Name KEY. Biology Developmental Biology Winter Quarter Midterm 3 KEY
|
|
|
- Jayson Roderick McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name KEY 100 Total Points Open Book Biology Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2009 Midterm 3 KEY All of the 25 multi-choice questions are single-answer. Choose the best answer. (4 pts each) Place your answer on the ScanTron sheet. Make sure you put on name and student number on the ScanTron sheet. 1. (p. 380) Lack of folic acid will increase the incidence of spina bifida because a. folic acid is need to specify the neural crest b. folic acid is needed for the expression of N-cadherin c. folic acid is needed to promote the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid in the spinal cord 2. (p. 384) If the BMP gradient were eliminated in the forming neural tube, what would happen to the specification of neural fates? a. no major change would occur because the Shh gradient is still intact b. the entire neural tube would adopt a floorplate identity because the Shh gradient would be unopposed by the BMP gradient c. random right-left asymmetries in cell fate specification would occur d. an expansion of ventral cell identities would occur e. the floorplate would disappear 3. (p. 383) If a morpholino to snakehead was injected into a fertilized zebrafish egg, the resulting phenotype would look like a. a chick embryo b. a snake embryo c. an embryo with a snake-like head d. an embryo with fang rudiments 1
2 4. (p. 468) The human cloaca is: a. the remnant of the primitive streak b. the precursor of the posterior endoderm c. a stem cell zone d. a transient allantois e. a dilation of the embryonic gut 5. (p. 409) Mutation of a Hox gene results in the mis-specification of neural crest cells in the region of the embryo spanning somites 1-7. Which of the following developmental defects would be expected to arise? a. an absence of the septum between the pulmonary arteries and the aorta b. loss of enteric ganglia c. loss of thoracic ribs d. a and b e. a, b, and c 6. (p. 413) A mutation in Pax3 prevents the binding of beta-catenin/lef1. Identify the phenotype that would result. a. bald person b. bald person with black beard c. grey-haired person d. black-haired person e. red-headed person 7. (p. 412) A knockdown of Ephrin in somites would result in: a. the inability of neural crest to migrate through the sclerotome b. change in fate of motor neurons c. ability of neural crest to migrate through posterior sclerotome d. loss of intercellular adhesion in the somite e. all of the above 2
3 8. (p. 419) In Harry Potter 1, the young wizards, Harry, Ron, and Hermione, confront a threeheaded dog named "Fluffy", a pet owned by Hagrid the Giant. Fluffy was created by the wizard Dumbledore, using embryological knowledge similar to what you have learned in Biology 411. Dumbledore overexpressed noggin in two ectopic sites of the anterior blastoderm of a dog embryo to obtain the three-headed dog phenotype (i.e. Fluffy). On a practical exam, Dumbledore asks the young wizards to create a "cat-dog". (Dumbledore came up with this idea after watching a cartoon character on the Muggles' TV Cartoon Network.) How would you advise Harry, Ron, and Hermione to create an animal with both a cat's head and a dog's head? (Hint: it is OK for the cat's head to end up with the brain of a dog) a. overexpress cat noggin in an ectopic site in a dog blastoderm b. overexpress dog noggin in an ectopic site in a dog blastoderm, then replace dog pharyngeal endoderm with cat pharyngeal endoderm c. overexpress cat noggin in an ectopic site in a dog blastoderm, then remove the cat cranial crest d. overexpress dog noggin in an ectopic site in a dog blastoderm, then replace dog cranial crest with cat cranial crest. e. ask "He-Who-Shall-Not-Be-Named" (i.e. Voldemort) for help 9. (paper from Discussion section) What effect would retinoic acid inhibitors have on the expression waves of her1 and her7 in zebrafish? a. loss of expression in the tailbud b. cardiac expression of the genes c. phase shift between the left and right sides of embryo d. cross-midline migration of the waves e. no effect at all 10. (p. 459) What would happen if the expression of Sox5 is upregulated in the diagram shown in Figure 14.19? a. more tendons would form b. more cartilage would be produced c. the sclerotome would not form 11. (p. 473) The endocardium arises from a. blood precursors b. endoderm c. intermediate mesoderm d. lateral plate mesoderm e. Purkinjie fibers 3
4 12. (pp ) Retinal ganglion cells follow a. pathways to the ipsilateral tectum b. pathways to the contralateral tectum (legend for Fig indicates this is correct) c. pathways to both tecta (this answer accepted as well as d.) 13. The blastopore in humans becomes a. the anus b. the cloaca c. the allantois d. the urethral opening 14. (pp ) Cardia bifida could arise if a. endoderm is not specified in the embryo b. the splanchnopleure fails to fuse in the lumbar region c. head mesenchyme cells fails to aggregate around the neural tube d. the liver primordium forms in an ectopic location e. all of the above 15. (p. 460) What would happen in intermediate mesoderm if it were cut in several places along the anterior-posterior axis of the trunk prior to the induction of the kidney rudiment? a. no kidney rudiment would be formed b. the notochord would stop secreting Shh c. there would be no effect on the induction of the kidney rudiment d. somites in these areas would not form e. the intermediate mesoderm would undergo a homeotic transformation into lateral plate mesoderm 16. (pp ) If a defective Notch receptor, with a null phenotype, were electroporated in the paraxial mesoderm of a chick embryo, what effect on segmentation would this have? a. no effect would be expected b. somites would double their length in the anterior-posterior dimension c. waves of c-hairy would cease to occur d. waves of c-hairy would reverse in direction e. cells with the defective Notch receptor would not form segment boundaries 17. (p. 425) Upregulation of Isl2 in the Column of Terni would a. convert sympathetic neurons into motor neurons b. have no effect on cell fate specification c. cause sympathetic neurons to target intercostal muscle 4
5 d. cause sympathetic neurons to target axial muscle 18. (p. 430) In an embryo that lacks Shh (Sonic Hedghog), the floor plate will not be specified. What effect will this have on the migration of commissural neurons? (From the figure it seems Shh guides ventrally, then Netrin-1 guides medially.) a. no effect b. apoptosis c. lack of chemotaxis toward the ventral midline d. increased chemotaxis toward the ventral midline 19. (p. 433) In a Robo-1 Drosophila mutant a. CNS neurons fail to respond to Netrin b. CNS neurons fail to respond to Slit c. CNS neurons upregulate Robo-3 d. CNS neurons downregulate Robo-3 e. CNS neurons fail to cross the midline 20. (p. 491) If N-cadherin was downregulated in endosteal osteoblasts, what would happen to HSC cells? a. HSC cells would upregulate N-cadherin b. HSC cells would downregulate N-cadherin c. HSC cells would leave the liver d. HSC cells would leave bone marrow e. HSC cells would die 21. (p. 579) An amphibian blastema treated with retinoic acid a. is unable to undergo patterning b. undergoes dorsalization c. is unable to form distal blastema fates d. induces proximal tissues to transdifferentiate 22. (pp ) If a hydra loses both its head and its basal disc a. it is unable to regenerate a body axis b. it regenerates two heads c. it regenerates two basal discs d. the remaining piece of tissue becomes tentacles 5
6 23. (pp ) Aging in C. elegans is linked to a. decreased response to reactive oxygen species b. activation of the dauer phenotype c. activation of an insulin receptor d. damage induced by reactive oxygen species e. lack of food 24. (p. 500) A respiratory diverticulum would be induced to branch by a. tracheal mesenchyme b. lung mesenchyme c. liver mesenchyme 25. (p ) Endochondral bone undergoes ossification by a. deposition of bone by the periosteum b. deposition of bone by the endosteum c. a conversion of chondrocytes to osteoblasts 6
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Bio Section III Organogenesis. The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification. Student Learning Objectives. Student Learning Objectives
 Bio 127 - Section III Organogenesis The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification Gilbert 9e Chapter 10 Student Learning Objectives 1. You should understand that the neural crest is an evolutionary advancement
Bio 127 - Section III Organogenesis The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification Gilbert 9e Chapter 10 Student Learning Objectives 1. You should understand that the neural crest is an evolutionary advancement
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Name. Biology Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY. Midterm 3
 Name 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY Midterm 3 Read the Following Instructions: * Answer 20 questions (5 points each) out of the available 25 questions
Name 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY Midterm 3 Read the Following Instructions: * Answer 20 questions (5 points each) out of the available 25 questions
Life Sciences For NET & SLET Exams Of UGC-CSIR. Section B and C. Volume-08. Contents A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1
 Section B and C Volume-08 Contents 5. DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1 B. GAMETOGENESIS, FERTILIZATION AND EARLY DEVELOPMENT 23 C. MORPHOGENESIS AND ORGANOGENESIS IN ANIMALS 91 0
Section B and C Volume-08 Contents 5. DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1 B. GAMETOGENESIS, FERTILIZATION AND EARLY DEVELOPMENT 23 C. MORPHOGENESIS AND ORGANOGENESIS IN ANIMALS 91 0
Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos
 Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm July 28, 2008 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm Overview Development of major mesodermal lineages Somites: formation specification and differentiation Mesodermal
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm July 28, 2008 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm Overview Development of major mesodermal lineages Somites: formation specification and differentiation Mesodermal
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006
 Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007
 Biology 4361 Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007 Name: ID: Multiple choice (1 point each. Indicate the best answer.) 1. During Drosophila gastrulation, mesoderm moves in through the a. primitives streak.
Biology 4361 Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007 Name: ID: Multiple choice (1 point each. Indicate the best answer.) 1. During Drosophila gastrulation, mesoderm moves in through the a. primitives streak.
Exam 3 ID#: July 31, 2009
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 3 ID#: July 31, 2009 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 3 ID#: July 31, 2009 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
4. Neural tube cells are specified by opposing dorsal-ventral gradients of a. Wnts and Nodal. b. FGF and Shh. c. BMPs and Wnts. d. BMPs and Shh.
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: August 1, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: August 1, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
Mesoderm Development
 Quiz rules: Spread out across available tables No phones, text books, or (lecture) notes on your desks No consultation with your colleagues No websites open other than the Quiz page No screen snap shots
Quiz rules: Spread out across available tables No phones, text books, or (lecture) notes on your desks No consultation with your colleagues No websites open other than the Quiz page No screen snap shots
!!!!!!!! DB3230 Midterm 2 12/13/2013 Name:
 1. (10 pts) Draw or describe the fate map of a late blastula stage sea urchin embryo. Draw or describe the corresponding fate map of the pluteus stage larva. Describe the sequence of gastrulation events
1. (10 pts) Draw or describe the fate map of a late blastula stage sea urchin embryo. Draw or describe the corresponding fate map of the pluteus stage larva. Describe the sequence of gastrulation events
Developmental processes Differential gene expression Introduction to determination The model organisms used to study developmental processes
 Date Title Topic(s) Learning Outcomes: Sept 28 Oct 3 1. What is developmental biology and why should we care? 2. What is so special about stem cells and gametes? Developmental processes Differential gene
Date Title Topic(s) Learning Outcomes: Sept 28 Oct 3 1. What is developmental biology and why should we care? 2. What is so special about stem cells and gametes? Developmental processes Differential gene
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning
 MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? 2. What embryonic regions contribute to the developing limb bud?
 Study Questions - Lecture 17 & 18 1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? The three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb are the proximal stylopod, zeugopod, and
Study Questions - Lecture 17 & 18 1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? The three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb are the proximal stylopod, zeugopod, and
2/23/09. Regional differentiation of mesoderm. Morphological changes at early postgastrulation. Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
 Regional differentiation of mesoderm Axial Paraxial Intermediate Somatic Splanchnic Chick embryo Morphological changes at early postgastrulation stages Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
Regional differentiation of mesoderm Axial Paraxial Intermediate Somatic Splanchnic Chick embryo Morphological changes at early postgastrulation stages Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
PRACTICE EXAM. 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos.
 PRACTICE EXAM 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos. No Low [] Fly Embryo Embryo Non-neural Genes Neuroectoderm Genes
PRACTICE EXAM 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos. No Low [] Fly Embryo Embryo Non-neural Genes Neuroectoderm Genes
Biology 218, practise Exam 2, 2011
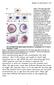 Figure 3 The long-range effect of Sqt does not depend on the induction of the endogenous cyc or sqt genes. a, Design and predictions for the experiments shown in b-e. b-e, Single-cell injection of 4 pg
Figure 3 The long-range effect of Sqt does not depend on the induction of the endogenous cyc or sqt genes. a, Design and predictions for the experiments shown in b-e. b-e, Single-cell injection of 4 pg
Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic)
 Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic) Fates of Mesoderm Paraxial - Dermis of skin - Axial Skeleton - Axial and limb muscles/tendons
Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic) Fates of Mesoderm Paraxial - Dermis of skin - Axial Skeleton - Axial and limb muscles/tendons
presumptiv e germ layers during Gastrulatio n and neurulation Somites
 Vertebrate embryos are similar at the phylotypic stage Patterning the Vertebrate Body Plan II: Mesoderm & Early Nervous System Wolpert L, Beddington R, Jessell T, Lawrence P, Meyerowitz E, Smith J. (2001)
Vertebrate embryos are similar at the phylotypic stage Patterning the Vertebrate Body Plan II: Mesoderm & Early Nervous System Wolpert L, Beddington R, Jessell T, Lawrence P, Meyerowitz E, Smith J. (2001)
Developmental Zoology. Ectodermal derivatives (ZOO ) Developmental Stages. Developmental Stages
 Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA
 Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA Instructor: Marianne Bronner Exam Length: 6 hours plus one 30-minute break at your discretion. It should take
Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA Instructor: Marianne Bronner Exam Length: 6 hours plus one 30-minute break at your discretion. It should take
Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002
 Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002 1) A variety of reagents and approaches are frequently used by developmental biologists to understand the tissue interactions and molecular signaling pathways
Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002 1) A variety of reagents and approaches are frequently used by developmental biologists to understand the tissue interactions and molecular signaling pathways
9/4/2015 INDUCTION CHAPTER 1. Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology. Fig 1.
 INDUCTION CHAPTER 1 Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology Fig 1.1 1 EVOLUTION OF METAZOAN BRAINS GASTRULATION MAKING THE 3 RD GERM LAYER
INDUCTION CHAPTER 1 Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology Fig 1.1 1 EVOLUTION OF METAZOAN BRAINS GASTRULATION MAKING THE 3 RD GERM LAYER
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Head and Face Development
 Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
Axon guidance I. Paul Garrity March 15, /9.013
 Axon guidance I Paul Garrity March 15, 2004 7.68/9.013 Neuronal Wiring: Functional Framework of the Nervous System Stretch reflex circuit Early theories of axonogenesis Schwann: many neurons link to form
Axon guidance I Paul Garrity March 15, 2004 7.68/9.013 Neuronal Wiring: Functional Framework of the Nervous System Stretch reflex circuit Early theories of axonogenesis Schwann: many neurons link to form
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology. Cell Cell Communication in Development. Developmental Activities Coordinated in this Way
 Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo
 Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo In the first part of this thesis work the physical properties of cilia-driven leftward flow were characterised in the rabbit embryo. Since its discovery
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo In the first part of this thesis work the physical properties of cilia-driven leftward flow were characterised in the rabbit embryo. Since its discovery
Conclusions. The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights
 C h a p t e r 5 Conclusions 5.1 Summary The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights into the cellular processes of assembly, and aggregation of neural crest and
C h a p t e r 5 Conclusions 5.1 Summary The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights into the cellular processes of assembly, and aggregation of neural crest and
The Radiata-Bilateria split. Second branching in the evolutionary tree
 The Radiata-Bilateria split Second branching in the evolutionary tree Two very important characteristics are used to distinguish between the second bifurcation of metazoans Body symmetry Germinal layers
The Radiata-Bilateria split Second branching in the evolutionary tree Two very important characteristics are used to distinguish between the second bifurcation of metazoans Body symmetry Germinal layers
Neural development its all connected
 Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Unit 4 Evaluation Question 1:
 Name: Unit 4 Evaluation Question 1: /7 points A naturally occurring dominant mutant in mice is the Doublefoot (Dbf) mutant. Below is an image of the bones from a wildtype (wt) and Doublefoot mutant mouse.
Name: Unit 4 Evaluation Question 1: /7 points A naturally occurring dominant mutant in mice is the Doublefoot (Dbf) mutant. Below is an image of the bones from a wildtype (wt) and Doublefoot mutant mouse.
Developmental Biology Biology Ectodermal Organs. November 22, 2005
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Ectodermal Organs November 22, 2005 Germinal neuroepithelium external limiting membrane neural tube neuroepithelium (stem cells) Figure 13.3 Figure 13.4 Neuroepithelial
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Ectodermal Organs November 22, 2005 Germinal neuroepithelium external limiting membrane neural tube neuroepithelium (stem cells) Figure 13.3 Figure 13.4 Neuroepithelial
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.32 - OVERVIEW OF ANIMALS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
!! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Review of Early Development of Humans.
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Review of Early Development of Humans Special Senses Review: Historical and Developmental Perspectives Ontogeny
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Review of Early Development of Humans Special Senses Review: Historical and Developmental Perspectives Ontogeny
Skeletal Development in Human
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Skeletal Development in Human Skeletal development in human - Long version I. Introduction I.1 Developmental genes in Drosophila I.2 Skeletal
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Skeletal Development in Human Skeletal development in human - Long version I. Introduction I.1 Developmental genes in Drosophila I.2 Skeletal
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Questions in developmental biology. Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration
 Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
Lecture 2 - Making babies: Organ formation in the Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm and Neural Crest. Outline August 15, 2016 Eddy De Robertis, M.D., Ph.D.
 Lecture 2 - Making babies: Organ formation in the Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm and Neural Crest Lecture Objectives Outline August 15, 2016, M.D., Ph.D. - To examine how the main organ systems are formed
Lecture 2 - Making babies: Organ formation in the Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm and Neural Crest Lecture Objectives Outline August 15, 2016, M.D., Ph.D. - To examine how the main organ systems are formed
Cell Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its
 Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
THE PROBLEMS OF DEVELOPMENT. Cell differentiation. Cell determination
 We emphasize these points from Kandel in Bi/CNS 150 Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience Read Lecture Lecture Friday, October 2, 2015 Development 1: pp 5-10 Introduction Brains evolved All higher animals have brains
We emphasize these points from Kandel in Bi/CNS 150 Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience Read Lecture Lecture Friday, October 2, 2015 Development 1: pp 5-10 Introduction Brains evolved All higher animals have brains
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines
 Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Reading. Lecture VI. Making Connections 9/17/12. Bio 3411 Lecture VI. Making Connections. Bio 3411 Monday September 17, 2012
 Lecture VI. Making Connections Bio 3411 Monday September 17, 2012!! 1! Reading NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp!507?536! 4 th ed, pp 577-609 Bentley, D., & Caudy, M. (1983). Nature, 304(5921), 62-65. Dickson,
Lecture VI. Making Connections Bio 3411 Monday September 17, 2012!! 1! Reading NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp!507?536! 4 th ed, pp 577-609 Bentley, D., & Caudy, M. (1983). Nature, 304(5921), 62-65. Dickson,
UNIVERSITY OF YORK BIOLOGY. Developmental Biology
 Examination Candidate Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Developmental Biology Desk Number: Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total
Examination Candidate Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Developmental Biology Desk Number: Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Axon Guidance. Multiple decision points along a growing axon s trajectory Different types of axon guidance cues:
 Axon Guidance Multiple decision points along a growing axon s trajectory Different types of axon guidance cues: Contact mediated - requires direct contact by growth cone Long range - growth cone responds
Axon Guidance Multiple decision points along a growing axon s trajectory Different types of axon guidance cues: Contact mediated - requires direct contact by growth cone Long range - growth cone responds
Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle.
 Spatial organization is a key difference between unicellular organisms and metazoans Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle. Cells differentiate as a
Spatial organization is a key difference between unicellular organisms and metazoans Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle. Cells differentiate as a
1/30/2009. Copyright The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 CHAPTER 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal New Designs for Living Zoologists recognize 34 major phyla of living multicellular animals Survivors of around 100 phyla that appeared 600 million years ago
CHAPTER 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal New Designs for Living Zoologists recognize 34 major phyla of living multicellular animals Survivors of around 100 phyla that appeared 600 million years ago
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 6, 2007 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 6, 2007 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Early Development in Invertebrates
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Early Development in Invertebrates October 25, 2006 Early Development Overview Cleavage rapid cell divisions divisions of fertilized egg into many cells Gastrulation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Early Development in Invertebrates October 25, 2006 Early Development Overview Cleavage rapid cell divisions divisions of fertilized egg into many cells Gastrulation
Principles of Experimental Embryology
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology June 16, 2008 Overview What forces affect embryonic development? The embryonic environment: external and internal How do forces
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology June 16, 2008 Overview What forces affect embryonic development? The embryonic environment: external and internal How do forces
Origin of mesenchymal stem cell
 Origin of mesenchymal stem cell Takumi Era Department of Cell Modulation, Institute of Molecular embryology and Genetics (IMEG) Kumamoto University Differentiation pathways of in vitro ES cell culture
Origin of mesenchymal stem cell Takumi Era Department of Cell Modulation, Institute of Molecular embryology and Genetics (IMEG) Kumamoto University Differentiation pathways of in vitro ES cell culture
Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11
 Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Genes, Development, and Evolution
 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Chapter 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Key Concepts 14.1 Development Involves Distinct but Overlapping Processes 14.2 Changes in Gene Expression Underlie Cell
14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Chapter 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Key Concepts 14.1 Development Involves Distinct but Overlapping Processes 14.2 Changes in Gene Expression Underlie Cell
Drosophila Life Cycle
 Drosophila Life Cycle 1 Early Drosophila Cleavage Nuclei migrate to periphery after 10 nuclear divisions. Cellularization occurs when plasma membrane folds in to divide nuclei into cells. Drosophila Superficial
Drosophila Life Cycle 1 Early Drosophila Cleavage Nuclei migrate to periphery after 10 nuclear divisions. Cellularization occurs when plasma membrane folds in to divide nuclei into cells. Drosophila Superficial
MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I. Slide #1. Cell Differentiation
 MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I Slide #1 Cell Differentiation Cell Differentiation I -Basic principles of differentiation (p1305-1320) -C-elegans (p1321-1327) Cell Differentiation II
MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I Slide #1 Cell Differentiation Cell Differentiation I -Basic principles of differentiation (p1305-1320) -C-elegans (p1321-1327) Cell Differentiation II
BIOLOGY 340 Exam Study Guide All Exams Comparative Embryology Dr. Stuart S. Sumida California State University San Bernardino; Department of Biology
 BIOLOGY 340 Exam Study Guide All Exams Comparative Embryology Dr. Stuart S. Sumida California State University San Bernardino; Department of Biology Midterm and final exams may include materials studied
BIOLOGY 340 Exam Study Guide All Exams Comparative Embryology Dr. Stuart S. Sumida California State University San Bernardino; Department of Biology Midterm and final exams may include materials studied
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila July 9, 2008 Drosophila Development Overview Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation Genetic control
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila July 9, 2008 Drosophila Development Overview Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation Genetic control
Introduction Chpt 1. Study Slides
 Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Chapter 9. Benefits of Being Large. Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity. Hierarchical Organization of Animal Complexity. Fig. 9.
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity Zoologists recognize
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity Zoologists recognize
Chapter 18 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Developmental Genetics
 Chapter 18 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Developmental Genetics Chapter Contents 18.1 Differentiated States Develop from Coordinated Programs of Gene Expression 18.2 Evolutionary Conservation
Chapter 18 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Developmental Genetics Chapter Contents 18.1 Differentiated States Develop from Coordinated Programs of Gene Expression 18.2 Evolutionary Conservation
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 12 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm chapters 10 and 11 followed the formation of various tissues from the vertebrate ectoderm. In this chapter and the next, we will follow the development of the mesodermal
12 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm chapters 10 and 11 followed the formation of various tissues from the vertebrate ectoderm. In this chapter and the next, we will follow the development of the mesodermal
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
Organization of Vertebrate Body. Organization of Vertebrate Body
 The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure
 The embryo is a Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure WEEK 4 EMBRYO General features Primordia of the brain Somites Primordia of the heart Branchial arches Primordia
The embryo is a Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure WEEK 4 EMBRYO General features Primordia of the brain Somites Primordia of the heart Branchial arches Primordia
BILD7: Problem Set. 2. What did Chargaff discover and why was this important?
 BILD7: Problem Set 1. What is the general structure of DNA? 2. What did Chargaff discover and why was this important? 3. What was the major contribution of Rosalind Franklin? 4. How did solving the structure
BILD7: Problem Set 1. What is the general structure of DNA? 2. What did Chargaff discover and why was this important? 3. What was the major contribution of Rosalind Franklin? 4. How did solving the structure
10/15/09. Tetrapod Limb Development & Pattern Formation. Developing limb region is an example of a morphogenetic field
 Tetrapod Limb Development & Pattern Formation Figure 16.5(1) Limb Bud Formation derived from lateral plate (somatic) & paraxial (myotome) Fig. 16.2 Prospective Forelimb Field of Salamander Ambystoma maculatum
Tetrapod Limb Development & Pattern Formation Figure 16.5(1) Limb Bud Formation derived from lateral plate (somatic) & paraxial (myotome) Fig. 16.2 Prospective Forelimb Field of Salamander Ambystoma maculatum
7.013 Problem Set
 7.013 Problem Set 5-2013 Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spot a huge grizzly bear. This emergency situation triggers a fight or flight response through a signaling pathway as shown below.
7.013 Problem Set 5-2013 Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spot a huge grizzly bear. This emergency situation triggers a fight or flight response through a signaling pathway as shown below.
Introduction to Animal Kingdom. Invertebrates and Vertebrates
 Introduction to Animal Kingdom Invertebrates and Vertebrates Introduction To Animals Vertebrate animal with a backbone. Invertebrate animal without a backbone; includes more than 95% of all animal species
Introduction to Animal Kingdom Invertebrates and Vertebrates Introduction To Animals Vertebrate animal with a backbone. Invertebrate animal without a backbone; includes more than 95% of all animal species
b. The maximum binding will decrease.
 Cell Signaling Receptors are a. proteins that change conformation upon interaction with a stimulus b. genes that change expression in response to a stimulus c. phosphorylation cascades that control cellular
Cell Signaling Receptors are a. proteins that change conformation upon interaction with a stimulus b. genes that change expression in response to a stimulus c. phosphorylation cascades that control cellular
Lesson 10. References: Chapter 8: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter 8:
 Lesson 10 Lesson Outline: General Features of the Skeletal System Axial Skeleton (Vertebral Column) Ontogenetic Origins (Morphogenesis) of the Skeletal System Functions of the Axial Skeleton Phylogenetic
Lesson 10 Lesson Outline: General Features of the Skeletal System Axial Skeleton (Vertebral Column) Ontogenetic Origins (Morphogenesis) of the Skeletal System Functions of the Axial Skeleton Phylogenetic
Midterm 1. Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77
 Midterm 1 Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77 NAME: TA (circle one) Jody Westbrook or Jessica Piel Section (circle one) Tue Wed Thur MCB 141 First Midterm Feb. 21, 2008 Only answer 4 of these 5 problems.
Midterm 1 Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77 NAME: TA (circle one) Jody Westbrook or Jessica Piel Section (circle one) Tue Wed Thur MCB 141 First Midterm Feb. 21, 2008 Only answer 4 of these 5 problems.
Chapter 32. Objectives. Table of Contents. Characteristics. Characteristics, continued. Section 1 The Nature of Animals
 Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Introduction to Animal Diversity. Chapter 23.1, 23.2 and additional
 Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 23.1, 23.2 and additional 1 Think of an Animal... Does your choice have hair or fur? Does it have a skeleton? Over a million species of animals described 95% have
Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 23.1, 23.2 and additional 1 Think of an Animal... Does your choice have hair or fur? Does it have a skeleton? Over a million species of animals described 95% have
Detailed Learning Outcomes
 Detailed Learning Outcomes Following lectures, workshops and directed study activities, students should: 1. Understand the principles behind the study of bioscience in relation to the profession of SLT
Detailed Learning Outcomes Following lectures, workshops and directed study activities, students should: 1. Understand the principles behind the study of bioscience in relation to the profession of SLT
Making Headway: The Roles of Hox Genes and Neural Crest Cells in Craniofacial Development
 Mini-Review TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2003) 3, 240 264 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2003.11 Making Headway: The Roles of Hox Genes and Neural Crest Cells in Craniofacial Development Paul A Trainor
Mini-Review TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2003) 3, 240 264 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2003.11 Making Headway: The Roles of Hox Genes and Neural Crest Cells in Craniofacial Development Paul A Trainor
Pamela E. Knapp, Ph.D. Dept. of Anatomy & Neurobiology DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHARYNGEAL (BRANCHIAL) ARCHES
 Embryology Pamela E. Knapp, Ph.D. Dept. of Anatomy & Neurobiology DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHARYNGEAL (BRANCHIAL) ARCHES READING: Larsen, 4 th Edition, Chapter 16; or, Langman, 8 th Edition, pp. 345-365 OBJECTIVES:
Embryology Pamela E. Knapp, Ph.D. Dept. of Anatomy & Neurobiology DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHARYNGEAL (BRANCHIAL) ARCHES READING: Larsen, 4 th Edition, Chapter 16; or, Langman, 8 th Edition, pp. 345-365 OBJECTIVES:
Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018
 Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018 Introduction 3. Books This module is based on the following books: - 'Principles of Developement', Lewis Wolpert, et al., fifth edition, 2015 - 'Developmental
Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018 Introduction 3. Books This module is based on the following books: - 'Principles of Developement', Lewis Wolpert, et al., fifth edition, 2015 - 'Developmental
10/2/2015. Chapter 4. Determination and Differentiation. Neuroanatomical Diversity
 Chapter 4 Determination and Differentiation Neuroanatomical Diversity 1 Neurochemical diversity: another important aspect of neuronal fate Neurotransmitters and their receptors Excitatory Glutamate Acetylcholine
Chapter 4 Determination and Differentiation Neuroanatomical Diversity 1 Neurochemical diversity: another important aspect of neuronal fate Neurotransmitters and their receptors Excitatory Glutamate Acetylcholine
Limb Development Involving the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles
 Limb Development Involving the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles 1 Objectives Timing and location of limb bud development The tissues from which limb buds are made Determining the position
Limb Development Involving the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles 1 Objectives Timing and location of limb bud development The tissues from which limb buds are made Determining the position
1. Why Dissect. Why are frogs a good model to use when studying the digestive system (as well as other systems)?
 Name: Date: Period: Frog Dissection Virtual Lab Use the frog Dissection link that follows to answer the questions. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/bl_16/bl_16.html Introduction 1. Why Dissect.
Name: Date: Period: Frog Dissection Virtual Lab Use the frog Dissection link that follows to answer the questions. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/bl_16/bl_16.html Introduction 1. Why Dissect.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2662
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Morphogenesis and specification of the muscle lineage during Xenopus laevis embryo development. Armbien F. Sabillo
 Morphogenesis and specification of the muscle lineage during Xenopus laevis embryo development by Armbien F. Sabillo A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree
Morphogenesis and specification of the muscle lineage during Xenopus laevis embryo development by Armbien F. Sabillo A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree
Lecture 3 - Molecular Regulation of Development. Growth factor signaling, Hox genes and the body plan
 Lecture 3 - Molecular Regulation of Development. Growth factor signaling, Hox genes and the body plan Lecture Objectives Outline August 18, 2015, M.D., Ph.D. To understand how cell differentiation and
Lecture 3 - Molecular Regulation of Development. Growth factor signaling, Hox genes and the body plan Lecture Objectives Outline August 18, 2015, M.D., Ph.D. To understand how cell differentiation and
Chapter 10 Development and Differentiation
 Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter Since ancient times, people have wondered how organisms are formed during the developmental process, and many researchers have worked tirelessly in search
Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter Since ancient times, people have wondered how organisms are formed during the developmental process, and many researchers have worked tirelessly in search
Cell Migration I: Neural Crest Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration I: Neural Crest Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Types of Cell Movement passive: active: cell sheets flow cilia or flagella ameboid adhesion
Cell Migration I: Neural Crest Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Types of Cell Movement passive: active: cell sheets flow cilia or flagella ameboid adhesion
Gut Tube Development. For it s rare that a man thinks of anything so seriously as his dinner!
 For it s rare that a man thinks of anything so seriously as his dinner! Ben Johnson Gut Tube Development This chapter will follow the development of the embryonic gut caudal to the developing pharynx,
For it s rare that a man thinks of anything so seriously as his dinner! Ben Johnson Gut Tube Development This chapter will follow the development of the embryonic gut caudal to the developing pharynx,
Developmental Biology Biology 4361
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 The Anatomical Tradition 2009 A hen is only an egg s way of making a new egg. Samuel Butler, 1885 The Anatomical Tradition - Overview What is developmental biology? How
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 The Anatomical Tradition 2009 A hen is only an egg s way of making a new egg. Samuel Butler, 1885 The Anatomical Tradition - Overview What is developmental biology? How
Axis determination in flies. Sem 9.3.B.5 Animal Science
 Axis determination in flies Sem 9.3.B.5 Animal Science All embryos are in lateral view (anterior to the left). Endoderm, midgut; mesoderm; central nervous system; foregut, hindgut and pole cells in yellow.
Axis determination in flies Sem 9.3.B.5 Animal Science All embryos are in lateral view (anterior to the left). Endoderm, midgut; mesoderm; central nervous system; foregut, hindgut and pole cells in yellow.
Tsukushi Modulates Xnr2, FGF and BMP Signaling: Regulation of Xenopus Germ Layer Formation
 Tsukushi Modulates Xnr2, FGF and BMP Signaling: Regulation of Xenopus Germ Layer Formation Samantha A. Morris 1 *, Alexandra D. Almeida 1, Hideaki Tanaka 2, Kunimasa Ohta 2, Shin-ichi Ohnuma 1 * 1 Department
Tsukushi Modulates Xnr2, FGF and BMP Signaling: Regulation of Xenopus Germ Layer Formation Samantha A. Morris 1 *, Alexandra D. Almeida 1, Hideaki Tanaka 2, Kunimasa Ohta 2, Shin-ichi Ohnuma 1 * 1 Department
Principles of Development
 Principles of Development Fourth Edition Lewis Wolpert I Cheryll Tickle Thomas jessell Peter Lawrence Elliot Meyerowitz Elizabeth Robertson Jim Smith OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS --.:. - of contents Preface
Principles of Development Fourth Edition Lewis Wolpert I Cheryll Tickle Thomas jessell Peter Lawrence Elliot Meyerowitz Elizabeth Robertson Jim Smith OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS --.:. - of contents Preface
Determination of Spatiotemporal Interactions Regulating Head/Trunk Axial Pattern in the Chick Embryo
 Eukaryon, Vol. 2, January 2006, Lake Forest ollege Senior Thesis Determination of Spatiotemporal Interactions Regulating Head/Trunk Axial Pattern in the hick Embryo David Mann * Department of Biology,
Eukaryon, Vol. 2, January 2006, Lake Forest ollege Senior Thesis Determination of Spatiotemporal Interactions Regulating Head/Trunk Axial Pattern in the hick Embryo David Mann * Department of Biology,
Goosecoid and HNF-3beta genetically interact to regulate neural tube patterning during mouse embryogenesis
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Rivera Lab Publications Pediatrics 7-1-1997 Goosecoid and HNF-3beta genetically interact to regulate neural tube patterning during mouse embryogenesis
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Rivera Lab Publications Pediatrics 7-1-1997 Goosecoid and HNF-3beta genetically interact to regulate neural tube patterning during mouse embryogenesis
Principles of Experimental Embryology
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology September 19, 2006 Major Research Questions How do forces outside the embryo affect its development? (Environmental Developmental
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology September 19, 2006 Major Research Questions How do forces outside the embryo affect its development? (Environmental Developmental
Dorsal and intermediate neuronal cell types of the spinal cord are established by a BMP signaling pathway
 Development 127, 1209-1220 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV8681 1209 Dorsal and intermediate neuronal cell types of the spinal cord are established by a BMP signaling
Development 127, 1209-1220 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV8681 1209 Dorsal and intermediate neuronal cell types of the spinal cord are established by a BMP signaling
