Part III Biological Physics course
|
|
|
- Helen Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Part III Biological Physics course Lecturers: Prof. Pietro Cicuta pc245 Dr Eileen Nugent en270 1
2 Pre-requisites: Part II Thermal Statistical Part II Soft Condensed Matter [or self study] Reading list: Phillips, Kondev, Theriot, Garcia Physical Biology of the Cell - 2 nd ed., Garland 2013 Phil Nelson Physical Models of Living Systems - Freeman 2015 Biological Physics - : Energy, Information, Life - Freeman 2007 Uri Alon An Introduction to Systems Biology - Chapman and Hall 2007 Bruce Alberts et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell- Garland (many editions, updated almost yearly) Kim Sneppen and Giovanni Zocchi Physics in Molecular Biology - CUP 2005 Kim Sneppen Models of Life - CUP 2014 Warning, this is a biology book 2
3 Useful Information: Website, linked from TiS: Send comments & errors to pc245 or en270. A list of known errors is maintained on the website. Supervisions available for students in Part III and MASt (3 supervisions, groups of 15-20, 2 times will be communicated). Dr Diana Fusco df390 for first sessions 3
4 Structure of the course: 24 lectures, in 7 modules: A - context/overview/intro/basics, networks B - stat mech and non-equilibrium machines C - dynamics in the cell D - elements of neuro-physics E - pattern formation in biology F - protein production and regulation of gene expression G - dynamical systems, switches and oscillations 4 lectures will be given by prominent biologists/biophysicists: material closer to active research (details not examinable) 4
5 Lengthscales e.g. photosynthesis Our course Biological systems have a hierarchical organization across many lengthscales Lengthscale Timescale hence emergence. Non-equilibrium (but considering separation of timescales, equilibrium often valid) Self assembly and self replication We focus in this course on scales where thermal noise and small number noise are at play - classical statistical mechanics. 5 e.g. ecological systems and evolution
6 Why is it a good time to deploy&develop physics here? e.g. photosynthesis Fantastic detailed knowledge of the molecules that make up living systems from decades of structural biology. Precise genetic code. The broadly correct understanding of mechanisms of action of many of these constituents. Quantitative datasets resolved on relevant lengths & times. Unique power of physics (stat mech, dynamical systems, soft matter) in linking up scales models that have the correct mechanism, and that represent an understanding. Our course 6 Physics is required. e.g. ecological systems and evolution
7 Physics is required. As in other fields (condensed matter, etc), what is our approach? Understand context - here, cell biology context. Make order of magnitude estimates. Become familiar with tools for model building. Critical analysis to determine limitations, and suggest refinement to models. 7
8 Crick s legacy - Polymer Languages Structure Space of Genotypes Space of Phenotypes Hierarchy of scales: both Information and Structure. 8
9 Gene regulation: the central dogma Crick
10 Nucleotides and DNA Adenine Thymine Guanine Cytosine Replaced by Uracil in RNA 10
11 The genetic code 11
12 Many ways to see a DNA double helix 12
13 Many ways to see a protein 13
14 Many ways to see a lipid membrane 14
15 To cells: Many ways to see a bacterium 15
16 What is right level of description? 16
17 What do we want to avoid? Example of population growth data f(t) = a1/[a2 (t/1yr)] or f(t) = a1 exp (a2 t) a1=10000, a2=2050 works very well Physical Models need to reflect a mechanism, and can point us to further key insights. 17
18 A success (but still ongoing): The Lac repressor- Stat mech and polymer physics meet biology of gene regulation 18
19 19
20 20
21 An example of important question that can be addressed in very different ways: How do cells regulate division to have a mean size? E.coli bacteria Imaged in fluorescence microscopy. In principle, control could be through sizer, timer or some combination. 21
22 Data on regulation of division From S.Jun, S.Taheri-Araghi, Trends in Microbiology 4, 23 (2015) 22
23 How do cells regulate division to have a mean size? One can also try to establish the general control theory, looking at the data. One can search for the molecular mechanism, but certainly more complex than the gene! Not so simple to come up with sizer mechanisms: plausible scenario put forward in yeast might involve sensing size through the balance between a species that has constant concentration in the cell volume as monomers, an adsorption equilibrium with the membrane (hence # prop to area), and a polymerisation sink. Concentration at the sink is then a membrane area sensor, triggering division. 23
24 Recap: - Spirit and remit of this course. - How physics contributes to this area of science. - A first overview of cell machinery. - Confidence in developing models and determining the right level of description. - 2 more intro lectures to come. 24
BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS MAJOR OPTION QUESTION SHEET 1 - will be covered in 1st of 3 supervisions
 1 BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS MAJOR OPTION 2017 - QUESTION SHEET 1 - will be covered in 1st of 3 supervisions MODULE A Lecture 1: Intro and concepts A1 Intro (a) Roughly 2-3 kg of bacteria are in your large intestine.
1 BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS MAJOR OPTION 2017 - QUESTION SHEET 1 - will be covered in 1st of 3 supervisions MODULE A Lecture 1: Intro and concepts A1 Intro (a) Roughly 2-3 kg of bacteria are in your large intestine.
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems
 Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Outline. Introduction, program and reference textbooks A few definition and facts Modeling of biological systems:
 Introduction 1 Outline Introduction, program and reference textbooks A few definition and facts Modeling of biological systems: Models in space and time: from molecules to the cell Quantitative models
Introduction 1 Outline Introduction, program and reference textbooks A few definition and facts Modeling of biological systems: Models in space and time: from molecules to the cell Quantitative models
2. What was the Avery-MacLeod-McCarty experiment and why was it significant? 3. What was the Hershey-Chase experiment and why was it significant?
 Name Date Period AP Exam Review Part 6: Molecular Genetics I. DNA and RNA Basics A. History of finding out what DNA really is 1. What was Griffith s experiment and why was it significant? 1 2. What was
Name Date Period AP Exam Review Part 6: Molecular Genetics I. DNA and RNA Basics A. History of finding out what DNA really is 1. What was Griffith s experiment and why was it significant? 1 2. What was
BCH 400/600 Introductory Biochemistry
 BCH 400/600 Introductory Biochemistry Instructor: David Shintani Office: 311C Fleischmann Ag. Lab: 308 Fleischmann Ag. E-mail: shintani@unr.edu Phone: (775) 784-4631 Before BCH 400 BCH 400 is heavy on
BCH 400/600 Introductory Biochemistry Instructor: David Shintani Office: 311C Fleischmann Ag. Lab: 308 Fleischmann Ag. E-mail: shintani@unr.edu Phone: (775) 784-4631 Before BCH 400 BCH 400 is heavy on
Bi 1x Spring 2014: LacI Titration
 Bi 1x Spring 2014: LacI Titration 1 Overview In this experiment, you will measure the effect of various mutated LacI repressor ribosome binding sites in an E. coli cell by measuring the expression of a
Bi 1x Spring 2014: LacI Titration 1 Overview In this experiment, you will measure the effect of various mutated LacI repressor ribosome binding sites in an E. coli cell by measuring the expression of a
Flow of Genetic Information
 presents Flow of Genetic Information A Montagud E Navarro P Fernández de Córdoba JF Urchueguía Elements Nucleic acid DNA RNA building block structure & organization genome building block types Amino acid
presents Flow of Genetic Information A Montagud E Navarro P Fernández de Córdoba JF Urchueguía Elements Nucleic acid DNA RNA building block structure & organization genome building block types Amino acid
Unit 5- Concept 1 THE DNA DISCOVERY
 Unit 5- Concept 1 THE DNA DISCOVERY Inheritance has always puzzled people No one really knew how it worked Mendel wasn t known till the late 1800 s He didn t even know what chromosomes were! DNA was discovered
Unit 5- Concept 1 THE DNA DISCOVERY Inheritance has always puzzled people No one really knew how it worked Mendel wasn t known till the late 1800 s He didn t even know what chromosomes were! DNA was discovered
2015 FALL FINAL REVIEW
 2015 FALL FINAL REVIEW Biomolecules & Enzymes Illustrate table and fill in parts missing 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
2015 FALL FINAL REVIEW Biomolecules & Enzymes Illustrate table and fill in parts missing 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control
 BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control Lecture 24 Unregulated Gene Expression Model Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 The genetic material inside a cell, encoded in its DNA, governs the response of a cell to various
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control Lecture 24 Unregulated Gene Expression Model Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 The genetic material inside a cell, encoded in its DNA, governs the response of a cell to various
Cells and the Stuff They re Made of. Indiana University P575 1
 Cells and the Stuff They re Made of Indiana University P575 1 Goal: Establish hierarchy of spatial and temporal scales, and governing processes at each scale of cellular function: o Where does emergent
Cells and the Stuff They re Made of Indiana University P575 1 Goal: Establish hierarchy of spatial and temporal scales, and governing processes at each scale of cellular function: o Where does emergent
Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide
 Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Information: Exam has 100 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencils and a four-function calculator on the day of the test. Review ALL vocabulary,
Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Information: Exam has 100 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencils and a four-function calculator on the day of the test. Review ALL vocabulary,
Define: Alleles. Define: Chromosome. In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways.
 Alleles Chromosome In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways. How do the bases A, C, G, T, and U match up in DNA? How about RNA? Summarize the cell process called protein synthesis!
Alleles Chromosome In DNA and RNA, molecules called bases pair up in certain ways. How do the bases A, C, G, T, and U match up in DNA? How about RNA? Summarize the cell process called protein synthesis!
Human Biology. The Chemistry of Living Things. Concepts and Current Issues. All Matter Consists of Elements Made of Atoms
 2 The Chemistry of Living Things PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation Robert J. Sullivan, Marist College Michael D. Johnson Human Biology Concepts and Current Issues THIRD EDITION Copyright 2006 Pearson
2 The Chemistry of Living Things PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation Robert J. Sullivan, Marist College Michael D. Johnson Human Biology Concepts and Current Issues THIRD EDITION Copyright 2006 Pearson
Lesson Overview The Structure of DNA
 12.2 THINK ABOUT IT The DNA molecule must somehow specify how to assemble proteins, which are needed to regulate the various functions of each cell. What kind of structure could serve this purpose without
12.2 THINK ABOUT IT The DNA molecule must somehow specify how to assemble proteins, which are needed to regulate the various functions of each cell. What kind of structure could serve this purpose without
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014
 Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) Biomolecules & Enzymes
 Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Videos. Bozeman, transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Crashcourse: Transcription and Translation - https://youtu.
 Translation Translation Videos Bozeman, transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Crashcourse: Transcription and Translation - https://youtu.be/itsb2sqr-r0 Translation Translation The
Translation Translation Videos Bozeman, transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Crashcourse: Transcription and Translation - https://youtu.be/itsb2sqr-r0 Translation Translation The
Chemistry Basics. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass Energy the ability to do work. Chemical Electrical Mechanical Radiant. Slide 2.
 Chemistry Basics Matter anything that occupies space and has mass Energy the ability to do work Chemical Electrical Mechanical Radiant Slide 2.1 Composition of Matter Elements Fundamental units of matter
Chemistry Basics Matter anything that occupies space and has mass Energy the ability to do work Chemical Electrical Mechanical Radiant Slide 2.1 Composition of Matter Elements Fundamental units of matter
Chapters 12&13 Notes: DNA, RNA & Protein Synthesis
 Chapters 12&13 Notes: DNA, RNA & Protein Synthesis Name Period Words to Know: nucleotides, DNA, complementary base pairing, replication, genes, proteins, mrna, rrna, trna, transcription, translation, codon,
Chapters 12&13 Notes: DNA, RNA & Protein Synthesis Name Period Words to Know: nucleotides, DNA, complementary base pairing, replication, genes, proteins, mrna, rrna, trna, transcription, translation, codon,
Biology 2018 Final Review. Miller and Levine
 Biology 2018 Final Review Miller and Levine bones blood cells elements All living things are made up of. cells If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is a(n). eukaryote prokaryote plant
Biology 2018 Final Review Miller and Levine bones blood cells elements All living things are made up of. cells If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is a(n). eukaryote prokaryote plant
F. Piazza Center for Molecular Biophysics and University of Orléans, France. Selected topic in Physical Biology. Lecture 1
 Zhou Pei-Yuan Centre for Applied Mathematics, Tsinghua University November 2013 F. Piazza Center for Molecular Biophysics and University of Orléans, France Selected topic in Physical Biology Lecture 1
Zhou Pei-Yuan Centre for Applied Mathematics, Tsinghua University November 2013 F. Piazza Center for Molecular Biophysics and University of Orléans, France Selected topic in Physical Biology Lecture 1
Map of AP-Aligned Bio-Rad Kits with Learning Objectives
 Map of AP-Aligned Bio-Rad Kits with Learning Objectives Cover more than one AP Biology Big Idea with these AP-aligned Bio-Rad kits. Big Idea 1 Big Idea 2 Big Idea 3 Big Idea 4 ThINQ! pglo Transformation
Map of AP-Aligned Bio-Rad Kits with Learning Objectives Cover more than one AP Biology Big Idea with these AP-aligned Bio-Rad kits. Big Idea 1 Big Idea 2 Big Idea 3 Big Idea 4 ThINQ! pglo Transformation
Lesson Overview. Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis 13.2
 13.2 The Genetic Code The first step in decoding genetic messages is to transcribe a nucleotide base sequence from DNA to mrna. This transcribed information contains a code for making proteins. The Genetic
13.2 The Genetic Code The first step in decoding genetic messages is to transcribe a nucleotide base sequence from DNA to mrna. This transcribed information contains a code for making proteins. The Genetic
Bio 101 General Biology 1
 Revised: Fall 2016 Bio 101 General Biology 1 COURSE OUTLINE Prerequisites: Prerequisite: Successful completion of MTE 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, and a placement recommendation for ENG 111, co-enrollment in ENF
Revised: Fall 2016 Bio 101 General Biology 1 COURSE OUTLINE Prerequisites: Prerequisite: Successful completion of MTE 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, and a placement recommendation for ENG 111, co-enrollment in ENF
Collaborators. Simon Levin Princeton University. James Elser Arizona State University
 Collaborators Simon Levin Princeton University James Elser Arizona State University Patterns in molecules and oceans: linking cellular machinery to global N:P ratios Irakli Loladze Department of Mathematics
Collaborators Simon Levin Princeton University James Elser Arizona State University Patterns in molecules and oceans: linking cellular machinery to global N:P ratios Irakli Loladze Department of Mathematics
Algorithms in Computational Biology (236522) spring 2008 Lecture #1
 Algorithms in Computational Biology (236522) spring 2008 Lecture #1 Lecturer: Shlomo Moran, Taub 639, tel 4363 Office hours: 15:30-16:30/by appointment TA: Ilan Gronau, Taub 700, tel 4894 Office hours:??
Algorithms in Computational Biology (236522) spring 2008 Lecture #1 Lecturer: Shlomo Moran, Taub 639, tel 4363 Office hours: 15:30-16:30/by appointment TA: Ilan Gronau, Taub 700, tel 4894 Office hours:??
The biomolecules of terrestrial life
 Functional groups in biomolecules Groups of atoms that are responsible for the chemical properties of biomolecules The biomolecules of terrestrial life Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo 1
Functional groups in biomolecules Groups of atoms that are responsible for the chemical properties of biomolecules The biomolecules of terrestrial life Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo 1
BME Engineering Molecular Cell Biology. Structure and Dynamics of Cellular Molecules. Basics of Cell Biology Literature Reading
 BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 05: Structure and Dynamics of Cellular Molecules Basics of Cell Biology Literature Reading BME42-620 Lecture 05, September 13, 2011 1 Outline Review:
BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 05: Structure and Dynamics of Cellular Molecules Basics of Cell Biology Literature Reading BME42-620 Lecture 05, September 13, 2011 1 Outline Review:
Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis)
 Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis) DNA Structure o Discovered by Watson and Crick o Double-stranded o Shape is a double helix (twisted ladder) o Made of chains of nucleotides: o Has four types
Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis) DNA Structure o Discovered by Watson and Crick o Double-stranded o Shape is a double helix (twisted ladder) o Made of chains of nucleotides: o Has four types
A A A A B B1
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR EACH BIG IDEA WITH ASSOCIATED SCIENCE PRACTICES AND ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Learning Objectives will be the target for AP Biology exam questions Learning Objectives Sci Prac Es Knowl
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR EACH BIG IDEA WITH ASSOCIATED SCIENCE PRACTICES AND ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Learning Objectives will be the target for AP Biology exam questions Learning Objectives Sci Prac Es Knowl
Sugars, such as glucose or fructose are the basic building blocks of more complex carbohydrates. Which of the following
 Name: Score: / Quiz 2 on Lectures 3 &4 Part 1 Sugars, such as glucose or fructose are the basic building blocks of more complex carbohydrates. Which of the following foods is not a significant source of
Name: Score: / Quiz 2 on Lectures 3 &4 Part 1 Sugars, such as glucose or fructose are the basic building blocks of more complex carbohydrates. Which of the following foods is not a significant source of
2012 Univ Aguilera Lecture. Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology
 2012 Univ. 1301 Aguilera Lecture Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the
2012 Univ. 1301 Aguilera Lecture Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the
3.B.1 Gene Regulation. Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization.
 3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
Basic Synthetic Biology circuits
 Basic Synthetic Biology circuits Note: these practices were obtained from the Computer Modelling Practicals lecture by Vincent Rouilly and Geoff Baldwin at Imperial College s course of Introduction to
Basic Synthetic Biology circuits Note: these practices were obtained from the Computer Modelling Practicals lecture by Vincent Rouilly and Geoff Baldwin at Imperial College s course of Introduction to
5. As compared to the human sperm cell, the human egg cell contains more... a) cytoplasm c) centrosomes b) mitochondria d) chromosomes
 BIOLOGY - 3201. Quiz: Cell Reproduction. NAME : Multiple Choice. (1% each) 1. Which of the following is NOT true of mitotic cell division? a) It involves nuclear division. b) It involves division of the
BIOLOGY - 3201. Quiz: Cell Reproduction. NAME : Multiple Choice. (1% each) 1. Which of the following is NOT true of mitotic cell division? a) It involves nuclear division. b) It involves division of the
Reading Assignments. A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides. Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype
 Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis
 Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis IN: How is transcription like making a jello mold? (be specific) What process does this diagram represent? A. Mutation B. Replication C.Transcription D.Translation
Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis IN: How is transcription like making a jello mold? (be specific) What process does this diagram represent? A. Mutation B. Replication C.Transcription D.Translation
Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains a fool forever.
 CSE 527 Computational Biology http://www.cs.washington.edu/527 Lecture 1: Overview & Bio Review Autumn 2004 Larry Ruzzo Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains
CSE 527 Computational Biology http://www.cs.washington.edu/527 Lecture 1: Overview & Bio Review Autumn 2004 Larry Ruzzo Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains
Organisms: We will need to have some examples in mind for our spherical cows.
 Lecture 4: Structure and Composition (Sept. 15) 4.1 Reading Assignment for Lectures 3-4: Phillips, Kondev, Theriot (PKT), Chapter 2 Problem Set 1 (due Sept. 24) now posted on the website. Cellular materials:
Lecture 4: Structure and Composition (Sept. 15) 4.1 Reading Assignment for Lectures 3-4: Phillips, Kondev, Theriot (PKT), Chapter 2 Problem Set 1 (due Sept. 24) now posted on the website. Cellular materials:
THINGS I NEED TO KNOW:
 THINGS I NEED TO KNOW: 1. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus. In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Both types of cells have ribosomes. Some
THINGS I NEED TO KNOW: 1. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus. In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Both types of cells have ribosomes. Some
CHAPTER 1 Life: Biological Principles and the Science of Zoology
 CHAPTER 1 Life: Biological Principles and the Science of Zoology 1-1 Zoology: The Uses of Principles The scientific study of animal life Does Life Have Defining Properties? No simple definition The history
CHAPTER 1 Life: Biological Principles and the Science of Zoology 1-1 Zoology: The Uses of Principles The scientific study of animal life Does Life Have Defining Properties? No simple definition The history
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 1
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 1 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 9, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 1 January 9, 2013 1 / 27 Outline Course in general Description Grading
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 1 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 9, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 1 January 9, 2013 1 / 27 Outline Course in general Description Grading
Virginia Western Community College BIO 101 General Biology I
 BIO 101 General Biology I Prerequisites Successful completion of MTE 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5; and a placement recommendation for ENG 111, co-enrollment in ENF 3/ENG 111, or successful completion of all developmental
BIO 101 General Biology I Prerequisites Successful completion of MTE 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5; and a placement recommendation for ENG 111, co-enrollment in ENF 3/ENG 111, or successful completion of all developmental
Bi 8 Lecture 11. Quantitative aspects of transcription factor binding and gene regulatory circuit design. Ellen Rothenberg 9 February 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 11 Quantitative aspects of transcription factor binding and gene regulatory circuit design Ellen Rothenberg 9 February 2016 Major take-home messages from λ phage system that apply to many
Bi 8 Lecture 11 Quantitative aspects of transcription factor binding and gene regulatory circuit design Ellen Rothenberg 9 February 2016 Major take-home messages from λ phage system that apply to many
Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology
 Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the molecular basis of disease? What
Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the molecular basis of disease? What
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 6
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 6 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 23, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 6 January 23, 2013 1 / 48 Outline Questions and answers Nucleic acids
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 6 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 23, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 6 January 23, 2013 1 / 48 Outline Questions and answers Nucleic acids
Formative/Summative Assessments (Tests, Quizzes, reflective writing, Journals, Presentations)
 Biology Curriculum Map 2017-18 2 Weeks- Introduction to Biology: Scientific method, lab safety, organizing and analyzing data, and psuedoscience. This unit establishes the fundamental nature of scientific
Biology Curriculum Map 2017-18 2 Weeks- Introduction to Biology: Scientific method, lab safety, organizing and analyzing data, and psuedoscience. This unit establishes the fundamental nature of scientific
Full file at https://fratstock.eu
 VanMeter: Microbiology for the Healthcare Professional Chapter 02: Chemistry of Life Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The atomic number equals the number of a. Protons b. Neutrons c. Electrons d. Protons and
VanMeter: Microbiology for the Healthcare Professional Chapter 02: Chemistry of Life Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The atomic number equals the number of a. Protons b. Neutrons c. Electrons d. Protons and
Enduring understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution.
 The AP Biology course is designed to enable you to develop advanced inquiry and reasoning skills, such as designing a plan for collecting data, analyzing data, applying mathematical routines, and connecting
The AP Biology course is designed to enable you to develop advanced inquiry and reasoning skills, such as designing a plan for collecting data, analyzing data, applying mathematical routines, and connecting
Introduction to molecular biology. Mitesh Shrestha
 Introduction to molecular biology Mitesh Shrestha Molecular biology: definition Molecular biology is the study of molecular underpinnings of the process of replication, transcription and translation of
Introduction to molecular biology Mitesh Shrestha Molecular biology: definition Molecular biology is the study of molecular underpinnings of the process of replication, transcription and translation of
7.32/7.81J/8.591J. Rm Rm (under construction) Alexander van Oudenaarden Jialing Li. Bernardo Pando. Rm.
 Introducing... 7.32/7.81J/8.591J Systems Biology modeling biological networks Lectures: Recitations: ti TR 1:00-2:30 PM W 4:00-5:00 PM Rm. 6-120 Rm. 26-204 (under construction) Alexander van Oudenaarden
Introducing... 7.32/7.81J/8.591J Systems Biology modeling biological networks Lectures: Recitations: ti TR 1:00-2:30 PM W 4:00-5:00 PM Rm. 6-120 Rm. 26-204 (under construction) Alexander van Oudenaarden
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression
 Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
CORE MOLIT ACTIVITIES at a glance
 CORE MOLIT ACTIVITIES at a glance 1. Amplification of Biochemical Signals: The ELISA Test http://molit.concord.org/database/activities/248.html The shape of molecules affects the way they function. A test
CORE MOLIT ACTIVITIES at a glance 1. Amplification of Biochemical Signals: The ELISA Test http://molit.concord.org/database/activities/248.html The shape of molecules affects the way they function. A test
Peddie Summer Day School
 Peddie Summer Day School Course Syllabus: BIOLOGY Teacher: Mr. Jeff Tuliszewski Text: Biology by Miller and Levine, Prentice Hall, 2010 edition ISBN 9780133669510 Guided Reading Workbook for Biology ISBN
Peddie Summer Day School Course Syllabus: BIOLOGY Teacher: Mr. Jeff Tuliszewski Text: Biology by Miller and Levine, Prentice Hall, 2010 edition ISBN 9780133669510 Guided Reading Workbook for Biology ISBN
Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW
 Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW 2013-2014 CP Biology Student Name: School/Teacher: Date: SPS CP Biology Midterm Review, January 2014 Page 1 Dear Biology Student,
Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW 2013-2014 CP Biology Student Name: School/Teacher: Date: SPS CP Biology Midterm Review, January 2014 Page 1 Dear Biology Student,
Chapter 1. DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d
 Chapter 1 1. Matching Questions DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d 2. Matching Questions : Unbranched polymer that, when folded into its three-dimensional shape,
Chapter 1 1. Matching Questions DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d 2. Matching Questions : Unbranched polymer that, when folded into its three-dimensional shape,
Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life.
 Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution. 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major
Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution. 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major
Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition
 Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Biology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Biology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Biology. Lessons: 15% Quizzes: 25% Projects: 30% Tests: 30% Assignment Weighting per Unit Without Projects. Lessons: 21% Quizzes: 36% Tests: 43%
 Biology This course consists of 12 units, which provide an overview of the basic concepts and natural laws of Biology. Unit 1 deals with the organization of living organisms. Unit 2 addresses the chemistry
Biology This course consists of 12 units, which provide an overview of the basic concepts and natural laws of Biology. Unit 1 deals with the organization of living organisms. Unit 2 addresses the chemistry
AP Curriculum Framework with Learning Objectives
 Big Ideas Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. AP Curriculum Framework with Learning Objectives Understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over
Big Ideas Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. AP Curriculum Framework with Learning Objectives Understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over
Teacher Instructions
 Teacher Instructions To print handouts for students Go to File print, change Print what: to handouts, change # per page if desired to enlarge slides on page Change Print range to slides and type in slide
Teacher Instructions To print handouts for students Go to File print, change Print what: to handouts, change # per page if desired to enlarge slides on page Change Print range to slides and type in slide
Lecture 5: Processes and Timescales: Rates for the fundamental processes 5.1
 Lecture 5: Processes and Timescales: Rates for the fundamental processes 5.1 Reading Assignment for Lectures 5-6: Phillips, Kondev, Theriot (PKT), Chapter 3 Life is not static. Organisms as a whole are
Lecture 5: Processes and Timescales: Rates for the fundamental processes 5.1 Reading Assignment for Lectures 5-6: Phillips, Kondev, Theriot (PKT), Chapter 3 Life is not static. Organisms as a whole are
Big Idea 1: Does the process of evolution drive the diversity and unit of life?
 AP Biology Syllabus 2016-2017 Course Overview: AP Biology is equivalent to an introductory college level biology program in order to develop student led inquiry into science. The class is designed to go
AP Biology Syllabus 2016-2017 Course Overview: AP Biology is equivalent to an introductory college level biology program in order to develop student led inquiry into science. The class is designed to go
1. Contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine.
 Protein Synthesis & Mutations RNA 1. Contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine. RNA Contains: 1. Adenine 2.
Protein Synthesis & Mutations RNA 1. Contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine. RNA Contains: 1. Adenine 2.
APh150: Physics of Biological Structure and Function
 APh150: Physics of Biological Structure and Function Winter 2003 When: To be determined Who: You and me (Rob Phillips, x 3374, phillips@aero.caltech.edu, 221 Steele) Where: 104 Watson What: See below!
APh150: Physics of Biological Structure and Function Winter 2003 When: To be determined Who: You and me (Rob Phillips, x 3374, phillips@aero.caltech.edu, 221 Steele) Where: 104 Watson What: See below!
Biology Final Review Ch pg Biology is the study of
 Biology Final Review Ch. 1 1-3 pg. 17-25 1. Biology is the study of Ch.2 2-3 pg. 45-49 2. All organic compounds contain. 3. Starch is an example of which type of organic compound? 4. What monomers make
Biology Final Review Ch. 1 1-3 pg. 17-25 1. Biology is the study of Ch.2 2-3 pg. 45-49 2. All organic compounds contain. 3. Starch is an example of which type of organic compound? 4. What monomers make
Biomolecules. Energetics in biology. Biomolecules inside the cell
 Biomolecules Energetics in biology Biomolecules inside the cell Energetics in biology The production of energy, its storage, and its use are central to the economy of the cell. Energy may be defined as
Biomolecules Energetics in biology Biomolecules inside the cell Energetics in biology The production of energy, its storage, and its use are central to the economy of the cell. Energy may be defined as
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 8 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 30 th 2013 Ahmad Ayyat Nucleic Acids: Molecules that carries information for growth and production of cells, and they are Polymers of "Nucleotides" (the monomers).01 Nucleotide
8 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 30 th 2013 Ahmad Ayyat Nucleic Acids: Molecules that carries information for growth and production of cells, and they are Polymers of "Nucleotides" (the monomers).01 Nucleotide
Unit 2: Basic Chemistry
 Unit 2: Basic Chemistry I. Matter and Energy A. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass (weight) B. Energy the ability to do work 1. Chemical 2. Electrical 3. Mechanical 4. Radiant C. Composition
Unit 2: Basic Chemistry I. Matter and Energy A. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass (weight) B. Energy the ability to do work 1. Chemical 2. Electrical 3. Mechanical 4. Radiant C. Composition
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS INTRO
 MR. POMERANTZ Page 1 of 6 Protein synthesis Intro. Use the text book to help properly answer the following questions 1. RNA differs from DNA in that RNA a. is single-stranded. c. contains the nitrogen
MR. POMERANTZ Page 1 of 6 Protein synthesis Intro. Use the text book to help properly answer the following questions 1. RNA differs from DNA in that RNA a. is single-stranded. c. contains the nitrogen
Gene Regulation and Expression
 THINK ABOUT IT Think of a library filled with how-to books. Would you ever need to use all of those books at the same time? Of course not. Now picture a tiny bacterium that contains more than 4000 genes.
THINK ABOUT IT Think of a library filled with how-to books. Would you ever need to use all of those books at the same time? Of course not. Now picture a tiny bacterium that contains more than 4000 genes.
Reductionist Paradox Are the laws of chemistry and physics sufficient for the discovery of new drugs?
 Quantitative Biology Colloquium, University of Arizona, March 1, 2011 Reductionist Paradox Are the laws of chemistry and physics sufficient for the discovery of new drugs? Gerry Maggiora, Ph.D. Adjunct
Quantitative Biology Colloquium, University of Arizona, March 1, 2011 Reductionist Paradox Are the laws of chemistry and physics sufficient for the discovery of new drugs? Gerry Maggiora, Ph.D. Adjunct
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, Gene Expression Regulation Mutations
 Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS MAJOR OPTION. ANSWERS - Question Sheet 1 MODULE A
 1 BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS MAJOR OPTION 017 ANSWERS - Question Sheet 1 MODULE A Lecture 1: Intro and concepts A1 Intro (a) Roughly -3 kg of bacteria are in your large intestine. Estimate the number of bacteria
1 BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS MAJOR OPTION 017 ANSWERS - Question Sheet 1 MODULE A Lecture 1: Intro and concepts A1 Intro (a) Roughly -3 kg of bacteria are in your large intestine. Estimate the number of bacteria
Activation of a receptor. Assembly of the complex
 Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Base pairing in DNA.
 TFY4215 Kjemisk fysikk og kvantemekanikk Våren 2007 Chemical physics Exercise 3 To be delivered by: Tuesday 08.05. Base pairing in DNA. Introduction DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid are the molecules that contain
TFY4215 Kjemisk fysikk og kvantemekanikk Våren 2007 Chemical physics Exercise 3 To be delivered by: Tuesday 08.05. Base pairing in DNA. Introduction DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid are the molecules that contain
Name: Date: Period: Biology Notes: Biochemistry Directions: Fill this out as we cover the following topics in class
 Name: Date: Period: Biology Notes: Biochemistry Directions: Fill this out as we cover the following topics in class Part I. Water Water Basics Polar: part of a molecule is slightly, while another part
Name: Date: Period: Biology Notes: Biochemistry Directions: Fill this out as we cover the following topics in class Part I. Water Water Basics Polar: part of a molecule is slightly, while another part
Scope and Sequence. Course / Grade Title: Biology
 Course / Grade Title: Biology Course / Grade Content: What will students be expected to know and do? Provide the core knowledge and skills (standards) that will be taught and assessed. Organize the essential
Course / Grade Title: Biology Course / Grade Content: What will students be expected to know and do? Provide the core knowledge and skills (standards) that will be taught and assessed. Organize the essential
Curriculum Map. Biology, Quarter 1 Big Ideas: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes (BIO1.LS1)
 1 Biology, Quarter 1 Big Ideas: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes (BIO1.LS1) Focus Standards BIO1.LS1.2 Evaluate comparative models of various cell types with a focus on organic molecules
1 Biology, Quarter 1 Big Ideas: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes (BIO1.LS1) Focus Standards BIO1.LS1.2 Evaluate comparative models of various cell types with a focus on organic molecules
BIO 181 GENERAL BIOLOGY I (MAJORS) with Lab (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Course Package
 GENERAL BIOLOGY I (MAJORS) with Lab (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Course Package COURSE INFORMATION Is this a new course or a proposed modification to an existing course? Please check the appropriate box.
GENERAL BIOLOGY I (MAJORS) with Lab (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Course Package COURSE INFORMATION Is this a new course or a proposed modification to an existing course? Please check the appropriate box.
Model Worksheet Teacher Key
 Introduction Despite the complexity of life on Earth, the most important large molecules found in all living things (biomolecules) can be classified into only four main categories: carbohydrates, lipids,
Introduction Despite the complexity of life on Earth, the most important large molecules found in all living things (biomolecules) can be classified into only four main categories: carbohydrates, lipids,
Cell Growth and Division
 Cell Growth and Division Why do cells divide* Life and reproduction require cell division You require constant cell reproduction to live Mitosis: development (a) mitotic cell division (b) mitotic cell
Cell Growth and Division Why do cells divide* Life and reproduction require cell division You require constant cell reproduction to live Mitosis: development (a) mitotic cell division (b) mitotic cell
Student Workbook BIOLOGY. for NGSS
 Student Workbook BIOLOGY for NGSS LS1.A Cell Specialization & Organization Key terms base-pairing rule cell DNA eukaryotic cell gene hierarchical structure nucleotide organelle organ system prokaryotic
Student Workbook BIOLOGY for NGSS LS1.A Cell Specialization & Organization Key terms base-pairing rule cell DNA eukaryotic cell gene hierarchical structure nucleotide organelle organ system prokaryotic
1. CHEMISTRY OF LIFE. Tutorial Outline
 Tutorial Outline North Carolina Tutorials are designed specifically for the Common Core State Standards for English language arts, the North Carolina Standard Course of Study for Math, and the North Carolina
Tutorial Outline North Carolina Tutorials are designed specifically for the Common Core State Standards for English language arts, the North Carolina Standard Course of Study for Math, and the North Carolina
Biology Scope and Sequence Student Outcomes (Objectives Skills/Verbs)
 C-4 N.12.A 1-6 N.12.B.1-4 Scientific Literacy/ Nature of (embedded throughout course) Scientific Inquiry is the process by which humans systematically examine the natural world. Scientific inquiry is a
C-4 N.12.A 1-6 N.12.B.1-4 Scientific Literacy/ Nature of (embedded throughout course) Scientific Inquiry is the process by which humans systematically examine the natural world. Scientific inquiry is a
SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT. Course Description. Instructional Strategies, Learning Practices, Activities, and Experiences.
 SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED COURSE OVERVIEW Course Title: Advanced Placement Biology Grade Level(s): 12 Units of Credit: 1.50 Classification: Elective Length of Course: 30 cycles Periods
SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED COURSE OVERVIEW Course Title: Advanced Placement Biology Grade Level(s): 12 Units of Credit: 1.50 Classification: Elective Length of Course: 30 cycles Periods
Genetic transcription and regulation
 Genetic transcription and regulation Central dogma of biology DNA codes for DNA DNA codes for RNA RNA codes for proteins not surprisingly, many points for regulation of the process https://www.youtube.com/
Genetic transcription and regulation Central dogma of biology DNA codes for DNA DNA codes for RNA RNA codes for proteins not surprisingly, many points for regulation of the process https://www.youtube.com/
Lecture 1 Modeling in Biology: an introduction
 Lecture 1 in Biology: an introduction Luca Bortolussi 1 Alberto Policriti 2 1 Dipartimento di Matematica ed Informatica Università degli studi di Trieste Via Valerio 12/a, 34100 Trieste. luca@dmi.units.it
Lecture 1 in Biology: an introduction Luca Bortolussi 1 Alberto Policriti 2 1 Dipartimento di Matematica ed Informatica Università degli studi di Trieste Via Valerio 12/a, 34100 Trieste. luca@dmi.units.it
Lecture 1: Introduction. Keywords: Mathematics as a language, Need of learning mathematics, Applications of mathematics in BIology
 NPTEL Syllabus Biomathematics - Video course COURSE OUTLINE Graphs and functions, Derivative of a function, Techniques of differentiation Differentiation and its application in Biology, Finding maxima,
NPTEL Syllabus Biomathematics - Video course COURSE OUTLINE Graphs and functions, Derivative of a function, Techniques of differentiation Differentiation and its application in Biology, Finding maxima,
GENE ACTIVITY Gene structure Transcription Transcript processing mrna transport mrna stability Translation Posttranslational modifications
 1 GENE ACTIVITY Gene structure Transcription Transcript processing mrna transport mrna stability Translation Posttranslational modifications 2 DNA Promoter Gene A Gene B Termination Signal Transcription
1 GENE ACTIVITY Gene structure Transcription Transcript processing mrna transport mrna stability Translation Posttranslational modifications 2 DNA Promoter Gene A Gene B Termination Signal Transcription
the noisy gene Biology of the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB)
 Biology of the the noisy gene Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB) day III: noisy bacteria - Regulation of noise (B. subtilis) - Intrinsic/Extrinsic
Biology of the the noisy gene Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB) day III: noisy bacteria - Regulation of noise (B. subtilis) - Intrinsic/Extrinsic
Today in Astronomy 106: the long molecules of life
 Today in Astronomy 106: the long molecules of life Wet chemistry of nucleobases Nuances of polymerization Replication or mass production of nucleic acids Transcription Codons The protein hemoglobin. From
Today in Astronomy 106: the long molecules of life Wet chemistry of nucleobases Nuances of polymerization Replication or mass production of nucleic acids Transcription Codons The protein hemoglobin. From
Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics
 Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics 1 Terms Alleles Chromosome Co dominance Crossover Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA Dominant Genetic code Genome Genotype Heredity Heritability Heritability estimate Heterozygous
Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics 1 Terms Alleles Chromosome Co dominance Crossover Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA Dominant Genetic code Genome Genotype Heredity Heritability Heritability estimate Heterozygous
Directed Reading B continued
 Directed Reading B continued 26. What is one example of a mutation that produces a harmful trait? 27. What kinds of traits are produced by most mutations? 28. What happens to a gene if a mutation occurs
Directed Reading B continued 26. What is one example of a mutation that produces a harmful trait? 27. What kinds of traits are produced by most mutations? 28. What happens to a gene if a mutation occurs
Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes. From Alberts et al
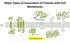 Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes From Alberts et al Proteins Are Polymers of Amino Acids Peptide Bond Formation Amino Acid central carbon atom to which are attached amino group
Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes From Alberts et al Proteins Are Polymers of Amino Acids Peptide Bond Formation Amino Acid central carbon atom to which are attached amino group
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record BIO 101
 Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record BIO 101 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog BIO 101 Biological Principles 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record BIO 101 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog BIO 101 Biological Principles 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Biological Sciences Department Manila*Malolos*Makati SYLLABUS
 CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Biological Sciences Department Manila*Malolos*Makati SYLLABUS PRBS 131 BIOSCI131 CELL BIOLOGY 3 units 3 hours lec Course Number Course Title Descriptive Title Credit Unit(s) Hour(s)/Week
CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Biological Sciences Department Manila*Malolos*Makati SYLLABUS PRBS 131 BIOSCI131 CELL BIOLOGY 3 units 3 hours lec Course Number Course Title Descriptive Title Credit Unit(s) Hour(s)/Week
Written Exam 15 December Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no
 Technical University of Denmark Written Exam 15 December 2008 Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no. 27041 Aids allowed: Open book exam Provide your answers and calculations on separate
Technical University of Denmark Written Exam 15 December 2008 Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no. 27041 Aids allowed: Open book exam Provide your answers and calculations on separate
UNIT 5. Protein Synthesis 11/22/16
 UNIT 5 Protein Synthesis IV. Transcription (8.4) A. RNA carries DNA s instruction 1. Francis Crick defined the central dogma of molecular biology a. Replication copies DNA b. Transcription converts DNA
UNIT 5 Protein Synthesis IV. Transcription (8.4) A. RNA carries DNA s instruction 1. Francis Crick defined the central dogma of molecular biology a. Replication copies DNA b. Transcription converts DNA
