S8P1C. STATES OF MATTER E.Q. WHAT ARE THE STATES OF MATTER? WHAT ARE THE CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH STATE OF MATTER?
|
|
|
- Randell Fowler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 S8P1C. STATES OF MATTER E.Q. WHAT ARE THE STATES OF MATTER? WHAT ARE THE CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH STATE OF MATTER?
3 ATOMIC MODEL PROJECT BE CREATIVE!!! MIXTURES VS. SUBSTANCES TASK DUE BY FRIDAY, NOVEMBER 6 TH THOSE WHO NEED TO COMPLETE LAB QUESTIONS NEED TO SEE ME ON TUESDAY DURING FIRST PERIOD. FINAL GRADES WILL BE GIVEN ON WEDNESDAY IN CLASS. PICTURES OF PROJECTS:
4 STATES OF MATTER NOTES SUBSTANCES CAN EXIST AS ANY STATE OF MATTER. WATER CAN BE FROZEN, WATER VAPOR, OR IN LIQUID FORM. EVEN THOUGH THEY ARE THE SAME SUBSTANCE AND IN DIFFERENT FORMS, THEY EACH HAVE DIFFERENT PHYSICAL QUALITIES.
5 STATES OF MATTER ALL MATTER IS MADE OF PARTICLES THAT ARE ALWAYS MOVING AND ARE ARRANGED DIFFERENTLY IN EACH STATE OF MATTER. THERE ARE 3 GENERAL STATES OF MATTER THAT EXISTS ON EARTH: SOLID LIQUID GAS NOTE: PARTICLE IS A WORD TO DESCRIBE SMALL THINGS OR THE SMALLEST BITS OF MATTER WHICH IN TURN ARE ATOMS.
6 QUESTIONS: SIMULATION SIMULATION SHOWING PARTICLE ARRANGEMENT OF EACH STATE OF MATTER 1. WHAT DO YOU NOTICE ABOUT SOLIDS? 2. WHAT DO YOU NOTICE ABOUT LIQUIDS? 3. WHAT DO YOU NOTICE ABOUT GASES? LOOK AT EACH EXAMPLE BELOW. DESCRIBE HOW THE PARTICLES (ATOMS) ARE ARRANGED ON A MOLECULAR LEVEL. A. (LIQUID- HYDROGEN PEROXIDE) B. (SOLID- SILVER) C. (GAS- NITROGEN OR SULFUR) OUT OF ALL 4 STATES OF MATTER, WHICH ONE NATURAL HAS THE HIGHEST KINETIC ENERGY? WHY DO YOU THINK IT HAS SUCH A HIGH AMOUNT OF KINETIC ENERGY?
7 SOLIDS HAVE A DEFINITE SHAPE (MAINTAINS SHAPE) AND A DEFINITE VOLUME (AMOUNT OF SPACE MATTER TAKES UP/OCCUPIES) THE PARTICLES OF A SOLID ARE PACKED VERY CLOSELY TOGETHER (IN A PATTERN OR CRYSTAL FORMATION). PARTICLES VIBRATE, BUT DON T SLIP PAST EACH OTHER. SO, WHY DO SOLIDS MAINTAIN A DEFINITE SHAPE AND VOLUME.
8 LIQUIDS THE PARTICLES ARE IN CONTACT WITH EACH OTHER. THE PARTICLES CLOSE, BUT MOVE QUICKLY ENOUGH TO MOVE AROUND EACH OTHER LIQUIDS DOES NOT HAVE A DEFINITE SHAPE, BUT DOES HAVE A DEFINITE/FIXED VOLUME. SO, WHY DON T LIQUIDS HAVE A DEFINITE SHAPE?
9 GAS PARTICLES ARE WIDELY SEPARATED AND MOVE AT GREAT SPEEDS. TAKE THE SHAPE OF THE CONTAINER AND THE VOLUME OF THE CONTAINER. WITHOUT A CONTAINER, PARTICLES DON T HAVE A FIXED SHAPE NOR FIXED VOLUME.
10 PLASMA IT IS ELECTRICALLY CHARGED GAS DOES NOT HAVE A DEFINITE VOLUME NOR SHAPE. FORMS AT VERY HIGH TEMPERATURES (TEMPERATURE IN STARS). AT HIGH TEMP, ATOMS COLLIDE WITH GREAT FORCE. THE FORCE ALLOWS THE ELECTRONS TO OVERCOME THE ATTRACTIVE FORCE BETWEEN THE PROTONS. THE RESULT, LOOSE ELECTRONS AND POSITIVELY CHARGED IONS THAT MAKES PLASMA ABLE TO CONDUCT ELECTRICITY! COMMON IN SPACE, BUT RARE ON EARTH (EXISTS IN LIGHTNING BOLTS AND IN SOME LIGHTBULBS)
11 COOL VIDEO ABOUT PLASMA!
12 WHAT ARE THE MAIN DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE FORMS OF MATTER? DISTANCE BETWEEN THE PARTICLES MOTION OF THE PARTICLES
13 INQUIRY LAB QUESTIONS 1. DESCRIBE THE NATURAL STATES OF EACH FORM OF MATTER (SOLID, LIQUID, GAS). BE SURE TO INCLUDE THE DISTANCE BETWEEN THE PARTICLES AND THE MOVEMENT OF PARTICLES. 2. IS THERE ANY RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THERMAL ENERGY AND KINETIC ENERGY OF THE PARTICLES FOUND IN MATTER? IF SO, HOW DO THEY RELATE? 3. WHAT OCCURS ON A MOLECULAR LEVEL AS MATTER BEGINS TO BOIL? 4. WHAT OCCURS ON A MOLECULES LEVEL AS MATTER FREEZES? THE HIGHER THE TEMPERATURE >>>>>THE MORE ENERGY IS GAINED>>>> THE FASTER THE PARTICLES MOVE THE LOWER THE TEMPERATURE>>>> THE LESS ENERGY AVAILABLE>>> THE SLOWER THE PARTICLES MOVE
14 WHAT CAUSES MATTER TO CHANGE FORM? THERMAL ENERGY AFFECTS PARTICLE MOVEMENT PARTICLES OF A SUBSTANCE ARE ALWAYS MOVING AND MOVE EVEN MORE WHEN IT S WARMER (KINETIC ENERGY= ENERGY IN MOTION). TEMPERATURE IS A MEASURE OF THE AVERAGE KINETIC ENERGY OF THE PARTICLES IN A SUBSTANCE. THE FASTER PARTICLES MOVE= HIGHER THE TEMPERATURE. THE SLOWER PARTICLES MOVE= LOWER THE TEMPERATURE. ZQJXBME MATTER CAN CHANGE PHYSICALLY CHANGING STATES: OCCURS WHEN MATTER CHANGES FROM A SOLID, LIQUID OR GAS. THERMAL ENERGY (HEAT) MUST BE ABSORBED OR RELEASED BY MATTER. THINK PAIR SHARE IS ENERGY GAINED OR LOST WHEN A SOLID CHANGES TO A LIQUID? IS ENERGY GAINED OR LOST WHEN A LIQUID CHANGES TO A GAS? IS ENERGY GAINED OR LOST WHEN A GAS CHANGES TO A LIQUID? IS ENERGY GAINED OR LOST WHEN A LIQUID CHANGES TO A SOLID?
15 ENERGY LOST OR GAINED SOLIDS GAIN OR ABSORBS ENERGY FROM HIGH TEMPERATURES THE PARTICLES MOVE FASTER CAUSING THE BONDS TO BREAK BETWEEN THEM CHANGING IT INTO A LIQUID. LIQUIDS GAIN/ABSORB ENERGY FROM HEAT. THE PARTICLES MOVE EVEN FASTER CHANGING IT TO A GAS. ENERGY IS LOST/RELEASED FROM PARTICLES IN A GAS WHEN THERMAL ENERGY IS LOW (COOLER) AND IT CHANGES TO A LIQUID. ENERGY IS LOST/RELEASED FROM PARTICLES IN A LIQUID AS LESS THERMAL ENERGY IS PRESENT (COLD) AND IT CHANGES TO A SOLID.
Chapter 14 9/21/15. Solids, Liquids & Gasses. Essential Questions! Kinetic Theory! Gas State! Gas State!
 Chapter 14 Solids, Liquids & Gasses Essential Questions What is the kinetic theory of matter? How do particles move in the different states of matter? How do particles behave at the boiling and melting
Chapter 14 Solids, Liquids & Gasses Essential Questions What is the kinetic theory of matter? How do particles move in the different states of matter? How do particles behave at the boiling and melting
Solids (cont.) Describe the movement of particles in a solid and the forces between them.
 Solids A solid is matter that has a definite shape and a definite volume. The attractive forces between the particles in a solid are strong and pull them close together. Solids (cont.) Describe the movement
Solids A solid is matter that has a definite shape and a definite volume. The attractive forces between the particles in a solid are strong and pull them close together. Solids (cont.) Describe the movement
Kinetic Theory of Matter
 1 Temperature and Thermal Energy Kinetic Theory of Matter The motion of the particles in matter is described by kinetic theory of matter. Matter is composed of particles that are atoms, molecules, or ions
1 Temperature and Thermal Energy Kinetic Theory of Matter The motion of the particles in matter is described by kinetic theory of matter. Matter is composed of particles that are atoms, molecules, or ions
Matter. Energy- which is a property of matter!! Matter: anything that takes up space and has mass
 Matter Matter: anything that takes up space and has mass Can you think of anything that is not made of matter? Energy- which is a property of matter!! Matter is made up of moving particles! Instead of
Matter Matter: anything that takes up space and has mass Can you think of anything that is not made of matter? Energy- which is a property of matter!! Matter is made up of moving particles! Instead of
ENERGY IN CHEMISTRY. R. Ashby Duplication by permission only.
 CH 11 TOPIC 28 CHANGING STATES OF MATTER 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) define or describe: ENERGY, POTENTIAL ENERGY, KINETIC ENERGY & KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY 2) define or describe HEAT
CH 11 TOPIC 28 CHANGING STATES OF MATTER 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) define or describe: ENERGY, POTENTIAL ENERGY, KINETIC ENERGY & KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY 2) define or describe HEAT
Chemistry Day 5. Friday, August 31 st Tuesday, September 4 th, 2018
 Chemistry Day 5 Friday, August 31 st Tuesday, September 4 th, 2018 Do-Now Title: BrainPOP: States of Matter 1. Write down today s FLT 2. List two examples of gases 3. List two examples of things that are
Chemistry Day 5 Friday, August 31 st Tuesday, September 4 th, 2018 Do-Now Title: BrainPOP: States of Matter 1. Write down today s FLT 2. List two examples of gases 3. List two examples of things that are
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy
 Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page!1. Chemistry A States of Matter Packet
 Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page!1 Chemistry A States of Matter Packet Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page!2 Worksheet #1: States of Matter In this packet we will
Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page!1 Chemistry A States of Matter Packet Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page!2 Worksheet #1: States of Matter In this packet we will
Most substances can be in three states: solid, liquid, and gas.
 States of Matter Most substances can be in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solid Particles Have Fixed Positions The particles in a solid are very close together and have an orderly, fixed arrangement.
States of Matter Most substances can be in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solid Particles Have Fixed Positions The particles in a solid are very close together and have an orderly, fixed arrangement.
4 Discuss and evaluate the 5th state of matter. 3 - Differentiate among the four states of matter in terms of energy,
 Goal: Differentiate among the four states of matter in terms of energy, particle motion, and phase transitions. 4 States of Mater Sections 3.1, 3.2 4 Discuss and evaluate the 5 th state of matter. 3 -
Goal: Differentiate among the four states of matter in terms of energy, particle motion, and phase transitions. 4 States of Mater Sections 3.1, 3.2 4 Discuss and evaluate the 5 th state of matter. 3 -
Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 1. Chemistry A States of Matter Packet
 Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 1 Chemistry A States of Matter Packet Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 2 Worksheet #1: States of Matter In this packet we will
Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 1 Chemistry A States of Matter Packet Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 2 Worksheet #1: States of Matter In this packet we will
CHAPTER 3 ATOMS ATOMS MATTER 10/17/2016. Matter- Anything that takes up space (volume) and has mass. Atom- basic unit of matter.
 CHAPTER 3 MATTER Matter- Anything that takes up space (volume) and has mass. Matter Combining Matter States of Matter Atom- basic unit of matter. Subatomic particles- protons, neutrons, and electrons.
CHAPTER 3 MATTER Matter- Anything that takes up space (volume) and has mass. Matter Combining Matter States of Matter Atom- basic unit of matter. Subatomic particles- protons, neutrons, and electrons.
* Defining Temperature * Temperature is proportional to the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. * Temperature * Internal energy
 * Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
* Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
Everything in the universe can be classified as either matter or energy. Kinetic Energy Theory: All particles of matter are in constant motion.
 Physical Science Everything in the universe can be classified as either matter or energy. Kinetic Energy Theory: All particles of matter are in constant motion. State of Matter Bose- Einstein Condensate
Physical Science Everything in the universe can be classified as either matter or energy. Kinetic Energy Theory: All particles of matter are in constant motion. State of Matter Bose- Einstein Condensate
Chapter 10 States of Matter
 Chapter 10 States of Matter 1 Section 10.1 The Nature of Gases Objectives: Describe the assumptions of the kinetic theory as it applies to gases. Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory. Define
Chapter 10 States of Matter 1 Section 10.1 The Nature of Gases Objectives: Describe the assumptions of the kinetic theory as it applies to gases. Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory. Define
Unit 3: States of Matter, Heat and Gas Laws
 Unit 3 - Stevens 1 Unit 3: States of Matter, Heat and Gas Laws Vocabulary: Solid Term Definition Example Liquid Gas No definite shape, but definite volume; Particles close together, but can move around
Unit 3 - Stevens 1 Unit 3: States of Matter, Heat and Gas Laws Vocabulary: Solid Term Definition Example Liquid Gas No definite shape, but definite volume; Particles close together, but can move around
Section 16.3 Phase Changes
 Section 16.3 Phase Changes Solid Liquid Gas 3 Phases of Matter Density of Matter How packed matter is (The amount of matter in a given space) Solid: Liquid: Gas: High Density Medium Density Low Density
Section 16.3 Phase Changes Solid Liquid Gas 3 Phases of Matter Density of Matter How packed matter is (The amount of matter in a given space) Solid: Liquid: Gas: High Density Medium Density Low Density
STATES OF MATTER. The Four States of Ma/er. Four States. Solid Liquid Gas Plasma
 STATES OF MATTER The Four States of Ma/er Solid Liquid Gas Plasma Four States STATES OF MATTER Ø What makes a substance a par:cular state of ma
STATES OF MATTER The Four States of Ma/er Solid Liquid Gas Plasma Four States STATES OF MATTER Ø What makes a substance a par:cular state of ma
Name Chemistry / / Understanding Phase Changes
 Name Chemistry / / Understanding Phase Changes As a piece of ice is exposed to a warmer environment, it begins to absorb heat. The heat causes the solid molecules to vibrate faster. Eventually, the ice
Name Chemistry / / Understanding Phase Changes As a piece of ice is exposed to a warmer environment, it begins to absorb heat. The heat causes the solid molecules to vibrate faster. Eventually, the ice
Chapter 22 States of matter. Section 1 matter Section 2 Changes of State
 Chapter 22 States of matter Section 1 matter Section 2 Changes of State States of Matter is a physical property ***Matter is made of atoms Atoms form chemical bonds to make matter **** Atoms vibrate constantly
Chapter 22 States of matter Section 1 matter Section 2 Changes of State States of Matter is a physical property ***Matter is made of atoms Atoms form chemical bonds to make matter **** Atoms vibrate constantly
Science 8 Chapter 7 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 7 Section 1 Describing Fluids (pp. 268-277) What is a fluid? Fluid: any thing that flows; a liquid or a gas While it would seem that some solids flow (sugar, salt, etc), they are not
Science 8 Chapter 7 Section 1 Describing Fluids (pp. 268-277) What is a fluid? Fluid: any thing that flows; a liquid or a gas While it would seem that some solids flow (sugar, salt, etc), they are not
Ch(3)Matter & Change. John Dalton
 Ch(3)Matter & Change John Dalton What is Matter? Matter is anything that contains mass & volume (takes up space) Energy, such as light, heat, and sound, is NOT matter. The Particle Theory of Matter 1.
Ch(3)Matter & Change John Dalton What is Matter? Matter is anything that contains mass & volume (takes up space) Energy, such as light, heat, and sound, is NOT matter. The Particle Theory of Matter 1.
Core Chemistry UNIT 1: Matter & Energy Section 1: The Law of Conservation of Mass Section 2: States of Matter & Intro to Thermodynamics
 Core Chemistry UNIT 1: Matter & Energy Section 1: The Law of Conservation of Mass Section 2: States of Matter & Intro to Thermodynamics UNIT 1 Synapsis In our first unit we will explore matter & energy
Core Chemistry UNIT 1: Matter & Energy Section 1: The Law of Conservation of Mass Section 2: States of Matter & Intro to Thermodynamics UNIT 1 Synapsis In our first unit we will explore matter & energy
The Can Demonstration
 The Can Demonstration With your table, make a prediction as to what will happen to the can. Discuss why you think that the can imploded. What are some reasons? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xg5niowf_zw&t=28s
The Can Demonstration With your table, make a prediction as to what will happen to the can. Discuss why you think that the can imploded. What are some reasons? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xg5niowf_zw&t=28s
WARM-UP. 1. What are the four states of matter? 2. What is melting point? 3. How does water change from a liquid to a gas? 4. Define viscosity.
 WARM-UP 1. What are the four states of matter? 2. What is melting point? 3. How does water change from a liquid to a gas? 4. Define viscosity. STATES OF MATTER: WEB QUEST With your lab partner, you will
WARM-UP 1. What are the four states of matter? 2. What is melting point? 3. How does water change from a liquid to a gas? 4. Define viscosity. STATES OF MATTER: WEB QUEST With your lab partner, you will
Matter & Energy. Kinetic Theory of Matter. Kinetic Theory of Matter. Kinetic Theory of Matter. Kinetic Theory of Matter. Temperature.
 Matter & Energy 1) All matter is made up of atoms and molecules that act as tiny particles. 1 2 2) These tiny particles are always in motion. State of matter depends on its molecular motion as measured
Matter & Energy 1) All matter is made up of atoms and molecules that act as tiny particles. 1 2 2) These tiny particles are always in motion. State of matter depends on its molecular motion as measured
States of Matter. Essential Question: How does the movement of atoms and molecules relate to matter s different phases?
 States of Matter Essential Question: How does the movement of atoms and molecules relate to matter s different phases? These notes come from pages 60 to 73 in your Physical Science Textbook All Matter
States of Matter Essential Question: How does the movement of atoms and molecules relate to matter s different phases? These notes come from pages 60 to 73 in your Physical Science Textbook All Matter
Chapter: Heat and States
 Table of Contents Chapter: Heat and States of Matter Section 1: Temperature and Thermal Energy Section 2: States of Matter Section 3: Transferring Thermal Energy Section 4: Using Thermal Energy 1 Temperature
Table of Contents Chapter: Heat and States of Matter Section 1: Temperature and Thermal Energy Section 2: States of Matter Section 3: Transferring Thermal Energy Section 4: Using Thermal Energy 1 Temperature
THE PHASES OF MATTER. Solid: holds its shape and does not flow. The molecules in a solid vibrate in place, but on average, don t move very far.
 THE QUESTIONS What are the phases of matter? What makes these phases different from each other? What is the difference between melting, freezing, boiling and condensation? How do you interpret a Temperature
THE QUESTIONS What are the phases of matter? What makes these phases different from each other? What is the difference between melting, freezing, boiling and condensation? How do you interpret a Temperature
Solids, Liquids, and Gases. Chapter 14
 Solids, Liquids, and Gases Chapter 14 Matter & Thermal Energy Matter can exist as a solid, a liquid, a gas or a plasma. The Molecular Kinetic Theory of Matter explains their differences and how they can
Solids, Liquids, and Gases Chapter 14 Matter & Thermal Energy Matter can exist as a solid, a liquid, a gas or a plasma. The Molecular Kinetic Theory of Matter explains their differences and how they can
Dissolving. Dissolving
 If divers surface too quickly from great depths, the nitrogen that has dissolved in their blood and other tissues bubbles out of solution. These bubbles can become trapped in joints and cause great pain,
If divers surface too quickly from great depths, the nitrogen that has dissolved in their blood and other tissues bubbles out of solution. These bubbles can become trapped in joints and cause great pain,
THE PARTICLE MODEL AND PROPERTIES OF THE GASES, LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS. STATES CHANGES
 THE PARTICLE MODEL AND PROPERTIES OF THE GASES, LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS. STATES CHANGES The particle model of a gas A gas has no fixed shape or volume, but always spreads out to fill any container. There are
THE PARTICLE MODEL AND PROPERTIES OF THE GASES, LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS. STATES CHANGES The particle model of a gas A gas has no fixed shape or volume, but always spreads out to fill any container. There are
Matter & Energy. Objectives: properties and structures of the different states of matter.
 Matter & Energy Objectives: 1. Use the kinetic theory to describe the properties and structures of the different states of matter. 2. Describe energy transfers involved in changes of state. 3. Describe
Matter & Energy Objectives: 1. Use the kinetic theory to describe the properties and structures of the different states of matter. 2. Describe energy transfers involved in changes of state. 3. Describe
SG 4 Elements and Chemical Bonds 5 States of Matter
 Name Date Period SG 4 Elements and Chemical Bonds 5 States of Matter 4.1 Electrons and Energy Levels Directions: On the line before each definition, write the term that matches it correctly. Each term
Name Date Period SG 4 Elements and Chemical Bonds 5 States of Matter 4.1 Electrons and Energy Levels Directions: On the line before each definition, write the term that matches it correctly. Each term
Matter. Gas. Solid Liquid. Both shape and volume are not fixed. It has a fixed shape and a fixed volume.
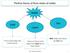 Matter Solid Liquid Gas It has a fixed shape and a fixed volume. It does not have a fixed shape, but it does have a fixed volume. Both shape and volume are not fixed. Felix Yung and John Polias 1 Matter
Matter Solid Liquid Gas It has a fixed shape and a fixed volume. It does not have a fixed shape, but it does have a fixed volume. Both shape and volume are not fixed. Felix Yung and John Polias 1 Matter
STATES OF MATTER. Chapter 3
 STATES OF MATTER Chapter 3 Labs done so far for ch. 3 sections 1 and 2: 1. Distilled wood and related read of temperatures with plateaus for substances produced 2. Distilling solution X (BP/CP evaporation/condensation)
STATES OF MATTER Chapter 3 Labs done so far for ch. 3 sections 1 and 2: 1. Distilled wood and related read of temperatures with plateaus for substances produced 2. Distilling solution X (BP/CP evaporation/condensation)
Chemistry Joke. Once you ve seen 6.02 x You ve seen a mole!
 States of Matter Chemistry Joke Once you ve seen 6.02 x 10 23 atoms You ve seen a mole! Kinetic Theory Kinetic Theory explains the states of matter based on the concept that the particles in all forms
States of Matter Chemistry Joke Once you ve seen 6.02 x 10 23 atoms You ve seen a mole! Kinetic Theory Kinetic Theory explains the states of matter based on the concept that the particles in all forms
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
 The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) CHAPTER 2, LESSON 1 HEAT, TEMPERATURE, AND CONDUCTION MS-PS1-4. Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) CHAPTER 2, LESSON 1 HEAT, TEMPERATURE, AND CONDUCTION MS-PS1-4. Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state
5 th Grade Science Chapter 14 Properties of Matter
 5 th Grade Science Chapter 14 Properties of Matter matter Anything that has mass and takes up space is matter http://www.chem4kids.com/files/matter_intro.html volume The amount of space an object takes
5 th Grade Science Chapter 14 Properties of Matter matter Anything that has mass and takes up space is matter http://www.chem4kids.com/files/matter_intro.html volume The amount of space an object takes
Changes in Matter. Introduction to Chemistry
 Changes in Matter Introduction to Chemistry Classifying Matter Matter: is anything that has mass and volume. Volume: the amount of space that something takes up Property: a characteristic of a material
Changes in Matter Introduction to Chemistry Classifying Matter Matter: is anything that has mass and volume. Volume: the amount of space that something takes up Property: a characteristic of a material
heat By cillian bryan and scott doyle
 heat By cillian bryan and scott doyle What is heat Heat energy is the result of the movement of tiny particles called atoms molecules or ions in solids, liquids and gases. Heat energy can be transferred
heat By cillian bryan and scott doyle What is heat Heat energy is the result of the movement of tiny particles called atoms molecules or ions in solids, liquids and gases. Heat energy can be transferred
What is a change of state? What happens during a change of state? What can happen when a substance loses or gains energy?
 CHAPTER 3 3 Changes of State SECTION States of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a change of state? What happens during a change
CHAPTER 3 3 Changes of State SECTION States of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a change of state? What happens during a change
Liquids & Solids: Section 12.3
 Liquids & Solids: Section 12.3 MAIN IDEA: The particles in and have a range of motion and are not easily. Why is it more difficult to pour syrup that is stored in the refrigerator than in the cabinet?
Liquids & Solids: Section 12.3 MAIN IDEA: The particles in and have a range of motion and are not easily. Why is it more difficult to pour syrup that is stored in the refrigerator than in the cabinet?
INPUT~ Explore It! Station Directions: This is one of the four INPUT stations. They may be completed in any order.
 INPUT~ Explore It! Station Directions: This is one of the four INPUT stations. They may be completed in any order. One member of the group will read the task cards in order. The group will be responsible
INPUT~ Explore It! Station Directions: This is one of the four INPUT stations. They may be completed in any order. One member of the group will read the task cards in order. The group will be responsible
Chemistry Final Study Guide KEY. 3. Define physical changes. A change in any physical property of a substance, not in the substance itself.
 Chemistry Final Study Guide KEY Unit 2: Matter & Its Properties, Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Properties & Changes 1. Define physical properties. The characteristics of a substance that can be observed
Chemistry Final Study Guide KEY Unit 2: Matter & Its Properties, Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Properties & Changes 1. Define physical properties. The characteristics of a substance that can be observed
The States of Matter
 The States of Matter AZ State Standards Concept 1: Structure and Properties of Matter Understand physical, chemical, and atomic properties of matter. PO 1. Describe substances based on their physical properties.
The States of Matter AZ State Standards Concept 1: Structure and Properties of Matter Understand physical, chemical, and atomic properties of matter. PO 1. Describe substances based on their physical properties.
Name Date Class THE NATURE OF GASES
 13.1 THE NATURE OF GASES Section Review Objectives Describe the assumptions of the kinetic theory as it applies to gases Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory Define the relationship between
13.1 THE NATURE OF GASES Section Review Objectives Describe the assumptions of the kinetic theory as it applies to gases Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory Define the relationship between
What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold?
 Heat and Temperature Section 1: Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? 1 Intro: Discussion A person
Heat and Temperature Section 1: Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? 1 Intro: Discussion A person
Matter: Properties and Change
 Matter: Properties and Change 6.P.2 Understand the structure, classifications and physical properties of matter. 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are
Matter: Properties and Change 6.P.2 Understand the structure, classifications and physical properties of matter. 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are
Name Class Date. What is a change of state? What happens during a change of state? What can happen when a substance loses or gains energy?
 CHAPTER 2 3 Changes of State SECTION States of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a change of state? What happens during a change
CHAPTER 2 3 Changes of State SECTION States of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a change of state? What happens during a change
SOLIDS, LIQUIDS AND GASES
 CHEMIS TRY CONTENTS 17 SOLIDS, LIQUIDS AND GASES 17 Solids, Liquids and Gases 147 18 Solutions and Crystallisation 155 19 Separating Mixtures 162 20 Elements, Compounds and Mixtures 171 All materials exist
CHEMIS TRY CONTENTS 17 SOLIDS, LIQUIDS AND GASES 17 Solids, Liquids and Gases 147 18 Solutions and Crystallisation 155 19 Separating Mixtures 162 20 Elements, Compounds and Mixtures 171 All materials exist
Unit 1 Lesson 6 Changes of State. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 The Fact of the Matter What happens when matter changes state? The three most familiar states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. A change of state is the change of a substance from one physical form
The Fact of the Matter What happens when matter changes state? The three most familiar states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. A change of state is the change of a substance from one physical form
CHAPTER 3: STATES OF MATTER. 3.1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases 3.2 The Gas Laws 3.3 Phase Changes
 CHAPTER 3: STATES OF MATTER 3.1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases 3.2 The Gas Laws 3.3 Phase Changes SECTION 3.1 SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & GASES n VOCABULARY: n solid n gas n liquid n kinetic energy n OBJECTIVES: n
CHAPTER 3: STATES OF MATTER 3.1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases 3.2 The Gas Laws 3.3 Phase Changes SECTION 3.1 SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & GASES n VOCABULARY: n solid n gas n liquid n kinetic energy n OBJECTIVES: n
Changing States of Matter By Cindy Grigg
 By Cindy Grigg 1 On Earth, almost all matter exists in just three states. Matter is usually a solid, a liquid, or a gas. Plasma, the fourth state of matter, is rare on Earth. It sometimes can be found
By Cindy Grigg 1 On Earth, almost all matter exists in just three states. Matter is usually a solid, a liquid, or a gas. Plasma, the fourth state of matter, is rare on Earth. It sometimes can be found
The lower the energy of a substance, the interaction between its atoms and molecules.
 PHYSICAL STATES OF MATTER Kinetic Molecular Theory To understand the different states in which matter can exist, we need to understand something called the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter. Kinetic Molecular
PHYSICAL STATES OF MATTER Kinetic Molecular Theory To understand the different states in which matter can exist, we need to understand something called the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter. Kinetic Molecular
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change. Chapter 12: States of Matter
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 12: States of Matter CHAPTER 12 States of Matter Section 12.1 Section 12.2 Section 12.3 Section 12.4 Gases Forces of Attraction Liquids and Solids Phase Changes Click
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 12: States of Matter CHAPTER 12 States of Matter Section 12.1 Section 12.2 Section 12.3 Section 12.4 Gases Forces of Attraction Liquids and Solids Phase Changes Click
KINETIC PARTICLE THEORY
 KINETIC PARTICLE THEORY IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS: The mixing process in gases or solutions due to the random motion of particles is called Diffusion. The process by which a liquid changes into a vapour at
KINETIC PARTICLE THEORY IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS: The mixing process in gases or solutions due to the random motion of particles is called Diffusion. The process by which a liquid changes into a vapour at
SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, AND GASES
 CHAPTER 2 SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, AND GASES SECTION 2 1 States of Matter (pages 56-60) This section explains how shape, volume, and the motion of particles are useful in describing solids, liquids, and gases.
CHAPTER 2 SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, AND GASES SECTION 2 1 States of Matter (pages 56-60) This section explains how shape, volume, and the motion of particles are useful in describing solids, liquids, and gases.
Chapter 2, Lesson 5: Changing State Melting
 Chapter 2, Lesson 5: Changing State Melting Key Concepts Melting is a process that causes a substance to change from a solid to a liquid. Melting occurs when the molecules of a solid speed up enough that
Chapter 2, Lesson 5: Changing State Melting Key Concepts Melting is a process that causes a substance to change from a solid to a liquid. Melting occurs when the molecules of a solid speed up enough that
INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 7
 INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 7 EXPLAINING MELTING AND SOLIDIFYING A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals Students should be able to explain melting and solidifying, by reference to the molecular
INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 7 EXPLAINING MELTING AND SOLIDIFYING A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals Students should be able to explain melting and solidifying, by reference to the molecular
CHM Solids, Liquids, and Phase Changes (r15) Charles Taylor 1/9
 CHM 111 - Solids, Liquids, and Phase Changes (r15) - 2015 Charles Taylor 1/9 Introduction In CHM 110, we used kinetic theory to explain the behavior of gases. Now, we will discuss solids and liquids. While
CHM 111 - Solids, Liquids, and Phase Changes (r15) - 2015 Charles Taylor 1/9 Introduction In CHM 110, we used kinetic theory to explain the behavior of gases. Now, we will discuss solids and liquids. While
STATES OF MATTER STATES OF MATTER. The Four States of Matter 3/5/2015. Solid. Liquid Commonly found on Gas Earth Plasma
 Unit 10: States of Matter Lesson 10.1: States and Their Changes (Review) STATES OF MATTER The Four States of Matter Solid } Liquid Commonly found on Gas Earth Plasma STATES OF MATTER Based upon particle
Unit 10: States of Matter Lesson 10.1: States and Their Changes (Review) STATES OF MATTER The Four States of Matter Solid } Liquid Commonly found on Gas Earth Plasma STATES OF MATTER Based upon particle
STATES OF MATTER STATES OF MATTER. The Four States of Matter 3/5/2015
 The Four States of Matter Unit 10: States of Matter Lesson 10.1: States and Their Changes (Review) Solid } Liquid Commonly found on Gas Earth Plasma Based upon particle arrangement Based upon energy of
The Four States of Matter Unit 10: States of Matter Lesson 10.1: States and Their Changes (Review) Solid } Liquid Commonly found on Gas Earth Plasma Based upon particle arrangement Based upon energy of
Term Info Picture. Anything that has mass and takes up space; everything is made of matter.
 Characteristics, Changes, and States of Matter S8P1. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the structure and properties of matter. B. Develop and use models to describe the movement of particles
Characteristics, Changes, and States of Matter S8P1. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the structure and properties of matter. B. Develop and use models to describe the movement of particles
The physical state of a substance can be changed by increasing or decreasing its temperature.
 Chemistry Lecture #63: Changes of State The physical state of a substance can be changed by increasing or decreasing its temperature. For example, a solid substance can be converted into a liquid by heating
Chemistry Lecture #63: Changes of State The physical state of a substance can be changed by increasing or decreasing its temperature. For example, a solid substance can be converted into a liquid by heating
Notes: Matter and Change
 Name Chemistry-PAP Notes: Matter and Change Period: I. What is Chemistry? is the study of composition, structure, and properties of matter and energy associated with the changes it undergoes. is defined
Name Chemistry-PAP Notes: Matter and Change Period: I. What is Chemistry? is the study of composition, structure, and properties of matter and energy associated with the changes it undergoes. is defined
Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont3. Temperature & Heat
 Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont3 Temperature & Heat What are we going to study? Heat Transfer Phases of Matter The Kinetic Theory of Gases Thermodynamics Specific Heat (Capacity) Specific Heat Latent Heat
Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont3 Temperature & Heat What are we going to study? Heat Transfer Phases of Matter The Kinetic Theory of Gases Thermodynamics Specific Heat (Capacity) Specific Heat Latent Heat
WELCOME TO PERIOD 5: THERMAL ENERGY, THE MICROSCOPIC PICTURE. Homework #4 is due today at the beginning of class.
 WELCOME TO PERIOD 5: THERMAL ENERGY, THE MICROSCOPIC PICTURE Homework #4 is due today at the beginning of class. PHYSICS 1104 PERIOD 5 How are temperatures measured? How do atoms and molecules act at different
WELCOME TO PERIOD 5: THERMAL ENERGY, THE MICROSCOPIC PICTURE Homework #4 is due today at the beginning of class. PHYSICS 1104 PERIOD 5 How are temperatures measured? How do atoms and molecules act at different
Chemistry Review Unit 5 Physical Behavior of Matter
 Chemistry Review Phases of Matter, Changes of Phase, Substances, Mixtures, Solutions, Effect of Solute on Solution, Energy, Kinetics of Solids, Liquids and Gases Matter, Phases and Gas Laws 1. Matter is
Chemistry Review Phases of Matter, Changes of Phase, Substances, Mixtures, Solutions, Effect of Solute on Solution, Energy, Kinetics of Solids, Liquids and Gases Matter, Phases and Gas Laws 1. Matter is
Chapter 8. Chapter 8. Preview. Bellringer. Chapter 8. Particles of Matter. Objectives. Chapter 8. Particles of Matter, continued
 States of Matter Preview Bellringer Section 2 Behavior of Gases In the kitchen, you might find three different forms of water. What are these three forms of water, and where exactly in the kitchen would
States of Matter Preview Bellringer Section 2 Behavior of Gases In the kitchen, you might find three different forms of water. What are these three forms of water, and where exactly in the kitchen would
Chemistry Chapter 1 Test Review
 Chemistry Chapter 1 Test Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Put the LETTER of the correct answer in the blank. 1. Inorganic chemistry
Chemistry Chapter 1 Test Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Put the LETTER of the correct answer in the blank. 1. Inorganic chemistry
Kinetic Theory of Matter notes 2012
 Kinetic Theory of Matter notes 2012 Kinetic Theory of Matter 3 parts: 1) All matter is made up of and that act as tiny 2) These tiny particles are always in. State of matter depends on its molecular motion
Kinetic Theory of Matter notes 2012 Kinetic Theory of Matter 3 parts: 1) All matter is made up of and that act as tiny 2) These tiny particles are always in. State of matter depends on its molecular motion
Thermal energy. Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules.
 Thermal energy Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between substances. Until the
Thermal energy Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between substances. Until the
What Is Air Temperature?
 2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
Copyright 2015 Edmentum - All rights reserved. During which of the following phase changes is there a gain in energy? I.
 Study Island Copyright 2015 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 03/16/2015 Generated By: Kristina Brown 1. Examine the phase-change diagram below. During which of the following phase changes
Study Island Copyright 2015 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 03/16/2015 Generated By: Kristina Brown 1. Examine the phase-change diagram below. During which of the following phase changes
Matter and Thermal Energy
 Section States of Matter Can you identify the states of matter present in the photo shown? Kinetic Theory The kinetic theory is an explanation of how particles in matter behave. Kinetic Theory The three
Section States of Matter Can you identify the states of matter present in the photo shown? Kinetic Theory The kinetic theory is an explanation of how particles in matter behave. Kinetic Theory The three
Kinetic Theory of Matter. Matter & Energy
 Kinetic Theory of Matter Matter & Energy 1 Kinetic Theory of Matter All matter is made up of atoms and molecules that act as tiny particles. 2 Kinetic Theory of Matter These tiny particles are always in
Kinetic Theory of Matter Matter & Energy 1 Kinetic Theory of Matter All matter is made up of atoms and molecules that act as tiny particles. 2 Kinetic Theory of Matter These tiny particles are always in
Chapter 8 notes. 8.1 Matter. 8.1 objectives. Earth Chemistry
 Chapter 8 notes Earth Chemistry 8.1 Matter 8.1 objectives Compare chemical properties and physical properties of matter. Describe the basic structure of an atom. Compare atomic number, mass number, and
Chapter 8 notes Earth Chemistry 8.1 Matter 8.1 objectives Compare chemical properties and physical properties of matter. Describe the basic structure of an atom. Compare atomic number, mass number, and
Chapter 3. Preview. Section 1 Three States of Matter. Section 2 Behavior of Gases. Section 3 Changes of State. States of Matter.
 States of Matter Preview Section 1 Three States of Matter Section 2 Behavior of Gases Section 3 Changes of State Concept Mapping Section 1 Three States of Matter Bellringer In the kitchen, you might find
States of Matter Preview Section 1 Three States of Matter Section 2 Behavior of Gases Section 3 Changes of State Concept Mapping Section 1 Three States of Matter Bellringer In the kitchen, you might find
Matter Notes (Part 1)
 Matter Notes (Part 1) Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Matter is identified by its properties; shape, size, color, mass, etc. There are two classifications of properties - physical
Matter Notes (Part 1) Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Matter is identified by its properties; shape, size, color, mass, etc. There are two classifications of properties - physical
Conceptual Chemistry
 Conceptual Chemistry Objective 1 Describe, at the molecular level, the difference between a gas, liquid, and solid phase. Solids Definite shape Definite volume Particles are vibrating and packed close
Conceptual Chemistry Objective 1 Describe, at the molecular level, the difference between a gas, liquid, and solid phase. Solids Definite shape Definite volume Particles are vibrating and packed close
States of Matter. What physical changes and energy changes occur as matter goes from one state to another?
 Name States of Matter Date What physical changes and energy changes occur as matter goes from one state to another? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about states of
Name States of Matter Date What physical changes and energy changes occur as matter goes from one state to another? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about states of
Content Standard 1: Motion: The velocity of an object is the rate of change of its position. National Science Standard
 1: Motion: The velocity of an object is the rate of change of its position. s 1.a) Position is defined relative to some choice of standard reference point and a set of reference directions. Identifying
1: Motion: The velocity of an object is the rate of change of its position. s 1.a) Position is defined relative to some choice of standard reference point and a set of reference directions. Identifying
THE CORPUSCULAR NATURE OF MATTER AND ITS PHYSICAL STATES
 THE CORPUSCULAR NATURE OF MATTER AND ITS PHYSICAL STATES In this unit we are going to study the matter from a microscopic point of view using the kinetic theory. We will understand the properties of the
THE CORPUSCULAR NATURE OF MATTER AND ITS PHYSICAL STATES In this unit we are going to study the matter from a microscopic point of view using the kinetic theory. We will understand the properties of the
What Do You Think? Investigate GOALS. Part A: Freezing Water
 Activity 5 Freezing Water GOALS In this activity you will: Determine the freezing point of water. Show graphically what happens to the temperature as water is cooled to freezing and while it is freezing.
Activity 5 Freezing Water GOALS In this activity you will: Determine the freezing point of water. Show graphically what happens to the temperature as water is cooled to freezing and while it is freezing.
Do Now Monday, January 23, 201
 Do Now Monday, January 23, 201 What do you recall about states of matter? Write your answer using complete sentences. 3.5 minutes Do Now Check By the end of the day today, IWBAT Describe the various states
Do Now Monday, January 23, 201 What do you recall about states of matter? Write your answer using complete sentences. 3.5 minutes Do Now Check By the end of the day today, IWBAT Describe the various states
The Kinetic Theory of Matter. Temperature. Temperature. Temperature. Temperature. Chapter 6 HEAT
 The Kinetic Theory of Matter Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 6 HEAT Kinetic Theory of Matter: Matter is made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules) that are always in
The Kinetic Theory of Matter Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 6 HEAT Kinetic Theory of Matter: Matter is made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules) that are always in
Chapter 3. States of Matter
 Chapter 3 States of Matter 1. Solid 2. Liquid 3. Gas States of Matter Two More (discuss later) Plasma Bose-Einstein condensate States of Matter Solid (definite shape and volume) Particles are tightly packed
Chapter 3 States of Matter 1. Solid 2. Liquid 3. Gas States of Matter Two More (discuss later) Plasma Bose-Einstein condensate States of Matter Solid (definite shape and volume) Particles are tightly packed
Physical Science Exam 3 Study Guide. Dr. Karoline Rostamiani. Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 Section 1 States of Matter What is matter made of? What are the three most common states of matter? How do particles behave in each state of matter? Solids, Liquids, and Gases Materials can be
Chapter 3 Section 1 States of Matter What is matter made of? What are the three most common states of matter? How do particles behave in each state of matter? Solids, Liquids, and Gases Materials can be
Thermochemistry. The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state.
 Energy Thermochemistry The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state. The Nature of Energy Energy - the ability to do work or produce heat Energy is stored in the
Energy Thermochemistry The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state. The Nature of Energy Energy - the ability to do work or produce heat Energy is stored in the
Phase Change: solid to liquid. Melting
 Phase Change: solid to liquid Melting Most solids shrink in size when frozen. What substance is an exception and actually expands? water Use the phase diagram below to answer the following question. What
Phase Change: solid to liquid Melting Most solids shrink in size when frozen. What substance is an exception and actually expands? water Use the phase diagram below to answer the following question. What
Properties and Structure of Matter
 Properties and Structure of Matter Chapter 10 You can use a spider map to organize the main ideas and supporting details of a topic such as properties of matter. Look at the example shown below. The central
Properties and Structure of Matter Chapter 10 You can use a spider map to organize the main ideas and supporting details of a topic such as properties of matter. Look at the example shown below. The central
8TH GRADE SCIENCE CONTENT STANDARDS
 8TH GRADE SCIENCE CONTENT STANDARDS (simplified from CA State Science Standards) DAVID GREENMYER COMPUTECH MIDDLE SCHOOL 1. MOTION a) In order to describe your position, you must use another position (reference
8TH GRADE SCIENCE CONTENT STANDARDS (simplified from CA State Science Standards) DAVID GREENMYER COMPUTECH MIDDLE SCHOOL 1. MOTION a) In order to describe your position, you must use another position (reference
Chemistry Topic 4. Physical Behavior of Matter
 Chemistry Topic 4 Physical Behavior of Matter 11/30 Chemistry Unit 4 Physical Behavior of Matter Aim: What are the 3 states of matter? Obj: SWBAT compare and contrast the states of matter Do now: 2H 2
Chemistry Topic 4 Physical Behavior of Matter 11/30 Chemistry Unit 4 Physical Behavior of Matter Aim: What are the 3 states of matter? Obj: SWBAT compare and contrast the states of matter Do now: 2H 2
Water SECTION The properties of water in all phases are determined by its structure.
 SECTION 10.5 Water Water commonly exists in all three physical states on Earth, where it is by far the most abundant liquid. It covers nearly three-quarters of Earth s surface. Water is an essential component
SECTION 10.5 Water Water commonly exists in all three physical states on Earth, where it is by far the most abundant liquid. It covers nearly three-quarters of Earth s surface. Water is an essential component
States of Matter 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016
 States of Matter 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 States of Matter 2 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are the three states of matter? 3 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 At any given temperature, all substances exist
States of Matter 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 States of Matter 2 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are the three states of matter? 3 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 At any given temperature, all substances exist
4. Every CHANGE in matter includes a change in, which is conserved in a chemical reaction and. TRANSFORMED from one form to another.
 Part C: Lesson 1.4 - Read pages 20-29 to answer these questions. Add to notes - 1. A physical change alters the form or appearance of matter, such as Change in size, a change in SIZE or. SHAPE shape, or
Part C: Lesson 1.4 - Read pages 20-29 to answer these questions. Add to notes - 1. A physical change alters the form or appearance of matter, such as Change in size, a change in SIZE or. SHAPE shape, or
The (Almost) Modern Atom Model. SUMMARY from previous lecture Energy comes in different forms. ENERGY IS ALWAYS CONSERVED.
 Announcements The midterm 1 exam scores will be available on OWL at 5:00 PM today. Login to OWL and click the Course Grades link to see your score. Your score has already been scaled to correspond to the
Announcements The midterm 1 exam scores will be available on OWL at 5:00 PM today. Login to OWL and click the Course Grades link to see your score. Your score has already been scaled to correspond to the
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Physics 5 - Thermal Properties of Matter Thermal Expansion You need to know thermal expansions for solids, liquids, and gases, and their applications. Thermal
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Physics 5 - Thermal Properties of Matter Thermal Expansion You need to know thermal expansions for solids, liquids, and gases, and their applications. Thermal
Chapter 2: Properties of Matter Student Outline 2.1 Classifying Matter A. Pure Substances
 Name: Date: Physical Science Period: Chapter 2: Properties of Matter Student Outline GA Performance Standards SPS1. Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. SPS2. Students will
Name: Date: Physical Science Period: Chapter 2: Properties of Matter Student Outline GA Performance Standards SPS1. Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. SPS2. Students will
