Animal reproduction. Parts of flowering. plants. Anchorage. Circulation. Gas exchange and. waste removal. Food production. Reproduction.
|
|
|
- Gladys Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Animal reproduction Parts of flowering plants Anchorage Circulation. Gas exchange and waste removal Food production. Reproduction. By the end of this Unit you will: Know the different parts of flowering plants and the job of each part. Place a plant into it s major flowering and non flowering taxonomic group. 1
2 Lesson 1 : Curriculum standards : 6.2 Every day millions of living things die. Organisms do not live for ever. Why is there still life on Earth? Pic cat Before most organisms die, they produce new organisms like themselves. Reproduction is producing young, so that the species continue to exist. التكاثر : هو انتاج الصغار, لك نحافظ على االنواع ف االستمرار و البقاء. In many animals a new life starts when the nucleus of a sperm (a specialized cell from the father) Fuses (combines) with the nucleus of the egg (a specialized cell from the mother). We call it Fertilization. Fertilization is the fusion of an egg with a sperm to form a zygote األخصاب :- هو اتحاد ب ن الح وان المنوي و البو ضه النتاج بو ضه ملقحة. Question: What do plants have instead of Sperms? 2
3 Different animals fertilize their eggs in different ways. Fertilization in Vertebrates: External fertilization Internal fertilization Fish and Amphibian Birds and reptiles Mammals young Develop in water young Develop on land Young Develop inside uterus External Fertilization: fertilization takes place outside the body الألخصاب الخارج : أخصاب حدث خارج الجسم. The female frogs and fish lay thousands of eggs in water, males will wait for the female frogs and fish to lay the eggs then they will release the sperms in water. بعد أن تضع أنثى االسماك و الضفادع أالف من الب ض ف الماء, المنو ة ف الماء لتلق ح الب ض. تقوم بعد ذلك الذكور بالقاء الح وانات Pic page 111 Pic Fertilization happens when a sperm and an egg meet by chance. The mothers do not take care of their young. و التلق ح حدث عندما تلتق الب وضة و الح وان المنوي عن طر ق الصدفه, و االم ال تقم بالعنا ة بصغارها. Internal fertilization: Fertilization happens inside the mother s body. األخصاب الداخل : اخصاب حدث داخل داخل جسم األم. 3
4 Mammals, reptiles and birds have a different, more efficient form of reproduction: The sperm and egg meet and fuse (combine) inside the mother s body. a. Birds and reptiles lay their eggs on land. The eggs are covered by hard shells. They contain lots of stored food. The mothers take care of their young until they can live on their own. - الط ور و الزواحف تضع ب ضها ف االرض, و الب ض كون مغطى بطبقة صلبه من القشرة و حتوي بداخلة على كم ة كب رة من الطعام المخزن. - و االم تقوم باالهتمام بصغارها حتى ستط عون االعتماد على أنفسه. b. Most mammals are different; their young grow in a special organ inside the mother s body. We call it a Uterus. The mother will take care of the young and feed them milk. - معظم الثد ات نمو صغارها ف عضو خاص داخل جسم األم دعى الرحم. و تقوم االم باالعتناء بصغارها و اعطائهم الحل ب. 4
5 Key words: Reproduction التكاثر Fertilization األخصاب External fertilization. األخصاب الخارج Internal fertilization. األخصاب الداخل Uterus الرحم Key ideas: All living things reproduce to have young that are identical to their parents. - جم ع الكائنات الح ه تتكاثر النتاج الصغار الت تكون مشابهه لوالد ها. Fertilization is the fusion (joining) of the sperm and egg to form a zygote. - االخصاب هو اتحاد الح وان المنوي مع البو ضه النتاج بو ضة ملقحه There are two types of fertilization, one that happens outside the mother's body we call it External fertilization and one that happens inside the mother's body, we call it Internal Fertilization. - هناك نوع ن من االخصاب, احدهم حدث خارج جسم االم و سمى االخصاب الخارج و االخر حدث داخل جسم االم و سمى االخصاب الداخل. The mammals have a special organ called the uterus to keep the young inside the mother s - الثد ات لد ها عضو خاص سمى) الرحم ) لالحتفاظ body. بالصغار داخل جسم المرأة. Key Questions: عرف التكاثر reproduction: Define عرف االخصاب Fertilization: Define عددأنواع االخصاب fertilization? What are the two types of Give an example on each type of fertilization: اذكر مثاال لكل نوع من أنواع االخصاب.. عرف الرحم :- uterus Define
6 It isn t just animals that are alive! Plants are alive too. Curriculum standards : 6.3 Plants reproduce, seeds grow into plants can sense where the light plants get rid of waste. New plants is. They can grow or move to Face the light. Most plants are made of four basic parts: معظم النباتات تتكون من أربعه أجزاء رئ س ة : Plants are different from animals because they can make their own food (producers). Each part (organs) of the flowering plants has one of the following specific jobs to do: دعامة النبات Anchorage. تبادل الغازتexchange Gas الدوران Circulation انتاج الغذاء Food production ازالة الماء waste removal التكاثر Reproduction 6
7 Plants take the water and nutrients that are important for food production from the soil. Most plants need to live in soil. Just like the ship s anchor, the roots hold the plant in the soil so that they do not come out easily. We say they anchor plants so that they don t get moved by wind or animals. The organ responsible for anchorage in plants is the root. الجذر : العضو المسؤال عن تثب ت النبات ف التربة. The larger and taller the plants are the bigger the roots they will need for anchoring. Different plants have different types of roots: - كل ما ازداد طول و عرض النبته كل ما احتاجت الى أن تكون الجذور كب رة لتثب تها ف التربة. - كل نوع من أنواع النباتات لها نوع مختلف من الجذور. Tip: In some plants like Carrots food is stored in the roots. 7
8 Plant roots are not just for Anchoring the plants in the soil. They have another job too. Main root Root hair Roots take in water and dissolved nutrients from the soil. The water goes through root hairs. We say root hairs absorb the water and nutrients from the soil.the water and nutrients are then transported from the root to the plant through special tubes. - جز س ان باحاث ن غج ظ فخ ا ان د ذة حثب ج ان باحاث ف انخشبت ن ا ظ ف أخش ا ضا : - ايخظاص ان اء االيالح ي انخشبت, ان اء ذخم ف شؼ شاث انجزس. - انشؼ شاث انجزس ت انخ حم و بؼ ه ت ايخظاص ان اء االيالح ي انخشبت, ثى ح خمم ان اء االيالح ي انخشبت ان ان بج ػ طش ك أ اب ب خاط. Activity: In order to show that the water enters the plant through the roots not the leaves, you can do the following experiment: Take two plants; put the first plant in water, with the roots in water. Put the leaves of the second plant in water. Observe what happens in a few days. 8
9 Once the water has been absorbed by the Roots, it needs to be transported up to the leaves.how are water and nutrients transported from the root to the rest of the plant? ان اء خض ػ طش ك انجز س نك ذخاج ان ا خمان ان اال ساق ك ف خمم ان اء االيالح ي انجزس ان اجضاء ان باث االخش Each part of the plant needs to get the water and food. In order to in order to know how they are transported through the plant you can do the following experiment: كم جضء ي أجضاء ان باث ذخاج ان اء انغزاء نك ؼشف رنك ك ػ م ز انخجشبت Materials: ان اد Celery stick, beaker, red food color, water. كشفظ / ك ط/أ ن أد ش نهطؼاو/ياء طر قة العمل Procedure: Cut 2.5 cm from the bottom of the celery stick, observe the tiny holes. الطغ 2.5 عى ي لاع عاق انكشفظ الدع انفخذاث انظغ شة Place the celery in the beaker that is filled with colored water. Observe what happens the next day. ضغ عاق انكشافظ ف انكأط ان هؤ بان اء ان ه الدع يارا ذذد ف ان و انخان You will notice that the plant turned red, if you cut the stem you will notice that the same tiny holes you had seen in the beginning عخالدع أ ان باث حذ ل إن انه األد ش ن لطؼج عاق ان باث ع ف ink. are filled with red حالدع انفخذاث انظغ شة انج سأ خ ا ف انبذا ت لذ يألث بانه األد ش 9
10 Just like the water is transported around in our house through pipes or tubes. Plants have tiny tubes to transport the water and food to and from the leaves The plant s Circulation system is made of two types of tubes: عمل ة الدوران ف النبات تتم ف أنبوب ن :- - Xylem which is: strong and thick tubes that transport the water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves. أناب ب الخشب : عبارة عن أن اب ب ة قوي و سم كة بتوص ل الماء و األمالح من الجذور إلى األوراق. قوم - Phloem which is: thin tubes that transport sugar around the plant. - اللحاء : عبارة عن أنبوب رق ق قوم بتوص ل السكر إلى جم ع أجزاء النبات. In order to see the tiny tubes inside the plants, scientists cut open the root and the stem and looked inside them using the microscope: In the leaf: - The Stem and roots: The long tubes run from one end of the root and stem to the other cells that are on top of each other. 10
11 Leaves come in different shapes, sizes and colors. Activity (1): األوراق تكون مختلفه ف الشكل, الحجم و االلوان. Get a single leaf from a tree and examine it with a hand lens. Describe the leaf and make a sketch of what you see. Make sure to compare between the upper and lower side of the leaf. microscope Activity (2) You will need: 1. single leaf from a tree 2. hot water 3. beaker 11
12 Put a hot water in a beaker, then inter the leaf, observe the bubbles. The tiny holes in the leaf are called Stomata. When the stomata are open, CO2 enters And O2 and gets out. - Photosynthesis. - breathing. ػ ذيا فخخ انثغش ذخم غاص ثا أكغ ذ انكشب خشج غاص األكغج. - ػ ه ت انب اء انض ئ - - ػ ه ت انخ فظ. plants loose extra water from the stomata To get rid of waste and to keep cool. - ان اء انضائذ ف ان باحاث خى فمذ ػ طش ك انثغش, رنك نهخخهض ي انفضالث ان ذافظت ػه انبش دة. The stomata are responsible for waste removal in plants. Stomata are the parts of plant responsible for gas exchange and waste removal. الثغر :- أجزاء النبات المسئولة عن تبادل الغازات و ازاله الماء. 12
13 Unlike us humans, plants can make their own food. The process by which green plants make their food is called: Photosynthesis is carried out in all the green parts of plants. (Leaves and stem). - انتاج الغذاء ف النبات تم عن طر ق عمل ة البناء الضوئ, و هذه العمل ه تتم ف االجزاء الخضراء ف النبات ( االوراق و الساق (النها تحتوي على صبغه خضراء تدعى الكلوروف ل. The leaves and stem are green because their cells contain a green pigment called Chlorophyll. The pigment will trap the light energy from the sun and make food. Plants also use Water and Carbon dioxide to make food. Water + CO2 + Sunlight Sugar + Oxygen الماء + ثان أكس د الكربون + ضوء الشمس سكر + أكسج ن Food that is produced in the plant is usually stored in the plant itself. Some plants store the food in the stem and others in theroot. - الغذاء المنتج ف النبات عادة خزن ف النبات نفسه, بعض النباتات تخزن الغذاء ف الساق و البعض االخر ف الجذر. To test for the presence of food try the following experiment: Activity: You will need: One potato, knife, iodine. What you will do: 13
14 Cut a piece of the potato. Add two drops of iodine. (The iodine will be blue to black if there is starch). The main function of the leaf is food production. The leaf has many characteristics that make it the best place for - الوظ فه الرئ س ة للورقة ه انتاح الغذاء, النها تملك عدة صفات مهمه تجعله production:,food المكان المناسب النتاج الغذاء : 1. The leaves are green because the cells on the surface (Palisade cells) are filled with chloroplasts. - األوراق خضراء ألن الخال ا الموجوده على السطح ه ( خال ا البالس ده ) مملوءة بمادة الكلوروبالست 2. The lower part of the leaf contains a lot of pores we called it Stomata, which allow the CO2 and sunlight to get inside the leaf. - الجزء السفل من الورقه حتوي على العد د من الثقوب تسمى الثغر, و الت تسمح بدخول غاز ثان أكس د الكربون و أشعه الشمس الى الورقة. 3. The leaf has Xylem and Phloem; The Xylem to transport the water and nutrients, and the phloem to take the produced food and transport it around the plant. - و الورقة تحتوي على الخشب و الحاء, الخشب لنقل الماء و االمالح و الحاء لنقل الغذاء المنتج الى جم ع أجزاء النبات. The green parts of the plant: leaves and stem are the parts responsible for food production. - االجضاء انخضشاء ف ان باث ( األ ساق انغاق ) : األجضاء ان غؤنت ػ ا خاج انغزاء ف ان باث. 14
15 Flowering plants grow from seeds. Seeds are made by flowers. Flowers are the parts of plant that are used for reproduction. الزهرة :- ه العضو المسؤول عن التكاثر ف النبات. Flowers from different plants come in different sizes, colors and shapes. But they all have the same basic parts. Flowers have male and female parts. They are either in the same flower or in different flowers. The following picture shows the main parts of a flower with male and female parts: الزهرة تحتوي على أجزاء ذكر ة و أجزاء أنثو ة. ف بعض االح ان تكون االجزاء االنثو ة و الذكر ة موجوده ف نفس الزهرة و هناك أنواع اخرى توجد االجزاء االنثو ة على زهره و الذكر ة على زهرة أخرى - الرسمة التال ة توضح االجزاء االنثو ة و الذكر ة على نفس الزهرة. 15
16 To make seeds, pollen grains must travel from anther to stigma. لتكو ن البذور البد من انتقال حبوب اللقاح من المتك الى ان غى. The traveling of pollen from the anther to stigma is called Pollination عمل ة التلق ح :- ه عمل ة انتقال حبوب القاح من المتك الى الم سم. Some plants use insects to carry the pollen, others the wind and water. Once the pollen reaches the stigma, the pollen will meet the egg (Ovule). The two cells will join together to form the seed. تستخدم النباتات عدة طرق لنقل حبوب اللقاح اما عن طر ق الحشرات, الر اح أو الماء. عندما تصل حبوب اللقاح الم سم,سوف تلتق حبوب اللقاح بالبو ضة و حدث انداج ب نهم النتاج البذور Fertilization is the fusion of the pollen and the egg to form a new seed. األخصاب:- هو اندماج حبوب اللقاح و الب ضة النتاج بذور جد دة. Reproduction in plants = Pollination + Fertilization. التكاثر ف النبات = التلق ح + االخصاب. 16
17 Key ideas: The plants are living things that have many functions. - النباتات كائنات ح ه لد ها العد د من الوظائف. Different parts of the plant do different jobs, the main functions of the parts of a flowering plant are: - أعضاء النبات المختلفه تؤدي وظائف مختلفه. o Anchorage الجذور تثب ت النبات Roots o Gas Exchange الثغر تبادل الغازات Stomata o Waste removal االخراج Stomataالثغر انتاج الغذاء o Food production الدوران o Circulation Leaf ان سل Xylem and الخشب و اللحاء Phloem o Reproduction الزهرة التكاثر flower Key words: دعامة Anchorage النبات الثغر Stomata الخشب Xylem ال لداء Phloem الدورانCirculation التلق ح Pollination Fertilization االخصاب Project: Plant the seeds of a flowering plant, observe and record the growth of the plant, and it's needs for Key Questions: ك ف تأخذ النباتات ما تحتاجه need? How do plants take in what they - Plant leaves are responsible for.. - أوراق النباتات مسؤله عن The part of the leaf responsible for taking in Oxygen and removing waste is called: - جزء الورقة المسؤل عن أخذ غاز االكسج ن و التخلص من الفضالت هو The water and minerals a plant needs go into it through.. They pass in special tubes through the root, stem and leaves, the tubes are called and. - الماء و االمالح الذي تحتاجه النباتات قوم بامتصاصه , ثم نتقلون من خالل أناب ب خاصة من الجذر, الساق و االوراق هذه االناب ب تدعى و The part of the plant responsible for reproduction is:... - عضو النبات المسؤل عن التكاثر هو : Flowering plants are made of 5 essential parts:..,,..,.,.. - النباتات الزهر ة مكونه من خمسة أجزاء رئ س ة هم : , , , ,
Life Science. Structure of a plant; Plants are living organisms just like. animals and humans. Like all living. things they need key things to live;
 6.6.3 Life Science Structure of a plant; Plants are living organisms just like animals and humans. Like all living things they need key things to live; water, sunlight, oxygen and food. Plants are different
6.6.3 Life Science Structure of a plant; Plants are living organisms just like animals and humans. Like all living things they need key things to live; water, sunlight, oxygen and food. Plants are different
The grade 5 English science unit, Plants, meets the academic content standards set in the Korean curriculum, which state students should:
 This unit deals with the structures and functions of plant organs including roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Students learn that a plant is sustained by the systematic functioning of all its organs.
This unit deals with the structures and functions of plant organs including roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Students learn that a plant is sustained by the systematic functioning of all its organs.
Organization of Plant Tissue. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Organization of Plant Tissue Plant Systems Shoot System The Leaf The Stem The Flower Root System The Shoot System Has two main functions: to conduct photosynthesis and to produce flowers for sexual reproduction
Organization of Plant Tissue Plant Systems Shoot System The Leaf The Stem The Flower Root System The Shoot System Has two main functions: to conduct photosynthesis and to produce flowers for sexual reproduction
Name Date Block. Plant Structures
 Name Date Block What are the Functions of Roots, Stems, and Leaves? Plant Structures Each part of a plant plays an important role in its structure and function. Roots, stems, and leaves are just three
Name Date Block What are the Functions of Roots, Stems, and Leaves? Plant Structures Each part of a plant plays an important role in its structure and function. Roots, stems, and leaves are just three
The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants.
 INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants. Plants are abundant in almost every environment that
INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants. Plants are abundant in almost every environment that
Plant Anatomy and Life Processes Study Guide
 Plant Anatomy and Life Processes Study Guide Science SOL 4.4 Please use this study guide to study daily for your test! Please keep this study guide in your HOMEWORK FOLDER so that you can use it to study
Plant Anatomy and Life Processes Study Guide Science SOL 4.4 Please use this study guide to study daily for your test! Please keep this study guide in your HOMEWORK FOLDER so that you can use it to study
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Date: 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Date: 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and
1 Evolution of Plants
 1 Evolution of Plants Plant Evolutionary Tree 1 How Did Plant Life Begin? BIBLICAL WORLDVIEW EVOLUTIONARY WORLDVIEW The Biblical worldview is that plants began on the third day of creation, created by
1 Evolution of Plants Plant Evolutionary Tree 1 How Did Plant Life Begin? BIBLICAL WORLDVIEW EVOLUTIONARY WORLDVIEW The Biblical worldview is that plants began on the third day of creation, created by
PLANT Labs summary questions (30 pts)
 PLANT Labs summary questions (30 pts) 1. SEEDS--Without this part of the seed, the embryo has no food to grow before photosynthesis. a. seed coat b. embryo c. leaves d. cotyledon e. tap root 2. SEEDS--Which
PLANT Labs summary questions (30 pts) 1. SEEDS--Without this part of the seed, the embryo has no food to grow before photosynthesis. a. seed coat b. embryo c. leaves d. cotyledon e. tap root 2. SEEDS--Which
Structures of Seed Plants
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
Plant parts and their functions
 UNIT 8 Plant parts and their functions In unit 2, we learnt about the classification and basic parts of plants. Here, we will learn in greater details about the different functions carried out by the plant
UNIT 8 Plant parts and their functions In unit 2, we learnt about the classification and basic parts of plants. Here, we will learn in greater details about the different functions carried out by the plant
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28
 Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Plants and Photosynthesis. Chapters 6 and 31
 Plants and Photosynthesis Chapters 6 and 31 Unit 11, Lecture 1 Topics: Introduction to Plants The Shoot System: The Flower Covers information from: Chapter 31 (PG 598 619) Terms to Describe Plants Eukaryotic
Plants and Photosynthesis Chapters 6 and 31 Unit 11, Lecture 1 Topics: Introduction to Plants The Shoot System: The Flower Covers information from: Chapter 31 (PG 598 619) Terms to Describe Plants Eukaryotic
plant cell tissue nerve cell paramecium
 plant or animal cell? these cells carry what cell? what cell? animal cell red blood oxygen sperm root hair cell (of plant) plant or animal cell? cell, tissue or organ? what cell? paramecium, amoeba or
plant or animal cell? these cells carry what cell? what cell? animal cell red blood oxygen sperm root hair cell (of plant) plant or animal cell? cell, tissue or organ? what cell? paramecium, amoeba or
Directed Reading A. Section: Structures of Seed Plants ROOTS. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Structures of Seed Plants Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What supplies a seed plant with the things it needs to survive? a.
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Structures of Seed Plants Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What supplies a seed plant with the things it needs to survive? a.
Plants and Photosynthesis
 Plants and Photosynthesis Name: Look for more resources at www.burtbooks.com 1 Date: Let s revise the parts of the plant. Look at the names of the parts carefully. Then turn to the next page and fill in
Plants and Photosynthesis Name: Look for more resources at www.burtbooks.com 1 Date: Let s revise the parts of the plant. Look at the names of the parts carefully. Then turn to the next page and fill in
Plants can be either herbaceous or woody.
 Plant Structure Plants can be either herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous plants are plants with growth which dies back to the ground each year, in contrast with woody plants Most herbaceous plants have stems
Plant Structure Plants can be either herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous plants are plants with growth which dies back to the ground each year, in contrast with woody plants Most herbaceous plants have stems
-Producers & Cellular Energy Notes-
 -Producers & Cellular Energy Notes- Part 1 Plants LT 5.1 - I can describe basic information about plants, including the ways they move materials, are classified, reproduce, and evolved. What are plants?
-Producers & Cellular Energy Notes- Part 1 Plants LT 5.1 - I can describe basic information about plants, including the ways they move materials, are classified, reproduce, and evolved. What are plants?
Grade 8 Unit L.4 - Photosynthesis
 - 1 - Curriculum Standards: 8.10.1, 8.10.2, 8.10.3, 8.10.4, 8.10.1 Objectives: Describe the structure and function of each plant cell Key Words Photosynthesis البىاء الضوئي Plant cell الخليت الىباتيت Chloroplast
- 1 - Curriculum Standards: 8.10.1, 8.10.2, 8.10.3, 8.10.4, 8.10.1 Objectives: Describe the structure and function of each plant cell Key Words Photosynthesis البىاء الضوئي Plant cell الخليت الىباتيت Chloroplast
All living things, big and small, are known as organisms.
 Lesson 3: Standard number: 6.1, 6.2, 1.2 All living things, big and small, are known as organisms. خ ع انكبئ بد انس خ,انكج شح انظغ شح تعشف ثبن خه لبد All living things Humans, animals and plants are living
Lesson 3: Standard number: 6.1, 6.2, 1.2 All living things, big and small, are known as organisms. خ ع انكبئ بد انس خ,انكج شح انظغ شح تعشف ثبن خه لبد All living things Humans, animals and plants are living
2a. General: Describe 3 specialised uses for plants. Plants can be used as: i. raw materials ii. foods iii. medicines
 1a. General: Give examples of advantages of there being a wide variety of plants. Greater number of characteristics for breeding. Bigger choice for use as raw materials, foods and medicines. Provide different
1a. General: Give examples of advantages of there being a wide variety of plants. Greater number of characteristics for breeding. Bigger choice for use as raw materials, foods and medicines. Provide different
Autotrophs/producers- make own energy through
 Name Class EXAM Date Unit 11 Plant Kingdom Characteristics of Plants Multicellular- made of cells Eukaryotes- have & membrane bound organelles Cell - made of Autotrophs/producers- make own energy through
Name Class EXAM Date Unit 11 Plant Kingdom Characteristics of Plants Multicellular- made of cells Eukaryotes- have & membrane bound organelles Cell - made of Autotrophs/producers- make own energy through
Internal Adaptations
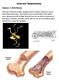 Station 1: Bird Bones Internal Adaptations The bones of birds have hollow openings inside. Therefore, bird bones are less dense than human bones. These hollow spaces cause the bird to have lighter mass,
Station 1: Bird Bones Internal Adaptations The bones of birds have hollow openings inside. Therefore, bird bones are less dense than human bones. These hollow spaces cause the bird to have lighter mass,
Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport
 Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport food, water and minerals throughout the plant. Water and
Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport food, water and minerals throughout the plant. Water and
Discuss: March 15, Plants part 2.notebook NITROGEN CYCLE. Animated Nitrogen Cycle. Jan 3 5:33 PM. Jan 3 8:20 PM. Carbon Cycle BrainPOP
 Plant Kingdom Review What cycles are needed for plant life? - Carbon-Oxygen Cycle (including Photosynthesis) - Nitrogen Cycle - Water Cycle Let's take a look at the first two... Jan 3 5:33 PM Jan 3 8:20
Plant Kingdom Review What cycles are needed for plant life? - Carbon-Oxygen Cycle (including Photosynthesis) - Nitrogen Cycle - Water Cycle Let's take a look at the first two... Jan 3 5:33 PM Jan 3 8:20
Name Date Class. As you read Chapter 12, which begins on page 278 of your textbook, answer the following questions.
 CHAPTER 12 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Plant Processes As you read Chapter 12, which begins on page 278 of your textbook, answer the following questions. Strange but True! (p. 278) 1. How do wasps act as
CHAPTER 12 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Plant Processes As you read Chapter 12, which begins on page 278 of your textbook, answer the following questions. Strange but True! (p. 278) 1. How do wasps act as
Vocabulary. photosynthesis p.48. chlorophyll p.49. sepal p.55. pistil p.55. stamen p.55. ovary p.56. fertilization p.56. dormant p.
 Name: Section: 2 3 4 Vocabulary Word Definition photosynthesis p.48 chlorophyll p.49 sepal p.55 pistil p.55 stamen p.55 ovary p.56 fertilization p.56 dormant p.62 5 6 7 Chapter 2 Lesson 1 What are plants
Name: Section: 2 3 4 Vocabulary Word Definition photosynthesis p.48 chlorophyll p.49 sepal p.55 pistil p.55 stamen p.55 ovary p.56 fertilization p.56 dormant p.62 5 6 7 Chapter 2 Lesson 1 What are plants
Plants Week 6 Booklet
 Plants Week 6 Booklet Living vs. Non-Living Foss Investigation #5 The Vascular System Part 1: What Happened to the Water? Part 2: Looking at Plant Structures Not in Foss- Nonvascular Systems Types of Roots
Plants Week 6 Booklet Living vs. Non-Living Foss Investigation #5 The Vascular System Part 1: What Happened to the Water? Part 2: Looking at Plant Structures Not in Foss- Nonvascular Systems Types of Roots
Shoot System. Root System. below-ground organs (roots) Dermal Tissue. Ground Tissue. Vascular Tissue. above-ground organs (leaves, stems, flowers)
 Shoot System above-ground organs (leaves, stems, flowers) Root System below-ground organs (roots) Dermal Tissue type of plant tissue that is the outer covering of the plant and serves as a protective barrier
Shoot System above-ground organs (leaves, stems, flowers) Root System below-ground organs (roots) Dermal Tissue type of plant tissue that is the outer covering of the plant and serves as a protective barrier
Next Generation Science Standards
 Flower Functions Students learn the basic structure of a plant and how each part works together as a system to obtain essential resources needed for the plant s survival. Grade Level: 1st Phenomena: How
Flower Functions Students learn the basic structure of a plant and how each part works together as a system to obtain essential resources needed for the plant s survival. Grade Level: 1st Phenomena: How
UNIT 3. PLANTS. 5 primary / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández Colegio La Presentación de Granada
 UNIT 3. PLANTS 5 primary / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández Colegio La Presentación de Granada CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANTS A plant is a living thing with limited mobility. There are many different
UNIT 3. PLANTS 5 primary / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández Colegio La Presentación de Granada CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANTS A plant is a living thing with limited mobility. There are many different
1.1 The Body of Seed Plants Seed Plants those
 1.1 The Body of Seed Plants Seed Plants those plants that make seeds. come in all shapes and sizes. have the same structures, which do the same job in all plants. Structures: Flowers each flower usually
1.1 The Body of Seed Plants Seed Plants those plants that make seeds. come in all shapes and sizes. have the same structures, which do the same job in all plants. Structures: Flowers each flower usually
The Flowering Plant and Photosynthesis
 The Flowering Plant and Photosynthesis AIM To name and identify some common Irish trees To identify the parts of a flowering plant To list the function of the flowers, stem, leaves and roots To explain
The Flowering Plant and Photosynthesis AIM To name and identify some common Irish trees To identify the parts of a flowering plant To list the function of the flowers, stem, leaves and roots To explain
Cell parts. nucleus cytoplasm cell surface membrane. cell wall vacuole chloroplast
 7Ab/12 Cell parts nucleus cytoplasm cell surface membrane cell wall vacuole chloroplast found in plant cells only found in plant cells only found in plant cells only found in animal and plant cells found
7Ab/12 Cell parts nucleus cytoplasm cell surface membrane cell wall vacuole chloroplast found in plant cells only found in plant cells only found in plant cells only found in animal and plant cells found
Plants Notes. Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light
 Plants Notes Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light Geotropism - roots knowing which direction is down Thigmotropism - a plant's response to touch Ex. a vine wrapping around and climbing a
Plants Notes Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light Geotropism - roots knowing which direction is down Thigmotropism - a plant's response to touch Ex. a vine wrapping around and climbing a
UNIT 3. PLANTS. PRIMARY 4/ Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 3. PLANTS PRIMARY 4/ Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández They help to keep it in place. Roots They take in the water and minerals a plant needs to make its food. They support the leaves.
UNIT 3. PLANTS PRIMARY 4/ Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández They help to keep it in place. Roots They take in the water and minerals a plant needs to make its food. They support the leaves.
Being a Biologist. Summary Sheets. Gleniffer High School
 Being a Biologist Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 DNA I have extracted DNA and understand its function. I can express an informed view of the risks and benefits of DNA profiling. SCN 3-14b Chromosomes
Being a Biologist Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 DNA I have extracted DNA and understand its function. I can express an informed view of the risks and benefits of DNA profiling. SCN 3-14b Chromosomes
Plants! Plants. Plants. Plants. Plant Classifications. Plant Classifications. All plants are multi-cellular, autotrophic.
 Plants Plants! An introduction All plants are multi-cellular, autotrophic. Lots of cells. Produces its own food using chlorophyll. Has a Nucleus. Plants The plant kingdom is one of the largest groups of
Plants Plants! An introduction All plants are multi-cellular, autotrophic. Lots of cells. Produces its own food using chlorophyll. Has a Nucleus. Plants The plant kingdom is one of the largest groups of
2018 Version. Photosynthesis Junior Science
 2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis. So, to review, for photosynthesis to occur a plant needs: Water Chemical Energy from Sunlight Chlorophyll Carbon Dioxide
 Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is one of the most important natural processes that occur. It is also one of the hardest processes to understand. If you are not sure what exactly photosynthesis is do not
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is one of the most important natural processes that occur. It is also one of the hardest processes to understand. If you are not sure what exactly photosynthesis is do not
Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls
 1 Plant Characteristics: Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls chloroplast vacuole Golgi body Cell wall nucleus mitochondria Cell membrane 2
1 Plant Characteristics: Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls chloroplast vacuole Golgi body Cell wall nucleus mitochondria Cell membrane 2
FAST! Tajweed Intensive Workshop! Rules of Noon Sakinah & Tanween Part 1
 FAST! Tajweed Intensive Workshop! Rules of Noon Sakinah & Tanween Part 1 1 Rules of Noon Sakinah and Tanween (Idhaar and Iqlaab) 2 Identifying Noon Sakinah and Tanween Noon Sakinah: When the letter Noon
FAST! Tajweed Intensive Workshop! Rules of Noon Sakinah & Tanween Part 1 1 Rules of Noon Sakinah and Tanween (Idhaar and Iqlaab) 2 Identifying Noon Sakinah and Tanween Noon Sakinah: When the letter Noon
(b) The foods synthesized by the plants are stored as. (c) In photosynthesis solar energy is captured by the pigment called.
 WORKSHEET -1 CHAPTER- HOW DO PLANTS LIVE SUBJECT-BIOLOGY GRADE:7 LEVEL 1 1. Fill in the blanks: (a) Green plants are called since they synthesize their own food. (b) The foods synthesized by the plants
WORKSHEET -1 CHAPTER- HOW DO PLANTS LIVE SUBJECT-BIOLOGY GRADE:7 LEVEL 1 1. Fill in the blanks: (a) Green plants are called since they synthesize their own food. (b) The foods synthesized by the plants
Jeddah Knowledge International School
 Jeddah Knowledge International School Biology Revision Pack Answer key 2016-2017 Quarter 3 Grade 9 Name: Section: ANSWER KEY- SCIENCE GRADE 9, QUARTER 3 1 Mark Scheme Multiple Choice Part A 1. Which gas
Jeddah Knowledge International School Biology Revision Pack Answer key 2016-2017 Quarter 3 Grade 9 Name: Section: ANSWER KEY- SCIENCE GRADE 9, QUARTER 3 1 Mark Scheme Multiple Choice Part A 1. Which gas
Kingdom Plantae. Biology : A Brief Survey of Plants. Jun 22 7:09 PM
 Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
Year 7 Science 7B1: Microscopes, Cells and Plant Reproduction PPA Challenge
 Year 7 Science 7B1: Microscopes, Cells and Plant Reproduction PPA Challenge Name: Form: Task Sheet 1 (Bronze Challenge): What parts does a microscope have? Use the words in the boxes below to label the
Year 7 Science 7B1: Microscopes, Cells and Plant Reproduction PPA Challenge Name: Form: Task Sheet 1 (Bronze Challenge): What parts does a microscope have? Use the words in the boxes below to label the
Flower Power!! Background knowledge material and dissection directions.
 Flower Power!! Background knowledge material and dissection directions. 96 Plant Dissection 3.2 Plants Essential Question: Why do plants have flowers? Questions: As you read the lab background, complete
Flower Power!! Background knowledge material and dissection directions. 96 Plant Dissection 3.2 Plants Essential Question: Why do plants have flowers? Questions: As you read the lab background, complete
Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card DFAD
 Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card DFAD Do First: Answer the following 3 questions in your DFAD Skip #1 in our DFAD I will only be grading #2 and #3 from your Do First today. Photosynthesis takes
Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card DFAD Do First: Answer the following 3 questions in your DFAD Skip #1 in our DFAD I will only be grading #2 and #3 from your Do First today. Photosynthesis takes
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this
 Unit B: Tree Growth and Development Lesson 2: Understanding the Growth and Decline of Forest Trees Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following
Unit B: Tree Growth and Development Lesson 2: Understanding the Growth and Decline of Forest Trees Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following
A leaf is. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
 The leaf system A leaf is Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy a plant organ, Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy that s photosynthetic, Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy contains chloroplasts, Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
The leaf system A leaf is Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy a plant organ, Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy that s photosynthetic, Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy contains chloroplasts, Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
Flowers Seeds Pollination Germination
 * Flowers Seeds Pollination Germination *In order for plants to be successful in many different environments they must be able to reproduce themselves. *The reproductive patterns of plants reflect the
* Flowers Seeds Pollination Germination *In order for plants to be successful in many different environments they must be able to reproduce themselves. *The reproductive patterns of plants reflect the
Chapter 23: Plant Diversity and Life Cycles
 Chapter 23: Plant Diversity and Life Cycles Section 1: Introduction to Plants Cuticle: a waxy or fatty and watertight layer on the external wall of epidermal cells Spore: a reproductive cell or multicellular
Chapter 23: Plant Diversity and Life Cycles Section 1: Introduction to Plants Cuticle: a waxy or fatty and watertight layer on the external wall of epidermal cells Spore: a reproductive cell or multicellular
OPTIMAL SHIFTING OF EIGENVALUES FOR LOAD FREQUENCY CONTROL SYSTEMS
 857 OPTIMAL SHIFTING OF EIGENVALUES FOR LOAD FREQUENCY CONTROL SYSTEMS Corresponding author E-mail address: drali_yousef@yahoocom Ali M Yousef Department of Electrical Eng, Faculty of Engineering, Assiut
857 OPTIMAL SHIFTING OF EIGENVALUES FOR LOAD FREQUENCY CONTROL SYSTEMS Corresponding author E-mail address: drali_yousef@yahoocom Ali M Yousef Department of Electrical Eng, Faculty of Engineering, Assiut
Unit 1 Plants - Extra Worksheets
 Unit 1 Plants - Extra Worksheets 1 Complete the sentences using the words in the box. Plants can make their own using light from the. They also need carbon gas and. 2 Label the parts of the diagram to
Unit 1 Plants - Extra Worksheets 1 Complete the sentences using the words in the box. Plants can make their own using light from the. They also need carbon gas and. 2 Label the parts of the diagram to
Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools
 Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools Supported by: National Science Foundation Life Sciences: 4.E.4 Seeds Part 1 of 3 Grade Level 4 Sessions
Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools Supported by: National Science Foundation Life Sciences: 4.E.4 Seeds Part 1 of 3 Grade Level 4 Sessions
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to the life cycle of flowering plants (90928)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90928) 2017 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to the life cycle of flowering plants (90928) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90928) 2017 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to the life cycle of flowering plants (90928) Evidence Statement QUESTION
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Plants Alive What are the characteristics of plants? All plants are multicellular, which means their bodies are made up of more than one cell. Plants are eukaryotes, which means
Introduction to Plants Plants Alive What are the characteristics of plants? All plants are multicellular, which means their bodies are made up of more than one cell. Plants are eukaryotes, which means
Standard Grade Biology Revision Notes
 Standard Grade Biology Revision Notes The Biosphere Habitat where an animal lives Community all the plants and animals in an area Ecosystem living and non living parts (habitat + community) Population
Standard Grade Biology Revision Notes The Biosphere Habitat where an animal lives Community all the plants and animals in an area Ecosystem living and non living parts (habitat + community) Population
Teacher s Discussion Notes Part 1
 Teacher s Discussion Notes Part 1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Vocabulary: Chlorophyll--A green substance which gives leaves their color. Chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight, which a plant uses to make food. Chloroplast--A
Teacher s Discussion Notes Part 1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Vocabulary: Chlorophyll--A green substance which gives leaves their color. Chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight, which a plant uses to make food. Chloroplast--A
Year 3 Science Expectations
 Year 3 Science Expectations Term Key Learning Autumn 1 Pupils should explore what happens when light reflects off a mirror or other reflective surfaces, including playing mirror games to help them answer
Year 3 Science Expectations Term Key Learning Autumn 1 Pupils should explore what happens when light reflects off a mirror or other reflective surfaces, including playing mirror games to help them answer
SCI-4 BNES 4.4 Summative Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SCI-4 BNES 4.4 Summative Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1LEHLS 1 Which seed is carried by the wind? A B C D 2 Which section of the plant is the roots? A Section 3 B Section 1 C
SCI-4 BNES 4.4 Summative Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1LEHLS 1 Which seed is carried by the wind? A B C D 2 Which section of the plant is the roots? A Section 3 B Section 1 C
2. Which of the following is an organism that is made of only one cell? A. a larva B. an oyster C. an amoeba D. a mold
 1. I am the barrier between the inside and the outside of the cell. I allow food, oxygen, and other needed materials to enter the cell. I am a part of animal and plant cells. A. cell membrane B. cell wall
1. I am the barrier between the inside and the outside of the cell. I allow food, oxygen, and other needed materials to enter the cell. I am a part of animal and plant cells. A. cell membrane B. cell wall
Kingdom Plantae. Plants or metaphytes are, autotrophic multicellular eukaryotes, with tissues.
 Kingdom Plantae Key words feature bryophytes herbaceous node to release pteridophytes sporangium, leaf (leaves) damp gymnosperms vascular apix cluster angiosperms rhizome sepal shrub tropism fronds calyx
Kingdom Plantae Key words feature bryophytes herbaceous node to release pteridophytes sporangium, leaf (leaves) damp gymnosperms vascular apix cluster angiosperms rhizome sepal shrub tropism fronds calyx
Behavioral and Structural Adaptations PPT Guided Notes
 A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
Study for Test April 26, Chapter 4. Review of Metabolism and Photosynthesis and Carbohydrates, Fats (Lipids) & Proteins
 Chapter 4 Review of Metabolism and Photosynthesis and Carbohydrates, Fats (Lipids) & Proteins GLCE's L.OL.07.61:Recognize the need for light to provide energy for the production of carbohydrates, proteins,
Chapter 4 Review of Metabolism and Photosynthesis and Carbohydrates, Fats (Lipids) & Proteins GLCE's L.OL.07.61:Recognize the need for light to provide energy for the production of carbohydrates, proteins,
PLANT LIFECYCLES. Name: Class:
 PLANT LIFECYCLES Name: Class: Directions: Match the words with the big ideas by writing the letter beside the idea. Use the same words in the short article below. Use key words and phrases from the article
PLANT LIFECYCLES Name: Class: Directions: Match the words with the big ideas by writing the letter beside the idea. Use the same words in the short article below. Use key words and phrases from the article
۲۷۹۶ 0 "' ی " #! ۴۳ و م د ; < : ی"98! ی"#"!
 *+, " ان ی" ت/ ر ل. د& ر/ ی/ ر 3 ی" ی" ق: یb نi ی: ی: ی: ره 0 ی/? ی 3 ۲۷۹۶ +* - د' #"! 6 آ (۱)4, 3 2 ا. -, & + ک& ) & ( % $ # ی ا 6 آ 4, / ) $ 2 & ) ر د آ ر د $ 2 ر د : 9-8 د > E < D 2 ا C د: B? > = A
*+, " ان ی" ت/ ر ل. د& ر/ ی/ ر 3 ی" ی" ق: یb نi ی: ی: ی: ره 0 ی/? ی 3 ۲۷۹۶ +* - د' #"! 6 آ (۱)4, 3 2 ا. -, & + ک& ) & ( % $ # ی ا 6 آ 4, / ) $ 2 & ) ر د آ ر د $ 2 ر د : 9-8 د > E < D 2 ا C د: B? > = A
Nonvascular plants Vascular plants Spore Gymnosperm Angiosperm Germinate. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Nonvascular plants Vascular plants Spore Gymnosperm Angiosperm Germinate Tubes for Transport Warm Up 1 Tubes for Transport Nonvascular plants are simple plants that lack vascular tissue, which easily transports
Nonvascular plants Vascular plants Spore Gymnosperm Angiosperm Germinate Tubes for Transport Warm Up 1 Tubes for Transport Nonvascular plants are simple plants that lack vascular tissue, which easily transports
1 Mendel and His Peas
 CHAPTER 6 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity 7.2.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? Who was
CHAPTER 6 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity 7.2.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? Who was
*Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats.
 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. Reproduction In Plants Plant reproduction is the production of new
Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. Reproduction In Plants Plant reproduction is the production of new
Plant Structure and Function. Roots, Stems, and Leaves
 Plant Structure and Function Roots, Stems, and Leaves What is a Plant? Plants are living things that have: roots, stems, and leaves (some have flowers) Plants are made of cells that have cell walls, a
Plant Structure and Function Roots, Stems, and Leaves What is a Plant? Plants are living things that have: roots, stems, and leaves (some have flowers) Plants are made of cells that have cell walls, a
1.1 Characteristics common to organisms
 Biology Form 3 Page 5 Ms. R. Buttigieg 1.1 Characteristics common to organisms see GCSE Biology pg. 292 Biology is the study of living things. We call living things organisms. Plants and animals are ALL
Biology Form 3 Page 5 Ms. R. Buttigieg 1.1 Characteristics common to organisms see GCSE Biology pg. 292 Biology is the study of living things. We call living things organisms. Plants and animals are ALL
Directed Reading A. Section: Structures of Seed Plants. is called a. shoots. c. phloem. b. xylem. d. leaves. is called ROOTS. size.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Structures of Seed Plants 1. Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals through a plant is called a. shoots. c. phloem. b. xylem. d. leaves. 2. Vascular
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Structures of Seed Plants 1. Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals through a plant is called a. shoots. c. phloem. b. xylem. d. leaves. 2. Vascular
Root cross-section (Ranunculus)
 Plant Lab Review Root cross-section (Ranunculus) Epidermis Cortex Vascular Cylinder Phloem Endodermis Xylem Ranunculus Root Cross section Give three functions of the root Anchor plant Absorb water and
Plant Lab Review Root cross-section (Ranunculus) Epidermis Cortex Vascular Cylinder Phloem Endodermis Xylem Ranunculus Root Cross section Give three functions of the root Anchor plant Absorb water and
2 sentences. Why your first answer was wrong Why your new answer is correct
 2 sentences Why your first answer was wrong Why your new answer is correct Which biochemical process is outlined in the diagram? A. Anaerobic Respiration B. Aerobic Respiration C. Photosynthesis D. Transpiration
2 sentences Why your first answer was wrong Why your new answer is correct Which biochemical process is outlined in the diagram? A. Anaerobic Respiration B. Aerobic Respiration C. Photosynthesis D. Transpiration
Cells Key Words. Task. Key words. Write a definition for each of the key words listed below. Microscope. Plant cell. Animal Cell.
 KS3 Science Cells Cells Key Words Task Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words Microscope Plant cell Animal Cell Nucleus Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cell wall Chloroplasts Mitochondria
KS3 Science Cells Cells Key Words Task Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words Microscope Plant cell Animal Cell Nucleus Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cell wall Chloroplasts Mitochondria
ì<(sk$m)=bdjidf< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Compare and Contrast Labels Captions Plants Diagrams Glossary Scott Foresman Science 6.5 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Compare and Contrast Labels Captions Plants Diagrams Glossary Scott Foresman Science 6.5 ì
Nerve cells have many branches that help them send signals throughout the body.
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
Chapter 8 Objectives
 CHAPTER 8 PLANTS 1 Chapter 8 Objectives Section 1: The Plant Kingdom 1. Identify the characteristics all plants share 2. Name the things that a plant needs to live successfully on land 3. Compare vascular
CHAPTER 8 PLANTS 1 Chapter 8 Objectives Section 1: The Plant Kingdom 1. Identify the characteristics all plants share 2. Name the things that a plant needs to live successfully on land 3. Compare vascular
1 Mendel and His Peas
 CHAPTER 5 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? How did Gregor Mendel study heredity? National
CHAPTER 5 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? How did Gregor Mendel study heredity? National
Roots, Shoots & Leaves
 Name Test Date Hour Plant Structure & Function #2 - Notebook Roots, Shoots & Leaves LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the functions of roots I can explain the nitrogen fixing process and why it is needed.
Name Test Date Hour Plant Structure & Function #2 - Notebook Roots, Shoots & Leaves LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the functions of roots I can explain the nitrogen fixing process and why it is needed.
vascular phloem These 68 vocabulary cards are part of a SCIENCE unit. Please keep this set in: Plants - Standard 6-8
 Instructions for Vocabulary Cards: Please photocopy the following pages onto heavy card stock (back to back, so the word is printed on the back side of the matching definition). Then, laminate each page.
Instructions for Vocabulary Cards: Please photocopy the following pages onto heavy card stock (back to back, so the word is printed on the back side of the matching definition). Then, laminate each page.
Haddie Beckham Due date: 11/8/13 Biology B Biology Plant Essay Plants play a vital role in the world s existance, they re hard workers in what many
 Haddie Beckham Due date: 11/8/13 Biology B Biology Plant Essay Plants play a vital role in the world s existance, they re hard workers in what many of all of us on this planet need to be able tor survive.
Haddie Beckham Due date: 11/8/13 Biology B Biology Plant Essay Plants play a vital role in the world s existance, they re hard workers in what many of all of us on this planet need to be able tor survive.
Plant Bodies as Systems
 Plant Bodies as Systems Objectives: Explain the organization of Plants Identify and describe the different body systems in a plant Evaluate how the survival needs of plants are met by systems working together
Plant Bodies as Systems Objectives: Explain the organization of Plants Identify and describe the different body systems in a plant Evaluate how the survival needs of plants are met by systems working together
Unit 6L.1: Cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A collection of specialized cells makes tissues.
 Unit 6L.1: Living things are made of Specialized cells Tissues and Organs Cell Division By the end of this unit you will know: All living organisms are made of cells. A collection of specialized cells
Unit 6L.1: Living things are made of Specialized cells Tissues and Organs Cell Division By the end of this unit you will know: All living organisms are made of cells. A collection of specialized cells
5. Many young insects look when they become adult insects. A. the same B. different
 REVIEW PACKET CHAPTER 4: LESSON 1 1. Number 1 to 3 in sequential order: Butterfly lands on a flower. Butterfly flies away. Butterfly drinks from nectar. 2. Butterflies are A. mammals B. insects C. birds
REVIEW PACKET CHAPTER 4: LESSON 1 1. Number 1 to 3 in sequential order: Butterfly lands on a flower. Butterfly flies away. Butterfly drinks from nectar. 2. Butterflies are A. mammals B. insects C. birds
1 Plant Characteristics!
 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Plant Characteristics! CHAPTER 1 Plant Characteristics! Identify common traits of plants. What are Plants? Plants are multicellular eukaryotic organisms with cell wallscellulosechloroplasts
www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Plant Characteristics! CHAPTER 1 Plant Characteristics! Identify common traits of plants. What are Plants? Plants are multicellular eukaryotic organisms with cell wallscellulosechloroplasts
Plant Vocabulary. Define
 Define Plant Vocabulary 1. Photosynthesis 2. Eukaryotic 3. Monocot 4. Dicot 5. Cotyledon 6. Roots 7. Stems 8. Leaves 9. Xylem 10. Phloem 11. Capillary action 12. Meristem 13. Apical meristem 14. Vascular
Define Plant Vocabulary 1. Photosynthesis 2. Eukaryotic 3. Monocot 4. Dicot 5. Cotyledon 6. Roots 7. Stems 8. Leaves 9. Xylem 10. Phloem 11. Capillary action 12. Meristem 13. Apical meristem 14. Vascular
Plant Anatomy and Physiology. What are the parts of the plant, and how do they work?
 Plant Anatomy and Physiology What are the parts of the plant, and how do they work? What is Classification GROUPING things according to their CHARACTERISTICS Plant Classification (5 Kingdoms) ANIMAL PLANT
Plant Anatomy and Physiology What are the parts of the plant, and how do they work? What is Classification GROUPING things according to their CHARACTERISTICS Plant Classification (5 Kingdoms) ANIMAL PLANT
5.5 Organisms (Living Systems)
 Science Trivia 5 th grade Updated 2012 5.5 Organisms (Living Systems) 1 The brain or center of a cell that controls its activities - 2 3 What is the liquid in a cell that contains chemicals needed to keep
Science Trivia 5 th grade Updated 2012 5.5 Organisms (Living Systems) 1 The brain or center of a cell that controls its activities - 2 3 What is the liquid in a cell that contains chemicals needed to keep
GRADE 7: Life science 4. UNIT 7L.4 7 hours. Growing plants. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 7: Life science 4 Growing plants UNIT 7L.4 7 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
GRADE 7: Life science 4 Growing plants UNIT 7L.4 7 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
Plant Biology Biology Concepts of Biology 10.1
 Plant Biology Biology 100 - Concepts of Biology 10.1 Name Instructor Lab Section Objectives: To gain an understanding of: The anatomy and physiology of plants Transport of water and nutrients Plant reproductive
Plant Biology Biology 100 - Concepts of Biology 10.1 Name Instructor Lab Section Objectives: To gain an understanding of: The anatomy and physiology of plants Transport of water and nutrients Plant reproductive
Embryology of the Muscular System
 Embryology of the Muscular System Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Development of Skeletal muscle Muscles of the head are derived from seven
Embryology of the Muscular System Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Development of Skeletal muscle Muscles of the head are derived from seven
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline)
 Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
Photosynthesis limiting factors
 Photosynthesis limiting factors What you should know by the end of this unit: Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants make their own food. Light energy is trapped by the green pigment chlorophyll.
Photosynthesis limiting factors What you should know by the end of this unit: Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants make their own food. Light energy is trapped by the green pigment chlorophyll.
Chapter 15 PLANT STRUCTURES AND TAXONOMY
 Chapter 15 PLANT STRUCTURES AND TAXONOMY Chapter 15: Parts of a plant Manufactures food by photosynthesis Attracts insects for pollination Contains seeds Supports branches and transports food and water
Chapter 15 PLANT STRUCTURES AND TAXONOMY Chapter 15: Parts of a plant Manufactures food by photosynthesis Attracts insects for pollination Contains seeds Supports branches and transports food and water
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 8.2 - Sexual Reproduction in Plants Sexual Reproduction in Plants In a plant, the flower is the sexual organ, and it has both male and females parts.
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 8.2 - Sexual Reproduction in Plants Sexual Reproduction in Plants In a plant, the flower is the sexual organ, and it has both male and females parts.
Biology Y9 HY Page 1 of 12
 S E C O N D A R Y S C H O O L - M R I E Ħ E L HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2017/2018 YEAR 9 Biology Time: 2 hours Name: Class: Section A: Answer ALL the questions in this section in the space provided. This
S E C O N D A R Y S C H O O L - M R I E Ħ E L HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2017/2018 YEAR 9 Biology Time: 2 hours Name: Class: Section A: Answer ALL the questions in this section in the space provided. This
