Kinematics in 2-Dimensions. Projectile Motion
|
|
|
- Sophia Roberts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had a ver practcal knowledge of projectle moton. The ma not have understood the exact trajector that a projectle would take, but b practce the could place a projectle on a target consstentl from a dstance of well over 00 ards. Durng a long sege of a castle, t was not uncommon to hurl bodes of anmals (and es, captves) back nto the beseged castle s water suppl (an earl form of bologcal warfare). Smlarl, a modern da hunter does not need to know the actual path that a bullet takes to a target n order to ht the target. A sharpshooter, however, does know the path and can make adjustments n the amng n order to ht a target at man dfferent ranges. In ths lab, ou wll become a sharpshooter of sorts. You wll use the equatons of moton to predct the path of a projectle and ht a target. Neglectng frctonal forces, such as ar resstance, an object projected from a launcher undergoes a moton that s the smple vector combnaton of unform veloct n the horzontal drecton and unform acceleraton n the vertcal drecton. For a projectle launched wth a speed, v, at an angle θ wth respect to the postve x axs, t can be shown that the trajector caused b such a combnaton predcts a parabolc shape. The followng knematc equatons descrbe ths moton: 008 Penn State Unverst Phscs 11: Lab Knematcs n -Dmensons
2 Horzontal Moton: Vertcal Moton: x ( t ) = x + v x t ( t) = + v t a t Eqn. 1 1 Eqn. + v ( t) = x v x v ( t ) = v + a t Eqn. 3 v ( t) ( ( t ) = v + a ) Eqn. 4 where v and v x are the ntal vertcal and horzontal components of the veloct respectvel. Notce that Equatons 1 and have a common varable, t. Equaton 1 predcts the x coordnate n terms of the parameter t, Equaton predcts the coordnate n terms of the parameter, t. B combnng these two equatons, the dependenc upon the parameter, t, can be elmnated. Smpl solvng Equaton 1 for t and substtutng t nto Equaton results n the followng: ( ) 1 x = + + v v x a x v x x Where: x = x( t) x whch smplfes to: v a ( x) = + x x v + x ( v ) x ( ) Furthermore, the components of the veloct can be wrtten n terms of the orgnal launch veloct as: v = v cosθ v = v snθ x Eqn. 5 These components, when combned wth Equaton 5 eld an equaton for (x) determned completel b v and Θ (the ntal launch speed and angle): a ( x) = + tanθ x + x ( v cosθ ) Eqn. 6 Notce that Equatons 5 and 6 descrbe the poston of the object but the do not sa when (at what tme) the object has an partcular poston. Also, notce that the relatonshp between and t n Equaton s quadratc (parabolc) n t because the values for a, v, and are constant. Smlarl, n Equatons 5 and 6, vertcal poston,, as a functon of horzontal poston, x, s quadratc (parabolc) n x because the values for a, v, and v x (t) are also constant. The equaton for (x) represents the trajector of the projectle. If a, x(t), x, θ, and are known, then t should be possble to determne the speed at whch the projectle was launched. Note: The famous Range Equaton for projectle moton s a specal case of the dervaton descrbed above. It can onl be used when a projectle starts and lands at exactl the same vertcal heght. It also defnes a coordnate axs for the trajector such that x = 0 and = 0. ( ) 008 Penn State Unverst Phscs 11: Lab Knematcs n -Dmensons
3 As an exercse, plot Equaton 6 as vs. x for a varet of realstc values for θ, v, and. What determnes the shape of the curve, the x poston of the maxmum, and the heght of the curve ( poston of the maxmum)? Expermentng wth the mathematcs of a trajector can eld tremendous nsght nto projectle moton. 008 Penn State Unverst Phscs 11: Lab Knematcs n -Dmensons
4 008 Penn State Unverst Phscs 11: Lab Knematcs n -Dmensons
5 Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton Goals: Resolve veloct vectors nto components. Determne the muzzle veloct of a projectle launcher. Predct the range of a projectle. Use Excel to analze the moton of a projectle. Equpment Lst: Projectle Launcher Steel projectle Meter Stck or Tape Measure Table clamp Carbon paper Excel Paper Target Scotch Tape Lab Actvt 1: Determnng Launch Veloct (Tabletop to tabletop launch) 1. Set up a projectle launcher at an arbtrar angle, other than 0 or 90 o. The launcher should be adjusted so that t projects the projectle onto the tabletop. The angle that ou set, θ, s the angle that ou wll use throughout actvtes 1 and. DO NOT pont our launcher n the drecton of the computer montors!. Carefull measure the heght from the tabletop to the launchng poston of the projectle. The manufacturer has placed a mark on the sde of the launcher for the purpose of ths measurement. Ths s the ntal vertcal poston,. 3. The launcher has three ranges: each range s determned b a clck n the sprng launcher and s also marked on the sde of the launcher. Be sure to use the second clck (medum range settng). 4. Fre the launcher and have a lab partner note the approxmate poston that the projectle strkes the table. Tape a pece of paper to the tabletop and place a sheet of carbon paper (carbon sde down) on top of the taped paper. It s not necessar to tape the carbon paper to the table. 008 Penn State Unverst Phscs 11: Lab Knematcs n -Dmensons
6 5. Fre for effect! Fre the launcher several tmes to obtan an average landng poston. Estmate the center poston of our pattern and measure the horzontal dstance from ths pont to a pont drectl below the launchng poston of the projectle. Ths s the horzontal range, x. 6. Use the values for a, x(t), x, θ, (x) and to calculate the speed, v, at whch the projectle left the launcher. (Assume that x = 0, and a = -g = -9.8 m/s.) 7. Record the values of θ and the calculated launch speed, v, for use n the next actvt. Lab Actvt : Determnng Projectle Range (Tabletop to floor launch) In the prevous actvt, ou determned the speed and drecton, hence the veloct, of a projectle beng fred from our launcher. You wll now use ths nformaton to predct the landng pont of a projectle that s launched from the tabletop to the floor. 1. Turn our launcher so that t faces awa from the table and towards an open space on the floor. Measure the vertcal dstance from the launchng pont of the projectle (on the sde of the launcher) to the floor. Ths wll be our new.. Use the value of v,, and θ to determne the horzontal dstance at whch a target must be placed n order to be ht wth our projectle. 3. Contact the nstructor when ou are read to fre our projectle. IMPORTANT: Do not take an shots before the TA s contacted or ou wll have our launcher angle changed and ou wll need to begn agan. 4. When the TA s read, fre for effect. Your score wll be the total ponts scored n fve shots. You wll be allowed one adjustment to the horzontal drecton of the launcher. 008 Penn State Unverst Phscs 11: Lab Knematcs n -Dmensons
7 Lab Actvt 3: Range vs. Angle Theor predcts that, when a projectle starts and lands from the same vertcal heght, the maxmum horzontal range should occur at 45 o. In addton, there should be two dstnct angles (complementar angles) of launch that would send a projectle to a partcular range less than the maxmum range. 1. Fre our projectle launcher (so that the projectle agan lands on the tabletop) at dfferent angles from 0 up to but not ncludng 90 at ether 5 or 10 ncrements (dependng on the amount of tme avalable but nclude a data pont for 45 ). Poston the launcher so that ts plumb bob hangs off of the edge of the table. Ths wll enable ou to make measurements at large angles. Record data for range and launch angle n a table, such as: Launch Angle (degrees) Range (meters). Usng Excel, make a graph of Range vs. Angle. 3. Based upon our graph, does the maxmum range occur at 45? If not, where does t occur? 4. From our graph, generate an estmated lst of at least 5 pars of angle measures that eld the same range values? Is each par a set of complementar angles? Explan. 008 Penn State Unverst Phscs 11: Lab Knematcs n -Dmensons
8 Name Secton # Name Name 008 Penn State Unverst Phscs 11: Lab Knematcs n -Dmensons
Gravitational Acceleration: A case of constant acceleration (approx. 2 hr.) (6/7/11)
 Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Physics 2A Chapter 3 HW Solutions
 Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Chapter 3. r r. Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Revisited
 Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
AP Physics 1 & 2 Summer Assignment
 AP Physcs 1 & 2 Summer Assgnment AP Physcs 1 requres an exceptonal profcency n algebra, trgonometry, and geometry. It was desgned by a select group of college professors and hgh school scence teachers
AP Physcs 1 & 2 Summer Assgnment AP Physcs 1 requres an exceptonal profcency n algebra, trgonometry, and geometry. It was desgned by a select group of college professors and hgh school scence teachers
GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SENIOR SECONDARY INTERVENTION PROGRAMME PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES)
 PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 1 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES) TOPIC 1: MECHANICS PROJECTILE MOTION Learner Note: Always draw a dagram of the stuaton and enter all the numercal alues onto your dagram. Remember to
PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 1 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES) TOPIC 1: MECHANICS PROJECTILE MOTION Learner Note: Always draw a dagram of the stuaton and enter all the numercal alues onto your dagram. Remember to
Supplemental Instruction sessions next week
 Homework #4 Wrtten homework due now Onlne homework due on Tue Mar 3 by 8 am Exam 1 Answer keys and scores wll be posted by end of the week Supplemental Instructon sessons next week Wednesday 8:45 10:00
Homework #4 Wrtten homework due now Onlne homework due on Tue Mar 3 by 8 am Exam 1 Answer keys and scores wll be posted by end of the week Supplemental Instructon sessons next week Wednesday 8:45 10:00
Slide. King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 5: MOTION IN 1-D (PART 2) LECTURE NO.
 Slde Kng Saud Unersty College of Scence Physcs & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 5: MOTION IN 1-D (PART ) LECTURE NO. 6 THIS PRESENTATION HAS BEEN PREPARED BY: DR. NASSR S. ALZAYED Lecture
Slde Kng Saud Unersty College of Scence Physcs & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 5: MOTION IN 1-D (PART ) LECTURE NO. 6 THIS PRESENTATION HAS BEEN PREPARED BY: DR. NASSR S. ALZAYED Lecture
11. Dynamics in Rotating Frames of Reference
 Unversty of Rhode Island DgtalCommons@URI Classcal Dynamcs Physcs Course Materals 2015 11. Dynamcs n Rotatng Frames of Reference Gerhard Müller Unversty of Rhode Island, gmuller@ur.edu Creatve Commons
Unversty of Rhode Island DgtalCommons@URI Classcal Dynamcs Physcs Course Materals 2015 11. Dynamcs n Rotatng Frames of Reference Gerhard Müller Unversty of Rhode Island, gmuller@ur.edu Creatve Commons
Moments of Inertia. and reminds us of the analogous equation for linear momentum p= mv, which is of the form. The kinetic energy of the body is.
 Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
Chapter 8. Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
 Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton of Energy In ths chapter we wll ntroduce the followng concepts: Potental Energy Conservatve and non-conservatve forces Mechancal Energy Conservaton of Mechancal
Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton of Energy In ths chapter we wll ntroduce the followng concepts: Potental Energy Conservatve and non-conservatve forces Mechancal Energy Conservaton of Mechancal
Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations
 Numercal Methods (CENG 00) CHAPTER-VI Numercal Soluton of Ordnar Dfferental Equatons 6 Introducton Dfferental equatons are equatons composed of an unknown functon and ts dervatves The followng are examples
Numercal Methods (CENG 00) CHAPTER-VI Numercal Soluton of Ordnar Dfferental Equatons 6 Introducton Dfferental equatons are equatons composed of an unknown functon and ts dervatves The followng are examples
How Differential Equations Arise. Newton s Second Law of Motion
 page 1 CHAPTER 1 Frst-Order Dfferental Equatons Among all of the mathematcal dscplnes the theory of dfferental equatons s the most mportant. It furnshes the explanaton of all those elementary manfestatons
page 1 CHAPTER 1 Frst-Order Dfferental Equatons Among all of the mathematcal dscplnes the theory of dfferental equatons s the most mportant. It furnshes the explanaton of all those elementary manfestatons
Physics 207: Lecture 20. Today s Agenda Homework for Monday
 Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
where v means the change in velocity, and t is the
 1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 4 MECHANICS (3) Ths lecture covers the eneral case of moton wth constant acceleraton and free fall (whch s one of the more mportant examples of moton wth constant acceleraton) n a more
1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 4 MECHANICS (3) Ths lecture covers the eneral case of moton wth constant acceleraton and free fall (whch s one of the more mportant examples of moton wth constant acceleraton) n a more
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #16
 PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #16 Monday, Mar. 4, 008 Potental Energy Conservatve and Non-conservatve Forces Conservaton o Mechancal Energy Power Today s homework s homework #8, due 9pm, Monday, Mar. 31!!
PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #16 Monday, Mar. 4, 008 Potental Energy Conservatve and Non-conservatve Forces Conservaton o Mechancal Energy Power Today s homework s homework #8, due 9pm, Monday, Mar. 31!!
Unit 5: Quadratic Equations & Functions
 Date Perod Unt 5: Quadratc Equatons & Functons DAY TOPIC 1 Modelng Data wth Quadratc Functons Factorng Quadratc Epressons 3 Solvng Quadratc Equatons 4 Comple Numbers Smplfcaton, Addton/Subtracton & Multplcaton
Date Perod Unt 5: Quadratc Equatons & Functons DAY TOPIC 1 Modelng Data wth Quadratc Functons Factorng Quadratc Epressons 3 Solvng Quadratc Equatons 4 Comple Numbers Smplfcaton, Addton/Subtracton & Multplcaton
12. The Hamilton-Jacobi Equation Michael Fowler
 1. The Hamlton-Jacob Equaton Mchael Fowler Back to Confguraton Space We ve establshed that the acton, regarded as a functon of ts coordnate endponts and tme, satsfes ( ) ( ) S q, t / t+ H qpt,, = 0, and
1. The Hamlton-Jacob Equaton Mchael Fowler Back to Confguraton Space We ve establshed that the acton, regarded as a functon of ts coordnate endponts and tme, satsfes ( ) ( ) S q, t / t+ H qpt,, = 0, and
Section 8.3 Polar Form of Complex Numbers
 80 Chapter 8 Secton 8 Polar Form of Complex Numbers From prevous classes, you may have encountered magnary numbers the square roots of negatve numbers and, more generally, complex numbers whch are the
80 Chapter 8 Secton 8 Polar Form of Complex Numbers From prevous classes, you may have encountered magnary numbers the square roots of negatve numbers and, more generally, complex numbers whch are the
Motion in One Dimension
 Moton n One Dmenson Speed ds tan ce traeled Aerage Speed tme of trael Mr. Wolf dres hs car on a long trp to a physcs store. Gen the dstance and tme data for hs trp, plot a graph of hs dstance ersus tme.
Moton n One Dmenson Speed ds tan ce traeled Aerage Speed tme of trael Mr. Wolf dres hs car on a long trp to a physcs store. Gen the dstance and tme data for hs trp, plot a graph of hs dstance ersus tme.
Physics 40 HW #4 Chapter 4 Key NEATNESS COUNTS! Solve but do not turn in the following problems from Chapter 4 Knight
 Physcs 40 HW #4 Chapter 4 Key NEATNESS COUNTS! Solve but do not turn n the ollowng problems rom Chapter 4 Knght Conceptual Questons: 8, 0, ; 4.8. Anta s approachng ball and movng away rom where ball was
Physcs 40 HW #4 Chapter 4 Key NEATNESS COUNTS! Solve but do not turn n the ollowng problems rom Chapter 4 Knght Conceptual Questons: 8, 0, ; 4.8. Anta s approachng ball and movng away rom where ball was
Module 14: THE INTEGRAL Exploring Calculus
 Module 14: THE INTEGRAL Explorng Calculus Part I Approxmatons and the Defnte Integral It was known n the 1600s before the calculus was developed that the area of an rregularly shaped regon could be approxmated
Module 14: THE INTEGRAL Explorng Calculus Part I Approxmatons and the Defnte Integral It was known n the 1600s before the calculus was developed that the area of an rregularly shaped regon could be approxmated
Name: PHYS 110 Dr. McGovern Spring 2018 Exam 1. Multiple Choice: Circle the answer that best evaluates the statement or completes the statement.
 Name: PHYS 110 Dr. McGoern Sprng 018 Exam 1 Multple Choce: Crcle the answer that best ealuates the statement or completes the statement. #1 - I the acceleraton o an object s negate, the object must be
Name: PHYS 110 Dr. McGoern Sprng 018 Exam 1 Multple Choce: Crcle the answer that best ealuates the statement or completes the statement. #1 - I the acceleraton o an object s negate, the object must be
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Homework 4: Work, Energy and Linear Momentum Due Friday March 1 st
 EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
Statistics MINITAB - Lab 2
 Statstcs 20080 MINITAB - Lab 2 1. Smple Lnear Regresson In smple lnear regresson we attempt to model a lnear relatonshp between two varables wth a straght lne and make statstcal nferences concernng that
Statstcs 20080 MINITAB - Lab 2 1. Smple Lnear Regresson In smple lnear regresson we attempt to model a lnear relatonshp between two varables wth a straght lne and make statstcal nferences concernng that
Modeling of Dynamic Systems
 Modelng of Dynamc Systems Ref: Control System Engneerng Norman Nse : Chapters & 3 Chapter objectves : Revew the Laplace transform Learn how to fnd a mathematcal model, called a transfer functon Learn how
Modelng of Dynamc Systems Ref: Control System Engneerng Norman Nse : Chapters & 3 Chapter objectves : Revew the Laplace transform Learn how to fnd a mathematcal model, called a transfer functon Learn how
Physics 2A Chapters 6 - Work & Energy Fall 2017
 Physcs A Chapters 6 - Work & Energy Fall 017 These notes are eght pages. A quck summary: The work-energy theorem s a combnaton o Chap and Chap 4 equatons. Work s dened as the product o the orce actng on
Physcs A Chapters 6 - Work & Energy Fall 017 These notes are eght pages. A quck summary: The work-energy theorem s a combnaton o Chap and Chap 4 equatons. Work s dened as the product o the orce actng on
Physics 207 Lecture 13. Lecture 13
 Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Goals: Lecture 3 Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Defne Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Develop and explot conservaton of energy prncple n problem
Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Goals: Lecture 3 Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Defne Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Develop and explot conservaton of energy prncple n problem
Resource Allocation and Decision Analysis (ECON 8010) Spring 2014 Foundations of Regression Analysis
 Resource Allocaton and Decson Analss (ECON 800) Sprng 04 Foundatons of Regresson Analss Readng: Regresson Analss (ECON 800 Coursepak, Page 3) Defntons and Concepts: Regresson Analss statstcal technques
Resource Allocaton and Decson Analss (ECON 800) Sprng 04 Foundatons of Regresson Analss Readng: Regresson Analss (ECON 800 Coursepak, Page 3) Defntons and Concepts: Regresson Analss statstcal technques
χ x B E (c) Figure 2.1.1: (a) a material particle in a body, (b) a place in space, (c) a configuration of the body
 Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
Work is the change in energy of a system (neglecting heat transfer). To examine what could
 Work Work s the change n energy o a system (neglectng heat transer). To eamne what could cause work, let s look at the dmensons o energy: L ML E M L F L so T T dmensonally energy s equal to a orce tmes
Work Work s the change n energy o a system (neglectng heat transer). To eamne what could cause work, let s look at the dmensons o energy: L ML E M L F L so T T dmensonally energy s equal to a orce tmes
SIMPLE LINEAR REGRESSION
 Smple Lnear Regresson and Correlaton Introducton Prevousl, our attenton has been focused on one varable whch we desgnated b x. Frequentl, t s desrable to learn somethng about the relatonshp between two
Smple Lnear Regresson and Correlaton Introducton Prevousl, our attenton has been focused on one varable whch we desgnated b x. Frequentl, t s desrable to learn somethng about the relatonshp between two
One Dimensional Axial Deformations
 One Dmensonal al Deformatons In ths secton, a specfc smple geometr s consdered, that of a long and thn straght component loaded n such a wa that t deforms n the aal drecton onl. The -as s taken as the
One Dmensonal al Deformatons In ths secton, a specfc smple geometr s consdered, that of a long and thn straght component loaded n such a wa that t deforms n the aal drecton onl. The -as s taken as the
SCALARS AND VECTORS All physical quantities in engineering mechanics are measured using either scalars or vectors.
 SCALARS AND ECTORS All phscal uanttes n engneerng mechancs are measured usng ether scalars or vectors. Scalar. A scalar s an postve or negatve phscal uantt that can be completel specfed b ts magntude.
SCALARS AND ECTORS All phscal uanttes n engneerng mechancs are measured usng ether scalars or vectors. Scalar. A scalar s an postve or negatve phscal uantt that can be completel specfed b ts magntude.
Physics 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1
 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Unversty of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Course Informaton: Lab report # 3. Exam # 2. Mult-Partcle
Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Unversty of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Course Informaton: Lab report # 3. Exam # 2. Mult-Partcle
MEASUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTIA
 1. measurement MESUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTI The am of ths measurement s to determne the moment of nerta of the rotor of an electrc motor. 1. General relatons Rotatng moton and moment of nerta Let us
1. measurement MESUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTI The am of ths measurement s to determne the moment of nerta of the rotor of an electrc motor. 1. General relatons Rotatng moton and moment of nerta Let us
ACTM State Calculus Competition Saturday April 30, 2011
 ACTM State Calculus Competton Saturday Aprl 30, 2011 ACTM State Calculus Competton Sprng 2011 Page 1 Instructons: For questons 1 through 25, mark the best answer choce on the answer sheet provde Afterward
ACTM State Calculus Competton Saturday Aprl 30, 2011 ACTM State Calculus Competton Sprng 2011 Page 1 Instructons: For questons 1 through 25, mark the best answer choce on the answer sheet provde Afterward
x yi In chapter 14, we want to perform inference (i.e. calculate confidence intervals and perform tests of significance) in this setting.
 The Practce of Statstcs, nd ed. Chapter 14 Inference for Regresson Introducton In chapter 3 we used a least-squares regresson lne (LSRL) to represent a lnear relatonshp etween two quanttatve explanator
The Practce of Statstcs, nd ed. Chapter 14 Inference for Regresson Introducton In chapter 3 we used a least-squares regresson lne (LSRL) to represent a lnear relatonshp etween two quanttatve explanator
DEMO #8 - GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION USING MATHEMATICA. 1. Matrices in Mathematica
 demo8.nb 1 DEMO #8 - GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION USING MATHEMATICA Obectves: - defne matrces n Mathematca - format the output of matrces - appl lnear algebra to solve a real problem - Use Mathematca to perform
demo8.nb 1 DEMO #8 - GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION USING MATHEMATICA Obectves: - defne matrces n Mathematca - format the output of matrces - appl lnear algebra to solve a real problem - Use Mathematca to perform
Recitation: Energy, Phys Energies. 1.2 Three stones. 1. Energy. 1. An acorn falling from an oak tree onto the sidewalk.
 Rectaton: Energy, Phys 207. Energy. Energes. An acorn fallng from an oak tree onto the sdewalk. The acorn ntal has gravtatonal potental energy. As t falls, t converts ths energy to knetc. When t hts the
Rectaton: Energy, Phys 207. Energy. Energes. An acorn fallng from an oak tree onto the sdewalk. The acorn ntal has gravtatonal potental energy. As t falls, t converts ths energy to knetc. When t hts the
Physics for Scientists and Engineers. Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum
 Physcs or Scentsts and Engneers Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum Sprng, 008 Ho Jung Pak Lnear Momentum Lnear momentum o an object o mass m movng wth a velocty v s dened to be p mv Momentum and lnear momentum
Physcs or Scentsts and Engneers Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum Sprng, 008 Ho Jung Pak Lnear Momentum Lnear momentum o an object o mass m movng wth a velocty v s dened to be p mv Momentum and lnear momentum
CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE
 CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE Analytcal soluton s usually not possble when exctaton vares arbtrarly wth tme or f the system s nonlnear. Such problems can be solved by numercal tmesteppng
CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE Analytcal soluton s usually not possble when exctaton vares arbtrarly wth tme or f the system s nonlnear. Such problems can be solved by numercal tmesteppng
Chapter 2. Pythagorean Theorem. Right Hand Rule. Position. Distance Formula
 Chapter Moton n One Dmenson Cartesan Coordnate System The most common coordnate system or representng postons n space s one based on three perpendcular spatal axes generally desgnated x, y, and z. Any
Chapter Moton n One Dmenson Cartesan Coordnate System The most common coordnate system or representng postons n space s one based on three perpendcular spatal axes generally desgnated x, y, and z. Any
First Law: A body at rest remains at rest, a body in motion continues to move at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force.
 Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
ONE-DIMENSIONAL COLLISIONS
 Purpose Theory ONE-DIMENSIONAL COLLISIONS a. To very the law o conservaton o lnear momentum n one-dmensonal collsons. b. To study conservaton o energy and lnear momentum n both elastc and nelastc onedmensonal
Purpose Theory ONE-DIMENSIONAL COLLISIONS a. To very the law o conservaton o lnear momentum n one-dmensonal collsons. b. To study conservaton o energy and lnear momentum n both elastc and nelastc onedmensonal
OPTIMISATION. Introduction Single Variable Unconstrained Optimisation Multivariable Unconstrained Optimisation Linear Programming
 OPTIMIATION Introducton ngle Varable Unconstraned Optmsaton Multvarable Unconstraned Optmsaton Lnear Programmng Chapter Optmsaton /. Introducton In an engneerng analss, sometmes etremtes, ether mnmum or
OPTIMIATION Introducton ngle Varable Unconstraned Optmsaton Multvarable Unconstraned Optmsaton Lnear Programmng Chapter Optmsaton /. Introducton In an engneerng analss, sometmes etremtes, ether mnmum or
Mathematics Intersection of Lines
 a place of mnd F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Currculum and Pedagog Mathematcs Intersecton of Lnes Scence and Mathematcs Educaton Research Group Supported b UBC Teachng and Learnng Enhancement
a place of mnd F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Currculum and Pedagog Mathematcs Intersecton of Lnes Scence and Mathematcs Educaton Research Group Supported b UBC Teachng and Learnng Enhancement
Section 8.1 Exercises
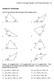 Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Week 9 Chapter 10 Section 1-5
 Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
PHYSICS 203-NYA-05 MECHANICS
 PHYSICS 03-NYA-05 MECHANICS PROF. S.D. MANOLI PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY CHAMPLAIN - ST. LAWRENCE 790 NÉRÉE-TREMBLAY QUÉBEC, QC GV 4K TELEPHONE: 48.656.69 EXT. 449 EMAIL: smanol@slc.qc.ca WEBPAGE: http:/web.slc.qc.ca/smanol/
PHYSICS 03-NYA-05 MECHANICS PROF. S.D. MANOLI PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY CHAMPLAIN - ST. LAWRENCE 790 NÉRÉE-TREMBLAY QUÉBEC, QC GV 4K TELEPHONE: 48.656.69 EXT. 449 EMAIL: smanol@slc.qc.ca WEBPAGE: http:/web.slc.qc.ca/smanol/
Week 6, Chapter 7 Sect 1-5
 Week 6, Chapter 7 Sect 1-5 Work and Knetc Energy Lecture Quz The frctonal force of the floor on a large sutcase s least when the sutcase s A.pushed by a force parallel to the floor. B.dragged by a force
Week 6, Chapter 7 Sect 1-5 Work and Knetc Energy Lecture Quz The frctonal force of the floor on a large sutcase s least when the sutcase s A.pushed by a force parallel to the floor. B.dragged by a force
Physics 207 Lecture 6
 Physcs 207 Lecture 6 Agenda: Physcs 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 25 Chapter 4 Frames of reference Chapter 5 ewton s Law Mass Inerta s (contact and non-contact) Frcton (a external force that opposes moton) Free
Physcs 207 Lecture 6 Agenda: Physcs 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 25 Chapter 4 Frames of reference Chapter 5 ewton s Law Mass Inerta s (contact and non-contact) Frcton (a external force that opposes moton) Free
Physics 2A Chapter 9 HW Solutions
 Phscs A Chapter 9 HW Solutons Chapter 9 Conceptual Queston:, 4, 8, 13 Problems: 3, 8, 1, 15, 3, 40, 51, 6 Q9.. Reason: We can nd the change n momentum o the objects b computng the mpulse on them and usng
Phscs A Chapter 9 HW Solutons Chapter 9 Conceptual Queston:, 4, 8, 13 Problems: 3, 8, 1, 15, 3, 40, 51, 6 Q9.. Reason: We can nd the change n momentum o the objects b computng the mpulse on them and usng
NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 482/582 ROBOT ENGINEERING. Dr. Stephen Bruder NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 482/582
 NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 482/582 ROBOT ENGINEERING Dr. Stephen Bruder NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 482/582 4. Moton Knematcs 4.2 Angular Velocty Knematcs Summary From the last lecture we concluded that: If the jonts
NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 482/582 ROBOT ENGINEERING Dr. Stephen Bruder NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 482/582 4. Moton Knematcs 4.2 Angular Velocty Knematcs Summary From the last lecture we concluded that: If the jonts
ENGN 40 Dynamics and Vibrations Homework # 7 Due: Friday, April 15
 NGN 40 ynamcs and Vbratons Homework # 7 ue: Frday, Aprl 15 1. Consder a concal hostng drum used n the mnng ndustry to host a mass up/down. A cable of dameter d has the mass connected at one end and s wound/unwound
NGN 40 ynamcs and Vbratons Homework # 7 ue: Frday, Aprl 15 1. Consder a concal hostng drum used n the mnng ndustry to host a mass up/down. A cable of dameter d has the mass connected at one end and s wound/unwound
Displacement at any time. Velocity at any displacement in the x-direction u 2 = v ] + 2 a x ( )
![Displacement at any time. Velocity at any displacement in the x-direction u 2 = v ] + 2 a x ( ) Displacement at any time. Velocity at any displacement in the x-direction u 2 = v ] + 2 a x ( )](/thumbs/89/97691613.jpg) The Language of Physcs Knematcs The branch of mechancs that descrbes the moton of a body wthout regard to the cause of that moton (p. 39). Average velocty The average rate at whch the dsplacement vector
The Language of Physcs Knematcs The branch of mechancs that descrbes the moton of a body wthout regard to the cause of that moton (p. 39). Average velocty The average rate at whch the dsplacement vector
Inner Product. Euclidean Space. Orthonormal Basis. Orthogonal
 Inner Product Defnton 1 () A Eucldean space s a fnte-dmensonal vector space over the reals R, wth an nner product,. Defnton 2 (Inner Product) An nner product, on a real vector space X s a symmetrc, blnear,
Inner Product Defnton 1 () A Eucldean space s a fnte-dmensonal vector space over the reals R, wth an nner product,. Defnton 2 (Inner Product) An nner product, on a real vector space X s a symmetrc, blnear,
For all questions, answer choice E) NOTA" means none of the above answers is correct.
 0 MA Natonal Conventon For all questons, answer choce " means none of the above answers s correct.. In calculus, one learns of functon representatons that are nfnte seres called power 3 4 5 seres. For
0 MA Natonal Conventon For all questons, answer choce " means none of the above answers s correct.. In calculus, one learns of functon representatons that are nfnte seres called power 3 4 5 seres. For
New Method for Solving Poisson Equation. on Irregular Domains
 Appled Mathematcal Scences Vol. 6 01 no. 8 369 380 New Method for Solvng Posson Equaton on Irregular Domans J. Izadan and N. Karamooz Department of Mathematcs Facult of Scences Mashhad BranchIslamc Azad
Appled Mathematcal Scences Vol. 6 01 no. 8 369 380 New Method for Solvng Posson Equaton on Irregular Domans J. Izadan and N. Karamooz Department of Mathematcs Facult of Scences Mashhad BranchIslamc Azad
Chapter 9: Statistical Inference and the Relationship between Two Variables
 Chapter 9: Statstcal Inference and the Relatonshp between Two Varables Key Words The Regresson Model The Sample Regresson Equaton The Pearson Correlaton Coeffcent Learnng Outcomes After studyng ths chapter,
Chapter 9: Statstcal Inference and the Relatonshp between Two Varables Key Words The Regresson Model The Sample Regresson Equaton The Pearson Correlaton Coeffcent Learnng Outcomes After studyng ths chapter,
Application to Plane (rigid) frame structure
 Advanced Computatonal echancs 18 Chapter 4 Applcaton to Plane rgd frame structure 1. Dscusson on degrees of freedom In case of truss structures, t was enough that the element force equaton provdes onl
Advanced Computatonal echancs 18 Chapter 4 Applcaton to Plane rgd frame structure 1. Dscusson on degrees of freedom In case of truss structures, t was enough that the element force equaton provdes onl
Available online at Kazuhiro Tsuboi a, * Received 31 January 2010; revised 7 March 2010; accepted 21 March 2010
 Avalable onlne at www.scencedrect.com Proceda Proceda Engneerng 00 (010) (009) 000 000 305 310 Proceda Engneerng www.elsever.com/locate/proceda 8 th Conference of the Internatonal Sports Engneerng Assocaton
Avalable onlne at www.scencedrect.com Proceda Proceda Engneerng 00 (010) (009) 000 000 305 310 Proceda Engneerng www.elsever.com/locate/proceda 8 th Conference of the Internatonal Sports Engneerng Assocaton
PHYS 1441 Section 001 Lecture #15 Wednesday, July 8, 2015
 PHYS 1441 Secton 001 Lecture #15 Wednesday, July 8, 2015 Concept of the Center of Mass Center of Mass & Center of Gravty Fundamentals of the Rotatonal Moton Rotatonal Knematcs Equatons of Rotatonal Knematcs
PHYS 1441 Secton 001 Lecture #15 Wednesday, July 8, 2015 Concept of the Center of Mass Center of Mass & Center of Gravty Fundamentals of the Rotatonal Moton Rotatonal Knematcs Equatons of Rotatonal Knematcs
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. D Alembert s Principle and The Lagrangian-1
 P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM
 ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
Linear Approximation with Regularization and Moving Least Squares
 Lnear Approxmaton wth Regularzaton and Movng Least Squares Igor Grešovn May 007 Revson 4.6 (Revson : March 004). 5 4 3 0.5 3 3.5 4 Contents: Lnear Fttng...4. Weghted Least Squares n Functon Approxmaton...
Lnear Approxmaton wth Regularzaton and Movng Least Squares Igor Grešovn May 007 Revson 4.6 (Revson : March 004). 5 4 3 0.5 3 3.5 4 Contents: Lnear Fttng...4. Weghted Least Squares n Functon Approxmaton...
Math1110 (Spring 2009) Prelim 3 - Solutions
 Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
Difference Equations
 Dfference Equatons c Jan Vrbk 1 Bascs Suppose a sequence of numbers, say a 0,a 1,a,a 3,... s defned by a certan general relatonshp between, say, three consecutve values of the sequence, e.g. a + +3a +1
Dfference Equatons c Jan Vrbk 1 Bascs Suppose a sequence of numbers, say a 0,a 1,a,a 3,... s defned by a certan general relatonshp between, say, three consecutve values of the sequence, e.g. a + +3a +1
THE CURRENT BALANCE Physics 258/259
 DSH 1988, 005 THE CURRENT BALANCE Physcs 58/59 The tme average force between two parallel conductors carryng an alternatng current s measured by balancng ths force aganst the gravtatonal force on a set
DSH 1988, 005 THE CURRENT BALANCE Physcs 58/59 The tme average force between two parallel conductors carryng an alternatng current s measured by balancng ths force aganst the gravtatonal force on a set
[The following data appear in Wooldridge Q2.3.] The table below contains the ACT score and college GPA for eight college students.
![[The following data appear in Wooldridge Q2.3.] The table below contains the ACT score and college GPA for eight college students. [The following data appear in Wooldridge Q2.3.] The table below contains the ACT score and college GPA for eight college students.](/thumbs/87/96001374.jpg) PPOL 59-3 Problem Set Exercses n Smple Regresson Due n class /8/7 In ths problem set, you are asked to compute varous statstcs by hand to gve you a better sense of the mechancs of the Pearson correlaton
PPOL 59-3 Problem Set Exercses n Smple Regresson Due n class /8/7 In ths problem set, you are asked to compute varous statstcs by hand to gve you a better sense of the mechancs of the Pearson correlaton
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
 COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS INTRODUCTION We know that x 0 for all x R e the square of a real number (whether postve, negatve or ero) s non-negatve Hence the equatons x, x, x + 7 0 etc are not
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS INTRODUCTION We know that x 0 for all x R e the square of a real number (whether postve, negatve or ero) s non-negatve Hence the equatons x, x, x + 7 0 etc are not
CHAPTER 4. Vector Spaces
 man 2007/2/16 page 234 CHAPTER 4 Vector Spaces To crtcze mathematcs for ts abstracton s to mss the pont entrel. Abstracton s what makes mathematcs work. Ian Stewart The man am of ths tet s to stud lnear
man 2007/2/16 page 234 CHAPTER 4 Vector Spaces To crtcze mathematcs for ts abstracton s to mss the pont entrel. Abstracton s what makes mathematcs work. Ian Stewart The man am of ths tet s to stud lnear
PHYS 1443 Section 004 Lecture #12 Thursday, Oct. 2, 2014
 PHYS 1443 Secton 004 Lecture #1 Thursday, Oct., 014 Work-Knetc Energy Theorem Work under rcton Potental Energy and the Conservatve Force Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Conservaton o
PHYS 1443 Secton 004 Lecture #1 Thursday, Oct., 014 Work-Knetc Energy Theorem Work under rcton Potental Energy and the Conservatve Force Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Conservaton o
Linear Momentum. Center of Mass.
 Lecture 6 Chapter 9 Physcs I 03.3.04 Lnear omentum. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.uml.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcssprng.html
Lecture 6 Chapter 9 Physcs I 03.3.04 Lnear omentum. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.uml.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcssprng.html
/ n ) are compared. The logic is: if the two
 STAT C141, Sprng 2005 Lecture 13 Two sample tests One sample tests: examples of goodness of ft tests, where we are testng whether our data supports predctons. Two sample tests: called as tests of ndependence
STAT C141, Sprng 2005 Lecture 13 Two sample tests One sample tests: examples of goodness of ft tests, where we are testng whether our data supports predctons. Two sample tests: called as tests of ndependence
Mathematical Preparations
 1 Introducton Mathematcal Preparatons The theory of relatvty was developed to explan experments whch studed the propagaton of electromagnetc radaton n movng coordnate systems. Wthn expermental error the
1 Introducton Mathematcal Preparatons The theory of relatvty was developed to explan experments whch studed the propagaton of electromagnetc radaton n movng coordnate systems. Wthn expermental error the
Chapter 13: Multiple Regression
 Chapter 13: Multple Regresson 13.1 Developng the multple-regresson Model The general model can be descrbed as: It smplfes for two ndependent varables: The sample ft parameter b 0, b 1, and b are used to
Chapter 13: Multple Regresson 13.1 Developng the multple-regresson Model The general model can be descrbed as: It smplfes for two ndependent varables: The sample ft parameter b 0, b 1, and b are used to
An Algorithm to Solve the Inverse Kinematics Problem of a Robotic Manipulator Based on Rotation Vectors
 An Algorthm to Solve the Inverse Knematcs Problem of a Robotc Manpulator Based on Rotaton Vectors Mohamad Z. Al-az*, Mazn Z. Othman**, and Baker B. Al-Bahr* *AL-Nahran Unversty, Computer Eng. Dep., Baghdad,
An Algorthm to Solve the Inverse Knematcs Problem of a Robotc Manpulator Based on Rotaton Vectors Mohamad Z. Al-az*, Mazn Z. Othman**, and Baker B. Al-Bahr* *AL-Nahran Unversty, Computer Eng. Dep., Baghdad,
2.3 Nilpotent endomorphisms
 s a block dagonal matrx, wth A Mat dm U (C) In fact, we can assume that B = B 1 B k, wth B an ordered bass of U, and that A = [f U ] B, where f U : U U s the restrcton of f to U 40 23 Nlpotent endomorphsms
s a block dagonal matrx, wth A Mat dm U (C) In fact, we can assume that B = B 1 B k, wth B an ordered bass of U, and that A = [f U ] B, where f U : U U s the restrcton of f to U 40 23 Nlpotent endomorphsms
Transfer Functions. Convenient representation of a linear, dynamic model. A transfer function (TF) relates one input and one output: ( ) system
 Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Lesson 4: Relative motion, Forces, Newton s laws (sections )
 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons 3.6-4.4) We start wth a projectle problem. A olf ball s ht from the round at 35 m/s at an anle of 55º. The round s leel.. How lon s the ball n the
Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons 3.6-4.4) We start wth a projectle problem. A olf ball s ht from the round at 35 m/s at an anle of 55º. The round s leel.. How lon s the ball n the
Chapter 5. Solution of System of Linear Equations. Module No. 6. Solution of Inconsistent and Ill Conditioned Systems
 Numercal Analyss by Dr. Anta Pal Assstant Professor Department of Mathematcs Natonal Insttute of Technology Durgapur Durgapur-713209 emal: anta.bue@gmal.com 1 . Chapter 5 Soluton of System of Lnear Equatons
Numercal Analyss by Dr. Anta Pal Assstant Professor Department of Mathematcs Natonal Insttute of Technology Durgapur Durgapur-713209 emal: anta.bue@gmal.com 1 . Chapter 5 Soluton of System of Lnear Equatons
Pre-Calculus Summer Assignment
 Pre-Calculus Summer Assgnment Dear Future Pre-Calculus Student, Congratulatons on our successful completon of Algebra! Below ou wll fnd the summer assgnment questons. It s assumed that these concepts,
Pre-Calculus Summer Assgnment Dear Future Pre-Calculus Student, Congratulatons on our successful completon of Algebra! Below ou wll fnd the summer assgnment questons. It s assumed that these concepts,
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #15
 PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #15 Monday, March 18, 013 Work wth rcton Potental Energy Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Mechancal Energy Conservaton Announcements Mdterm comprehensve exam
PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #15 Monday, March 18, 013 Work wth rcton Potental Energy Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Mechancal Energy Conservaton Announcements Mdterm comprehensve exam
Chapter 14 Simple Linear Regression
 Chapter 4 Smple Lnear Regresson Chapter 4 - Smple Lnear Regresson Manageral decsons often are based on the relatonshp between two or more varables. Regresson analss can be used to develop an equaton showng
Chapter 4 Smple Lnear Regresson Chapter 4 - Smple Lnear Regresson Manageral decsons often are based on the relatonshp between two or more varables. Regresson analss can be used to develop an equaton showng
THE VIBRATIONS OF MOLECULES II THE CARBON DIOXIDE MOLECULE Student Instructions
 THE VIBRATIONS OF MOLECULES II THE CARBON DIOXIDE MOLECULE Student Instructons by George Hardgrove Chemstry Department St. Olaf College Northfeld, MN 55057 hardgrov@lars.acc.stolaf.edu Copyrght George
THE VIBRATIONS OF MOLECULES II THE CARBON DIOXIDE MOLECULE Student Instructons by George Hardgrove Chemstry Department St. Olaf College Northfeld, MN 55057 hardgrov@lars.acc.stolaf.edu Copyrght George
coordinates. Then, the position vectors are described by
 Revewng, what we have dscussed so far: Generalzed coordnates Any number of varables (say, n) suffcent to specfy the confguraton of the system at each nstant to tme (need not be the mnmum number). In general,
Revewng, what we have dscussed so far: Generalzed coordnates Any number of varables (say, n) suffcent to specfy the confguraton of the system at each nstant to tme (need not be the mnmum number). In general,
I have not received unauthorized aid in the completion of this exam.
 ME 270 Sprng 2013 Fnal Examnaton Please read and respond to the followng statement, I have not receved unauthorzed ad n the completon of ths exam. Agree Dsagree Sgnature INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem
ME 270 Sprng 2013 Fnal Examnaton Please read and respond to the followng statement, I have not receved unauthorzed ad n the completon of ths exam. Agree Dsagree Sgnature INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem
The equation of motion of a dynamical system is given by a set of differential equations. That is (1)
 Dynamcal Systems Many engneerng and natural systems are dynamcal systems. For example a pendulum s a dynamcal system. State l The state of the dynamcal system specfes t condtons. For a pendulum n the absence
Dynamcal Systems Many engneerng and natural systems are dynamcal systems. For example a pendulum s a dynamcal system. State l The state of the dynamcal system specfes t condtons. For a pendulum n the absence
Introduction to Vapor/Liquid Equilibrium, part 2. Raoult s Law:
 CE304, Sprng 2004 Lecture 4 Introducton to Vapor/Lqud Equlbrum, part 2 Raoult s Law: The smplest model that allows us do VLE calculatons s obtaned when we assume that the vapor phase s an deal gas, and
CE304, Sprng 2004 Lecture 4 Introducton to Vapor/Lqud Equlbrum, part 2 Raoult s Law: The smplest model that allows us do VLE calculatons s obtaned when we assume that the vapor phase s an deal gas, and
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Homework 7: Rigid Body Kinematics
 N40: ynamcs and Vbratons Homewor 7: Rgd Body Knematcs School of ngneerng Brown Unversty 1. In the fgure below, bar AB rotates counterclocwse at 4 rad/s. What are the angular veloctes of bars BC and C?.
N40: ynamcs and Vbratons Homewor 7: Rgd Body Knematcs School of ngneerng Brown Unversty 1. In the fgure below, bar AB rotates counterclocwse at 4 rad/s. What are the angular veloctes of bars BC and C?.
CHAPTER 14 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY
 CHAPTER 4 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY 4 Introducton A partcle n orbt around a pont mass or a sphercally symmetrc mass dstrbuton s movng n a gravtatonal potental of the form GM / r In ths potental t moves
CHAPTER 4 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY 4 Introducton A partcle n orbt around a pont mass or a sphercally symmetrc mass dstrbuton s movng n a gravtatonal potental of the form GM / r In ths potental t moves
PHYS 1443 Section 003 Lecture #17
 PHYS 144 Secton 00 ecture #17 Wednesda, Oct. 9, 00 1. Rollng oton of a Rgd od. Torque. oment of Inerta 4. Rotatonal Knetc Energ 5. Torque and Vector Products Remember the nd term eam (ch 6 11), onda, Nov.!
PHYS 144 Secton 00 ecture #17 Wednesda, Oct. 9, 00 1. Rollng oton of a Rgd od. Torque. oment of Inerta 4. Rotatonal Knetc Energ 5. Torque and Vector Products Remember the nd term eam (ch 6 11), onda, Nov.!
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION
 NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 Introducton Dfferentaton s a method to compute the rate at whch a dependent output y changes wth respect to the change n the ndependent nput x. Ths rate of change s called the
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 Introducton Dfferentaton s a method to compute the rate at whch a dependent output y changes wth respect to the change n the ndependent nput x. Ths rate of change s called the
Homework 2: Kinematics and Dynamics of Particles Due Friday Feb 7, 2014 Max Score 45 Points + 8 Extra Credit
 EN40: Dynamcs and Vbratons School of Engneerng Brown Unversty Homework : Knematcs and Dynamcs of Partcles Due Frday Feb 7, 014 Max Score 45 Ponts + 8 Extra Credt 1. An expermental mcro-robot (see a descrpton
EN40: Dynamcs and Vbratons School of Engneerng Brown Unversty Homework : Knematcs and Dynamcs of Partcles Due Frday Feb 7, 014 Max Score 45 Ponts + 8 Extra Credt 1. An expermental mcro-robot (see a descrpton
Problem While being compressed, A) What is the work done on it by gravity? B) What is the work done on it by the spring force?
 Problem 07-50 A 0.25 kg block s dropped on a relaed sprng that has a sprng constant o k 250.0 N/m (2.5 N/cm). The block becomes attached to the sprng and compresses t 0.12 m beore momentarl stoppng. Whle
Problem 07-50 A 0.25 kg block s dropped on a relaed sprng that has a sprng constant o k 250.0 N/m (2.5 N/cm). The block becomes attached to the sprng and compresses t 0.12 m beore momentarl stoppng. Whle
Correlation and Regression. Correlation 9.1. Correlation. Chapter 9
 Chapter 9 Correlaton and Regresson 9. Correlaton Correlaton A correlaton s a relatonshp between two varables. The data can be represented b the ordered pars (, ) where s the ndependent (or eplanator) varable,
Chapter 9 Correlaton and Regresson 9. Correlaton Correlaton A correlaton s a relatonshp between two varables. The data can be represented b the ordered pars (, ) where s the ndependent (or eplanator) varable,
Chapter Newton s Method
 Chapter 9. Newton s Method After readng ths chapter, you should be able to:. Understand how Newton s method s dfferent from the Golden Secton Search method. Understand how Newton s method works 3. Solve
Chapter 9. Newton s Method After readng ths chapter, you should be able to:. Understand how Newton s method s dfferent from the Golden Secton Search method. Understand how Newton s method works 3. Solve
Spin-rotation coupling of the angularly accelerated rigid body
 Spn-rotaton couplng of the angularly accelerated rgd body Loua Hassan Elzen Basher Khartoum, Sudan. Postal code:11123 E-mal: louaelzen@gmal.com November 1, 2017 All Rghts Reserved. Abstract Ths paper s
Spn-rotaton couplng of the angularly accelerated rgd body Loua Hassan Elzen Basher Khartoum, Sudan. Postal code:11123 E-mal: louaelzen@gmal.com November 1, 2017 All Rghts Reserved. Abstract Ths paper s
ONE DIMENSIONAL TRIANGULAR FIN EXPERIMENT. Technical Advisor: Dr. D.C. Look, Jr. Version: 11/03/00
 ONE IMENSIONAL TRIANGULAR FIN EXPERIMENT Techncal Advsor: r..c. Look, Jr. Verson: /3/ 7. GENERAL OJECTIVES a) To understand a one-dmensonal epermental appromaton. b) To understand the art of epermental
ONE IMENSIONAL TRIANGULAR FIN EXPERIMENT Techncal Advsor: r..c. Look, Jr. Verson: /3/ 7. GENERAL OJECTIVES a) To understand a one-dmensonal epermental appromaton. b) To understand the art of epermental
