BIOLOGY 345 Midterm II - 15 November 2010 PART I. Multiple choice questions (4 points each, 32 points total).
|
|
|
- Brittney Byrd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOLOGY 345 Name Midterm II - 15 November 2010 PART I. Multiple choice questions (4 points each, 32 points total). 1. Considering the multitude of potential metabolic processes available to Bacteria and Archaea, which of the following is used to best describe specific types of phototrophic metabolisms? A. Energy source B. Carbon source C. Electron source D. Hydrogen source E. All of the above 2. If an oxidation reaction occurs, a reduction reaction must also occur because: A. Electrons cannot exist alone in solution. B. A carbon source requires it. C. Half reactions are written that way. D. Actually, reduction is not necessary if oxidation occurs. E. All of the above. 3. Which of the following electron acceptors has the greatest potential to provide the largest amount of free energy? A. 2- SO 4 B. H 2 C. O 2 D. Fe 3+ E. + NH 4 4. Which of the following energy and/or electron carriers contains a nucleotide as part of its molecular structure? A. NADP + + H + B. FADH 2 C. ATP D. Acetyl CoA E. All of the above Page 1 of 8
2 5. There are many ways to produce organic carbon inside the cell, which of the following is NOT considered a mechanisms for fixing CO 2? A. Calvin cycle B. Reverse TCA C. Proteorhodopsin D. Hydroxyproprionate E. Methanogenesis 6. Consider the soluble hydrogenase. Which of the following electron carriers is directly associated with this hydrogenase? A. FADH 2 B. ferredoxin C. cytochrome C D. plastoquinone E. NADH+H + 7. The elegant porphyrin ring made it possible for many metabolic pathways. Which of the following is a combination of an element that can be found in center of a porphyrin ring along with its corresponding metabolic pathway? A. Co / methanogenesis B. Fe / photosynthesis C. Mg / aerobic respiration D. S / sulphate reduction E. C / fermentation 8. Two parts: (I)Which fermentation pathway is detected when using the Voges-Proskauer test? AND (II) Which fermentation pathway is detected when using the methyl red test when differentiating among enteric bacteria? Make sure to circle two answers! A. Butanediol fermentation B. Mixed acid fermentation C. Ethanol fermentation D. Lactic acid fermentation E. Proprionic acid fermentation F. Acetone/Butanol fermentation Page 2 of 8
3 PART II. Short answer questions (Number of points in parentheses, 88 points total). 9. (3 points) What is simply meant by the statement that: All bacteria are osmotrophs? 10. (6 points) During what metabolic process are the source of electrons and the source of energy uncoupled (i.e., not the same)? 11. (12 points) ATP is produced by processes known as: (A) substrate-level phosphorylation, (B) oxidative-phosphorylation, or (C) photo-phosphorylation Indicate (using A, B, &/or C) which of the following three phosphorylation reactions listed above are usually responsible for ATP generation (recycling) in the following types of metabolisms. Note: Some forms of metabolism may involve more than one process. (I) fermentation (II) anaerobic respiration (III) aerobic respiration (IV) chemolithotrophy (V) anoxygenic phototrophy (VI) oxygenic phototrophy Page 3 of 8
4 12. (6 points) What is meant by sulfur disproportionation? Can you also name a similar type of metabolism for either nitrogen or carbon compounds? 13. (6 points) What is the purpose of an anammoxosome AND why does it not fit into the usual paradigm regarding membrane bound organelles? 14. (6 points) Why is the Entner-Doudoroff pathway, when compared to the classical Embden-Myerhof pathway of glycolysis, thought to be the predecessor of the two in terms of efficiency? 15. (6 points) What new twist has recently arisen concerning the ability to produce ATP during fermentation (why is this new format considered so unusual?) AND what are the names of at least one pair of organic acids that are involved? Page 4 of 8
5 16. (8 points) In terms of electron donors and acceptors, why was the development of oxygenic photosynthesis such a major advancement? And, in terms of light harvesting capability (e.g., absorption spectra), why are cyanobacteria so efficient at oxygenic photosynthesis? 17. (6 points) What is the special feature that is represented by occurrence of ferredoxin in phototrophs? (In other words, what can they do that other phototrophs cannot?) 18. (6 points) Why do the non-cyanobacterial phototrophs have such a diverse array of bacteriochlorophyll structures and associated carotenoid pigments? In other words, why such diversity among the anoxygenic photosynthesizers? Page 5 of 8
6 19. (15 points) For the following list of key enzymes and/or molecular structures. Your job is to name the group of microorganisms that uses each characteristic enzyme and/or structure AND briefly describe how each might be used in that group s characteristic metabolic pathway. Example Phosphofructokinase: Heterotrophs Glycolysis Rusticyanin: Coenzyme F 420 : Membrane-bound Hydrogenase: Crotonyl-CoA: Cytochrome C oxidase: 20. (8 points) As aerobic heterotrophic bacteria are devoid of autonomous organelles, (A) which two entire metabolic pathways require enzymes that are bound exclusively within the inner face of the cell membrane, also (B) name one other key pathway where a single enzyme step is also found here? Bonus (4 points) which step in this pathway is it? Page 6 of 8
7 PART III. Short Essay (Number of points in parentheses, 30 points total). 21. (15 points) Consider the chemoorganotrophic pathways associated with sulphatereducing bacteria (SRBs) and methanogens. (A) Please describe each groups sources of energy, electrons, and carbon. (B) What is the main reason that one group is exclusively made of Archaea? (C) In terms of redox couples and available free energy, which group do you think could out compete the other if they were found in the same habitat, i.e., the flip-side is, which group has to work the hardest to make its ATP? Page 7 of 8
8 22. (15 points) The endosymbiotic theory combined with ribosomal phylogeny indicates that both mitochondria and chloroplasts were once free-living bacteria (α-proteobacteria and cyanobacteria, respectively). We also consider these organelles to be semi-autonomous as each contains its own localized genomic DNA. As evolution has progressed, the pattern has been the slow but steady transference of organelle gene sequences to the nucleus. The amount of the genome that has been transferred is dramatically greater in mitochondria than chloroplasts. (A) With what you know about the availability of oxygen, what was the relative occurrence of oxygenic photosynthesis as opposed to aerobic respiration (i.e., when did each first occur)? (B) Why does this seem somewhat counterintuitive relative to the occurrence of these organelles in multicellular organisms (i.e., plants & animals)? (C) Suggest an explanation as to how you might resolve this conundrum? Page 8 of 8
Energy for Life 12/11/14. Light Absorption in Chloroplasts
 Energy for Life Biochemical pathways A series of reactions where the products of one reaction is used in the next reaction Light Absorption in Chloroplasts Chloroplasts Two membranes Grana- layered stacks
Energy for Life Biochemical pathways A series of reactions where the products of one reaction is used in the next reaction Light Absorption in Chloroplasts Chloroplasts Two membranes Grana- layered stacks
Name Date Class. Photosynthesis and Respiration
 Concept Mapping Photosynthesis and Respiration Complete the Venn diagram about photosynthesis and respiration. These terms may be used more than once: absorbs, Calvin cycle, chlorophyll, CO 2, H 2 O, Krebs
Concept Mapping Photosynthesis and Respiration Complete the Venn diagram about photosynthesis and respiration. These terms may be used more than once: absorbs, Calvin cycle, chlorophyll, CO 2, H 2 O, Krebs
Chapter 5. Table of Contents. Section 1 Energy and Living Things. Section 2 Photosynthesis. Section 3 Cellular Respiration
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Table of Contents Section 1 Energy and Living Things Section 2 Photosynthesis Section 3 Cellular Respiration Section 1 Energy and Living Things Objectives Analyze
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Table of Contents Section 1 Energy and Living Things Section 2 Photosynthesis Section 3 Cellular Respiration Section 1 Energy and Living Things Objectives Analyze
Cellular respiration. How do living things stay alive? Cellular Respiration Burning. Photosynthesis. Cellular Respiration
 How do living things stay alive? Cellular Respiration Burning Happens in ALL living things inside cells and has the main goal of producing ATP the fuel of life It does not matter whether the organisms
How do living things stay alive? Cellular Respiration Burning Happens in ALL living things inside cells and has the main goal of producing ATP the fuel of life It does not matter whether the organisms
BBS2710 Microbial Physiology. Module 5 - Energy and Metabolism
 BBS2710 Microbial Physiology Module 5 - Energy and Metabolism Topics Energy production - an overview Fermentation Aerobic respiration Alternative approaches to respiration Photosynthesis Summary Introduction
BBS2710 Microbial Physiology Module 5 - Energy and Metabolism Topics Energy production - an overview Fermentation Aerobic respiration Alternative approaches to respiration Photosynthesis Summary Introduction
Photosynthesis and cellular respirations
 The Introduction of Biology Defining of life Basic chemistry, the chemistry of organic molecules Classification of living things History of cells and Cells structures and functions Photosynthesis and cellular
The Introduction of Biology Defining of life Basic chemistry, the chemistry of organic molecules Classification of living things History of cells and Cells structures and functions Photosynthesis and cellular
Cell Energetics. How plants make food and everyone makes energy!
 Cell Energetics How plants make food and everyone makes energy! Carbon Cycle Where did the mitochondria and chloroplast come from? Endosymbiotic Theory Endosymbiotic theory = a theory that some of the
Cell Energetics How plants make food and everyone makes energy! Carbon Cycle Where did the mitochondria and chloroplast come from? Endosymbiotic Theory Endosymbiotic theory = a theory that some of the
Cell Energy Notes ATP THE ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY. CELL ENERGY Cells usable source of is called ATP stands for. Name Per
 Cell Energy Notes Name Per THE ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY The Endosymbiotic theory is the idea that a long time ago, engulfed other prokaryotic cells by. This resulted in the first First proposed by Explains
Cell Energy Notes Name Per THE ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY The Endosymbiotic theory is the idea that a long time ago, engulfed other prokaryotic cells by. This resulted in the first First proposed by Explains
CP Biology Unit 5 Cell Energy Study Guide. Electron Carriers Electron Transport Chain Fermentation Glycolysis Krebs cycle Light-Dependent Reactions
 Name: KEY CP Biology Unit 5 Cell Energy Study Guide Vocabulary to know: ATP ADP Aerobic Anaerobic ATP Synthases Cellular Respiration Chlorophyll Chloroplast Electron Carriers Electron Transport Chain Fermentation
Name: KEY CP Biology Unit 5 Cell Energy Study Guide Vocabulary to know: ATP ADP Aerobic Anaerobic ATP Synthases Cellular Respiration Chlorophyll Chloroplast Electron Carriers Electron Transport Chain Fermentation
Bio102 Problems Photosynthesis
 Bio102 Problems Photosynthesis 1. Why is it advantageous for chloroplasts to have a very large (in surface area) thylakoid membrane contained within the inner membrane? A. This limits the amount of stroma
Bio102 Problems Photosynthesis 1. Why is it advantageous for chloroplasts to have a very large (in surface area) thylakoid membrane contained within the inner membrane? A. This limits the amount of stroma
Be sure to understand:
 Learning Targets & Focus Questions for Unit 6: Bioenergetics Chapter 8: Thermodynamics Chapter 9: Cell Resp Focus Q Ch. 10: Photosynthesis Chapter 8 (141-150) 1. I can explain how living systems adhere
Learning Targets & Focus Questions for Unit 6: Bioenergetics Chapter 8: Thermodynamics Chapter 9: Cell Resp Focus Q Ch. 10: Photosynthesis Chapter 8 (141-150) 1. I can explain how living systems adhere
Center for Academic Services & Advising
 March 2, 2017 Biology I CSI Worksheet 6 1. List the four components of cellular respiration, where it occurs in the cell, and list major products consumed and produced in each step. i. Hint: Think about
March 2, 2017 Biology I CSI Worksheet 6 1. List the four components of cellular respiration, where it occurs in the cell, and list major products consumed and produced in each step. i. Hint: Think about
4. Label the diagram below of the electron movement with regard to the coenzyme NAD+.
 AP Biology Reading Packet 3- Respiration and Photosynthesis Name Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration 1. Use the following terms correctly in a sentence: redox reactions, oxidation, reduction, reducing agent
AP Biology Reading Packet 3- Respiration and Photosynthesis Name Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration 1. Use the following terms correctly in a sentence: redox reactions, oxidation, reduction, reducing agent
Unit 3: Cell Energy Guided Notes
 Enzymes Unit 3: Cell Energy Guided Notes 1 We get energy from the food we eat by breaking apart the chemical bonds where food is stored. energy is in the bonds, energy is the energy we use to do things.
Enzymes Unit 3: Cell Energy Guided Notes 1 We get energy from the food we eat by breaking apart the chemical bonds where food is stored. energy is in the bonds, energy is the energy we use to do things.
2015 AP Biology PRETEST Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Week of October
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ 2015 AP Biology PRETEST Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Week of 19-23 October Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which
Name: Class: _ Date: _ 2015 AP Biology PRETEST Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Week of 19-23 October Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which
Energy Exchanges Exam: What to Study
 Energy Exchanges Exam: What to Study Here s what you will need to make sure you understand in order to prepare for our exam: Free Energy Conceptual understanding of free energy as available energy in a
Energy Exchanges Exam: What to Study Here s what you will need to make sure you understand in order to prepare for our exam: Free Energy Conceptual understanding of free energy as available energy in a
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Unit
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Unit All cellular activities require energy. Directly or indirectly nearly all energy for life comes from the sun. Autotrophs: organisms that can make their own
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Unit All cellular activities require energy. Directly or indirectly nearly all energy for life comes from the sun. Autotrophs: organisms that can make their own
Cellular Energy. How Organisms Obtain Energy Section 2: Photosynthesis Section 3: Cellular Respiration. Click on a lesson name to select.
 Section 1: How Organisms Obtain Energy Section 2: Photosynthesis Section 3: Cellular Respiration Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 How Organisms Obtain Energy Transformation of Energy Energy
Section 1: How Organisms Obtain Energy Section 2: Photosynthesis Section 3: Cellular Respiration Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 How Organisms Obtain Energy Transformation of Energy Energy
6CO 2 + 6H 2 O C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2. sun. Occurs in chloroplasts ATP. enzymes CO 2 O 2 H 2 O. sugars
 4.2 8.2 Overview Photosynthesis: of Photosynthesis An Overview Photosynthesis process by which plants make food using energy from the sun Plants are autotrophs that make their own source of chemical energy.
4.2 8.2 Overview Photosynthesis: of Photosynthesis An Overview Photosynthesis process by which plants make food using energy from the sun Plants are autotrophs that make their own source of chemical energy.
State state describe
 Warm-Up State the products of the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis, state which product has chemical energy, and describe how that product is made. KREBS ETC FADH 2 Glucose Pyruvate H 2 O NADH
Warm-Up State the products of the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis, state which product has chemical energy, and describe how that product is made. KREBS ETC FADH 2 Glucose Pyruvate H 2 O NADH
OBJECTIVES OUTCOMES FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT
 GOAL: A great diversity of metabolic and biochemical are seen among the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya yet some common metabolic pathways exist across all domains. OBJECTIVES OUTCOMES FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT
GOAL: A great diversity of metabolic and biochemical are seen among the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya yet some common metabolic pathways exist across all domains. OBJECTIVES OUTCOMES FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT
PHOTOSYNTHESIS STARTS WITH
 Name Date Period PHOTOSYNTHESIS STARTS WITH 1. Molecules that collect light energy are called _P. 2. Chlorophyll a and b absorb _B -_V and _R wavelengths of light best. 3. _C is the main light absorbing
Name Date Period PHOTOSYNTHESIS STARTS WITH 1. Molecules that collect light energy are called _P. 2. Chlorophyll a and b absorb _B -_V and _R wavelengths of light best. 3. _C is the main light absorbing
Cellular Energetics Review
 Cellular Energetics Review 1. What two molecules are formed when a phosphate is removed from ATP? 2. Describe how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are reverse processes. 3. What is the function
Cellular Energetics Review 1. What two molecules are formed when a phosphate is removed from ATP? 2. Describe how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are reverse processes. 3. What is the function
Respiration and Photosynthesis
 Respiration and Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Glycolysis The Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chains Anabolic Pathway Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Flow of Energy Energy is needed to support all forms
Respiration and Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Glycolysis The Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chains Anabolic Pathway Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Flow of Energy Energy is needed to support all forms
1. Which of the following species have strains that are capable of undergoing the process of conjugation?
 Biology 3340 Summer 2005 Second Examination Version A Name Be sure to put your name on the mark-sense sheet as well Directions: Write your name in the correct space on the mark-sense sheet and the exam
Biology 3340 Summer 2005 Second Examination Version A Name Be sure to put your name on the mark-sense sheet as well Directions: Write your name in the correct space on the mark-sense sheet and the exam
Life 21 - Aerobic respiration Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts)
 1 Life 21 - Aerobic respiration Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts) Objectives 1: Describe the overall action of the Krebs cycle in generating ATP, NADH and FADH 2 from acetyl-coa 2: Understand the generation
1 Life 21 - Aerobic respiration Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts) Objectives 1: Describe the overall action of the Krebs cycle in generating ATP, NADH and FADH 2 from acetyl-coa 2: Understand the generation
Review Questions - Lecture 5: Metabolism, Part 1
 Review Questions - Lecture 5: Metabolism, Part 1 Questions: 1. What is metabolism? 2. What does it mean to say that a cell has emergent properties? 3. Define metabolic pathway. 4. What is the difference
Review Questions - Lecture 5: Metabolism, Part 1 Questions: 1. What is metabolism? 2. What does it mean to say that a cell has emergent properties? 3. Define metabolic pathway. 4. What is the difference
chapter five: microbial metabolism
 chapter five: microbial metabolism Revised 9/22/2016 oxidation-reduction redox reaction: coupled reactions e- donor oxidized donor Ox Red ADP + P i ATP Ox Red reduced A chemical A redox reactions aerobic
chapter five: microbial metabolism Revised 9/22/2016 oxidation-reduction redox reaction: coupled reactions e- donor oxidized donor Ox Red ADP + P i ATP Ox Red reduced A chemical A redox reactions aerobic
Edexcel (B) Biology A-level
 Edexcel (B) Biology A-level Topic 5: Energy for Biological Processes Notes Aerobic Respiration Aerobic respiration as splitting of the respiratory substrate, to release carbon dioxide as a waste product
Edexcel (B) Biology A-level Topic 5: Energy for Biological Processes Notes Aerobic Respiration Aerobic respiration as splitting of the respiratory substrate, to release carbon dioxide as a waste product
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Practice Test Name
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which H+ has just passed through the
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which H+ has just passed through the
Metabolism. Fermentation vs. Respiration. End products of fermentations are waste products and not fully.
 Outline: Metabolism Part I: Fermentations Part II: Respiration Part III: Metabolic Diversity Learning objectives are: Learn about respiratory metabolism, ATP generation by respiration linked (oxidative)
Outline: Metabolism Part I: Fermentations Part II: Respiration Part III: Metabolic Diversity Learning objectives are: Learn about respiratory metabolism, ATP generation by respiration linked (oxidative)
Chapter 8.1. How Organisms Obtain Energy
 Chapter 8.1 How Organisms Obtain Energy Main Idea All living organisms use energy to carry out all biological processes. Energy Energy is the ability to do work. Quick Review: Heterotrophs are organisms
Chapter 8.1 How Organisms Obtain Energy Main Idea All living organisms use energy to carry out all biological processes. Energy Energy is the ability to do work. Quick Review: Heterotrophs are organisms
Energy in the World of Life
 Cellular Energy Energy in the World of Life Sustaining life s organization requires ongoing energy inputs Assembly of the molecules of life starts with energy input into living cells Energy Conversion
Cellular Energy Energy in the World of Life Sustaining life s organization requires ongoing energy inputs Assembly of the molecules of life starts with energy input into living cells Energy Conversion
Unit 5 Cellular Energy
 Unit 5 Cellular Energy I. Enzymes (159) 1.Are CATALYSTS: Speed up chemical reactions that would otherwise happen too slowly to support life. Catalysts DO NOT make reactions happen that couldn t happen
Unit 5 Cellular Energy I. Enzymes (159) 1.Are CATALYSTS: Speed up chemical reactions that would otherwise happen too slowly to support life. Catalysts DO NOT make reactions happen that couldn t happen
Transformation of Energy! Energy is the ability to do work.! Thermodynamics is the study of the flow and transformation of energy in the universe.
 Section 1 How Organisms Obtain Energy Transformation of Energy! Energy is the ability to do work.! Thermodynamics is the study of the flow and transformation of energy in the universe. Section 1 How Organisms
Section 1 How Organisms Obtain Energy Transformation of Energy! Energy is the ability to do work.! Thermodynamics is the study of the flow and transformation of energy in the universe. Section 1 How Organisms
Cellular Energetics. Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 Cellular Energetics Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration and Fermentation TEKS B.4 Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that
Cellular Energetics Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration and Fermentation TEKS B.4 Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that
Cell Energy: The Big Picture. So, What Exactly is ATP. Adenosine Triphosphate. Your turn to Practice converting ATP to ADP:
 Understanding How Living Things Obtain and Use Energy. Cell Energy: The Big Picture Most Autotrophs produce food (sugar) using light energy during Photosynthesis. Then, both Autotrophs and Heterotroph
Understanding How Living Things Obtain and Use Energy. Cell Energy: The Big Picture Most Autotrophs produce food (sugar) using light energy during Photosynthesis. Then, both Autotrophs and Heterotroph
Microbiology Helmut Pospiech.
 Microbiology 28.03.2018 Helmut Pospiech http://www.thescientificcartoonist.com/?p=107 Energy metabolism of Microorganisms Fermentation ADP +Pi Motility ATP Active transport (nutrient uptake) Lactic Acid
Microbiology 28.03.2018 Helmut Pospiech http://www.thescientificcartoonist.com/?p=107 Energy metabolism of Microorganisms Fermentation ADP +Pi Motility ATP Active transport (nutrient uptake) Lactic Acid
Unit 8 Cell Metabolism. Foldable Notes
 Unit 8 Cell Metabolism Foldable Notes Silently read pages 94-96 of your biology textbook Middle Inside Top Vocabulary 1. ATP 2. ADP 3. Product 4. Reactant 5. Chloroplast 6. Mitochondria 7. Heterotroph
Unit 8 Cell Metabolism Foldable Notes Silently read pages 94-96 of your biology textbook Middle Inside Top Vocabulary 1. ATP 2. ADP 3. Product 4. Reactant 5. Chloroplast 6. Mitochondria 7. Heterotroph
Photosynthesis Harness light energy and use it to move electrons through an electron transport chain. Electron carriers are arranged, in order of
 Photosynthesis Harness light energy and use it to move electrons through an electron transport chain. Electron carriers are arranged, in order of increasing electro positivity within a membrane. Through
Photosynthesis Harness light energy and use it to move electrons through an electron transport chain. Electron carriers are arranged, in order of increasing electro positivity within a membrane. Through
METABOLISM. What is metabolism? Categories of metabolic reactions. Total of all chemical reactions occurring within the body
 METABOLISM What is metabolism? METABOLISM Total of all chemical reactions occurring within the body Categories of metabolic reactions Catabolic reactions Degradation pathways Anabolic reactions Synthesis
METABOLISM What is metabolism? METABOLISM Total of all chemical reactions occurring within the body Categories of metabolic reactions Catabolic reactions Degradation pathways Anabolic reactions Synthesis
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 TEST PREP PRETEST Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each
Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 TEST PREP PRETEST Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each
Photosynthesis 1. Light Reactions and Photosynthetic Phosphorylation. Lecture 31. Key Concepts. Overview of photosynthesis and carbon fixation
 Photosynthesis 1 Light Reactions and Photosynthetic Phosphorylation Lecture 31 Key Concepts Overview of photosynthesis and carbon fixation Chlorophyll molecules convert light energy to redox energy The
Photosynthesis 1 Light Reactions and Photosynthetic Phosphorylation Lecture 31 Key Concepts Overview of photosynthesis and carbon fixation Chlorophyll molecules convert light energy to redox energy The
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration All cellular activities require energy. Directly or indirectly nearly all energy for life comes from the sun. Autotrophs:
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration All cellular activities require energy. Directly or indirectly nearly all energy for life comes from the sun. Autotrophs:
1 Which of the following organisms do NOT carry on photosynthesis?
 1 Which of the following organisms do NOT carry on photosynthesis? plants algae some bacteria 2 3 animals The correct description of the relationship between photosynthesis and the living world is. herbivores,
1 Which of the following organisms do NOT carry on photosynthesis? plants algae some bacteria 2 3 animals The correct description of the relationship between photosynthesis and the living world is. herbivores,
2.A.2- Capture and Storage of Free Energy
 2.A.2- Capture and Storage of Free Energy Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce, and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. EU 2.A- Growth, reproduction
2.A.2- Capture and Storage of Free Energy Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce, and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. EU 2.A- Growth, reproduction
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Survey
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Survey Multiple Choice - Choose the best and most complete answer. 1. Which type of energy transformation occurs in photosynthesis? A. heat to electrical B. light
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Survey Multiple Choice - Choose the best and most complete answer. 1. Which type of energy transformation occurs in photosynthesis? A. heat to electrical B. light
Unit 1C Practice Exam (v.2: KEY)
 Unit 1C Practice Exam (v.2: KEY) 1. Which of the following statements concerning photosynthetic pigments (chlorophylls a and b, carotenes, and xanthophylls) is correct? (PT1-12) a. The R f values obtained
Unit 1C Practice Exam (v.2: KEY) 1. Which of the following statements concerning photosynthetic pigments (chlorophylls a and b, carotenes, and xanthophylls) is correct? (PT1-12) a. The R f values obtained
Energy Metabolism exergonic reaction endergonic reaction Energy of activation
 Metabolism Energy Living things require energy to grow and reproduce Most energy used originates from the sun Plants capture 2% of solar energy Some captured energy is lost as metabolic heat All energy
Metabolism Energy Living things require energy to grow and reproduce Most energy used originates from the sun Plants capture 2% of solar energy Some captured energy is lost as metabolic heat All energy
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 AP Exam Chapters 9 and 10; Photosynthesis and Respiration Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Carbon dioxide (CO2) is released
AP Exam Chapters 9 and 10; Photosynthesis and Respiration Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Carbon dioxide (CO2) is released
Overview of Photosynthesis
 Overview of Photosynthesis Most autotrophs (organisms that create their own food), make organic compounds (sugars/glucose) using a process called photosynthesis. This process occurs only in plants. Overview
Overview of Photosynthesis Most autotrophs (organisms that create their own food), make organic compounds (sugars/glucose) using a process called photosynthesis. This process occurs only in plants. Overview
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Note-taking Guide
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Note-taking Guide Preview to Photosynthesis glucose, reactions, light-dependent, Calvin cycle, thylakoid, photosystem II, oxygen, light-harvesting, two, chloroplasts,
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Note-taking Guide Preview to Photosynthesis glucose, reactions, light-dependent, Calvin cycle, thylakoid, photosystem II, oxygen, light-harvesting, two, chloroplasts,
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Outline I. Energy and Carbon Cycle II. Photosynthesis A. Introduction B. Reactions II. Cellular Respiration A. Introduction B. Reactions Carbon Cycle All organisms
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Outline I. Energy and Carbon Cycle II. Photosynthesis A. Introduction B. Reactions II. Cellular Respiration A. Introduction B. Reactions Carbon Cycle All organisms
Endosymbiotic Theory
 Endosymbiotic Theory Evolution of Prokaryotes The oldest known fossils are 3.5 bya = stromatolites which are rock like layers of bacteria and sediment. Earliest life forms may have emerged as early as
Endosymbiotic Theory Evolution of Prokaryotes The oldest known fossils are 3.5 bya = stromatolites which are rock like layers of bacteria and sediment. Earliest life forms may have emerged as early as
AP Bio-Ms.Bell Unit#3 Cellular Energies Name
 AP Bio-Ms.Bell Unit#3 Cellular Energies Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the image below. 7. Base your answer to the following question on Which of the following choices correctly
AP Bio-Ms.Bell Unit#3 Cellular Energies Name 1. Base your answer to the following question on the image below. 7. Base your answer to the following question on Which of the following choices correctly
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy. 9.1 Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy 9.1 Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels 9.2 Glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate 9.3 The citric acid
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy 9.1 Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels 9.2 Glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate 9.3 The citric acid
The Life of a Cell. The Chemistry of Life. A View of the Cell. Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle. Energy in a Cell
 The Life of a Cell The Chemistry of Life A View of the Cell Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle Energy in a Cell Chapter 9 Energy in a Cell 9.1: The Need for Energy 9.1: Section Check 9.2: Photosynthesis:
The Life of a Cell The Chemistry of Life A View of the Cell Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle Energy in a Cell Chapter 9 Energy in a Cell 9.1: The Need for Energy 9.1: Section Check 9.2: Photosynthesis:
Ch. 9 - Cellular Respiration/Fermentation Study Guide
 Ch. 9 - Cellular Respiration/Fermentation Study Guide A. Introduction 1. All living things need energy for metabolism. a. Plants produce glucose through photosynthesis; break down glucose during cellular
Ch. 9 - Cellular Respiration/Fermentation Study Guide A. Introduction 1. All living things need energy for metabolism. a. Plants produce glucose through photosynthesis; break down glucose during cellular
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Overview 10 reactions u convert () to pyruvate (3C) u produces: 4 & NADH u consumes: u net: & NADH C-C-C-C-C-C fructose-1,6bp P-C-C-C-C-C-C-P DHAP P-C-C-C G3P C-C-C-P H P i P i pyruvate C-C-C 4 4 NAD +
Overview 10 reactions u convert () to pyruvate (3C) u produces: 4 & NADH u consumes: u net: & NADH C-C-C-C-C-C fructose-1,6bp P-C-C-C-C-C-C-P DHAP P-C-C-C G3P C-C-C-P H P i P i pyruvate C-C-C 4 4 NAD +
AP Biology Exam Review 5: Enzymes & Metabolism (Photosynthesis & Respiration)
 Name: Date: AP Biology Exam Review 5: Enzymes & Metabolism (Photosynthesis & Respiration) Helpful Videos and Animations: 1. Bozeman Biology: Photosynthesis and Respiration 2. Bozeman Biology: Photosynthesis
Name: Date: AP Biology Exam Review 5: Enzymes & Metabolism (Photosynthesis & Respiration) Helpful Videos and Animations: 1. Bozeman Biology: Photosynthesis and Respiration 2. Bozeman Biology: Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Note-taking Guide
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Note-taking Guide Preview to Photosynthesis glucose, reectlons, light-dependent, Calvin cycle, thylakoid, oxygen, light-harvesting, two, chloroplasts, photosynthesis,
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Note-taking Guide Preview to Photosynthesis glucose, reectlons, light-dependent, Calvin cycle, thylakoid, oxygen, light-harvesting, two, chloroplasts, photosynthesis,
Anaerobic processes. Annual production of cells a -1 Mean generation time in sediments
 Anaerobic processes Motivation Where are they? Number of prokaryotes on earth 4-6 * 10 30 Cells in open ocean 1.2 * 10 29 in marine sediments 3.5 * 10 30 in soil 2.6 * 10 29 sub-terrestrial 0.5 2.5 * 10
Anaerobic processes Motivation Where are they? Number of prokaryotes on earth 4-6 * 10 30 Cells in open ocean 1.2 * 10 29 in marine sediments 3.5 * 10 30 in soil 2.6 * 10 29 sub-terrestrial 0.5 2.5 * 10
Energy Transformation. Metabolism = total chemical reactions in cells.
 Energy Transformation Metabolism = total chemical reactions in cells. metabole = change Metabolism is concerned with managing the material and energy resources of the cell -Catabolism -Anabolism -Catabolism
Energy Transformation Metabolism = total chemical reactions in cells. metabole = change Metabolism is concerned with managing the material and energy resources of the cell -Catabolism -Anabolism -Catabolism
Unit 3: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
 Unit 3: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Monday/Tuesday Wednesday/Thursday Friday Bell Ringer Answer Daily Goal HOMEWORK Bell Ringer Answer Monday/Tuesday Wednesday/Thursday Friday Daily Goal HOMEWORK
Unit 3: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Monday/Tuesday Wednesday/Thursday Friday Bell Ringer Answer Daily Goal HOMEWORK Bell Ringer Answer Monday/Tuesday Wednesday/Thursday Friday Daily Goal HOMEWORK
METABOLISM CHAPTER 04 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Dr. Lawrence G. Altman Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I CHAPTER 04 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. CELLULAR METABOLISM Dr. Lawrence G. Altman
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I CHAPTER 04 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. CELLULAR METABOLISM Dr. Lawrence G. Altman
CELL METABOLISM OVERVIEW Keep the big picture in mind as we discuss the particulars!
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I CHAPTER 04 CELLULAR METABOLISM 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. Dr. Lawrence G. Altman
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I CHAPTER 04 CELLULAR METABOLISM 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. Dr. Lawrence G. Altman
Metabolism Review. A. Top 10
 A. Top 10 Metabolism Review 1. Energy production through chemiosmosis a. pumping of H+ ions onto one side of a membrane through protein pumps in an Electron Transport Chain (ETC) b. flow of H+ ions across
A. Top 10 Metabolism Review 1. Energy production through chemiosmosis a. pumping of H+ ions onto one side of a membrane through protein pumps in an Electron Transport Chain (ETC) b. flow of H+ ions across
ATP. Chapter 4. Photosynthesis. Cell Respiration. Energy of Life. All organisms need energy in order to survive
 ATP Chapter 4 Photosynthesis Energy of Life All organisms need energy in order to survive 2 Major groups of organisms: A. autotrophs make their own food Ex: plants B. heterotrophs must eat others living
ATP Chapter 4 Photosynthesis Energy of Life All organisms need energy in order to survive 2 Major groups of organisms: A. autotrophs make their own food Ex: plants B. heterotrophs must eat others living
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Final Summary
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Final Summary DO NOT MAKE ANY MARKS ON THIS TEST PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS IN SCANTRON WRITTEN ANSWERS TO GO ON LOOSE LEAF Be sure to answer every question.
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Final Summary DO NOT MAKE ANY MARKS ON THIS TEST PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS IN SCANTRON WRITTEN ANSWERS TO GO ON LOOSE LEAF Be sure to answer every question.
In Cellular Respiration, are removed from sugar and transferred to
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1101 Lec. 5, Part A (Guided Notes) Chapter 6: Cellular Respiration Energy is needed by cells to do work Chemical energy, a form of potential energy, is stored in bonds of food molecules (such
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1101 Lec. 5, Part A (Guided Notes) Chapter 6: Cellular Respiration Energy is needed by cells to do work Chemical energy, a form of potential energy, is stored in bonds of food molecules (such
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration What you will learn: GPS Standard SB3a Explain the cycling of energy through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration. IN OTHER WORDS Photosynthesis and Cellular
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration What you will learn: GPS Standard SB3a Explain the cycling of energy through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration. IN OTHER WORDS Photosynthesis and Cellular
A + B = C C + D = E E + F = A
 Photosynthesis - Plants obtain energy directly from the sun - Organisms that do this are autotrophs (make their own food from inorganic forms) - Photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions where the
Photosynthesis - Plants obtain energy directly from the sun - Organisms that do this are autotrophs (make their own food from inorganic forms) - Photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions where the
PHOTOSYNTHESIS. The Details
 PHOTOSYNTHESIS The Details Photosynthesis is divided into 2 sequential processes: 1. The Light Dependent Reactions (stages 1 & 2) 2. The Light Independent Reactions (stage 3) a.k.a. the Calvin Cycle THE
PHOTOSYNTHESIS The Details Photosynthesis is divided into 2 sequential processes: 1. The Light Dependent Reactions (stages 1 & 2) 2. The Light Independent Reactions (stage 3) a.k.a. the Calvin Cycle THE
A word of caution about a little knowing Lab organisms limit the view of the world of microbiology
 Diversity The world of living things (Figure from Madigan et al. 2002) Microbes in all three domains Two of the domains are exclusively prokaryotic and microbial The third contains both unicellular and
Diversity The world of living things (Figure from Madigan et al. 2002) Microbes in all three domains Two of the domains are exclusively prokaryotic and microbial The third contains both unicellular and
BIOLOGY SECOND QUARTER UNIT 3
 BIOLOGY SECOND QUARTER UNIT 3 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Energy for Life 4.1 Photosynthesis: Sugar as Food 4.2 Powering the Cell:Cellular Respiration 4.3 Anaerobic Respiration 4.4 Name Class
BIOLOGY SECOND QUARTER UNIT 3 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Energy for Life 4.1 Photosynthesis: Sugar as Food 4.2 Powering the Cell:Cellular Respiration 4.3 Anaerobic Respiration 4.4 Name Class
Respiration and Photosynthesis. The Ying and Yang of Life.
 Respiration and Photosynthesis The Ying and Yang of Life. Why? You ve always been told that you must eat and breathe. Why? In this unit we will attempt to answer those questions. 1 st Law of Thermodynamics
Respiration and Photosynthesis The Ying and Yang of Life. Why? You ve always been told that you must eat and breathe. Why? In this unit we will attempt to answer those questions. 1 st Law of Thermodynamics
Chapter 5. The Chloroplast. 5.1 Matter and Energy Pathways in Living Systems. Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
 Chapter 5 Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration 5.1 Matter and Energy Pathways in Living Systems Both cellular respiration and photosynthesis are examples of biological processes that involve matter &
Chapter 5 Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration 5.1 Matter and Energy Pathways in Living Systems Both cellular respiration and photosynthesis are examples of biological processes that involve matter &
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 DIRECTED READING Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 5-1: Energy and Living Things Energy Flows Between Organisms in Living Systems In the space provided, write the
Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 DIRECTED READING Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 5-1: Energy and Living Things Energy Flows Between Organisms in Living Systems In the space provided, write the
AHL Topic 8 IB Biology Miss Werba
 CELL RESPIRATION & PHOTOSYNTHESIS AHL Topic 8 IB Biology Miss Werba TOPIC 8 CELL RESPIRATION & PHOTOSYNTHESIS 8.1 CELL RESPIRATION 1. STATE that oxidation involves the loss of electrons from an element,
CELL RESPIRATION & PHOTOSYNTHESIS AHL Topic 8 IB Biology Miss Werba TOPIC 8 CELL RESPIRATION & PHOTOSYNTHESIS 8.1 CELL RESPIRATION 1. STATE that oxidation involves the loss of electrons from an element,
Academic Biology: Midterm Review
 Academic Biology: Midterm Review Quarter #1 Chapter 1: The Science of Biology Biology the study of the living world Scientific Method Step 1: Observation Step 2: Forming a Question Step 3: Form a Hypothesis
Academic Biology: Midterm Review Quarter #1 Chapter 1: The Science of Biology Biology the study of the living world Scientific Method Step 1: Observation Step 2: Forming a Question Step 3: Form a Hypothesis
7.014 Quiz III Handout
 7.014 Quiz III Handout Quiz III: Wednesday, April 14 12:05-12:55 Walker Gym **This will be a closed book exam** Quiz Review Session: Tuesday, April 13 7:00-9:00 pm room 54-100 Open Tutoring Session: Monday,
7.014 Quiz III Handout Quiz III: Wednesday, April 14 12:05-12:55 Walker Gym **This will be a closed book exam** Quiz Review Session: Tuesday, April 13 7:00-9:00 pm room 54-100 Open Tutoring Session: Monday,
GR QUIZ WITH ANS KEY Cellular Processes. Part I: Multiple Choice. 1. In leaf cell, the synthesis of ATP occurs in which of the following?
 GR QUIZ WITH ANS KEY Cellular Processes Part I: Multiple Choice 1. In leaf cell, the synthesis of ATP occurs in which of the following? I. Ribosomes II. Mitochondria III. Chloroplasts A. I only B. II only
GR QUIZ WITH ANS KEY Cellular Processes Part I: Multiple Choice 1. In leaf cell, the synthesis of ATP occurs in which of the following? I. Ribosomes II. Mitochondria III. Chloroplasts A. I only B. II only
STUDY GUIDE ~ Biology Level 10
 NAME PERIOD STUDY GUIDE ~ Biology Level 10 UNIT 4: Bioenergetics This is a study GUIDE. Your best resources for information and reinforcing concepts is the CLASS POWERPOINT SLIDES (available on SchoolWires
NAME PERIOD STUDY GUIDE ~ Biology Level 10 UNIT 4: Bioenergetics This is a study GUIDE. Your best resources for information and reinforcing concepts is the CLASS POWERPOINT SLIDES (available on SchoolWires
1/25/2018. Bio 1101 Lec. 5, Part A Chapter 6: Cellular Respiration
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1101 Lec. 5, Part A Chapter 6: Cellular Respiration Energy is needed by cells to do work Chemical energy, a form of potential energy, is stored in bonds of food molecules (such as glucose)
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1101 Lec. 5, Part A Chapter 6: Cellular Respiration Energy is needed by cells to do work Chemical energy, a form of potential energy, is stored in bonds of food molecules (such as glucose)
X Biology I. Unit 1-4: Cellular Energy
 NOTE/STUDY GUIDE: Unit 1-4, Cellular Energy X Biology I, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology I Unit 1-4: Cellular Energy Additional
NOTE/STUDY GUIDE: Unit 1-4, Cellular Energy X Biology I, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology I Unit 1-4: Cellular Energy Additional
The Prokaryotic World
 The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes
 The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
Ch. 6 & 7 Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
 Ch. 6 & 7 Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration 6.1 Energy Reactions The Cycle of Energy Sun CO 2 H 2 O Photosynthesis (energy stored) Cellular Respiration (energy released) O 2 Glucose Obtaining Energy
Ch. 6 & 7 Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration 6.1 Energy Reactions The Cycle of Energy Sun CO 2 H 2 O Photosynthesis (energy stored) Cellular Respiration (energy released) O 2 Glucose Obtaining Energy
PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Chapter 8
 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Chapter 8 ENERGY & LIFE ENERGY The ability to do work. Can be stored in chemical bonds. Cells need energy to do things like active transport, dividing, moving, and producing and storing
PHOTOSYNTHESIS Chapter 8 ENERGY & LIFE ENERGY The ability to do work. Can be stored in chemical bonds. Cells need energy to do things like active transport, dividing, moving, and producing and storing
Life: Levels of Organization, Cell Structure & Function, Major Processes for Fueling Life s Activity
 1 EVPP 110 Lecture Dr. Largen - Fall 2003 Life: Levels of Organization, Cell Structure & Function, Major Processes for Fueling Life s Activity 2 Levels of Organization of Life Levels of organization of
1 EVPP 110 Lecture Dr. Largen - Fall 2003 Life: Levels of Organization, Cell Structure & Function, Major Processes for Fueling Life s Activity 2 Levels of Organization of Life Levels of organization of
Biology Unit 4 Energy and Life. 4:1 Energy All living things require a constant supply of ENERGY.
 Biology Unit 4 Energy and Life 4:1 Energy All living things require a constant supply of ENERGY. GLUCOSE: (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) the form of energy used for fuel by ALL living cells It requires energy to form
Biology Unit 4 Energy and Life 4:1 Energy All living things require a constant supply of ENERGY. GLUCOSE: (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) the form of energy used for fuel by ALL living cells It requires energy to form
Cellular Energy: Respiration. Goals: Anaerobic respiration
 Cellular Energy: Respiration Anaerobic respiration Goals: Define and describe the 3 sets of chemical reactions that comprise aerobic cellular respiration Describe the types of anaerobic respiration Compare
Cellular Energy: Respiration Anaerobic respiration Goals: Define and describe the 3 sets of chemical reactions that comprise aerobic cellular respiration Describe the types of anaerobic respiration Compare
4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP. KEY CONCEPT All cells need chemical energy.
 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP KEY CONCEPT All cells need chemical energy. 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP The chemical energy used for most cell processes is carried by ATP. Molecules in food store chemical
4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP KEY CONCEPT All cells need chemical energy. 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP The chemical energy used for most cell processes is carried by ATP. Molecules in food store chemical
All Cells need energy. (Ability to perform work) What do cells use energy for? Mitosis. Repair. Active transport. Movement.
 Cell Energetics All Cells need energy. (Ability to perform work) What do cells use energy for? Mitosis. Repair. Active transport. Movement. What Is ATP? ATP adenosine triphosphate is a chemical molecule
Cell Energetics All Cells need energy. (Ability to perform work) What do cells use energy for? Mitosis. Repair. Active transport. Movement. What Is ATP? ATP adenosine triphosphate is a chemical molecule
Photosynthesis. Chapter 10. Active Lecture Questions for use with Classroom Response Systems Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 10 Photosynthesis Active Lecture Questions for use with Classroom Response Systems Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Edited by William Wischusen, Louisiana State University
Chapter 10 Photosynthesis Active Lecture Questions for use with Classroom Response Systems Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Edited by William Wischusen, Louisiana State University
Biology Midterm Review
 Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic
Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic
Cellular Energy. The cell will store energy in molecules like sugars and ATP
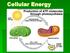 Cellular Energy Cellular Energy The cell will store energy in molecules like sugars and ATP Most cells have small stores of ATP that only last a few seconds, but cannot store energy there long-term. Cells
Cellular Energy Cellular Energy The cell will store energy in molecules like sugars and ATP Most cells have small stores of ATP that only last a few seconds, but cannot store energy there long-term. Cells
Outline - Photosynthesis
 Outlin Photosynthesis Photosynthesis 1. An Overview of Photosynthesis & Respiration 2. Autotrophs and producers 3. Electromagnetic Spectrum & light energy 4. Chloroplasts: Structure and Function 5. Photosynthetic
Outlin Photosynthesis Photosynthesis 1. An Overview of Photosynthesis & Respiration 2. Autotrophs and producers 3. Electromagnetic Spectrum & light energy 4. Chloroplasts: Structure and Function 5. Photosynthetic
Concept 10.1 Photosynthesis converts light energy to the chemical energy of food
 Name Period Chapter 10: Photosynthesis This chapter is as challenging as the one you just finished on cellular respiration. However, conceptually it will be a little easier because the concepts learned
Name Period Chapter 10: Photosynthesis This chapter is as challenging as the one you just finished on cellular respiration. However, conceptually it will be a little easier because the concepts learned
Metabolismo Biología de 12º
 DEPARTAMENTO DE CIENCIAS NATURALES Metabolismo Biología de 12º Nombre y Apellidos FOTOSÍNTESIS 1) Organisms that can exist with light as an energy source and an inorganic form of carbon and other raw materials
DEPARTAMENTO DE CIENCIAS NATURALES Metabolismo Biología de 12º Nombre y Apellidos FOTOSÍNTESIS 1) Organisms that can exist with light as an energy source and an inorganic form of carbon and other raw materials
