Lesson 4: Relative motion, Forces, Newton s laws (sections )
|
|
|
- Donald Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons ) We start wth a projectle problem. A olf ball s ht from the round at 35 m/s at an anle of 55º. The round s leel.. How lon s the ball n the ar?. What s the maxmum heht of the ball? 3. How far from the launchn pont does the ball ht the round? 4. What s the ball s poston after.0 seconds? When does t reach ths heht aan? 5. When s the ball 0 m aboe the round? In the plot below, all unts are n meters = 55 o x Soluton:. When the ball hts the round, = 0. t 0 t( a ( t) a t) Snce the onl wa a product can equal zero s when one of the factors equals zero, t 0 or ( a t) 0 Lesson 4, pae
2 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons ) The frst condton tells us that the olf ball starts from the round. The second es us the tme of flht, tf ( a t) 0 a t t f a Ths s more useful f we use a = and = sn (see the daram below the trajector plot). t f a sn (35m/s)sn m/s 5.85s What anle maxmzes the tme of flht? The anle that maxmzes sn. The larest sne can be s and that occurs at 90º. Ht the ball straht up!. At the maxmum heht, f = 0. f 0 sn t t h a t h sn But ths s ½ the tme of flht. When the ball s shot oer leel round half of the tme the ball s on up, the other half of the tme t s on down. It takes half the total tme to reach the hhest pont. The heht at ths tme s h t sn t sn a ( t) h ( t sn h ) sn Lesson 4, pae
3 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons ) h sn (35m/s) sn 55 (9.8 m/s ) 4.9 m sn sn What anle maxmzes the heht? We need to fnd the maxmum of sn. The maxmum of sn occurs at the maxmum of sn, whch aan s 90º. Ht t straht up. 3. The ball hts the round when t = tf. The horzontal dsplacement from the launch pont to where the ball hts the round s called the rane (R). x t x R cost sn cos sn cos Ths can be rewrtten usn the dentt sn = sn cos, sn R (35 m/s) sn[(55 )] 9.8m/s 7 m What anle maxmzes the rane? Ths tme we want to fnd the maxmum of sn. The maxmum of sne occurs at 90º. Ths tme = 90º or = 45º. The anle requred for maxmum rane oer leel round s 45º. Also the rane s smmetrc about 45º. For some anle, and sn[ (45 )] sn(90 ) cos sn[ (45 )] sn(90 ) cos( ) cos f Lesson 4, pae 3
4 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons ) The rane for = 45º + s the same for = 45º. Another wa s to sa f the ranes are the same! (45 ) (45 ) Where s the ball at.0 seconds? Its horzontal poston s found usn Its ertcal poston s t 37.7 m x snt x t cost (35m/s) cos m a ( t) ( t) (35m/s)sn 55 (.0s) f s (9.8 m/s )(.0s) When s t at ths heht aan? There are man was to fnd ths. Frst, note that the tme of flht of the ball s 5.85 s from part. Snce the trajector s smmetrc, f t reaches ths heht.0 s after launch, t wll reach t aan.0 s before t lands, t 5.85s.00s 3.85s Lesson 4, pae 4
5 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons ) Another wa s to use the smmetr of the -component of the eloct. The - components of the eloctes at the same hehts hae the same mantudes but opposte sns. At.0 s f f a t sn t (35m/s)sn 55 (9.8m/s )(s) 9.07 m/s When s the speed 9.07 m/s? f f a sn t t t f 9.07 m/s (35m/s) sn m/s 3.85s sn Fnall, the worst wa s to just sole for t usn the quadratc formula, (9.8m/s )( t) (4.9 m/s )( t) (35m/s)sn 55 t 37.7 m 0 (8.67m/s) t 37.7 m 0 t snt 37.7 m (35m/s)sn 55 t b t ( 8.67) s, 3.86s a ( t) ( t) b 4ac a (8.67) (4.9) (9.8m/s )( t) 4(4.9)(37.7) The frst answer s when t reaches 37.7 m whle ascendn (we knew t would be.0 s), the second s when t reaches 37.7 m whle descendn. (I qut wrtn unts n the quadratc because t makes the equaton een more unweld.) Lesson 4, pae 5
6 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons ) 5. To fnd when the ball reaches 0 m we use the quadratc equaton aan, (9.8m/s )( t) (4.9 m/s )( t) (35m/s)sn 55 t 0m 0 (8.67m/s) t 0m 0 t snt 0m (35m/s)sn 55 t b t a ( t) b 4ac a ( 8.67) s, 5.04s ( t) (8.67) (4.9) Notce that the sum of these tmes s 5.85 s, the tme of flht. (9.8m/s )( t) 4(4.9)(0) Summar: Dered equatons for a projectle launched from leel round wth ntal eloct at an anle aboe the round: Tme of flht Tme to maxmum heht Maxmum heht Rane t f sn sn th h sn sn R t f If the round s not leel, for example thrown a ball from the top of a buldn, these equatons wll not appl (unless the ntal and fnal hehts are the same)! The projectle traels n a parabolc path as lon as we nelect ar resstance. The moton s smmetrc about the maxmum heht (the ertex of the parabola). Relate eloct s a reat example of addn ectors. Hae ou eer had ths happen to ou? Whle sttn n our car at a red traffc lht, the car besde ou slowl drfts forward. You mash on the brake to stop our car from rolln backwards, but our car s not mon. Lesson 4, pae 6
7 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons ) Wthn our enronment, there s no wa to dstnush between our car mon backwards and the car besdes ou mon forward. The eloct s relate. We need a reference frame (the traffc lht, for example) to defne who s mon. The tran moes at 0 m/s and Wanda can walk at m/s. How fast wll Gre see Wanda walk? Wanda s eloct relate to Gre s the sum of the eloct of the Wanda relate to the tran plus the eloct of tran relate to Gre. WG Notce the order of the subscrpts. We hae the Ts cancelln from the two terms on the rht. Ths equaton wll alwas hold, but how do we use t? What s our rule about ectors? WT WE DO NOT DEAL WITH VECTORS. WE DEAL WITH THEIR COMPONENTS. Take the x-component: TG WGx WTx TGx ( m/s) ( 0 m/s) m/s Gre sees Wanda walkn to the rht at m/s. What happens when she walks back to her seat? WGx WTx TGx ( m/s) ( 0 m/s) 9m/s Accordn to Gre, Wanda s walkn at 9 m/s to the rht. Lesson 4, pae 7
8 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons ) Hopefull, ths s prett eas. But what about ths? From Example 3.0. Jack wants to row drectl across the rer from the east shore to a pont on the west shore. The current 0.6 m/s and Jack can row at.6 m/s. What drecton must he pont the boat and what s hs eloct across the rer? The eloct of the rowboat relate to the shore s equal to the eloct of the rowboat relate to the water plus the eloct of the water relate to the shore. RS WS The rowboat s to head drectl to the west. Take components. RSx and x WSx RS WS The daram s the ke to soln relate eloct problems. For the x-component, RSx RS x WSx cos 0 cos The -component, RS 0 WS WS sn sn Lesson 4, pae 8 WS
9 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons ) Our unknowns are and RS. From the -component equaton, From the x-component equaton. WS sn WS 3.7 sn 0.6m/s.6 m/s RS cos m/s 0.56 (.6 m/s) cos 3.7 The boat must pont 3.7º N of W upstream. Its speed across the water s 0.99 m/s. Chapter 4 Force and Newton s Laws of Moton We can descrbe moton, but wh do thns moe? Forces: Objects nteract throuh forces. A force s a push or pull. Forces can be lon rane (rat, electrc, manetc, etc.) or contact (normal force, tenson, etc.). F Obousl, forces are ector quanttes snce ther effect depends on the drectons of the forces. The net force s the ector sum of all forces actn on an object. Lesson 4, pae 9
10 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons ) F net F F F F n A free-bod daram (FBD) s an essental tool for fndn the net force actn on an object. (See pae 96.) Draw the object n a smplfed wa Identf all the forces that are exerted on the object. Draw ector arrows representn all the forces on the object. Examples. Freel falln object.. Object hann from a rope. 3. Object sttn on a horzontal table. 4. Object sttn on a horzontal table ben pulled b a rope. T N N T W W W W Drawn the free-bod daram s the ke to soln problems. Newton s Frst Law (law of nerta): An object s eloct ector remans constant f and onl f the net force actn on the object s zero (pae 97). An object mon at constant eloct has no net force! A reolutonar dea. An object mon at constant eloct s sad to be n translatonal equlbrum. That eloct could be zero. Lesson 4, pae 0
11 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons ) Inerta s the resstance to chanes n eloct. Newton s Second law: The rate of chane of an object s eloct s proportonal to the net force actn on t and nersel proportonal to ts mass (pae 0). F m a Recall our rule: we neer deal wth ectors, we deal wth ther components. A far more useful form of Newton s second law wll be F x ma x F ma The left hand sde s suppled b the free-bod daram. The rht hand sde s suppled b our knowlede of the moton. The SI unt of force s the newton. N = k m/s. What s mass? Mass s a measure of nerta. Mass s not the same as weht. When an object s dropped t s pulled down b ts weht and ts acceleraton s downward. Appln Newton s second law es W Lesson 4, pae
12 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons ) F W ma m and the relatonshp between weht and mass s W = m. Newton s Thrd Law: In an nteracton between two objects, each object exerts a force on the other. These forces are equal n mantude and opposte n drecton (pae 03). If two objects A and B are exertn forces on each other, F BA A B F AB F AB F BA The forces are equal n mantude and opposte n drecton. Newton s Laws of Moton (paes 97-03). An object s eloct ector remans constant f and onl f the net force actn on the object s zero.. When a nonzero net force acts on an object, the object s eloct chanes. The object s acceleraton f proportonal to the net force actn on t and nersel proportonal to ts mass. F x max F ma 3. In an nteracton between two objects, each object exerts a force on the other. These forces are equal n mantude and opposte n drecton. F AB F BA Lesson 4, pae
Projectile Motion. Parabolic Motion curved motion in the shape of a parabola. In the y direction, the equation of motion has a t 2.
 Projectle Moton Phc Inentor Parabolc Moton cured oton n the hape of a parabola. In the drecton, the equaton of oton ha a t ter Projectle Moton the parabolc oton of an object, where the horzontal coponent
Projectle Moton Phc Inentor Parabolc Moton cured oton n the hape of a parabola. In the drecton, the equaton of oton ha a t ter Projectle Moton the parabolc oton of an object, where the horzontal coponent
Chapter 3 Motion in a Plane
 Chapter 3 Motion in a Plane Introduce ectors and scalars. Vectors hae direction as well as magnitude. The are represented b arrows. The arrow points in the direction of the ector and its length is related
Chapter 3 Motion in a Plane Introduce ectors and scalars. Vectors hae direction as well as magnitude. The are represented b arrows. The arrow points in the direction of the ector and its length is related
where v means the change in velocity, and t is the
 1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 4 MECHANICS (3) Ths lecture covers the eneral case of moton wth constant acceleraton and free fall (whch s one of the more mportant examples of moton wth constant acceleraton) n a more
1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 4 MECHANICS (3) Ths lecture covers the eneral case of moton wth constant acceleraton and free fall (whch s one of the more mportant examples of moton wth constant acceleraton) n a more
1 cos. where v v sin. Range Equations: for an object that lands at the same height at which it starts. v sin 2 i. t g. and. sin g
 SPH3UW Unt.5 Projectle Moton Pae 1 of 10 Note Phc Inventor Parabolc Moton curved oton n the hape of a parabola. In the drecton, the equaton of oton ha a t ter Projectle Moton the parabolc oton of an object,
SPH3UW Unt.5 Projectle Moton Pae 1 of 10 Note Phc Inventor Parabolc Moton curved oton n the hape of a parabola. In the drecton, the equaton of oton ha a t ter Projectle Moton the parabolc oton of an object,
GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SENIOR SECONDARY INTERVENTION PROGRAMME PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES)
 PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 1 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES) TOPIC 1: MECHANICS PROJECTILE MOTION Learner Note: Always draw a dagram of the stuaton and enter all the numercal alues onto your dagram. Remember to
PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 1 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES) TOPIC 1: MECHANICS PROJECTILE MOTION Learner Note: Always draw a dagram of the stuaton and enter all the numercal alues onto your dagram. Remember to
Physics 2A Chapter 3 HW Solutions
 Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
Name: PHYS 110 Dr. McGovern Spring 2018 Exam 1. Multiple Choice: Circle the answer that best evaluates the statement or completes the statement.
 Name: PHYS 110 Dr. McGoern Sprng 018 Exam 1 Multple Choce: Crcle the answer that best ealuates the statement or completes the statement. #1 - I the acceleraton o an object s negate, the object must be
Name: PHYS 110 Dr. McGoern Sprng 018 Exam 1 Multple Choce: Crcle the answer that best ealuates the statement or completes the statement. #1 - I the acceleraton o an object s negate, the object must be
Conservation of Energy
 Chapter 8 Conseraton o Ener 8.3 U + K = U + K mh + = m ( ) + m ( 3.5 ) = ( ) + F= m = 3. n+ m= m 3. n = m = m =.m 3 n =. 5. 9.8 m s =.98 N downward FIG. 8.3 (5. 3.) Δ A B 8.4 (a) K = W = W = m Δ h = m
Chapter 8 Conseraton o Ener 8.3 U + K = U + K mh + = m ( ) + m ( 3.5 ) = ( ) + F= m = 3. n+ m= m 3. n = m = m =.m 3 n =. 5. 9.8 m s =.98 N downward FIG. 8.3 (5. 3.) Δ A B 8.4 (a) K = W = W = m Δ h = m
Slide. King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 5: MOTION IN 1-D (PART 2) LECTURE NO.
 Slde Kng Saud Unersty College of Scence Physcs & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 5: MOTION IN 1-D (PART ) LECTURE NO. 6 THIS PRESENTATION HAS BEEN PREPARED BY: DR. NASSR S. ALZAYED Lecture
Slde Kng Saud Unersty College of Scence Physcs & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 5: MOTION IN 1-D (PART ) LECTURE NO. 6 THIS PRESENTATION HAS BEEN PREPARED BY: DR. NASSR S. ALZAYED Lecture
Problem While being compressed, A) What is the work done on it by gravity? B) What is the work done on it by the spring force?
 Problem 07-50 A 0.25 kg block s dropped on a relaed sprng that has a sprng constant o k 250.0 N/m (2.5 N/cm). The block becomes attached to the sprng and compresses t 0.12 m beore momentarl stoppng. Whle
Problem 07-50 A 0.25 kg block s dropped on a relaed sprng that has a sprng constant o k 250.0 N/m (2.5 N/cm). The block becomes attached to the sprng and compresses t 0.12 m beore momentarl stoppng. Whle
Chapter 5. Answers to Even Numbered Problems m kj. 6. (a) 900 J (b) (a) 31.9 J (b) 0 (c) 0 (d) 31.9 J. 10.
 Answers to Even Numbered Problems Chapter 5. 3.6 m 4..6 J 6. (a) 9 J (b).383 8. (a) 3.9 J (b) (c) (d) 3.9 J. 6 m s. (a) 68 J (b) 84 J (c) 5 J (d) 48 J (e) 5.64 m s 4. 9. J 6. (a). J (b) 5. m s (c) 6.3
Answers to Even Numbered Problems Chapter 5. 3.6 m 4..6 J 6. (a) 9 J (b).383 8. (a) 3.9 J (b) (c) (d) 3.9 J. 6 m s. (a) 68 J (b) 84 J (c) 5 J (d) 48 J (e) 5.64 m s 4. 9. J 6. (a). J (b) 5. m s (c) 6.3
Dynamics 4600:203 Homework 08 Due: March 28, Solution: We identify the displacements of the blocks A and B with the coordinates x and y,
 Dynamcs 46:23 Homework 8 Due: March 28, 28 Name: Please denote your answers clearly,.e., box n, star, etc., and wrte neatly. There are no ponts for small, messy, unreadable work... please use lots of paper.
Dynamcs 46:23 Homework 8 Due: March 28, 28 Name: Please denote your answers clearly,.e., box n, star, etc., and wrte neatly. There are no ponts for small, messy, unreadable work... please use lots of paper.
For the three forces. find: (a) the resultant force R~ (a) (b) the magnitude of the resultant force. Three coplanar forces, A
 WorkSHEE 8. Vector applcatons ame: or the three forces, and, fnd: the resultant force R R the mantude of the resultant force. R hree coplanar forces,, B and C have mantudes of 8, 6 and 9 respectvely. nd
WorkSHEE 8. Vector applcatons ame: or the three forces, and, fnd: the resultant force R R the mantude of the resultant force. R hree coplanar forces,, B and C have mantudes of 8, 6 and 9 respectvely. nd
Physics 207: Lecture 20. Today s Agenda Homework for Monday
 Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
First Law: A body at rest remains at rest, a body in motion continues to move at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force.
 Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
Chapter 3. r r. Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Revisited
 Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
Kinematics in 2-Dimensions. Projectile Motion
 Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.net.net.au/~rmne/ht/ht0.html#5 Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had
Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.net.net.au/~rmne/ht/ht0.html#5 Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had
Physics 105: Mechanics Lecture 13
 Physcs 05: Mechancs Lecture 3 Wenda Cao NJIT Physcs Department Momentum and Momentum Conseraton Momentum Impulse Conseraton o Momentum Collsons Lnear Momentum A new undamental quantty, lke orce, energy
Physcs 05: Mechancs Lecture 3 Wenda Cao NJIT Physcs Department Momentum and Momentum Conseraton Momentum Impulse Conseraton o Momentum Collsons Lnear Momentum A new undamental quantty, lke orce, energy
Supplemental Instruction sessions next week
 Homework #4 Wrtten homework due now Onlne homework due on Tue Mar 3 by 8 am Exam 1 Answer keys and scores wll be posted by end of the week Supplemental Instructon sessons next week Wednesday 8:45 10:00
Homework #4 Wrtten homework due now Onlne homework due on Tue Mar 3 by 8 am Exam 1 Answer keys and scores wll be posted by end of the week Supplemental Instructon sessons next week Wednesday 8:45 10:00
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Linear Momentum. Center of Mass.
 Lecture 6 Chapter 9 Physcs I 03.3.04 Lnear omentum. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.uml.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcssprng.html
Lecture 6 Chapter 9 Physcs I 03.3.04 Lnear omentum. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.uml.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcssprng.html
PHYSICS 203-NYA-05 MECHANICS
 PHYSICS 03-NYA-05 MECHANICS PROF. S.D. MANOLI PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY CHAMPLAIN - ST. LAWRENCE 790 NÉRÉE-TREMBLAY QUÉBEC, QC GV 4K TELEPHONE: 48.656.69 EXT. 449 EMAIL: smanol@slc.qc.ca WEBPAGE: http:/web.slc.qc.ca/smanol/
PHYSICS 03-NYA-05 MECHANICS PROF. S.D. MANOLI PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY CHAMPLAIN - ST. LAWRENCE 790 NÉRÉE-TREMBLAY QUÉBEC, QC GV 4K TELEPHONE: 48.656.69 EXT. 449 EMAIL: smanol@slc.qc.ca WEBPAGE: http:/web.slc.qc.ca/smanol/
From Newton s 2 nd Law: v v. The time rate of change of the linear momentum of a particle is equal to the net force acting on the particle.
 From Newton s 2 nd Law: F ma d dm ( ) m dt dt F d dt The tme rate of change of the lnear momentum of a artcle s equal to the net force actng on the artcle. Conseraton of Momentum +x The toy rocket n dee
From Newton s 2 nd Law: F ma d dm ( ) m dt dt F d dt The tme rate of change of the lnear momentum of a artcle s equal to the net force actng on the artcle. Conseraton of Momentum +x The toy rocket n dee
Physics 101 Lecture 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions
 Physcs 0 Lecture 9 Lnear Momentum and Collsons Dr. Al ÖVGÜN EMU Physcs Department www.aogun.com Lnear Momentum and Collsons q q q q q q q Conseraton o Energy Momentum Impulse Conseraton o Momentum -D Collsons
Physcs 0 Lecture 9 Lnear Momentum and Collsons Dr. Al ÖVGÜN EMU Physcs Department www.aogun.com Lnear Momentum and Collsons q q q q q q q Conseraton o Energy Momentum Impulse Conseraton o Momentum -D Collsons
Study Guide For Exam Two
 Study Gude For Exam Two Physcs 2210 Albretsen Updated: 08/02/2018 All Other Prevous Study Gudes Modules 01-06 Module 07 Work Work done by a constant force F over a dstance s : Work done by varyng force
Study Gude For Exam Two Physcs 2210 Albretsen Updated: 08/02/2018 All Other Prevous Study Gudes Modules 01-06 Module 07 Work Work done by a constant force F over a dstance s : Work done by varyng force
= 1.23 m/s 2 [W] Required: t. Solution:!t = = 17 m/s [W]! m/s [W] (two extra digits carried) = 2.1 m/s [W]
![= 1.23 m/s 2 [W] Required: t. Solution:!t = = 17 m/s [W]! m/s [W] (two extra digits carried) = 2.1 m/s [W] = 1.23 m/s 2 [W] Required: t. Solution:!t = = 17 m/s [W]! m/s [W] (two extra digits carried) = 2.1 m/s [W]](/thumbs/78/76802454.jpg) Secton 1.3: Acceleraton Tutoral 1 Practce, page 24 1. Gven: 0 m/s; 15.0 m/s [S]; t 12.5 s Requred: Analyss: a av v t v f v t a v av f v t 15.0 m/s [S] 0 m/s 12.5 s 15.0 m/s [S] 12.5 s 1.20 m/s 2 [S] Statement:
Secton 1.3: Acceleraton Tutoral 1 Practce, page 24 1. Gven: 0 m/s; 15.0 m/s [S]; t 12.5 s Requred: Analyss: a av v t v f v t a v av f v t 15.0 m/s [S] 0 m/s 12.5 s 15.0 m/s [S] 12.5 s 1.20 m/s 2 [S] Statement:
Physics 40 HW #4 Chapter 4 Key NEATNESS COUNTS! Solve but do not turn in the following problems from Chapter 4 Knight
 Physcs 40 HW #4 Chapter 4 Key NEATNESS COUNTS! Solve but do not turn n the ollowng problems rom Chapter 4 Knght Conceptual Questons: 8, 0, ; 4.8. Anta s approachng ball and movng away rom where ball was
Physcs 40 HW #4 Chapter 4 Key NEATNESS COUNTS! Solve but do not turn n the ollowng problems rom Chapter 4 Knght Conceptual Questons: 8, 0, ; 4.8. Anta s approachng ball and movng away rom where ball was
Chapter 2. Pythagorean Theorem. Right Hand Rule. Position. Distance Formula
 Chapter Moton n One Dmenson Cartesan Coordnate System The most common coordnate system or representng postons n space s one based on three perpendcular spatal axes generally desgnated x, y, and z. Any
Chapter Moton n One Dmenson Cartesan Coordnate System The most common coordnate system or representng postons n space s one based on three perpendcular spatal axes generally desgnated x, y, and z. Any
The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Objective To use the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra to solve polynomial equations with complex solutions
 5-6 The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Content Standards N.CN.7 Solve quadratc equatons wth real coeffcents that have comple solutons. N.CN.8 Etend polnomal denttes to the comple numbers. Also N.CN.9,
5-6 The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Content Standards N.CN.7 Solve quadratc equatons wth real coeffcents that have comple solutons. N.CN.8 Etend polnomal denttes to the comple numbers. Also N.CN.9,
Momentum. Momentum. Impulse. Momentum and Collisions
 Momentum Momentum and Collsons From Newton s laws: orce must be present to change an object s elocty (speed and/or drecton) Wsh to consder eects o collsons and correspondng change n elocty Gol ball ntally
Momentum Momentum and Collsons From Newton s laws: orce must be present to change an object s elocty (speed and/or drecton) Wsh to consder eects o collsons and correspondng change n elocty Gol ball ntally
Physics 207 Lecture 6
 Physcs 207 Lecture 6 Agenda: Physcs 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 25 Chapter 4 Frames of reference Chapter 5 ewton s Law Mass Inerta s (contact and non-contact) Frcton (a external force that opposes moton) Free
Physcs 207 Lecture 6 Agenda: Physcs 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 25 Chapter 4 Frames of reference Chapter 5 ewton s Law Mass Inerta s (contact and non-contact) Frcton (a external force that opposes moton) Free
EMU Physics Department.
 Physcs 0 Lecture 9 Lnear Momentum and Collsons Assst. Pro. Dr. Al ÖVGÜN EMU Physcs Department www.aogun.com Lnear Momentum q Conseraton o Energy q Momentum q Impulse q Conseraton o Momentum q -D Collsons
Physcs 0 Lecture 9 Lnear Momentum and Collsons Assst. Pro. Dr. Al ÖVGÜN EMU Physcs Department www.aogun.com Lnear Momentum q Conseraton o Energy q Momentum q Impulse q Conseraton o Momentum q -D Collsons
Motion in One Dimension
 Moton n One Dmenson Speed ds tan ce traeled Aerage Speed tme of trael Mr. Wolf dres hs car on a long trp to a physcs store. Gen the dstance and tme data for hs trp, plot a graph of hs dstance ersus tme.
Moton n One Dmenson Speed ds tan ce traeled Aerage Speed tme of trael Mr. Wolf dres hs car on a long trp to a physcs store. Gen the dstance and tme data for hs trp, plot a graph of hs dstance ersus tme.
Linear Momentum. Center of Mass.
 Lecture 16 Chapter 9 Physcs I 11.06.2013 Lnear oentu. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.ul.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.ul.edu/danylov2013/physcs1fall.htl
Lecture 16 Chapter 9 Physcs I 11.06.2013 Lnear oentu. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.ul.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.ul.edu/danylov2013/physcs1fall.htl
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 11
 Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
Week 11: Chapter 11. The Vector Product. The Vector Product Defined. The Vector Product and Torque. More About the Vector Product
 The Vector Product Week 11: Chapter 11 Angular Momentum There are nstances where the product of two vectors s another vector Earler we saw where the product of two vectors was a scalar Ths was called the
The Vector Product Week 11: Chapter 11 Angular Momentum There are nstances where the product of two vectors s another vector Earler we saw where the product of two vectors was a scalar Ths was called the
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 Newton s Laws of Moton 4.1 Forces and Interactons Fundamental forces. There are four types of fundamental forces: electromagnetc, weak, strong and gravtatonal. The frst two had been successfully
Chapter 4 Newton s Laws of Moton 4.1 Forces and Interactons Fundamental forces. There are four types of fundamental forces: electromagnetc, weak, strong and gravtatonal. The frst two had been successfully
Physics for Scientists and Engineers. Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum
 Physcs or Scentsts and Engneers Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum Sprng, 008 Ho Jung Pak Lnear Momentum Lnear momentum o an object o mass m movng wth a velocty v s dened to be p mv Momentum and lnear momentum
Physcs or Scentsts and Engneers Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum Sprng, 008 Ho Jung Pak Lnear Momentum Lnear momentum o an object o mass m movng wth a velocty v s dened to be p mv Momentum and lnear momentum
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. Principle of Virtual Work-1
 P. Guterrez 1 Introducton Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs Prncple of Vrtual Work The frst varatonal prncple we encounter n mechancs s the prncple of vrtual work. It establshes the equlbrum condton of a mechancal
P. Guterrez 1 Introducton Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs Prncple of Vrtual Work The frst varatonal prncple we encounter n mechancs s the prncple of vrtual work. It establshes the equlbrum condton of a mechancal
PHYS 2211L - Principles of Physics Laboratory I
 PHYS L - Prncples of Physcs Laboratory I Laboratory Adanced Sheet Ballstc Pendulu. Objecte. The objecte of ths laboratory s to use the ballstc pendulu to predct the ntal elocty of a projectle usn the prncples
PHYS L - Prncples of Physcs Laboratory I Laboratory Adanced Sheet Ballstc Pendulu. Objecte. The objecte of ths laboratory s to use the ballstc pendulu to predct the ntal elocty of a projectle usn the prncples
total If no external forces act, the total linear momentum of the system is conserved. This occurs in collisions and explosions.
 Lesson 0: Collsons, Rotatonal netc Energy, Torque, Center o Graty (Sectons 7.8 Last te we used ewton s second law to deelop the pulse-oentu theore. In words, the theore states that the change n lnear oentu
Lesson 0: Collsons, Rotatonal netc Energy, Torque, Center o Graty (Sectons 7.8 Last te we used ewton s second law to deelop the pulse-oentu theore. In words, the theore states that the change n lnear oentu
Section 8.1 Exercises
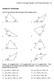 Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
ENGN 40 Dynamics and Vibrations Homework # 7 Due: Friday, April 15
 NGN 40 ynamcs and Vbratons Homework # 7 ue: Frday, Aprl 15 1. Consder a concal hostng drum used n the mnng ndustry to host a mass up/down. A cable of dameter d has the mass connected at one end and s wound/unwound
NGN 40 ynamcs and Vbratons Homework # 7 ue: Frday, Aprl 15 1. Consder a concal hostng drum used n the mnng ndustry to host a mass up/down. A cable of dameter d has the mass connected at one end and s wound/unwound
Period & Frequency. Work and Energy. Methods of Energy Transfer: Energy. Work-KE Theorem 3/4/16. Ranking: Which has the greatest kinetic energy?
 Perod & Frequency Perod (T): Tme to complete one ull rotaton Frequency (): Number o rotatons completed per second. = 1/T, T = 1/ v = πr/t Work and Energy Work: W = F!d (pcks out parallel components) F
Perod & Frequency Perod (T): Tme to complete one ull rotaton Frequency (): Number o rotatons completed per second. = 1/T, T = 1/ v = πr/t Work and Energy Work: W = F!d (pcks out parallel components) F
Modeling of Dynamic Systems
 Modelng of Dynamc Systems Ref: Control System Engneerng Norman Nse : Chapters & 3 Chapter objectves : Revew the Laplace transform Learn how to fnd a mathematcal model, called a transfer functon Learn how
Modelng of Dynamc Systems Ref: Control System Engneerng Norman Nse : Chapters & 3 Chapter objectves : Revew the Laplace transform Learn how to fnd a mathematcal model, called a transfer functon Learn how
PHYS 1443 Section 003 Lecture #17
 PHYS 144 Secton 00 ecture #17 Wednesda, Oct. 9, 00 1. Rollng oton of a Rgd od. Torque. oment of Inerta 4. Rotatonal Knetc Energ 5. Torque and Vector Products Remember the nd term eam (ch 6 11), onda, Nov.!
PHYS 144 Secton 00 ecture #17 Wednesda, Oct. 9, 00 1. Rollng oton of a Rgd od. Torque. oment of Inerta 4. Rotatonal Knetc Energ 5. Torque and Vector Products Remember the nd term eam (ch 6 11), onda, Nov.!
Chapter 11: Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11: ngular Momentum Statc Equlbrum In Chap. 4 we studed the equlbrum of pontobjects (mass m) wth the applcaton of Newton s aws F 0 F x y, 0 Therefore, no lnear (translatonal) acceleraton, a0 For
Chapter 11: ngular Momentum Statc Equlbrum In Chap. 4 we studed the equlbrum of pontobjects (mass m) wth the applcaton of Newton s aws F 0 F x y, 0 Therefore, no lnear (translatonal) acceleraton, a0 For
Spring 2002 Lecture #13
 44-50 Sprng 00 ecture # Dr. Jaehoon Yu. Rotatonal Energy. Computaton of oments of nerta. Parallel-as Theorem 4. Torque & Angular Acceleraton 5. Work, Power, & Energy of Rotatonal otons Remember the md-term
44-50 Sprng 00 ecture # Dr. Jaehoon Yu. Rotatonal Energy. Computaton of oments of nerta. Parallel-as Theorem 4. Torque & Angular Acceleraton 5. Work, Power, & Energy of Rotatonal otons Remember the md-term
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Analyss Model: Nonsolated System (Angular Momentum) Angular Momentum of a Rotatng Rgd Object Analyss Model: Isolated System (Angular Momentum) Angular Momentum of a Partcle
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Analyss Model: Nonsolated System (Angular Momentum) Angular Momentum of a Rotatng Rgd Object Analyss Model: Isolated System (Angular Momentum) Angular Momentum of a Partcle
SCALARS AND VECTORS All physical quantities in engineering mechanics are measured using either scalars or vectors.
 SCALARS AND ECTORS All phscal uanttes n engneerng mechancs are measured usng ether scalars or vectors. Scalar. A scalar s an postve or negatve phscal uantt that can be completel specfed b ts magntude.
SCALARS AND ECTORS All phscal uanttes n engneerng mechancs are measured usng ether scalars or vectors. Scalar. A scalar s an postve or negatve phscal uantt that can be completel specfed b ts magntude.
Week 6, Chapter 7 Sect 1-5
 Week 6, Chapter 7 Sect 1-5 Work and Knetc Energy Lecture Quz The frctonal force of the floor on a large sutcase s least when the sutcase s A.pushed by a force parallel to the floor. B.dragged by a force
Week 6, Chapter 7 Sect 1-5 Work and Knetc Energy Lecture Quz The frctonal force of the floor on a large sutcase s least when the sutcase s A.pushed by a force parallel to the floor. B.dragged by a force
Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 ME 270 Sprng 2017 Exam 1 NAME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: Instructor s Name
ME 270 Sprng 2017 Exam 1 NAME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: Instructor s Name
Physics 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1
 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Unversty of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Course Informaton: Lab report # 3. Exam # 2. Mult-Partcle
Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Unversty of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Course Informaton: Lab report # 3. Exam # 2. Mult-Partcle
Chapter 12 Equilibrium & Elasticity
 Chapter 12 Equlbrum & Elastcty If there s a net force, an object wll experence a lnear acceleraton. (perod, end of story!) If there s a net torque, an object wll experence an angular acceleraton. (perod,
Chapter 12 Equlbrum & Elastcty If there s a net force, an object wll experence a lnear acceleraton. (perod, end of story!) If there s a net torque, an object wll experence an angular acceleraton. (perod,
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Homework 7: Rigid Body Kinematics
 N40: ynamcs and Vbratons Homewor 7: Rgd Body Knematcs School of ngneerng Brown Unversty 1. In the fgure below, bar AB rotates counterclocwse at 4 rad/s. What are the angular veloctes of bars BC and C?.
N40: ynamcs and Vbratons Homewor 7: Rgd Body Knematcs School of ngneerng Brown Unversty 1. In the fgure below, bar AB rotates counterclocwse at 4 rad/s. What are the angular veloctes of bars BC and C?.
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Homework 4: Work, Energy and Linear Momentum Due Friday March 1 st
 EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
Part C Dynamics and Statics of Rigid Body. Chapter 5 Rotation of a Rigid Body About a Fixed Axis
 Part C Dynamcs and Statcs of Rgd Body Chapter 5 Rotaton of a Rgd Body About a Fxed Axs 5.. Rotatonal Varables 5.. Rotaton wth Constant Angular Acceleraton 5.3. Knetc Energy of Rotaton, Rotatonal Inerta
Part C Dynamcs and Statcs of Rgd Body Chapter 5 Rotaton of a Rgd Body About a Fxed Axs 5.. Rotatonal Varables 5.. Rotaton wth Constant Angular Acceleraton 5.3. Knetc Energy of Rotaton, Rotatonal Inerta
Angular Momentum and Fixed Axis Rotation. 8.01t Nov 10, 2004
 Angular Momentum and Fxed Axs Rotaton 8.01t Nov 10, 2004 Dynamcs: Translatonal and Rotatonal Moton Translatonal Dynamcs Total Force Torque Angular Momentum about Dynamcs of Rotaton F ext Momentum of a
Angular Momentum and Fxed Axs Rotaton 8.01t Nov 10, 2004 Dynamcs: Translatonal and Rotatonal Moton Translatonal Dynamcs Total Force Torque Angular Momentum about Dynamcs of Rotaton F ext Momentum of a
Start with the equation of motion for a linear multi-degree of freedom system with base ground excitation:
 SE 80 Earthquake Enneern November 3, 00 STEP-BY-STEP PROCEDURE FOR SETTING UP A SPREADSHEET FOR USING NEWMARK S METHOD AND MODAL ANALYSIS TO SOLVE FOR THE RESPONSE OF A MULTI-DEGREE OF FREEDOM (MDOF) SYSTEM
SE 80 Earthquake Enneern November 3, 00 STEP-BY-STEP PROCEDURE FOR SETTING UP A SPREADSHEET FOR USING NEWMARK S METHOD AND MODAL ANALYSIS TO SOLVE FOR THE RESPONSE OF A MULTI-DEGREE OF FREEDOM (MDOF) SYSTEM
Physics 207 Lecture 13. Lecture 13
 Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Goals: Lecture 3 Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Defne Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Develop and explot conservaton of energy prncple n problem
Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Goals: Lecture 3 Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Defne Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Develop and explot conservaton of energy prncple n problem
Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 NME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem n the space
NME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem n the space
11. Dynamics in Rotating Frames of Reference
 Unversty of Rhode Island DgtalCommons@URI Classcal Dynamcs Physcs Course Materals 2015 11. Dynamcs n Rotatng Frames of Reference Gerhard Müller Unversty of Rhode Island, gmuller@ur.edu Creatve Commons
Unversty of Rhode Island DgtalCommons@URI Classcal Dynamcs Physcs Course Materals 2015 11. Dynamcs n Rotatng Frames of Reference Gerhard Müller Unversty of Rhode Island, gmuller@ur.edu Creatve Commons
Prof. Dr. I. Nasser T /16/2017
 Pro. Dr. I. Nasser T-171 10/16/017 Chapter Part 1 Moton n one dmenson Sectons -,, 3, 4, 5 - Moton n 1 dmenson We le n a 3-dmensonal world, so why bother analyzng 1-dmensonal stuatons? Bascally, because
Pro. Dr. I. Nasser T-171 10/16/017 Chapter Part 1 Moton n one dmenson Sectons -,, 3, 4, 5 - Moton n 1 dmenson We le n a 3-dmensonal world, so why bother analyzng 1-dmensonal stuatons? Bascally, because
Physics 207: Lecture 27. Announcements
 Physcs 07: ecture 7 Announcements ake-up labs are ths week Fnal hwk assgned ths week, fnal quz next week Revew sesson on Thursday ay 9, :30 4:00pm, Here Today s Agenda Statcs recap Beam & Strngs» What
Physcs 07: ecture 7 Announcements ake-up labs are ths week Fnal hwk assgned ths week, fnal quz next week Revew sesson on Thursday ay 9, :30 4:00pm, Here Today s Agenda Statcs recap Beam & Strngs» What
PHYS 1443 Section 004 Lecture #12 Thursday, Oct. 2, 2014
 PHYS 1443 Secton 004 Lecture #1 Thursday, Oct., 014 Work-Knetc Energy Theorem Work under rcton Potental Energy and the Conservatve Force Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Conservaton o
PHYS 1443 Secton 004 Lecture #1 Thursday, Oct., 014 Work-Knetc Energy Theorem Work under rcton Potental Energy and the Conservatve Force Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Conservaton o
Physics 207, Lecture 13, Oct. 15. Energy
 Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Physcs 07, Lecture 3, Oct. 5 Goals: Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Dene Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Deelop and explot conseraton o energy prncple
Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Physcs 07, Lecture 3, Oct. 5 Goals: Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Dene Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Deelop and explot conseraton o energy prncple
Dynamics of Rotational Motion
 Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton Torque: the rotatonal analogue of force Torque = force x moment arm = Fl moment arm = perpendcular dstance through whch the force acts a.k.a. leer arm l F l F l F l F = Fl =
Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton Torque: the rotatonal analogue of force Torque = force x moment arm = Fl moment arm = perpendcular dstance through whch the force acts a.k.a. leer arm l F l F l F l F = Fl =
Physics 201, Lecture 4. Vectors and Scalars. Chapters Covered q Chapter 1: Physics and Measurement.
 Phscs 01, Lecture 4 Toda s Topcs n Vectors chap 3) n Scalars and Vectors n Vector ddton ule n Vector n a Coordnator Sstem n Decomposton of a Vector n Epected from prevew: n Scalars and Vectors, Vector
Phscs 01, Lecture 4 Toda s Topcs n Vectors chap 3) n Scalars and Vectors n Vector ddton ule n Vector n a Coordnator Sstem n Decomposton of a Vector n Epected from prevew: n Scalars and Vectors, Vector
Physics 201 Lecture 4
 Phscs 1 Lectue 4 ltoda: hapte 3 Lectue 4 v Intoduce scalas and vectos v Peom basc vecto aleba (addton and subtacton) v Inteconvet between atesan & Pola coodnates Stat n nteestn 1D moton poblem: ace 9.8
Phscs 1 Lectue 4 ltoda: hapte 3 Lectue 4 v Intoduce scalas and vectos v Peom basc vecto aleba (addton and subtacton) v Inteconvet between atesan & Pola coodnates Stat n nteestn 1D moton poblem: ace 9.8
Gravitational Acceleration: A case of constant acceleration (approx. 2 hr.) (6/7/11)
 Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Chapter 11 Torque and Angular Momentum
 Chapter Torque and Angular Momentum I. Torque II. Angular momentum - Defnton III. Newton s second law n angular form IV. Angular momentum - System of partcles - Rgd body - Conservaton I. Torque - Vector
Chapter Torque and Angular Momentum I. Torque II. Angular momentum - Defnton III. Newton s second law n angular form IV. Angular momentum - System of partcles - Rgd body - Conservaton I. Torque - Vector
Week 9 Chapter 10 Section 1-5
 Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Homework Key #7 - Phy 375R
 HMWK7-75R.nb Homewor Ke #7 - Ph 75R Problem #: See Ke for Homewor # Problem #: Transform the lne element... The nverse transformaton s t' = ÅÅÅÅ t tanh- ÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅ + ÅÅÅÅÅ ' = $%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
HMWK7-75R.nb Homewor Ke #7 - Ph 75R Problem #: See Ke for Homewor # Problem #: Transform the lne element... The nverse transformaton s t' = ÅÅÅÅ t tanh- ÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅÅ + ÅÅÅÅÅ ' = $%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
Lesson 3: Free fall, Vectors, Motion in a plane (sections )
 Lesson 3: Free fall, Vectors, Motion in a plane (sections.6-3.5) Last time we looked at position s. time and acceleration s. time graphs. Since the instantaneous elocit is lim t 0 t the (instantaneous)
Lesson 3: Free fall, Vectors, Motion in a plane (sections.6-3.5) Last time we looked at position s. time and acceleration s. time graphs. Since the instantaneous elocit is lim t 0 t the (instantaneous)
IX Mechanics of Rigid Bodies: Planar Motion
 X Mechancs of Rd Bodes: Panar Moton Center of Mass of a Rd Bod Rotaton of a Rd Bod About a Fed As Moent of nerta Penduu, A Genera heore Concernn Anuar Moentu puse and Coson nvovn Rd Bodes. Rd bod: dea
X Mechancs of Rd Bodes: Panar Moton Center of Mass of a Rd Bod Rotaton of a Rd Bod About a Fed As Moent of nerta Penduu, A Genera heore Concernn Anuar Moentu puse and Coson nvovn Rd Bodes. Rd bod: dea
Use these variables to select a formula. x = t Average speed = 100 m/s = distance / time t = x/v = ~2 m / 100 m/s = 0.02 s or 20 milliseconds
 The speed o a nere mpulse n the human body s about 100 m/s. I you accdentally stub your toe n the dark, estmatethe tme t takes the nere mpulse to trael to your bran. Tps: pcture, poste drecton, and lst
The speed o a nere mpulse n the human body s about 100 m/s. I you accdentally stub your toe n the dark, estmatethe tme t takes the nere mpulse to trael to your bran. Tps: pcture, poste drecton, and lst
Rigid body simulation
 Rgd bod smulaton Rgd bod smulaton Once we consder an object wth spacal etent, partcle sstem smulaton s no longer suffcent Problems Problems Unconstraned sstem rotatonal moton torques and angular momentum
Rgd bod smulaton Rgd bod smulaton Once we consder an object wth spacal etent, partcle sstem smulaton s no longer suffcent Problems Problems Unconstraned sstem rotatonal moton torques and angular momentum
The equation of motion of a dynamical system is given by a set of differential equations. That is (1)
 Dynamcal Systems Many engneerng and natural systems are dynamcal systems. For example a pendulum s a dynamcal system. State l The state of the dynamcal system specfes t condtons. For a pendulum n the absence
Dynamcal Systems Many engneerng and natural systems are dynamcal systems. For example a pendulum s a dynamcal system. State l The state of the dynamcal system specfes t condtons. For a pendulum n the absence
Please initial the statement below to show that you have read it
 EN40: Dynamcs and Vbratons Mdterm Examnaton Thursday March 5 009 Dvson of Engneerng rown Unversty NME: Isaac Newton General Instructons No collaboraton of any knd s permtted on ths examnaton. You may brng
EN40: Dynamcs and Vbratons Mdterm Examnaton Thursday March 5 009 Dvson of Engneerng rown Unversty NME: Isaac Newton General Instructons No collaboraton of any knd s permtted on ths examnaton. You may brng
Physics 4B. A positive value is obtained, so the current is counterclockwise around the circuit.
 Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
So far: simple (planar) geometries
 Physcs 06 ecture 5 Torque and Angular Momentum as Vectors SJ 7thEd.: Chap. to 3 Rotatonal quanttes as vectors Cross product Torque epressed as a vector Angular momentum defned Angular momentum as a vector
Physcs 06 ecture 5 Torque and Angular Momentum as Vectors SJ 7thEd.: Chap. to 3 Rotatonal quanttes as vectors Cross product Torque epressed as a vector Angular momentum defned Angular momentum as a vector
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 2
 PHYSICS 31 Revew problems for mdterm Topc 5: Energy and Work and Power Topc 6: Momentum and Collsons Topc 7: Oscllatons (sprng and pendulum) Topc 8: Rotatonal Moton The nd exam wll be Wednesday October
PHYSICS 31 Revew problems for mdterm Topc 5: Energy and Work and Power Topc 6: Momentum and Collsons Topc 7: Oscllatons (sprng and pendulum) Topc 8: Rotatonal Moton The nd exam wll be Wednesday October
Physics 512. Motion Graphs Review
 Physics 512 Mr. Greenberg Name Test 1-2 Review Motion Graphs Review Type of Motion on a position vs. time graph on a velocity vs. time graph on an acceleration vs. time graph At Rest Moving forward at
Physics 512 Mr. Greenberg Name Test 1-2 Review Motion Graphs Review Type of Motion on a position vs. time graph on a velocity vs. time graph on an acceleration vs. time graph At Rest Moving forward at
WYSE Academic Challenge 2004 State Finals Physics Solution Set
 WYSE Acaemc Challenge 00 State nals Physcs Soluton Set. Answer: c. Ths s the enton o the quantty acceleraton.. Answer: b. Pressure s orce per area. J/m N m/m N/m, unts o orce per area.. Answer: e. Aerage
WYSE Acaemc Challenge 00 State nals Physcs Soluton Set. Answer: c. Ths s the enton o the quantty acceleraton.. Answer: b. Pressure s orce per area. J/m N m/m N/m, unts o orce per area.. Answer: e. Aerage
Chapter 8. Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
 Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton of Energy In ths chapter we wll ntroduce the followng concepts: Potental Energy Conservatve and non-conservatve forces Mechancal Energy Conservaton of Mechancal
Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton of Energy In ths chapter we wll ntroduce the followng concepts: Potental Energy Conservatve and non-conservatve forces Mechancal Energy Conservaton of Mechancal
Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: Instructor s Name and Secton: (Crcle Your Secton) Sectons:
Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: Instructor s Name and Secton: (Crcle Your Secton) Sectons:
Page 1. Clicker Question 9: Physics 131: Lecture 15. Today s Agenda. Clicker Question 9: Energy. Energy is Conserved.
 Physcs 3: Lecture 5 Today s Agenda Intro to Conseraton o Energy Intro to some derent knds o energy Knetc Potental Denton o Mechancal Energy Conseraton o Mechancal Energy Conserate orces Examples Pendulum
Physcs 3: Lecture 5 Today s Agenda Intro to Conseraton o Energy Intro to some derent knds o energy Knetc Potental Denton o Mechancal Energy Conseraton o Mechancal Energy Conserate orces Examples Pendulum
AP Physics 1 & 2 Summer Assignment
 AP Physcs 1 & 2 Summer Assgnment AP Physcs 1 requres an exceptonal profcency n algebra, trgonometry, and geometry. It was desgned by a select group of college professors and hgh school scence teachers
AP Physcs 1 & 2 Summer Assgnment AP Physcs 1 requres an exceptonal profcency n algebra, trgonometry, and geometry. It was desgned by a select group of college professors and hgh school scence teachers
CHAPTER 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 HAPTER 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Solution Guide to WebAssign Problems 3.1 [] The truck has a displacement of 18 + (16) blocks north and 1 blocks east. The resultant has a magnitude of +
HAPTER 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Solution Guide to WebAssign Problems 3.1 [] The truck has a displacement of 18 + (16) blocks north and 1 blocks east. The resultant has a magnitude of +
Momentum and Collisions. Rosendo Physics 12-B
 Moentu and Collsons Rosendo Physcs -B Conseraton o Energy Moentu Ipulse Conseraton o Moentu -D Collsons -D Collsons The Center o Mass Lnear Moentu and Collsons February 7, 08 Conseraton o Energy D E =
Moentu and Collsons Rosendo Physcs -B Conseraton o Energy Moentu Ipulse Conseraton o Moentu -D Collsons -D Collsons The Center o Mass Lnear Moentu and Collsons February 7, 08 Conseraton o Energy D E =
Rotational Dynamics. Physics 1425 Lecture 19. Michael Fowler, UVa
 Rotatonal Dynamcs Physcs 1425 Lecture 19 Mchael Fowler, UVa Rotatonal Dynamcs Newton s Frst Law: a rotatng body wll contnue to rotate at constant angular velocty as long as there s no torque actng on t.
Rotatonal Dynamcs Physcs 1425 Lecture 19 Mchael Fowler, UVa Rotatonal Dynamcs Newton s Frst Law: a rotatng body wll contnue to rotate at constant angular velocty as long as there s no torque actng on t.
Page 1. SPH4U: Lecture 7. New Topic: Friction. Today s Agenda. Surface Friction... Surface Friction...
 SPH4U: Lecture 7 Today s Agenda rcton What s t? Systeatc catagores of forces How do we characterze t? Model of frcton Statc & Knetc frcton (knetc = dynac n soe languages) Soe probles nvolvng frcton ew
SPH4U: Lecture 7 Today s Agenda rcton What s t? Systeatc catagores of forces How do we characterze t? Model of frcton Statc & Knetc frcton (knetc = dynac n soe languages) Soe probles nvolvng frcton ew
MATH 5630: Discrete Time-Space Model Hung Phan, UMass Lowell March 1, 2018
 MATH 5630: Dscrete Tme-Space Model Hung Phan, UMass Lowell March, 08 Newton s Law of Coolng Consder the coolng of a well strred coffee so that the temperature does not depend on space Newton s law of collng
MATH 5630: Dscrete Tme-Space Model Hung Phan, UMass Lowell March, 08 Newton s Law of Coolng Consder the coolng of a well strred coffee so that the temperature does not depend on space Newton s law of collng
Linear Momentum. Equation 1
 Lnear Momentum OBJECTIVE Obsere collsons between two carts, testng or the conseraton o momentum. Measure energy changes durng derent types o collsons. Classy collsons as elastc, nelastc, or completely
Lnear Momentum OBJECTIVE Obsere collsons between two carts, testng or the conseraton o momentum. Measure energy changes durng derent types o collsons. Classy collsons as elastc, nelastc, or completely
Physics 53. Rotational Motion 3. Sir, I have found you an argument, but I am not obliged to find you an understanding.
 Physcs 53 Rotatonal Moton 3 Sr, I have found you an argument, but I am not oblged to fnd you an understandng. Samuel Johnson Angular momentum Wth respect to rotatonal moton of a body, moment of nerta plays
Physcs 53 Rotatonal Moton 3 Sr, I have found you an argument, but I am not oblged to fnd you an understandng. Samuel Johnson Angular momentum Wth respect to rotatonal moton of a body, moment of nerta plays
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #15
 PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #15 Monday, March 18, 013 Work wth rcton Potental Energy Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Mechancal Energy Conservaton Announcements Mdterm comprehensve exam
PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #15 Monday, March 18, 013 Work wth rcton Potental Energy Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Mechancal Energy Conservaton Announcements Mdterm comprehensve exam
Pre-Calculus Summer Assignment
 Pre-Calculus Summer Assgnment Dear Future Pre-Calculus Student, Congratulatons on our successful completon of Algebra! Below ou wll fnd the summer assgnment questons. It s assumed that these concepts,
Pre-Calculus Summer Assgnment Dear Future Pre-Calculus Student, Congratulatons on our successful completon of Algebra! Below ou wll fnd the summer assgnment questons. It s assumed that these concepts,
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #16
 PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #16 Monday, Mar. 4, 008 Potental Energy Conservatve and Non-conservatve Forces Conservaton o Mechancal Energy Power Today s homework s homework #8, due 9pm, Monday, Mar. 31!!
PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #16 Monday, Mar. 4, 008 Potental Energy Conservatve and Non-conservatve Forces Conservaton o Mechancal Energy Power Today s homework s homework #8, due 9pm, Monday, Mar. 31!!
4. The diagram below represents two concurrent forces.
 1. Two 20.-newton forces act concurrently on an object. What angle between these forces will produce a resultant force with the greatest magnitude? A) 0º B) 45º C) 90.º D) 180.º 2. Two forces act concurrently
1. Two 20.-newton forces act concurrently on an object. What angle between these forces will produce a resultant force with the greatest magnitude? A) 0º B) 45º C) 90.º D) 180.º 2. Two forces act concurrently
SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2011/2012 DYNAMICS ME247 DR. N.D.D. MICHÉ
 s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING ND MTHEMTICS SEMESTER EXMINTIONS 011/01 DYNMICS ME47 DR. N.D.D. MICHÉ Tme allowed: THREE hours nswer: ny FOUR from SIX questons Each queston carres 5 marks Ths s a CLOSED-BOOK
s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING ND MTHEMTICS SEMESTER EXMINTIONS 011/01 DYNMICS ME47 DR. N.D.D. MICHÉ Tme allowed: THREE hours nswer: ny FOUR from SIX questons Each queston carres 5 marks Ths s a CLOSED-BOOK
