!!!!!!!! DB3230 Midterm 2 12/13/2013 Name:
|
|
|
- Emil Clarence Thornton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. (10 pts) Draw or describe the fate map of a late blastula stage sea urchin embryo. Draw or describe the corresponding fate map of the pluteus stage larva. Describe the sequence of gastrulation events that lead to the pluteus stage larva. Primary mesenchyme (micromeres) form skeletal rods (spicules). Secondary mesenchyme form muscle. Vegetal plate (Veg1 and Veg2 layers) form gut tube. An1 and An2 form epidermal layer and nerve cells. 1. Thickening of vegetal plate 2. ingression of primary mesenchyme 3. Invagination of vegetal plate to from blastopore 4. Convergent extension to form archenteron 5. Ingression of secondary mesenchyme cell from tip of archenteron. 6. Contact of archenteron with blastocoel ectodermal wall and induction of mouth.
2 2. (10 pts) Describe Spemann and Mangold s Nobel prizing winning experiments and the implications of their experiments for embryonic pattern formation. They showed that the only tissue specified in the late blastula was the dorsal lip of the future blastopore by transplantation experiments. Further, they put forth the idea that this tissue behaved as an organizer and because it would alter the patterning of the surrounding host cells. They showed this tiny bit of transplanted tissue could induce an embryonic pattern duplication.
3 3. (10pts) What are the most important maternal effect genes specifying the patterning of the fly embryo? Briefly describe how they function to set up the major axis and termini of the embryo. Bicoid and Nanos morphogen gradients effectively antagonize each other to set up the A-P embryo allocation. Torso is activated only at the termini to specify terminal structures. Default is telson. Acron develops due to Bicoid acting with Torso. The opposing morphogen gradients of DPP (from dorsal midline) and nuclear Dorsal from the ventral midline antagonistically allocate pattern along the dorso-ventral axis.
4 4. (10 pts) Describe the sequence of events and molecular mechanisms of hydra HEAD regeneration based on the required review reading assignment. What cellular process is both necessary and sufficient for head regeneration? What is the suggested head morphogen? Increased apoptosis is associated with early phases of head regeneration. After mid-gastric bisection in Hydra, MAPK signaling leads to rapid activation of the transcription factor CREB in fragments regenerating a head. MAPK/CREB activity is required for stimulating a wave of apoptosis in interstitial cells near the site of injury. These apoptotic cells secrete Wnt3, inducing a (head organizer) zone of proliferation below the region of apoptosis.
5 5. (15 pts) We discussed two major models of pattern formation in developing embryos. Are they necessarily independent, i.e., can the embryonic field use both patterning mechanisms simultaneously? Provide and example. 1. Alan Turing s Reaction Diffusion Model 2. Simple morphogen gradient model with defined source of morphogen. These two mechanism can both act simultaneously within an embryonic field and rely on threshold values of morphogens that specify positional information and differential cell fates. One example would be pattern of bone development in the limb. Reaction diffusion model would determine the number of bones as the limb field grows, while the gradients from the ZPA, e.g. shh would specify bone identity via threshold values for HOX gene expression.
6 6. (10 pts) Describe how you might generate a fly that has halteres associated with each thoracic and abdominal segment, but localized too far ventrally in each of the segments. Delete (use CRISPR or gene targeting by homologous recombination, etc.) Antp, Ubx, AbdA and AbdB. Or you can say delete all Hox genes posterior to Scr or to misexpress Scr in segments T1-A8. This will give a fly with all T1 segment identities posterior to T1. Next cause the gradients of either Dorsal to be too small or DPP to be too big to alter the DV location of the halteres, e.g., add extra copies of the DPP gene to the fly.
7 7. (15pt) Describe the three axial patterning systems in vertebrate limb development. What is the phenotype of the Wnt-7a KO mouse and what important concept of axial patterning is illustrated by the fact that the KO phenotype is more complex than you might have expected? Proximal-Distal axis is established by exposure to the Fgf morphogen gradient from the AER. The longer cells stay in the zone of polarizing activity (Pz) the higher the exposure to Fgf and the more distal their identity when they leave the Pz and they differentiate appropriately. Anterior-Posterior Retinoic acid and Hox genes induce the ZPA to express Shh and the distance from the posterior ZPA dictates what A-P structures will form. Limb field cells closer to the ZPA and exposed to higher concentrations of shh will differentiate into more posterior pattern elements. Dorsal-Ventral Dorsal mesoderm induces rfng and Wnt7a in the limb bud. The ventral mesoderm induces engrailed-1 expression in the ventral limb bud. The inhibitory relationship between rfng and engrailed-1 in the dorsal and ventral mesoderm determines the position of the AER at the equatorial margin and D-V patterning across the limb field. The Wnt7a KO mouse has a ventralized limb that is also missing posterior pattern elements and is truncated. It is the coordination among axial patterning systems that ensures that the right structures develop. This is illustrated by the complexity of the Wnt7a KO mouse. Wnt7a is a positive regulator of the Shh pathway and the loss of the activator and its targets lead to both A-P and P-D defects.
8 8. (10pt) What is the default fate of all the cells that do not pass through the blastopore during mammalian gastrulation? How are the separate differentiated fates of these cells determined? How is the anterior to posterior pattern of the midline non-gastrulating cells determined? Default state is neural ectoderm. The organizer (and chordomesoderm) secretes Chordin, Follistatin, and Noggin which binds to and blocks the anti-neuralizing affect of BMP secreted by the lateral plate mesoderm (and later the epidermal ectoderm). Anterior posterior patterning of the neural axis is by the morphogen gradients of retinoic,fgf and Wnt from the organizer (posterior pattern) and Cereberus, Dickkopf, and Tlc from the Anterior Visceral Endoderm. (Students do not have to list all morphogens from organizer and AVE. 2 from each is enough for full credit.)
9 9. (10pt) Define 10 of the following for full credit. Extra credit [1 pt/ ea] for additional definitions. a. cyclopamine toxin from Corn Lily inhibits shh and causes cyclops lambs b. Koller s sickle posterior margin hypoblast cells involved in A-P patterning of chick blastodisc c. nanos mrna fly posterior group determinant d. N-cadherin Ca++ dependent cell adhesion molecule whose expression correlates with neural plate segregation from epidermal ectoderm. e. Space regulation Turing Reaction-Diffusion model where inhibitor diffuses a short distance relative to field size, e.g., scales on a fish, hairs on your arm. f. TBX5 - transcription factor specifies forelimb identity g. Homeo Domain highly conserved DNA binding motif share by all HOX and HOM genes h. Maternal effect gene - Phenotype of embryo is dependent on maternal gene and not zygotic gene. i. NFkb mammalian Dorsal homolog critical for immune function j. organizer group of cells that release morphogen gradient to specify pattern of nearby cells, e.g., ZPA, Speman s Oranizer, micromeres, midbrain-hindbrain junction, anterior cut edge of hydra. k. Ed Lewis identified and characterized the homeotic mutations in fly that specify the identify of each segment.
10 l. AVE anterior visceral endoderm. Important for induction signal for patterning anterior neural axis m. Toll maternal effect gene required for Dorsal activation n. Chordamesoderm mesoderm at dorsal midline that induces neural plate formation. Becomes notochord which patterns DV neural axis. o. Ubx ultrabithorax. First gene of the Bithorax Complex and famous because its deletion leads to the 4 winged fly.
Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006
 Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
Drosophila Life Cycle
 Drosophila Life Cycle 1 Early Drosophila Cleavage Nuclei migrate to periphery after 10 nuclear divisions. Cellularization occurs when plasma membrane folds in to divide nuclei into cells. Drosophila Superficial
Drosophila Life Cycle 1 Early Drosophila Cleavage Nuclei migrate to periphery after 10 nuclear divisions. Cellularization occurs when plasma membrane folds in to divide nuclei into cells. Drosophila Superficial
Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos
 Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
10/15/09. Tetrapod Limb Development & Pattern Formation. Developing limb region is an example of a morphogenetic field
 Tetrapod Limb Development & Pattern Formation Figure 16.5(1) Limb Bud Formation derived from lateral plate (somatic) & paraxial (myotome) Fig. 16.2 Prospective Forelimb Field of Salamander Ambystoma maculatum
Tetrapod Limb Development & Pattern Formation Figure 16.5(1) Limb Bud Formation derived from lateral plate (somatic) & paraxial (myotome) Fig. 16.2 Prospective Forelimb Field of Salamander Ambystoma maculatum
1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? 2. What embryonic regions contribute to the developing limb bud?
 Study Questions - Lecture 17 & 18 1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? The three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb are the proximal stylopod, zeugopod, and
Study Questions - Lecture 17 & 18 1. What are the three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb? The three general areas of the developing vertebrate limb are the proximal stylopod, zeugopod, and
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila July 9, 2008 Drosophila Development Overview Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation Genetic control
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila July 9, 2008 Drosophila Development Overview Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation Genetic control
Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle.
 Spatial organization is a key difference between unicellular organisms and metazoans Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle. Cells differentiate as a
Spatial organization is a key difference between unicellular organisms and metazoans Unicellular: Cells change function in response to a temporal plan, such as the cell cycle. Cells differentiate as a
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 6, 2007 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 6, 2007 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
MOLECULAR CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC PATTERN FORMATION
 MOLECULAR CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC PATTERN FORMATION Drosophila is the best understood of all developmental systems, especially at the genetic level, and although it is an invertebrate it has had an enormous
MOLECULAR CONTROL OF EMBRYONIC PATTERN FORMATION Drosophila is the best understood of all developmental systems, especially at the genetic level, and although it is an invertebrate it has had an enormous
2/23/09. Regional differentiation of mesoderm. Morphological changes at early postgastrulation. Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
 Regional differentiation of mesoderm Axial Paraxial Intermediate Somatic Splanchnic Chick embryo Morphological changes at early postgastrulation stages Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
Regional differentiation of mesoderm Axial Paraxial Intermediate Somatic Splanchnic Chick embryo Morphological changes at early postgastrulation stages Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
9/4/2015 INDUCTION CHAPTER 1. Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology. Fig 1.
 INDUCTION CHAPTER 1 Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology Fig 1.1 1 EVOLUTION OF METAZOAN BRAINS GASTRULATION MAKING THE 3 RD GERM LAYER
INDUCTION CHAPTER 1 Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology Fig 1.1 1 EVOLUTION OF METAZOAN BRAINS GASTRULATION MAKING THE 3 RD GERM LAYER
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Developmental processes Differential gene expression Introduction to determination The model organisms used to study developmental processes
 Date Title Topic(s) Learning Outcomes: Sept 28 Oct 3 1. What is developmental biology and why should we care? 2. What is so special about stem cells and gametes? Developmental processes Differential gene
Date Title Topic(s) Learning Outcomes: Sept 28 Oct 3 1. What is developmental biology and why should we care? 2. What is so special about stem cells and gametes? Developmental processes Differential gene
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning
 MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
Homeotic genes in flies. Sem 9.3.B.6 Animal Science
 Homeotic genes in flies Sem 9.3.B.6 Animal Science So far We have seen that identities of each segment is determined by various regulators of segment polarity genes In arthopods, and in flies, each segment
Homeotic genes in flies Sem 9.3.B.6 Animal Science So far We have seen that identities of each segment is determined by various regulators of segment polarity genes In arthopods, and in flies, each segment
Life Sciences For NET & SLET Exams Of UGC-CSIR. Section B and C. Volume-08. Contents A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1
 Section B and C Volume-08 Contents 5. DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1 B. GAMETOGENESIS, FERTILIZATION AND EARLY DEVELOPMENT 23 C. MORPHOGENESIS AND ORGANOGENESIS IN ANIMALS 91 0
Section B and C Volume-08 Contents 5. DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1 B. GAMETOGENESIS, FERTILIZATION AND EARLY DEVELOPMENT 23 C. MORPHOGENESIS AND ORGANOGENESIS IN ANIMALS 91 0
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #8 1. Inductive signaling is a hallmark of vertebrate and mammalian development. In early neural development, there are multiple signaling pathways
Biology 218, practise Exam 2, 2011
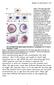 Figure 3 The long-range effect of Sqt does not depend on the induction of the endogenous cyc or sqt genes. a, Design and predictions for the experiments shown in b-e. b-e, Single-cell injection of 4 pg
Figure 3 The long-range effect of Sqt does not depend on the induction of the endogenous cyc or sqt genes. a, Design and predictions for the experiments shown in b-e. b-e, Single-cell injection of 4 pg
Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002
 Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002 1) A variety of reagents and approaches are frequently used by developmental biologists to understand the tissue interactions and molecular signaling pathways
Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002 1) A variety of reagents and approaches are frequently used by developmental biologists to understand the tissue interactions and molecular signaling pathways
MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I. Slide #1. Cell Differentiation
 MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I Slide #1 Cell Differentiation Cell Differentiation I -Basic principles of differentiation (p1305-1320) -C-elegans (p1321-1327) Cell Differentiation II
MBios 401/501: Lecture 14.2 Cell Differentiation I Slide #1 Cell Differentiation Cell Differentiation I -Basic principles of differentiation (p1305-1320) -C-elegans (p1321-1327) Cell Differentiation II
Early Development in Invertebrates
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Early Development in Invertebrates October 25, 2006 Early Development Overview Cleavage rapid cell divisions divisions of fertilized egg into many cells Gastrulation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Early Development in Invertebrates October 25, 2006 Early Development Overview Cleavage rapid cell divisions divisions of fertilized egg into many cells Gastrulation
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018
 Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018 Introduction 3. Books This module is based on the following books: - 'Principles of Developement', Lewis Wolpert, et al., fifth edition, 2015 - 'Developmental
Mesoderm Induction CBT, 2018 Hand-out CBT March 2018 Introduction 3. Books This module is based on the following books: - 'Principles of Developement', Lewis Wolpert, et al., fifth edition, 2015 - 'Developmental
Why Flies? stages of embryogenesis. The Fly in History
 The Fly in History 1859 Darwin 1866 Mendel c. 1890 Driesch, Roux (experimental embryology) 1900 rediscovery of Mendel (birth of genetics) 1910 first mutant (white) (Morgan) 1913 first genetic map (Sturtevant
The Fly in History 1859 Darwin 1866 Mendel c. 1890 Driesch, Roux (experimental embryology) 1900 rediscovery of Mendel (birth of genetics) 1910 first mutant (white) (Morgan) 1913 first genetic map (Sturtevant
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines
 Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Lecture 7. Development of the Fruit Fly Drosophila
 BIOLOGY 205/SECTION 7 DEVELOPMENT- LILJEGREN Lecture 7 Development of the Fruit Fly Drosophila 1. The fruit fly- a highly successful, specialized organism a. Quick life cycle includes three larval stages
BIOLOGY 205/SECTION 7 DEVELOPMENT- LILJEGREN Lecture 7 Development of the Fruit Fly Drosophila 1. The fruit fly- a highly successful, specialized organism a. Quick life cycle includes three larval stages
2. Fertilization activates the egg and bring together the nuclei of sperm and egg
 2. Fertilization activates the egg and bring together the nuclei of sperm and egg Sea urchins (what phylum?) are models for the study of the early development of deuterostomes (like us, right?). Sea urchin
2. Fertilization activates the egg and bring together the nuclei of sperm and egg Sea urchins (what phylum?) are models for the study of the early development of deuterostomes (like us, right?). Sea urchin
Drosophila melanogaster- Morphogen Gradient
 NPTEL Biotechnology - Systems Biology Drosophila melanogaster- Morphogen Gradient Dr. M. Vijayalakshmi School of Chemical and Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by
NPTEL Biotechnology - Systems Biology Drosophila melanogaster- Morphogen Gradient Dr. M. Vijayalakshmi School of Chemical and Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by
Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006 Multiple choice (one point each) Circle the best answer. 1. Inducers of Xenopus lens and optic vesicle include a. pharyngeal endoderm and anterior neural
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 2 ID#: November 9, 2006 Multiple choice (one point each) Circle the best answer. 1. Inducers of Xenopus lens and optic vesicle include a. pharyngeal endoderm and anterior neural
Transcript: Introduction to Limb Development
 Limbs undeniably give us the greatest ability to do things. Our legs provide us with the locomotion to move. Whether for running, climbing or swimming through the water, our limbs help us to traverse sometimes
Limbs undeniably give us the greatest ability to do things. Our legs provide us with the locomotion to move. Whether for running, climbing or swimming through the water, our limbs help us to traverse sometimes
PRACTICE EXAM. 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos.
 PRACTICE EXAM 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos. No Low [] Fly Embryo Embryo Non-neural Genes Neuroectoderm Genes
PRACTICE EXAM 20 pts: 1. With the aid of a diagram, indicate how initial dorsal-ventral polarity is created in fruit fly and frog embryos. No Low [] Fly Embryo Embryo Non-neural Genes Neuroectoderm Genes
Development Team. Developmental Biology Axis Specification in Drosophila. Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi
 Paper No. : 11 Module : 6 Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof. Namita Agrawal Department of Zoology, University
Paper No. : 11 Module : 6 Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof. Namita Agrawal Department of Zoology, University
Midterm 1. Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77
 Midterm 1 Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77 NAME: TA (circle one) Jody Westbrook or Jessica Piel Section (circle one) Tue Wed Thur MCB 141 First Midterm Feb. 21, 2008 Only answer 4 of these 5 problems.
Midterm 1 Average score: 74.4 Median score: 77 NAME: TA (circle one) Jody Westbrook or Jessica Piel Section (circle one) Tue Wed Thur MCB 141 First Midterm Feb. 21, 2008 Only answer 4 of these 5 problems.
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm July 28, 2008 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm Overview Development of major mesodermal lineages Somites: formation specification and differentiation Mesodermal
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm July 28, 2008 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm Overview Development of major mesodermal lineages Somites: formation specification and differentiation Mesodermal
Limb Development Involving the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles
 Limb Development Involving the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles 1 Objectives Timing and location of limb bud development The tissues from which limb buds are made Determining the position
Limb Development Involving the development of the appendicular skeleton and muscles 1 Objectives Timing and location of limb bud development The tissues from which limb buds are made Determining the position
BILD7: Problem Set. 2. What did Chargaff discover and why was this important?
 BILD7: Problem Set 1. What is the general structure of DNA? 2. What did Chargaff discover and why was this important? 3. What was the major contribution of Rosalind Franklin? 4. How did solving the structure
BILD7: Problem Set 1. What is the general structure of DNA? 2. What did Chargaff discover and why was this important? 3. What was the major contribution of Rosalind Franklin? 4. How did solving the structure
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
Genes, Development, and Evolution
 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Chapter 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Key Concepts 14.1 Development Involves Distinct but Overlapping Processes 14.2 Changes in Gene Expression Underlie Cell
14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Chapter 14 Genes, Development, and Evolution Key Concepts 14.1 Development Involves Distinct but Overlapping Processes 14.2 Changes in Gene Expression Underlie Cell
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology The Genetics of Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology The Genetics of Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 EARLY DROSOPHILA DEVELOPMENT Fertilization 1) Drosophila egg activation occurs at ovulation - eggs are
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology The Genetics of Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 EARLY DROSOPHILA DEVELOPMENT Fertilization 1) Drosophila egg activation occurs at ovulation - eggs are
Questions in developmental biology. Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration
 Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
UNIVERSITY OF YORK BIOLOGY. Developmental Biology
 Examination Candidate Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Developmental Biology Desk Number: Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total
Examination Candidate Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Developmental Biology Desk Number: Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total
Development of Drosophila
 Development of Drosophila Hand-out CBT Chapter 2 Wolpert, 5 th edition March 2018 Introduction 6. Introduction Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is found in all warm countries. In cooler regions,
Development of Drosophila Hand-out CBT Chapter 2 Wolpert, 5 th edition March 2018 Introduction 6. Introduction Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is found in all warm countries. In cooler regions,
Chapter 10 Development and Differentiation
 Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter Since ancient times, people have wondered how organisms are formed during the developmental process, and many researchers have worked tirelessly in search
Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter Since ancient times, people have wondered how organisms are formed during the developmental process, and many researchers have worked tirelessly in search
Name. Biology Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY. Midterm 3
 Name 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY Midterm 3 Read the Following Instructions: * Answer 20 questions (5 points each) out of the available 25 questions
Name 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY Midterm 3 Read the Following Instructions: * Answer 20 questions (5 points each) out of the available 25 questions
Name KEY. Biology Developmental Biology Winter Quarter Midterm 3 KEY
 Name KEY 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2009 Midterm 3 KEY All of the 25 multi-choice questions are single-answer. Choose the best answer. (4 pts each) Place
Name KEY 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2009 Midterm 3 KEY All of the 25 multi-choice questions are single-answer. Choose the best answer. (4 pts each) Place
Morphogens in biological development: Drosophila example
 LSM5194 Morphogens in biological development: Drosophila example Lecture 29 The concept of morphogen gradients The concept of morphogens was proposed by L. Wolpert as a part of the positional information
LSM5194 Morphogens in biological development: Drosophila example Lecture 29 The concept of morphogen gradients The concept of morphogens was proposed by L. Wolpert as a part of the positional information
Unit 4 Evaluation Question 1:
 Name: Unit 4 Evaluation Question 1: /7 points A naturally occurring dominant mutant in mice is the Doublefoot (Dbf) mutant. Below is an image of the bones from a wildtype (wt) and Doublefoot mutant mouse.
Name: Unit 4 Evaluation Question 1: /7 points A naturally occurring dominant mutant in mice is the Doublefoot (Dbf) mutant. Below is an image of the bones from a wildtype (wt) and Doublefoot mutant mouse.
Principles of Experimental Embryology
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology June 16, 2008 Overview What forces affect embryonic development? The embryonic environment: external and internal How do forces
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology June 16, 2008 Overview What forces affect embryonic development? The embryonic environment: external and internal How do forces
Developmental genetics: finding the genes that regulate development
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 9 Developmental genetics: finding the genes that regulate development Introduction The application of genetic analysis and DNA technology to the study of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 9 Developmental genetics: finding the genes that regulate development Introduction The application of genetic analysis and DNA technology to the study of
Lecture 3 - Molecular Regulation of Development. Growth factor signaling, Hox genes and the body plan
 Lecture 3 - Molecular Regulation of Development. Growth factor signaling, Hox genes and the body plan Lecture Objectives Outline August 18, 2015, M.D., Ph.D. To understand how cell differentiation and
Lecture 3 - Molecular Regulation of Development. Growth factor signaling, Hox genes and the body plan Lecture Objectives Outline August 18, 2015, M.D., Ph.D. To understand how cell differentiation and
presumptiv e germ layers during Gastrulatio n and neurulation Somites
 Vertebrate embryos are similar at the phylotypic stage Patterning the Vertebrate Body Plan II: Mesoderm & Early Nervous System Wolpert L, Beddington R, Jessell T, Lawrence P, Meyerowitz E, Smith J. (2001)
Vertebrate embryos are similar at the phylotypic stage Patterning the Vertebrate Body Plan II: Mesoderm & Early Nervous System Wolpert L, Beddington R, Jessell T, Lawrence P, Meyerowitz E, Smith J. (2001)
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements
 Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal Body Plans
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal Body Plans
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.32 - OVERVIEW OF ANIMALS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
!! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
Chapter 18 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Developmental Genetics
 Chapter 18 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Developmental Genetics Chapter Contents 18.1 Differentiated States Develop from Coordinated Programs of Gene Expression 18.2 Evolutionary Conservation
Chapter 18 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Developmental Genetics Chapter Contents 18.1 Differentiated States Develop from Coordinated Programs of Gene Expression 18.2 Evolutionary Conservation
Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007
 Biology 4361 Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007 Name: ID: Multiple choice (1 point each. Indicate the best answer.) 1. During Drosophila gastrulation, mesoderm moves in through the a. primitives streak.
Biology 4361 Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007 Name: ID: Multiple choice (1 point each. Indicate the best answer.) 1. During Drosophila gastrulation, mesoderm moves in through the a. primitives streak.
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo
 Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo In the first part of this thesis work the physical properties of cilia-driven leftward flow were characterised in the rabbit embryo. Since its discovery
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling in the rabbit embryo In the first part of this thesis work the physical properties of cilia-driven leftward flow were characterised in the rabbit embryo. Since its discovery
v Scientists have identified 1.3 million living species of animals v The definition of an animal
 Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements BIOSC 041 v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements BIOSC 041 v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal
18.4 Embryonic development involves cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis
 18.4 Embryonic development involves cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis An organism arises from a fertilized egg cell as the result of three interrelated processes: cell division, cell
18.4 Embryonic development involves cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis An organism arises from a fertilized egg cell as the result of three interrelated processes: cell division, cell
Neural development its all connected
 Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 19, 2009
 Write your name and student ID# on EVERY PAGE of your exam MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 19, 2009 Circle the name of your TA Jessica Lyons Alberto Stolfi Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 TOTAL
Write your name and student ID# on EVERY PAGE of your exam MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 19, 2009 Circle the name of your TA Jessica Lyons Alberto Stolfi Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 TOTAL
Tsukushi Modulates Xnr2, FGF and BMP Signaling: Regulation of Xenopus Germ Layer Formation
 Tsukushi Modulates Xnr2, FGF and BMP Signaling: Regulation of Xenopus Germ Layer Formation Samantha A. Morris 1 *, Alexandra D. Almeida 1, Hideaki Tanaka 2, Kunimasa Ohta 2, Shin-ichi Ohnuma 1 * 1 Department
Tsukushi Modulates Xnr2, FGF and BMP Signaling: Regulation of Xenopus Germ Layer Formation Samantha A. Morris 1 *, Alexandra D. Almeida 1, Hideaki Tanaka 2, Kunimasa Ohta 2, Shin-ichi Ohnuma 1 * 1 Department
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review
 AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review 1. What does the regulatory gene code for? 2. Is the repressor by default active/inactive? 3. What changes the repressor activity? 4. What does repressor
AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review 1. What does the regulatory gene code for? 2. Is the repressor by default active/inactive? 3. What changes the repressor activity? 4. What does repressor
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its
 Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
Outline. v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: v Animal Phylogeny
 BIOSC 041 Overview of Animal Diversity: Animal Body Plans Reference: Chapter 32 Outline v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: Body symmetry Tissues
BIOSC 041 Overview of Animal Diversity: Animal Body Plans Reference: Chapter 32 Outline v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: Body symmetry Tissues
Exam 3 ID#: July 31, 2009
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 3 ID#: July 31, 2009 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 3 ID#: July 31, 2009 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
Axis determination in flies. Sem 9.3.B.5 Animal Science
 Axis determination in flies Sem 9.3.B.5 Animal Science All embryos are in lateral view (anterior to the left). Endoderm, midgut; mesoderm; central nervous system; foregut, hindgut and pole cells in yellow.
Axis determination in flies Sem 9.3.B.5 Animal Science All embryos are in lateral view (anterior to the left). Endoderm, midgut; mesoderm; central nervous system; foregut, hindgut and pole cells in yellow.
Exam 4 ID#: July 7, 2008
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: July 7, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. RNA polymerase II is not able to transcribe RNA unless a. it is first bound to TFIIB. b. its
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: July 7, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. RNA polymerase II is not able to transcribe RNA unless a. it is first bound to TFIIB. b. its
Drosophila Somatic Anterior-Posterior Axis (A-P Axis) Formation
 Home Biol 4241 Luria-Delbruck 1943 Hershey-Chase 1952 Meselson-Stahl 1958 Garapin et al. 1978 McClintock 1953 King-Wilson 1975 Sanger et al. 1977 Rothberg et al. 2011 Jeffreys et al. 1985 Bacterial Genetics
Home Biol 4241 Luria-Delbruck 1943 Hershey-Chase 1952 Meselson-Stahl 1958 Garapin et al. 1978 McClintock 1953 King-Wilson 1975 Sanger et al. 1977 Rothberg et al. 2011 Jeffreys et al. 1985 Bacterial Genetics
Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA
 Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA Instructor: Marianne Bronner Exam Length: 6 hours plus one 30-minute break at your discretion. It should take
Bi 117 Final (60 pts) DUE by 11:00 am on March 15, 2012 Box by Beckman Institute B9 or to a TA Instructor: Marianne Bronner Exam Length: 6 hours plus one 30-minute break at your discretion. It should take
BIS &003 Answers to Assigned Problems May 23, Week /18.6 How would you distinguish between an enhancer and a promoter?
 Week 9 Study Questions from the textbook: 6 th Edition: Chapter 19-19.6, 19.7, 19.15, 19.17 OR 7 th Edition: Chapter 18-18.6 18.7, 18.15, 18.17 19.6/18.6 How would you distinguish between an enhancer and
Week 9 Study Questions from the textbook: 6 th Edition: Chapter 19-19.6, 19.7, 19.15, 19.17 OR 7 th Edition: Chapter 18-18.6 18.7, 18.15, 18.17 19.6/18.6 How would you distinguish between an enhancer and
Mesoderm induction: from caps to chips
 Mesoderm induction: from caps to chips David Kimelman Abstract Vertebrate mesoderm induction is one of the classical problems in developmental biology. Various developmental biology approaches, particularly
Mesoderm induction: from caps to chips David Kimelman Abstract Vertebrate mesoderm induction is one of the classical problems in developmental biology. Various developmental biology approaches, particularly
Exam 1 ID#: October 4, 2007
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 1 ID#: October 4, 2007 Multiple choice (one point each) (1-25) 1. The process of cells forming tissues and organs is called a. morphogenesis. b. differentiation. c. allometry.
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 1 ID#: October 4, 2007 Multiple choice (one point each) (1-25) 1. The process of cells forming tissues and organs is called a. morphogenesis. b. differentiation. c. allometry.
Animal Origins and Evolution
 Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
7.013 Problem Set
 7.013 Problem Set 5-2013 Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spot a huge grizzly bear. This emergency situation triggers a fight or flight response through a signaling pathway as shown below.
7.013 Problem Set 5-2013 Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spot a huge grizzly bear. This emergency situation triggers a fight or flight response through a signaling pathway as shown below.
Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11
 Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Mesoderm Development
 Quiz rules: Spread out across available tables No phones, text books, or (lecture) notes on your desks No consultation with your colleagues No websites open other than the Quiz page No screen snap shots
Quiz rules: Spread out across available tables No phones, text books, or (lecture) notes on your desks No consultation with your colleagues No websites open other than the Quiz page No screen snap shots
Cell Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
b. The maximum binding will decrease.
 Cell Signaling Receptors are a. proteins that change conformation upon interaction with a stimulus b. genes that change expression in response to a stimulus c. phosphorylation cascades that control cellular
Cell Signaling Receptors are a. proteins that change conformation upon interaction with a stimulus b. genes that change expression in response to a stimulus c. phosphorylation cascades that control cellular
Principles of Experimental Embryology
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology September 19, 2006 Major Research Questions How do forces outside the embryo affect its development? (Environmental Developmental
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology September 19, 2006 Major Research Questions How do forces outside the embryo affect its development? (Environmental Developmental
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology. Cell Cell Communication in Development. Developmental Activities Coordinated in this Way
 Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Bio 127 Section I Introduction to Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development Gilbert 9e Chapter 3 It has to be EXTREMELY well coordinated for the single celled fertilized ovum to develop
Conclusions. The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights
 C h a p t e r 5 Conclusions 5.1 Summary The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights into the cellular processes of assembly, and aggregation of neural crest and
C h a p t e r 5 Conclusions 5.1 Summary The experimental studies presented in this thesis provide the first molecular insights into the cellular processes of assembly, and aggregation of neural crest and
MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 14, 2012
 Write your name and student ID# on EVERY PAGE of your exam MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 14, 2012 Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 BONUS / 28 pts / 27 pts / 25 pts / 20 pts / 1 pt TOTAL / 100 pts
Write your name and student ID# on EVERY PAGE of your exam MCB 141 Midterm I Feb. 14, 2012 Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 BONUS / 28 pts / 27 pts / 25 pts / 20 pts / 1 pt TOTAL / 100 pts
1. General Features of Animals
 Chapter 32: An Overview of Animal Diversity 1. General Features of Animals 2. The History of Animals 1. General Features of Animals General Characteristics of Animals animals are multicellular eukaryotic
Chapter 32: An Overview of Animal Diversity 1. General Features of Animals 2. The History of Animals 1. General Features of Animals General Characteristics of Animals animals are multicellular eukaryotic
Introduction to Animal Kingdom. Invertebrates and Vertebrates
 Introduction to Animal Kingdom Invertebrates and Vertebrates Introduction To Animals Vertebrate animal with a backbone. Invertebrate animal without a backbone; includes more than 95% of all animal species
Introduction to Animal Kingdom Invertebrates and Vertebrates Introduction To Animals Vertebrate animal with a backbone. Invertebrate animal without a backbone; includes more than 95% of all animal species
Skeletal Development in Human
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Skeletal Development in Human Skeletal development in human - Long version I. Introduction I.1 Developmental genes in Drosophila I.2 Skeletal
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Skeletal Development in Human Skeletal development in human - Long version I. Introduction I.1 Developmental genes in Drosophila I.2 Skeletal
The Radiata-Bilateria split. Second branching in the evolutionary tree
 The Radiata-Bilateria split Second branching in the evolutionary tree Two very important characteristics are used to distinguish between the second bifurcation of metazoans Body symmetry Germinal layers
The Radiata-Bilateria split Second branching in the evolutionary tree Two very important characteristics are used to distinguish between the second bifurcation of metazoans Body symmetry Germinal layers
Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
 KAP Biology Dept Kenyon College Differential gene expression and development Mechanisms of cellular determination Induction Pattern formation Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
KAP Biology Dept Kenyon College Differential gene expression and development Mechanisms of cellular determination Induction Pattern formation Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
Organizer and axes formation as a self-organizing process
 Int. J. Dev. Biol. 45: 177-188 (2001) Organizer and axes formation as a self-organizing process 177 Organizer and axes formation as a self-organizing process HANS MEINHARDT Max-Planck-Institut für Entwicklungsbiologie,
Int. J. Dev. Biol. 45: 177-188 (2001) Organizer and axes formation as a self-organizing process 177 Organizer and axes formation as a self-organizing process HANS MEINHARDT Max-Planck-Institut für Entwicklungsbiologie,
Langman's Medical Embryology
 Langman's Medical Embryology Developmental Biology Differentiation Morphogenesis) Epigenetic landscape (Waddington) ips Langman's Medical Embryology Morphogen gradient FGF8 in mouse limb bud Gilbert "Developmental
Langman's Medical Embryology Developmental Biology Differentiation Morphogenesis) Epigenetic landscape (Waddington) ips Langman's Medical Embryology Morphogen gradient FGF8 in mouse limb bud Gilbert "Developmental
Bio Section III Organogenesis. The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification. Student Learning Objectives. Student Learning Objectives
 Bio 127 - Section III Organogenesis The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification Gilbert 9e Chapter 10 Student Learning Objectives 1. You should understand that the neural crest is an evolutionary advancement
Bio 127 - Section III Organogenesis The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification Gilbert 9e Chapter 10 Student Learning Objectives 1. You should understand that the neural crest is an evolutionary advancement
Determination of Spatiotemporal Interactions Regulating Head/Trunk Axial Pattern in the Chick Embryo
 Eukaryon, Vol. 2, January 2006, Lake Forest ollege Senior Thesis Determination of Spatiotemporal Interactions Regulating Head/Trunk Axial Pattern in the hick Embryo David Mann * Department of Biology,
Eukaryon, Vol. 2, January 2006, Lake Forest ollege Senior Thesis Determination of Spatiotemporal Interactions Regulating Head/Trunk Axial Pattern in the hick Embryo David Mann * Department of Biology,
Introduction to Animal Diversity. Chapter 23.1, 23.2 and additional
 Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 23.1, 23.2 and additional 1 Think of an Animal... Does your choice have hair or fur? Does it have a skeleton? Over a million species of animals described 95% have
Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 23.1, 23.2 and additional 1 Think of an Animal... Does your choice have hair or fur? Does it have a skeleton? Over a million species of animals described 95% have
Evolution of Transcription factor function: Homeotic (Hox) proteins
 Evolution of Transcription factor function: Homeotic (Hox) proteins Hox proteins regulate morphology in cellular zones on the anterior-posterior axis of embryos via the activation/repression of unknown
Evolution of Transcription factor function: Homeotic (Hox) proteins Hox proteins regulate morphology in cellular zones on the anterior-posterior axis of embryos via the activation/repression of unknown
BONE MORPHOGENETIC PROTEINS AS REGULATORS OF NEURAL TUBE DEVELOPMENT
 Papers on Anthropology XX, 2011, pp. 314 326 BONE MORPHOGENETIC PROTEINS AS REGULATORS OF NEURAL TUBE DEVELOPMENT Aimar Namm 1,2, Andres Arend 1, Marina Aunapuu 1,2 1 Department of Anatomy, University
Papers on Anthropology XX, 2011, pp. 314 326 BONE MORPHOGENETIC PROTEINS AS REGULATORS OF NEURAL TUBE DEVELOPMENT Aimar Namm 1,2, Andres Arend 1, Marina Aunapuu 1,2 1 Department of Anatomy, University
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
Molecular Genetics of Axis Formation in Zebrafish
 Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005. 39:561 613 First published online as a Review in Advance on August 9, 2005 The Annual Review of Genetics is online at genet.annualreviews.org doi: 10.1146/ annurev.genet.37.110801.143752
Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005. 39:561 613 First published online as a Review in Advance on August 9, 2005 The Annual Review of Genetics is online at genet.annualreviews.org doi: 10.1146/ annurev.genet.37.110801.143752
Section 4 Professor Donald McFarlane
 Characteristics Section 4 Professor Donald McFarlane Lecture 11 Animals: Origins and Bauplans Multicellular heterotroph Cells lack cell walls Most have nerves, muscles, capacity to move at some point in
Characteristics Section 4 Professor Donald McFarlane Lecture 11 Animals: Origins and Bauplans Multicellular heterotroph Cells lack cell walls Most have nerves, muscles, capacity to move at some point in
Coordination of Cell Differentiation and Migration in Mathematical Models of Caudal Embryonic Axis Extension
 Coordination of Cell Differentiation and Migration in Mathematical Models of Caudal Embryonic Axis Extension Nigel C. Harrison 1, Ruth Diez del Corral 2 *, Bakhtier Vasiev 1 * 1 Department of Mathematical
Coordination of Cell Differentiation and Migration in Mathematical Models of Caudal Embryonic Axis Extension Nigel C. Harrison 1, Ruth Diez del Corral 2 *, Bakhtier Vasiev 1 * 1 Department of Mathematical
