Recitation: Energy, Phys Energies. 1.2 Three stones. 1. Energy. 1. An acorn falling from an oak tree onto the sidewalk.
|
|
|
- Pierce Walsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rectaton: Energy, Phys 207. Energy. Energes. An acorn fallng from an oak tree onto the sdewalk. The acorn ntal has gravtatonal potental energy. As t falls, t converts ths energy to knetc. When t hts the ground, the knetc energy s converted nto heat, and vbratonal energy. 2. A baseball durng ts trajectory from home plate to over the rght feld fence. The baseball has knetc energy mmedately after t s ht by the bat. A porton of the knetc energy s transformed nto potental as t rses. Then as t falls back towards the ground, the potental energy s converted back to knetc. 3. A car starts from rest then accelerates to a velocty There s gas n the car's tank. Ths s energy stored n the hydrocarbons n the gas. Combuston of gas releases energy, whch s transformed nto both knetc energy of the car, usng the mechansms n the motor, as well as heat and sound. 4. You eat a plate of spaghett then run up a hll the next day There s chemcal energy stored n the chemcal bonds of the pasta. Your body converts ths to heat, and also knetc energy of your movng lmbs. Ths knetc energy s then turned nto gravtatonal potental as you clmb the hll. 5. A rocket s launched nto orbt There s chemcal energy that s stored n the rocket fuel. Ths s converted nto knetc energy of the movng rocket. As the rocket goes nto orbt, the knetc energy s transformed nto gravtatonal potental. As t orbts, t has both knetc and gravtatonal potental energy..2 Three stones For each case, the ntal mechancal energy wll equal the fnal mechancal energy: The ntal mechancal energy s a combnaton of potental and knetc: The fnal mechancal energy s all knetc, snce the stones wll be at y = 0: = f = KE + U = m v 2 + mgh 2 Equatng these two: Thus, for each case, we can solve for v f :. Case : the stone s launched straght up: 2. Case 2: the stone s launched straght horzontally: 3. Case 3: the stone s launched straght down: f = KE + U = m v f m v 2 + mgh = m v f = v f = v f2 = v f3 2gh + v 2 2gh + v 2 2gh + v 2 All three cases end wth the same speed. Page
2 speed One of our knematc equatons was: v 2 = v + 2aΔx f 2 Ths s the same equaton..3 Partcle n a bowl Intal Poston: the partcle s at rest, at some heght above the ground. Fnal Poston: at the bottom of the bowl, the partcles s movng. So, t has a knetc energy value, but we can say ts potental energy s zero at that locaton. h = R( cosθ) The ntal mechancal energy wll be equal to the fnal: = f mgh = mgr( cosθ) = mv 2 2 Thus, we can solve for v: v = 2gR( cosθ) functon s non-lnear θ v 0 0 m/s m/s m/s m/s m/s m/s m/s degrees Just solve the conservaton of energy equaton for θ nstead of v: θ = cos v 2 ( ) 2gr Page 2
3 .4 Energy Conservaton Page 3
4 Page 4
5 Page 5
6 Page 6
7 Page 7
8 .5 Energy Graphs Page 8
9 2. Work 2. Some sketches. A marble fallng straght down to the ground n free fall, startng from rest a few meters off Page 9
10 the ground. 2. A pece of steel s on the ground at a constructon ste. A crane lfts the pece of steel at a unform velocty to a hgh floor of the buldng. 3. The crane s used to to brng a worker from the roof to the ground. 4. A skateboarder rdng down a (frctonless) hll. Page 0
11 5. A skateboarder who has fallen off the skateboard and s now sldng down the very hgh frcton hll. 6. A car at t travels around a curved road. 2.2 More Work W = ΔKE = m v 2 = = 25 J 2 f 2 W = F d = F d cosθ = cos 20 = 7575 J The work done wll be 0. (force s to dsplacement) Work s gven by the force tmes the dstance. h s the heght of the ESB. W = F G h = = 3734 J W = ΔKE = mv 2 m v 2 = Fd cosθ = mgd cosθ 2 f 2 v f = v 2 2mgd cos( 82 ) + = 6.6 m/s m Page
in state i at t i, Initial State E = E i
 Physcs 01, Lecture 1 Today s Topcs n More Energy and Work (chapters 7 & 8) n Conservatve Work and Potental Energy n Sprng Force and Sprng (Elastc) Potental Energy n Conservaton of Mechanc Energy n Exercse
Physcs 01, Lecture 1 Today s Topcs n More Energy and Work (chapters 7 & 8) n Conservatve Work and Potental Energy n Sprng Force and Sprng (Elastc) Potental Energy n Conservaton of Mechanc Energy n Exercse
Spring Force and Power
 Lecture 13 Chapter 9 Sprng Force and Power Yeah, energy s better than orces. What s net? Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn how to solve problems
Lecture 13 Chapter 9 Sprng Force and Power Yeah, energy s better than orces. What s net? Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn how to solve problems
Physics 207 Lecture 13. Lecture 13
 Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Goals: Lecture 3 Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Defne Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Develop and explot conservaton of energy prncple n problem
Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Goals: Lecture 3 Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Defne Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Develop and explot conservaton of energy prncple n problem
Physics 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1
 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Unversty of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Course Informaton: Lab report # 3. Exam # 2. Mult-Partcle
Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Unversty of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Course Informaton: Lab report # 3. Exam # 2. Mult-Partcle
Chapter 3. r r. Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Revisited
 Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
Chapter 8. Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
 Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton of Energy In ths chapter we wll ntroduce the followng concepts: Potental Energy Conservatve and non-conservatve forces Mechancal Energy Conservaton of Mechancal
Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton of Energy In ths chapter we wll ntroduce the followng concepts: Potental Energy Conservatve and non-conservatve forces Mechancal Energy Conservaton of Mechancal
Conservation of Energy
 Lecture 3 Chapter 8 Physcs I 0.3.03 Conservaton o Energy Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcsall.html 95.4, Fall 03,
Lecture 3 Chapter 8 Physcs I 0.3.03 Conservaton o Energy Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcsall.html 95.4, Fall 03,
Chapter 07: Kinetic Energy and Work
 Chapter 07: Knetc Energy and Work Conservaton o Energy s one o Nature s undamental laws that s not volated. Energy can take on derent orms n a gven system. Ths chapter we wll dscuss work and knetc energy.
Chapter 07: Knetc Energy and Work Conservaton o Energy s one o Nature s undamental laws that s not volated. Energy can take on derent orms n a gven system. Ths chapter we wll dscuss work and knetc energy.
Lecture 16. Chapter 11. Energy Dissipation Linear Momentum. Physics I. Department of Physics and Applied Physics
 Lecture 16 Chapter 11 Physcs I Energy Dsspaton Lnear Momentum Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Department o Physcs and Appled Physcs IN IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn
Lecture 16 Chapter 11 Physcs I Energy Dsspaton Lnear Momentum Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Department o Physcs and Appled Physcs IN IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn
PHYS 1443 Section 004 Lecture #12 Thursday, Oct. 2, 2014
 PHYS 1443 Secton 004 Lecture #1 Thursday, Oct., 014 Work-Knetc Energy Theorem Work under rcton Potental Energy and the Conservatve Force Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Conservaton o
PHYS 1443 Secton 004 Lecture #1 Thursday, Oct., 014 Work-Knetc Energy Theorem Work under rcton Potental Energy and the Conservatve Force Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Conservaton o
Page 1. Physics 131: Lecture 14. Today s Agenda. Things that stay the same. Impulse and Momentum Non-constant forces
 Physcs 131: Lecture 14 Today s Agenda Imulse and Momentum Non-constant forces Imulse-momentum momentum thm Conservaton of Lnear momentum Eternal/Internal forces Eamles Physcs 201: Lecture 1, Pg 1 Physcs
Physcs 131: Lecture 14 Today s Agenda Imulse and Momentum Non-constant forces Imulse-momentum momentum thm Conservaton of Lnear momentum Eternal/Internal forces Eamles Physcs 201: Lecture 1, Pg 1 Physcs
CHAPTER 8 Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
 CHAPTER 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton o Energy One orm o energy can be converted nto another orm o energy. Conservatve and non-conservatve orces Physcs 1 Knetc energy: Potental energy: Energy assocated
CHAPTER 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton o Energy One orm o energy can be converted nto another orm o energy. Conservatve and non-conservatve orces Physcs 1 Knetc energy: Potental energy: Energy assocated
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #16
 PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #16 Monday, Mar. 4, 008 Potental Energy Conservatve and Non-conservatve Forces Conservaton o Mechancal Energy Power Today s homework s homework #8, due 9pm, Monday, Mar. 31!!
PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #16 Monday, Mar. 4, 008 Potental Energy Conservatve and Non-conservatve Forces Conservaton o Mechancal Energy Power Today s homework s homework #8, due 9pm, Monday, Mar. 31!!
You will analyze the motion of the block at different moments using the law of conservation of energy.
 Physcs 00A Homework 7 Chapter 8 Where s the Energy? In ths problem, we wll consder the ollowng stuaton as depcted n the dagram: A block o mass m sldes at a speed v along a horzontal smooth table. It next
Physcs 00A Homework 7 Chapter 8 Where s the Energy? In ths problem, we wll consder the ollowng stuaton as depcted n the dagram: A block o mass m sldes at a speed v along a horzontal smooth table. It next
Chapter 8 Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy Important Terms (For chapters 7 and 8)
 Pro. Dr. I. Nasser Chapter8_I November 3, 07 Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton o Energy Important Terms (For chapters 7 and 8) conservatve orce: a orce whch does wor on an object whch s ndependent
Pro. Dr. I. Nasser Chapter8_I November 3, 07 Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton o Energy Important Terms (For chapters 7 and 8) conservatve orce: a orce whch does wor on an object whch s ndependent
11. Dynamics in Rotating Frames of Reference
 Unversty of Rhode Island DgtalCommons@URI Classcal Dynamcs Physcs Course Materals 2015 11. Dynamcs n Rotatng Frames of Reference Gerhard Müller Unversty of Rhode Island, gmuller@ur.edu Creatve Commons
Unversty of Rhode Island DgtalCommons@URI Classcal Dynamcs Physcs Course Materals 2015 11. Dynamcs n Rotatng Frames of Reference Gerhard Müller Unversty of Rhode Island, gmuller@ur.edu Creatve Commons
Chapter 8: Potential Energy and The Conservation of Total Energy
 Chapter 8: Potental Energy and The Conservaton o Total Energy Work and knetc energy are energes o moton. K K K mv r v v F dr Potental energy s an energy that depends on locaton. -Dmenson F x d U( x) dx
Chapter 8: Potental Energy and The Conservaton o Total Energy Work and knetc energy are energes o moton. K K K mv r v v F dr Potental energy s an energy that depends on locaton. -Dmenson F x d U( x) dx
First Law: A body at rest remains at rest, a body in motion continues to move at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force.
 Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
Study Guide For Exam Two
 Study Gude For Exam Two Physcs 2210 Albretsen Updated: 08/02/2018 All Other Prevous Study Gudes Modules 01-06 Module 07 Work Work done by a constant force F over a dstance s : Work done by varyng force
Study Gude For Exam Two Physcs 2210 Albretsen Updated: 08/02/2018 All Other Prevous Study Gudes Modules 01-06 Module 07 Work Work done by a constant force F over a dstance s : Work done by varyng force
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 2
 PHYSICS 31 Revew problems for mdterm Topc 5: Energy and Work and Power Topc 6: Momentum and Collsons Topc 7: Oscllatons (sprng and pendulum) Topc 8: Rotatonal Moton The nd exam wll be Wednesday October
PHYSICS 31 Revew problems for mdterm Topc 5: Energy and Work and Power Topc 6: Momentum and Collsons Topc 7: Oscllatons (sprng and pendulum) Topc 8: Rotatonal Moton The nd exam wll be Wednesday October
Conservation of Energy
 Conservaton o nergy The total energy o a system can change only by amounts o energy that are transerred nto or out o the system W mec th nt Ths s one o the great conservaton laws n nature! Other conservaton
Conservaton o nergy The total energy o a system can change only by amounts o energy that are transerred nto or out o the system W mec th nt Ths s one o the great conservaton laws n nature! Other conservaton
Motion in One Dimension
 Moton n One Dmenson Speed ds tan ce traeled Aerage Speed tme of trael Mr. Wolf dres hs car on a long trp to a physcs store. Gen the dstance and tme data for hs trp, plot a graph of hs dstance ersus tme.
Moton n One Dmenson Speed ds tan ce traeled Aerage Speed tme of trael Mr. Wolf dres hs car on a long trp to a physcs store. Gen the dstance and tme data for hs trp, plot a graph of hs dstance ersus tme.
Chapter 3 and Chapter 4
 Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 Chapter 3 Energy 3. Introducton:Work Work W s energy transerred to or rom an object by means o a orce actng on the object. Energy transerred to the object s postve work, and energy
Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 Chapter 3 Energy 3. Introducton:Work Work W s energy transerred to or rom an object by means o a orce actng on the object. Energy transerred to the object s postve work, and energy
Physics 207: Lecture 20. Today s Agenda Homework for Monday
 Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Period & Frequency. Work and Energy. Methods of Energy Transfer: Energy. Work-KE Theorem 3/4/16. Ranking: Which has the greatest kinetic energy?
 Perod & Frequency Perod (T): Tme to complete one ull rotaton Frequency (): Number o rotatons completed per second. = 1/T, T = 1/ v = πr/t Work and Energy Work: W = F!d (pcks out parallel components) F
Perod & Frequency Perod (T): Tme to complete one ull rotaton Frequency (): Number o rotatons completed per second. = 1/T, T = 1/ v = πr/t Work and Energy Work: W = F!d (pcks out parallel components) F
Physics 181. Particle Systems
 Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Homework 4: Work, Energy and Linear Momentum Due Friday March 1 st
 EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #15
 PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #15 Monday, March 18, 013 Work wth rcton Potental Energy Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Mechancal Energy Conservaton Announcements Mdterm comprehensve exam
PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #15 Monday, March 18, 013 Work wth rcton Potental Energy Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Mechancal Energy Conservaton Announcements Mdterm comprehensve exam
= 1.23 m/s 2 [W] Required: t. Solution:!t = = 17 m/s [W]! m/s [W] (two extra digits carried) = 2.1 m/s [W]
![= 1.23 m/s 2 [W] Required: t. Solution:!t = = 17 m/s [W]! m/s [W] (two extra digits carried) = 2.1 m/s [W] = 1.23 m/s 2 [W] Required: t. Solution:!t = = 17 m/s [W]! m/s [W] (two extra digits carried) = 2.1 m/s [W]](/thumbs/78/76802454.jpg) Secton 1.3: Acceleraton Tutoral 1 Practce, page 24 1. Gven: 0 m/s; 15.0 m/s [S]; t 12.5 s Requred: Analyss: a av v t v f v t a v av f v t 15.0 m/s [S] 0 m/s 12.5 s 15.0 m/s [S] 12.5 s 1.20 m/s 2 [S] Statement:
Secton 1.3: Acceleraton Tutoral 1 Practce, page 24 1. Gven: 0 m/s; 15.0 m/s [S]; t 12.5 s Requred: Analyss: a av v t v f v t a v av f v t 15.0 m/s [S] 0 m/s 12.5 s 15.0 m/s [S] 12.5 s 1.20 m/s 2 [S] Statement:
K = 100 J. [kg (m/s) ] K = mv = (0.15)(36.5) !!! Lethal energies. m [kg ] J s (Joule) Kinetic Energy (energy of motion) E or KE.
![K = 100 J. [kg (m/s) ] K = mv = (0.15)(36.5) !!! Lethal energies. m [kg ] J s (Joule) Kinetic Energy (energy of motion) E or KE. K = 100 J. [kg (m/s) ] K = mv = (0.15)(36.5) !!! Lethal energies. m [kg ] J s (Joule) Kinetic Energy (energy of motion) E or KE.](/thumbs/80/81648220.jpg) Knetc Energy (energy of moton) E or KE K = m v = m(v + v y + v z ) eample baseball m=0.5 kg ptche at v = 69 mph = 36.5 m/s K = mv = (0.5)(36.5) [kg (m/s) ] Unts m [kg ] J s (Joule) v = 69 mph K = 00 J
Knetc Energy (energy of moton) E or KE K = m v = m(v + v y + v z ) eample baseball m=0.5 kg ptche at v = 69 mph = 36.5 m/s K = mv = (0.5)(36.5) [kg (m/s) ] Unts m [kg ] J s (Joule) v = 69 mph K = 00 J
Supplemental Instruction sessions next week
 Homework #4 Wrtten homework due now Onlne homework due on Tue Mar 3 by 8 am Exam 1 Answer keys and scores wll be posted by end of the week Supplemental Instructon sessons next week Wednesday 8:45 10:00
Homework #4 Wrtten homework due now Onlne homework due on Tue Mar 3 by 8 am Exam 1 Answer keys and scores wll be posted by end of the week Supplemental Instructon sessons next week Wednesday 8:45 10:00
Physics 2A Chapter 3 HW Solutions
 Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SENIOR SECONDARY INTERVENTION PROGRAMME PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES)
 PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 1 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES) TOPIC 1: MECHANICS PROJECTILE MOTION Learner Note: Always draw a dagram of the stuaton and enter all the numercal alues onto your dagram. Remember to
PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 1 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES) TOPIC 1: MECHANICS PROJECTILE MOTION Learner Note: Always draw a dagram of the stuaton and enter all the numercal alues onto your dagram. Remember to
Angular Momentum and Fixed Axis Rotation. 8.01t Nov 10, 2004
 Angular Momentum and Fxed Axs Rotaton 8.01t Nov 10, 2004 Dynamcs: Translatonal and Rotatonal Moton Translatonal Dynamcs Total Force Torque Angular Momentum about Dynamcs of Rotaton F ext Momentum of a
Angular Momentum and Fxed Axs Rotaton 8.01t Nov 10, 2004 Dynamcs: Translatonal and Rotatonal Moton Translatonal Dynamcs Total Force Torque Angular Momentum about Dynamcs of Rotaton F ext Momentum of a
Please initial the statement below to show that you have read it
 EN40: Dynamcs and Vbratons Mdterm Examnaton Thursday March 5 009 Dvson of Engneerng rown Unversty NME: Isaac Newton General Instructons No collaboraton of any knd s permtted on ths examnaton. You may brng
EN40: Dynamcs and Vbratons Mdterm Examnaton Thursday March 5 009 Dvson of Engneerng rown Unversty NME: Isaac Newton General Instructons No collaboraton of any knd s permtted on ths examnaton. You may brng
Chapter 7. Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
 Chapter 7 Potental Energy and Conservaton o Energy 1 Forms o Energy There are many orms o energy, but they can all be put nto two categores Knetc Knetc energy s energy o moton Potental Potental energy
Chapter 7 Potental Energy and Conservaton o Energy 1 Forms o Energy There are many orms o energy, but they can all be put nto two categores Knetc Knetc energy s energy o moton Potental Potental energy
Displacement at any time. Velocity at any displacement in the x-direction u 2 = v ] + 2 a x ( )
![Displacement at any time. Velocity at any displacement in the x-direction u 2 = v ] + 2 a x ( ) Displacement at any time. Velocity at any displacement in the x-direction u 2 = v ] + 2 a x ( )](/thumbs/89/97691613.jpg) The Language of Physcs Knematcs The branch of mechancs that descrbes the moton of a body wthout regard to the cause of that moton (p. 39). Average velocty The average rate at whch the dsplacement vector
The Language of Physcs Knematcs The branch of mechancs that descrbes the moton of a body wthout regard to the cause of that moton (p. 39). Average velocty The average rate at whch the dsplacement vector
Ch04 Work, Energy and Power What is work in physics?
 Eunl Won Dept o Physcs, Korea Unversty 1 Ch04 Work, Energy and Power What s work n physcs? Eunl Won Dept o Physcs, Korea Unversty Eunl Won Dept o Physcs, Korea Unversty 3 Work W F d W Fd cosφ W Fd ο cos
Eunl Won Dept o Physcs, Korea Unversty 1 Ch04 Work, Energy and Power What s work n physcs? Eunl Won Dept o Physcs, Korea Unversty Eunl Won Dept o Physcs, Korea Unversty 3 Work W F d W Fd cosφ W Fd ο cos
Week 9 Chapter 10 Section 1-5
 Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
10/23/2003 PHY Lecture 14R 1
 Announcements. Remember -- Tuesday, Oct. 8 th, 9:30 AM Second exam (coverng Chapters 9-4 of HRW) Brng the followng: a) equaton sheet b) Calculator c) Pencl d) Clear head e) Note: If you have kept up wth
Announcements. Remember -- Tuesday, Oct. 8 th, 9:30 AM Second exam (coverng Chapters 9-4 of HRW) Brng the followng: a) equaton sheet b) Calculator c) Pencl d) Clear head e) Note: If you have kept up wth
A Tale of Friction Basic Rollercoaster Physics. Fahrenheit Rollercoaster, Hershey, PA max height = 121 ft max speed = 58 mph
 A Tale o Frcton Basc Rollercoaster Physcs Fahrenhet Rollercoaster, Hershey, PA max heght = 11 t max speed = 58 mph PLAY PLAY PLAY PLAY Rotatonal Movement Knematcs Smlar to how lnear velocty s dened, angular
A Tale o Frcton Basc Rollercoaster Physcs Fahrenhet Rollercoaster, Hershey, PA max heght = 11 t max speed = 58 mph PLAY PLAY PLAY PLAY Rotatonal Movement Knematcs Smlar to how lnear velocty s dened, angular
τ rf = Iα I point = mr 2 L35 F 11/14/14 a*er lecture 1
 A mass s attached to a long, massless rod. The mass s close to one end of the rod. Is t easer to balance the rod on end wth the mass near the top or near the bottom? Hnt: Small α means sluggsh behavor
A mass s attached to a long, massless rod. The mass s close to one end of the rod. Is t easer to balance the rod on end wth the mass near the top or near the bottom? Hnt: Small α means sluggsh behavor
χ x B E (c) Figure 2.1.1: (a) a material particle in a body, (b) a place in space, (c) a configuration of the body
 Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
Physics 131: Lecture 16. Today s Agenda
 Physcs 131: Lecture 16 Today s Agenda Intro to Conseraton o Energy Intro to some derent knds o energy Knetc Potental Denton t o Mechancal Energy Conseraton o Mechancal Energy Conserate orces Examples Pendulum
Physcs 131: Lecture 16 Today s Agenda Intro to Conseraton o Energy Intro to some derent knds o energy Knetc Potental Denton t o Mechancal Energy Conseraton o Mechancal Energy Conserate orces Examples Pendulum
1.3 Hence, calculate a formula for the force required to break the bond (i.e. the maximum value of F)
 EN40: Dynacs and Vbratons Hoework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Moentu Due Frday March 6 th School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The Rydberg potental s a sple odel of atoc nteractons. It specfes the potental
EN40: Dynacs and Vbratons Hoework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Moentu Due Frday March 6 th School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The Rydberg potental s a sple odel of atoc nteractons. It specfes the potental
Physics for Scientists and Engineers. Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum
 Physcs or Scentsts and Engneers Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum Sprng, 008 Ho Jung Pak Lnear Momentum Lnear momentum o an object o mass m movng wth a velocty v s dened to be p mv Momentum and lnear momentum
Physcs or Scentsts and Engneers Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum Sprng, 008 Ho Jung Pak Lnear Momentum Lnear momentum o an object o mass m movng wth a velocty v s dened to be p mv Momentum and lnear momentum
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Newtonian Mechanics
 1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Newtonan Mechancs Quck Revew of Newtonan Mechancs Basc Descrpton: -An dealzed pont partcle or a system of pont partcles n an nertal reference frame [Rgd bodes (ch. 5 later)]
1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Newtonan Mechancs Quck Revew of Newtonan Mechancs Basc Descrpton: -An dealzed pont partcle or a system of pont partcles n an nertal reference frame [Rgd bodes (ch. 5 later)]
Page 1. Clicker Question 9: Physics 131: Lecture 15. Today s Agenda. Clicker Question 9: Energy. Energy is Conserved.
 Physcs 3: Lecture 5 Today s Agenda Intro to Conseraton o Energy Intro to some derent knds o energy Knetc Potental Denton o Mechancal Energy Conseraton o Mechancal Energy Conserate orces Examples Pendulum
Physcs 3: Lecture 5 Today s Agenda Intro to Conseraton o Energy Intro to some derent knds o energy Knetc Potental Denton o Mechancal Energy Conseraton o Mechancal Energy Conserate orces Examples Pendulum
Mechanics Cycle 3 Chapter 9++ Chapter 9++
 Chapter 9++ More on Knetc Energy and Potental Energy BACK TO THE FUTURE I++ More Predctons wth Energy Conservaton Revst: Knetc energy for rotaton Potental energy M total g y CM for a body n constant gravty
Chapter 9++ More on Knetc Energy and Potental Energy BACK TO THE FUTURE I++ More Predctons wth Energy Conservaton Revst: Knetc energy for rotaton Potental energy M total g y CM for a body n constant gravty
Week 6, Chapter 7 Sect 1-5
 Week 6, Chapter 7 Sect 1-5 Work and Knetc Energy Lecture Quz The frctonal force of the floor on a large sutcase s least when the sutcase s A.pushed by a force parallel to the floor. B.dragged by a force
Week 6, Chapter 7 Sect 1-5 Work and Knetc Energy Lecture Quz The frctonal force of the floor on a large sutcase s least when the sutcase s A.pushed by a force parallel to the floor. B.dragged by a force
Physics 40 HW #4 Chapter 4 Key NEATNESS COUNTS! Solve but do not turn in the following problems from Chapter 4 Knight
 Physcs 40 HW #4 Chapter 4 Key NEATNESS COUNTS! Solve but do not turn n the ollowng problems rom Chapter 4 Knght Conceptual Questons: 8, 0, ; 4.8. Anta s approachng ball and movng away rom where ball was
Physcs 40 HW #4 Chapter 4 Key NEATNESS COUNTS! Solve but do not turn n the ollowng problems rom Chapter 4 Knght Conceptual Questons: 8, 0, ; 4.8. Anta s approachng ball and movng away rom where ball was
EMU Physics Department
 Physcs 0 Lecture 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton Assst. Pro. Dr. Al ÖVGÜN EMU Physcs Department www.aovgun.com Denton o Work W q The work, W, done by a constant orce on an object s dened as the product
Physcs 0 Lecture 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton Assst. Pro. Dr. Al ÖVGÜN EMU Physcs Department www.aovgun.com Denton o Work W q The work, W, done by a constant orce on an object s dened as the product
Chapter 7: Conservation of Energy
 Lecture 7: Conservaton o nergy Chapter 7: Conservaton o nergy Introucton I the quantty o a subject oes not change wth tme, t means that the quantty s conserve. The quantty o that subject remans constant
Lecture 7: Conservaton o nergy Chapter 7: Conservaton o nergy Introucton I the quantty o a subject oes not change wth tme, t means that the quantty s conserve. The quantty o that subject remans constant
Section 8.1 Exercises
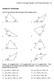 Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Part C Dynamics and Statics of Rigid Body. Chapter 5 Rotation of a Rigid Body About a Fixed Axis
 Part C Dynamcs and Statcs of Rgd Body Chapter 5 Rotaton of a Rgd Body About a Fxed Axs 5.. Rotatonal Varables 5.. Rotaton wth Constant Angular Acceleraton 5.3. Knetc Energy of Rotaton, Rotatonal Inerta
Part C Dynamcs and Statcs of Rgd Body Chapter 5 Rotaton of a Rgd Body About a Fxed Axs 5.. Rotatonal Varables 5.. Rotaton wth Constant Angular Acceleraton 5.3. Knetc Energy of Rotaton, Rotatonal Inerta
Physics 207, Lecture 13, Oct. 15. Energy
 Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Physcs 07, Lecture 3, Oct. 5 Goals: Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Dene Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Deelop and explot conseraton o energy prncple
Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Physcs 07, Lecture 3, Oct. 5 Goals: Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Dene Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Deelop and explot conseraton o energy prncple
Name: PHYS 110 Dr. McGovern Spring 2018 Exam 1. Multiple Choice: Circle the answer that best evaluates the statement or completes the statement.
 Name: PHYS 110 Dr. McGoern Sprng 018 Exam 1 Multple Choce: Crcle the answer that best ealuates the statement or completes the statement. #1 - I the acceleraton o an object s negate, the object must be
Name: PHYS 110 Dr. McGoern Sprng 018 Exam 1 Multple Choce: Crcle the answer that best ealuates the statement or completes the statement. #1 - I the acceleraton o an object s negate, the object must be
TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES. PHYS 2211, Exam 2 Section 1 Version 1 October 18, 2013 Total Weight: 100 points
 TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS, Exam Secton Verson October 8, 03 Total Weght: 00 ponts. Check your examnaton or completeness pror to startng. There are a total o nne
TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS, Exam Secton Verson October 8, 03 Total Weght: 00 ponts. Check your examnaton or completeness pror to startng. There are a total o nne
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Linear Momentum, cont. Linear Momentum. Lectures 17 and 18. Linear Momentum and Collisions
 PC Fundamentals of Physcs I Lectures 7 and 8 Lnear omentum and Collsons Dr Tay Seng Chuan Ground Rules Swtch off your handphone and pager Swtch off your laptop computer and keep t No talkng whle lecture
PC Fundamentals of Physcs I Lectures 7 and 8 Lnear omentum and Collsons Dr Tay Seng Chuan Ground Rules Swtch off your handphone and pager Swtch off your laptop computer and keep t No talkng whle lecture
Kinematics in 2-Dimensions. Projectile Motion
 Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.net.net.au/~rmne/ht/ht0.html#5 Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had
Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.net.net.au/~rmne/ht/ht0.html#5 Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had
Work is the change in energy of a system (neglecting heat transfer). To examine what could
 Work Work s the change n energy o a system (neglectng heat transer). To eamne what could cause work, let s look at the dmensons o energy: L ML E M L F L so T T dmensonally energy s equal to a orce tmes
Work Work s the change n energy o a system (neglectng heat transer). To eamne what could cause work, let s look at the dmensons o energy: L ML E M L F L so T T dmensonally energy s equal to a orce tmes
Spring 2002 Lecture #13
 44-50 Sprng 00 ecture # Dr. Jaehoon Yu. Rotatonal Energy. Computaton of oments of nerta. Parallel-as Theorem 4. Torque & Angular Acceleraton 5. Work, Power, & Energy of Rotatonal otons Remember the md-term
44-50 Sprng 00 ecture # Dr. Jaehoon Yu. Rotatonal Energy. Computaton of oments of nerta. Parallel-as Theorem 4. Torque & Angular Acceleraton 5. Work, Power, & Energy of Rotatonal otons Remember the md-term
SUMMARY Phys 2113 (General Physics I) Compiled by Prof. Erickson. v = r t. v = lim t 0. p = mv. a = v. a = lim
 SUMMARY Phys 2113 (General Physcs I) Compled by Prof. Erckson Poston Vector (m): r = xˆx + yŷ + zẑ Average Velocty (m/s): v = r Instantaneous Velocty (m/s): v = lm 0 r = ṙ Lnear Momentum (kg m/s): p =
SUMMARY Phys 2113 (General Physcs I) Compled by Prof. Erckson Poston Vector (m): r = xˆx + yŷ + zẑ Average Velocty (m/s): v = r Instantaneous Velocty (m/s): v = lm 0 r = ṙ Lnear Momentum (kg m/s): p =
Linear Momentum. Center of Mass.
 Lecture 6 Chapter 9 Physcs I 03.3.04 Lnear omentum. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.uml.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcssprng.html
Lecture 6 Chapter 9 Physcs I 03.3.04 Lnear omentum. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.uml.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcssprng.html
Slide. King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 5: MOTION IN 1-D (PART 2) LECTURE NO.
 Slde Kng Saud Unersty College of Scence Physcs & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 5: MOTION IN 1-D (PART ) LECTURE NO. 6 THIS PRESENTATION HAS BEEN PREPARED BY: DR. NASSR S. ALZAYED Lecture
Slde Kng Saud Unersty College of Scence Physcs & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 103 (GENERAL PHYSICS) CHAPTER 5: MOTION IN 1-D (PART ) LECTURE NO. 6 THIS PRESENTATION HAS BEEN PREPARED BY: DR. NASSR S. ALZAYED Lecture
Mathematics Intersection of Lines
 a place of mnd F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Currculum and Pedagog Mathematcs Intersecton of Lnes Scence and Mathematcs Educaton Research Group Supported b UBC Teachng and Learnng Enhancement
a place of mnd F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Currculum and Pedagog Mathematcs Intersecton of Lnes Scence and Mathematcs Educaton Research Group Supported b UBC Teachng and Learnng Enhancement
AP Physics 1 & 2 Summer Assignment
 AP Physcs 1 & 2 Summer Assgnment AP Physcs 1 requres an exceptonal profcency n algebra, trgonometry, and geometry. It was desgned by a select group of college professors and hgh school scence teachers
AP Physcs 1 & 2 Summer Assgnment AP Physcs 1 requres an exceptonal profcency n algebra, trgonometry, and geometry. It was desgned by a select group of college professors and hgh school scence teachers
Gravitational Acceleration: A case of constant acceleration (approx. 2 hr.) (6/7/11)
 Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
CHAPTER 7 ENERGY BALANCES SYSTEM SYSTEM. * What is energy? * Forms of Energy. - Kinetic energy (KE) - Potential energy (PE) PE = mgz
 SYSTM CHAPTR 7 NRGY BALANCS 1 7.1-7. SYSTM nergy & 1st Law of Thermodynamcs * What s energy? * Forms of nergy - Knetc energy (K) K 1 mv - Potental energy (P) P mgz - Internal energy (U) * Total nergy,
SYSTM CHAPTR 7 NRGY BALANCS 1 7.1-7. SYSTM nergy & 1st Law of Thermodynamcs * What s energy? * Forms of nergy - Knetc energy (K) K 1 mv - Potental energy (P) P mgz - Internal energy (U) * Total nergy,
PY2101 Classical Mechanics Dr. Síle Nic Chormaic, Room 215 D Kane Bldg
 PY2101 Classcal Mechancs Dr. Síle Nc Chormac, Room 215 D Kane Bldg s.ncchormac@ucc.e Lectures stll some ssues to resolve. Slots shared between PY2101 and PY2104. Hope to have t fnalsed by tomorrow. Mondays
PY2101 Classcal Mechancs Dr. Síle Nc Chormac, Room 215 D Kane Bldg s.ncchormac@ucc.e Lectures stll some ssues to resolve. Slots shared between PY2101 and PY2104. Hope to have t fnalsed by tomorrow. Mondays
Slide 1 / 76. Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems
 Slide 1 / 76 Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems Slide 2 / 76 1 A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to
Slide 1 / 76 Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems Slide 2 / 76 1 A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to
Physics 114 Exam 2 Spring Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam Sprng 013 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red wth the amount beng
Physcs 114 Exam Sprng 013 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red wth the amount beng
Week 8: Chapter 9. Linear Momentum. Newton Law and Momentum. Linear Momentum, cont. Conservation of Linear Momentum. Conservation of Momentum, 2
 Lnear omentum Week 8: Chapter 9 Lnear omentum and Collsons The lnear momentum of a partcle, or an object that can be modeled as a partcle, of mass m movng wth a velocty v s defned to be the product of
Lnear omentum Week 8: Chapter 9 Lnear omentum and Collsons The lnear momentum of a partcle, or an object that can be modeled as a partcle, of mass m movng wth a velocty v s defned to be the product of
Electric Potential Energy & Potential. Electric Potential Energy. Potential Energy. Potential Energy. Example: Charge launcher
 Electrc & Electrc Gravtatonal Increases as you move farther from Earth mgh Sprng Increases as you ncrease sprng extenson/comp resson Δ Increases or decreases as you move farther from the charge U ncreases
Electrc & Electrc Gravtatonal Increases as you move farther from Earth mgh Sprng Increases as you ncrease sprng extenson/comp resson Δ Increases or decreases as you move farther from the charge U ncreases
Chapter 2. Pythagorean Theorem. Right Hand Rule. Position. Distance Formula
 Chapter Moton n One Dmenson Cartesan Coordnate System The most common coordnate system or representng postons n space s one based on three perpendcular spatal axes generally desgnated x, y, and z. Any
Chapter Moton n One Dmenson Cartesan Coordnate System The most common coordnate system or representng postons n space s one based on three perpendcular spatal axes generally desgnated x, y, and z. Any
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. D Alembert s Principle and The Lagrangian-1
 P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
Moments of Inertia. and reminds us of the analogous equation for linear momentum p= mv, which is of the form. The kinetic energy of the body is.
 Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
A particle in a state of uniform motion remain in that state of motion unless acted upon by external force.
 The fundamental prncples of classcal mechancs were lad down by Galleo and Newton n the 16th and 17th centures. In 1686, Newton wrote the Prncpa where he gave us three laws of moton, one law of gravty,
The fundamental prncples of classcal mechancs were lad down by Galleo and Newton n the 16th and 17th centures. In 1686, Newton wrote the Prncpa where he gave us three laws of moton, one law of gravty,
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 11
 Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
PHYSICS 203-NYA-05 MECHANICS
 PHYSICS 03-NYA-05 MECHANICS PROF. S.D. MANOLI PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY CHAMPLAIN - ST. LAWRENCE 790 NÉRÉE-TREMBLAY QUÉBEC, QC GV 4K TELEPHONE: 48.656.69 EXT. 449 EMAIL: smanol@slc.qc.ca WEBPAGE: http:/web.slc.qc.ca/smanol/
PHYSICS 03-NYA-05 MECHANICS PROF. S.D. MANOLI PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY CHAMPLAIN - ST. LAWRENCE 790 NÉRÉE-TREMBLAY QUÉBEC, QC GV 4K TELEPHONE: 48.656.69 EXT. 449 EMAIL: smanol@slc.qc.ca WEBPAGE: http:/web.slc.qc.ca/smanol/
Important Dates: Post Test: Dec during recitations. If you have taken the post test, don t come to recitation!
 Important Dates: Post Test: Dec. 8 0 durng rectatons. If you have taken the post test, don t come to rectaton! Post Test Make-Up Sessons n ARC 03: Sat Dec. 6, 0 AM noon, and Sun Dec. 7, 8 PM 0 PM. Post
Important Dates: Post Test: Dec. 8 0 durng rectatons. If you have taken the post test, don t come to rectaton! Post Test Make-Up Sessons n ARC 03: Sat Dec. 6, 0 AM noon, and Sun Dec. 7, 8 PM 0 PM. Post
Chapter 5. Answers to Even Numbered Problems m kj. 6. (a) 900 J (b) (a) 31.9 J (b) 0 (c) 0 (d) 31.9 J. 10.
 Answers to Even Numbered Problems Chapter 5. 3.6 m 4..6 J 6. (a) 9 J (b).383 8. (a) 3.9 J (b) (c) (d) 3.9 J. 6 m s. (a) 68 J (b) 84 J (c) 5 J (d) 48 J (e) 5.64 m s 4. 9. J 6. (a). J (b) 5. m s (c) 6.3
Answers to Even Numbered Problems Chapter 5. 3.6 m 4..6 J 6. (a) 9 J (b).383 8. (a) 3.9 J (b) (c) (d) 3.9 J. 6 m s. (a) 68 J (b) 84 J (c) 5 J (d) 48 J (e) 5.64 m s 4. 9. J 6. (a). J (b) 5. m s (c) 6.3
Physics 114 Exam 2 Fall 2014 Solutions. Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam Fall 014 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse ndcated,
Physcs 114 Exam Fall 014 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse ndcated,
coordinates. Then, the position vectors are described by
 Revewng, what we have dscussed so far: Generalzed coordnates Any number of varables (say, n) suffcent to specfy the confguraton of the system at each nstant to tme (need not be the mnmum number). In general,
Revewng, what we have dscussed so far: Generalzed coordnates Any number of varables (say, n) suffcent to specfy the confguraton of the system at each nstant to tme (need not be the mnmum number). In general,
ONE-DIMENSIONAL COLLISIONS
 Purpose Theory ONE-DIMENSIONAL COLLISIONS a. To very the law o conservaton o lnear momentum n one-dmensonal collsons. b. To study conservaton o energy and lnear momentum n both elastc and nelastc onedmensonal
Purpose Theory ONE-DIMENSIONAL COLLISIONS a. To very the law o conservaton o lnear momentum n one-dmensonal collsons. b. To study conservaton o energy and lnear momentum n both elastc and nelastc onedmensonal
Conservation of Angular Momentum = "Spin"
 Page 1 of 6 Conservaton of Angular Momentum = "Spn" We can assgn a drecton to the angular velocty: drecton of = drecton of axs + rght hand rule (wth rght hand, curl fngers n drecton of rotaton, thumb ponts
Page 1 of 6 Conservaton of Angular Momentum = "Spn" We can assgn a drecton to the angular velocty: drecton of = drecton of axs + rght hand rule (wth rght hand, curl fngers n drecton of rotaton, thumb ponts
ˆ (0.10 m) E ( N m /C ) 36 ˆj ( j C m)
 7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
So far: simple (planar) geometries
 Physcs 06 ecture 5 Torque and Angular Momentum as Vectors SJ 7thEd.: Chap. to 3 Rotatonal quanttes as vectors Cross product Torque epressed as a vector Angular momentum defned Angular momentum as a vector
Physcs 06 ecture 5 Torque and Angular Momentum as Vectors SJ 7thEd.: Chap. to 3 Rotatonal quanttes as vectors Cross product Torque epressed as a vector Angular momentum defned Angular momentum as a vector
(T > w) F R = T - w. Going up. T - w = ma
 ANSES Suspended Acceleratng-Objects A resultant orce causes a syste to accelerate. he drecton o the acceleraton s n the drecton o the resultant orce. As llustrated belo, hen suspended objects accelerate,
ANSES Suspended Acceleratng-Objects A resultant orce causes a syste to accelerate. he drecton o the acceleraton s n the drecton o the resultant orce. As llustrated belo, hen suspended objects accelerate,
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecture 3 Contnuous Systems an Fels (Chapter 3) Where Are We Now? We ve fnshe all the essentals Fnal wll cover Lectures through Last two lectures: Classcal Fel Theory Start wth wave equatons
Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecture 3 Contnuous Systems an Fels (Chapter 3) Where Are We Now? We ve fnshe all the essentals Fnal wll cover Lectures through Last two lectures: Classcal Fel Theory Start wth wave equatons
10/24/2013. PHY 113 C General Physics I 11 AM 12:15 PM TR Olin 101. Plan for Lecture 17: Review of Chapters 9-13, 15-16
 0/4/03 PHY 3 C General Physcs I AM :5 PM T Oln 0 Plan or Lecture 7: evew o Chapters 9-3, 5-6. Comment on exam and advce or preparaton. evew 3. Example problems 0/4/03 PHY 3 C Fall 03 -- Lecture 7 0/4/03
0/4/03 PHY 3 C General Physcs I AM :5 PM T Oln 0 Plan or Lecture 7: evew o Chapters 9-3, 5-6. Comment on exam and advce or preparaton. evew 3. Example problems 0/4/03 PHY 3 C Fall 03 -- Lecture 7 0/4/03
Classical Mechanics Virtual Work & d Alembert s Principle
 Classcal Mechancs Vrtual Work & d Alembert s Prncple Dpan Kumar Ghosh UM-DAE Centre for Excellence n Basc Scences Kalna, Mumba 400098 August 15, 2016 1 Constrants Moton of a system of partcles s often
Classcal Mechancs Vrtual Work & d Alembert s Prncple Dpan Kumar Ghosh UM-DAE Centre for Excellence n Basc Scences Kalna, Mumba 400098 August 15, 2016 1 Constrants Moton of a system of partcles s often
CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM, IMPULSE AND COLLISIONS
 CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM, IMPULSE AND COLLISIONS 103 Phy 1 9.1 Lnear Momentum The prncple o energy conervaton can be ued to olve problem that are harder to olve jut ung Newton law. It ued to decrbe moton
CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM, IMPULSE AND COLLISIONS 103 Phy 1 9.1 Lnear Momentum The prncple o energy conervaton can be ued to olve problem that are harder to olve jut ung Newton law. It ued to decrbe moton
Thermodynamics General
 Thermodynamcs General Lecture 1 Lecture 1 s devoted to establshng buldng blocks for dscussng thermodynamcs. In addton, the equaton of state wll be establshed. I. Buldng blocks for thermodynamcs A. Dmensons,
Thermodynamcs General Lecture 1 Lecture 1 s devoted to establshng buldng blocks for dscussng thermodynamcs. In addton, the equaton of state wll be establshed. I. Buldng blocks for thermodynamcs A. Dmensons,
THE VIBRATIONS OF MOLECULES II THE CARBON DIOXIDE MOLECULE Student Instructions
 THE VIBRATIONS OF MOLECULES II THE CARBON DIOXIDE MOLECULE Student Instructons by George Hardgrove Chemstry Department St. Olaf College Northfeld, MN 55057 hardgrov@lars.acc.stolaf.edu Copyrght George
THE VIBRATIONS OF MOLECULES II THE CARBON DIOXIDE MOLECULE Student Instructons by George Hardgrove Chemstry Department St. Olaf College Northfeld, MN 55057 hardgrov@lars.acc.stolaf.edu Copyrght George
Week 11: Chapter 11. The Vector Product. The Vector Product Defined. The Vector Product and Torque. More About the Vector Product
 The Vector Product Week 11: Chapter 11 Angular Momentum There are nstances where the product of two vectors s another vector Earler we saw where the product of two vectors was a scalar Ths was called the
The Vector Product Week 11: Chapter 11 Angular Momentum There are nstances where the product of two vectors s another vector Earler we saw where the product of two vectors was a scalar Ths was called the
Energy and Energy Transfer
 Energy and Energy Transer Chapter 7 Scalar Product (Dot) Work Done by a Constant Force F s constant over the dsplacement r 1 Denton o the scalar (dot) product o vectors Scalar product o unt vectors = 1
Energy and Energy Transer Chapter 7 Scalar Product (Dot) Work Done by a Constant Force F s constant over the dsplacement r 1 Denton o the scalar (dot) product o vectors Scalar product o unt vectors = 1
THE CURRENT BALANCE Physics 258/259
 DSH 1988, 005 THE CURRENT BALANCE Physcs 58/59 The tme average force between two parallel conductors carryng an alternatng current s measured by balancng ths force aganst the gravtatonal force on a set
DSH 1988, 005 THE CURRENT BALANCE Physcs 58/59 The tme average force between two parallel conductors carryng an alternatng current s measured by balancng ths force aganst the gravtatonal force on a set
Dynamics of Rotational Motion
 Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton Torque: the rotatonal analogue of force Torque = force x moment arm = Fl moment arm = perpendcular dstance through whch the force acts a.k.a. leer arm l F l F l F l F = Fl =
Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton Torque: the rotatonal analogue of force Torque = force x moment arm = Fl moment arm = perpendcular dstance through whch the force acts a.k.a. leer arm l F l F l F l F = Fl =
