genomics and molecular biology
|
|
|
- Mark Copeland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biological Control and Pasteuria penetrans: genomics and molecular biology Keith Davies Post-graduate International Nematology Course Ghent, Belgium Plant Pathology and Microbiology, Rothamsted Research, Harpenden, Hertfordshire, UK
2 Structure of talk: Introduction and context Immunological approach to host specificity Genomics and taxonomy In vitro culture Collagen and the mechanism of attachment Three types of cuticle variation
3 Generalised life cycle of a root-knot nematode Meloidogyne spp.
4 The life-cycle of Pasteuria penetrans on root-knot nematodes (Advances in Parasitol. In press) Penetration peg Adhesion to cuticle Rhizoids Rod Mature endospores Maturation Sporulation Granular masses
5 Increase in tomato yield following application ofpasteuria penetrans to root-knot infected soils in Equador adapted from Trudgill et al., (2000) Nematology 2, Fallow Tomato Tomato J2 per g Soil %J2 +spores Yield Kg/plot Na Two Major Problems 1) Mass production 2) Infection and host specificity
6 Pasteuria penetrans Differential Host Range Test M. javanica M. incognita M. arenaria PNG PP1 PMJ PCl PP4 PPW PPN PHC H. avenae H. glycines H. schachtii H. cajani G. pallida G. rostochiensis NA - - NA NA NA NA NA , no attachment; +, 1-10 spores; ++, spores; +++ > 21 spores
7 ENDOSPORE ATTACHMENT Reaction of secondstage juvenile cuticle by a polyclonal antibody Meloidogyne incognita Meloidogyne arenaria Davies & Danks Parasitology 105,
8 Percentage of juveniles of Meloidogyne arenaria and M. incognita to which no spores attached Davies et al., 2001, Parasitology 122,
9 Immunofluorescence of Pasteuria endospores No fluorescence Low fluorescence High fluorescence Davies et al., Let. Appl. Microb. 19,
10 Immunofluorescence of Pasteuria endospores attached to nematodes Polyclonal antibody Monoclonal antibody (Adapted from Preston et al., J. Nematology)
11 Cuticle characterisation using Mabs to Pasteuria M. incognita Race 1: tobacco M. arenaria Race 1: peanut M. javanica: tobacco M. incognita Race 3: cotton Davies et al., Let. Appl. Microb. 19,
12 Cuticle characterisation using Mabs to Pasteuria M. incognita Race 1: tobacco M. arenaria Race 1: peanut M. javanica: tobacco M. incognita Race 3: cotton Davies et al., Let. Appl. Microb. 19,
13 % fluorescent spores % fluorescent spores % fluorescent spores Cuticle characterisation using Mabs to Pasteuria M. incognita Race 2 M. incognita Race Pp/12 Pp/53 Pp/84 Pp/117 Pp/134 Con+ve Pp/12 Pp/53 Pp/84 Pp/117 Pp/134 Con+ve 0 Antibodies 0 Antibodies M. arenaria race Pp/12 Pp/53 Pp/84 Pp/117 Pp/134 Con+ve Characterisation of endospores attached to different nematode populations by 5 Mabs 0 Antibodies Davies et al., Let. Appl. Microb. 19,
14 Tritrophic interaction Mixed population of nematodes: PEANUT susceptible to Race 1 of M. arenaria Increase in Race 1 M. arenaria pathogenic Pasteuria M. arenaria Race 1: peanut (After Davies, K.G., 2005, Advances in Applied Microbiology 57, 53-78)
15 Tritrophic interaction Mixed population of nematodes: TOMATO universally susceptible maintaining a diverse Pasteuria population (After Davies, K.G., 2005, Advances in Applied Microbiology 57, 53-78)
16 Genomics DNA extraction by bead beating DNA Extraction based on robust endospores 1) Infected females dissected from roots 2) Homogenised to extract spores 3) Enzyme digestion Proteinase K, lyzozyme, DNAase, RNAase 4) Heat treatment, protinase K, heat treatment 5) Bead beating 6) DNA amplification using kit 7) Sequencing: Sanger (2003) and 454 (2008) Unbeaten Beaten
17 Genomics THE BIG PICTURE Sanger Sequence 2.5 Mbp 8.6 Mbp Contigs (782 > 2 kb) Largest contig 2.5 kb 54.7 kb GC content 62 % 45 % Bacterial genomes range from: < 1 Mbp Mycoplasma genitalium to > 9 Mbp Nostoc punctiforma
18 Genomics Bacillus anthracis Bacillus cerus Bacillus subtilis Bacillus halodurans Pasteuria penetrans Staphylococcus aureus Lactococcus lactis Streptococcus pyogenes Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma genitalium Mycobacterium leprae Mycobacterium tuberculosis Aquifex aeolicus Campylobacter jejuni Heliobacter pylori Rickettsia prowazekii Neisseria meningitidis Xylella fastidiosa Pseudomonas aeruginosa Escherichia coli Buchnera aphidicola Pasteurella multocida Haemophilus influenzae Chlamydophila pneumoniae Chlamydia trachomatis Chlamydia muridarum Borrelia burgdorferi Treponema pallidum Phylogenetic analysis undertaken using 27 full-length genes Gram positive Gram negative Charles et al., 2005, J. Bact.
19 Two major problems prohibiting Pasteuria penetrans from being developed into a commercial product related to endospore production Forget about the genome. And let s say, It s great. We ve got all these sequences. Thank you very much for all the people that helped to get them - please get us some more. And let s get on with the biology. Sydney Brenner, January 2003, San Diego, California Plant and Animal Genome Conference 1) In vitro mass production 2) Spore type and attachment specificity
20 Comparison of endospore formation in Bacillus thuringiensis and Pasteuria penetrans From Chen et al., (1997) Phytopathology 87,
21 Genomics 6-7 % GO analysis Sm all-molecule metabolism Broad regulatory functions Macromolecular metabolism Cell processes Sporulation Transposons Other Conserved hypothetical Unknown function Sporulation governed by Spo0F Driks, 2002 Trends Microbiol. 10: 251
22 Phosphorelay pathway KinB KinA Kinases Nutrient Starvation Temperature or ph extremes Cell crowding Antibiotic exposure Spo0B Spo0F RapB RapA Phosphatases Spo0A DNA binding domain Inactive Spo0A DNA binding domain Active Sporulation abrb Diagram of proteins involved in the phosphorelay required for initiating the sporulation signal transduction pathway in B. subtilis (from Feher et al., 1997). The red arrows represent environmental signals which initiate the transfer of the phosphoryl group via the Phosphorelay pathway.
23 spo0f, Pasteuria and Bacillus species Bsu MMNEK--ILIVDDQYGIRILLNEVFNKEGYQTFQAANGLQALDIVTKERPDLVLLDMKIPGMDG Ban VMEGK--ILIVDDQYGIRVLLHEVFQKEGYQTFQAANGFQALDIVKKDNPDLVVLDMKIPGMDG Bha -MN-K--ILVVDDQYGIRVLLNEILQKDGYQMFQAANGIQALAIVEEETPDLVLLDMKIPGMDG Ppe MMNEKKLILIVDDQYAIRLLLKEIFSQDGIIVLQAAGGXEAIELVAQQQPDLMLLDMKMPGMDG b1 a1 b2 a2 b3 Bsu IEILKRMKVIDENIRVIIMTAYGELDMIQESKELGALTHFAKPFDIDEIRDAVKKYLPLKSN Ban IEILKHVKEIDESIKVILMTAYGELDMIQEAKDLGALMHFAKPFDIDEIRQAVRNELAVEA- Bha LEILRRIKDMNPNIEVIMMTAYGELNMINEAMQLGAVTHFAKPFDIDDVRAVIAENMKSS - Ppe LEILRRVRQVIPALKVIVMTAYGELEMMEKIRSLGVVMHFPKPFDVRAVRCGVLRYLXXXXX a3 b4 a4 b5 a5 Residues in red are identical between Ppe and the Bacillus species. Residues in green are conservative exterior substitutions. The positions of b-strands and a-helices are indicated. Conserved active-site residues are highlighted in bold (arrows). Kojetin, et al., 2005, Biometals 18,
24 STRUCTURE OF Spo0F charged aspartic acids line the pocket of the active site A divalent metal is required Thought to be Mg 2+ or Mn 2+ Without the metal ion, phosphorylation will not occur WHAT ABOUT OTHER IONS? Kojetin, et al., 2005, Biometals 18,
25 Relative amount of KinA~P or Spo0F~P Divalent Metal Dependent Phosphorylation Phospho-transfer from KinA~P to Spo0F MgCl 2 ZnCl 2 CuCl Mg KinA~P Mg OF~P Zn KinA~P Zn 0F~P Cu KinA~P Cu OF~P um um um KinA~P Spo0F~P Kojetin, et al., 2005, Biometals 18,
26 Growth of Pasteuria in culture is affected by divalent cations + Cu +2 - Cu +2 Kojetin, et al., 2005, Biometals 18,
27 Percentage of juveniles of Meloidogyne arenaria and M. incognita to which no spores attached Davies et al., 2001, Parasitology 122,
28 Attachment is a key determinant for infection Pasteuria penetans endospore Bacillus anthracis endospore Davies, Advances in Parasitol. In prep.
29 GENOMICS & ENDOSPORE ATTACHMENT B. Anthracis Strain G-x-y repeat region Number Filament G-x-y length repeats (nm) Ames NA R, A2R, 6183R R Structure of BclA collagen-like repeats and their relationship to filament length in Bacillus anthracis (adapted from Sylvestre et al., J Bact. 185; 2003)
30 COMPARATIVE GENOMICS as of 2003 Gene organisation for the encoding proteins of the exosporium for Bacillus anthracis, B. thuringiensis & B. subtilis clop BclA rfba rfbc rfbb rfbd fab1 yjbx cotz-1 coty Ba X Bt Bs X X X X X X X X X X X yjbv X cotx cotw cotv yjca yjcb yjcc cotz-2 yjcc yjcd yjce yjcf yjcg yjch X X X X X Ba X X X X X Bt X X Bs Solid red genes denote BLAST hits (e -14 ) to Pasteuria (dashed red e -4 ) (Davies & Opperman, IOBC Bulletin, 2006, )
31 COMPARATIVE GENOMICS as of 2008 Gene organisation for the encoding proteins of the exosporium for Bacillus anthracis, B. thuringiensis & B. subtilis clop BclA rfba rfbc rfbb rfbd fab1 yjbx cotz-1 coty Ba X Bt Bs X X X X X X X X X X X yjbv X cotx cotw cotv yjca yjcb yjcc cotz-2 yjcc yjcd yjce yjcf yjcg yjch X X X X X Ba X X X X X Bt X X Bs Solid red genes denote BLAST hits (e -14 ) to Pasteuria (dashed red e -4 ) (Davies & Opperman, IOBC Bulletin, 2006, )
32 GENOMICS & ENDOSPORE ATTACHMENT >Contig1_2 (Ppenetrans-147) IFLGTTIGRLEFSGREFALGREGQQEHRGGPTTGPPGPPGAHGIQGPPGAQGIQGPAGTP GAQGIQGPPGPAGTPGAQGIQGPPGPAGPAGPAGAAGSPGTPGPAGPAGPAGAAGSPGTP GSPGTPGPAGPAGPAGPAGTPGTPGSPGTPGPAGPAGPAGTPGTPGAAGSPGTPGPAGPA GPAGPAGTPGTPGPAGPQGTPGAPGPAGPQGTPGAPGPAGPQGTTGAAGPTGPQGTTGPQ GTQGTQGPQGIQGIQGPVGPQGATGATGPGLNTSMTIVAGGGADTQFITPTPEGATGTAV TLETGNGQRYGSGDIQLIGTTDILLPSTGTYLMSFHIDANYTSAAGAPVAGAYGSYVAYF RQFTTDFFFNQIVAFWVGPALVNDAFDSSISNTVLGCVSDIPPHGLNNHMVRHESDVANS LNTRRSQPQX >Contig2_1 (Ppenetrans-147) LQDQTNSPFRLEPEMWSINNIHSFNHMNKRKKQNIFFHTFSLGGLEDNHFMKHWIGRNSG CIHYKNNGKIRNTITHTPSPRRSEGNRFVKHWIGRKSVYINSDYRDQHNHHNSSRTTLYR NCEKCDNNQYEEFDNDHCEEFDNNHCCDCCLCNRCKCRVTGPTGPTGPTGRTGSTGRTGP TGPTGRTGSTGRTGPTGPTGPTGPTGPTGRTGFTGRTGSTGSTGRTGPTGSTGRTGSTGS TGRTGPTGSTGRTGSTGSTGRTGSTGSTSRPLVGRRNSR 79 G-X-Y repeats 36 G-X-Y repeats >Contig3_4 (Ppenetrans-147) VANSRLEGWTAGPAGAQGISGPPGEPGIQGPAGTPGAQGIQGPPGPAGTPGAQGIQGPPG PAGPTGPAGAAGSPGTPGPAGPAGPAGAAGSPGTPGSPGTPGPAGPAGPAGPAGTPGAPG PAGPQGTPGAPGPAGPQGTPGAPGPAGPQGTTGAAGPTGPQGTTGPQGTQGTQGPQGIQG IQGPVGPQGATGATGPGLNTSMTIVAGGGADTQFITPTPEGPTGPGGTFEPGNGPKYREG GELHLIGTHRFSSSRVPGPF 62 G-X-Y repeats Total of 12 Pasteuria penetrans collagens with G-X-Y repeats 5 unique to RES147, 4 unique tofl-1, 3 in common
33 Number of Gxy repeats collagen filament length (nm) GENOMICS & ENDOSPORE ATTACHMENT Pasteuria Amino Filament Contig G-x-ys upstream downstream acids length (nm) Con 1_2 79 Yes Yes Con Yes Yes Con 3_4 62 Yes Yes y = x R 2 = y = x R 2 = Prediction of Pasteuria filament length from the equation y = x Number of amino acids in BclA (Davies & Opperman, IOBC Bulletin, 2006, )
34 Spore attachment: Velcro-like mechanism 2 um Davies, Advances in Parasitology In press.
35 Spore attachment: Velcro-like mechanism But what about Specificity? Davies, 2008, Advances in Parasitology in prep.
36 Reproductive mechanisms in major groups of Root-knot nematodes Meloidogyne spp. Nematode spp. M. arenaria M. incognita M. javanica M. hapla Race A M. hapla Race B Chromosome No polyploid 41-46; polyploid 42-48; polyploid 13-17; n 43-48; polyploid Mode of reproduction Mitotic parthenogenesis Mitotic parthenogenesis Mitotic parthenogenesis Amphimixis & meiotic parth. Mitotic parthenogenesis After Evans, AAF (1998) In: The Physiology and Biochemistry of Freeliving and Plant-parasitic nematodes CABI (Eds RN Perry & DJ Wright)
37 M. incognita Experimental design M. hapla VW8 & VW9 Single egg mass Single egg mass Routinely subcultured every 4-6 months 18 generations of single egg mass 3 spore 26 spore VW8 single juveniles VW9 single juveniles 8 single egg mass populations 8 single egg mass populations 2 single egg masses from 2 single J2 populations 2 single egg masses from 3 single J2 populations Tested against PP3 & RES147 Tested against PP3 & RES147 Tested against PP3 & RES147 Tested against PP3 & RES147 Davies, Rowe & Williamson 2008 Int. J. Parasit.,38,
38 Endospore attachment of Pasteuria populations RES147 & PP3 to Meloidogyne hapla strains VW8 & VW9 and M. incognita ANOVA P < VW8 VW9 Mi VW8 VW9 Mi Davies, Rowe & Williamson 2008 Int. J. Parasit.,38,
39 Spores, RES147 & PP3, attaching to single juvenile descent lines arising of M. hapla VW9K1 (light grey), VW9K2 (dark grey), VW9K3 (black) Segregation in spore attachment ANOVA P < Davies, Rowe & Williamson 2008 Int. J. Parasit.,38,
40 Endospore attachment of Pasteuria population PP3 to single juvenile descent lines of Meloidogyne incognita Somaclonal variation in spore attachment ANOVA P < Davies, Rowe & Williamson 2008 Int. J. Parasit.,38,
41 Endospore attachment of Pasteuria population RES147 to Meloidogyne incognita Somaclonal variation in spore attachment ANOVA P < Davies, Rowe & Williamson 2008 Int. J. Parasit.,38,
42 Relationship between juvenile age and spore attachment Davies et al., 1991 Revue de Nematol 14,
43 DAF-2, IGF & innate immunity in worms Anne Millet and Jonathan Ewbank 2004 Curr. Opin. Immunol. 16, 4-9
44 An evolutionary conserved phosphorylation cascade involving the insulin/insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor is well characterised in C. elegans Activation of phosphorylation pathway begins with binding of insulin-like ligand to DAF-2 receptor (38 present in Ce only a few characterised) DAF-2 activates AGE-1 which converts phosphatidylinositol biphosphate to a triphosphate PiP 3 binds to the AKT-1/AKT2 complex that phosphorylates the Forkhead transcription factor DAF-16 DAF-16+P cannot be translocated to nucleus to activate DAF-2 pathways DAF-16 can enter nucleus L1 and L2 activates dauer formation L3 adults activates stress response and anti-microbial genes (Millet & Ewbank, 2004)
45 DAF-2 mutants can alter a number of important metabolic activities Dauer formation Alter lipid metabolism Alter fertility Inhibition of DAF-2 Alter lifespan Activate stress response
46 DAF-2 mutants can alter a number of important metabolic activities Dauer formation Alter lipid metabolism Alter fertility Inhibition of DAF-2 Alter lifespan Activate stress response
47 Increase in cell number (%) EPL001 is peptide that inhibits IGF: 72 hours after application EPL001 inhibits Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) & Insulin Growth Factor (IGF) stimulated MCF-7 cells (breast carcinoma cell line) MCF-7 Cells EGF stimulated 1.00E E E E-06 EPL001 (20 mer version) IGF-I stimulated John Haylor et al., in prep.
48 Accumulated larvae Number of larvae Total larvae produced per day Control EPL01 EPL days Manipulation of life-span and fecundity in C. elegans Mean larvae per adult Control EPL001 EPL % -64% Control EPL001 EPL030 ANOVA P < Time days Davies and Hart (2008) Nematology 10,
49 The effects of EPL001 and EPL030 on the attachment of Pasteuria to root-knot J2s Meloidogyne incognita allowed to hatch in water Treat with 1µM of EPL001 and EPL030 (water control) At 0, 18, 21 and 27 hrs wash (x3) water Endospore (strain RES147) attachment test by centrifugation Count endospores adhering to the cuticle
50 Spores per J2 The effects of EPL001 and EPL030 on the attachment of Pasteuria to root-knot J2s ANOVA P < WATER EPL001 2 EPL T0 T18 T21 T27 Davies unpublished
51 Modulation of surface coat through EPL001 and EPL030 Excretory/secretory products Microvilli Epicuticle Exocuticle Struts Endocuticle Young Time line Old DAF-2 modulation of E/S products Davies unpublished
52 Three types of cuticle variation Constituative variation: under genetic control and can segregate Clonal vartiation: probable under epigenetic control Induced variation: modulated by environmental parameters
53 Acknowledgements ROTHAMSTED Sofia Costa Brian Kerry Rosa Manzanilla-Lopez Sharad Mohan Chris Rawlings Janet Rowe Shashi Sharma Andrew Warry NORTH CAROLINA S. U. David Bird Lauren Charles Charlie Opperman Jenn Schaff Betsy Scholl Jenora Waterman PASTEURIA BIOSCIENCES Tom Hewlett Susan Griswold Kelly Smith U. C. DAVIS Valerie Williamson Plant Nematode Genetics Group North Carolina State University
Link to proceedings: contents.pdf
 Research Archive Citation for published version: K. G. Davies, A. Srivastava, K. Kumar, and S. Mohan, Understanding nematode suppressive soils: molecular interactions between Pasteuria endospores and the
Research Archive Citation for published version: K. G. Davies, A. Srivastava, K. Kumar, and S. Mohan, Understanding nematode suppressive soils: molecular interactions between Pasteuria endospores and the
The Minimal-Gene-Set -Kapil PHY498BIO, HW 3
 The Minimal-Gene-Set -Kapil Rajaraman(rajaramn@uiuc.edu) PHY498BIO, HW 3 The number of genes in organisms varies from around 480 (for parasitic bacterium Mycoplasma genitalium) to the order of 100,000
The Minimal-Gene-Set -Kapil Rajaraman(rajaramn@uiuc.edu) PHY498BIO, HW 3 The number of genes in organisms varies from around 480 (for parasitic bacterium Mycoplasma genitalium) to the order of 100,000
2 Genome evolution: gene fusion versus gene fission
 2 Genome evolution: gene fusion versus gene fission Berend Snel, Peer Bork and Martijn A. Huynen Trends in Genetics 16 (2000) 9-11 13 Chapter 2 Introduction With the advent of complete genome sequencing,
2 Genome evolution: gene fusion versus gene fission Berend Snel, Peer Bork and Martijn A. Huynen Trends in Genetics 16 (2000) 9-11 13 Chapter 2 Introduction With the advent of complete genome sequencing,
Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair. 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination.
 Answer the following questions 1. Define genetic recombination. Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination. 3. List 3 types of bacterial
Answer the following questions 1. Define genetic recombination. Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination. 3. List 3 types of bacterial
Essentiality in B. subtilis
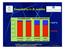 Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Evolutionary Analysis by Whole-Genome Comparisons
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Apr. 2002, p. 2260 2272 Vol. 184, No. 8 0021-9193/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 184.8.2260 2272.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evolutionary Analysis
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Apr. 2002, p. 2260 2272 Vol. 184, No. 8 0021-9193/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 184.8.2260 2272.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evolutionary Analysis
Introduction to Bioinformatics Integrated Science, 11/9/05
 1 Introduction to Bioinformatics Integrated Science, 11/9/05 Morris Levy Biological Sciences Research: Evolutionary Ecology, Plant- Fungal Pathogen Interactions Coordinator: BIOL 495S/CS490B/STAT490B Introduction
1 Introduction to Bioinformatics Integrated Science, 11/9/05 Morris Levy Biological Sciences Research: Evolutionary Ecology, Plant- Fungal Pathogen Interactions Coordinator: BIOL 495S/CS490B/STAT490B Introduction
ABSTRACT. As a result of recent successes in genome scale studies, especially genome
 ABSTRACT Title of Dissertation / Thesis: COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSES OF MICROBIAL GENOMES OPERONS, PROTEIN FAMILIES AND LATERAL GENE TRANSFER. Yongpan Yan, Doctor of Philosophy, 2005 Dissertation / Thesis Directed
ABSTRACT Title of Dissertation / Thesis: COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSES OF MICROBIAL GENOMES OPERONS, PROTEIN FAMILIES AND LATERAL GENE TRANSFER. Yongpan Yan, Doctor of Philosophy, 2005 Dissertation / Thesis Directed
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm
 Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
By signing below, you acknowledge that you have ensured that you are complying with the above statement.
 Instructions: This exam consists of 31 multiple choice questions on 8 pages, including this one. Please submit your answers on the scantron sheet provided and on this copy of the exam. This exam is closed
Instructions: This exam consists of 31 multiple choice questions on 8 pages, including this one. Please submit your answers on the scantron sheet provided and on this copy of the exam. This exam is closed
Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1
 Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
Microbial Taxonomy. Classification of living organisms into groups. A group or level of classification
 Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
The minimal prokaryotic genome. The minimal prokaryotic genome. The minimal prokaryotic genome. The minimal prokaryotic genome
 Dr. Dirk Gevers 1,2 1 Laboratorium voor Microbiologie 2 Bioinformatics & Evolutionary Genomics The bacterial species in the genomic era CTACCATGAAAGACTTGTGAATCCAGGAAGAGAGACTGACTGGGCAACATGTTATTCAG GTACAAAAAGATTTGGACTGTAACTTAAAAATGATCAAATTATGTTTCCCATGCATCAGG
Dr. Dirk Gevers 1,2 1 Laboratorium voor Microbiologie 2 Bioinformatics & Evolutionary Genomics The bacterial species in the genomic era CTACCATGAAAGACTTGTGAATCCAGGAAGAGAGACTGACTGGGCAACATGTTATTCAG GTACAAAAAGATTTGGACTGTAACTTAAAAATGATCAAATTATGTTTCCCATGCATCAGG
Figure Page 117 Microbiology: An Introduction, 10e (Tortora/ Funke/ Case)
 Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
TER 26. Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny. Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains. Nitrogen cycle
 Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains TER 26 Nitrogen cycle Mycobacterium tuberculosis Color-enhanced images shows rod-shaped bacterium responsible for tuberculosis
Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains TER 26 Nitrogen cycle Mycobacterium tuberculosis Color-enhanced images shows rod-shaped bacterium responsible for tuberculosis
Additional file 1 for Structural correlations in bacterial metabolic networks by S. Bernhardsson, P. Gerlee & L. Lizana
 Additional file 1 for Structural correlations in bacterial metabolic networks by S. Bernhardsson, P. Gerlee & L. Lizana Table S1 The species marked with belong to the Proteobacteria subset and those marked
Additional file 1 for Structural correlations in bacterial metabolic networks by S. Bernhardsson, P. Gerlee & L. Lizana Table S1 The species marked with belong to the Proteobacteria subset and those marked
C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence. Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy
 C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy C. elegans : a model organism Mechanisms of apoptosis, RNA interference Neuronal function and development
C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy C. elegans : a model organism Mechanisms of apoptosis, RNA interference Neuronal function and development
CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
 CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria
 Mechanisms of Infectious Disease Fall 2009 Genetics I Jonathan Dworkin, PhD Department of Microbiology jonathan.dworkin@columbia.edu Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material
Mechanisms of Infectious Disease Fall 2009 Genetics I Jonathan Dworkin, PhD Department of Microbiology jonathan.dworkin@columbia.edu Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material
Objects of the Medical Microbiology revision a) Pathogenic microbes (causing diseases of human beings or animals) b) Normal microflora (microbes commo
 Institute for Microbiology, Medical Faculty of Masaryk University and St. Anna Faculty Hospital in Brno Miroslav Votava MORPHOLOGY AND STRUCTURE OF BACTERIAL CELL The 2nd lecture for 2nd-year students
Institute for Microbiology, Medical Faculty of Masaryk University and St. Anna Faculty Hospital in Brno Miroslav Votava MORPHOLOGY AND STRUCTURE OF BACTERIAL CELL The 2nd lecture for 2nd-year students
LECTURE 13. THE BACTERIA (cont.) Photosynthetic Bacteria, phylogenetically widespread. And many Proteobacteria. Photosynthetic Bacteria
 Photosynthetic Bacteria, phylogenetically widespread LECTURE 13 THE BACTERIA (cont.) And many Proteobacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria > Green Sulfur > Green Nonsulfur > Purple Sulfur > Purple Nonsulfur
Photosynthetic Bacteria, phylogenetically widespread LECTURE 13 THE BACTERIA (cont.) And many Proteobacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria > Green Sulfur > Green Nonsulfur > Purple Sulfur > Purple Nonsulfur
1. Prokaryotic Nutritional & Metabolic Adaptations
 Chapter 27B: Bacteria and Archaea 1. Prokaryotic Nutritional & Metabolic Adaptations 2. Survey of Prokaryotic Groups A. Domain Bacteria Gram-negative groups B. Domain Bacteria Gram-positive groups C. Domain
Chapter 27B: Bacteria and Archaea 1. Prokaryotic Nutritional & Metabolic Adaptations 2. Survey of Prokaryotic Groups A. Domain Bacteria Gram-negative groups B. Domain Bacteria Gram-positive groups C. Domain
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & Eubacteria)
 Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
BACTERIA. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 BACTERIA CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Prokaryotes Prokaryotic cells possess simpler structures than eukaryotic cells, since they do not have a nucleus or a lot of cytoplasmic organelles.
BACTERIA CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Prokaryotes Prokaryotic cells possess simpler structures than eukaryotic cells, since they do not have a nucleus or a lot of cytoplasmic organelles.
Regulation and signaling. Overview. Control of gene expression. Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on
 Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
# shared OGs (spa, spb) Size of the smallest genome. dist (spa, spb) = 1. Neighbor joining. OG1 OG2 OG3 OG4 sp sp sp
 Bioinformatics and Evolutionary Genomics: Genome Evolution in terms of Gene Content 3/10/2014 1 Gene Content Evolution What about HGT / genome sizes? Genome trees based on gene content: shared genes Haemophilus
Bioinformatics and Evolutionary Genomics: Genome Evolution in terms of Gene Content 3/10/2014 1 Gene Content Evolution What about HGT / genome sizes? Genome trees based on gene content: shared genes Haemophilus
CHAPTER : Prokaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
Obligate anaerobes - cannot grow in the presence of oxygen Facultative anaerobes - can grow with or without oxygen Aerobic - require oxygen
 PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
INTRODUCTION. Gram Stain
 INTRODUCTION In microbiology, organisms are so small that additional techniques are often required for proper viewing under the microscope. Cytological stains, or dyes that stain cells or cellular features,
INTRODUCTION In microbiology, organisms are so small that additional techniques are often required for proper viewing under the microscope. Cytological stains, or dyes that stain cells or cellular features,
The use of gene clusters to infer functional coupling
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 96, pp. 2896 2901, March 1999 Genetics The use of gene clusters to infer functional coupling ROSS OVERBEEK*, MICHAEL FONSTEIN, MARK D SOUZA*, GORDON D. PUSCH*, AND NATALIA
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 96, pp. 2896 2901, March 1999 Genetics The use of gene clusters to infer functional coupling ROSS OVERBEEK*, MICHAEL FONSTEIN, MARK D SOUZA*, GORDON D. PUSCH*, AND NATALIA
Multifractal characterisation of complete genomes
 arxiv:physics/1854v1 [physics.bio-ph] 28 Aug 21 Multifractal characterisation of complete genomes Vo Anh 1, Ka-Sing Lau 2 and Zu-Guo Yu 1,3 1 Centre in Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics, Queensland
arxiv:physics/1854v1 [physics.bio-ph] 28 Aug 21 Multifractal characterisation of complete genomes Vo Anh 1, Ka-Sing Lau 2 and Zu-Guo Yu 1,3 1 Centre in Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics, Queensland
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer
 Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Map of AP-Aligned Bio-Rad Kits with Learning Objectives
 Map of AP-Aligned Bio-Rad Kits with Learning Objectives Cover more than one AP Biology Big Idea with these AP-aligned Bio-Rad kits. Big Idea 1 Big Idea 2 Big Idea 3 Big Idea 4 ThINQ! pglo Transformation
Map of AP-Aligned Bio-Rad Kits with Learning Objectives Cover more than one AP Biology Big Idea with these AP-aligned Bio-Rad kits. Big Idea 1 Big Idea 2 Big Idea 3 Big Idea 4 ThINQ! pglo Transformation
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences
 Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 3. Cell Structure and Taxonomy Chapter 3 Outline Introduction Eucaryotic Cell Structure Procaryotic Cell Structure Summary of Structural Differences
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 3. Cell Structure and Taxonomy Chapter 3 Outline Introduction Eucaryotic Cell Structure Procaryotic Cell Structure Summary of Structural Differences
Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Ch 27: The Prokaryotes Bacteria & Archaea Older: (Eu)bacteria & Archae(bacteria)
 Ch 27: The Prokaryotes Bacteria & Archaea Older: (Eu)bacteria & Archae(bacteria) (don t study Concept 27.2) Some phyla Remember: Bacterial cell structure and shapes 1 Usually very small but some are unusually
Ch 27: The Prokaryotes Bacteria & Archaea Older: (Eu)bacteria & Archae(bacteria) (don t study Concept 27.2) Some phyla Remember: Bacterial cell structure and shapes 1 Usually very small but some are unusually
rho Is Not Essential for Viability or Virulence in Staphylococcus aureus
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 2001, p. 1099 1103 Vol. 45, No. 4 0066-4804/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.4.1099 1103.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 2001, p. 1099 1103 Vol. 45, No. 4 0066-4804/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.4.1099 1103.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Kharkov National Medical University. Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich
 Kharkov National Medical University Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich Tkachenko Victoria 1, 5, 11, 14, 19, 21, 30 Kovalenko Natalia 2, 12, 25, 29 Siritsa
Kharkov National Medical University Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich Tkachenko Victoria 1, 5, 11, 14, 19, 21, 30 Kovalenko Natalia 2, 12, 25, 29 Siritsa
no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan
 no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan Introduction to microbiology Let's start! As you might have concluded, microbiology is the study of all organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, Ex:
no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan Introduction to microbiology Let's start! As you might have concluded, microbiology is the study of all organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, Ex:
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan
 Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-formicrobiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-edition-by-cowan Chapter
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-formicrobiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-edition-by-cowan Chapter
B. Correct! Bacillus anthraces produces spores that can cause anthrax. D. Incorrect! Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 09 - The Prokaryotes No. 1 of 10 1. Bacillus anthraces is most closely associated with which of the following? (A) Botulism poisoning (B) Anthrax (C) Gangrene (D) Diphtheria
Microbiology - Problem Drill 09 - The Prokaryotes No. 1 of 10 1. Bacillus anthraces is most closely associated with which of the following? (A) Botulism poisoning (B) Anthrax (C) Gangrene (D) Diphtheria
Microbe Mission C Test
 Microbe Mission C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Page 2 Part 1: Microscopes Names the following
Microbe Mission C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Page 2 Part 1: Microscopes Names the following
9/8/2017. Bacteria and Archaea. Three domain system: The present tree of life. Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success
 5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
UNIVERSITY OF YORK. BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations Department : BIOLOGY. Title of Exam: Molecular microbiology
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations 2017-8 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular microbiology Time Allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes Marking
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations 2017-8 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular microbiology Time Allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes Marking
Evolutionary Use of Domain Recombination: A Distinction. Between Membrane and Soluble Proteins
 1 Evolutionary Use of Domain Recombination: A Distinction Between Membrane and Soluble Proteins Yang Liu, Mark Gerstein, Donald M. Engelman Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry, Yale University,
1 Evolutionary Use of Domain Recombination: A Distinction Between Membrane and Soluble Proteins Yang Liu, Mark Gerstein, Donald M. Engelman Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry, Yale University,
Rise and Fall of Mutator Bacteria
 Rise and Fall of Mutator Bacteria The Evolution of Mutation Rates in Bacteria Yoav Ram Hadany Evolutionary Theory Lab 29 May 2011 Bacteria Bacteria are unicellular, haploid and asexual Reproduce by binary
Rise and Fall of Mutator Bacteria The Evolution of Mutation Rates in Bacteria Yoav Ram Hadany Evolutionary Theory Lab 29 May 2011 Bacteria Bacteria are unicellular, haploid and asexual Reproduce by binary
chapter one: the history of microbiology
 chapter one: the history of microbiology Revised 6/19/2018 microbes microscopic (small) organisms, viruses, prions prefix sci. notation frac. equivalent dec. equivalent kilo- (k) 1 10 3 1000/1 = 1000 1000
chapter one: the history of microbiology Revised 6/19/2018 microbes microscopic (small) organisms, viruses, prions prefix sci. notation frac. equivalent dec. equivalent kilo- (k) 1 10 3 1000/1 = 1000 1000
Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th November 2009
 Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 20 th November 2009 Introduction The natural tetracyclines, including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and demethylchlortetracycline
Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 20 th November 2009 Introduction The natural tetracyclines, including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and demethylchlortetracycline
Bacterial Genetics & Operons
 Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Ch 3. Bacteria and Archaea
 Ch 3 Bacteria and Archaea SLOs for Culturing of Microorganisms Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. List structures all bacteria possess. Describe three basic
Ch 3 Bacteria and Archaea SLOs for Culturing of Microorganisms Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. List structures all bacteria possess. Describe three basic
In vitro the effect of intestinal normal flora on some pathogenic bacteria.
 In vitro the effect of intestinal normal flora on some pathogenic bacteria. Abstract: Dr.abbass shaker Ali adel Leena abd Al-Redha The effect of two types of intestinal bacterial normal floral ( and klebsiella)
In vitro the effect of intestinal normal flora on some pathogenic bacteria. Abstract: Dr.abbass shaker Ali adel Leena abd Al-Redha The effect of two types of intestinal bacterial normal floral ( and klebsiella)
Insect/Bacterial Symbioses Aphid/Buchnera association
 Insect/Bacterial Symbioses Aphid/Buchnera association I. Introduction A. Intracellular symbioses are common in the order Homoptera, which includes aphids, mealy bugs, whiteflies, and cicadas, Blattaria,
Insect/Bacterial Symbioses Aphid/Buchnera association I. Introduction A. Intracellular symbioses are common in the order Homoptera, which includes aphids, mealy bugs, whiteflies, and cicadas, Blattaria,
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309. Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012
 MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
Prereq: Concurrent 3 CH
 0201107 0201101 General Biology (1) General Biology (1) is an introductory course which covers the basics of cell biology in a traditional order, from the structure and function of molecules to the structure
0201107 0201101 General Biology (1) General Biology (1) is an introductory course which covers the basics of cell biology in a traditional order, from the structure and function of molecules to the structure
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan
 Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bankfor-microbiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-by-cowan/ Chapter 1: The Main Themes
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bankfor-microbiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-by-cowan/ Chapter 1: The Main Themes
Types of biological networks. I. Intra-cellurar networks
 Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
 KAP Biology Dept Kenyon College Differential gene expression and development Mechanisms of cellular determination Induction Pattern formation Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
KAP Biology Dept Kenyon College Differential gene expression and development Mechanisms of cellular determination Induction Pattern formation Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
Host-Pathogen Interaction. PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur
 Host-Pathogen Interaction PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur-176062 PATHOGEN DEFENCE IN PLANTS A BIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR VIEW Two types of plant resistance response to potential
Host-Pathogen Interaction PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur-176062 PATHOGEN DEFENCE IN PLANTS A BIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR VIEW Two types of plant resistance response to potential
BEFORE TAKING THIS MODULE YOU MUST ( TAKE BIO-4013Y OR TAKE BIO-
 2018/9 - BIO-4001A BIODIVERSITY Autumn Semester, Level 4 module (Maximum 150 Students) Organiser: Dr Harriet Jones Timetable Slot:DD This module explores life on Earth. You will be introduced to the major
2018/9 - BIO-4001A BIODIVERSITY Autumn Semester, Level 4 module (Maximum 150 Students) Organiser: Dr Harriet Jones Timetable Slot:DD This module explores life on Earth. You will be introduced to the major
PLPA ENROLLED STUDENT TRANSCRIPT EVALUATION
 PLPA ENROLLED STUDENT TRANSCRIPT EVALUATION NAME: ADMISSION DATE: LOCAL ADDRESS: PHONE #: LAB ROOM #: LAB PHONE #: MAJOR PROFESSOR: ROTATION 1: ROTATION 2: ROTATION 3: CORE COURSES TO BE TAKEN PLPA 200
PLPA ENROLLED STUDENT TRANSCRIPT EVALUATION NAME: ADMISSION DATE: LOCAL ADDRESS: PHONE #: LAB ROOM #: LAB PHONE #: MAJOR PROFESSOR: ROTATION 1: ROTATION 2: ROTATION 3: CORE COURSES TO BE TAKEN PLPA 200
Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg Lapets ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies 2004, 2:
 1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
Characteristics. Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome
 Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Signal Transduction. Dr. Chaidir, Apt
 Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Nitroxoline Rationale for the NAK clinical breakpoints, version th October 2013
 Nitroxoline Rationale for the NAK clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 4 th October 2013 Foreword NAK The German Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Committee (NAK - Nationales Antibiotika-Sensitivitätstest
Nitroxoline Rationale for the NAK clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 4 th October 2013 Foreword NAK The German Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Committee (NAK - Nationales Antibiotika-Sensitivitätstest
Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures
 Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures Nadya Andini 1, Bo Wang 2, Pornpat Athamanolap 3, Justin Hardick 4, Billie J. Masek 5, Simone Thair 1, Annie Hu 1, Gideon Avornu 5, Stephen Peterson
Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures Nadya Andini 1, Bo Wang 2, Pornpat Athamanolap 3, Justin Hardick 4, Billie J. Masek 5, Simone Thair 1, Annie Hu 1, Gideon Avornu 5, Stephen Peterson
MICROBIOLOGY ECOLOGY. Introduction RESEARCH ARTICLE. Sharad Mohan 1,2, Tim H. Mauchline 1, Janet Rowe 1, Penny R. Hirsch 1 & Keith G.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Pasteuria endospores from Heterodera cajani (Nematoda: Heteroderidae) exhibit inverted attachment and altered germination in cross-infection studies with Globodera pallida (Nematoda: Heteroderidae)
RESEARCH ARTICLE Pasteuria endospores from Heterodera cajani (Nematoda: Heteroderidae) exhibit inverted attachment and altered germination in cross-infection studies with Globodera pallida (Nematoda: Heteroderidae)
Bio Microbiology - Spring 2014 Learning Guide 04.
 Bio 230 - Microbiology - Spring 2014 Learning Guide 04 http://pessimistcomic.blogspot.com/ Cell division is a part of a replication cycle that takes place throughout the life of the bacterium A septum
Bio 230 - Microbiology - Spring 2014 Learning Guide 04 http://pessimistcomic.blogspot.com/ Cell division is a part of a replication cycle that takes place throughout the life of the bacterium A septum
KINGDOM MONERA. Bacterial Cell Shape 8/22/2010. The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN
 INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Tuesday, December 27, 16
 Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.B: Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.B: Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular
DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY. Microbiology Programme: Bachelor of Science (Honours) Microbiology
 DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY Microbiology Programme: Bachelor of Science (Honours) Microbiology Philosophy Microbiology is simply a natural science that deals with the study of microbes: their structure,
DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY Microbiology Programme: Bachelor of Science (Honours) Microbiology Philosophy Microbiology is simply a natural science that deals with the study of microbes: their structure,
Mechanisms of evolution in experiment and theory. Christopher Knight
 Mechanisms of evolution in experiment and theory Christopher Knight Evolution and molecular biology Nothing in Biology makes sense except in the light of evolution (Dobzhansy 1964 in Biology, molecular
Mechanisms of evolution in experiment and theory Christopher Knight Evolution and molecular biology Nothing in Biology makes sense except in the light of evolution (Dobzhansy 1964 in Biology, molecular
Evidence that entry into sporulation in Bacillus subtilis is governed by a gradual increase in the level and activity of the master regulator Spo0A
 Evidence that entry into sporulation in Bacillus subtilis is governed by a gradual increase in the level and activity of the master regulator Spo0A Masaya Fujita and Richard Losick 1 Department of Molecular
Evidence that entry into sporulation in Bacillus subtilis is governed by a gradual increase in the level and activity of the master regulator Spo0A Masaya Fujita and Richard Losick 1 Department of Molecular
Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
 Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY What are microbes? Germs, microbe s s microorganisms are minute living things that individually
Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY What are microbes? Germs, microbe s s microorganisms are minute living things that individually
Name: Block: Date: Microbiology Chapters 1 and 2 Review
 Name: Block: Date: Microbiology Chapters 1 and 2 Review Complete the following short answer questions. 1. Define microbiology. The study of microorganisms. 2. What are the six major groups of organisms
Name: Block: Date: Microbiology Chapters 1 and 2 Review Complete the following short answer questions. 1. Define microbiology. The study of microorganisms. 2. What are the six major groups of organisms
Midterm Exam #1 : In-class questions! MB 451 Microbial Diversity : Spring 2015!
 Midterm Exam #1 : In-class questions MB 451 Microbial Diversity : Spring 2015 Honor pledge: I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this test. Signed : Name : Date : TOTAL = 45 points 1.
Midterm Exam #1 : In-class questions MB 451 Microbial Diversity : Spring 2015 Honor pledge: I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this test. Signed : Name : Date : TOTAL = 45 points 1.
Bacterial Morphology and Structure م.م رنا مشعل
 Bacterial Morphology and Structure م.م رنا مشعل SIZE OF BACTERIA Unit for measurement : Micron or micrometer, μm: 1μm=10-3 mm Size: Varies with kinds of bacteria, and also related to their age and external
Bacterial Morphology and Structure م.م رنا مشعل SIZE OF BACTERIA Unit for measurement : Micron or micrometer, μm: 1μm=10-3 mm Size: Varies with kinds of bacteria, and also related to their age and external
Warm Up. What are some examples of living things? Describe the characteristics of living things
 Warm Up What are some examples of living things? Describe the characteristics of living things Objectives Identify the levels of biological organization and explain their relationships Describe cell structure
Warm Up What are some examples of living things? Describe the characteristics of living things Objectives Identify the levels of biological organization and explain their relationships Describe cell structure
Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY Telephone Number: (845) ext Fax Number: (845)
 Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY 12549 Telephone Number: (845)457-2400 ext. 18121 Fax Number: (845)457-4254 Advance Placement Biology Presented to the Board of Education
Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY 12549 Telephone Number: (845)457-2400 ext. 18121 Fax Number: (845)457-4254 Advance Placement Biology Presented to the Board of Education
Shape, Arrangement, and Size. Cocci (s., coccus) bacillus (pl., bacilli) 9/21/2013
 Shape, Arrangement, and Size Cocci (s., coccus) are roughly spherical cells. The other common shape is that of a rod, sometimes called a bacillus (pl., bacilli). Spiral-shaped procaryotes can be either
Shape, Arrangement, and Size Cocci (s., coccus) are roughly spherical cells. The other common shape is that of a rod, sometimes called a bacillus (pl., bacilli). Spiral-shaped procaryotes can be either
Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table:
 Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
Outline. Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea. Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea
 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Name Chapter 10: Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis Mrs. Laux Take home test #7 DUE: MONDAY, NOVEMBER 16, 2009 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
The outer membrane of Borrelia 7/3/2014. LDA Conference Richard Bingham 1. The Outer Membrane of Borrelia; The Interface Between Them and Us
 The Outer Membrane of Borrelia; The Interface Between Them and Us Richard Bingham The University of Huddersfield Lecture Outline I will give an overview of the outer membrane of Borrelia I will present
The Outer Membrane of Borrelia; The Interface Between Them and Us Richard Bingham The University of Huddersfield Lecture Outline I will give an overview of the outer membrane of Borrelia I will present
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES
 Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Regulation of gene expression. Premedical - Biology
 Regulation of gene expression Premedical - Biology Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cell Operon units system of negative feedback positive and negative regulation in eukaryotic cell - at any
Regulation of gene expression Premedical - Biology Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cell Operon units system of negative feedback positive and negative regulation in eukaryotic cell - at any
Microbe Mission B Test
 Microbe Mission B Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Part 1: Microscopes Names the following structures
Microbe Mission B Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Part 1: Microscopes Names the following structures
Regents Review Assignment #8-A08 Living Environment: Comet Part A Questions
 Part A Questions 1. A student notices that fruit flies with the curlywing trait develop straight wings if kept at a temperature of 16 C, but develop curly wings if kept at 25 C. The best explanation for
Part A Questions 1. A student notices that fruit flies with the curlywing trait develop straight wings if kept at a temperature of 16 C, but develop curly wings if kept at 25 C. The best explanation for
Cell Structure and Function. The Development of Cell Theory
 Cell Structure and Function The Development of Cell Theory Hooke's original microscope, that he used at Oxford University, in 1665. Robert Hooke first examined a thin piece of cork (see below), and coined
Cell Structure and Function The Development of Cell Theory Hooke's original microscope, that he used at Oxford University, in 1665. Robert Hooke first examined a thin piece of cork (see below), and coined
Microbiology Helmut Pospiech
 Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Biased biological functions of horizontally transferred genes in prokaryotic genomes
 Biased biological functions of horizontally transferred genes in prokaryotic genomes Yoji Nakamura 1,5, Takeshi Itoh 2,3, Hideo Matsuda 4 & Takashi Gojobori 1,2 Horizontal gene transfer is one of the main
Biased biological functions of horizontally transferred genes in prokaryotic genomes Yoji Nakamura 1,5, Takeshi Itoh 2,3, Hideo Matsuda 4 & Takashi Gojobori 1,2 Horizontal gene transfer is one of the main
Chapter 03 Microscopy and Cell Structure
 Chapter 03 Microscopy and Cell Structure Multiple Choice Questions 1. Eukaryotic cells are A. less complex than prokaryotic cells. B. members of the Domains Bacteria and Archaea. C. defined by the presence
Chapter 03 Microscopy and Cell Structure Multiple Choice Questions 1. Eukaryotic cells are A. less complex than prokaryotic cells. B. members of the Domains Bacteria and Archaea. C. defined by the presence
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
Microbiology / Active Lecture Questions Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms 1 Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms
 1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
Reception The target cell s detection of a signal coming from outside the cell May Occur by: Direct connect Through signal molecules
 Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS
 CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
Measure representation and multifractal analysis of complete genomes
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 64, 031903 Measure representation and multifractal analysis of complete genomes Zu-Guo Yu, 1,2, * Vo Anh, 1 and Ka-Sing Lau 3 1 Centre in Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 64, 031903 Measure representation and multifractal analysis of complete genomes Zu-Guo Yu, 1,2, * Vo Anh, 1 and Ka-Sing Lau 3 1 Centre in Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics,
The genomic tree of living organisms based on a fractal model
 Physics Letters A 317 (2003) 293 302 www.elsevier.com/locate/pla The genomic tree of living organisms based on a fractal model Zu-Guo Yu a,b,,voanh a, Ka-Sing Lau c, Ka-Hou Chu d a Program in Statistics
Physics Letters A 317 (2003) 293 302 www.elsevier.com/locate/pla The genomic tree of living organisms based on a fractal model Zu-Guo Yu a,b,,voanh a, Ka-Sing Lau c, Ka-Hou Chu d a Program in Statistics
Major Events in the History of Earth
 Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 10
 56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 10 Temporal Programs and the Global Structure The single-input module (SIM) network motif The network motifs we have studied so far all had a defined number of nodes.
56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 10 Temporal Programs and the Global Structure The single-input module (SIM) network motif The network motifs we have studied so far all had a defined number of nodes.
