CHEM-E3215 Advanced Biochemistry
|
|
|
- Flora Grant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHEM-E3215 Advanced Biochemistry 30. Jan Prof. Silvan Scheller Lecture 10 Energy conservation general (some calculations) Energy conservation in anaerobes: e.g. methanogensis Life close to the thermodynamic limit Electron bifurcation Electromicrobiology Details for project work 1
2 ΔG: The Gibbs Energy (free energy) A + B Substrates C + D Products Free Energy A + B -ΔG Free Energy +ΔG C + D C + D A + B Progress of reaction ΔG <0 (negative) Exergonic reaction Can proceed (if TS not too high..) Progress of reaction ΔG > 0 (positive) Endergonic reaction Would proceed into other direction
3 Energy conservation (in metabolisms): Utilize exergonic catabolic reaction to store (conserve) the energy Reaction can be coupled to the generation of ATP (substrate level phosphorylation, SLP) Reaction can be coupled to the production of an ion gradient (ion pump) Similar concept: Electron bifurcation (later this lecture) à May be considered as 3 rd way of energy conservation
4 Biochemical Thermodynamics ΔG = ΔH TΔS change in free energy = change in enthalpy - Temperature x change in entropy A + B Substrates C + D Products G = G + RT ln [C][D] [A][B] At equilibrium ΔG=0 G = -RT ln [C][D] [A][B] R= gas constant T= absolute temperature [A] [B] = molar concentrations G = standard free energy of change G= free-energy of change The standard free energy change ( G ) When all reactants and products at standard concentrations (1M) are allowed to reach equilibrium under standard conditions (25 C and 1atm). Depends on the nature of the reactants and the products G ʹ=Free-energy change under biochemical standard condition at ph=7, unit activities, 25 C = 298 K
5 ATP (adenosine triphosphate) ATP is the principal short-term energy-storage compound of the cells Standard free energy change of ATP hydrolysis: ATP + H 2 O ADP + Pi G = kj/mol Coupling the hydrolysis of ATP to reactions with a positive free energy change makes the latter favourable à Calculation: How much is one mol of ATP worth in a cell? (a base) Adenosine AMP ADP ATP Adenine Ribose
6 ATP yield from glucose oxidation Reaction sequence ATP yield per glucose molecule Glycolysis: Conversion of glucose into pyruvate (in the cytoplasm) Phosphorylation of glucose 21 Phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate 21 Dephosphorylation of 2 molecules of 1,3-BPG 12 Dephosphorylation of 2 molecules of phosphoenolpyruvate 12 2 molecules of NADH are formed in the oxidation of 2 molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Conversion of pyruvate into acetyl CoA (inside mitochondria) 2 molecules of NADH are formed Citric acid cycle (inside mitochondria) 2 molecules of adenosine triphosphate are formed from 2 molecules of succinyl CoA 12 6 molecules of NADH are formed in the oxidation of 2 molecules each of isocitrate, a-ketoglutarate, and malate 2 molecules of FADH 2 are formed in the oxidation of 2 molecules of succinate Oxidative phosphorylation (inside mitochondria) 2 molecules of NADH formed in glycolysis; each yields 1.5 molecules of ATP (assuming transport of NADH by the glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle) 13 2 molecules of NADH formed in the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate; each yields 2.5 molecules of ATP 15 2 molecules of FADH 2 formed in the citric acid cycle; each yields 1.5 molecules of ATP 13 6 molecules of NADH formed in the citric acid cycle; each yields 2.5 molecules of ATP 115 ATP Glucose Pyruvate Acetyl CoA Citric acid cycle 8 e Glycolysis CO 2 2 e 2 CO 2 Figure 17.4 The link between glycolysis Oxidative phosphorylation Net Yield per Molecule of Glucose 130 Source: The ATP yield of oxidative phosphorylation is based on values given in P. C. Hinkle, M. A. Kumar, From Stryer 7 th edition ~ 30 ATP
7 Standard reduction potentials of biol. relevant reactions Table 18.1 Standard reduction potentials of some reactions Oxidant Reductant n E9 0 (V) Succinate 1 CO 2 a-ketoglutarate Acetate Acetaldehyde Ferredoxin (oxidized) Ferredoxin (reduced) H 1 H NAD 1 NADH 1 H NADP 1 NADPH 1 H Lipoate (oxidized) Lipoate (reduced) Glutathione (oxidized) Glutathione (reduced) FAD FADH Acetaldehyde Ethanol Pyruvate Lactate Fumarate Succinate Cytochrome b (13) Cytochrome b (12) Dehydroascorbate Ascorbate Ubiquinone (oxidized) Ubiquinone (reduced) Cytochrome c (13) Cytochrome c (12) Fe (13) Fe (12) / 2 O H 1 H 2 O à Calculation: How much energy from NADH (FADH 2 ) + O 2? Note: E9 0 is the standard oxidation reduction potential (ph 7, 258C) and n is the number of electrons transferred. E9 0 refers to the partial reaction written as Oxidant 1 e 2 S reductant From Stryer 7 th edition
8 C metabolism Aerobic (e.g. glycolysis) Anaerobic (e.g. methanogenesis) Thauer et al. Nature reviews in microbiology 2008, 579
9 Energy conservation in anaerobes Differences aerobic in anaerobic respiration: No oxygen available Often reaction close to the thermodynamic equilibrium Challenges for anaerobic microbes: How to generate less than one ATP per substrate? How to ensure a flat energy profile? à How to couple endergonic with exergonic steps Awesome review: Thauer et al. Bacteriological Reviews 1977,
10 Extra slide: Acetoclastic methanogens and ATP mm acetate needed for growth (à Conserves more energy, outcompetes Methanosaeta at high substrate concentrations) 7 70 μm acetate needed for growth (à Conserves less energy, grows slower, but outcompetes Methanosarcina at low substrate concentrations) à Niche differentiation! Welte et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014, 1130; Jetten et al. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 181
11 How hydrogenotrophic methanogens generate ATP H 2 CO H 2 à CH H 2 O H 2 Methyl-transferase pumps 2 Na + outside H 2 ATPase uses Na + (assumed 4Na + /ATP) à 0.5 ATP per CH 4 produced. H 2
12 Look at pathway and its energy profile ΔG (kj mol -1 ) CO 2 Formyl!MFR Formyl!H 4 MPT MFR H 4 MPT MFR H 2 CO H 2 à CH H 2 O -5 Methenyl!H 4 MPT ΔG = -131 kj mol -1 (1 bar H 2 ) ΔG = -40 kj mol -1 (0.1 mbar H 2 )! These numbers assume that H 2 is directly used for all reduction steps, which is not the case. (Calculated from: Thauer et al. Nat. rev. in microbiol. 2008, 579, Box1) Methylen!H 4 MPT CH 3!H 4 MPT CH 3!S!CoM CH 4 H!S!CoM H 4 MPT H!S!CoB CoM!S!S!CoB -55 H 2 H 2 H
13 Look at pathway and its energy profile ΔG (kj mol -1 ) CO 2 Formyl!MFR Formyl!H 4 MPT MFR H 4 MPT MFR H 2 Concentrations of intermediates?? -5 Methenyl!H 4 MPT à Pathway needs to have reasonable concentrations for all intermediates to be efficient. Diffusion Occupy active site of next enzymes Allowing for flux of metabolites Methylen!H 4 MPT CH 3!H 4 MPT CH 3!S!CoM CH 4 H!S!CoM H 4 MPT H!S!CoB CoM!S!S!CoB -55 H 2 H 2 H
14 Solution: For methanogens with cytochromes growing on H 2 Energy conservation in Methanosarcina barkeri growing on CO 2 and H 2. (Rare case, usually cytochrome-containing methanogens do CH 3 -X fermentation, no) The first and last steps are chemiosmotically coupled. Thauer et al. Nature reviews in microbiology 2008, 579
15 Hydrogenotrophic methanogens without cytochromes: First and last step also coupled (RPG effect) Gunsalus + Wolfe Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1977, 790
16 RPG effect: How should this work?? Chemiosmotic coupling not possible, because no cytochromes (and anyway cell- extract used). Somehow the first and the last step needs to be coupled. Gunsalus + Wolfe Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1977, 790
17 Methanogens without cytochromes How is the first and last steps are coupled? Proposal by R. K. Thauer: Reduction of CoM-S-S-CoB and of Fd together by 2 H 2 Catalysed by the hydrogenase (MvhADG) heterodisulphide reductase (HdrABC) complex à Flavin-based electron bifurcation! Proposed: Thauer et al. Nature reviews in microbiology 2008, 579 Biochemisty: Kaster et al. PNAS 2011, 2981
18 Flavin-based electron bifurcation X-ray: Wagner et al., Science 2017, 699
19 Flavin-based electron bifurcation Proposed electron-transfer pathway. Wagner et al., Science 2017, 699
20 Methanogens without cytochromes Energy conservation in methanogens without cytochromes growing on CO 2 and H 2. The first and last steps are coupled by flavin-based electron bifurcation (yellow). W. Buckel + R.K. Thauer Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 2013, 94
21 Other example of flavin-based electron bifurcation (yellow) Flavin-based electron bifurcation (yellow): The electron donor (H 2 ) is split into a stronger (Fd 2- ) and a weaker donor (NADH) electron donor. Rnf complex: The strong electron donor (Fd 2- ) is converted into the weaker donor NADH and energy is conserved by pumping one ion outside the cell. Although the elucidation of the mechanisms of energy conservation in acetogens is still in its infancy,. Genome analyses will certainly pave the way toward a better understanding of the energetics, biochemistry, and physiology of acetogens. (Müller Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 6345) Buckel + Thauer
22 Summary of energy conservation See lecture notes. Further reading: Origin of life: The Origin of Membrane Bioenergetics : Lane et al. Cell 2012, 1406 Origin of life: Early bioenergetic evolution : Sousa et al. Phil Trans R Soc B 2013, 368 Life at G close to 0: The Minimum Biological Energy Quantum : Müller + Hess Frontiers in Microbiology 2017, V8-A2019
23 Project presentation Friday Feb. 2 nd at 9.15 in D422 Presentation: keep it short, max 20 min (send slides afterwards) 1 Page summary for your colleagues Additional slides/data, texts, pictures, tables, further information etc. (send electronically)
24 Additional slides (not part of exam): Electromicrobiology Pfeffer et al. Nature 2012, 218 General review see: Shi et al. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 651
25 Cable bacteria Pfeffer et al. Nature 2012, 218
26 Mechanism of electrical conductance Pirbadian + El Naggar Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 13802
27 Disputed mechanism of conductance: via aromatic aa Lovely Current Opinion in Electrochemistry 2017, 190
28 Possible applications of electromicrobiology Choi and Sang Biotechnol Biofuels 2016, 9:11
29 Possible applications of electromicrobiology Cheng et al. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 3953
30 Possible applications of electromicrobiology Methane to electricity Or reverse! Figure by McGlynn et al. Nature 2015, 534 See also: Wegener et al. Nature 2015, 587 Scheller et al. Science 2016, 703
31 Possible applications of electromicrobiology Butane to electricity Or reverse! Laso-Pérez et al. Nature 2016, 396
Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy
 Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Bioenergetics and high-energy compounds
 Bioenergetics and high-energy compounds Tomáš Kučera tomas.kucera@lfmotol.cuni.cz Department of Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Motol
Bioenergetics and high-energy compounds Tomáš Kučera tomas.kucera@lfmotol.cuni.cz Department of Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Motol
Photosynthetic autotrophs use the energy of sunlight to convert low-g CO 2 and H 2 O into energy-rich complex sugar molecules.
 Chapters 7 & 10 Bioenergetics To live, organisms must obtain energy from their environment and use it to do the work of building and organizing cell components such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids,
Chapters 7 & 10 Bioenergetics To live, organisms must obtain energy from their environment and use it to do the work of building and organizing cell components such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids,
Biochemical Pathways
 Biochemical Pathways Living organisms can be divided into two large groups according to the chemical form in which they obtain carbon from the environment. Autotrophs can use carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
Biochemical Pathways Living organisms can be divided into two large groups according to the chemical form in which they obtain carbon from the environment. Autotrophs can use carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
BIOCHEMISTRY. František Vácha. JKU, Linz.
 BIOCHEMISTRY František Vácha http://www.prf.jcu.cz/~vacha/ JKU, Linz Recommended reading: D.L. Nelson, M.M. Cox Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry D.J. Voet, J.G. Voet, C.W. Pratt Principles of Biochemistry
BIOCHEMISTRY František Vácha http://www.prf.jcu.cz/~vacha/ JKU, Linz Recommended reading: D.L. Nelson, M.M. Cox Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry D.J. Voet, J.G. Voet, C.W. Pratt Principles of Biochemistry
Lecture 10. Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis. Oxidative. Photo-Phosphorylation
 Lecture 10 Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis Oxidative Phosphorylation Photo-Phosphorylation Model of the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Glycerol-3-P Shuttle Outer Mitochondrial Membrane G3P DHAP
Lecture 10 Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis Oxidative Phosphorylation Photo-Phosphorylation Model of the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Glycerol-3-P Shuttle Outer Mitochondrial Membrane G3P DHAP
Principles of Bioenergetics. Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 14
 1 Principles of Bioenergetics Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 14 2 Metabolism A highly coordinated cellular activity aimed at achieving the following goals: Obtain chemical energy. Convert nutrient molecules
1 Principles of Bioenergetics Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 14 2 Metabolism A highly coordinated cellular activity aimed at achieving the following goals: Obtain chemical energy. Convert nutrient molecules
The products have more enthalpy and are more ordered than the reactants.
 hapters 7 & 10 Bioenergetics To live, organisms must obtain energy from their environment and use it to do the work of building and organizing cell components such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids,
hapters 7 & 10 Bioenergetics To live, organisms must obtain energy from their environment and use it to do the work of building and organizing cell components such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids,
2015 AP Biology PRETEST Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Week of October
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ 2015 AP Biology PRETEST Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Week of 19-23 October Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which
Name: Class: _ Date: _ 2015 AP Biology PRETEST Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Week of 19-23 October Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which
Change to Office Hours this Friday and next Monday. Tomorrow (Abel): 8:30 10:30 am. Monday (Katrina): Cancelled (05/04)
 Change to Office Hours this Friday and next Monday Tomorrow (Abel): 8:30 10:30 am Monday (Katrina): Cancelled (05/04) Lecture 10 Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis Oxidative Phosphorylation Photo-Phosphorylation
Change to Office Hours this Friday and next Monday Tomorrow (Abel): 8:30 10:30 am Monday (Katrina): Cancelled (05/04) Lecture 10 Proton Gradient-dependent ATP Synthesis Oxidative Phosphorylation Photo-Phosphorylation
Cell Energy: The Big Picture. So, What Exactly is ATP. Adenosine Triphosphate. Your turn to Practice converting ATP to ADP:
 Understanding How Living Things Obtain and Use Energy. Cell Energy: The Big Picture Most Autotrophs produce food (sugar) using light energy during Photosynthesis. Then, both Autotrophs and Heterotroph
Understanding How Living Things Obtain and Use Energy. Cell Energy: The Big Picture Most Autotrophs produce food (sugar) using light energy during Photosynthesis. Then, both Autotrophs and Heterotroph
BBS2710 Microbial Physiology. Module 5 - Energy and Metabolism
 BBS2710 Microbial Physiology Module 5 - Energy and Metabolism Topics Energy production - an overview Fermentation Aerobic respiration Alternative approaches to respiration Photosynthesis Summary Introduction
BBS2710 Microbial Physiology Module 5 - Energy and Metabolism Topics Energy production - an overview Fermentation Aerobic respiration Alternative approaches to respiration Photosynthesis Summary Introduction
Giving you the energy you need!
 Giving you the energy you need! Use your dominant hand Open and close the pin (with your thumb and forefinger) as many times as you can for 20 seconds while holding the other fingers straight out! Repeat
Giving you the energy you need! Use your dominant hand Open and close the pin (with your thumb and forefinger) as many times as you can for 20 seconds while holding the other fingers straight out! Repeat
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge. Biochemistry II. Bioenergetics
 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge II. Bioenergetics Slide 1 Bioenergetics Bioenergetics is the quantitative study of energy relationships and energy conversion in biological
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge II. Bioenergetics Slide 1 Bioenergetics Bioenergetics is the quantitative study of energy relationships and energy conversion in biological
Metabolism. Fermentation vs. Respiration. End products of fermentations are waste products and not fully.
 Outline: Metabolism Part I: Fermentations Part II: Respiration Part III: Metabolic Diversity Learning objectives are: Learn about respiratory metabolism, ATP generation by respiration linked (oxidative)
Outline: Metabolism Part I: Fermentations Part II: Respiration Part III: Metabolic Diversity Learning objectives are: Learn about respiratory metabolism, ATP generation by respiration linked (oxidative)
Chapter 15 part 2. Biochemistry I Introduction to Metabolism Bioenergetics: Thermodynamics in Biochemistry. ATP 4- + H 2 O ADP 3- + P i + H +
 Biochemistry I Introduction to Metabolism Bioenergetics: Thermodynamics in Biochemistry ATP 4- + 2 ADP 3- + P i 2- + + Chapter 15 part 2 Dr. Ray 1 Energy flow in biological systems: Energy Transformations
Biochemistry I Introduction to Metabolism Bioenergetics: Thermodynamics in Biochemistry ATP 4- + 2 ADP 3- + P i 2- + + Chapter 15 part 2 Dr. Ray 1 Energy flow in biological systems: Energy Transformations
This is an example of cellular respiration, which can be used to make beer and wine using different metabolic pathways For these reasons we call this
 Chapter 6 Carvings from ancient Egypt show barley being crushed and mixed with water (left) and then put into closed vessels (centre) where airless conditions are suitable for the production of alcohol
Chapter 6 Carvings from ancient Egypt show barley being crushed and mixed with water (left) and then put into closed vessels (centre) where airless conditions are suitable for the production of alcohol
Name Date Class. Photosynthesis and Respiration
 Concept Mapping Photosynthesis and Respiration Complete the Venn diagram about photosynthesis and respiration. These terms may be used more than once: absorbs, Calvin cycle, chlorophyll, CO 2, H 2 O, Krebs
Concept Mapping Photosynthesis and Respiration Complete the Venn diagram about photosynthesis and respiration. These terms may be used more than once: absorbs, Calvin cycle, chlorophyll, CO 2, H 2 O, Krebs
Life 21 - Aerobic respiration Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts)
 1 Life 21 - Aerobic respiration Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts) Objectives 1: Describe the overall action of the Krebs cycle in generating ATP, NADH and FADH 2 from acetyl-coa 2: Understand the generation
1 Life 21 - Aerobic respiration Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts) Objectives 1: Describe the overall action of the Krebs cycle in generating ATP, NADH and FADH 2 from acetyl-coa 2: Understand the generation
Review Questions - Lecture 5: Metabolism, Part 1
 Review Questions - Lecture 5: Metabolism, Part 1 Questions: 1. What is metabolism? 2. What does it mean to say that a cell has emergent properties? 3. Define metabolic pathway. 4. What is the difference
Review Questions - Lecture 5: Metabolism, Part 1 Questions: 1. What is metabolism? 2. What does it mean to say that a cell has emergent properties? 3. Define metabolic pathway. 4. What is the difference
Kuntarti. PDF Created with deskpdf PDF Writer - Trial ::
 Kuntarti Principles of Bioenergetics Definitions the study of energy transformations in living organism (Albert L Lehninger) the study of the balance between energy intake in the form of food and energy
Kuntarti Principles of Bioenergetics Definitions the study of energy transformations in living organism (Albert L Lehninger) the study of the balance between energy intake in the form of food and energy
Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways
 Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways 1. Reaction a. Thermodynamics b. Kinetics 2. Enzyme a. Structure and Function b. Regulation of Activity c. Kinetics d. Inhibition 3. Metabolic Pathways a. REDOX
Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways 1. Reaction a. Thermodynamics b. Kinetics 2. Enzyme a. Structure and Function b. Regulation of Activity c. Kinetics d. Inhibition 3. Metabolic Pathways a. REDOX
Energy Transformation. Metabolism = total chemical reactions in cells.
 Energy Transformation Metabolism = total chemical reactions in cells. metabole = change Metabolism is concerned with managing the material and energy resources of the cell -Catabolism -Anabolism -Catabolism
Energy Transformation Metabolism = total chemical reactions in cells. metabole = change Metabolism is concerned with managing the material and energy resources of the cell -Catabolism -Anabolism -Catabolism
20. Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
 20. Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20.1 What Role Does Electron Transport Play in Metabolism? Electron transport - Role of oxygen in metabolism as final acceptor of electrons - In inner
20. Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20.1 What Role Does Electron Transport Play in Metabolism? Electron transport - Role of oxygen in metabolism as final acceptor of electrons - In inner
Be sure to understand:
 Learning Targets & Focus Questions for Unit 6: Bioenergetics Chapter 8: Thermodynamics Chapter 9: Cell Resp Focus Q Ch. 10: Photosynthesis Chapter 8 (141-150) 1. I can explain how living systems adhere
Learning Targets & Focus Questions for Unit 6: Bioenergetics Chapter 8: Thermodynamics Chapter 9: Cell Resp Focus Q Ch. 10: Photosynthesis Chapter 8 (141-150) 1. I can explain how living systems adhere
Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy
 6 Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy Energy is stored in chemical bonds and can be released and transformed by metabolic pathways. Chemical energy available to do work is termed free energy
6 Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy Energy is stored in chemical bonds and can be released and transformed by metabolic pathways. Chemical energy available to do work is termed free energy
Chapter 13 Principles of Bioenergetics
 Chapter 13 Principles of Bioenergetics 1. Cells need energy to do all their work To generate and maintain its highly ordered structure (biosynthesis of macromolecules) To generate all kinds of movement
Chapter 13 Principles of Bioenergetics 1. Cells need energy to do all their work To generate and maintain its highly ordered structure (biosynthesis of macromolecules) To generate all kinds of movement
CP Biology Unit 5 Cell Energy Study Guide. Electron Carriers Electron Transport Chain Fermentation Glycolysis Krebs cycle Light-Dependent Reactions
 Name: KEY CP Biology Unit 5 Cell Energy Study Guide Vocabulary to know: ATP ADP Aerobic Anaerobic ATP Synthases Cellular Respiration Chlorophyll Chloroplast Electron Carriers Electron Transport Chain Fermentation
Name: KEY CP Biology Unit 5 Cell Energy Study Guide Vocabulary to know: ATP ADP Aerobic Anaerobic ATP Synthases Cellular Respiration Chlorophyll Chloroplast Electron Carriers Electron Transport Chain Fermentation
RESPIRATION AND FERMENTATION: AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC OXIDATION OF ORGANIC MOLECULES. Bio 107 Week 6
 RESPIRATION AND FERMENTATION: AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC OXIDATION OF ORGANIC MOLECULES Bio 107 Week 6 Procedure 7.2 Label test tubes well, including group name 1) Add solutions listed to small test tubes 2)
RESPIRATION AND FERMENTATION: AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC OXIDATION OF ORGANIC MOLECULES Bio 107 Week 6 Procedure 7.2 Label test tubes well, including group name 1) Add solutions listed to small test tubes 2)
Cellular Energetics. Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 Cellular Energetics Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration and Fermentation TEKS B.4 Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that
Cellular Energetics Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration and Fermentation TEKS B.4 Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that
Energy and Cells. Appendix 1. The two primary energy transformations in plants are photosynthesis and respiration.
 Energy and Cells Appendix 1 Energy transformations play a key role in all physical and chemical processes that occur in plants. Energy by itself is insufficient to drive plant growth and development. Enzymes
Energy and Cells Appendix 1 Energy transformations play a key role in all physical and chemical processes that occur in plants. Energy by itself is insufficient to drive plant growth and development. Enzymes
Basic Concepts of Metabolism. Stages of Catabolism. Key intermediates 10/12/2015. Chapter 15, Stryer Short Course
 Basic Concepts of Metabolism Chapter 15, Stryer Short Course Digestion Formation of key intermediate small molecules Formation of ATP Stages of Catabolism Key intermediates 1 Fundamental Needs for Energy
Basic Concepts of Metabolism Chapter 15, Stryer Short Course Digestion Formation of key intermediate small molecules Formation of ATP Stages of Catabolism Key intermediates 1 Fundamental Needs for Energy
Activity: Identifying forms of energy
 Activity: Identifying forms of energy INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM Metabolism Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in an organism Metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and ends with
Activity: Identifying forms of energy INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM Metabolism Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in an organism Metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and ends with
Outline. Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes. Forms of Energy. Chapter 6
 Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes Chapter 6 Forms of Energy Outline Laws of Thermodynamics Metabolic Reactions ATP Metabolic Pathways Energy of Activation Enzymes Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration 1 2 Forms
Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes Chapter 6 Forms of Energy Outline Laws of Thermodynamics Metabolic Reactions ATP Metabolic Pathways Energy of Activation Enzymes Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration 1 2 Forms
Lecture 7: Enzymes and Energetics
 Lecture 7: Enzymes and Energetics I. Biological Background A. Biological work requires energy 1. Energy is the capacity to do work a. Energy is expressed in units of work (kilojoules) or heat energy (kilocalories)
Lecture 7: Enzymes and Energetics I. Biological Background A. Biological work requires energy 1. Energy is the capacity to do work a. Energy is expressed in units of work (kilojoules) or heat energy (kilocalories)
3.1 Metabolism and Energy
 3.1 Metabolism and Energy Metabolism All of the chemical reactions in a cell To transform matter and energy Step-by-step sequences metabolic pathways Metabolic Pathways Anabolic reactions Build large molecules
3.1 Metabolism and Energy Metabolism All of the chemical reactions in a cell To transform matter and energy Step-by-step sequences metabolic pathways Metabolic Pathways Anabolic reactions Build large molecules
Cellular Energy: Respiration. Goals: Anaerobic respiration
 Cellular Energy: Respiration Anaerobic respiration Goals: Define and describe the 3 sets of chemical reactions that comprise aerobic cellular respiration Describe the types of anaerobic respiration Compare
Cellular Energy: Respiration Anaerobic respiration Goals: Define and describe the 3 sets of chemical reactions that comprise aerobic cellular respiration Describe the types of anaerobic respiration Compare
Bioenergetics, or biochemical thermodynamics, is the study of the energy changes accompanying biochemical reactions. Biologic systems are essentially
 Bioenergetics Bioenergetics, or biochemical thermodynamics, is the study of the energy changes accompanying biochemical reactions. Biologic systems are essentially isothermic and use chemical energy to
Bioenergetics Bioenergetics, or biochemical thermodynamics, is the study of the energy changes accompanying biochemical reactions. Biologic systems are essentially isothermic and use chemical energy to
Energy Exchanges Exam: What to Study
 Energy Exchanges Exam: What to Study Here s what you will need to make sure you understand in order to prepare for our exam: Free Energy Conceptual understanding of free energy as available energy in a
Energy Exchanges Exam: What to Study Here s what you will need to make sure you understand in order to prepare for our exam: Free Energy Conceptual understanding of free energy as available energy in a
Microbiology II Microbial physiology I Energetics
 Microbiology II Microbial physiology I Energetics Catabolism Heat Efficiency ~ 60% Efficiency ~ 40% Anabolism Chemical energy (chemotrophic) Light energy (phototrophic) ATP +/ 50 kj/mol ADP + P i Biosyntheses
Microbiology II Microbial physiology I Energetics Catabolism Heat Efficiency ~ 60% Efficiency ~ 40% Anabolism Chemical energy (chemotrophic) Light energy (phototrophic) ATP +/ 50 kj/mol ADP + P i Biosyntheses
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy. 9.1 Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy 9.1 Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels 9.2 Glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate 9.3 The citric acid
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy 9.1 Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels 9.2 Glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate 9.3 The citric acid
Cell Energy Notes ATP THE ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY. CELL ENERGY Cells usable source of is called ATP stands for. Name Per
 Cell Energy Notes Name Per THE ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY The Endosymbiotic theory is the idea that a long time ago, engulfed other prokaryotic cells by. This resulted in the first First proposed by Explains
Cell Energy Notes Name Per THE ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY The Endosymbiotic theory is the idea that a long time ago, engulfed other prokaryotic cells by. This resulted in the first First proposed by Explains
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 AP Exam Chapters 9 and 10; Photosynthesis and Respiration Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Carbon dioxide (CO2) is released
AP Exam Chapters 9 and 10; Photosynthesis and Respiration Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Carbon dioxide (CO2) is released
Energy Metabolism exergonic reaction endergonic reaction Energy of activation
 Metabolism Energy Living things require energy to grow and reproduce Most energy used originates from the sun Plants capture 2% of solar energy Some captured energy is lost as metabolic heat All energy
Metabolism Energy Living things require energy to grow and reproduce Most energy used originates from the sun Plants capture 2% of solar energy Some captured energy is lost as metabolic heat All energy
Overview of Metabolism and Bioenergetics!
 verview of Metabolism and Bioenergetics! Wichit Suthammarak Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital -- July 30 th, 2014! Metabolism Chemical transformation! Cell or organism! A
verview of Metabolism and Bioenergetics! Wichit Suthammarak Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital -- July 30 th, 2014! Metabolism Chemical transformation! Cell or organism! A
Welcome to Class 8! Introductory Biochemistry! Announcements / Reminders! Midterm TA led Review Sessions!
 Announcements / Reminders Midterm TA led Review Sessions Welcome to Class 8 Sunday, February 23 from 8-10pm Location: Science Center Main Room (315) Office Hours Prof Salomon: SFH 270 on Thursday Feb 20,
Announcements / Reminders Midterm TA led Review Sessions Welcome to Class 8 Sunday, February 23 from 8-10pm Location: Science Center Main Room (315) Office Hours Prof Salomon: SFH 270 on Thursday Feb 20,
Dr. Mallery Biology 150 Workshop Fall Semester ENERGY and METABOLISM ANSWERS
 Dr. Mallery Biology 150 Workshop Fall Semester ENERGY and METABOLISM ANSWERS IN THE GRAND SCHEME The purpose of this workshop is to get the Learning Communities to begin thinking about why certain chemical
Dr. Mallery Biology 150 Workshop Fall Semester ENERGY and METABOLISM ANSWERS IN THE GRAND SCHEME The purpose of this workshop is to get the Learning Communities to begin thinking about why certain chemical
Cellular Energy. How Organisms Obtain Energy Section 2: Photosynthesis Section 3: Cellular Respiration. Click on a lesson name to select.
 Section 1: How Organisms Obtain Energy Section 2: Photosynthesis Section 3: Cellular Respiration Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 How Organisms Obtain Energy Transformation of Energy Energy
Section 1: How Organisms Obtain Energy Section 2: Photosynthesis Section 3: Cellular Respiration Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 How Organisms Obtain Energy Transformation of Energy Energy
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Unit
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Unit All cellular activities require energy. Directly or indirectly nearly all energy for life comes from the sun. Autotrophs: organisms that can make their own
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Unit All cellular activities require energy. Directly or indirectly nearly all energy for life comes from the sun. Autotrophs: organisms that can make their own
C. Incorrect! Catalysts themselves are not altered or consumed during the reaction.
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 04: Enzymes and Energy Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed, (3) Pick the answer,
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 04: Enzymes and Energy Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed, (3) Pick the answer,
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Outer Glycolysis mitochondrial membrane Glucose ATP
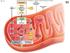 Fig. 7.5 uter Glycolysis mitochondrial membrane Glucose Intermembrane space xidation Mitochondrial matrix Acetyl-oA Krebs FAD e NAD + FAD Inner mitochondrial membrane e Electron e Transport hain hemiosmosis
Fig. 7.5 uter Glycolysis mitochondrial membrane Glucose Intermembrane space xidation Mitochondrial matrix Acetyl-oA Krebs FAD e NAD + FAD Inner mitochondrial membrane e Electron e Transport hain hemiosmosis
METABOLISM CHAPTER 04 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Dr. Lawrence G. Altman Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I CHAPTER 04 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. CELLULAR METABOLISM Dr. Lawrence G. Altman
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I CHAPTER 04 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. CELLULAR METABOLISM Dr. Lawrence G. Altman
CELL METABOLISM OVERVIEW Keep the big picture in mind as we discuss the particulars!
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I CHAPTER 04 CELLULAR METABOLISM 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. Dr. Lawrence G. Altman
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I CHAPTER 04 CELLULAR METABOLISM 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. Dr. Lawrence G. Altman
Respiration and Photosynthesis. The Ying and Yang of Life.
 Respiration and Photosynthesis The Ying and Yang of Life. Why? You ve always been told that you must eat and breathe. Why? In this unit we will attempt to answer those questions. 1 st Law of Thermodynamics
Respiration and Photosynthesis The Ying and Yang of Life. Why? You ve always been told that you must eat and breathe. Why? In this unit we will attempt to answer those questions. 1 st Law of Thermodynamics
PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Chapter 8
 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Chapter 8 ENERGY & LIFE ENERGY The ability to do work. Can be stored in chemical bonds. Cells need energy to do things like active transport, dividing, moving, and producing and storing
PHOTOSYNTHESIS Chapter 8 ENERGY & LIFE ENERGY The ability to do work. Can be stored in chemical bonds. Cells need energy to do things like active transport, dividing, moving, and producing and storing
All organisms require a constant expenditure of energy to maintain the living state - "LIFE".
 CELLULAR RESPIRATION All organisms require a constant expenditure of energy to maintain the living state - "LIFE". Where does the energy come from and how is it made available for life? With rare exception,
CELLULAR RESPIRATION All organisms require a constant expenditure of energy to maintain the living state - "LIFE". Where does the energy come from and how is it made available for life? With rare exception,
Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Guided Reading Questions (50 pts total)
 AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 10th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Name: Chapter 8 An Introduction to Metabolism Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Guided
AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 10th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Name: Chapter 8 An Introduction to Metabolism Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Guided
Photosynthesis and cellular respirations
 The Introduction of Biology Defining of life Basic chemistry, the chemistry of organic molecules Classification of living things History of cells and Cells structures and functions Photosynthesis and cellular
The Introduction of Biology Defining of life Basic chemistry, the chemistry of organic molecules Classification of living things History of cells and Cells structures and functions Photosynthesis and cellular
Center for Academic Services & Advising
 March 2, 2017 Biology I CSI Worksheet 6 1. List the four components of cellular respiration, where it occurs in the cell, and list major products consumed and produced in each step. i. Hint: Think about
March 2, 2017 Biology I CSI Worksheet 6 1. List the four components of cellular respiration, where it occurs in the cell, and list major products consumed and produced in each step. i. Hint: Think about
AP Bio-Ms.Bell Unit#3 Cellular Energies Name
 AP Bio-Ms.Bell Unit#3 Cellular Energies Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the image below. 7. Base your answer to the following question on Which of the following choices correctly
AP Bio-Ms.Bell Unit#3 Cellular Energies Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the image below. 7. Base your answer to the following question on Which of the following choices correctly
A + B = C C + D = E E + F = A
 Photosynthesis - Plants obtain energy directly from the sun - Organisms that do this are autotrophs (make their own food from inorganic forms) - Photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions where the
Photosynthesis - Plants obtain energy directly from the sun - Organisms that do this are autotrophs (make their own food from inorganic forms) - Photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions where the
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration All cellular activities require energy. Directly or indirectly nearly all energy for life comes from the sun. Autotrophs:
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration All cellular activities require energy. Directly or indirectly nearly all energy for life comes from the sun. Autotrophs:
Lecture 2: Biological Thermodynamics [PDF] Key Concepts
![Lecture 2: Biological Thermodynamics [PDF] Key Concepts Lecture 2: Biological Thermodynamics [PDF] Key Concepts](/thumbs/76/73872045.jpg) Lecture 2: Biological Thermodynamics [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer: pp. 11-14; pp. 208-210 problems in textbook: chapter 1, pp. 23-24, #4; and thermodynamics practice problems [PDF] Updated on:
Lecture 2: Biological Thermodynamics [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer: pp. 11-14; pp. 208-210 problems in textbook: chapter 1, pp. 23-24, #4; and thermodynamics practice problems [PDF] Updated on:
2.A.2- Capture and Storage of Free Energy
 2.A.2- Capture and Storage of Free Energy Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce, and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. EU 2.A- Growth, reproduction
2.A.2- Capture and Storage of Free Energy Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce, and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. EU 2.A- Growth, reproduction
Lecture 21 - Introduction to Metabolism: Bioenergetics
 Lecture 21 - Introduction to Metabolism: Bioenergetics Key Concepts Energy conversion in biological systems Metabolic redox reactions Review of thermodynamic principles and coupled reactions The adenylate
Lecture 21 - Introduction to Metabolism: Bioenergetics Key Concepts Energy conversion in biological systems Metabolic redox reactions Review of thermodynamic principles and coupled reactions The adenylate
MitoSeminar II: Some calculations in bioenergetics
 MitoSeminar II: Some calculations in bioenergetics MUDr. Jan Pláteník, PhD. Ústav lékařské biochemie 1.LF UK Helpful comments of Prof. MUDr. Jiří Kraml, DrSc., are acknowledged. 1 Respiratory chain and
MitoSeminar II: Some calculations in bioenergetics MUDr. Jan Pláteník, PhD. Ústav lékařské biochemie 1.LF UK Helpful comments of Prof. MUDr. Jiří Kraml, DrSc., are acknowledged. 1 Respiratory chain and
CHAPTER 15 Metabolism: Basic Concepts and Design
 CHAPTER 15 Metabolism: Basic Concepts and Design Chapter 15 An overview of Metabolism Metabolism is the sum of cellular reactions - Metabolism the entire network of chemical reactions carried out by living
CHAPTER 15 Metabolism: Basic Concepts and Design Chapter 15 An overview of Metabolism Metabolism is the sum of cellular reactions - Metabolism the entire network of chemical reactions carried out by living
Cellular Respiration. The mechanism of creating cellular energy. Thursday, 11 October, 12
 Cellular Respiration The mechanism of creating cellular energy What do we know?? What do we know?? Grade 5 - Food --> Energy What do we know?? Grade 5 - Food --> Energy Grade 10 - glu. + O2 --> CO2 + H20
Cellular Respiration The mechanism of creating cellular energy What do we know?? What do we know?? Grade 5 - Food --> Energy What do we know?? Grade 5 - Food --> Energy Grade 10 - glu. + O2 --> CO2 + H20
Cellular Respiration. Mitochondria Rule! Mr. Kurt Kristensen
 Cellular Respiration Mitochondria Rule! Mr. Kurt Kristensen Harvard Biovisions Mitochondria Summer Session Week 1: Cellular Respiration Students should. 1) Understand the locations, and functions of the
Cellular Respiration Mitochondria Rule! Mr. Kurt Kristensen Harvard Biovisions Mitochondria Summer Session Week 1: Cellular Respiration Students should. 1) Understand the locations, and functions of the
Electron Transport Chain (Respiratory Chain) - exercise - Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Electron Transport Chain (Respiratory Chain) - exercise - Vladimíra Kvasnicová Respiratory chain (RCH) a) is found in all cells b) is located in a mitochondrion c) includes enzymes integrated in the inner
Electron Transport Chain (Respiratory Chain) - exercise - Vladimíra Kvasnicová Respiratory chain (RCH) a) is found in all cells b) is located in a mitochondrion c) includes enzymes integrated in the inner
Energy in Chemical and Biochemical Reactions
 Energy in Chemical and Biochemical Reactions Reaction Progress Diagram for Exothermic Reaction Reactants activated complex Products ENERGY A + B Reactants E a C + D Products Δ rxn Reaction coordinate The
Energy in Chemical and Biochemical Reactions Reaction Progress Diagram for Exothermic Reaction Reactants activated complex Products ENERGY A + B Reactants E a C + D Products Δ rxn Reaction coordinate The
Transformation of Energy! Energy is the ability to do work.! Thermodynamics is the study of the flow and transformation of energy in the universe.
 Section 1 How Organisms Obtain Energy Transformation of Energy! Energy is the ability to do work.! Thermodynamics is the study of the flow and transformation of energy in the universe. Section 1 How Organisms
Section 1 How Organisms Obtain Energy Transformation of Energy! Energy is the ability to do work.! Thermodynamics is the study of the flow and transformation of energy in the universe. Section 1 How Organisms
Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 Chapter 10 Chemotrophic Energy Metabolism: Aerobic Respiration Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Figure 10-1 Figure 10-6 Conversion of pyruvate The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl
Chapter 10 Chemotrophic Energy Metabolism: Aerobic Respiration Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Figure 10-1 Figure 10-6 Conversion of pyruvate The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Outline I. Energy and Carbon Cycle II. Photosynthesis A. Introduction B. Reactions II. Cellular Respiration A. Introduction B. Reactions Carbon Cycle All organisms
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Outline I. Energy and Carbon Cycle II. Photosynthesis A. Introduction B. Reactions II. Cellular Respiration A. Introduction B. Reactions Carbon Cycle All organisms
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information S1. General values for all the cases studied Table S1: Conditions (the same for all case studies) Variable Value Unit ph intracellular 7.00 - ph extracellular 7.00
Electronic Supplementary Information S1. General values for all the cases studied Table S1: Conditions (the same for all case studies) Variable Value Unit ph intracellular 7.00 - ph extracellular 7.00
AP Biology Day 16. Monday, September 26, 2016
 AP Biology Day 16 Monday, September 26, 2016 CW/HW Assignments 1. Ch. 9 Guided Reading 2. Ch. 9 Video Cornell Notes (2) PLANNER 1. Ch. 9 Video Cornell Notes (weebly) 2. Study & schedule test retake! unit
AP Biology Day 16 Monday, September 26, 2016 CW/HW Assignments 1. Ch. 9 Guided Reading 2. Ch. 9 Video Cornell Notes (2) PLANNER 1. Ch. 9 Video Cornell Notes (weebly) 2. Study & schedule test retake! unit
6CO 2 + 6H 2 O C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2. sun. Occurs in chloroplasts ATP. enzymes CO 2 O 2 H 2 O. sugars
 4.2 8.2 Overview Photosynthesis: of Photosynthesis An Overview Photosynthesis process by which plants make food using energy from the sun Plants are autotrophs that make their own source of chemical energy.
4.2 8.2 Overview Photosynthesis: of Photosynthesis An Overview Photosynthesis process by which plants make food using energy from the sun Plants are autotrophs that make their own source of chemical energy.
Chapter 5. Table of Contents. Section 1 Energy and Living Things. Section 2 Photosynthesis. Section 3 Cellular Respiration
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Table of Contents Section 1 Energy and Living Things Section 2 Photosynthesis Section 3 Cellular Respiration Section 1 Energy and Living Things Objectives Analyze
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Table of Contents Section 1 Energy and Living Things Section 2 Photosynthesis Section 3 Cellular Respiration Section 1 Energy and Living Things Objectives Analyze
Cellular respiration. How do living things stay alive? Cellular Respiration Burning. Photosynthesis. Cellular Respiration
 How do living things stay alive? Cellular Respiration Burning Happens in ALL living things inside cells and has the main goal of producing ATP the fuel of life It does not matter whether the organisms
How do living things stay alive? Cellular Respiration Burning Happens in ALL living things inside cells and has the main goal of producing ATP the fuel of life It does not matter whether the organisms
ATP: Energy for Life ATP. Chapter 6. What Is ATP? What Does ATP Do for You? Photosynthesis. Cell Respiration. Chemical Structure of ATP
 Chapter 6 Photosynthesis : Energy for Life Cell Respiration What Is? Energy used by all Cells Chemical Structure of Adenine Base Adenosine Triphosphate Organic molecule containing highenergy Phosphate
Chapter 6 Photosynthesis : Energy for Life Cell Respiration What Is? Energy used by all Cells Chemical Structure of Adenine Base Adenosine Triphosphate Organic molecule containing highenergy Phosphate
The Life of a Cell. The Chemistry of Life. A View of the Cell. Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle. Energy in a Cell
 The Life of a Cell The Chemistry of Life A View of the Cell Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle Energy in a Cell Chapter 9 Energy in a Cell 9.1: The Need for Energy 9.1: Section Check 9.2: Photosynthesis:
The Life of a Cell The Chemistry of Life A View of the Cell Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle Energy in a Cell Chapter 9 Energy in a Cell 9.1: The Need for Energy 9.1: Section Check 9.2: Photosynthesis:
Bio102 Problems Photosynthesis
 Bio102 Problems Photosynthesis 1. Why is it advantageous for chloroplasts to have a very large (in surface area) thylakoid membrane contained within the inner membrane? A. This limits the amount of stroma
Bio102 Problems Photosynthesis 1. Why is it advantageous for chloroplasts to have a very large (in surface area) thylakoid membrane contained within the inner membrane? A. This limits the amount of stroma
Respiration and Photosynthesis
 Respiration and Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Glycolysis The Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chains Anabolic Pathway Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Flow of Energy Energy is needed to support all forms
Respiration and Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Glycolysis The Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chains Anabolic Pathway Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Flow of Energy Energy is needed to support all forms
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE. Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge. FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison
 BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison 8 Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge Roadmap 8 In this chapter you will learn how Enzymes use
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison 8 Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge Roadmap 8 In this chapter you will learn how Enzymes use
Chapter 8. Biology. Energy Processing. Metabolism & ATP. Slide 1 / 142 Slide 2 / 142. Slide 3 / 142. Slide 4 / 142. Slide 5 / 142.
 Slide 1 / 142 Slide 2 / 142 Biology Energy Processing www.njctl.org Acetyl Co-A aerobic anabolic pathway anaerobic synthase Calvin Cycle catabolic pathway cellular respiration chlorophyll citric acid cycle
Slide 1 / 142 Slide 2 / 142 Biology Energy Processing www.njctl.org Acetyl Co-A aerobic anabolic pathway anaerobic synthase Calvin Cycle catabolic pathway cellular respiration chlorophyll citric acid cycle
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush
 number 6 Done by أنس القيشاوي Corrected by Zaid Emad Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush 1 P a g e In the previous lecture, we talked about redox reactions and the reduction potential briefly and how it can help
number 6 Done by أنس القيشاوي Corrected by Zaid Emad Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush 1 P a g e In the previous lecture, we talked about redox reactions and the reduction potential briefly and how it can help
Energy Transformation, Cellular Energy & Enzymes (Outline)
 Energy Transformation, Cellular Energy & Enzymes (Outline) Energy conversions and recycling of matter in the ecosystem. Forms of energy: potential and kinetic energy The two laws of thermodynamic and definitions
Energy Transformation, Cellular Energy & Enzymes (Outline) Energy conversions and recycling of matter in the ecosystem. Forms of energy: potential and kinetic energy The two laws of thermodynamic and definitions
I. Flow of Energy in Living Things II. Laws of Thermodynamics & Free Energy III. Activation Energy IV. Enzymes V. Reaction Coupling VI.
 Chapter 6 Energy & Metabolism I. Flow of Energy in Living Things II. Laws of Thermodynamics & Free Energy III. Activation Energy IV. Enzymes V. Reaction Coupling VI. Metabolism I. Flow of Energy in Living
Chapter 6 Energy & Metabolism I. Flow of Energy in Living Things II. Laws of Thermodynamics & Free Energy III. Activation Energy IV. Enzymes V. Reaction Coupling VI. Metabolism I. Flow of Energy in Living
A staggering number of organism-organism and organism- environment interactions underlie global biogeochemistry These can be studied at vastly
 Geobiology Week 3 How do microbes garner energy and carbon? Review of redox couples, reaction potential and free energy yields Hydrogen as an energy currency for subsurface microbes. Acknowledgements:
Geobiology Week 3 How do microbes garner energy and carbon? Review of redox couples, reaction potential and free energy yields Hydrogen as an energy currency for subsurface microbes. Acknowledgements:
Energy and Cellular Metabolism
 1 Chapter 4 About This Chapter Energy and Cellular Metabolism 2 Energy in biological systems Chemical reactions Enzymes Metabolism Figure 4.1 Energy transfer in the environment Table 4.1 Properties of
1 Chapter 4 About This Chapter Energy and Cellular Metabolism 2 Energy in biological systems Chemical reactions Enzymes Metabolism Figure 4.1 Energy transfer in the environment Table 4.1 Properties of
Biology Reading Assignments:
 Biology 205 5.13.08 Reading Assignments: Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis and Biosynthesis pgs. 83-94; 106-116 (Note the various roles of nucleotide based carrier molecules); work questions 3-2 and 3-3 Chapter
Biology 205 5.13.08 Reading Assignments: Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis and Biosynthesis pgs. 83-94; 106-116 (Note the various roles of nucleotide based carrier molecules); work questions 3-2 and 3-3 Chapter
*The entropy of a system may decrease, but the entropy of the system plus its surroundings must always increase
 AP biology Notes: Metabolism Metabolism = totality of an organism's chemical process concerned with managing cellular resources. Metabolic reactions are organized into pathways that are orderly series
AP biology Notes: Metabolism Metabolism = totality of an organism's chemical process concerned with managing cellular resources. Metabolic reactions are organized into pathways that are orderly series
TCA Cycle. Voet Biochemistry 3e John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 TCA Cycle Voet Biochemistry 3e Voet Biochemistry 3e The Electron Transport System (ETS) and Oxidative Phosphorylation (OxPhos) We have seen that glycolysis, the linking step, and TCA generate a large number
TCA Cycle Voet Biochemistry 3e Voet Biochemistry 3e The Electron Transport System (ETS) and Oxidative Phosphorylation (OxPhos) We have seen that glycolysis, the linking step, and TCA generate a large number
ATP. Chapter 4. Photosynthesis. Cell Respiration. Energy of Life. All organisms need energy in order to survive
 ATP Chapter 4 Photosynthesis Energy of Life All organisms need energy in order to survive 2 Major groups of organisms: A. autotrophs make their own food Ex: plants B. heterotrophs must eat others living
ATP Chapter 4 Photosynthesis Energy of Life All organisms need energy in order to survive 2 Major groups of organisms: A. autotrophs make their own food Ex: plants B. heterotrophs must eat others living
Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013
 Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013 Lecture 10. Biochemical Transformations II. Phosphoryl transfer and the kinetics and thermodynamics of energy currency in the cell: ATP and GTP.
Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013 Lecture 10. Biochemical Transformations II. Phosphoryl transfer and the kinetics and thermodynamics of energy currency in the cell: ATP and GTP.
Ch. 6 & 7 Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
 Ch. 6 & 7 Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration 6.1 Energy Reactions The Cycle of Energy Sun CO 2 H 2 O Photosynthesis (energy stored) Cellular Respiration (energy released) O 2 Glucose Obtaining Energy
Ch. 6 & 7 Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration 6.1 Energy Reactions The Cycle of Energy Sun CO 2 H 2 O Photosynthesis (energy stored) Cellular Respiration (energy released) O 2 Glucose Obtaining Energy
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 8
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 8 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 28, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 8 January 28, 2013 1 / 33 Outline Questions and answers Energy and
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 8 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 28, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 8 January 28, 2013 1 / 33 Outline Questions and answers Energy and
Energy & Life: Cellular Respiration PART I: HARVESTING CHEMICAL ENERGY
 Energy & Life: Cellular Respiration PART I: HARVESTING CHEMICAL ENERGY Energy u Energy is not created or destroyed, it is transformed, changed. u E= ability to do work u Living things depend on energy
Energy & Life: Cellular Respiration PART I: HARVESTING CHEMICAL ENERGY Energy u Energy is not created or destroyed, it is transformed, changed. u E= ability to do work u Living things depend on energy
Energy for Life 12/11/14. Light Absorption in Chloroplasts
 Energy for Life Biochemical pathways A series of reactions where the products of one reaction is used in the next reaction Light Absorption in Chloroplasts Chloroplasts Two membranes Grana- layered stacks
Energy for Life Biochemical pathways A series of reactions where the products of one reaction is used in the next reaction Light Absorption in Chloroplasts Chloroplasts Two membranes Grana- layered stacks
Energy in the World of Life
 Cellular Energy Energy in the World of Life Sustaining life s organization requires ongoing energy inputs Assembly of the molecules of life starts with energy input into living cells Energy Conversion
Cellular Energy Energy in the World of Life Sustaining life s organization requires ongoing energy inputs Assembly of the molecules of life starts with energy input into living cells Energy Conversion
