Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 12 Molecular Shapes
|
|
|
- Agnes Melton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chem 115 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 12 Mlecular Shapes Why? Cntrary t the impressin that Lewis structures may give, many mlecules have threedimensinal gemetries. These mlecular shapes are very imprtant t understanding hw mlecules interact with each ther, bth chemically and physically. Althugh the Lewis structures themselves d nt cnvey shape infrmatin, they can be used as the starting pint fr applying a cnceptually simple but pwerful apprach t predicting mlecular gemetries. This methd is called the Valence Shell Electrn Repulsin Thery, r VSEPR fr shrt. Knwing the shape f a mlecule enables us t predict whether r nt it has an electrical plarity, which is an imprtant prperty determining hw the species interacts with ther mlecules. Learning Objective Understand the basis f the VSEPR thery. Knw the expected gemetries fr ne thrugh six electrn dmains abut a central atm Understand hw bnd pairs and lne pairs abut a central atm interact t prduce the mlecular shape Knw hw bnd plarity and mlecular shape cmbine t make a mlecule plar r nnplar. Success Criteria Be able t use a Lewis structure and VSEPR thery t predict the shape f mlecules Be able t sketch the shapes f simple mlecules Be able t name electrn dmain and mlecular shape gemetries f simple mlecules Be able t predict whether a particular mlecule is plar r nnplar Prerequisite Have read sectins
2 Infrmatin (Basic Dmain Shapes frm VSEPR Thery) One f the mst successful appraches t predicting the shapes f mlecules is based almst slely n cnsideratins f hw best t minimize electrn-pair repulsins abut a central atm. This apprach, which was riginated by Nyhlm and Gillespie in the 1950's, has becme knwn 1 as the Valence Shell Electrn Pair Repulsin Thery, r VSEPR. thery. The fundamental premise f this thery can be stated as fllws: Electrns in bnded atms ccupy spatially riented rbitals in such a way as t minimize electrn-electrn repulsins arising mainly frm electrstatic (culmbic) frces. The apprach is remarkably accurate in predicting the basic shapes f mlecules f nntransitin elements, althugh sme details f bnd angle and bnd length are nt well explained by electrn repulsin alne. At this pint we will nt be cncerned with the identity f the spatially riented rbitals. Hwever, assuming that such rbitals are available, we can determine fr varius numbers f pairs f electrns abut a central atm the mst favrable electrn pair gemetry t minimize electrn-electrn repulsins. T illustrate the apprach, let us cnsider a number f mlecules in which all f the valence electrns abut the central atm are engaged in bnd frmatin with uter-lying (pendant) atms. Cnsider BeCl, fr which the Lewis dt structure is 2 There are tw pairs f electrns arund the central Be atm. If they are riented 180 frm each ther their repulsins will be minimized. Therefre, the best electrn pair gemetry fr tw pairs is a linear arrangement. Bth pairs are invlved in frming single bnds in BeCl 2, s the resulting mlecular gemetry r shape f the mlecule is als linear. Cnsider BCl 3, fr which the Lewis dt structure is This has three pairs arund the central B atm. Electrn-pair repulsins are minimized by placing these three pairs at 120 apart in a plane, called a trignal planar arrangement. All three 1 Mre recently, Gillespie has prpsed renaming this Electrn Dmain Thery r ED thery, but mst chemists persist in calling it VSEPR thery. See R. J. Gillespie. J. Chem. Educ. 1992, 69, 116.
3 pairs are invlved in bnd frmatin, s the mlecular shape is trignal planar, as a result f the electrn pair gemetry. Cnsider methane, CH 4, fr which the Lewis dt structure is Cntrary t what this mdel seems t suggest, a square planar arrangement f the fur pairs abut carbn is nt the best fr minimizing electrn repulsins. By assuming the threedimensinal tetrahedral arrangement, the pairs will be in psitins apart. Thus methane is tetrahedral. Given the prevalence f an ctet abut a central atm, this electrn pair gemetry ccurs in many cmpunds. It is a highly symmetrical arrangement in which all fur psitins are equivalent. When representing this three-dimensin structure in a tw-dimensinal sketch, we ften emply drawings such as the fllwing:: The slid lines are psitins in the plane f the page. The slid wedge is a psitin cming ut f the plane f the page, and the dtted line is a psitin ging back belw the plane f the page. It is imprtant t realize that regardless f the drawing, any psitin is surrunded by three thers, all making an angle f t each ther. N psitin is acrss frm any ther, as culd be the case in a square planar arrangement. Cnsider PCl 5. This is a case f hypervalence, with five pairs f electrns abut the central atm. The best electrn pair gemetry is a trignal bipyramid. 2 A trignal bipyramid has tw kinds f psitins, which are nt equivalent t each ther. The tw axial psitins make a 180 angle t each ther and a 90 t the plane f the three equatrial psitins. The equatrial psitins frm a 120 angle between each ther. equivalent. 2 This is the nly basic gemetry we will cnsider in which all psitins are nt
4 Cnsider SF 6, a hypervalent mlecule with six pairs abut the central sulfur atm. The best electrn pair gemetry is achieved by placing all pairs at 90 t ne anther, as with the axes f a Cartesian crdinate system. This arrangement is ctahedral. Unlike the trignal bipyramid, all psitins in the ctahedrn are equivalent. Electrn pairs invlved in multiple bnd frmatin ccupy the same regin f space. Therefre, all pairs in a duble r triple bnd functin in the same way as a single pair in determining gemetry. Fr this reasn, we shuld lk at the number f electrn dmains abut the central atm, rather than the number f electrn pairs, particularly when multiple bnds are invlved. Fr example, frmaldehyde, H2CO, has the fllwing Lewis structure, with three electrn dmains arund the central atm Althugh there are fur pairs abut the central carbn atm, they are gruped int nly three dmains, tw fr single C H bnds and a third fr the C=O bnd. The best arrangement t minimize repulsins is trignal planar. All bnd angles will nt be perfectly 120. The larger xygen atm frces the tw hydrgen atms tgether slightly, s that the H-C-H angle is smewhat less than 120. Similarly, HCN is a linear mlecule because the fur pairs arund the central carbn atm are arranged in tw dmains:
5 H C N: The shapes f mlecules that are resnance hybrids can be deduced frm any ne f the hypthetical resnance frms. Fr example, any ne f the three principal resnance frms f the nitrate in shws fur pairs arund the central nitrgen atm arranged in three dmains: Recall that in resnance frms like these, there are n real duble bnds, and all the N O bnds are equivalent (bnd rder f 1a). Therefre, the structure f the nitrate in is truly trignal planar, with 120 O N O angles. Key Questins 1. Give the names fr the shapes f the dmain gemetries fr tw thrugh six regins f electrn density abut a central atm. 2. Draw Lewis structures fr the fllwing mlecules, and predict the the shapes n the basis f VSEPR cnsideratins: SnH, CO, AsF, Cl CO Infrmatin (Shapes f Mlecules with Lne Pairs) In many mlecules sme pairs f valence electrns arund the central atm may be nn-bnding lne pairs. In these cases, the electrn dmain arrangements will be the same fr the ttal number f electrn pairs, but the mlecular shape will be different. Keep in mind that the shape f a mlecule refers t the gemetrical arrangement f its atms, nt the dmain gemetry f its electrn pairs. Hwever, the resulting shape fr mlecules with lne pairs n the central atm will be based n the electrn dmain gemetries we have just seen. Bnd angles in these mlecules will ften deviate frm the ideal angles f the electrn dmain gemetries. This is the result f differences in the strengths f repulsins between electrns invlved in bnd frmatin and thse that are nt. In general, the strengths f electrn pair repulsins decline in the rder lne pair - lne pair > lne pair - bnd pair > bnd pair - bnd pair When adding lne pairs in electrn dmain gemetries in which all psitins are equivalent the arrangement that clearly minimizes lne pair - lne pair repulsin results. We will nt g thrugh every pssible shape here, but the case f NH 3 serves t illustrate the effects f lne pair - bnd pair repulsins n the resulting shape. The Lewis dt structure is shwn belw:
6 With fur dmains abut the central N atm, the electrn dmain gemetry is tetrahedral. But the shape f the mlecule cannt be described as tetrahedral, because there are nly three bnds. The cmbinatin f three bnd pairs and ne lne pair (3 b.p. + 1 l.p.) results in a tripd-like arrangement f the atms, called a trignal pyramid. The lne-pair - bnd-pair repulsins, being strnger than bnd-pair repulsins, cause all H N H angles t clse dwn frm the ideal f the tetrahedrn, becming ~107 in ammnia. Cases invlving five dmains abut a central atm require sme care in placing any lne pairs. Such hypervalent structures are all based n a trignal bipyramidal (tbp) gemetry f the electrn dmains. But as we previusly nted, there are tw kinds f psitins fr tbp: axial and equatrial. Fr mst cases in which the central atm is a main-grup element, the axial psitins are smewhat lnger than the equatrial psitins. A lne pair is assciated with nly ne nucleus, whereas a bnd pair is assciated with tw. Therefre, in structures based n a tbp dmain gemetry, any lne pair will be clser t the ne nucleus with which it is assciated if it is in ne f the shrter equatrial psitins. Therefre, when building shapes based n a tbp dmain gemetry, always place the lne pairs in the equatrial psitins. SF 4 illustrates the effect n shape f placing a lne pair in an equatrial psitin f a tbp dmain gemetry. Withut careful cnsideratin, SF 4 might seem t be a tetrahedral mlecule, but as the Lewis dt structure shws it is a hypervalent case with five electrn dmains..
7 This is a case f 4 b.p. + 1 l.p. Placing the lne pair in an equatrial psitin results in the fllwing mlecular shape, with the rientatin f the mlecule flipped in the secnd sketch: When flipped, as shwn n the right, the shape resembles a playgrund see-saw with the tw equatrial-type psitins functining as the fulcrum and the tw axial-type psitins frming the plank. The fficial name f this is irregular tetrahedrn, althugh mathematicians call the 3 related slid plygn a disphenid. Nte that SF 4 has tw kinds f bnds with tw different lengths: the tw axial bnds f the tbp and the tw remaining equatrial bnds f the tbp. The lne-pair repulsins cause the angle between the tw axial-type bnds t be less than 180, and cause the angle between the tw equatrial-type bnds t be less than 120. The table in Appendix A summarizes the expected shapes fr all cmbinatins f bnd pairs (b.p.) and lne pairs (l.p.) fr tw thrugh six electrn dmains (ED). All f these shapes are illustrated in Tables 9.2 and 9.3 f yur text. Be sure that yu becme s familiar with all the pssibilities that yu d nt need t refer t Appendix A r a similar table t determine the shape f a mlecule by VSEPR thery. Anther useful way t rganize yur thinking abut mlecular gemetries is t cnsider what the pssible shapes are fr a certain number f pendant atms attached t a central atm. This helps rule ut impssible shapes at the start. The table in Appendix B rearranges the infrmatin in Appendix A n the basis f mlecular frmulas. Fr example, if a mlecule has a frmula MX 2, the fact that it is cmpsed f nly three atms means that they are either all aligned (linear) r they are nt (bent), regardless f the dmain gemetry that gave rise t the shape. N ther shapes are pssible. It makes n sense t say that a mlecule with a frmula MX 2 is trignal planar, tetrahedral, r trignal bipyramidal just because we can identify three, fur, r five dmains abut the central M atm. The first tw cases wuld be bent, and the last wuld be linear. Beynd this, we shuld expect a X M X angle slightly less than 120 if the shape is based n three dmains, and slightly less than if based n fur dmains. 3See
8 Key Questins 3. Fr each f the fllwing mlecules r ins, sketch the shape and name it. Yu shuld start with a valid Lewis structure in each case, befre applying VSEPR cnsideratins. + SeCl 4, I 3, PSCl 3, IF 4, IF 4, PH 2, N 3, PH4 4. Describe the structure and bnding f the nitrite in, NO 2. Infrmatin (Mlecular Plarity and Diple Mments) The plarity f a mlecule is measured as its diple mment, defined as ì = äd + where ì is the diple mment, ä is the charge n each end f the mlecule (ä and ä ), separated acrss the mlecule by a distance d. The units f diple mment are the debye (D), defined as x 10 C m. (C = culmb) In a diatmic mlecule the charges, which are generally much less than unit charges, reside n the tw atms and d is their internuclear separatin (bnd length). Fr a diatmic mlecule the mdel is smething like the fllwing: Fr heternuclear diatmic mlecules, the bnd has plarity, s the mlecule will have a diple mment. Thus, all heternuclear diatmic mlecules are plar. All hmnuclear diatmic mlecules have n diple mment. The fllwing data illustrate: Mlecule ì Mlecule ì H-H 0 D H-F 1.82 D F-F 0 D H-Cl 1.08 D Cl-Cl 0 D H-I 0.44 D Fr plyatmic mlecules, plarity depends n bth shape and cmpsitin. A mlecule is nnplar when all individual bnd plarities are cunterbalanced by ther identical bnd plarities. A mlecule is plar when any ne f its individual bnd plarities is nt cunterbalanced by identical bnd plarities. Lack f cunter balancing plarities may result frm a less symmetrical shape (shape). Lack f cunterbalancing plarities als may result frm
9 a unique bnd in the mlecule, having a different bnd strength r bnding t a different element (cmpsitin). In highly symmetric binary mlecules (tw elements), individual bnd plarities may cancel, leaving the mlecule with n net diple mment, as in all f the fllwing cases. If a binary mlecule has a gemetry that gives it a sense f up r dwn r right and left it is plar. If a ternary mlecule has its bnds asymmetrically arranged, it may be plar even thugh its shape wuld be nnplar fr a binary mlecule. The fllwing cases have shapes that wuld be nnplar fr binary mlecules but which are plar because there are tw different kinds f bnds arund the central atm that are nt symmetrically arranged.
10 Key Questins 5. Fr all the mlecules r ins whse shapes yu determined in Key Questin 3. indicate whether r nt the species is plar. 6. Cnsider the fllwing Lewis structures fr sme simple rganic cmpunds. (Lne pairs n pendant atms have been mitted fr simplicity.) Redraw each f these n the basis f VSEPR cnsideratins, and indicate whether r nt the mlecule is plar A certain cmpund with a frmula AB is fund t be plar. Mrever, it is determined that there are tw different bnd lengths, tw lng nes and tw shrt nes. What is the prbable shape f the mlecule? Explain yur reasning.
11 Appendix A: Shapes f Mlecules fr Varius Electrn Dmain (ED) Gemetries ED Dmain Gemetry Bnd Dmains Lne Pairs Mlecular Shape Examples 2 linear 2 0 linear MX2 BeF 2, CO2 3 trignal planar 3 0 trignal planar MX3 BF 3, NO bent MX 2 (<120 ) SnCl 2, NO2 4 tetrahedral 4 0 tetrahedral MX4 CH4 3 1 trignal pyramidal MX3 NH3 2 2 bent MX 2 (<109.5 ) H2O 5 trignal bipyramidal 5 0 trignal bipyramidal MX5 PCl5 4 1 irregular tetrahedrn MX4 SF4 3 2 T-shaped MX3 ClF3 2 3 linear MX2 XeF2 6 ctahedral 6 0 ctahedral MX6 SF6 5 1 square pyramid MX5 IF5 4 2 square planar MX4 XeF4 Nte: In this table, bnd means a linkage between tw atms in a mlecule. Thus, a single-, duble-, r triple-bnd cnstitutes nly ne bnd.
12 Appendix B: Pssible Shapes f Mlecules with Frmulas MX n, n = 2 6 Frmula Case Shape Example MX2 2 bnds + 0 lne pairs linear BeF2 2 bnds + 1 lne pair bent (<120 ) SnCl 2 2 bnds + 2 lne pairs bent (<109.5 ) H2O 2 bnds + 3 lne pairs linear XeF 2 MX3 3 bnds + 0 lne pairs trignal planar BF3 3 bnds + 1 lne pair trignal pyramidal NH 3 3 bnds + 2 lne pairs T-shape ClF 3 MX4 4 bnds + 0 lne pairs tetrahedral CH4 4 bnds + 1 lne pair irregular tetrahedrn SF 4 4 bnds + 2 lne pairs square planar XeF 4 MX5 5 bnds + 0 lne pairs trignal bipyramid (tbp) PF5 5 bnds + 1 lne pair square pyramid IF 5 MX6 6 bnds + 0 lne pairs ctahedral SF6 Nte: In this table, bnd means a linkage between tw atms in a mlecule. Thus, a single-, duble-, r triple-bnd cnstitutes nly ne bnd.
4 electron domains: 3 bonding and 1 non-bonding. 2 electron domains: 2 bonding and 0 non-bonding. 3 electron domains: 2 bonding and 1 non-bonding
 [4.3D VSEPR] pg. 1 f 7 Curriculum The use f VSEPR thery t predict the electrn dmain gemetry and the mlecular gemetry fr species with tw, three and fur electrn dmains. Shapes f species are determined by
[4.3D VSEPR] pg. 1 f 7 Curriculum The use f VSEPR thery t predict the electrn dmain gemetry and the mlecular gemetry fr species with tw, three and fur electrn dmains. Shapes f species are determined by
Chapter 8 Predicting Molecular Geometries
 Chapter 8 Predicting Mlecular Gemetries 8-1 Mlecular shape The Lewis diagram we learned t make in the last chapter are a way t find bnds between atms and lne pais f electrns n atms, but are nt intended
Chapter 8 Predicting Mlecular Gemetries 8-1 Mlecular shape The Lewis diagram we learned t make in the last chapter are a way t find bnds between atms and lne pais f electrns n atms, but are nt intended
Chemistry 20 Lesson 11 Electronegativity, Polarity and Shapes
 Chemistry 20 Lessn 11 Electrnegativity, Plarity and Shapes In ur previus wrk we learned why atms frm cvalent bnds and hw t draw the resulting rganizatin f atms. In this lessn we will learn (a) hw the cmbinatin
Chemistry 20 Lessn 11 Electrnegativity, Plarity and Shapes In ur previus wrk we learned why atms frm cvalent bnds and hw t draw the resulting rganizatin f atms. In this lessn we will learn (a) hw the cmbinatin
ATOMIC ORBITAL MODEL OF THE ATOM Be able to draw rough sketches of s, p and d orbitals with different principal quantum numbers
 Chapter 7 Atmic Structure and Peridicity ATOMIC ORBITAL MODEL OF THE ATOM Be able t draw rugh sketches f s, p and d rbitals with different principal quantum numbers ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATIONS Knw the difference
Chapter 7 Atmic Structure and Peridicity ATOMIC ORBITAL MODEL OF THE ATOM Be able t draw rugh sketches f s, p and d rbitals with different principal quantum numbers ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATIONS Knw the difference
Name Honors Chemistry / /
 Name Hnrs Chemistry / / Beynd Lewis Structures Exceptins t the Octet Rule Mdel Hydrgen is an exceptin t the ctet rule because it fills its uter energy level with nly 2 electrns. The secnd rw elements B
Name Hnrs Chemistry / / Beynd Lewis Structures Exceptins t the Octet Rule Mdel Hydrgen is an exceptin t the ctet rule because it fills its uter energy level with nly 2 electrns. The secnd rw elements B
Name: Period: Date: BONDING NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
Name: Period: Date: BONDING NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
Principles of Organic Chemistry lecture 5, page 1
 Principles f Organic Chemistry lecture 5, page 1 Bnding Mdels Fact: electrns hld mlecules tgether. Theries: mre than ne way t cnceptualize bnding. Let s fllw Carrll in the cnsideratin f tw theries f bnding.
Principles f Organic Chemistry lecture 5, page 1 Bnding Mdels Fact: electrns hld mlecules tgether. Theries: mre than ne way t cnceptualize bnding. Let s fllw Carrll in the cnsideratin f tw theries f bnding.
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts
 Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bnding: General Cncepts Types f Chemical Bnds Infrmatin abut the strength f a bnding interactin is btained by measuring the bnd energy, which is the energy required t
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bnding: General Cncepts Types f Chemical Bnds Infrmatin abut the strength f a bnding interactin is btained by measuring the bnd energy, which is the energy required t
Trimester 2 Exam 3 Study Guide Honors Chemistry. Honors Chemistry Exam 3 Review
 Trimester 2 Exam 3 Study Guide Hnrs Chemistry BOND POLARITY Hnrs Chemistry Exam 3 Review Identify whether a bnd is plar r nnplar based ff difference in electrnegativity btwn 2 atms (electrnegativity values
Trimester 2 Exam 3 Study Guide Hnrs Chemistry BOND POLARITY Hnrs Chemistry Exam 3 Review Identify whether a bnd is plar r nnplar based ff difference in electrnegativity btwn 2 atms (electrnegativity values
SCIENCE 10: CHEMISTRY,
 , 1 Atmic Thery and Bnding The Nucleus - The particles that make up an atm are called subatmic particles - The three subatmic particles are prtns, neutrns and electrns. - Prtns, which have a +1 (psitive)
, 1 Atmic Thery and Bnding The Nucleus - The particles that make up an atm are called subatmic particles - The three subatmic particles are prtns, neutrns and electrns. - Prtns, which have a +1 (psitive)
Midterm Review Notes - Unit 1 Intro
 Midterm Review Ntes - Unit 1 Intr 3 States f Matter Slid definite shape, definite vlume, very little mlecular mvement Liquid definite vlume, takes shape f cntainer, mlecules mve faster Gas des nt have
Midterm Review Ntes - Unit 1 Intr 3 States f Matter Slid definite shape, definite vlume, very little mlecular mvement Liquid definite vlume, takes shape f cntainer, mlecules mve faster Gas des nt have
lecture 5: Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
 lecture 5: Nuclephilic Substitutin Reactins Substitutin unimlecular (SN1): substitutin nuclephilic, unimlecular. It is first rder. The rate is dependent upn ne mlecule, that is the substrate, t frm the
lecture 5: Nuclephilic Substitutin Reactins Substitutin unimlecular (SN1): substitutin nuclephilic, unimlecular. It is first rder. The rate is dependent upn ne mlecule, that is the substrate, t frm the
Chem 111 Summer 2013 Key III Whelan
 Chem 111 Summer 2013 Key III Whelan Questin 1 6 Pints Classify each f the fllwing mlecules as plar r nnplar? a) NO + : c) CH 2 Cl 2 : b) XeF 4 : Questin 2 The hypthetical mlecule PY 3 Z 2 has the general
Chem 111 Summer 2013 Key III Whelan Questin 1 6 Pints Classify each f the fllwing mlecules as plar r nnplar? a) NO + : c) CH 2 Cl 2 : b) XeF 4 : Questin 2 The hypthetical mlecule PY 3 Z 2 has the general
Interference is when two (or more) sets of waves meet and combine to produce a new pattern.
 Interference Interference is when tw (r mre) sets f waves meet and cmbine t prduce a new pattern. This pattern can vary depending n the riginal wave directin, wavelength, amplitude, etc. The tw mst extreme
Interference Interference is when tw (r mre) sets f waves meet and cmbine t prduce a new pattern. This pattern can vary depending n the riginal wave directin, wavelength, amplitude, etc. The tw mst extreme
Name: Period: Date: PERIODIC TABLE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: PERIODIC TABLE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
Name: Perid: Date: PERIODIC TABLE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
Name: Period: Date: PERIODIC TABLE NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: PERIODIC TABLE NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
Name: Perid: Date: PERIODIC TABLE NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
Group Theory Problems
 Grup Thery Prblems The fllwing table shws the vibratinal frequencies f CH. Assuming CH belngs t the T d pint grup, fill in the gaps in the table. Use fr and fr t designate type f vibratin. tretchorend
Grup Thery Prblems The fllwing table shws the vibratinal frequencies f CH. Assuming CH belngs t the T d pint grup, fill in the gaps in the table. Use fr and fr t designate type f vibratin. tretchorend
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 3 - Solutions Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, Solids, and Solutions
 Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 3 - Slutins Intermlecular Frces, Liquids, Slids, and Slutins Key Questins 1. Is the average kinetic energy f mlecules greater r lesser than the energy f intermlecular frces
Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 3 - Slutins Intermlecular Frces, Liquids, Slids, and Slutins Key Questins 1. Is the average kinetic energy f mlecules greater r lesser than the energy f intermlecular frces
Matter Content from State Frameworks and Other State Documents
 Atms and Mlecules Mlecules are made f smaller entities (atms) which are bnded tgether. Therefre mlecules are divisible. Miscnceptin: Element and atm are synnyms. Prper cnceptin: Elements are atms with
Atms and Mlecules Mlecules are made f smaller entities (atms) which are bnded tgether. Therefre mlecules are divisible. Miscnceptin: Element and atm are synnyms. Prper cnceptin: Elements are atms with
In the spaces provided, explain the meanings of the following terms. You may use an equation or diagram where appropriate.
 CEM1405 2007-J-2 June 2007 In the spaces prvided, explain the meanings f the fllwing terms. Yu may use an equatin r diagram where apprpriate. 5 (a) hydrgen bnding An unusually strng diple-diple interactin
CEM1405 2007-J-2 June 2007 In the spaces prvided, explain the meanings f the fllwing terms. Yu may use an equatin r diagram where apprpriate. 5 (a) hydrgen bnding An unusually strng diple-diple interactin
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 10 Alkenes (I) Chem alkenes hydrocarbons containing a C=C (not in a benzene ring)
 I. Intrductin t Alkenes Classifying Alkenes Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 10 Alkenes (I) Chem 2310 There are several categries that can be used t describe cmpunds cntaining carbn-carbn duble bnds. alkenes
I. Intrductin t Alkenes Classifying Alkenes Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 10 Alkenes (I) Chem 2310 There are several categries that can be used t describe cmpunds cntaining carbn-carbn duble bnds. alkenes
RECENT studies undertaken in this Institute on the crystal structure
 522 Structural similarities f sme secndary lead minerals By L. FANFANI and P. F. ZANAZZI Istitut di Mineralgia dell 'Universita di Perugia, Perugia (Italy) [Taken as read 2 Nvember 1967] Summary. Sme structural
522 Structural similarities f sme secndary lead minerals By L. FANFANI and P. F. ZANAZZI Istitut di Mineralgia dell 'Universita di Perugia, Perugia (Italy) [Taken as read 2 Nvember 1967] Summary. Sme structural
Semester 1 Honors Chemistry Notebook (unit 1)
 Semester 1 Hnrs Chemistry Ntebk (unit 1) Basic infrmatin Chemistry: study f matter Matter: has mass and takes up space Organized by using the peridic table cntains elements Prtns, neutrns, and electrns
Semester 1 Hnrs Chemistry Ntebk (unit 1) Basic infrmatin Chemistry: study f matter Matter: has mass and takes up space Organized by using the peridic table cntains elements Prtns, neutrns, and electrns
Thermodynamics Partial Outline of Topics
 Thermdynamics Partial Outline f Tpics I. The secnd law f thermdynamics addresses the issue f spntaneity and invlves a functin called entrpy (S): If a prcess is spntaneus, then Suniverse > 0 (2 nd Law!)
Thermdynamics Partial Outline f Tpics I. The secnd law f thermdynamics addresses the issue f spntaneity and invlves a functin called entrpy (S): If a prcess is spntaneus, then Suniverse > 0 (2 nd Law!)
Course/ Subject: Chemistry I Grade: Teacher: Hill Oberto Month: September/October (6-8 weeks)
 Curse/ Subject: Chemistry I Grade: 11-12 Teacher: Hill Obert Mnth: September/Octber (6-8 weeks) Natinal Benchmark being addressed State Standards Skills/Cmpetencies Assessment Matter Unit I.All matter
Curse/ Subject: Chemistry I Grade: 11-12 Teacher: Hill Obert Mnth: September/Octber (6-8 weeks) Natinal Benchmark being addressed State Standards Skills/Cmpetencies Assessment Matter Unit I.All matter
QCE Chemistry. Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, Chemistry: Revision Notes. By Sophie (1 ATAR)
 QCE Chemistry Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, 2017 11 Chemistry: Revisin Ntes By Sphie (1 ATAR) Pwered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.rg) Yur ntes authr, Sphie. Sphie achieved an ATAR f 1 in 2016 while
QCE Chemistry Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, 2017 11 Chemistry: Revisin Ntes By Sphie (1 ATAR) Pwered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.rg) Yur ntes authr, Sphie. Sphie achieved an ATAR f 1 in 2016 while
A Chemical Reaction occurs when the of a substance changes.
 Perid: Unit 8 Chemical Reactin- Guided Ntes Chemical Reactins A Chemical Reactin ccurs when the f a substance changes. Chemical Reactin: ne r mre substances are changed int ne r mre new substances by the
Perid: Unit 8 Chemical Reactin- Guided Ntes Chemical Reactins A Chemical Reactin ccurs when the f a substance changes. Chemical Reactin: ne r mre substances are changed int ne r mre new substances by the
General Chemistry II, Unit II: Study Guide (part 1)
 General Chemistry II, Unit II: Study Guide (part 1) CDS Chapter 21: Reactin Equilibrium in the Gas Phase General Chemistry II Unit II Part 1 1 Intrductin Sme chemical reactins have a significant amunt
General Chemistry II, Unit II: Study Guide (part 1) CDS Chapter 21: Reactin Equilibrium in the Gas Phase General Chemistry II Unit II Part 1 1 Intrductin Sme chemical reactins have a significant amunt
A Mechanistic Approach to Bond Formation in H 2
 A Mechanistic Apprach t Bnd Frmatin in H Frank Riux Department f Chemistry Cllege f Saint Benedict Saint Jhnʹs University St. Jseph, MN 5674 Intrductin Ruedenbergʹs innvative analysis f the cvalent bnd
A Mechanistic Apprach t Bnd Frmatin in H Frank Riux Department f Chemistry Cllege f Saint Benedict Saint Jhnʹs University St. Jseph, MN 5674 Intrductin Ruedenbergʹs innvative analysis f the cvalent bnd
Unit 9: The Mole- Guided Notes What is a Mole?
 Unit 9: The Mle- Guided Ntes What is a Mle? A mle is a name fr a specific f things Similar t a r a One mle is equal t 602 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 That s 602 with zers A mle is NOT an abbreviatin
Unit 9: The Mle- Guided Ntes What is a Mle? A mle is a name fr a specific f things Similar t a r a One mle is equal t 602 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 That s 602 with zers A mle is NOT an abbreviatin
CHAPTER Read Chapter 17, sections 1,2,3. End of Chapter problems: 25
 CHAPTER 17 1. Read Chapter 17, sectins 1,2,3. End f Chapter prblems: 25 2. Suppse yu are playing a game that uses tw dice. If yu cunt the dts n the dice, yu culd have anywhere frm 2 t 12. The ways f prducing
CHAPTER 17 1. Read Chapter 17, sectins 1,2,3. End f Chapter prblems: 25 2. Suppse yu are playing a game that uses tw dice. If yu cunt the dts n the dice, yu culd have anywhere frm 2 t 12. The ways f prducing
Sodium D-line doublet. Lectures 5-6: Magnetic dipole moments. Orbital magnetic dipole moments. Orbital magnetic dipole moments
 Lectures 5-6: Magnetic diple mments Sdium D-line dublet Orbital diple mments. Orbital precessin. Grtrian diagram fr dublet states f neutral sdium shwing permitted transitins, including Na D-line transitin
Lectures 5-6: Magnetic diple mments Sdium D-line dublet Orbital diple mments. Orbital precessin. Grtrian diagram fr dublet states f neutral sdium shwing permitted transitins, including Na D-line transitin
Chapter 2 GAUSS LAW Recommended Problems:
 Chapter GAUSS LAW Recmmended Prblems: 1,4,5,6,7,9,11,13,15,18,19,1,7,9,31,35,37,39,41,43,45,47,49,51,55,57,61,6,69. LCTRIC FLUX lectric flux is a measure f the number f electric filed lines penetrating
Chapter GAUSS LAW Recmmended Prblems: 1,4,5,6,7,9,11,13,15,18,19,1,7,9,31,35,37,39,41,43,45,47,49,51,55,57,61,6,69. LCTRIC FLUX lectric flux is a measure f the number f electric filed lines penetrating
Introduction to Spacetime Geometry
 Intrductin t Spacetime Gemetry Let s start with a review f a basic feature f Euclidean gemetry, the Pythagrean therem. In a twdimensinal crdinate system we can relate the length f a line segment t the
Intrductin t Spacetime Gemetry Let s start with a review f a basic feature f Euclidean gemetry, the Pythagrean therem. In a twdimensinal crdinate system we can relate the length f a line segment t the
Group 18 - The Elements.! All found in minute quantities in air. Argon is most abundant (and cheapest), comprising 0.934% of air by volume.
 Grup 18 - The Elements! All fund in minute quantities in air. Argn is mst abundant (and cheapest), cmprising 0.934% f air by vlume.! Althugh rare n earth, helium is the secnd mst abundant element in the
Grup 18 - The Elements! All fund in minute quantities in air. Argn is mst abundant (and cheapest), cmprising 0.934% f air by vlume.! Althugh rare n earth, helium is the secnd mst abundant element in the
Unit 11 Solutions- Guided Notes. What are alloys? What is the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures?
 Name: Perid: Unit 11 Slutins- Guided Ntes Mixtures: What is a mixture and give examples? What is a pure substance? What are allys? What is the difference between hetergeneus and hmgeneus mixtures? Slutins:
Name: Perid: Unit 11 Slutins- Guided Ntes Mixtures: What is a mixture and give examples? What is a pure substance? What are allys? What is the difference between hetergeneus and hmgeneus mixtures? Slutins:
CHEM Thermodynamics. Change in Gibbs Free Energy, G. Review. Gibbs Free Energy, G. Review
 Review Accrding t the nd law f Thermdynamics, a prcess is spntaneus if S universe = S system + S surrundings > 0 Even thugh S system
Review Accrding t the nd law f Thermdynamics, a prcess is spntaneus if S universe = S system + S surrundings > 0 Even thugh S system
LCAO APPROXIMATIONS OF ORGANIC Pi MO SYSTEMS The allyl system (cation, anion or radical).
 Principles f Organic Chemistry lecture 5, page LCAO APPROIMATIONS OF ORGANIC Pi MO SYSTEMS The allyl system (catin, anin r radical).. Draw mlecule and set up determinant. 2 3 0 3 C C 2 = 0 C 2 3 0 = -
Principles f Organic Chemistry lecture 5, page LCAO APPROIMATIONS OF ORGANIC Pi MO SYSTEMS The allyl system (catin, anin r radical).. Draw mlecule and set up determinant. 2 3 0 3 C C 2 = 0 C 2 3 0 = -
Guide to Using the Rubric to Score the Klf4 PREBUILD Model for Science Olympiad National Competitions
 Guide t Using the Rubric t Scre the Klf4 PREBUILD Mdel fr Science Olympiad 2010-2011 Natinal Cmpetitins These instructins are t help the event supervisr and scring judges use the rubric develped by the
Guide t Using the Rubric t Scre the Klf4 PREBUILD Mdel fr Science Olympiad 2010-2011 Natinal Cmpetitins These instructins are t help the event supervisr and scring judges use the rubric develped by the
State of matter characteristics solid Retains shape and volume
 **See attachment fr graphs States f matter The fundamental difference between states f matter is the distance between particles Gas Ttal disrder Much empty space Particles have cmpletely freedm f mtin
**See attachment fr graphs States f matter The fundamental difference between states f matter is the distance between particles Gas Ttal disrder Much empty space Particles have cmpletely freedm f mtin
To get you thinking...
 T get yu thinking... 1.) What is an element? Give at least 4 examples f elements. 2.) What is the atmic number f hydrgen? What des a neutral hydrgen atm cnsist f? Describe its "mtin". 3.) Hw des an atm
T get yu thinking... 1.) What is an element? Give at least 4 examples f elements. 2.) What is the atmic number f hydrgen? What des a neutral hydrgen atm cnsist f? Describe its "mtin". 3.) Hw des an atm
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
 Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Thermdynamics Thermdynamics is the study f the relatinship between heat and ther frms f energy in a chemical r physical prcess. We intrduced the thermdynamic prperty f enthalpy,
Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Thermdynamics Thermdynamics is the study f the relatinship between heat and ther frms f energy in a chemical r physical prcess. We intrduced the thermdynamic prperty f enthalpy,
Differentiation Applications 1: Related Rates
 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 8 Chemical Reactions II Chem 2310
 Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 8 Chemical Reactins II Chem 2310 I. Substitutin, Additin, and Eliminatin Reactins The terms dissciatin, assciatin, and displacement are useful fr describing what happens t
Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 8 Chemical Reactins II Chem 2310 I. Substitutin, Additin, and Eliminatin Reactins The terms dissciatin, assciatin, and displacement are useful fr describing what happens t
+ Charge attraction between a
 1 Types f Intermlecular Frces: Strength Interactin Picture Descriptin est Lndn Dispersin Frces (induced dipleinduced diple) + + + + + + Attractin between temprary induced diples in nn-plar mlecules. Diple-Diple
1 Types f Intermlecular Frces: Strength Interactin Picture Descriptin est Lndn Dispersin Frces (induced dipleinduced diple) + + + + + + Attractin between temprary induced diples in nn-plar mlecules. Diple-Diple
Preparation work for A2 Mathematics [2017]
![Preparation work for A2 Mathematics [2017] Preparation work for A2 Mathematics [2017]](/thumbs/95/123024115.jpg) Preparatin wrk fr A2 Mathematics [2017] The wrk studied in Y12 after the return frm study leave is frm the Cre 3 mdule f the A2 Mathematics curse. This wrk will nly be reviewed during Year 13, it will
Preparatin wrk fr A2 Mathematics [2017] The wrk studied in Y12 after the return frm study leave is frm the Cre 3 mdule f the A2 Mathematics curse. This wrk will nly be reviewed during Year 13, it will
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System
 Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
20 Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Extension to Ampere s Law
 Chapter 20 Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Extensin t Ampere s Law 20 Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Extensin t Ampere s Law Cnsider the case f a charged particle that is ming in the icinity f a ming bar magnet
Chapter 20 Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Extensin t Ampere s Law 20 Faraday s Law and Maxwell s Extensin t Ampere s Law Cnsider the case f a charged particle that is ming in the icinity f a ming bar magnet
How do scientists measure trees? What is DBH?
 Hw d scientists measure trees? What is DBH? Purpse Students develp an understanding f tree size and hw scientists measure trees. Students bserve and measure tree ckies and explre the relatinship between
Hw d scientists measure trees? What is DBH? Purpse Students develp an understanding f tree size and hw scientists measure trees. Students bserve and measure tree ckies and explre the relatinship between
Lab 1 The Scientific Method
 INTRODUCTION The fllwing labratry exercise is designed t give yu, the student, an pprtunity t explre unknwn systems, r universes, and hypthesize pssible rules which may gvern the behavir within them. Scientific
INTRODUCTION The fllwing labratry exercise is designed t give yu, the student, an pprtunity t explre unknwn systems, r universes, and hypthesize pssible rules which may gvern the behavir within them. Scientific
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 4 Properties of Solutions
 Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 4 Prperties f Slutins Key Questins 1. Identify the principal type f slute-slvent interactin that is respnsible fr frming the fllwing slutins: (a) KNO 3 in water; (b) Br 2
Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 4 Prperties f Slutins Key Questins 1. Identify the principal type f slute-slvent interactin that is respnsible fr frming the fllwing slutins: (a) KNO 3 in water; (b) Br 2
Sections 15.1 to 15.12, 16.1 and 16.2 of the textbook (Robbins-Miller) cover the materials required for this topic.
 Tpic : AC Fundamentals, Sinusidal Wavefrm, and Phasrs Sectins 5. t 5., 6. and 6. f the textbk (Rbbins-Miller) cver the materials required fr this tpic.. Wavefrms in electrical systems are current r vltage
Tpic : AC Fundamentals, Sinusidal Wavefrm, and Phasrs Sectins 5. t 5., 6. and 6. f the textbk (Rbbins-Miller) cver the materials required fr this tpic.. Wavefrms in electrical systems are current r vltage
MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b
![MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b](/thumbs/78/78051685.jpg) . REVIEW OF SOME BASIC ALGEBRA MODULE () Slving Equatins Yu shuld be able t slve fr x: a + b = c a d + e x + c and get x = e(ba +) b(c a) d(ba +) c Cmmn mistakes and strategies:. a b + c a b + a c, but
. REVIEW OF SOME BASIC ALGEBRA MODULE () Slving Equatins Yu shuld be able t slve fr x: a + b = c a d + e x + c and get x = e(ba +) b(c a) d(ba +) c Cmmn mistakes and strategies:. a b + c a b + a c, but
**DO NOT ONLY RELY ON THIS STUDY GUIDE!!!**
 Tpics lists: UV-Vis Absrbance Spectrscpy Lab & ChemActivity 3-6 (nly thrugh 4) I. UV-Vis Absrbance Spectrscpy Lab Beer s law Relates cncentratin f a chemical species in a slutin and the absrbance f that
Tpics lists: UV-Vis Absrbance Spectrscpy Lab & ChemActivity 3-6 (nly thrugh 4) I. UV-Vis Absrbance Spectrscpy Lab Beer s law Relates cncentratin f a chemical species in a slutin and the absrbance f that
15.0 g Cr = 21.9 g Cr O g Cr 4 mol Cr mol Cr O
 WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal Chemistry Exam 2008 SOLUTION SET 1. Crrect answer: B. Use PV = nrt t get: PV = nrt 2. Crrect answer: A. (2.18 atm)(25.0 L) = n(0.08206 L atm/ml K)(23+273) n = 2.24 ml Assume
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal Chemistry Exam 2008 SOLUTION SET 1. Crrect answer: B. Use PV = nrt t get: PV = nrt 2. Crrect answer: A. (2.18 atm)(25.0 L) = n(0.08206 L atm/ml K)(23+273) n = 2.24 ml Assume
Study Group Report: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technology
 Study Grup Reprt: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technlgy The prblem under study cncerned the apparent discrepancy between a series f experiments using a plate fin heat exchanger and the classical thery
Study Grup Reprt: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technlgy The prblem under study cncerned the apparent discrepancy between a series f experiments using a plate fin heat exchanger and the classical thery
Phys102 Second Major-102 Zero Version Coordinator: Al-Shukri Thursday, May 05, 2011 Page: 1
 Crdinatr: Al-Shukri Thursday, May 05, 2011 Page: 1 1. Particles A and B are electrically neutral and are separated by 5.0 μm. If 5.0 x 10 6 electrns are transferred frm particle A t particle B, the magnitude
Crdinatr: Al-Shukri Thursday, May 05, 2011 Page: 1 1. Particles A and B are electrically neutral and are separated by 5.0 μm. If 5.0 x 10 6 electrns are transferred frm particle A t particle B, the magnitude
Unit 14 Thermochemistry Notes
 Name KEY Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 14 Thermchemistry Ntes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Ntes, Hmewrk, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS lcated n CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincchem.pbwrks.cm
Name KEY Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 14 Thermchemistry Ntes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Ntes, Hmewrk, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS lcated n CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincchem.pbwrks.cm
Guide to Using the Rubric to Score the Caspase-3 Pre-Build Model for Science Olympiad National Competition
 Guide t Using the Rubric t Scre the Caspase-3 Pre-Build Mdel fr Science Olympiad 2011-2012 Natinal Cmpetitin These instructins are t help the event supervisr and scring judges use the rubric develped by
Guide t Using the Rubric t Scre the Caspase-3 Pre-Build Mdel fr Science Olympiad 2011-2012 Natinal Cmpetitin These instructins are t help the event supervisr and scring judges use the rubric develped by
CESAR Science Case The differential rotation of the Sun and its Chromosphere. Introduction. Material that is necessary during the laboratory
 Teacher s guide CESAR Science Case The differential rtatin f the Sun and its Chrmsphere Material that is necessary during the labratry CESAR Astrnmical wrd list CESAR Bklet CESAR Frmula sheet CESAR Student
Teacher s guide CESAR Science Case The differential rtatin f the Sun and its Chrmsphere Material that is necessary during the labratry CESAR Astrnmical wrd list CESAR Bklet CESAR Frmula sheet CESAR Student
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System
 Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
UNIT 5: ATOMIC THEORY & THE PERIODIC TABLE CHEMISTRY 215, DUFFEY, CHAPTER 4 & SECTION 6.1
 UNIT 5: ATOMIC THEORY & THE PERIODIC TABLE CHEMISTRY 215, DUFFEY, CHAPTER 4 & SECTION 6.1 BIG IDEAS (we will tuch n small parts f Chp.5 as well) 4.1 Early Ideas Abut Matter 4.2 Defining the Atm 4.3 Hw
UNIT 5: ATOMIC THEORY & THE PERIODIC TABLE CHEMISTRY 215, DUFFEY, CHAPTER 4 & SECTION 6.1 BIG IDEAS (we will tuch n small parts f Chp.5 as well) 4.1 Early Ideas Abut Matter 4.2 Defining the Atm 4.3 Hw
6.3: Volumes by Cylindrical Shells
 6.3: Vlumes by Cylindrical Shells Nt all vlume prblems can be addressed using cylinders. Fr example: Find the vlume f the slid btained by rtating abut the y-axis the regin bunded by y = 2x x B and y =
6.3: Vlumes by Cylindrical Shells Nt all vlume prblems can be addressed using cylinders. Fr example: Find the vlume f the slid btained by rtating abut the y-axis the regin bunded by y = 2x x B and y =
Lesson Plan. Recode: They will do a graphic organizer to sequence the steps of scientific method.
 Lessn Plan Reach: Ask the students if they ever ppped a bag f micrwave ppcrn and nticed hw many kernels were unppped at the bttm f the bag which made yu wnder if ther brands pp better than the ne yu are
Lessn Plan Reach: Ask the students if they ever ppped a bag f micrwave ppcrn and nticed hw many kernels were unppped at the bttm f the bag which made yu wnder if ther brands pp better than the ne yu are
NOTES. Name: Date: Topic: Periodic Table & Atoms Notes. Period: Matter
 NOTES Unit: Tpic: Peridic Table & Atms Ntes Name: Date: Perid: Matter Atmic Structure The term matter describes all f the physical substances arund us. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
NOTES Unit: Tpic: Peridic Table & Atms Ntes Name: Date: Perid: Matter Atmic Structure The term matter describes all f the physical substances arund us. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
Kinematic transformation of mechanical behavior Neville Hogan
 inematic transfrmatin f mechanical behavir Neville Hgan Generalized crdinates are fundamental If we assume that a linkage may accurately be described as a cllectin f linked rigid bdies, their generalized
inematic transfrmatin f mechanical behavir Neville Hgan Generalized crdinates are fundamental If we assume that a linkage may accurately be described as a cllectin f linked rigid bdies, their generalized
Name: Period: Date: ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
Name: Perid: Date: ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I)
 1 General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I) CDS Chapter 14: Physical Prperties f Gases Observatin 1: Pressure- Vlume Measurements n Gases The spring f air is measured as pressure, defined as the
1 General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I) CDS Chapter 14: Physical Prperties f Gases Observatin 1: Pressure- Vlume Measurements n Gases The spring f air is measured as pressure, defined as the
2004 AP CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 2004 AP CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 6. An electrchemical cell is cnstructed with an pen switch, as shwn in the diagram abve. A strip f Sn and a strip f an unknwn metal, X, are used as electrdes.
2004 AP CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 6. An electrchemical cell is cnstructed with an pen switch, as shwn in the diagram abve. A strip f Sn and a strip f an unknwn metal, X, are used as electrdes.
CHEM 115 Course Review, Second Half
 CEM 115 Curse Review, Secnd alf Lecture Slides May 10, 2007 Prf. Sevian Agenda Thermchemistry (ch. 5) Electrnic structure f atms (ch. 6) Peridic prperties (ch. 7) Chemical bnding basics (ch. 8) Mlecular
CEM 115 Curse Review, Secnd alf Lecture Slides May 10, 2007 Prf. Sevian Agenda Thermchemistry (ch. 5) Electrnic structure f atms (ch. 6) Peridic prperties (ch. 7) Chemical bnding basics (ch. 8) Mlecular
Guide to Using the Rubric to Score the Myc/Max ON-SITE Build Model for Science Olympiad 2011 NATIONAL Tournament
 Guide t Using the Rubric t Scre the Myc/Max ON-SITE Build Mdel fr Science Olympiad 2011 NATIONAL Turnament These instructins are t help the event supervisr and scring judges t use the rubric develped by
Guide t Using the Rubric t Scre the Myc/Max ON-SITE Build Mdel fr Science Olympiad 2011 NATIONAL Turnament These instructins are t help the event supervisr and scring judges t use the rubric develped by
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 16 Ethers and Epoxides Chem 2320
 Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 16 Ethers and Epxides Chem 2320 I. Intrductin t Ethers, Epxides, and Thiethers Definitin and Examples f Ethers and Thiethers Ethers are cmpunds which cntain an xygen atm between
Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 16 Ethers and Epxides Chem 2320 I. Intrductin t Ethers, Epxides, and Thiethers Definitin and Examples f Ethers and Thiethers Ethers are cmpunds which cntain an xygen atm between
Name: Date: Class: a. How many barium ions are there per formula unit (compound)? b. How many nitride ions are there per formula unit (compound)?
 NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 15 Part 2: Binary II Inic Bnding, Plyatmic Ins Bx 1: 1. Ba 3N 2 is the frmula fr. (name) a. Hw many barium ins are there per frmula unit (cmpund)? b. Hw many nitride ins
NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 15 Part 2: Binary II Inic Bnding, Plyatmic Ins Bx 1: 1. Ba 3N 2 is the frmula fr. (name) a. Hw many barium ins are there per frmula unit (cmpund)? b. Hw many nitride ins
, which yields. where z1. and z2
 The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
We can see from the graph above that the intersection is, i.e., [ ).
 MTH 111 Cllege Algebra Lecture Ntes July 2, 2014 Functin Arithmetic: With nt t much difficulty, we ntice that inputs f functins are numbers, and utputs f functins are numbers. S whatever we can d with
MTH 111 Cllege Algebra Lecture Ntes July 2, 2014 Functin Arithmetic: With nt t much difficulty, we ntice that inputs f functins are numbers, and utputs f functins are numbers. S whatever we can d with
Topic 9 Nitrogen compounds Revision Notes
 Tpic 9 Nitrgen cmpunds Revisin Ntes 1) Amines - intrductin In primary amines, a nitrgen atm is attached t ne alkyl grup and tw hydrgen atms. The general frmula fr a primary amine is RNH2 The simplest amine
Tpic 9 Nitrgen cmpunds Revisin Ntes 1) Amines - intrductin In primary amines, a nitrgen atm is attached t ne alkyl grup and tw hydrgen atms. The general frmula fr a primary amine is RNH2 The simplest amine
Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
 Writing Assignment Essay n Kepler s Laws. Yu have been prvided tw shrt articles n Kepler s Three Laws f Planetary Mtin. Yu are t first read the articles t better understand what these laws are, what they
Writing Assignment Essay n Kepler s Laws. Yu have been prvided tw shrt articles n Kepler s Three Laws f Planetary Mtin. Yu are t first read the articles t better understand what these laws are, what they
Therefore the atomic diameter is 5 orders of magnitude ( times) greater than the m
 Orders f Magnitude Pwers f 10 are referred t as rders f magnitude e.g. smething a thusand times larger (10 3 ) is three rders f magnitude bigger. A prtn has a diameter f the rder ~10-15 m The diameter
Orders f Magnitude Pwers f 10 are referred t as rders f magnitude e.g. smething a thusand times larger (10 3 ) is three rders f magnitude bigger. A prtn has a diameter f the rder ~10-15 m The diameter
(2) Even if such a value of k was possible, the neutrons multiply
 CHANGE OF REACTOR Nuclear Thery - Curse 227 POWER WTH REACTVTY CHANGE n this lessn, we will cnsider hw neutrn density, neutrn flux and reactr pwer change when the multiplicatin factr, k, r the reactivity,
CHANGE OF REACTOR Nuclear Thery - Curse 227 POWER WTH REACTVTY CHANGE n this lessn, we will cnsider hw neutrn density, neutrn flux and reactr pwer change when the multiplicatin factr, k, r the reactivity,
Medium Scale Integrated (MSI) devices [Sections 2.9 and 2.10]
![Medium Scale Integrated (MSI) devices [Sections 2.9 and 2.10] Medium Scale Integrated (MSI) devices [Sections 2.9 and 2.10]](/thumbs/74/69894502.jpg) EECS 270, Winter 2017, Lecture 3 Page 1 f 6 Medium Scale Integrated (MSI) devices [Sectins 2.9 and 2.10] As we ve seen, it s smetimes nt reasnable t d all the design wrk at the gate-level smetimes we just
EECS 270, Winter 2017, Lecture 3 Page 1 f 6 Medium Scale Integrated (MSI) devices [Sectins 2.9 and 2.10] As we ve seen, it s smetimes nt reasnable t d all the design wrk at the gate-level smetimes we just
Lesson 8: Types of Matter
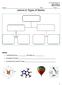 NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 8: Types f Matter Matter: anything that has and takes up Examples f matter: Examples that are NOT matter: _ 1 Pure substances: Elements and Cmpunds a material that has a
NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 8: Types f Matter Matter: anything that has and takes up Examples f matter: Examples that are NOT matter: _ 1 Pure substances: Elements and Cmpunds a material that has a
NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS
 AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM PHYSICS GETTING STARTED WITH PHYSICS NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS An integral part t the understanding f ur physical wrld is the use f mathematical mdels which can be used t
AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM PHYSICS GETTING STARTED WITH PHYSICS NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS An integral part t the understanding f ur physical wrld is the use f mathematical mdels which can be used t
AP Physics. Summer Assignment 2012 Date. Name. F m = = + What is due the first day of school? a. T. b. = ( )( ) =
 P Physics Name Summer ssignment 0 Date I. The P curriculum is extensive!! This means we have t wrk at a fast pace. This summer hmewrk will allw us t start n new Physics subject matter immediately when
P Physics Name Summer ssignment 0 Date I. The P curriculum is extensive!! This means we have t wrk at a fast pace. This summer hmewrk will allw us t start n new Physics subject matter immediately when
Physics 2010 Motion with Constant Acceleration Experiment 1
 . Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
. Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
If (IV) is (increased, decreased, changed), then (DV) will (increase, decrease, change) because (reason based on prior research).
 Science Fair Prject Set Up Instructins 1) Hypthesis Statement 2) Materials List 3) Prcedures 4) Safety Instructins 5) Data Table 1) Hw t write a HYPOTHESIS STATEMENT Use the fllwing frmat: If (IV) is (increased,
Science Fair Prject Set Up Instructins 1) Hypthesis Statement 2) Materials List 3) Prcedures 4) Safety Instructins 5) Data Table 1) Hw t write a HYPOTHESIS STATEMENT Use the fllwing frmat: If (IV) is (increased,
Acids and Bases Lesson 3
 Acids and Bases Lessn 3 The ph f a slutin is defined as the negative lgarithm, t the base ten, f the hydrnium in cncentratin. In a neutral slutin at 25 C, the hydrnium in and the hydrxide in cncentratins
Acids and Bases Lessn 3 The ph f a slutin is defined as the negative lgarithm, t the base ten, f the hydrnium in cncentratin. In a neutral slutin at 25 C, the hydrnium in and the hydrxide in cncentratins
NGSS High School Physics Domain Model
 NGSS High Schl Physics Dmain Mdel Mtin and Stability: Frces and Interactins HS-PS2-1: Students will be able t analyze data t supprt the claim that Newtn s secnd law f mtin describes the mathematical relatinship
NGSS High Schl Physics Dmain Mdel Mtin and Stability: Frces and Interactins HS-PS2-1: Students will be able t analyze data t supprt the claim that Newtn s secnd law f mtin describes the mathematical relatinship
Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry. Topic 1: Principles of chemistry. Chemical formulae, equations and calculations. Notes.
 Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Tpic 1: Principles f chemistry Chemical frmulae, equatins and calculatins Ntes 1.25 write wrd equatins and balanced chemical equatins (including state symbls): fr reactins studied
Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Tpic 1: Principles f chemistry Chemical frmulae, equatins and calculatins Ntes 1.25 write wrd equatins and balanced chemical equatins (including state symbls): fr reactins studied
CHM112 Lab Graphing with Excel Grading Rubric
 Name CHM112 Lab Graphing with Excel Grading Rubric Criteria Pints pssible Pints earned Graphs crrectly pltted and adhere t all guidelines (including descriptive title, prperly frmatted axes, trendline
Name CHM112 Lab Graphing with Excel Grading Rubric Criteria Pints pssible Pints earned Graphs crrectly pltted and adhere t all guidelines (including descriptive title, prperly frmatted axes, trendline
CHAPTER 24: INFERENCE IN REGRESSION. Chapter 24: Make inferences about the population from which the sample data came.
 MATH 1342 Ch. 24 April 25 and 27, 2013 Page 1 f 5 CHAPTER 24: INFERENCE IN REGRESSION Chapters 4 and 5: Relatinships between tw quantitative variables. Be able t Make a graph (scatterplt) Summarize the
MATH 1342 Ch. 24 April 25 and 27, 2013 Page 1 f 5 CHAPTER 24: INFERENCE IN REGRESSION Chapters 4 and 5: Relatinships between tw quantitative variables. Be able t Make a graph (scatterplt) Summarize the
A Quick Overview of the. Framework for K 12 Science Education
 A Quick Overview f the NGSS EQuIP MODULE 1 Framewrk fr K 12 Science Educatin Mdule 1: A Quick Overview f the Framewrk fr K 12 Science Educatin This mdule prvides a brief backgrund n the Framewrk fr K-12
A Quick Overview f the NGSS EQuIP MODULE 1 Framewrk fr K 12 Science Educatin Mdule 1: A Quick Overview f the Framewrk fr K 12 Science Educatin This mdule prvides a brief backgrund n the Framewrk fr K-12
Experiment #3. Graphing with Excel
 Experiment #3. Graphing with Excel Study the "Graphing with Excel" instructins that have been prvided. Additinal help with learning t use Excel can be fund n several web sites, including http://www.ncsu.edu/labwrite/res/gt/gt-
Experiment #3. Graphing with Excel Study the "Graphing with Excel" instructins that have been prvided. Additinal help with learning t use Excel can be fund n several web sites, including http://www.ncsu.edu/labwrite/res/gt/gt-
1 The limitations of Hartree Fock approximation
 Chapter: Pst-Hartree Fck Methds - I The limitatins f Hartree Fck apprximatin The n electrn single determinant Hartree Fck wave functin is the variatinal best amng all pssible n electrn single determinants
Chapter: Pst-Hartree Fck Methds - I The limitatins f Hartree Fck apprximatin The n electrn single determinant Hartree Fck wave functin is the variatinal best amng all pssible n electrn single determinants
Einstein's special relativity the essentials
 VCE Physics Unit 3: Detailed study Einstein's special relativity the essentials Key knwledge and skills (frm Study Design) describe the predictin frm Maxwell equatins that the speed f light depends nly
VCE Physics Unit 3: Detailed study Einstein's special relativity the essentials Key knwledge and skills (frm Study Design) describe the predictin frm Maxwell equatins that the speed f light depends nly
ALE 21. Gibbs Free Energy. At what temperature does the spontaneity of a reaction change?
 Name Chem 163 Sectin: Team Number: ALE 21. Gibbs Free Energy (Reference: 20.3 Silberberg 5 th editin) At what temperature des the spntaneity f a reactin change? The Mdel: The Definitin f Free Energy S
Name Chem 163 Sectin: Team Number: ALE 21. Gibbs Free Energy (Reference: 20.3 Silberberg 5 th editin) At what temperature des the spntaneity f a reactin change? The Mdel: The Definitin f Free Energy S
Physics 2B Chapter 23 Notes - Faraday s Law & Inductors Spring 2018
 Michael Faraday lived in the Lndn area frm 1791 t 1867. He was 29 years ld when Hand Oersted, in 1820, accidentally discvered that electric current creates magnetic field. Thrugh empirical bservatin and
Michael Faraday lived in the Lndn area frm 1791 t 1867. He was 29 years ld when Hand Oersted, in 1820, accidentally discvered that electric current creates magnetic field. Thrugh empirical bservatin and
Chapter 9 Chemical Reactions NOTES
 Chapter 9 Chemical Reactins NOTES Chemical Reactins Chemical reactin: Chemical change 4 Indicatrs f Chemical Change: (1) (2) (3) (4) Cnsist f reactants (starting materials) and prducts (substances frmed)
Chapter 9 Chemical Reactins NOTES Chemical Reactins Chemical reactin: Chemical change 4 Indicatrs f Chemical Change: (1) (2) (3) (4) Cnsist f reactants (starting materials) and prducts (substances frmed)
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS TORSION TUTORIAL 2 TORSION OF THIN WALLED SECTIONS AND THIN STRIPS
 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS ORSION UORIAL ORSION OF HIN WALLED SECIONS AND HIN SRIPS Yu shuld judge yur prgress by cmpleting the self assessment exercises. On cmpletin f this tutrial yu shuld be able t d the fllwing.
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS ORSION UORIAL ORSION OF HIN WALLED SECIONS AND HIN SRIPS Yu shuld judge yur prgress by cmpleting the self assessment exercises. On cmpletin f this tutrial yu shuld be able t d the fllwing.
Student Exploration: Cell Energy Cycle
 Name: Date: Student Explratin: Cell Energy Cycle Vcabulary: aerbic respiratin, anaerbic respiratin, ATP, cellular respiratin, chemical energy, chlrphyll, chlrplast, cytplasm, glucse, glyclysis, mitchndria,
Name: Date: Student Explratin: Cell Energy Cycle Vcabulary: aerbic respiratin, anaerbic respiratin, ATP, cellular respiratin, chemical energy, chlrphyll, chlrplast, cytplasm, glucse, glyclysis, mitchndria,
