The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems
|
|
|
- Myra Simmons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Swiss Federl Insiue of Pge 1 The Finie Elemen Mehod for he Anlysis of Non-Liner nd Dynmic Sysems Prof. Dr. Michel Hvbro Fber Dr. Nebojs Mojsilovic Swiss Federl Insiue of ETH Zurich, Swizerlnd Mehod of Finie Elemens II
2 Swiss Federl Insiue of Conens of Tody's Lecure Pge 2 Moivion, i overview nd orgnizion i of he course Inroducion o non-liner nlysis Formulion of he coninuum mechnics incremenl equions of moion Mehod of Finie Elemens II
3 Swiss Federl Insiue of Moivion, overview nd orgnizion of he course Pge 3 Moivion i In FEM 1 we lerned bou he sedy se nlysis of liner sysems however; he sysems we re deling wih in srucurl engineering re generlly no sedy se nd lso no liner We mus be ble o ssess he need for priculr ype of nlysis nd we mus be ble o perform i Mehod of Finie Elemens II
4 Swiss Federl Insiue of Moivion, overview nd orgnizion of he course Pge 4 Moivion Wh kind of problems re no sedy se nd liner? E.g. when he: meril behves non-linerly deformions become big (p-δ effecs) lods vry fs compred o he eigenfrequencies of he srucure Generl feure: Response becomes lod ph dependen Mehod of Finie Elemens II
5 Swiss Federl Insiue of Moivion, overview nd orgnizion of he course Pge 5 Moivion Wh is he dded vlue of being ble o ssess he non-liner non-sedy se response of srucures? E.g. ssessing he; - srucurl response of srucures o exreme evens (rock-fll, erhquke, hurricnes) - performnce (filures nd deformions) of soils - verifying simple models Mehod of Finie Elemens II
6 Swiss Federl Insiue of Moivion, overview nd orgnizion of he course Pge 6 Sedy se problems (Liner/Non-liner): The response of he sysem does no chnge over ime KU = R Propgion problems (Liner/Non-liner): The response of he sysem chnges over ime MU&& () + CU& () + KU () = R () Eigenvlue problems: No unique soluion o he response of he sysem Av = λ Bv Mehod of Finie Elemens II
7 Swiss Federl Insiue of Moivion, overview nd orgnizion of he course Pge 7 Orgnision i The lecures will be given by: M. H. Fber nd N. Mojsilovic Exercises will be orgnized/ended by: K. Nishijim Office hours: 14:00 16:00 on Thursdys, HIL E22.3. Mehod of Finie Elemens II
8 Swiss Federl Insiue of Moivion, overview nd orgnizion of he course Pge 8 Orgnision i PowerPoin files wih he presenions will be up-loded on our home-pge one dy in dvnce of he lecures hp:// _ II The lecure s such will follow he book: "Finie Elemen Procedures" by K.J. Bhe, Prenice Hll, 1996 Mehod of Finie Elemens II
9 Swiss Federl Insiue of Moivion, overview nd orgnizion of he course Pge 9 Overview De Subjec(s) Course book Pges: Non-liner Finie Elemen Clculions in solids nd srucurl mechnics Inroducion o non-liner clculions The incremenl pproch o coninuum mechnics Non-liner Finie Elemen Clculions in solids nd srucurl mechnics Deformion grdiens, srin nd sress ensors The Lngrngin formulion only meril nonlineriy Non-liner Finie Elemen Clculions in solids nd srucurl mechnics Displcemen bsed iso-prmeric finie elemens in coninuum mechnics Non-liner Finie Elemen Clculions in solids nd srucurl mechnics Displcemen bsed iso-prmeric finie elemens in coninuum mechnics Mehod of Finie Elemens II
10 Swiss Federl Insiue of Moivion, overview nd orgnizion of he course Pge 10 Overview De Subjec(s) Course book Pges: Non-liner Finie Elemen Clculions in solids nd srucurl mechnics Tol Lngrngin formulion Exended Lngrngin formulion Srucurl elemens Non-liner Finie Elemen Clculions in solids nd srucurl mechnics Inroducion of consiuive relions Non-liner consiuive relions Non-liner Finie Elemen Clculions in solids nd srucurl mechnics Conc problems Prcicl considerions Dynmicl Finie Elemen Clculions Inroducion Direc inegrion mehods Mehod of Finie Elemens II
11 Swiss Federl Insiue of Moivion, overview nd orgnizion of he course Pge 11 Overview De Subjec(s) Course book Pges: Dynmicl Finie Elemen Clculions Mode superposiion Dynmicl Finie Elemen Clculions Anlysis of direc inegrion mehods Dynmicl Finie Elemen Clculions Soluion of dynmicl non-liner problems Soluion of Eigen vlue problems The vecor ierion mehod Soluion of Eigen vlue problems The rnsformion mehod Mehod of Finie Elemens II
12 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Pge 12 Previsously we considered d he soluion of he following liner nd sic problem: KU = R for hese problems we hve he convenien propery of lineriy, i.e: KU = λr U = λu If his is no he cse we re deling wih non-liner problem! Mehod of Finie Elemens II
13 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Pge 13 Previsously we considered d he soluion of he following liner nd sic problem: KU = R we ssumed: smll displcemens when developing he siffness mrix K nd he lod vecor R, becuse we performed ll inegrions over he originl elemen volume h he B mrix is consn independen of elemen displcemens he sress-srin mrix C is consn boundry consrins re consn Mehod of Finie Elemens II
14 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Pge 14 Clssificion of non-liner nlysis Type of nlysis Descripion Typicl formulion used Sress nd srin mesures used Merilly-nonliner only Infiniesiml displcemens nd Merillynonliner-only Engineering srin nd sress srins; sress rin relion is nonliner (MNO) Lrge displcemens, lrge roions bu smll Displcemens nd roions of fibers re lrge; bu fiber Tol Lgrnge (TL) Second Piol- Kirchoff sress, Green-Lgrnge srins exensions nd ngle chnges srin beween fibers re smll; sress srin Upded Lgrnge (UL) Cuchy sress, Almnsi srin relionship my be Lrge displcemens, lrge roions nd lrge srins Mehod of Finie Elemens II liner or non-liner Displcemens nd roions of fibers re lrge; fiber exensions nd ngle chnges beween fibers my lso be lrge; sress srin relionship my be liner or non-liner Tol Lgrnge (TL) Second Piol- Kirchoff sress, Green-Lgrnge Upded Lgrnge (UL) srin Cuchy sress, Logrihmic srin
15 Swiss Federl Insiue of Pge 15 Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Clssificion of non-liner nlysis σ Δ P 2 σ = P / A E L ε = σ / E 1 P 2 Δ=ε L ε < 0.04 ε L Liner elsic (infiniesiml displcemens) Mehod of Finie Elemens II
16 Swiss Federl Insiue of Pge 16 Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis L Clssificion of non-liner nlysis Δ P 2 P 2 σ = P / A ε ε < σ σ σy E E T Y = σ σ Y 1 E P / A 1 E T ε L Merilly nonliner only (infiniesiml displcemens, bu nonliner sress-srin relion) Mehod of Finie Elemens II
17 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Pge 17 Clssificion of non-liner nlysis y x L ε < 0.04 Δ= ε L Lrge displcemens nd lrge roions bu smll srins (liner or nonliner meril behvior) Mehod of Finie Elemens II
18 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Pge 18 Clssificion of non-liner nlysis Lrge displcemens nd lrge roions nd lrge srins (liner or nonliner meril behvior) Mehod of Finie Elemens II
19 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Pge 19 Clssificion of non-liner nlysis P 2 P 2 Δ Chnging boundry condiions Mehod of Finie Elemens II
20 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Pge Exmple: Simple br srucure E = 10 N / cm R Are = 1cm Secion L = 10cm 2 u Secion b L = R 5cm σ σ Y 1 E 1 ε = E T ET = 10 N / cm σ Y :yield sress ε :yield srin ε Y ε Mehod of Finie Elemens II
21 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Exmple: Simple br srucure ε Are = 1cm Secion L = 10cm 2 u =, εb = L + σb = σ R A σ A u Secion b L = u L b R 5cm σ σ Y R E 1 ε = ε = (elsic region) E σ σ Y Δσ ε = εy + (plsic region) i ) Δ ε = (unloding) E E T Mehod of Finie Elemens II E T 7 2 E = 10 N / cm 5 2 ET = 10 N / cm σ : yield sress Y ε Y : yield srin ε Pge 21
22 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis u Exmple: Simple br srucure ε, Are = 1cm Secion L = 10cm 2 u Secion b L = R 5cm σ σ Y R E 1 1 ε = E T E = 10 N / cm ET = 10 N / cm σ Y : yield sress ε : yield srin Y ε = εb = L R+ σ A= σ A b σ ε = E ε = ε + Δ ε = Y u L b (elsic region) σ σy E T Δσ (unloding) E Pge 22 (plsic region) Boh secions elsic 1 1 R = EA u ( + ) u = L L 310 R R 2 R σ =, σb = 3 A 3 A b 6 Mehod of Finie Elemens II
23 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis u Exmple: Simple br srucure 7 2 E = 10 N / cm ε, Are = 1cm Secion L = 10cm 2 u Secion b L = R 5cm secion b will be plsic when R = σ u u = E, b ET( Y) Y L σ = L ε σ b EA u ET A u R = + ETεYA+ σya L L σ σ Y R E 1 ε = E T 5 2 ET = 10 N / cm σ Y : yield sress ε : yield srin Y ε Secion is elsic while secion b is plsic T Y Y Mehod of Finie Elemens II b 2 σ A 3 Y R / A + E ε σ R u = = E/ L + E/ L b 2 = εb = L R+ σ A= σ A b σ u L b Pge 23 ε = (elsic region) E σ σy ε = εy + (plsic region) ET Δσ Δ ε = (unloding) E
24 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Pge 24 Wh did we lern from he exmple? The bsic problem in generl nonliner nlysis is o find se of equilibrium beween exernlly pplied lods nd elemen nodl forces R F = 0 R = R + R + R B S C We mus chieve equilibrium for ll ime seps when incremening he loding Very generl pproch F = F R I = B τ dv m V ( m) ( m) T ( m) ( m) includes implicily lso dynmic nlysis! Mehod of Finie Elemens II
25 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Pge 25 The bsic pproch in incremenl nylsis is R F = 0 +Δ +Δ +Δ ssuming h R is independen of he deformions we hve +Δ F = F+ F We know he soluion F ime nd F is he incremen in he nodl poin forces corresponding o n incremen in he displcemens nd sresses from ime o ime +Δ his we cn pproxime by F = KU Tngen siffness mrix Mehod of Finie Elemens II F K = U
26 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Pge 26 The bsic pproch in incremenl nylsis is We my now subsiue he ngen siffness mrix ino he equlibrium relion KU = R F +Δ U = U+ U +Δ which h gives us scheme for he clculion l of he displcemens he exc displcemens ime +Δ correspond o he pplied lods +Δ however we only deermined hese pproximely s we used ngen siffness mrix hus we my hve o iere o find he soluion Mehod of Finie Elemens II
27 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Pge 27 The bsic pproch in incremenl nylsis is We my use he Newon-Rphson ierion scheme o find he equlibrium wihin ech lod incremen K Δ U = R F (ou of blnce lod vecor) +Δ ( i 1) ( i) +Δ +Δ ( i 1) U = U +ΔU +Δ () i +Δ ( i 1) () i wih iniil condiions U = U ; K = K ; F = F +Δ (0) +Δ (0) +Δ (0) Mehod of Finie Elemens II
28 Swiss Federl Insiue of Inroducion i o non-liner nlysis Pge 28 The bsic pproch in incremenl nylsis is I my be expensive o clcule he ngen siffness mrix nd; in he Modified Newon-Rphson ierion scheme i is hus only clculed in he beginning of ech new lod sep in he qusi-newon ierion schemes he secn siffness mrix is used insed of he ngen mrix Mehod of Finie Elemens II
29 Swiss Federl Insiue of The coninuum mechnics incremenl equions Pge 29 The bsic problem: We wn o esblish he soluion using n incremenl formulion The equilibrium mus be esblished for he considered body in is curren configurion In proceeding we dop Lgrngin formulion where rck he movemen of ll pricles of he body (loced in Cresin coordine sysem) Anoher pproch would be n Eulerin formulion where he moion of meril hrough sionry conrol volume is considered Mehod of Finie Elemens II
30 Swiss Federl Insiue of The coninuum mechnics incremenl equions Pge 30 The bsic problem: x 3 δu 1 δu = δu2 δu 3 Configurion corresponding o vriion in displcemens +Δ δu u Configurion ime +Δ Surfce re Volume +Δ V +Δ S x 2 Configurion ime 0 Surfce re Volume 0 V 0 S Configurion ime Surfce re Volume V S x (or x, x, x ) 0 + Δ Mehod of Finie Elemens II
31 Swiss Federl Insiue of The coninuum mechnics incremenl equions The Lgrngin formulion We express equilibrium of he body ime +Δ using he principle of virul displcemens +Δ +Δ +Δ τδ ed V R +Δ V +Δ +Δ ij = +Δ ij +Δ +Δ j x 3 x (or x, x, x ) 0 + Δ δu1 δu = δu2 δu 3 Configurion corresponding o vriion in displcemens +Δ δu u 0 Surfce re S 0 Volume V x 2 Pge 31 Configurion ime + Δ +Δ Surfce re S +Δ Volume V Configurion ime Surfce re S Configurion ime 0 Volume V τ : Cresin componens of he Cuchy sress ensor 1 δu δ u i j δ e = ( + ) = srin ensor corresponding o virul displcemens 2 x x i δui : Componens of virul displcemen vecor imposed ime +Δ +Δ xi : Cresin coordine ime +Δ +Δ V : Volume ime +Δ +Δ +Δ B +Δ +Δ S S +Δ R = f δ ud V = f δ u d S V Mehod of Finie Elemens II i i i i S +Δ +Δ f
32 Swiss Federl Insiue of The coninuum mechnics incremenl equions The Lgrngin formulion We express equilibrium of he body ime +Δ using he principle of virul displcemens R= f δud V = f δu d S +Δ +Δ B +Δ +Δ S S +Δ i i i i where f +Δ +Δ : exernlly pllied forces per uni volume V S f +Δ B i +Δ S fi +Δ S f : surfce ime +Δ S +Δ δui : δui evlued he surfce Sf x 3 x (or x, x, x ) 0 + Δ : exernlly pllied surfce rcions per uni surfce δu1 δu = δu2 δu 3 Configurion corresponding o vriion in displcemens +Δ δu u 0 Surfce re S 0 Volume V x 2 Pge 32 Configurion ime + Δ +Δ Surfce re S +Δ Volume V Configurion ime Surfce re S Configurion ime 0 Volume V Mehod of Finie Elemens II
33 Swiss Federl Insiue of The coninuum mechnics incremenl equions Pge 33 The Lgrngin formulion We recognize h our derivions from liner finie elemen heory re unchnged bu pplied o he body in he configurion ime +Δ Mehod of Finie Elemens II
34 Swiss Federl Insiue of The coninuum mechnics incremenl equions Pge 34 In he furher we inroduce n pproprie noion: Coordines nd displcemens re reled s: x = x + u 0 i i i x = x + u +Δ 0 +Δ i i i Incremens in displcemens re reled s: +Δ ui = ui ui Reference configurions re indexed s e.g.: f +Δ S 0 i where he lower lef index indices he reference configurion τ = τ +Δ +Δ ij +Δ ij Differeniion is indexed s: u +Δ 0 +Δ i 0 m 0 u i, j=, x = 0 +Δ m, n +Δ xj xn x Mehod of Finie Elemens II
September 20 Homework Solutions
 College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
5.1-The Initial-Value Problems For Ordinary Differential Equations
 5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
M r. d 2. R t a M. Structural Mechanics Section. Exam CT5141 Theory of Elasticity Friday 31 October 2003, 9:00 12:00 hours. Problem 1 (3 points)
 Delf Universiy of Technology Fculy of Civil Engineering nd Geosciences Srucurl echnics Secion Wrie your nme nd sudy numer he op righ-hnd of your work. Exm CT5 Theory of Elsiciy Fridy Ocoer 00, 9:00 :00
Delf Universiy of Technology Fculy of Civil Engineering nd Geosciences Srucurl echnics Secion Wrie your nme nd sudy numer he op righ-hnd of your work. Exm CT5 Theory of Elsiciy Fridy Ocoer 00, 9:00 :00
e t dt e t dt = lim e t dt T (1 e T ) = 1
 Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
Average & instantaneous velocity and acceleration Motion with constant acceleration
 Physics 7: Lecure Reminders Discussion nd Lb secions sr meeing ne week Fill ou Pink dd/drop form if you need o swich o differen secion h is FULL. Do i TODAY. Homework Ch. : 5, 7,, 3,, nd 6 Ch.: 6,, 3 Submission
Physics 7: Lecure Reminders Discussion nd Lb secions sr meeing ne week Fill ou Pink dd/drop form if you need o swich o differen secion h is FULL. Do i TODAY. Homework Ch. : 5, 7,, 3,, nd 6 Ch.: 6,, 3 Submission
0 for t < 0 1 for t > 0
 8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
4.8 Improper Integrals
 4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
Chapter Direct Method of Interpolation
 Chper 5. Direc Mehod of Inerpolion Afer reding his chper, you should be ble o:. pply he direc mehod of inerpolion,. sole problems using he direc mehod of inerpolion, nd. use he direc mehod inerpolns o
Chper 5. Direc Mehod of Inerpolion Afer reding his chper, you should be ble o:. pply he direc mehod of inerpolion,. sole problems using he direc mehod of inerpolion, nd. use he direc mehod inerpolns o
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 9: The High Beta Tokamak
 .65, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 9: The High e Tokmk Summry of he Properies of n Ohmic Tokmk. Advnges:. good euilibrium (smll shif) b. good sbiliy ( ) c. good confinemen ( τ nr )
.65, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 9: The High e Tokmk Summry of he Properies of n Ohmic Tokmk. Advnges:. good euilibrium (smll shif) b. good sbiliy ( ) c. good confinemen ( τ nr )
1.0 Electrical Systems
 . Elecricl Sysems The ypes of dynmicl sysems we will e sudying cn e modeled in erms of lgeric equions, differenil equions, or inegrl equions. We will egin y looking fmilir mhemicl models of idel resisors,
. Elecricl Sysems The ypes of dynmicl sysems we will e sudying cn e modeled in erms of lgeric equions, differenil equions, or inegrl equions. We will egin y looking fmilir mhemicl models of idel resisors,
Motion. Part 2: Constant Acceleration. Acceleration. October Lab Physics. Ms. Levine 1. Acceleration. Acceleration. Units for Acceleration.
 Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line. 9/9/2015 Physics 218
 Chper Moion long srigh line 9/9/05 Physics 8 Gols for Chper How o describe srigh line moion in erms of displcemen nd erge elociy. The mening of insnneous elociy nd speed. Aerge elociy/insnneous elociy
Chper Moion long srigh line 9/9/05 Physics 8 Gols for Chper How o describe srigh line moion in erms of displcemen nd erge elociy. The mening of insnneous elociy nd speed. Aerge elociy/insnneous elociy
Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering
 Srucural Dynamics and Earhquae Engineering Course 1 Inroducion. Single degree of freedom sysems: Equaions of moion, problem saemen, soluion mehods. Course noes are available for download a hp://www.c.up.ro/users/aurelsraan/
Srucural Dynamics and Earhquae Engineering Course 1 Inroducion. Single degree of freedom sysems: Equaions of moion, problem saemen, soluion mehods. Course noes are available for download a hp://www.c.up.ro/users/aurelsraan/
RESPONSE UNDER A GENERAL PERIODIC FORCE. When the external force F(t) is periodic with periodτ = 2π
 RESPONSE UNDER A GENERAL PERIODIC FORCE When he exernl force F() is periodic wih periodτ / ω,i cn be expnded in Fourier series F( ) o α ω α b ω () where τ F( ) ω d, τ,,,... () nd b τ F( ) ω d, τ,,... (3)
RESPONSE UNDER A GENERAL PERIODIC FORCE When he exernl force F() is periodic wih periodτ / ω,i cn be expnded in Fourier series F( ) o α ω α b ω () where τ F( ) ω d, τ,,,... () nd b τ F( ) ω d, τ,,... (3)
PHYSICS 1210 Exam 1 University of Wyoming 14 February points
 PHYSICS 1210 Em 1 Uniersiy of Wyoming 14 Februry 2013 150 poins This es is open-noe nd closed-book. Clculors re permied bu compuers re no. No collborion, consulion, or communicion wih oher people (oher
PHYSICS 1210 Em 1 Uniersiy of Wyoming 14 Februry 2013 150 poins This es is open-noe nd closed-book. Clculors re permied bu compuers re no. No collborion, consulion, or communicion wih oher people (oher
Physics 2A HW #3 Solutions
 Chper 3 Focus on Conceps: 3, 4, 6, 9 Problems: 9, 9, 3, 41, 66, 7, 75, 77 Phsics A HW #3 Soluions Focus On Conceps 3-3 (c) The ccelerion due o grvi is he sme for boh blls, despie he fc h he hve differen
Chper 3 Focus on Conceps: 3, 4, 6, 9 Problems: 9, 9, 3, 41, 66, 7, 75, 77 Phsics A HW #3 Soluions Focus On Conceps 3-3 (c) The ccelerion due o grvi is he sme for boh blls, despie he fc h he hve differen
Contraction Mapping Principle Approach to Differential Equations
 epl Journl of Science echnology 0 (009) 49-53 Conrcion pping Principle pproch o Differenil Equions Bishnu P. Dhungn Deprmen of hemics, hendr Rn Cmpus ribhuvn Universiy, Khmu epl bsrc Using n eension of
epl Journl of Science echnology 0 (009) 49-53 Conrcion pping Principle pproch o Differenil Equions Bishnu P. Dhungn Deprmen of hemics, hendr Rn Cmpus ribhuvn Universiy, Khmu epl bsrc Using n eension of
1 jordan.mcd Eigenvalue-eigenvector approach to solving first order ODEs. -- Jordan normal (canonical) form. Instructor: Nam Sun Wang
 jordnmcd Eigenvlue-eigenvecor pproch o solving firs order ODEs -- ordn norml (cnonicl) form Insrucor: Nm Sun Wng Consider he following se of coupled firs order ODEs d d x x 5 x x d d x d d x x x 5 x x
jordnmcd Eigenvlue-eigenvecor pproch o solving firs order ODEs -- ordn norml (cnonicl) form Insrucor: Nm Sun Wng Consider he following se of coupled firs order ODEs d d x x 5 x x d d x d d x x x 5 x x
MATH 124 AND 125 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 2008)
 MATH 14 AND 15 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 8) The following quesions cn be used s review for Mh 14/ 15 These quesions re no cul smples of quesions h will pper on he finl em, bu hey will provide
MATH 14 AND 15 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 8) The following quesions cn be used s review for Mh 14/ 15 These quesions re no cul smples of quesions h will pper on he finl em, bu hey will provide
Green s Functions and Comparison Theorems for Differential Equations on Measure Chains
 Green s Funcions nd Comprison Theorems for Differenil Equions on Mesure Chins Lynn Erbe nd Alln Peerson Deprmen of Mhemics nd Sisics, Universiy of Nebrsk-Lincoln Lincoln,NE 68588-0323 lerbe@@mh.unl.edu
Green s Funcions nd Comprison Theorems for Differenil Equions on Mesure Chins Lynn Erbe nd Alln Peerson Deprmen of Mhemics nd Sisics, Universiy of Nebrsk-Lincoln Lincoln,NE 68588-0323 lerbe@@mh.unl.edu
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mathematics The Integral of a Function as a Function
 ENGR 1990 Engineering Mhemics The Inegrl of Funcion s Funcion Previously, we lerned how o esime he inegrl of funcion f( ) over some inervl y dding he res of finie se of rpezoids h represen he re under
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mhemics The Inegrl of Funcion s Funcion Previously, we lerned how o esime he inegrl of funcion f( ) over some inervl y dding he res of finie se of rpezoids h represen he re under
The solution is often represented as a vector: 2xI + 4X2 + 2X3 + 4X4 + 2X5 = 4 2xI + 4X2 + 3X3 + 3X4 + 3X5 = 4. 3xI + 6X2 + 6X3 + 3X4 + 6X5 = 6.
 [~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
[~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
Think of the Relationship Between Time and Space Again
 Repor nd Opinion, 1(3),009 hp://wwwsciencepubne sciencepub@gmilcom Think of he Relionship Beween Time nd Spce Agin Yng F-cheng Compny of Ruid Cenre in Xinjing 15 Hongxing Sree, Klmyi, Xingjing 834000,
Repor nd Opinion, 1(3),009 hp://wwwsciencepubne sciencepub@gmilcom Think of he Relionship Beween Time nd Spce Agin Yng F-cheng Compny of Ruid Cenre in Xinjing 15 Hongxing Sree, Klmyi, Xingjing 834000,
A Kalman filtering simulation
 A Klmn filering simulion The performnce of Klmn filering hs been esed on he bsis of wo differen dynmicl models, ssuming eiher moion wih consn elociy or wih consn ccelerion. The former is epeced o beer
A Klmn filering simulion The performnce of Klmn filering hs been esed on he bsis of wo differen dynmicl models, ssuming eiher moion wih consn elociy or wih consn ccelerion. The former is epeced o beer
Version 001 test-1 swinney (57010) 1. is constant at m/s.
 Version 001 es-1 swinne (57010) 1 This prin-ou should hve 20 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions m coninue on he nex column or pge find ll choices before nswering. CubeUniVec1x76 001 10.0 poins Acubeis1.4fee
Version 001 es-1 swinne (57010) 1 This prin-ou should hve 20 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions m coninue on he nex column or pge find ll choices before nswering. CubeUniVec1x76 001 10.0 poins Acubeis1.4fee
6. Gas dynamics. Ideal gases Speed of infinitesimal disturbances in still gas
 6. Gs dynmics Dr. Gergely Krisóf De. of Fluid echnics, BE Februry, 009. Seed of infiniesiml disurbnces in sill gs dv d, dv d, Coninuiy: ( dv)( ) dv omenum r r heorem: ( ( dv) ) d 3443 4 q m dv d dv llievi
6. Gs dynmics Dr. Gergely Krisóf De. of Fluid echnics, BE Februry, 009. Seed of infiniesiml disurbnces in sill gs dv d, dv d, Coninuiy: ( dv)( ) dv omenum r r heorem: ( ( dv) ) d 3443 4 q m dv d dv llievi
Location is relative. Coordinate Systems. Which of the following can be described with vectors??
 Locion is relive Coordine Sysems The posiion o hing is sed relive o noher hing (rel or virul) review o he physicl sis h governs mhemicl represenions Reerence oec mus e deined Disnce mus e nown Direcion
Locion is relive Coordine Sysems The posiion o hing is sed relive o noher hing (rel or virul) review o he physicl sis h governs mhemicl represenions Reerence oec mus e deined Disnce mus e nown Direcion
Chapter 2: Evaluative Feedback
 Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
An object moving with speed v around a point at distance r, has an angular velocity. m/s m
 Roion The mosphere roes wih he erh n moions wihin he mosphere clerly follow cure phs (cyclones, nicyclones, hurricnes, ornoes ec.) We nee o epress roion quniiely. For soli objec or ny mss h oes no isor
Roion The mosphere roes wih he erh n moions wihin he mosphere clerly follow cure phs (cyclones, nicyclones, hurricnes, ornoes ec.) We nee o epress roion quniiely. For soli objec or ny mss h oes no isor
Seismic history analysis of asymmetrical adjacent buildings with soil-structure interaction consideration
 Universiy of Wollongong Reserch Online Fculy of Engineering - Ppers (Archive) Fculy of Engineering nd Informion Sciences 2011 Seismic hisory nlysis of symmericl djcen buildings wih soil-srucure inercion
Universiy of Wollongong Reserch Online Fculy of Engineering - Ppers (Archive) Fculy of Engineering nd Informion Sciences 2011 Seismic hisory nlysis of symmericl djcen buildings wih soil-srucure inercion
Some Inequalities variations on a common theme Lecture I, UL 2007
 Some Inequliies vriions on common heme Lecure I, UL 2007 Finbrr Hollnd, Deprmen of Mhemics, Universiy College Cork, fhollnd@uccie; July 2, 2007 Three Problems Problem Assume i, b i, c i, i =, 2, 3 re rel
Some Inequliies vriions on common heme Lecure I, UL 2007 Finbrr Hollnd, Deprmen of Mhemics, Universiy College Cork, fhollnd@uccie; July 2, 2007 Three Problems Problem Assume i, b i, c i, i =, 2, 3 re rel
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 10: The High Beta Tokamak Con d and the High Flux Conserving Tokamak.
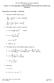 .615, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 1: The High Be Tokmk Con d nd he High Flux Conserving Tokmk Proeries of he High Tokmk 1. Evlue he MHD sfey fcor: ψ B * ( ) 1 3 ρ 1+ ν ρ ρ cosθ *
.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 1: The High Be Tokmk Con d nd he High Flux Conserving Tokmk Proeries of he High Tokmk 1. Evlue he MHD sfey fcor: ψ B * ( ) 1 3 ρ 1+ ν ρ ρ cosθ *
Dynamic Crack kpropagation in Fiber Reinforced Composites
 Presened e COMSO Conference 2009 Miln COMSO CONFERENCE MIAN 2009 OCTOBER 14-16 Dynmic Crck kpropgion in Fiber Reinforced Composies P. onei, C. Cruso, A. Mnn DYNAMIC FRACTURE MECHANICS MONOITIC MATERIAS
Presened e COMSO Conference 2009 Miln COMSO CONFERENCE MIAN 2009 OCTOBER 14-16 Dynmic Crck kpropgion in Fiber Reinforced Composies P. onei, C. Cruso, A. Mnn DYNAMIC FRACTURE MECHANICS MONOITIC MATERIAS
Probability, Estimators, and Stationarity
 Chper Probbiliy, Esimors, nd Sionriy Consider signl genered by dynmicl process, R, R. Considering s funcion of ime, we re opering in he ime domin. A fundmenl wy o chrcerize he dynmics using he ime domin
Chper Probbiliy, Esimors, nd Sionriy Consider signl genered by dynmicl process, R, R. Considering s funcion of ime, we re opering in he ime domin. A fundmenl wy o chrcerize he dynmics using he ime domin
Solutions to Problems from Chapter 2
 Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
A 1.3 m 2.5 m 2.8 m. x = m m = 8400 m. y = 4900 m 3200 m = 1700 m
 PHYS : Soluions o Chper 3 Home Work. SSM REASONING The displcemen is ecor drwn from he iniil posiion o he finl posiion. The mgniude of he displcemen is he shores disnce beween he posiions. Noe h i is onl
PHYS : Soluions o Chper 3 Home Work. SSM REASONING The displcemen is ecor drwn from he iniil posiion o he finl posiion. The mgniude of he displcemen is he shores disnce beween he posiions. Noe h i is onl
Magnetostatics Bar Magnet. Magnetostatics Oersted s Experiment
 Mgneosics Br Mgne As fr bck s 4500 yers go, he Chinese discovered h cerin ypes of iron ore could rc ech oher nd cerin mels. Iron filings "mp" of br mgne s field Crefully suspended slivers of his mel were
Mgneosics Br Mgne As fr bck s 4500 yers go, he Chinese discovered h cerin ypes of iron ore could rc ech oher nd cerin mels. Iron filings "mp" of br mgne s field Crefully suspended slivers of his mel were
Procedia Computer Science
 Procedi Compuer Science 00 (0) 000 000 Procedi Compuer Science www.elsevier.com/loce/procedi The Third Informion Sysems Inernionl Conference The Exisence of Polynomil Soluion of he Nonliner Dynmicl Sysems
Procedi Compuer Science 00 (0) 000 000 Procedi Compuer Science www.elsevier.com/loce/procedi The Third Informion Sysems Inernionl Conference The Exisence of Polynomil Soluion of he Nonliner Dynmicl Sysems
Finite element method for structural dynamic and stability analyses
 Finie elemen mehod for srucural dynamic and sabiliy analyses Module- Nonlinear FE Models Lecure-39 Toal and updaed Lagrangian formulaions Prof C Manohar Deparmen of Civil Engineering IIc, Bangalore 56
Finie elemen mehod for srucural dynamic and sabiliy analyses Module- Nonlinear FE Models Lecure-39 Toal and updaed Lagrangian formulaions Prof C Manohar Deparmen of Civil Engineering IIc, Bangalore 56
2D Motion WS. A horizontally launched projectile s initial vertical velocity is zero. Solve the following problems with this information.
 Nme D Moion WS The equions of moion h rele o projeciles were discussed in he Projecile Moion Anlsis Acii. ou found h projecile moes wih consn eloci in he horizonl direcion nd consn ccelerion in he ericl
Nme D Moion WS The equions of moion h rele o projeciles were discussed in he Projecile Moion Anlsis Acii. ou found h projecile moes wih consn eloci in he horizonl direcion nd consn ccelerion in he ericl
A Simple Model for Axial Displacement in a Cylindrical Pipe With Internal Shock Loading
 A Simple Model for Axil Displcemen in Cylindricl Pipe Wih Inernl Shock Loding Nel P. Bier e-mil: nbier@clech.edu Joseph E. Shepherd Grdue Aerospce Lborories, Cliforni Insiue of Technology, Psden, CA 91125
A Simple Model for Axil Displcemen in Cylindricl Pipe Wih Inernl Shock Loding Nel P. Bier e-mil: nbier@clech.edu Joseph E. Shepherd Grdue Aerospce Lborories, Cliforni Insiue of Technology, Psden, CA 91125
Finite Element Analysis of Structures
 KAIT OE5 Finie Elemen Analysis of rucures Mid-erm Exam, Fall 9 (p) m. As shown in Fig., we model a russ srucure of uniform area (lengh, Area Am ) subjeced o a uniform body force ( f B e x N / m ) using
KAIT OE5 Finie Elemen Analysis of rucures Mid-erm Exam, Fall 9 (p) m. As shown in Fig., we model a russ srucure of uniform area (lengh, Area Am ) subjeced o a uniform body force ( f B e x N / m ) using
(b) 10 yr. (b) 13 m. 1.6 m s, m s m s (c) 13.1 s. 32. (a) 20.0 s (b) No, the minimum distance to stop = 1.00 km. 1.
 Answers o Een Numbered Problems Chper. () 7 m s, 6 m s (b) 8 5 yr 4.. m ih 6. () 5. m s (b).5 m s (c).5 m s (d) 3.33 m s (e) 8. ().3 min (b) 64 mi..3 h. ().3 s (b) 3 m 4..8 mi wes of he flgpole 6. (b)
Answers o Een Numbered Problems Chper. () 7 m s, 6 m s (b) 8 5 yr 4.. m ih 6. () 5. m s (b).5 m s (c).5 m s (d) 3.33 m s (e) 8. ().3 min (b) 64 mi..3 h. ().3 s (b) 3 m 4..8 mi wes of he flgpole 6. (b)
ME 141. Engineering Mechanics
 ME 141 Engineeing Mechnics Lecue 13: Kinemics of igid bodies hmd Shhedi Shkil Lecue, ep. of Mechnicl Engg, UET E-mil: sshkil@me.bue.c.bd, shkil6791@gmil.com Websie: eche.bue.c.bd/sshkil Couesy: Veco Mechnics
ME 141 Engineeing Mechnics Lecue 13: Kinemics of igid bodies hmd Shhedi Shkil Lecue, ep. of Mechnicl Engg, UET E-mil: sshkil@me.bue.c.bd, shkil6791@gmil.com Websie: eche.bue.c.bd/sshkil Couesy: Veco Mechnics
Convergence of Singular Integral Operators in Weighted Lebesgue Spaces
 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS Vol. 10, No. 2, 2017, 335-347 ISSN 1307-5543 www.ejpm.com Published by New York Business Globl Convergence of Singulr Inegrl Operors in Weighed Lebesgue
EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS Vol. 10, No. 2, 2017, 335-347 ISSN 1307-5543 www.ejpm.com Published by New York Business Globl Convergence of Singulr Inegrl Operors in Weighed Lebesgue
IX.1.1 The Laplace Transform Definition 700. IX.1.2 Properties 701. IX.1.3 Examples 702. IX.1.4 Solution of IVP for ODEs 704
 Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 4, 7 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 4, 7 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
DEFORMATION OF ACTIVE FLEXIBLE RODS WITH MEMORY SHAPE ALLOY FIBERS
 DEFORMTION OF CTIVE FLEXIBLE RODS WITH MEMORY SHPE LLOY FIBERS Sefni DONESCU Technicl Universiy of Civil Engineering, Dep. of Mhemics, Bdul Lcul Tei 4, Buchres 7 In his pper we consider hin rod of luminum
DEFORMTION OF CTIVE FLEXIBLE RODS WITH MEMORY SHPE LLOY FIBERS Sefni DONESCU Technicl Universiy of Civil Engineering, Dep. of Mhemics, Bdul Lcul Tei 4, Buchres 7 In his pper we consider hin rod of luminum
An integral having either an infinite limit of integration or an unbounded integrand is called improper. Here are two examples.
 Improper Inegrls To his poin we hve only considered inegrls f(x) wih he is of inegrion nd b finie nd he inegrnd f(x) bounded (nd in fc coninuous excep possibly for finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegrl
Improper Inegrls To his poin we hve only considered inegrls f(x) wih he is of inegrion nd b finie nd he inegrnd f(x) bounded (nd in fc coninuous excep possibly for finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegrl
Hamilton-Jacobi irrotational hydrodynamics for binary neutron star inspiral
 Hmilon-Jcoi irroionl hydrodynmics for inry neuron sr inspirl Chrlmpos Mrkkis Mhemicl Sciences, Universiy of Souhmpon work in progress in collorion wih: John Friedmn, Msru Shi, Nils Andersson, Nicls Moldenhuer,
Hmilon-Jcoi irroionl hydrodynmics for inry neuron sr inspirl Chrlmpos Mrkkis Mhemicl Sciences, Universiy of Souhmpon work in progress in collorion wih: John Friedmn, Msru Shi, Nils Andersson, Nicls Moldenhuer,
This UR does not apply to CSR Bulk Carriers and Oil Tankers or to container ships to which UR S11A is applicable.
 (1989) (Rev.1 199) (Rev. Nov 001) (Rev. June 00) (Rev.4 July 004) (Rev.5 Jn 006) (Rev.6 My 0) (Rev.7 Nov 0) (Rev.8 June 015) Longiudinl Srengh Sndrd.1 Applicion This requiremen pplies only o seel ships
(1989) (Rev.1 199) (Rev. Nov 001) (Rev. June 00) (Rev.4 July 004) (Rev.5 Jn 006) (Rev.6 My 0) (Rev.7 Nov 0) (Rev.8 June 015) Longiudinl Srengh Sndrd.1 Applicion This requiremen pplies only o seel ships
3. Renewal Limit Theorems
 Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
3 Motion with constant acceleration: Linear and projectile motion
 3 Moion wih consn ccelerion: Liner nd projecile moion cons, In he precedin Lecure we he considered moion wih consn ccelerion lon he is: Noe h,, cn be posiie nd neie h leds o rie of behiors. Clerl similr
3 Moion wih consn ccelerion: Liner nd projecile moion cons, In he precedin Lecure we he considered moion wih consn ccelerion lon he is: Noe h,, cn be posiie nd neie h leds o rie of behiors. Clerl similr
A new model for limit order book dynamics
 Anewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics JeffreyR.Russell UniversiyofChicgo,GrdueSchoolofBusiness TejinKim UniversiyofChicgo,DeprmenofSisics Absrc:Thispperproposesnewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics.Thelimiorderbookconsiss
Anewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics JeffreyR.Russell UniversiyofChicgo,GrdueSchoolofBusiness TejinKim UniversiyofChicgo,DeprmenofSisics Absrc:Thispperproposesnewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics.Thelimiorderbookconsiss
Lecture 10: Wave equation, solution by spherical means
 Lecure : Wave equaion, soluion by spherical means Physical modeling eample: Elasodynamics u (; ) displacemen vecor in elasic body occupying a domain U R n, U, The posiion of he maerial poin siing a U in
Lecure : Wave equaion, soluion by spherical means Physical modeling eample: Elasodynamics u (; ) displacemen vecor in elasic body occupying a domain U R n, U, The posiion of he maerial poin siing a U in
New effective moduli of isotropic viscoelastic composites. Part I. Theoretical justification
 IOP Conference Series: Maerials Science and Engineering PAPE OPEN ACCESS New effecive moduli of isoropic viscoelasic composies. Par I. Theoreical jusificaion To cie his aricle: A A Sveashkov and A A akurov
IOP Conference Series: Maerials Science and Engineering PAPE OPEN ACCESS New effecive moduli of isoropic viscoelasic composies. Par I. Theoreical jusificaion To cie his aricle: A A Sveashkov and A A akurov
Physics 101 Lecture 4 Motion in 2D and 3D
 Phsics 11 Lecure 4 Moion in D nd 3D Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Deprmen www.ogun.com Vecor nd is componens The componens re he legs of he righ ringle whose hpoenuse is A A A A A n ( θ ) A Acos( θ) A A A nd
Phsics 11 Lecure 4 Moion in D nd 3D Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Deprmen www.ogun.com Vecor nd is componens The componens re he legs of he righ ringle whose hpoenuse is A A A A A n ( θ ) A Acos( θ) A A A nd
Physic 231 Lecture 4. Mi it ftd l t. Main points of today s lecture: Example: addition of velocities Trajectories of objects in 2 = =
 Mi i fd l Phsic 3 Lecure 4 Min poins of od s lecure: Emple: ddiion of elociies Trjecories of objecs in dimensions: dimensions: g 9.8m/s downwrds ( ) g o g g Emple: A foobll pler runs he pern gien in he
Mi i fd l Phsic 3 Lecure 4 Min poins of od s lecure: Emple: ddiion of elociies Trjecories of objecs in dimensions: dimensions: g 9.8m/s downwrds ( ) g o g g Emple: A foobll pler runs he pern gien in he
AN ANALYTICAL TOOL TO PREDICT LOAD DISTRIBUTION OF MULTI-BOLT SINGLE-LAP THICK LAMINATE JOINTS
 8 TH INTERNATIONAL CONERENCE ON COMOITE MATERIAL AN ANALYTICAL TOOL TO REDICT LOAD DITRIBUTION O MULTI-BOLT INGLE-LA THIC LAMINATE JOINT Longqun Liu*, Ying Mo, Rn Wei chool of Aeronuics nd Asronuics, hnghi
8 TH INTERNATIONAL CONERENCE ON COMOITE MATERIAL AN ANALYTICAL TOOL TO REDICT LOAD DITRIBUTION O MULTI-BOLT INGLE-LA THIC LAMINATE JOINT Longqun Liu*, Ying Mo, Rn Wei chool of Aeronuics nd Asronuics, hnghi
Science Advertisement Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: The Physical Science Basis 2/3/2007 Physics 253
 Science Adeisemen Inegoenmenl Pnel on Clime Chnge: The Phsicl Science Bsis hp://www.ipcc.ch/spmfeb7.pdf /3/7 Phsics 53 hp://www.fonews.com/pojecs/pdf/spmfeb7.pdf /3/7 Phsics 53 3 Sus: Uni, Chpe 3 Vecos
Science Adeisemen Inegoenmenl Pnel on Clime Chnge: The Phsicl Science Bsis hp://www.ipcc.ch/spmfeb7.pdf /3/7 Phsics 53 hp://www.fonews.com/pojecs/pdf/spmfeb7.pdf /3/7 Phsics 53 3 Sus: Uni, Chpe 3 Vecos
IX.1.1 The Laplace Transform Definition 700. IX.1.2 Properties 701. IX.1.3 Examples 702. IX.1.4 Solution of IVP for ODEs 704
 Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 6, 8 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 6, 8 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
LAPLACE TRANSFORM OVERCOMING PRINCIPLE DRAWBACKS IN APPLICATION OF THE VARIATIONAL ITERATION METHOD TO FRACTIONAL HEAT EQUATIONS
 Wu, G.-.: Lplce Trnsform Overcoming Principle Drwbcks in Applicion... THERMAL SIENE: Yer 22, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 257-26 257 Open forum LAPLAE TRANSFORM OVEROMING PRINIPLE DRAWBAKS IN APPLIATION OF THE VARIATIONAL
Wu, G.-.: Lplce Trnsform Overcoming Principle Drwbcks in Applicion... THERMAL SIENE: Yer 22, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 257-26 257 Open forum LAPLAE TRANSFORM OVEROMING PRINIPLE DRAWBAKS IN APPLIATION OF THE VARIATIONAL
EXERCISE - 01 CHECK YOUR GRASP
 UNIT # 09 PARABOLA, ELLIPSE & HYPERBOLA PARABOLA EXERCISE - 0 CHECK YOUR GRASP. Hin : Disnce beween direcri nd focus is 5. Given (, be one end of focl chord hen oher end be, lengh of focl chord 6. Focus
UNIT # 09 PARABOLA, ELLIPSE & HYPERBOLA PARABOLA EXERCISE - 0 CHECK YOUR GRASP. Hin : Disnce beween direcri nd focus is 5. Given (, be one end of focl chord hen oher end be, lengh of focl chord 6. Focus
Mathematical Modeling
 ME pplie Engineering nlsis Chper Mhemicl Moeling Professor Ti-Rn Hsu, Ph.D. Deprmen of Mechnicl n erospce Engineering Sn Jose Se Universi Sn Jose, Cliforni, US Jnur Chper Lerning Ojecives Mhemicl moeling
ME pplie Engineering nlsis Chper Mhemicl Moeling Professor Ti-Rn Hsu, Ph.D. Deprmen of Mechnicl n erospce Engineering Sn Jose Se Universi Sn Jose, Cliforni, US Jnur Chper Lerning Ojecives Mhemicl moeling
Observability of flow dependent structure functions and their use in data assimilation
 Oserviliy of flow dependen srucure funcions nd heir use in d ssimilion Pierre Guhier nd Crisin Lupu Collorion wih Séphne Lroche, Mrk Buehner nd Ahmed Mhidji (Env. Cnd) 3rd meeing of he HORPEX DAOS-WG Monrél
Oserviliy of flow dependen srucure funcions nd heir use in d ssimilion Pierre Guhier nd Crisin Lupu Collorion wih Séphne Lroche, Mrk Buehner nd Ahmed Mhidji (Env. Cnd) 3rd meeing of he HORPEX DAOS-WG Monrél
3D Transformations. Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 1/26/07 1
 D Trnsformions Compuer Grphics COMP 770 (6) Spring 007 Insrucor: Brndon Lloyd /6/07 Geomery Geomeric eniies, such s poins in spce, exis wihou numers. Coordines re nming scheme. The sme poin cn e descried
D Trnsformions Compuer Grphics COMP 770 (6) Spring 007 Insrucor: Brndon Lloyd /6/07 Geomery Geomeric eniies, such s poins in spce, exis wihou numers. Coordines re nming scheme. The sme poin cn e descried
Transport Phenomena and Shrinkage Modeling During Convective Drying of Vegetables.
 Excerp from he Proceedings of he COMSOL Conference 2009 Miln Trnspor Phenomen nd Shringe Modeling During Convecive Drying of Vegebles. Sefno Curcio *1 nd Mri Avers 1 1 Deprmen of Engineering Modelling
Excerp from he Proceedings of he COMSOL Conference 2009 Miln Trnspor Phenomen nd Shringe Modeling During Convecive Drying of Vegebles. Sefno Curcio *1 nd Mri Avers 1 1 Deprmen of Engineering Modelling
Longitudinal Strength Standard. S11 (cont) S11
 (1989) (Rev.1 199) (Rev. Nov 001) (Rev. June 00) (Rev.4 July 004) (Rev.5 Jn 006) (Rev.6 My 0) Longiudinl Srengh Sndrd.1 Applicion This requiremen pplies only o seel ships of lengh 90 m nd greer in unresriced
(1989) (Rev.1 199) (Rev. Nov 001) (Rev. June 00) (Rev.4 July 004) (Rev.5 Jn 006) (Rev.6 My 0) Longiudinl Srengh Sndrd.1 Applicion This requiremen pplies only o seel ships of lengh 90 m nd greer in unresriced
SOME USEFUL MATHEMATICS
 SOME USEFU MAHEMAICS SOME USEFU MAHEMAICS I is esy o mesure n preic he behvior of n elecricl circui h conins only c volges n currens. However, mos useful elecricl signls h crry informion vry wih ime. Since
SOME USEFU MAHEMAICS SOME USEFU MAHEMAICS I is esy o mesure n preic he behvior of n elecricl circui h conins only c volges n currens. However, mos useful elecricl signls h crry informion vry wih ime. Since
T-Match: Matching Techniques For Driving Yagi-Uda Antennas: T-Match. 2a s. Z in. (Sections 9.5 & 9.7 of Balanis)
 3/0/018 _mch.doc Pge 1 of 6 T-Mch: Mching Techniques For Driving Ygi-Ud Anenns: T-Mch (Secions 9.5 & 9.7 of Blnis) l s l / l / in The T-Mch is shun-mching echnique h cn be used o feed he driven elemen
3/0/018 _mch.doc Pge 1 of 6 T-Mch: Mching Techniques For Driving Ygi-Ud Anenns: T-Mch (Secions 9.5 & 9.7 of Blnis) l s l / l / in The T-Mch is shun-mching echnique h cn be used o feed he driven elemen
Development of a New Scheme for the Solution of Initial Value Problems in Ordinary Differential Equations
 IOS Journl o Memics IOSJM ISSN: 78-78 Volume Issue July-Aug PP -9 www.iosrjournls.org Developmen o New Sceme or e Soluion o Iniil Vlue Problems in Ordinry Dierenil Equions Ogunrinde. B. dugb S. E. Deprmen
IOS Journl o Memics IOSJM ISSN: 78-78 Volume Issue July-Aug PP -9 www.iosrjournls.org Developmen o New Sceme or e Soluion o Iniil Vlue Problems in Ordinry Dierenil Equions Ogunrinde. B. dugb S. E. Deprmen
6.01: Introduction to EECS I Lecture 8 March 29, 2011
 6.01: Inroducion o EES I Lecure 8 March 29, 2011 6.01: Inroducion o EES I Op-Amps Las Time: The ircui Absracion ircuis represen sysems as connecions of elemens hrough which currens (hrough variables) flow
6.01: Inroducion o EES I Lecure 8 March 29, 2011 6.01: Inroducion o EES I Op-Amps Las Time: The ircui Absracion ircuis represen sysems as connecions of elemens hrough which currens (hrough variables) flow
Nonlinear System Modelling: How to Estimate the. Highest Significant Order
 IEEE Insrumenion nd Mesuremen Technology Conference nchorge,, US, - My Nonliner Sysem Modelling: ow o Esime he ighes Significn Order Neophyos Chirs, Ceri Evns nd Dvid Rees, Michel Solomou School of Elecronics,
IEEE Insrumenion nd Mesuremen Technology Conference nchorge,, US, - My Nonliner Sysem Modelling: ow o Esime he ighes Significn Order Neophyos Chirs, Ceri Evns nd Dvid Rees, Michel Solomou School of Elecronics,
3.1.3 INTRODUCTION TO DYNAMIC OPTIMIZATION: DISCRETE TIME PROBLEMS. A. The Hamiltonian and First-Order Conditions in a Finite Time Horizon
 3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
Asymptotic relationship between trajectories of nominal and uncertain nonlinear systems on time scales
 Asympoic relionship beween rjecories of nominl nd uncerin nonliner sysems on ime scles Fim Zohr Tousser 1,2, Michel Defoor 1, Boudekhil Chfi 2 nd Mohmed Djemï 1 Absrc This pper sudies he relionship beween
Asympoic relionship beween rjecories of nominl nd uncerin nonliner sysems on ime scles Fim Zohr Tousser 1,2, Michel Defoor 1, Boudekhil Chfi 2 nd Mohmed Djemï 1 Absrc This pper sudies he relionship beween
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( y )
 8. Lengh of Plne Curve The mos fmous heorem in ll of mhemics is he Pyhgoren Theorem. I s formulion s he disnce formul is used o find he lenghs of line segmens in he coordine plne. In his secion you ll
8. Lengh of Plne Curve The mos fmous heorem in ll of mhemics is he Pyhgoren Theorem. I s formulion s he disnce formul is used o find he lenghs of line segmens in he coordine plne. In his secion you ll
Road noise sensitivity analysis with respect to suspension geometry
 Rod noise sensiiviy nlysis wih respec o suspension geomery Fumihiko KOSAKA 1 ; Hiroki MIZUNO ; Tsuyoshi INOUE 3 ; Kenro TAKAGI 4 1, MITSUBISHI MOTORS ORPORATION, Jpn 3, 4 Ngoy Universiy, Jpn ABSTRAT In
Rod noise sensiiviy nlysis wih respec o suspension geomery Fumihiko KOSAKA 1 ; Hiroki MIZUNO ; Tsuyoshi INOUE 3 ; Kenro TAKAGI 4 1, MITSUBISHI MOTORS ORPORATION, Jpn 3, 4 Ngoy Universiy, Jpn ABSTRAT In
A new model for solving fuzzy linear fractional programming problem with ranking function
 J. ppl. Res. Ind. Eng. Vol. 4 No. 07 89 96 Journl of pplied Reserch on Indusril Engineering www.journl-prie.com new model for solving fuzzy liner frcionl progrmming prolem wih rning funcion Spn Kumr Ds
J. ppl. Res. Ind. Eng. Vol. 4 No. 07 89 96 Journl of pplied Reserch on Indusril Engineering www.journl-prie.com new model for solving fuzzy liner frcionl progrmming prolem wih rning funcion Spn Kumr Ds
NEW FRACTIONAL DERIVATIVES WITH NON-LOCAL AND NON-SINGULAR KERNEL Theory and Application to Heat Transfer Model
 Angn, A., e l.: New Frcionl Derivives wih Non-Locl nd THERMAL SCIENCE, Yer 216, Vol. 2, No. 2, pp. 763-769 763 NEW FRACTIONAL DERIVATIVES WITH NON-LOCAL AND NON-SINGULAR KERNEL Theory nd Applicion o He
Angn, A., e l.: New Frcionl Derivives wih Non-Locl nd THERMAL SCIENCE, Yer 216, Vol. 2, No. 2, pp. 763-769 763 NEW FRACTIONAL DERIVATIVES WITH NON-LOCAL AND NON-SINGULAR KERNEL Theory nd Applicion o He
IX.2 THE FOURIER TRANSFORM
 Chper IX The Inegrl Trnsform Mehods IX. The Fourier Trnsform November, 7 7 IX. THE FOURIER TRANSFORM IX.. The Fourier Trnsform Definiion 7 IX.. Properies 73 IX..3 Emples 74 IX..4 Soluion of ODE 76 IX..5
Chper IX The Inegrl Trnsform Mehods IX. The Fourier Trnsform November, 7 7 IX. THE FOURIER TRANSFORM IX.. The Fourier Trnsform Definiion 7 IX.. Properies 73 IX..3 Emples 74 IX..4 Soluion of ODE 76 IX..5
LECTURE 5. is defined by the position vectors r, 1. and. The displacement vector (from P 1 to P 2 ) is defined through r and 1.
 LECTURE 5 ] DESCRIPTION OF PARTICLE MOTION IN SPACE -The displcemen, veloci nd cceleion in -D moion evel hei veco nue (diecion) houh he cuion h one mus p o hei sin. Thei full veco menin ppes when he picle
LECTURE 5 ] DESCRIPTION OF PARTICLE MOTION IN SPACE -The displcemen, veloci nd cceleion in -D moion evel hei veco nue (diecion) houh he cuion h one mus p o hei sin. Thei full veco menin ppes when he picle
P441 Analytical Mechanics - I. Coupled Oscillators. c Alex R. Dzierba
 Lecure 3 Mondy - Deceber 5, 005 Wrien or ls upded: Deceber 3, 005 P44 Anlyicl Mechnics - I oupled Oscillors c Alex R. Dzierb oupled oscillors - rix echnique In Figure we show n exple of wo coupled oscillors,
Lecure 3 Mondy - Deceber 5, 005 Wrien or ls upded: Deceber 3, 005 P44 Anlyicl Mechnics - I oupled Oscillors c Alex R. Dzierb oupled oscillors - rix echnique In Figure we show n exple of wo coupled oscillors,
Calculation method of flux measurements by static chambers
 lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers P.S. Kroon Presened he NiroEurope Workshop, 15h - 17h December 28, openhgen, Denmrk EN-L--9-11 December 28 lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers
lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers P.S. Kroon Presened he NiroEurope Workshop, 15h - 17h December 28, openhgen, Denmrk EN-L--9-11 December 28 lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers
Systems Variables and Structural Controllability: An Inverted Pendulum Case
 Reserch Journl of Applied Sciences, Engineering nd echnology 6(: 46-4, 3 ISSN: 4-7459; e-issn: 4-7467 Mxwell Scienific Orgniion, 3 Submied: Jnury 5, 3 Acceped: Mrch 7, 3 Published: November, 3 Sysems Vribles
Reserch Journl of Applied Sciences, Engineering nd echnology 6(: 46-4, 3 ISSN: 4-7459; e-issn: 4-7467 Mxwell Scienific Orgniion, 3 Submied: Jnury 5, 3 Acceped: Mrch 7, 3 Published: November, 3 Sysems Vribles
Physics 100: Lecture 1
 Physics : Lecure Agen for Toy Aice Scope of his course Mesuremen n Unis Funmenl unis Sysems of unis Conering beween sysems of unis Dimensionl Anlysis -D Kinemics (reiew) Aerge & insnneous elociy n ccelerion
Physics : Lecure Agen for Toy Aice Scope of his course Mesuremen n Unis Funmenl unis Sysems of unis Conering beween sysems of unis Dimensionl Anlysis -D Kinemics (reiew) Aerge & insnneous elociy n ccelerion
Solutions for Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations By Tan-Cot Method
 IOSR Journl of Mhemics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578. Volume 5, Issue 3 (Jn. - Feb. 13), PP 6-11 Soluions for Nonliner Pril Differenil Equions By Tn-Co Mehod Mhmood Jwd Abdul Rsool Abu Al-Sheer Al -Rfidin Universiy
IOSR Journl of Mhemics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578. Volume 5, Issue 3 (Jn. - Feb. 13), PP 6-11 Soluions for Nonliner Pril Differenil Equions By Tn-Co Mehod Mhmood Jwd Abdul Rsool Abu Al-Sheer Al -Rfidin Universiy
Soil-Pile Dynamic Interaction in the Viscous Damping Layered Soils
 1 The Open Civil Engineering Journl, 11, 5, 1-18 Soil-Pile Dynmic Inercion in he Viscous Dmping Lyered Soils Open Access Yinhui Wng 1, Kuihu Wng, Zhixing Zh 1, * nd Reno Que 1 Deprmen of Civil Engineering
1 The Open Civil Engineering Journl, 11, 5, 1-18 Soil-Pile Dynmic Inercion in he Viscous Dmping Lyered Soils Open Access Yinhui Wng 1, Kuihu Wng, Zhixing Zh 1, * nd Reno Que 1 Deprmen of Civil Engineering
Neural assembly binding in linguistic representation
 Neurl ssembly binding in linguisic represenion Frnk vn der Velde & Mrc de Kmps Cogniive Psychology Uni, Universiy of Leiden, Wssenrseweg 52, 2333 AK Leiden, The Neherlnds, vdvelde@fsw.leidenuniv.nl Absrc.
Neurl ssembly binding in linguisic represenion Frnk vn der Velde & Mrc de Kmps Cogniive Psychology Uni, Universiy of Leiden, Wssenrseweg 52, 2333 AK Leiden, The Neherlnds, vdvelde@fsw.leidenuniv.nl Absrc.
Ch.4 Motion in 2D. Ch.4 Motion in 2D
 Moion in plne, such s in he sceen, is clled 2-dimensionl (2D) moion. 1. Posiion, displcemen nd eloci ecos If he picle s posiion is ( 1, 1 ) 1, nd ( 2, 2 ) 2, he posiions ecos e 1 = 1 1 2 = 2 2 Aege eloci
Moion in plne, such s in he sceen, is clled 2-dimensionl (2D) moion. 1. Posiion, displcemen nd eloci ecos If he picle s posiion is ( 1, 1 ) 1, nd ( 2, 2 ) 2, he posiions ecos e 1 = 1 1 2 = 2 2 Aege eloci
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Physics for Scientists and Engineers I
 Physics for Scieniss nd Engineers I PHY 48, Secion 4 Dr. Beriz Roldán Cueny Uniersiy of Cenrl Florid, Physics Deprmen, Orlndo, FL Chper - Inroducion I. Generl II. Inernionl Sysem of Unis III. Conersion
Physics for Scieniss nd Engineers I PHY 48, Secion 4 Dr. Beriz Roldán Cueny Uniersiy of Cenrl Florid, Physics Deprmen, Orlndo, FL Chper - Inroducion I. Generl II. Inernionl Sysem of Unis III. Conersion
f t f a f x dx By Lin McMullin f x dx= f b f a. 2
 Accumulion: Thoughs On () By Lin McMullin f f f d = + The gols of he AP* Clculus progrm include he semen, Sudens should undersnd he definie inegrl s he ne ccumulion of chnge. 1 The Topicl Ouline includes
Accumulion: Thoughs On () By Lin McMullin f f f d = + The gols of he AP* Clculus progrm include he semen, Sudens should undersnd he definie inegrl s he ne ccumulion of chnge. 1 The Topicl Ouline includes
Virtual 3D Sculpting
 In Journl of Visulizion nd Compuer Animion, John Wiley & Sons, 11(), pp. 155-1, July 2. Virul D Sculping Jnis P.Y. Wong Rynson W.H. Lu Lizhung M Deprmen of Compuer Science, Ciy Universiy of Hong Kong,
In Journl of Visulizion nd Compuer Animion, John Wiley & Sons, 11(), pp. 155-1, July 2. Virul D Sculping Jnis P.Y. Wong Rynson W.H. Lu Lizhung M Deprmen of Compuer Science, Ciy Universiy of Hong Kong,
A NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF THE URYSOHN-TYPE FREDHOLM INTEGRAL EQUATIONS
 A NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF THE URYSOHN-TYPE FREDHOLM INTEGRAL EQUATIONS A JAFARIAN 1,, SA MEASOOMY 1,b, ALIREZA K GOLMANKHANEH 1,c, D BALEANU 2,3,4 1 Deprmen of Mhemics, Urmi Brnch, Islmic Azd Universiy,
A NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF THE URYSOHN-TYPE FREDHOLM INTEGRAL EQUATIONS A JAFARIAN 1,, SA MEASOOMY 1,b, ALIREZA K GOLMANKHANEH 1,c, D BALEANU 2,3,4 1 Deprmen of Mhemics, Urmi Brnch, Islmic Azd Universiy,
Honours Introductory Maths Course 2011 Integration, Differential and Difference Equations
 Honours Inroducory Mhs Course 0 Inegrion, Differenil nd Difference Equions Reding: Ching Chper 4 Noe: These noes do no fully cover he meril in Ching, u re men o supplemen your reding in Ching. Thus fr
Honours Inroducory Mhs Course 0 Inegrion, Differenil nd Difference Equions Reding: Ching Chper 4 Noe: These noes do no fully cover he meril in Ching, u re men o supplemen your reding in Ching. Thus fr
Ch.1. Group Work Units. Continuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPC
 Ch.. Group Work Unis Coninuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPC Uni 2 Jusify wheher he following saemens are rue or false: a) Two sreamlines, corresponding o a same insan of ime, can never inersec
Ch.. Group Work Unis Coninuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPC Uni 2 Jusify wheher he following saemens are rue or false: a) Two sreamlines, corresponding o a same insan of ime, can never inersec
EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEM
 Elecronic Journl of Differenil Equions, Vol. 208 (208), No. 50, pp. 6. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mh.xse.edu or hp://ejde.mh.un.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE
Elecronic Journl of Differenil Equions, Vol. 208 (208), No. 50, pp. 6. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mh.xse.edu or hp://ejde.mh.un.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE)
 QUESTION BANK 6 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddhrh Ngr, Nrynvnm Rod 5758 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subjec wih Code :Engineering Mhemic-I (6HS6) Coure & Brnch: B.Tech Com o ll Yer & Sem:
QUESTION BANK 6 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddhrh Ngr, Nrynvnm Rod 5758 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subjec wih Code :Engineering Mhemic-I (6HS6) Coure & Brnch: B.Tech Com o ll Yer & Sem:
10. State Space Methods
 . Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
. Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
