systems Engineer Embedded Control Controls Engineer Mechatronic
Acceleration Feedback Mechanical Engineer Modeling & Simulation Electro- Mechanics Electrical- Electronics Engineer Sensors Actuators Computer Systems Engineer Embedded Control Controls Engineer Mechatronic
A unified approach for proportional-integral-derivative controller design for time delay processes
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 32(4), 583-596 (2015) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-014-0237-6 INVITED REVIEW PAPER INVITED REVIEW PAPER pissn: 0256-1115 eissn: 1975-7220 A unified approach for proportional-integral-derivative
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 32(4), 583-596 (2015) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-014-0237-6 INVITED REVIEW PAPER INVITED REVIEW PAPER pissn: 0256-1115 eissn: 1975-7220 A unified approach for proportional-integral-derivative
Introduction to System Identification and Adaptive Control
 Introduction to System Identification and Adaptive Control A. Khaki Sedigh Control Systems Group Faculty of Electrical and Computer Engineering K. N. Toosi University of Technology May 2009 Introduction
Introduction to System Identification and Adaptive Control A. Khaki Sedigh Control Systems Group Faculty of Electrical and Computer Engineering K. N. Toosi University of Technology May 2009 Introduction
Multiple Model Based Adaptive Control for Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Process
 Multiple Model Based Adaptive Control for Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Process R. Manikandan Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering, Annamalai University, Annamalai
Multiple Model Based Adaptive Control for Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Process R. Manikandan Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering, Annamalai University, Annamalai
Soft Computing Technique and Conventional Controller for Conical Tank Level Control
 Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Informatics (IJEEI) Vol. 4, No. 1, March 016, pp. 65~73 ISSN: 089-37, DOI: 10.11591/ijeei.v4i1.196 65 Soft Computing Technique and Conventional Controller
Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Informatics (IJEEI) Vol. 4, No. 1, March 016, pp. 65~73 ISSN: 089-37, DOI: 10.11591/ijeei.v4i1.196 65 Soft Computing Technique and Conventional Controller
Should we forget the Smith Predictor?
 FrBT3. Should we forget the Smith Predictor? Chriss Grimholt Sigurd Skogestad* Abstract: The / controller is the most used controller in industry. However, for processes with large time delays, the common
FrBT3. Should we forget the Smith Predictor? Chriss Grimholt Sigurd Skogestad* Abstract: The / controller is the most used controller in industry. However, for processes with large time delays, the common
Control of Neutralization Process in Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)
 Control of Neutralization Process in Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) Dr. Magan P. Ghatule Department of Computer Science, Sinhgad College of Science, Ambegaon (Bk), Pune-41. gmagan@rediffmail.com
Control of Neutralization Process in Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) Dr. Magan P. Ghatule Department of Computer Science, Sinhgad College of Science, Ambegaon (Bk), Pune-41. gmagan@rediffmail.com
Gain Scheduling. Bo Bernhardsson and Karl Johan Åström. Department of Automatic Control LTH, Lund University
 Department of Automatic Control LTH, Lund University What is gain scheduling? How to find schedules? Applications What can go wrong? Some theoretical results LPV design via LMIs Conclusions To read: Leith
Department of Automatic Control LTH, Lund University What is gain scheduling? How to find schedules? Applications What can go wrong? Some theoretical results LPV design via LMIs Conclusions To read: Leith
Innovative Solutions from the Process Control Professionals
 Control Station Innovative Solutions from the Process Control Professionals Software For Process Control Analysis, Tuning & Training Control Station Software For Process Control Analysis, Tuning & Training
Control Station Innovative Solutions from the Process Control Professionals Software For Process Control Analysis, Tuning & Training Control Station Software For Process Control Analysis, Tuning & Training
Wannabe-MPC for Large Systems Based on Multiple Iterative PI Controllers
 Wannabe-MPC for Large Systems Based on Multiple Iterative PI Controllers Pasi Airikka, Mats Friman Metso Corp., Finland 17th Nordic Process Control Workshop Jan 26-27 2012 DTU Denmark Content Motivation
Wannabe-MPC for Large Systems Based on Multiple Iterative PI Controllers Pasi Airikka, Mats Friman Metso Corp., Finland 17th Nordic Process Control Workshop Jan 26-27 2012 DTU Denmark Content Motivation
CANDU Safety #3 - Nuclear Safety Characteristics Dr. V.G. Snell Director Safety & Licensing
 CANDU Safety #3 - Nuclear Safety Characteristics Dr. V.G. Snell Director Safety & Licensing 24/05/01 CANDU Safety - #3 - Nuclear Safety Characteristics.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 1 What Makes A Safe Nuclear Design?
CANDU Safety #3 - Nuclear Safety Characteristics Dr. V.G. Snell Director Safety & Licensing 24/05/01 CANDU Safety - #3 - Nuclear Safety Characteristics.ppt Rev. 0 vgs 1 What Makes A Safe Nuclear Design?
