Inverse design of indoor environment using an adjoint RNG k-ε turbulence model
|
|
|
- Juliana Young
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Zho, X. nd Chen, Q Inverse design of indoor environmen using n djoin RNG k ε urbulence model, Acceped by Indoor Air Inverse design of indoor environmen using n djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model X. Zho 1 nd Q. Chen, * 1 Tinjin Key Lborory of Indoor Air Environmenl Quliy Conrol, School of Environmenl Science nd Engineering, Tinjin Universiy, Tinjin 0007, Chin School of Mechnicl Engineering, Purdue Universiy, Wes Lfyee, IN 47907, USA *Corresponding uhor s phone: (765) , emil ddress: ynchen@purdue.edu Absrc The djoin mehod cn deermine design vribles of n indoor environmen ccording o he opiml design objecive, such s miniml prediced men voe (PMV) for herml comfor. The mehod clcules he grdien of he objecive funcion over he design vribles so h he objecive funcion cn be minimized long he fses direcion using n opimizion lgorihm. Since he objecive funcion is conrolled by he Reynolds-verged Nvier-Sokes (RANS) equions wih he RNG k-ε model during he opimizion process, ll he corresponding djoin equions should be solved, rher hn he frozen urbulence ssumpion used in previous sudies. This invesigion developed djoin equions for he RNG k-ε urbulence model nd pplied i o wo-dimensionl veniled cviy nd hree-dimensionl, wo-person office. Design processes wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model led o ner-zero design funcion for he wo cses, while hose wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion did no. This invesigion hs successfully used he new mehod o design wo-person office wih opiml herml comfor level round he wo occupns. KEYWORDS Inverse design, Indoor environmen, Adjoin mehod, Numericl lgorihm, Vlidion, Turbulence model Prcicl Implicions This invesigion developed n djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model for opiml design of he indoor environmen. The djoin mehod wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model cn be used o design he opiml indoor environmen for buildings. Design objecive could include ir velociy disribuion, emperure disribuion, nd he combinion of vribles clculed by CFD, such s herml comfor, indoor ir quliy, ec. Nomenclure g grviy vecor J objecive funcion k urbulen kineic energy k djoin urbulen kineic energy L ugmened objecive funcion N incompressible Nvier-Sokes equions in vecor form 1
2 p ir pressure p djoin pressure R residul form of he RNG k-ε urbulence model equions T ir emperure T djoin emperure Top opering ir emperure V ir velociy djoin velociy V Subscrips djoin mehod op opere Greek symbols γ herml expnsion coefficien of ir δ smll consn se by designer ε urbulen energy dissipion re ε djoin urbulen energy dissipion re Θ design domin κ effecive herml conduciviy ν kinemic (lminr) viscosiy νeff effecive viscosiy νk effecive diffusiviy for k ν urbulen viscosiy νε effecive diffusiviy for ε ξ design vribles 1 INTRODUCTION To cree hermlly comforble nd helhy indoor environmen, convenionl designs use ril-nd-error process 1 h ssumes cerin hermo-fluid boundry condiions (B.C.), such s ir supply inle size, number, nd locions, ir supply velociy nd emperure, ec. An pproprie mehod is hen used o esime he resuling disribuions of ir emperure, velociy, relive humidiy, nd conminn concenrions. The ril-nd-error process is very ime consuming becuse he ssumed hermo-fluid B.C. my no be desirble. Recenly, inverse or opiml design processes hve emerged, such s he compuionl fluid dynmics (CFD)-bsed geneic lgorihm (GA) mehod 4, CFD-bsed proper orhogonl decomposiion (POD) mehod 5, CFD-bsed rificil neurl nework (ANN) mehod 6, nd djoin mehod 7. To design desirble indoor environmen, he CFD-bsed GA mehod mus clcule lrge number of smples, nd he number of clculions increses exponenilly wih he number of design vribles. To reduce compuing effor, Wei e l. 5 developed CFD-bsed POD mehod h cn rnsform he nonliner problem ino liner one nd build cuse-effec mpping relionship beween he objecive funcion nd design vribles. Since i is reduced-order mehod, he ccurcy of his mehod is grely reduced. The CFD-bsed ANN
3 mehod cn lso build he mpping relionship beween he objecive funcion nd design vribles, in his cse by selecing cerin number of smples o rin he ANN model. Wih well-rined ANN model, he design objecive cn be prediced wihou CFD clculions. However, he ccurcy of his mehod depends on he number of smples. In ddiion, he mpping relionship esblished by eiher he CFD-bsed POD mehod or he CFD-bsed ANN mehod is pplicble only o specific cse. For differen cse, he relionship would chnge. The djoin mehod cn quickly find he opiml design of n indoor environmen using n opimizion lgorihm wihou building mpping relionship for ech new problem, lhough i my become rpped in locl opim 8. The djoin mehod is he mos efficien nd suible mehod for he inverse design of hermlly comforble nd helhy indoor environmen. The djoin mehod ws developed recenly 9 for inversely designing n indoor environmen by solving se of Nvier-Sokes equions nd djoin equions, lernively. The djoin equions re derived from he coninuous Nvier-Sokes equions 10. Liu nd Chen 9 used he djoin mehod o inversely idenify he hermo-fluid B.C. required o chieve he opiml design of venilion for n enclosed environmen. Liu e l. 11 hen doped his mehod o improve he herml comfor level for n irline cbin. Zho e l. 1 lso emped o use he djoin mehod combined wih re-consrined opology nd cluser nlysis o design hermlly comforble indoor environmen. However, he resuls of hese sudies indiced h his mehod cnno mke he objecive funcions rech he idel vlues. One reson my be h he objecive funcions become rpped in locl opim. Anoher reson my be h he djoin mehod, which ws used in previous sudies 9, 11-14, derives only he djoin equions of he RANS equions wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion. Wih he ssumpion, he k nd ε will no feel chnges of he design vribles nd use he soluion (k nd ε) of he flow equions when he djoin equions re solved. The ssumpion cn reduce deriving mnully effor 14, 15 by neglecing vriions in he urbulen vribles. However, his mehod cn provide only pproxime grdiens, or even incorrec grdiens, which my no led o globl opim for he design. A vrin of he mehod is he discree djoin mehod 16, which firs discreizes he Nvier-Sokes equions nd hen derives he discree djoin equions from he discree Nvier-Sokes equions. Since he discree djoin mehod derives he complee djoin equions h include he djoin equions for clculing urbulen viscosiy, i cn provide ccure grdiens 17. However, i requires lrge moun of compuionl memory, which my no be ffordble in prcice. To obin ccure grdiens nd reduce compuionl memory, one opion is o develop coninuous djoin mehod wihou using he frozen urbulence ssumpion 18. Since he urbulen viscosiy ν in he momenum equion cn be solved by inroducing n pproprie urbulence model, some sudies hve derived he complee coninuous djoin equions wih n pproprie djoin urbulence model. Zymris e l. proposed Splr-Allmrs one-equion djoin urbulence model 19 nd sndrd k-ε djoin urbulence model 0 o minimize duc pressure losses. Ppousis-Kichgis 1 developed
4 low-reynolds-number Lunder-Shrm k-ε djoin urbulence model o opimize duc shpe, wih he im of minimizing viscous losses. All hese pplicions hve proved h n pproprie djoin urbulence model cn provide n ccure grdien of he objecive funcion over he design vribles. However, none of he bove urbulence models is suible for inversely designing n indoor environmen. Chen, Conceição e l., Zhng e l. 4 nd Zhng e l. 5 compred differen urbulence models nd found h he RNG k-ε urbulence model shows he bes overll performnce for solving indoor irflow mong vrious RANS models. In ddiion, here do no hve he corresponding djoin equion. Therefore, his sudy imed o develop n djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model for inversely designing n indoor environmen. METHODS.1 Adjoin mehod wih djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model To design n indoor environmen using he djoin mehod, we mus firs consruc suible objecive funcion. For exmple, he objecive funcion J is desirble disribuion of ir velociy V nd emperure T in he design domin Θ: ξ ( V T ) Θ J f, d (1) where ξ is vecor h represens he design vribles, such s ir supply inle size, number, nd locions; ir supply velociy, Vinle; ir supply emperure, Tinle, ec., h could led o he desirble disribuion. In his sudy, ir velociy V nd emperure T in he design domin Θ, s shown in Eq. (1), re conrolled by he incompressible, sedy-se RANS equions, s shown in Eqs. (), (), nd (4), closed wih he RNG k-ε urbulence model 6, s expressed by Eqs. (5) nd (6). N V 0 () 1 (N,N,N ) ( V) Vp ( D( V)) g (TT ) 0 () T 4 eff op 5 N V T T 0 (4) R V k k P G 0 (5) 1 k k b where R V C1Pk CGbC k C 1 / k (6) 4
5 165 ; c eff k ;P k V xj x i xj Vi j V i ; i, j x, y, z; 1 V V i j Sk/ ; S ( SijSij ); Sij ; Gb g xj x i Pr T (7) In hese equions, p represens he ir pressure; D(V) = (V+(V) T )/ is he re of srin ensor; k is he urbulen kineic energy; ε is he urbulen energy dissipion; cμ = ; η0 = 4.8; β = 0.01; Cε1 = 1.4; Cε = 1.68; Cε = 1; Gb is he buoyncy producion res of urbulen kineic energy; Pk is he sher producion res of he urbulence kineic energy; Pr urbulence Prndl number for emperure; S is he modulus of he men re-of-srin ensor; N represens he incompressible, sedy-se RANS equions in residul form; nd R represens he residul form of he RNG k-ε urbulence model equions. To minimize he objecive funcion s shown in Eq. (1), his invesigion used he seepes decen mehod 7 s shown in Eq. (8) o upde he design vribles. Therefore, he djoin mehod ws used o clcule he grdiens used in Eq. (8). dj ξn1 ξnn dξ where ξn, ξn+1 re design vribles curren nd succeeding design cycles, respecively; n represens he design cycle nd λ is he consn sep size. The djoin mehod inroduces n ugmened objecive funcion L s shown in Eq. (9) nd rnsforms he consrined design problem ino n unconsrined opimizion problem. Ω, k 5 n L J p, V,T, N, R dω (9) where Ω represens he compuionl domin nd p, V, T, k, nd ε re he djoin pressure, djoin velociy, djoin emperure, djoin urbulence kineic energy, nd djoin re of dissipion of urbulen energy, respecively. From Eq. (9) we cn hen derive he following djoin equions of he RANS equions closed wih he RNG k-ε urbulence model. Deiled inermedie derivion process of he djoin equions cn be found in 1. Adjoin coninuiy equion: V J 0 (10) p (8)
6 Adjoin momenum equion: V V V V p D V TT kk 6 eff V V J k C V i j 1 xj k xj x i 4 4 / 0 0 x j 1 1 Adjoin energy equion: / C 0 T T γ gk V V g Pr J C1C g 0 Pr k T Adjoin urbulen kineic energy equion: Vk kk 4 DVV TT kk k Pr k k k k P k gt C Pk k k Pr k k k k 1 J CC T C k 1 g Pr k k / 0 0 C C / 1/ 1 k 1 k Adjoin equion for he dissipion re of urbulen kineic energy: Pk g Pr k V DVV T T k k Pr 1 1 J k k T k C 4 4 / / 0 C 1 / 0 0 C k 1 k k (11) (1) (1) (14)
7 We lso give finl grdien of he ugmened objecive funcion over he design vribles: dl S p +S inle,inle V inle inle V,inle +S inle V inle V,inle S eff inle d dv n inle,i +S inle T inle T,inle S inle k inle k,inle S inle inle,inle dl dt V,inle d gv Vol S ( V T T gk n,inle inle inle inle,inle,inle,inle inle dn dn Pr CC g ) 1,inle Pr k e i (15) where Vinle, i is he inle ir velociy in he i h direcion, i = x, y, z; Sinle is he ouwrd-poining fce re vecor of inle cell; p, inle, V, inle, T, inle, k, inle nd ε, inle re he djoin pressure, djoin velociy, djoin emperure, he djoin urbulen kineic energy nd he djoin urbulen energy dissipion re he cell djcen o he corresponding boundry fce, respecively; kinle nd εinle re he urbulen kineic energy nd he urbulen energy dissipion re inle boundry fce, respecively; dn is he direcion vecor beween n inle cell cener nd he boundry fce cener; ei is he uni vecor in he i h direcion, i = x, y, z; Volinle is he inle cell volume. When he RANS equions closed wih he RNG k-ε urbulence model nd he djoin equions re numericlly solved in succession, ll se fields nd djoin fields needed for clculing he grdien of he objecive funcion over he design vribles re vilble.. Adjoin boundry condiions The djoin inle boundry condiions re h zero p, V, T, k, nd ε long he inle. V, T, k, nd ε re se o zero nd zero grdien boundry condiion of p he wll. While he djoin oule boundry condiions cn be deermined by: n V V V Vn n V p ntntk nk n eff V V i j k C1 n k x j x i / Cn / j (16) J (17) V j 0 J n n n n+ (18) T V T k g C1C g 0 Pr Pr k T 1 1 J knk knv TnT V 4 DVn+ 0 (19) Pr k k k 7
8 J DVV 0 n Vn+ n + (0) where n is he norml componen nd JΓ is he objecive funcion defined on boundry.. Numericl mehod The djoin mehod wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion nd he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model were previously implemened in OpenFOAM (Open Field Operion And Mnipulion) 9. The convecion nd diffusion erms of he RANS equions closed wih he urbulence model nd djoin equions were discreized by he firs-order upwind scheme nd he cenrl difference scheme, respecively. Previous sudies 1,7-9, 11-1 ll used he firs-order upwind scheme o discreize he convecion erms of boh se of equions nd none of he sudies hve no repored ny ccurcy issues. Thus, we used he sme scheme nd did no explore high-order numericl scheme. The Boussinesq pproximion 0 ws used o simule he herml plume genered by he emperure difference. The convergence crierion ws se s Jn-Jn-1 < δ (where n nd δ = 10 - ), where Jn-1, Jn re he objecive funcion previous nd curren design cycles, respecively. RESULTS In order o verify he performnce of he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model for inverse design of n indoor environmen, his sudy firs esed he proposed mehod by pplying i o wo-dimensionl veniled cviy 1 nd wo-person office hrough sep-by-sep process. The wo-dimensionl veniled cviy is simple cse wih mixed venilion, while he hree-dimensionl veniled office represens complee indoor environmen wih complex geomeries nd displcemen venilion. To prove he ccurcy of he proposed mehod nd he necessiy of developing new mehod, he djoin mehod wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion ws conduced s comprison. Finlly, his sudy used he vlided mehod o inversely design n opiml indoor environmen for he wo-person office..1 Two-dimensionl veniled cviy The firs cse is simple wo-dimensionl veniled cviy, s shown in Figure 1, wih experimenl d (i.e., velociy nd emperure) long he green cener lines nd deiled informion bou ll B.C. vilble 1. The experimen supplied ir hrough he inle he op of he lef wll nd exhused ir hrough he oule he boom of he righ wll. Wih he excepion of he floor, which ws heed o 5.5 ºC, he emperures of he ceiling nd wlls were ll conrolled 15.0 ºC. 8
9 FIGURE 1 Schemic of wo-dimensionl veniled cviy CFD simulion: Before sring he inverse design process, we needed o prove h we hd he biliy o conduc he CFD simulion correcly. This invesigion conduced CFD simulion using experimenl B.C. Experimenl d long he green cener lines ws used o verify he resuls of he simulion. Figure compres he ir velociy nd emperure profiles prediced by CFD wih he RNG k-ε urbulence model nd he experimenl d x = 0.5 l. The comprison indices h we were ble o predic he ir disribuion ccurely in he veniled cviy. However, he simulion resuls did no coincide compleely wih he experimenl resuls. The men relive error of he ir emperure beween he CFD simulion resuls nd he experimenl d is.%. However, he men relive error of he ir velociy is lile higher, h is becuse he velociy he cener of he cviy is very smll. Thus, here were errors beween he experimenl d nd he resuls prediced by CFD. The discrepncies my hve risen from mesuremen errors nd unconrollble fcors in he experimen nd numericl errors in he CFD simulion, especilly he RNG k-ε model. Such errors my ffec he inverse design resuls. If he experimenl d long he green lines were used s rge funcion for inverse modeling, he soluion would no be idel due o he inheried errors from he CFD in he djoin equions. Thus, i is beer o use CFD resuls long he green lines s rge funcion becuse he numericl errors in he CFD simulion re he sme s hose in he inversed simulion. 97 9
10 FIGURE Comprison of ir velociy nd emperure profiles prediced by CFD wih he RNG k-ε urbulence model nd experimenl d from Bly e l. 1 long he x = 0.5 l secion. Inverse design process: Since our purpose ws o verify he performnce of he proposed mehod using he numericl mehod, we se he CFD simulion resuls long he wo mid-secions (green lines) s rge vlues o elimine he influence of experimenl errors nd numericl errors, nd he ir supply prmeers s he design vribles o consruc he objecive funcion. If he ir supply prmeers idenified were found o be consisen wih he experimenl ir supply prmeers, he proposed mehod would be verified. For his cse, we used he prediced ir velociy V0, ii (vecor) nd ir emperure T0, ii in design domin (he vlues long he wo mid-secions), Θ, s he rge vlues o consruc he objecive funcion, which cn be expressed s: where m m 1 norm ii 0,ii norm ii 0, ii J ξ W V V V W T T T (1) ii1 1 1 V ;T ii1 norm V norm inle, x Tmx Tm in where W1 nd W re he weighing fcors, ssumed o be 0.5 in his sudy; Vnorm nd Tnorm re he normlizion fcors; nd Tmx nd Tmin re equl o 5.5ºC nd 15.0ºC, respecively; m is he ol number d in he design domin; Vii nd Tii re he inversely designed resuls in he design domin, in his cse, respecively. Wih he bove objecive funcion, he djoin mehod wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model sred is inverse design process from he iniil inle B.C. These B.C. were Vinle = (0.8, 0) m/s nd Tinle =.0ºC. For ech design cycle, boh he RANS equions closed wih he urbulence model nd he djoin equions were clculed wih he use of,000 ierions o ensure convergence. To sudy he ccurcy of he grdien clculed by he proposed mehod nd rule ou he influence of sep size, we doped he seepes descen mehod wih proper consn sep size in Eq. (8) o upde he design vribles. Since n improper consn sep size could cuse he objecive funcion o become rpped in locl opim or he clculion o diverge, his invesigion es differen sep sizes for proper sep sizes (0.016 for upding Vinle is nd 00 for upding Tinle). Wih he proper sep sizes nd he sme iniilized ir supply prmeers, we lso used he djoin mehod wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion o inversely idenify he opiml design vribles for he veniled cviy, in order o illusre he need for he new mehod. Figure compred he k wih k (djoin k) of hese wo mehods when solving he djoin () 10
11 equions he firs design cycle h ws becuse hese wo mehods hve he sme ir supply prmeers only in his design cycle during he inverse design process. The k is he urbulen energy, while he k is djoin urbulen energy. The urbulen energy represens he degree of chos of he flow, while he djoin urbulen energy is he opposie. They re very differen becuse wo ses of equions re differen. As resul, he grdiens clculed by hese wo mehods re differen. When he objecive funcion minimized by he djoin mehod wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion me he convergence crieri, s shown in Figure 4, he objecive funcion minimized by he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model reched he sme vlue lmos he sme ime. However, he new mehod cn cuse he objecive funcion o coninue o decrese. The design vribles idenified by he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model for Cse A- were lmos he sme s he known experimenl d, s shown in Tble 1. This indices h he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model hs higher clculion ccurcy. k k () (b) FIGURE Comprison of () k soluion of he flow equion nd (b) k clculed by he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model he firs design cycle FIGURE 4 Vriion in he objecive funcion wih he design cycle for he wo-dimensionl veniled cviy 11
12 TABLE 1 Design vribles idenified by wo mehods compred wih he experimenl B.C. Vinle, x Vinle, y Tinle (m/s) (m/s) (K) J Wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion E Wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model E E-4 Experimenl d Afer he opiml ir supply prmeers, s shown in Tble 1, hd been idenified by he wo mehods, we conduced CFD simulion wih he RNG k-ε urbulence model o deermine wheher he opimized ir disribuion ws consisen wih he rge vlues (red line/dos). Figure 5 illusres he velociy vecor nd emperure profiles in he design domin prediced wih he ir supply prmeers idenified by he djoin mehod wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion (green line/dos) nd wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model (blue lines/dos). The ir disribuion in he design domin opimized wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model ws closer o he rge vlues hn he disribuion opimized wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion, especilly in he cener of he design domin. The ir emperures x = 0.5 l prediced wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion were lso much lower hn he cul vlues. Thus, he performnce of he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model ws beer. Inle Wll Design domin 75 y x Floor Oule FIGURE 5 Comprison of ir velociy vecors in he design domin nd emperure profiles x = 0.5 l prediced by he experimenl B.C. from Bly e l. 1 nd he ir supply prmeers idenified by he djoin mehod wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion nd wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model 1
13 Three-dimensionl veniled office The second cse is hree-dimensionl veniled office, s shown in Figure 6, wih experimenl d. In he experimen, he office ws veniled by displcemen venilion sysem wih n ir supply velociy of Vinle = (0.09, 0, 0) m/s nd ir supply emperure of Tinle = 17 ºC. The ir ws supplied hrough wll diffuser floor level nd exhused hrough n oule ceiling level. This office ws more compliced hn he wo-dimensionl veniled cviy nd closer o reliy, lhough he occupns, compuers, cbines, nd lighs were ll simplified s recngulr boxes. Therefore, i ws more prcicl o use his office for inversely idenifying he opiml ir supply prmeers. Similr o he previous cse, we used CFD simulion resuls long lines 1,, 5, 7, nd 9 o consruc he objecive funcion s expressed by Eqs. (1) nd (). We used srucured grid of hexhedrl elemens in his geomeric model, wih 7,51 cells ccording o our grid-independence ess FIGURE 6 Schemic of wo-person office, nd he design domin locion where he numbers 1 o 9 indice locions where ir velociy nd emperure profiles were mesured in he experimen. To sr he inverse design process, he inle B.C. were iniilized s Vinle = (0.5, 0, 0) m/s nd Tinle = 0ºC. Noe h he sep sizes for upding Vinle nd Tinle were 0.0 nd 100, respecively. Figure 7 shows he vriion in he objecive funcion wih he design cycle during he inverse design process, wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion nd wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model. The convergence speed wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion ws en imes fser hn h he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model. This occurred becuse he grdiens clculed wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion were lrger hn hose clculed wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model in he firs wo design cycles. However, wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model, one could obin n objecive funcion close o zero. 1
14 FIGURE 7 Vriion in he objecive funcion wih he design cycle for he hree-dimensionl veniled office cse TABLE Design vribles idenified by wo mehods compred wih experimenl B.C. Vinle, x Vinle, y Vinle, z Tinle (ºC) (m/s) (m/s) (m/s) Wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion E-4.5E Wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model E-6.1E Experimenl d As shown in Tble, he ir supply prmeers finlly idenified by he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model were close o he experimenl d. We hen used hese prmeers o conduc CFD simulions o deermine wheher he idenified ir supply prmeers formed he sme ir disribuion s he resuls wih experimenl B.C. Figure 8 quniively compres he prediced ir velociy nd ir emperure profiles wih he experimenl profiles he cener of he room (line ) s n exmple. The ir supply prmeers idenified by he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model were much beer hn hose wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion. 14
15 FIGURE 8 Comprison of ir velociy nd emperure profiles prediced by he experimenl B.C. from Yun e l. nd he ir supply prmeers idenified by he djoin mehod wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion nd wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model wih he experimenl d in he cener of he room. Inverse design of comforble indoor environmen for he hree-dimensionl veniled office Using he vlided djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model, his invesigion nex conduced n opiml design of he indoor environmen for he wo-person office. In he opiml design process, he design domin ws he surfces disnce of 0.1 m wy from he occupns, s shown in Figure 9. We used he prediced men voe (PMV) 4 o evlue he herml comfor level in he domin. The rnge of PMV vlues is from - o, nd PMV = 0 signifies high comfor level. Our design gol ws o idenify he opiml ξ (ir supply velociy Vinle nd ir supply emperure Tinle) h would mke he verge PMV in he design domin close or equl o zero. Thus, he objecive funcion cn be expressed by PMV d Jξ () d For comforble indoor environmen, he ir quliy mus sisfy he design crieri. According o he ASHRAE Hndbook 5, he generl design crierion used for office buildings is les 4 ir chnges per hour, nd he corresponding fce velociy for his office ws m/s. Therefore, we dded his consrin (Vinle, x m/s) o insure indoor ir quliy 15
16 during he inverse design process FIGURE 9 Schemic of wo-person office nd inverse design domin Figure 10 depics he vriion in he objecive funcion wih he design cycle during he inverse design process. The inverse design process chieved he convergence crierion fer 18 design cycles. The finl objecive funcion minimized by he djoin mehod wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model ws 0.1 nd did no chieve zero. The reson my be h he objecive funcion ws rpped in locl opim. The finl B.C. idenified were Vinle = (0.184, -5.0E-04, 1.E-04) m/s nd Tinle = ºC FIGURE 10 Vriion in he objecive funcion wih he design cycle during he opiml design processes wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model. Figure 11 depics he PMV disribuions round he occupns inversely designed by he djoin mehod wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model. The men PMV vlue round he occupn is 0.1 nd PMV disribuions re ll ner zero. Hence, he djoin mehod wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model hs good performnce in he opiml design of he indoor environmen. 16
17 FIGURE 11 PMV disribuions round he occupns inversely designed by he djoin mehod wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model 4 DISCUSSION The djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model improved he opiml design ccurcy, bu i could no overcome he inheren disdvnges of he djoin mehod. The objecive funcion could lso become rpped in locl opim. If he iniil design vribles were fr wy from he opiml vlues or he sep size ws no pproprie, he clculion migh no led o he opiml design. This sudy used only PMV o evlue he herml comfor level nd o dd consrin o ensure h he indoor ir quliy me he sndrd. Wih he djoin mehod, one could dd furher design objecives wihou incresing he compuing coss. The design vribles deermined in Secion. did no mke he objecive funcion equl o zero. This resul my imply h he consrins were oo resricive. For exmple, he design process did no llow chnges in he posiion, size, or shpe of he ir supply inles. For he sme cse wih differen objecive funcions in secions. nd., he convergence speed is no comprble. This ws becuse he relionship beween he objecive funcion nd he design vribles ws no explici. This invesigion only used he firs-order upwind scheme nd he cenrl difference scheme o discreize he convecion nd diffusion erms of he RANS equions closed wih he urbulence model nd djoin equions, respecively. While, he influence of differen discreizion schemes on he inverse design resuls is no cler he momen nd our fuure reserch will conduc n in-deph sudy nd nlysis of his issue. 5 CONCLUSIONS This invesigion developed n djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model for he djoin mehod for opiml design of he indoor environmen. The following conclusions cn be drwn from his sudy: The design process wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model idenified design 17
18 vribles h were more ccure hn hose idenified wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion. However, he design vribles idenified wih he frozen urbulence ssumpion were more sble during he inverse design process. The djoin mehod wih he djoin RNG k-ε urbulence model cn be used o design he opiml indoor environmen for n office. Design objecive could include ir velociy disribuion, emperure disribuion, nd he combinion of vribles clculed by CFD, such s herml comfor, indoor ir quliy, ec. The design vribles mus no be overly resricive. Oherwise, he objecive funcions my no rech zero, even fer numerous design cycles. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This reserch ws prilly suppored by he Nionl Key R&D Progrm of he Minisry of Science nd Technology, Chin, on Green Buildings nd Building Indusrilizion hrough Grn No. 016YFC nd by he Nionl Nurl Science Foundion of Chin hrough Grn No REFERENCES 1. Liu W, Zhng T, Xue Y, e l. Se-of-he-r mehods for inverse design of n enclosed environmen. Build Environ. 015; 91: Chen Q, Zhi Z, You X, Zhng T. Inverse Design Mehods for Buil Environmen. Rouledge, Oxford, Englnd; Chen Q. Venilion performnce predicion for buildings: A mehod overview nd recen pplicions. Build Environ. 009; 44: Xue Y, Zhi ZJ, Chen Q. Inverse predicion nd opimizion of flow conrol condiions for confined spces using CFD-bsed geneic lgorihm. Build Environ. 01; 64: Wei Y, Zhng TT, Wng S. Promp design of he ir-supply opening size for commercil irplne bsed on he proper orhogonl decomposiion of flows. Build Environ. 016; 96: Zhng T, You X. A simulion-bsed inverse design of prese ircrf cbin environmen. Build Environ. 014; 8: W. Liu, M. Jin, C. Chen, Q. Chen. Opimizion of ir supply locion, size, nd prmeers in enclosed environmens using compuionl fluid dynmics-bsed djoin mehod. J Build Perform Simu. 016; 9(): Liu W, You R, Zhng J, Chen Q. Developmen of fs fluid dynmics-bsed djoin mehod for he inverse design of indoor environmens. J Build Perform Simu. 016; 10(): Liu W, Chen Q. Opiml ir disribuion design in enclosed spces using n djoin mehod. Inverse Probl Sci En. 015; (5): Ndrjh S, Jmeson A. A comprison of he coninuous nd discree djoin pproch o uomic erodynmic opimizion. In 8h Aerospce Sciences Meeing nd Exhibi. 000; Liu W, Dun R, Chen C, e l. Inverse design of he herml environmen in n irliner cbin by use of he CFD-bsed djoin mehod. Energ Buildings. 015; 104(): Zho X, Liu W, Li D, Chen Q. Opiml design of n indoor environmen by he 18
19 CFD-bsed djoin mehod wih re-consrined opology nd cluser nlysis. Build Environ. 018; 18: Zho X, Liu W, Liu S, e l. Inverse design of n indoor environmen using CFD-bsed djoin mehod wih he dpive sep size for djusing he design prmeers. Numer He Tr A-Appl. 017; 71(7): Ohmer C. A coninuous djoin formulion for he compuion of opologicl nd surfce sensiiviies of duced flows. In J Numer Meh Fl. 008; 58(8): Kim CS, Kim C, Rho OH. Fesibiliy sudy of consn eddy-viscosiy ssumpion in grdien-bsed design opimizion. J Aircrf. 00; 40(6): Dwigh RP, Brezillon J. Effec of pproximions of he discree djoin on grdien-bsed opimizion. AIAA J. 006; 44(1): Towr M, Numnn U. A discree djoin model for OpenFOAM. Procedi Compuer Science. 01; 18: Ppdimiriou DI, Ginnkoglou KC. A coninuous djoin mehod wih objecive funcion derivives bsed on boundry inegrls for inviscid nd viscous flows. Compu Fluids. 007; 6 (): Zymris AS, Ppdimiriou DI, Ginnkoglou KC, Ohmer C. Coninuous djoin pproch o he splr-llmrs urbulence model for incompressible flows. Compu Fluids. 009; 8 (8): Zymris AS, Ppdimiriou DI, Ginnkoglou KC, Ohmer C. Adjoin wll funcions: A new concep for use in erodynmic shpe opimizion. J Compu Phys. 010; 9 (1): Ppousis-Kichgis EM, Zymris AS, Kvvdis IS, e l. The coninuous djoin pproch o he k-ε urbulence model for shpe opimizion nd opiml cive conrol of urbulen flows. Eng Opimiz. 015; 47(): Chen Q. Comprison of differen k-ε models for indoor ir flow compuions. Numer He Tr B-Fund. 1995; 8: Conceição EZE, Lúcio M. Numericl simulion of he pplicion of solr rdin sysems, inernl irflow nd occupns presence in he improvemen of comfor in winer condiions[j]. Buildings, 016; 6(): Zhng T, Li P, Zho Y, Wng S. Vrious ir disribuion modes on commercil irplnes-pr : Compuionl fluid dynmics modeling nd vlidion. HVAC&R Res. 01; 19(5): Zhng Z, Zhng W, Zhi ZJ, Chen QY. Evluion of vrious urbulence models in predicing irflow nd urbulence in enclosed environmens by CFD: Pr -Comprison wih experimenl d from lierure. HVAC&R Res. 007; 1 (6): Ykho V, Orszg S A, Thngm S, e l. Developmen of urbulence models for sher flows by double expnsion echnique [J]. Phys Fluid Fluid Dynm, 199; 4(7): Oreg BJM, Rheinbold WC. Ierive Soluion of Nonliner Equions in Severl Vribles. Chp. 8, Acdemic Press, New York, Kuzmin D, Mierk O, Turek S. On he implemenion of he k-ε urbulence model in incompressible flow solvers bsed on finie elemen discreizion. In J Compu Mh. 007; 1(-4): OpenFOAM. The Open Source CFD Toolbox. hp://
20 Boussinesq J. Theorie Anlyique de l Chleur, Guhier-Villrs; Bly D, Mergui S, Nicule C. Confined urbulen mixed convecion in he presence of horizonl buoyn wll je. Fundmenls of Mixed Convecion, ASME HTD. 199; 1: Yun X, Chen Q, Glicksmn LR, e l. Mesuremens nd compuions of room irflow wih displcemen venilion. ASHRAE Trns. 1999; 105: Zhng TT, Lee K, Chen Q. A simplified pproch o describe complex diffusers in displcemen venilion for CFD simulions. Indoor Air. 009; 19(): Fnger PO. Therml Comfor. Rober E. Kn'cger Publishing Compny, Florid; ASHRAE. ASHRAE Hndbook - HVAC Applicions (SI). Aln: Americn Sociey of Heing, Refrigering nd Air Condiioning Engineers
Motion. Part 2: Constant Acceleration. Acceleration. October Lab Physics. Ms. Levine 1. Acceleration. Acceleration. Units for Acceleration.
 Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
e t dt e t dt = lim e t dt T (1 e T ) = 1
 Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
A Kalman filtering simulation
 A Klmn filering simulion The performnce of Klmn filering hs been esed on he bsis of wo differen dynmicl models, ssuming eiher moion wih consn elociy or wih consn ccelerion. The former is epeced o beer
A Klmn filering simulion The performnce of Klmn filering hs been esed on he bsis of wo differen dynmicl models, ssuming eiher moion wih consn elociy or wih consn ccelerion. The former is epeced o beer
September 20 Homework Solutions
 College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
Contraction Mapping Principle Approach to Differential Equations
 epl Journl of Science echnology 0 (009) 49-53 Conrcion pping Principle pproch o Differenil Equions Bishnu P. Dhungn Deprmen of hemics, hendr Rn Cmpus ribhuvn Universiy, Khmu epl bsrc Using n eension of
epl Journl of Science echnology 0 (009) 49-53 Conrcion pping Principle pproch o Differenil Equions Bishnu P. Dhungn Deprmen of hemics, hendr Rn Cmpus ribhuvn Universiy, Khmu epl bsrc Using n eension of
Physics 2A HW #3 Solutions
 Chper 3 Focus on Conceps: 3, 4, 6, 9 Problems: 9, 9, 3, 41, 66, 7, 75, 77 Phsics A HW #3 Soluions Focus On Conceps 3-3 (c) The ccelerion due o grvi is he sme for boh blls, despie he fc h he hve differen
Chper 3 Focus on Conceps: 3, 4, 6, 9 Problems: 9, 9, 3, 41, 66, 7, 75, 77 Phsics A HW #3 Soluions Focus On Conceps 3-3 (c) The ccelerion due o grvi is he sme for boh blls, despie he fc h he hve differen
Chapter 2: Evaluative Feedback
 Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
0 for t < 0 1 for t > 0
 8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
Version 001 test-1 swinney (57010) 1. is constant at m/s.
 Version 001 es-1 swinne (57010) 1 This prin-ou should hve 20 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions m coninue on he nex column or pge find ll choices before nswering. CubeUniVec1x76 001 10.0 poins Acubeis1.4fee
Version 001 es-1 swinne (57010) 1 This prin-ou should hve 20 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions m coninue on he nex column or pge find ll choices before nswering. CubeUniVec1x76 001 10.0 poins Acubeis1.4fee
The solution is often represented as a vector: 2xI + 4X2 + 2X3 + 4X4 + 2X5 = 4 2xI + 4X2 + 3X3 + 3X4 + 3X5 = 4. 3xI + 6X2 + 6X3 + 3X4 + 6X5 = 6.
 [~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
[~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mathematics The Integral of a Function as a Function
 ENGR 1990 Engineering Mhemics The Inegrl of Funcion s Funcion Previously, we lerned how o esime he inegrl of funcion f( ) over some inervl y dding he res of finie se of rpezoids h represen he re under
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mhemics The Inegrl of Funcion s Funcion Previously, we lerned how o esime he inegrl of funcion f( ) over some inervl y dding he res of finie se of rpezoids h represen he re under
f t f a f x dx By Lin McMullin f x dx= f b f a. 2
 Accumulion: Thoughs On () By Lin McMullin f f f d = + The gols of he AP* Clculus progrm include he semen, Sudens should undersnd he definie inegrl s he ne ccumulion of chnge. 1 The Topicl Ouline includes
Accumulion: Thoughs On () By Lin McMullin f f f d = + The gols of he AP* Clculus progrm include he semen, Sudens should undersnd he definie inegrl s he ne ccumulion of chnge. 1 The Topicl Ouline includes
5.1-The Initial-Value Problems For Ordinary Differential Equations
 5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
MATH 124 AND 125 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 2008)
 MATH 14 AND 15 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 8) The following quesions cn be used s review for Mh 14/ 15 These quesions re no cul smples of quesions h will pper on he finl em, bu hey will provide
MATH 14 AND 15 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 8) The following quesions cn be used s review for Mh 14/ 15 These quesions re no cul smples of quesions h will pper on he finl em, bu hey will provide
1.0 Electrical Systems
 . Elecricl Sysems The ypes of dynmicl sysems we will e sudying cn e modeled in erms of lgeric equions, differenil equions, or inegrl equions. We will egin y looking fmilir mhemicl models of idel resisors,
. Elecricl Sysems The ypes of dynmicl sysems we will e sudying cn e modeled in erms of lgeric equions, differenil equions, or inegrl equions. We will egin y looking fmilir mhemicl models of idel resisors,
A new model for limit order book dynamics
 Anewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics JeffreyR.Russell UniversiyofChicgo,GrdueSchoolofBusiness TejinKim UniversiyofChicgo,DeprmenofSisics Absrc:Thispperproposesnewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics.Thelimiorderbookconsiss
Anewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics JeffreyR.Russell UniversiyofChicgo,GrdueSchoolofBusiness TejinKim UniversiyofChicgo,DeprmenofSisics Absrc:Thispperproposesnewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics.Thelimiorderbookconsiss
3. Renewal Limit Theorems
 Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
4.8 Improper Integrals
 4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEM
 Elecronic Journl of Differenil Equions, Vol. 208 (208), No. 50, pp. 6. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mh.xse.edu or hp://ejde.mh.un.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE
Elecronic Journl of Differenil Equions, Vol. 208 (208), No. 50, pp. 6. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mh.xse.edu or hp://ejde.mh.un.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE
1 jordan.mcd Eigenvalue-eigenvector approach to solving first order ODEs. -- Jordan normal (canonical) form. Instructor: Nam Sun Wang
 jordnmcd Eigenvlue-eigenvecor pproch o solving firs order ODEs -- ordn norml (cnonicl) form Insrucor: Nm Sun Wng Consider he following se of coupled firs order ODEs d d x x 5 x x d d x d d x x x 5 x x
jordnmcd Eigenvlue-eigenvecor pproch o solving firs order ODEs -- ordn norml (cnonicl) form Insrucor: Nm Sun Wng Consider he following se of coupled firs order ODEs d d x x 5 x x d d x d d x x x 5 x x
A 1.3 m 2.5 m 2.8 m. x = m m = 8400 m. y = 4900 m 3200 m = 1700 m
 PHYS : Soluions o Chper 3 Home Work. SSM REASONING The displcemen is ecor drwn from he iniil posiion o he finl posiion. The mgniude of he displcemen is he shores disnce beween he posiions. Noe h i is onl
PHYS : Soluions o Chper 3 Home Work. SSM REASONING The displcemen is ecor drwn from he iniil posiion o he finl posiion. The mgniude of he displcemen is he shores disnce beween he posiions. Noe h i is onl
PHYSICS 1210 Exam 1 University of Wyoming 14 February points
 PHYSICS 1210 Em 1 Uniersiy of Wyoming 14 Februry 2013 150 poins This es is open-noe nd closed-book. Clculors re permied bu compuers re no. No collborion, consulion, or communicion wih oher people (oher
PHYSICS 1210 Em 1 Uniersiy of Wyoming 14 Februry 2013 150 poins This es is open-noe nd closed-book. Clculors re permied bu compuers re no. No collborion, consulion, or communicion wih oher people (oher
Convergence of Singular Integral Operators in Weighted Lebesgue Spaces
 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS Vol. 10, No. 2, 2017, 335-347 ISSN 1307-5543 www.ejpm.com Published by New York Business Globl Convergence of Singulr Inegrl Operors in Weighed Lebesgue
EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS Vol. 10, No. 2, 2017, 335-347 ISSN 1307-5543 www.ejpm.com Published by New York Business Globl Convergence of Singulr Inegrl Operors in Weighed Lebesgue
Average & instantaneous velocity and acceleration Motion with constant acceleration
 Physics 7: Lecure Reminders Discussion nd Lb secions sr meeing ne week Fill ou Pink dd/drop form if you need o swich o differen secion h is FULL. Do i TODAY. Homework Ch. : 5, 7,, 3,, nd 6 Ch.: 6,, 3 Submission
Physics 7: Lecure Reminders Discussion nd Lb secions sr meeing ne week Fill ou Pink dd/drop form if you need o swich o differen secion h is FULL. Do i TODAY. Homework Ch. : 5, 7,, 3,, nd 6 Ch.: 6,, 3 Submission
HORIZONTAL POSITION OPTIMAL SOLUTION DETERMINATION FOR THE SATELLITE LASER RANGING SLOPE MODEL
 HOIZONAL POSIION OPIMAL SOLUION DEEMINAION FO HE SAELLIE LASE ANGING SLOPE MODEL Yu Wng,* Yu Ai b Yu Hu b enli Wng b Xi n Surveying nd Mpping Insiue, No. 1 Middle Yn od, Xi n, Chin, 710054-640677@qq.com
HOIZONAL POSIION OPIMAL SOLUION DEEMINAION FO HE SAELLIE LASE ANGING SLOPE MODEL Yu Wng,* Yu Ai b Yu Hu b enli Wng b Xi n Surveying nd Mpping Insiue, No. 1 Middle Yn od, Xi n, Chin, 710054-640677@qq.com
M r. d 2. R t a M. Structural Mechanics Section. Exam CT5141 Theory of Elasticity Friday 31 October 2003, 9:00 12:00 hours. Problem 1 (3 points)
 Delf Universiy of Technology Fculy of Civil Engineering nd Geosciences Srucurl echnics Secion Wrie your nme nd sudy numer he op righ-hnd of your work. Exm CT5 Theory of Elsiciy Fridy Ocoer 00, 9:00 :00
Delf Universiy of Technology Fculy of Civil Engineering nd Geosciences Srucurl echnics Secion Wrie your nme nd sudy numer he op righ-hnd of your work. Exm CT5 Theory of Elsiciy Fridy Ocoer 00, 9:00 :00
A Time Truncated Improved Group Sampling Plans for Rayleigh and Log - Logistic Distributions
 ISSNOnline : 39-8753 ISSN Prin : 347-67 An ISO 397: 7 Cerified Orgnizion Vol. 5, Issue 5, My 6 A Time Trunced Improved Group Smpling Plns for Ryleigh nd og - ogisic Disribuions P.Kvipriy, A.R. Sudmni Rmswmy
ISSNOnline : 39-8753 ISSN Prin : 347-67 An ISO 397: 7 Cerified Orgnizion Vol. 5, Issue 5, My 6 A Time Trunced Improved Group Smpling Plns for Ryleigh nd og - ogisic Disribuions P.Kvipriy, A.R. Sudmni Rmswmy
On the Pseudo-Spectral Method of Solving Linear Ordinary Differential Equations
 Journl of Mhemics nd Sisics 5 ():136-14, 9 ISS 1549-3644 9 Science Publicions On he Pseudo-Specrl Mehod of Solving Liner Ordinry Differenil Equions B.S. Ogundre Deprmen of Pure nd Applied Mhemics, Universiy
Journl of Mhemics nd Sisics 5 ():136-14, 9 ISS 1549-3644 9 Science Publicions On he Pseudo-Specrl Mehod of Solving Liner Ordinry Differenil Equions B.S. Ogundre Deprmen of Pure nd Applied Mhemics, Universiy
Thermal neutron self-shielding factor in foils: a universal curve
 Proceedings of he Inernionl Conference on Reserch Recor Uilizion, Sfey, Decommissioning, Fuel nd Wse Mngemen (Snigo, Chile, -4 Nov.3) Pper IAEA-CN-/, IAEA Proceedings Series, Vienn, 5 Therml neuron self-shielding
Proceedings of he Inernionl Conference on Reserch Recor Uilizion, Sfey, Decommissioning, Fuel nd Wse Mngemen (Snigo, Chile, -4 Nov.3) Pper IAEA-CN-/, IAEA Proceedings Series, Vienn, 5 Therml neuron self-shielding
1. Consider a PSA initially at rest in the beginning of the left-hand end of a long ISS corridor. Assume xo = 0 on the left end of the ISS corridor.
 In Eercise 1, use sndrd recngulr Cresin coordine sysem. Le ime be represened long he horizonl is. Assume ll ccelerions nd decelerions re consn. 1. Consider PSA iniilly res in he beginning of he lef-hnd
In Eercise 1, use sndrd recngulr Cresin coordine sysem. Le ime be represened long he horizonl is. Assume ll ccelerions nd decelerions re consn. 1. Consider PSA iniilly res in he beginning of he lef-hnd
FM Applications of Integration 1.Centroid of Area
 FM Applicions of Inegrion.Cenroid of Are The cenroid of ody is is geomeric cenre. For n ojec mde of uniform meril, he cenroid coincides wih he poin which he ody cn e suppored in perfecly lnced se ie, is
FM Applicions of Inegrion.Cenroid of Are The cenroid of ody is is geomeric cenre. For n ojec mde of uniform meril, he cenroid coincides wih he poin which he ody cn e suppored in perfecly lnced se ie, is
Solutions for Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations By Tan-Cot Method
 IOSR Journl of Mhemics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578. Volume 5, Issue 3 (Jn. - Feb. 13), PP 6-11 Soluions for Nonliner Pril Differenil Equions By Tn-Co Mehod Mhmood Jwd Abdul Rsool Abu Al-Sheer Al -Rfidin Universiy
IOSR Journl of Mhemics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578. Volume 5, Issue 3 (Jn. - Feb. 13), PP 6-11 Soluions for Nonliner Pril Differenil Equions By Tn-Co Mehod Mhmood Jwd Abdul Rsool Abu Al-Sheer Al -Rfidin Universiy
2D Motion WS. A horizontally launched projectile s initial vertical velocity is zero. Solve the following problems with this information.
 Nme D Moion WS The equions of moion h rele o projeciles were discussed in he Projecile Moion Anlsis Acii. ou found h projecile moes wih consn eloci in he horizonl direcion nd consn ccelerion in he ericl
Nme D Moion WS The equions of moion h rele o projeciles were discussed in he Projecile Moion Anlsis Acii. ou found h projecile moes wih consn eloci in he horizonl direcion nd consn ccelerion in he ericl
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 9: The High Beta Tokamak
 .65, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 9: The High e Tokmk Summry of he Properies of n Ohmic Tokmk. Advnges:. good euilibrium (smll shif) b. good sbiliy ( ) c. good confinemen ( τ nr )
.65, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 9: The High e Tokmk Summry of he Properies of n Ohmic Tokmk. Advnges:. good euilibrium (smll shif) b. good sbiliy ( ) c. good confinemen ( τ nr )
6. Gas dynamics. Ideal gases Speed of infinitesimal disturbances in still gas
 6. Gs dynmics Dr. Gergely Krisóf De. of Fluid echnics, BE Februry, 009. Seed of infiniesiml disurbnces in sill gs dv d, dv d, Coninuiy: ( dv)( ) dv omenum r r heorem: ( ( dv) ) d 3443 4 q m dv d dv llievi
6. Gs dynmics Dr. Gergely Krisóf De. of Fluid echnics, BE Februry, 009. Seed of infiniesiml disurbnces in sill gs dv d, dv d, Coninuiy: ( dv)( ) dv omenum r r heorem: ( ( dv) ) d 3443 4 q m dv d dv llievi
Nonlinear System Modelling: How to Estimate the. Highest Significant Order
 IEEE Insrumenion nd Mesuremen Technology Conference nchorge,, US, - My Nonliner Sysem Modelling: ow o Esime he ighes Significn Order Neophyos Chirs, Ceri Evns nd Dvid Rees, Michel Solomou School of Elecronics,
IEEE Insrumenion nd Mesuremen Technology Conference nchorge,, US, - My Nonliner Sysem Modelling: ow o Esime he ighes Significn Order Neophyos Chirs, Ceri Evns nd Dvid Rees, Michel Solomou School of Elecronics,
LAPLACE TRANSFORM OVERCOMING PRINCIPLE DRAWBACKS IN APPLICATION OF THE VARIATIONAL ITERATION METHOD TO FRACTIONAL HEAT EQUATIONS
 Wu, G.-.: Lplce Trnsform Overcoming Principle Drwbcks in Applicion... THERMAL SIENE: Yer 22, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 257-26 257 Open forum LAPLAE TRANSFORM OVEROMING PRINIPLE DRAWBAKS IN APPLIATION OF THE VARIATIONAL
Wu, G.-.: Lplce Trnsform Overcoming Principle Drwbcks in Applicion... THERMAL SIENE: Yer 22, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 257-26 257 Open forum LAPLAE TRANSFORM OVEROMING PRINIPLE DRAWBAKS IN APPLIATION OF THE VARIATIONAL
RESPONSE UNDER A GENERAL PERIODIC FORCE. When the external force F(t) is periodic with periodτ = 2π
 RESPONSE UNDER A GENERAL PERIODIC FORCE When he exernl force F() is periodic wih periodτ / ω,i cn be expnded in Fourier series F( ) o α ω α b ω () where τ F( ) ω d, τ,,,... () nd b τ F( ) ω d, τ,,... (3)
RESPONSE UNDER A GENERAL PERIODIC FORCE When he exernl force F() is periodic wih periodτ / ω,i cn be expnded in Fourier series F( ) o α ω α b ω () where τ F( ) ω d, τ,,,... () nd b τ F( ) ω d, τ,,... (3)
A LIMIT-POINT CRITERION FOR A SECOND-ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR IAN KNOWLES
 A LIMIT-POINT CRITERION FOR A SECOND-ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR j IAN KNOWLES 1. Inroducion Consider he forml differenil operor T defined by el, (1) where he funcion q{) is rel-vlued nd loclly
A LIMIT-POINT CRITERION FOR A SECOND-ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR j IAN KNOWLES 1. Inroducion Consider he forml differenil operor T defined by el, (1) where he funcion q{) is rel-vlued nd loclly
Neural assembly binding in linguistic representation
 Neurl ssembly binding in linguisic represenion Frnk vn der Velde & Mrc de Kmps Cogniive Psychology Uni, Universiy of Leiden, Wssenrseweg 52, 2333 AK Leiden, The Neherlnds, vdvelde@fsw.leidenuniv.nl Absrc.
Neurl ssembly binding in linguisic represenion Frnk vn der Velde & Mrc de Kmps Cogniive Psychology Uni, Universiy of Leiden, Wssenrseweg 52, 2333 AK Leiden, The Neherlnds, vdvelde@fsw.leidenuniv.nl Absrc.
An integral having either an infinite limit of integration or an unbounded integrand is called improper. Here are two examples.
 Improper Inegrls To his poin we hve only considered inegrls f(x) wih he is of inegrion nd b finie nd he inegrnd f(x) bounded (nd in fc coninuous excep possibly for finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegrl
Improper Inegrls To his poin we hve only considered inegrls f(x) wih he is of inegrion nd b finie nd he inegrnd f(x) bounded (nd in fc coninuous excep possibly for finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegrl
Temperature Rise of the Earth
 Avilble online www.sciencedirec.com ScienceDirec Procedi - Socil nd Behviorl Scien ce s 88 ( 2013 ) 220 224 Socil nd Behviorl Sciences Symposium, 4 h Inernionl Science, Socil Science, Engineering nd Energy
Avilble online www.sciencedirec.com ScienceDirec Procedi - Socil nd Behviorl Scien ce s 88 ( 2013 ) 220 224 Socil nd Behviorl Sciences Symposium, 4 h Inernionl Science, Socil Science, Engineering nd Energy
S Radio transmission and network access Exercise 1-2
 S-7.330 Rdio rnsmission nd nework ccess Exercise 1 - P1 In four-symbol digil sysem wih eqully probble symbols he pulses in he figure re used in rnsmission over AWGN-chnnel. s () s () s () s () 1 3 4 )
S-7.330 Rdio rnsmission nd nework ccess Exercise 1 - P1 In four-symbol digil sysem wih eqully probble symbols he pulses in he figure re used in rnsmission over AWGN-chnnel. s () s () s () s () 1 3 4 )
Observability of flow dependent structure functions and their use in data assimilation
 Oserviliy of flow dependen srucure funcions nd heir use in d ssimilion Pierre Guhier nd Crisin Lupu Collorion wih Séphne Lroche, Mrk Buehner nd Ahmed Mhidji (Env. Cnd) 3rd meeing of he HORPEX DAOS-WG Monrél
Oserviliy of flow dependen srucure funcions nd heir use in d ssimilion Pierre Guhier nd Crisin Lupu Collorion wih Séphne Lroche, Mrk Buehner nd Ahmed Mhidji (Env. Cnd) 3rd meeing of he HORPEX DAOS-WG Monrél
SOLUTION FOR A SYSTEM OF FRACTIONAL HEAT EQUATIONS OF NANOFLUID ALONG A WEDGE
 Ibrhim, R. W., e l.: Soluion for Sysem of Frcionl He Equions of THERMA SCIENCE, Yer 015, Vol. 19, Suppl. 1, pp. S51-S57 S51 SOUTION FOR A SYSTEM OF FRACTIONA HEAT EQUATIONS OF NANOFUID AONG A WEDGE by
Ibrhim, R. W., e l.: Soluion for Sysem of Frcionl He Equions of THERMA SCIENCE, Yer 015, Vol. 19, Suppl. 1, pp. S51-S57 S51 SOUTION FOR A SYSTEM OF FRACTIONA HEAT EQUATIONS OF NANOFUID AONG A WEDGE by
Solutions to Problems from Chapter 2
 Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
A new model for solving fuzzy linear fractional programming problem with ranking function
 J. ppl. Res. Ind. Eng. Vol. 4 No. 07 89 96 Journl of pplied Reserch on Indusril Engineering www.journl-prie.com new model for solving fuzzy liner frcionl progrmming prolem wih rning funcion Spn Kumr Ds
J. ppl. Res. Ind. Eng. Vol. 4 No. 07 89 96 Journl of pplied Reserch on Indusril Engineering www.journl-prie.com new model for solving fuzzy liner frcionl progrmming prolem wih rning funcion Spn Kumr Ds
Procedia Computer Science
 Procedi Compuer Science 00 (0) 000 000 Procedi Compuer Science www.elsevier.com/loce/procedi The Third Informion Sysems Inernionl Conference The Exisence of Polynomil Soluion of he Nonliner Dynmicl Sysems
Procedi Compuer Science 00 (0) 000 000 Procedi Compuer Science www.elsevier.com/loce/procedi The Third Informion Sysems Inernionl Conference The Exisence of Polynomil Soluion of he Nonliner Dynmicl Sysems
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS ON HUMIDITY DISTRIBUTION IN A VENTILATED ROOM
 NMERIAL ANALYSIS ON HMIDIY DISRIBION IN A ENILAED ROOM Asushi Iwme Deprmen of Archiecure, School of Science nd Engineering, KINKI niversi, Osk, Jpn ABSRA e lred hve hd heoreicl model o predic emperure
NMERIAL ANALYSIS ON HMIDIY DISRIBION IN A ENILAED ROOM Asushi Iwme Deprmen of Archiecure, School of Science nd Engineering, KINKI niversi, Osk, Jpn ABSRA e lred hve hd heoreicl model o predic emperure
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( y )
 8. Lengh of Plne Curve The mos fmous heorem in ll of mhemics is he Pyhgoren Theorem. I s formulion s he disnce formul is used o find he lenghs of line segmens in he coordine plne. In his secion you ll
8. Lengh of Plne Curve The mos fmous heorem in ll of mhemics is he Pyhgoren Theorem. I s formulion s he disnce formul is used o find he lenghs of line segmens in he coordine plne. In his secion you ll
Think of the Relationship Between Time and Space Again
 Repor nd Opinion, 1(3),009 hp://wwwsciencepubne sciencepub@gmilcom Think of he Relionship Beween Time nd Spce Agin Yng F-cheng Compny of Ruid Cenre in Xinjing 15 Hongxing Sree, Klmyi, Xingjing 834000,
Repor nd Opinion, 1(3),009 hp://wwwsciencepubne sciencepub@gmilcom Think of he Relionship Beween Time nd Spce Agin Yng F-cheng Compny of Ruid Cenre in Xinjing 15 Hongxing Sree, Klmyi, Xingjing 834000,
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems
 Swiss Federl Insiue of Pge 1 The Finie Elemen Mehod for he Anlysis of Non-Liner nd Dynmic Sysems Prof. Dr. Michel Hvbro Fber Dr. Nebojs Mojsilovic Swiss Federl Insiue of ETH Zurich, Swizerlnd Mehod of
Swiss Federl Insiue of Pge 1 The Finie Elemen Mehod for he Anlysis of Non-Liner nd Dynmic Sysems Prof. Dr. Michel Hvbro Fber Dr. Nebojs Mojsilovic Swiss Federl Insiue of ETH Zurich, Swizerlnd Mehod of
Probability, Estimators, and Stationarity
 Chper Probbiliy, Esimors, nd Sionriy Consider signl genered by dynmicl process, R, R. Considering s funcion of ime, we re opering in he ime domin. A fundmenl wy o chrcerize he dynmics using he ime domin
Chper Probbiliy, Esimors, nd Sionriy Consider signl genered by dynmicl process, R, R. Considering s funcion of ime, we re opering in he ime domin. A fundmenl wy o chrcerize he dynmics using he ime domin
3 Motion with constant acceleration: Linear and projectile motion
 3 Moion wih consn ccelerion: Liner nd projecile moion cons, In he precedin Lecure we he considered moion wih consn ccelerion lon he is: Noe h,, cn be posiie nd neie h leds o rie of behiors. Clerl similr
3 Moion wih consn ccelerion: Liner nd projecile moion cons, In he precedin Lecure we he considered moion wih consn ccelerion lon he is: Noe h,, cn be posiie nd neie h leds o rie of behiors. Clerl similr
Estimating the population parameter, r, q and K based on surplus production model. Wang, Chien-Hsiung
 SCTB15 Working Pper ALB 7 Esiming he populion prmeer, r, q nd K bsed on surplus producion model Wng, Chien-Hsiung Biologicl nd Fishery Division Insiue of Ocenogrphy Nionl Tiwn Universiy Tipei, Tiwn Tile:
SCTB15 Working Pper ALB 7 Esiming he populion prmeer, r, q nd K bsed on surplus producion model Wng, Chien-Hsiung Biologicl nd Fishery Division Insiue of Ocenogrphy Nionl Tiwn Universiy Tipei, Tiwn Tile:
Systems Variables and Structural Controllability: An Inverted Pendulum Case
 Reserch Journl of Applied Sciences, Engineering nd echnology 6(: 46-4, 3 ISSN: 4-7459; e-issn: 4-7467 Mxwell Scienific Orgniion, 3 Submied: Jnury 5, 3 Acceped: Mrch 7, 3 Published: November, 3 Sysems Vribles
Reserch Journl of Applied Sciences, Engineering nd echnology 6(: 46-4, 3 ISSN: 4-7459; e-issn: 4-7467 Mxwell Scienific Orgniion, 3 Submied: Jnury 5, 3 Acceped: Mrch 7, 3 Published: November, 3 Sysems Vribles
Chapter Direct Method of Interpolation
 Chper 5. Direc Mehod of Inerpolion Afer reding his chper, you should be ble o:. pply he direc mehod of inerpolion,. sole problems using he direc mehod of inerpolion, nd. use he direc mehod inerpolns o
Chper 5. Direc Mehod of Inerpolion Afer reding his chper, you should be ble o:. pply he direc mehod of inerpolion,. sole problems using he direc mehod of inerpolion, nd. use he direc mehod inerpolns o
Magnetostatics Bar Magnet. Magnetostatics Oersted s Experiment
 Mgneosics Br Mgne As fr bck s 4500 yers go, he Chinese discovered h cerin ypes of iron ore could rc ech oher nd cerin mels. Iron filings "mp" of br mgne s field Crefully suspended slivers of his mel were
Mgneosics Br Mgne As fr bck s 4500 yers go, he Chinese discovered h cerin ypes of iron ore could rc ech oher nd cerin mels. Iron filings "mp" of br mgne s field Crefully suspended slivers of his mel were
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"
 36 3 1!!!!!!"!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!" 1 1 3 3 1. 401331. 610000 3. 610000!!!!!!", ( ),,,,,,, ; ; ; ; ; TE973.6 A 100106 (010) 0300104 0 D /m; β
36 3 1!!!!!!"!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!" 1 1 3 3 1. 401331. 610000 3. 610000!!!!!!", ( ),,,,,,, ; ; ; ; ; TE973.6 A 100106 (010) 0300104 0 D /m; β
MTH 146 Class 11 Notes
 8.- Are of Surfce of Revoluion MTH 6 Clss Noes Suppose we wish o revolve curve C round n is nd find he surfce re of he resuling solid. Suppose f( ) is nonnegive funcion wih coninuous firs derivive on he
8.- Are of Surfce of Revoluion MTH 6 Clss Noes Suppose we wish o revolve curve C round n is nd find he surfce re of he resuling solid. Suppose f( ) is nonnegive funcion wih coninuous firs derivive on he
Mathematics 805 Final Examination Answers
 . 5 poins Se he Weiersrss M-es. Mhemics 85 Finl Eminion Answers Answer: Suppose h A R, nd f n : A R. Suppose furher h f n M n for ll A, nd h Mn converges. Then f n converges uniformly on A.. 5 poins Se
. 5 poins Se he Weiersrss M-es. Mhemics 85 Finl Eminion Answers Answer: Suppose h A R, nd f n : A R. Suppose furher h f n M n for ll A, nd h Mn converges. Then f n converges uniformly on A.. 5 poins Se
Deposition of Submicron Charged Spherical Particles in the Trachea of the Human Airways.
 eposiion of Submicron Chrged Sphericl Pricles in he Trche of he Humn Airwys. eprmen of Engineering Sciences nd Mhemics ivision of Fluid nd Experimenl Mechnics Luleå Universiy of Technology Corresponding
eposiion of Submicron Chrged Sphericl Pricles in he Trche of he Humn Airwys. eprmen of Engineering Sciences nd Mhemics ivision of Fluid nd Experimenl Mechnics Luleå Universiy of Technology Corresponding
Green s Functions and Comparison Theorems for Differential Equations on Measure Chains
 Green s Funcions nd Comprison Theorems for Differenil Equions on Mesure Chins Lynn Erbe nd Alln Peerson Deprmen of Mhemics nd Sisics, Universiy of Nebrsk-Lincoln Lincoln,NE 68588-0323 lerbe@@mh.unl.edu
Green s Funcions nd Comprison Theorems for Differenil Equions on Mesure Chins Lynn Erbe nd Alln Peerson Deprmen of Mhemics nd Sisics, Universiy of Nebrsk-Lincoln Lincoln,NE 68588-0323 lerbe@@mh.unl.edu
(b) 10 yr. (b) 13 m. 1.6 m s, m s m s (c) 13.1 s. 32. (a) 20.0 s (b) No, the minimum distance to stop = 1.00 km. 1.
 Answers o Een Numbered Problems Chper. () 7 m s, 6 m s (b) 8 5 yr 4.. m ih 6. () 5. m s (b).5 m s (c).5 m s (d) 3.33 m s (e) 8. ().3 min (b) 64 mi..3 h. ().3 s (b) 3 m 4..8 mi wes of he flgpole 6. (b)
Answers o Een Numbered Problems Chper. () 7 m s, 6 m s (b) 8 5 yr 4.. m ih 6. () 5. m s (b).5 m s (c).5 m s (d) 3.33 m s (e) 8. ().3 min (b) 64 mi..3 h. ().3 s (b) 3 m 4..8 mi wes of he flgpole 6. (b)
A Numerical Model of Commodity Moisture Loss and Temperature Distribution During Refrigerated Storage
 A Numericl Model of Commodiy Moiure Lo nd Temperure Diribuion During Refrigered Sorge B.R. Becker nd B.A. Fricke Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Univeriy of Miouri-Kn Ciy 5 Rockhill Rod, Kn Ciy, MO 64-2499
A Numericl Model of Commodiy Moiure Lo nd Temperure Diribuion During Refrigered Sorge B.R. Becker nd B.A. Fricke Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Univeriy of Miouri-Kn Ciy 5 Rockhill Rod, Kn Ciy, MO 64-2499
Question Details Int Vocab 1 [ ] Question Details Int Vocab 2 [ ]
![Question Details Int Vocab 1 [ ] Question Details Int Vocab 2 [ ] Question Details Int Vocab 1 [ ] Question Details Int Vocab 2 [ ]](/thumbs/92/109283538.jpg) /3/5 Assignmen Previewer 3 Bsic: Definie Inegrls (67795) Due: Wed Apr 5 5 9: AM MDT Quesion 3 5 6 7 8 9 3 5 6 7 8 9 3 5 6 Insrucions Red ody's Noes nd Lerning Gols. Quesion Deils In Vocb [37897] The chnge
/3/5 Assignmen Previewer 3 Bsic: Definie Inegrls (67795) Due: Wed Apr 5 5 9: AM MDT Quesion 3 5 6 7 8 9 3 5 6 7 8 9 3 5 6 Insrucions Red ody's Noes nd Lerning Gols. Quesion Deils In Vocb [37897] The chnge
1. Introduction. 1 b b
 Journl of Mhemicl Inequliies Volume, Number 3 (007), 45 436 SOME IMPROVEMENTS OF GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITY N. ELEZOVIĆ, LJ. MARANGUNIĆ AND J. PEČARIĆ (communiced b A. Čižmešij) Absrc. In his pper some inequliies
Journl of Mhemicl Inequliies Volume, Number 3 (007), 45 436 SOME IMPROVEMENTS OF GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITY N. ELEZOVIĆ, LJ. MARANGUNIĆ AND J. PEČARIĆ (communiced b A. Čižmešij) Absrc. In his pper some inequliies
The order of reaction is defined as the number of atoms or molecules whose concentration change during the chemical reaction.
 www.hechemisryguru.com Re Lw Expression Order of Recion The order of recion is defined s he number of oms or molecules whose concenrion chnge during he chemicl recion. Or The ol number of molecules or
www.hechemisryguru.com Re Lw Expression Order of Recion The order of recion is defined s he number of oms or molecules whose concenrion chnge during he chemicl recion. Or The ol number of molecules or
INVESTIGATION OF REINFORCEMENT LEARNING FOR BUILDING THERMAL MASS CONTROL
 INVESTIGATION OF REINFORCEMENT LEARNING FOR BUILDING THERMAL MASS CONTROL Simeng Liu nd Gregor P. Henze, Ph.D., P.E. Universiy of Nebrsk Lincoln, Archiecurl Engineering 1110 Souh 67 h Sree, Peer Kiewi
INVESTIGATION OF REINFORCEMENT LEARNING FOR BUILDING THERMAL MASS CONTROL Simeng Liu nd Gregor P. Henze, Ph.D., P.E. Universiy of Nebrsk Lincoln, Archiecurl Engineering 1110 Souh 67 h Sree, Peer Kiewi
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line. 9/9/2015 Physics 218
 Chper Moion long srigh line 9/9/05 Physics 8 Gols for Chper How o describe srigh line moion in erms of displcemen nd erge elociy. The mening of insnneous elociy nd speed. Aerge elociy/insnneous elociy
Chper Moion long srigh line 9/9/05 Physics 8 Gols for Chper How o describe srigh line moion in erms of displcemen nd erge elociy. The mening of insnneous elociy nd speed. Aerge elociy/insnneous elociy
Calculation method of flux measurements by static chambers
 lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers P.S. Kroon Presened he NiroEurope Workshop, 15h - 17h December 28, openhgen, Denmrk EN-L--9-11 December 28 lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers
lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers P.S. Kroon Presened he NiroEurope Workshop, 15h - 17h December 28, openhgen, Denmrk EN-L--9-11 December 28 lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers
IX.1.1 The Laplace Transform Definition 700. IX.1.2 Properties 701. IX.1.3 Examples 702. IX.1.4 Solution of IVP for ODEs 704
 Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 4, 7 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 4, 7 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
USING ITERATIVE LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL TO TIME SERIES MODELS
 Elecronic Journl of Applied Sisicl Anlysis EJASA (202), Elecron. J. App. S. Anl., Vol. 5, Issue 2, 37 50 e-issn 2070-5948, DOI 0.285/i20705948v5n2p37 202 Universià del Sleno hp://sib-ese.unile.i/index.php/ejs/index
Elecronic Journl of Applied Sisicl Anlysis EJASA (202), Elecron. J. App. S. Anl., Vol. 5, Issue 2, 37 50 e-issn 2070-5948, DOI 0.285/i20705948v5n2p37 202 Universià del Sleno hp://sib-ese.unile.i/index.php/ejs/index
INTEGRALS. Exercise 1. Let f : [a, b] R be bounded, and let P and Q be partitions of [a, b]. Prove that if P Q then U(P ) U(Q) and L(P ) L(Q).
![INTEGRALS. Exercise 1. Let f : [a, b] R be bounded, and let P and Q be partitions of [a, b]. Prove that if P Q then U(P ) U(Q) and L(P ) L(Q). INTEGRALS. Exercise 1. Let f : [a, b] R be bounded, and let P and Q be partitions of [a, b]. Prove that if P Q then U(P ) U(Q) and L(P ) L(Q).](/thumbs/78/77677920.jpg) INTEGRALS JOHN QUIGG Eercise. Le f : [, b] R be bounded, nd le P nd Q be priions of [, b]. Prove h if P Q hen U(P ) U(Q) nd L(P ) L(Q). Soluion: Le P = {,..., n }. Since Q is obined from P by dding finiely
INTEGRALS JOHN QUIGG Eercise. Le f : [, b] R be bounded, nd le P nd Q be priions of [, b]. Prove h if P Q hen U(P ) U(Q) nd L(P ) L(Q). Soluion: Le P = {,..., n }. Since Q is obined from P by dding finiely
A Simple Method to Solve Quartic Equations. Key words: Polynomials, Quartics, Equations of the Fourth Degree INTRODUCTION
 Ausrlin Journl of Bsic nd Applied Sciences, 6(6): -6, 0 ISSN 99-878 A Simple Mehod o Solve Quric Equions Amir Fhi, Poo Mobdersn, Rhim Fhi Deprmen of Elecricl Engineering, Urmi brnch, Islmic Ad Universi,
Ausrlin Journl of Bsic nd Applied Sciences, 6(6): -6, 0 ISSN 99-878 A Simple Mehod o Solve Quric Equions Amir Fhi, Poo Mobdersn, Rhim Fhi Deprmen of Elecricl Engineering, Urmi brnch, Islmic Ad Universi,
THE COMBINED FORECASTING MODEL OF GRAY MODEL BASED ON LINEAR TIME-VARIANT AND ARIMA MODEL
 IJRRAS 6 (3) Sepember 03 www.rppress.com/volumes/vol6issue3/ijrras_6_3_0.pdf THE COMINED FORECASTING MODEL OF GRAY MODEL ASED ON LINEAR TIME-VARIANT AND ARIMA MODEL Xi Long,, Yong Wei, Jie Li 3 & Zho Long
IJRRAS 6 (3) Sepember 03 www.rppress.com/volumes/vol6issue3/ijrras_6_3_0.pdf THE COMINED FORECASTING MODEL OF GRAY MODEL ASED ON LINEAR TIME-VARIANT AND ARIMA MODEL Xi Long,, Yong Wei, Jie Li 3 & Zho Long
Lecture 3: 1-D Kinematics. This Week s Announcements: Class Webpage: visit regularly
 Lecure 3: 1-D Kinemics This Week s Announcemens: Clss Webpge: hp://kesrel.nm.edu/~dmeier/phys121/phys121.hml isi regulrly Our TA is Lorrine Bowmn Week 2 Reding: Chper 2 - Gincoli Week 2 Assignmens: Due:
Lecure 3: 1-D Kinemics This Week s Announcemens: Clss Webpge: hp://kesrel.nm.edu/~dmeier/phys121/phys121.hml isi regulrly Our TA is Lorrine Bowmn Week 2 Reding: Chper 2 - Gincoli Week 2 Assignmens: Due:
FRACTIONAL-order differential equations (FDEs) are
 Proceedings of he Inernionl MuliConference of Engineers nd Compuer Scieniss 218 Vol I IMECS 218 Mrch 14-16 218 Hong Kong Comprison of Anlyicl nd Numericl Soluions of Frcionl-Order Bloch Equions using Relible
Proceedings of he Inernionl MuliConference of Engineers nd Compuer Scieniss 218 Vol I IMECS 218 Mrch 14-16 218 Hong Kong Comprison of Anlyicl nd Numericl Soluions of Frcionl-Order Bloch Equions using Relible
A NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF THE URYSOHN-TYPE FREDHOLM INTEGRAL EQUATIONS
 A NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF THE URYSOHN-TYPE FREDHOLM INTEGRAL EQUATIONS A JAFARIAN 1,, SA MEASOOMY 1,b, ALIREZA K GOLMANKHANEH 1,c, D BALEANU 2,3,4 1 Deprmen of Mhemics, Urmi Brnch, Islmic Azd Universiy,
A NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF THE URYSOHN-TYPE FREDHOLM INTEGRAL EQUATIONS A JAFARIAN 1,, SA MEASOOMY 1,b, ALIREZA K GOLMANKHANEH 1,c, D BALEANU 2,3,4 1 Deprmen of Mhemics, Urmi Brnch, Islmic Azd Universiy,
P441 Analytical Mechanics - I. Coupled Oscillators. c Alex R. Dzierba
 Lecure 3 Mondy - Deceber 5, 005 Wrien or ls upded: Deceber 3, 005 P44 Anlyicl Mechnics - I oupled Oscillors c Alex R. Dzierb oupled oscillors - rix echnique In Figure we show n exple of wo coupled oscillors,
Lecure 3 Mondy - Deceber 5, 005 Wrien or ls upded: Deceber 3, 005 P44 Anlyicl Mechnics - I oupled Oscillors c Alex R. Dzierb oupled oscillors - rix echnique In Figure we show n exple of wo coupled oscillors,
1 Sterile Resources. This is the simplest case of exhaustion of a finite resource. We will use the terminology
 Cmbridge Universiy Press 978--5-8997-7 - Susinble Nurl Resource Mngemen for Scieniss nd Engineers Excerp More informion Serile Resources In his chper, we inroduce he simple concepion of scrce resource,
Cmbridge Universiy Press 978--5-8997-7 - Susinble Nurl Resource Mngemen for Scieniss nd Engineers Excerp More informion Serile Resources In his chper, we inroduce he simple concepion of scrce resource,
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 10: The High Beta Tokamak Con d and the High Flux Conserving Tokamak.
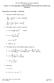 .615, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 1: The High Be Tokmk Con d nd he High Flux Conserving Tokmk Proeries of he High Tokmk 1. Evlue he MHD sfey fcor: ψ B * ( ) 1 3 ρ 1+ ν ρ ρ cosθ *
.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 1: The High Be Tokmk Con d nd he High Flux Conserving Tokmk Proeries of he High Tokmk 1. Evlue he MHD sfey fcor: ψ B * ( ) 1 3 ρ 1+ ν ρ ρ cosθ *
T-Match: Matching Techniques For Driving Yagi-Uda Antennas: T-Match. 2a s. Z in. (Sections 9.5 & 9.7 of Balanis)
 3/0/018 _mch.doc Pge 1 of 6 T-Mch: Mching Techniques For Driving Ygi-Ud Anenns: T-Mch (Secions 9.5 & 9.7 of Blnis) l s l / l / in The T-Mch is shun-mching echnique h cn be used o feed he driven elemen
3/0/018 _mch.doc Pge 1 of 6 T-Mch: Mching Techniques For Driving Ygi-Ud Anenns: T-Mch (Secions 9.5 & 9.7 of Blnis) l s l / l / in The T-Mch is shun-mching echnique h cn be used o feed he driven elemen
An object moving with speed v around a point at distance r, has an angular velocity. m/s m
 Roion The mosphere roes wih he erh n moions wihin he mosphere clerly follow cure phs (cyclones, nicyclones, hurricnes, ornoes ec.) We nee o epress roion quniiely. For soli objec or ny mss h oes no isor
Roion The mosphere roes wih he erh n moions wihin he mosphere clerly follow cure phs (cyclones, nicyclones, hurricnes, ornoes ec.) We nee o epress roion quniiely. For soli objec or ny mss h oes no isor
Tax Audit and Vertical Externalities
 T Audi nd Vericl Eernliies Hidey Ko Misuyoshi Yngihr Ngoy Keizi Universiy Ngoy Universiy 1. Inroducion The vericl fiscl eernliies rise when he differen levels of governmens, such s he federl nd se governmens,
T Audi nd Vericl Eernliies Hidey Ko Misuyoshi Yngihr Ngoy Keizi Universiy Ngoy Universiy 1. Inroducion The vericl fiscl eernliies rise when he differen levels of governmens, such s he federl nd se governmens,
IX.2 THE FOURIER TRANSFORM
 Chper IX The Inegrl Trnsform Mehods IX. The Fourier Trnsform November, 7 7 IX. THE FOURIER TRANSFORM IX.. The Fourier Trnsform Definiion 7 IX.. Properies 73 IX..3 Emples 74 IX..4 Soluion of ODE 76 IX..5
Chper IX The Inegrl Trnsform Mehods IX. The Fourier Trnsform November, 7 7 IX. THE FOURIER TRANSFORM IX.. The Fourier Trnsform Definiion 7 IX.. Properies 73 IX..3 Emples 74 IX..4 Soluion of ODE 76 IX..5
Positive and negative solutions of a boundary value problem for a
 Invenion Journl of Reerch Technology in Engineering & Mngemen (IJRTEM) ISSN: 2455-3689 www.ijrem.com Volume 2 Iue 9 ǁ Sepemer 28 ǁ PP 73-83 Poiive nd negive oluion of oundry vlue prolem for frcionl, -difference
Invenion Journl of Reerch Technology in Engineering & Mngemen (IJRTEM) ISSN: 2455-3689 www.ijrem.com Volume 2 Iue 9 ǁ Sepemer 28 ǁ PP 73-83 Poiive nd negive oluion of oundry vlue prolem for frcionl, -difference
Reduction of Cross-Field Plasma Transport in Tokamaks due to Power Input Redistribution and Sheared Flow Profile Modification
 TH/P8-6 Reducion of Cross-Field Plsm Trnspor in Tokmks due o Power Inpu Redisribuion nd Shered Flow Profile Modificion V.P. Psukhov, N.V. Chudin RRC «Kurchov Insiue», 8 Moscow, Russin Federion e-mil conc
TH/P8-6 Reducion of Cross-Field Plsm Trnspor in Tokmks due o Power Inpu Redisribuion nd Shered Flow Profile Modificion V.P. Psukhov, N.V. Chudin RRC «Kurchov Insiue», 8 Moscow, Russin Federion e-mil conc
Dipartimento di Elettronica Informazione e Bioingegneria Robotics
 Diprimeno di Eleronic Inormzione e Bioingegneri Roboics From moion plnning o rjecories @ 015 robo clssiicions Robos cn be described by Applicion(seelesson1) Geomery (see lesson mechnics) Precision (see
Diprimeno di Eleronic Inormzione e Bioingegneri Roboics From moion plnning o rjecories @ 015 robo clssiicions Robos cn be described by Applicion(seelesson1) Geomery (see lesson mechnics) Precision (see
Problems on transformer main dimensions and windings
 Probles_Trn_winding Probles on rnsforer in diensions nd windings. Deerine he in diensions of he core nd window for 500 ka, /400, 50Hz, Single phse core ype, oil iersed, self cooled rnsforer. Assue: Flux
Probles_Trn_winding Probles on rnsforer in diensions nd windings. Deerine he in diensions of he core nd window for 500 ka, /400, 50Hz, Single phse core ype, oil iersed, self cooled rnsforer. Assue: Flux
Introduction to LoggerPro
 Inroducion o LoggerPro Sr/Sop collecion Define zero Se d collecion prmeers Auoscle D Browser Open file Sensor seup window To sr d collecion, click he green Collec buon on he ool br. There is dely of second
Inroducion o LoggerPro Sr/Sop collecion Define zero Se d collecion prmeers Auoscle D Browser Open file Sensor seup window To sr d collecion, click he green Collec buon on he ool br. There is dely of second
ECE Microwave Engineering
 EE 537-635 Microwve Engineering Adped from noes y Prof. Jeffery T. Willims Fll 8 Prof. Dvid R. Jcson Dep. of EE Noes Wveguiding Srucures Pr 7: Trnsverse Equivlen Newor (N) Wveguide Trnsmission Line Model
EE 537-635 Microwve Engineering Adped from noes y Prof. Jeffery T. Willims Fll 8 Prof. Dvid R. Jcson Dep. of EE Noes Wveguiding Srucures Pr 7: Trnsverse Equivlen Newor (N) Wveguide Trnsmission Line Model
Properties of Logarithms. Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations. Properties of Logarithms. Properties of Logarithms. ( x)
 Properies of Logrihms Solving Eponenil nd Logrihmic Equions Properies of Logrihms Produc Rule ( ) log mn = log m + log n ( ) log = log + log Properies of Logrihms Quoien Rule log m = logm logn n log7 =
Properies of Logrihms Solving Eponenil nd Logrihmic Equions Properies of Logrihms Produc Rule ( ) log mn = log m + log n ( ) log = log + log Properies of Logrihms Quoien Rule log m = logm logn n log7 =
ECE Microwave Engineering. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 10. Waveguides Part 7: Transverse Equivalent Network (TEN)
 EE 537-635 Microwve Engineering Fll 7 Prof. Dvid R. Jcson Dep. of EE Noes Wveguides Pr 7: Trnsverse Equivlen Newor (N) Wveguide Trnsmission Line Model Our gol is o come up wih rnsmission line model for
EE 537-635 Microwve Engineering Fll 7 Prof. Dvid R. Jcson Dep. of EE Noes Wveguides Pr 7: Trnsverse Equivlen Newor (N) Wveguide Trnsmission Line Model Our gol is o come up wih rnsmission line model for
An Efficient Digital Circuit for Implementing Sequence Alignment Algorithm
 An Efficien Digil Circui for Implemening Sequence Alignmen Algorihm Vmsi Kundei Yunsi Fei (vmsik@engr.uconn.edu) (yfei@engr.uconn.edu) CSE Deprmen ECE Deprmen Universiy of Connecicu Universiy of Connecicu
An Efficien Digil Circui for Implemening Sequence Alignmen Algorihm Vmsi Kundei Yunsi Fei (vmsik@engr.uconn.edu) (yfei@engr.uconn.edu) CSE Deprmen ECE Deprmen Universiy of Connecicu Universiy of Connecicu
The motions of the celt on a horizontal plane with viscous friction
 The h Join Inernaional Conference on Mulibody Sysem Dynamics June 8, 18, Lisboa, Porugal The moions of he cel on a horizonal plane wih viscous fricion Maria A. Munisyna 1 1 Moscow Insiue of Physics and
The h Join Inernaional Conference on Mulibody Sysem Dynamics June 8, 18, Lisboa, Porugal The moions of he cel on a horizonal plane wih viscous fricion Maria A. Munisyna 1 1 Moscow Insiue of Physics and
NEW FRACTIONAL DERIVATIVES WITH NON-LOCAL AND NON-SINGULAR KERNEL Theory and Application to Heat Transfer Model
 Angn, A., e l.: New Frcionl Derivives wih Non-Locl nd THERMAL SCIENCE, Yer 216, Vol. 2, No. 2, pp. 763-769 763 NEW FRACTIONAL DERIVATIVES WITH NON-LOCAL AND NON-SINGULAR KERNEL Theory nd Applicion o He
Angn, A., e l.: New Frcionl Derivives wih Non-Locl nd THERMAL SCIENCE, Yer 216, Vol. 2, No. 2, pp. 763-769 763 NEW FRACTIONAL DERIVATIVES WITH NON-LOCAL AND NON-SINGULAR KERNEL Theory nd Applicion o He
IX.1.1 The Laplace Transform Definition 700. IX.1.2 Properties 701. IX.1.3 Examples 702. IX.1.4 Solution of IVP for ODEs 704
 Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 6, 8 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 6, 8 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
