INVESTIGATION OF REINFORCEMENT LEARNING FOR BUILDING THERMAL MASS CONTROL
|
|
|
- Marjory Baldwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INVESTIGATION OF REINFORCEMENT LEARNING FOR BUILDING THERMAL MASS CONTROL Simeng Liu nd Gregor P. Henze, Ph.D., P.E. Universiy of Nebrsk Lincoln, Archiecurl Engineering 1110 Souh 67 h Sree, Peer Kiewi Insiue, Omh, Nebrsk U.S.A. ABSTRACT This pper describes simulion-bsed invesigion of mchine-lerning conrol for he supervisory conrol of building herml mss. Model-free reinforcemen lerning conrol is invesiged for he operion of elecriclly driven chilled wer sysems in hevy-mss commercil buildings. The reinforcemen lerning conroller lerns o precool he building nigh before he onse of occupncy bsed on he feedbck i receives from ps conrol cions. The lerning gen inercs wih is environmen by commnding he globl zone emperure sepoins nd exrcs cues bou he environmen solely bsed on he reinforcemen feedbck i receives, which in his sudy is he monery cos of ech conrol cion. No predicion or sysem model is required. Over ime nd by exploring he environmen, he reinforcemen lerning conroller esblishes sisicl summry of pln operion, which is coninuously upded s operion coninues. The conroller lerns o ccoun for he ime-dependen cos of elecriciy, he vilbiliy of pssive herml sorge invenory, nd weher condiions. This sudy reveled h lerning conrol is fesible mehodology o find ner-opiml sepoin profile for exploiing he pssive building herml sorge cpciy. The freedom from building model mkes i especilly rcive in rel-ime conrol problems, nd heoreiclly i cn rech he rue opimum evenully, no mer wh building i is deling wih, if only he environmen could be smpled for n infinie period of ime. The nlysis showed h he lerning conroller is ffeced by he dimension of he cion nd se spce, he uiliy re differenils beween on- nd off-pek, lerning re nd severl oher fcors. Moreover, lerning speed is relively low when deling wih problems wih lrge se spce nd cion spce. INTRODUCTION The moivion of his reserch sems from reserch projec funded by he U.S. Deprmen of Energy h invesiges predicive opiml conrol of cive nd pssive building herml sorge invenory. The gol of his projec is o develop model-bsed supervisory building conroller o exploi he poenil of boh cive nd pssive building herml sorge cpciy. In he firs wo yers of his sudy, boh numericl nlysis nd lborory experimen hve demonsred cos sving poenil when pplying opiml conrol o he uilizion of cive nd pssive building herml sorge invenory. However, modeling complexiy nd inccurcy of his model-bsed pproch hve been reveled s well. Menwhile, numerous pplicion of reinforcemen lerning conrol o engineering problems provides new direcion o ckle his conrol problem in more efficien mnner. To his end, n invesigion hs been crried ou o deermine he fesibiliy nd meris of lerning conrol pplied o he conrol of building cive nd pssive herml sorge invenory. As n iniil sep, simulion environmen in Simulink ws developed o invesige he fesibiliy of pplying reinforcemen lerning conrol o pssive building herml sorge only. REVIEW OF PAST WORK Previous sudies on building herml mss uilizion demonsred he poenil of pek cooling lod reducion nd ssocied elecricl demnd. However, cos svings vry widely mong he published cse sudies (Rbl nd Norford 1991; Conniff 1991; Morris e l. 1994; Keeney nd Brun 1997). In simulion sudy presened by Brun (1990), cos svings for design dy vried from 0-35% depending on sysem ype nd uiliy re. Andresen nd Brndemuehl (1992) demonsred energy nd cos svings poenil by precooling he building srucure, clling enion o he impornce of he mss of furnishing which significnly ffecs he precooling sregy. Brun e l. (2001) developed ool o evlue differen precooling sregies by compring he HVAC uiliy coss in ech pplicion. Simulion sudies hve been crried ou for seleced locions, climes, nd uiliy re srucures. A comprison showed cos svings vrying from 40% bes o zero or even excess coss for some less fvorble cses. In review ricle on lod conrol using building herml mss, Brun (2003) concluded h he svings poenil is very sensiive o he uiliy res, building nd pln chrcerisics, nd weher condiions nd occupncy schedule. The grees cos svings were relized for he cse of hevy consrucion, good pr-lod chrcerisics nd low mbien SimBuild 2004, IBPSA-USA Nionl Conference Boulder, CO, Augus 4-6, Pge 1 of 11
2 emperure which enbled free cooling during nigh venilion. A simulion sudy ws crried ou by Henze e l. (2004) o invesige he combined usge of boh cive nd pssive building herml sorge invenory. The erm cive refers o herml energy sorge (TES) sysem, which is eiher bsed on chilled wer or ice, nd pssive refers o he building mss iself including srucure nd furniure. The nlysis uses model-bsed pproch o find he opiml globl zone ir emperure sepoin nd TES opering commnds. Subsnil uilizion of boh sorge medi ws observed using perfec building model. However, in rel-ime pplicions, mismch beween building model nd he cul building cn never be compleely voided. In compnion sudy by Liu nd Henze (2004) on he impc of model ccurcy on he quliy of he opimizion sysem, i ws found h mismch of inernl he gin nd building consrucion will significnly ffec he opiml zone ir emperure sepoin. I is desired o hve model clibrion procedure in plce o preven lrge deviions of he model, bu his will increse he compuionl cos nd my lso no be prcicl for rel-ime conrol. Menwhile, even hough he predicive opiml conrol lwys looks forwrd by relying on shor-erm forecss, he knowledge gined from he ps hs been ignored. Consequenly, he reinforcemen lerning conrol prdigm provides n lernive pproch h elimines he need for model nd is buil enirely upon experience while voiding he disdvnges of model-bsed conrol such s modeling complexiy, inccurcy, nd need for predicion. Alhough echniques of mchine lerning hve been widely pplied in mny indusries, he concep of lerning conrol ppers sill new in he re of HVAC conrol. Krechmr e l. (2001) employed reinforcemen lerning ssised by rificil neurl neworks o lern o improve muliple-inpu mulipleoupu (MIMO) conrol performnce of heing sysem wihin sble environmen gurneed by robus conrol. Henze nd Dodier (1997) invesiged lerning conrol of grid-independen phoovolic sysem consising of collecor, bery sorge, nd lod. Q-lerning, model-free reinforcemen lerning lgorihm ws pplied o opimize conrol performnce of he sysem. Simulion nlysis compred he performnce beween he convenionl PV-prioriy conrol nd he opiml conrol. Beer performnce ws found by pplying he reinforcemen lerning o opimize he operion of he sysem. Henze nd Schoenmnn (2003) pplied reinforcemen lerning conrol o he opimizion of cive herml energy sorge sysems. Though reinforcemen lerning conrol proved sensiive o he selecion of se vribles, level of discreizion, nd lerning re, i effecively lerns difficul sk of conrolling herml energy sorge nd displys good performnce. The cos svings compre fvorbly wih convenionl cool sorge conrol sregies, bu do no rech he level of predicive opiml conrol. INTRODUCTION TO LEARNING CONTROL Reinforcemen lerning conrol sems from he developmen of wo differen disciplines, which re psychology nd opiml conrol (Suon nd Bro 1998). I is defined s process in which n gen lerns nd improves is behvior by ril-nd-error inercions wih dynmic environmen o chieve long-erm gol. Algorihms hve been well pplied o solve sequenil decision mking problems. Se Environmen policy Agen Rewrd Acion Figure 1: Schemic of sequenil decision mking problems Figure 1 presens schemic of ypicl sequenil decision mking problem. A ech ime sep or sge, he gen will execue n cion seleced from cion spce A ccording o policy; he environmen will hen be rnsmied from se s o s +1, long wih feedbck signl r, which is defined s rewrd or reinforcemen. The gol of he sequenil decision mking problem is o find n opiml policy h mximizes he ccumuled rewrds in he fuure sring from priculr se 2 k k + 1 k = 0 R = r + r + r +... = r. (1) A policy is he gen s selecion of cions in given se, i.e., i is mpping beween se nd cions, : S A. In Eq.1, is inroduced s discouning fcor, which is used o weigh he fuure rewrds. One of he mos widely pplied pproches o solve sequenil decision mking problems is dynmic SimBuild 2004, IBPSA-USA Nionl Conference Boulder, CO, Augus 4-6, Pge 2 of 11
3 progrmming (Bellmn 1957), which ssumes here is n explici model of he environmen vilble. The rnsiion of he environmen se is defined s rnsiion probbiliy funcion Pss ' = Pr( s + 1 = s ' s = s, = ) The expression of he rnsiion in erms of probbiliy densiy funcion llows for rndom effecs o be considered. Similrly, he insn rewrd is lso defined s funcion of curren se, curren cion nd nex se rss ' = E( r + 1 s = s, =, s + 1 = s '). In dynmic progrmming, he policy is usully defined s probbiliy funcion (s,) of king cion when in se s. Given policy nd cerin se, he se vlue funcion is defined s V ( s) = E R s = s { } k (2) = E r + k + 1 s = s. k = 0 Similrly, we define he vlue of king cion in se s ccording o policy s Q ( s, ) = E R s = s, = { } k (3) = E r + k + 1 s = s, = k = 0 The gol of he opimizion is o find he opiml policy o mximize he se vlue funcion. Bellmn s principle of opimliy ses h whever he iniil se nd cion re, he remining decisions mus consiue n opiml policy wih regrd o he se resuling from he firs decision. Bellmn s opimliy equion cn be wrien s * * V ( s) = mx Pss '[ rss ' + V ( s ')] (4) s ' Bsed on he recursive nure of dynmic progrmming, reinforcemen lerning lgorihms were developed o del wih problems when here is no explici model vilble of he environmen. The only ccess of he gen o he informion bou he environmen is vi he direc inercions wih he environmen including percepion of he se nd he rewrd. The vlue funcion is progressively esimed by coninuous smpling vlues ssocied wih priculr policy. This so-clled Mone Crlo mehod overcomes he necessiy of he rnsiion probbiliy funcion P. ss ' The rel power of reinforcemen lerning lies in he fc h he gen does no hve o wi unil he erminl cos is incurred o djus is policy (Kelbling e l. 1996). This is relized by he emporl difference (TD) mehod inroduced by Suon (Suon 1988), in which he vlue funcion for priculr se is upded bsed on he previous esimion, immedie rewrd nd he esimed vlue of he nex se. The simples TD mehod, known s TD(0), is defined s: V ( s ) V ( s ) + α[ r + V ( s ) V ( s )] (5) where α is defined s lerning re. The Q-Lerning Algorihm Developed by Wkins (Wkins 1992), he Q-Lerning lgorihm is one of he mos widely pplied reinforcemen lerning lgorihms. The quliy vlue Q( s, ) ssocied wih se-cion pir is inroduced, which cn be considered n esime of he cumulive rewrds by performing cion in se s. Bellmn s opimliy equion cn be formuled s Q( s, ) = Pss '[ rss ' + mx Q( s ', ')] (6) s ' The Q funcion cn be lerned by he lgorihm TD (0), which smples he rnsiion probbiliy hrough repeed cions. Given he se s he gen jus visied, he seleced cion, he nex se s ', nd he reinforcemen r( s,, s '), he vlue funcion cn be upded ccording o: Q( s, ) Q( s, ) + α (7) r( s,, s ') + mx Q( s ', ') Q( s, ) ' An imporn issue for reinforcemen lerning lgorihm is he rde-off beween explorion nd exploiion. The online smpling lgorihm relies on repeedly visiing every se-cion pir o upde he ssocied Q -vlue by mens of explorion process. On he oher hnd, o conrol effecively, he gen should pick n cion for conrol, e.g., he cion wih he highes Q vlue, which is known s greedy exploiion policy. Algorihms hve been inroduced o blnce explorion nd exploiion. One of simples pproches is clled ε-greedy mehod, in which, insed of being greedy ll of he ime, he gen kes non-greedy explorory cions wih probbiliy of ε. Anoher cegory of mehods is clled sofmx cion selecion mehods, mong which, Gibbs or Bolzmnn disribuion is one of he mos populr mehods. I defines he rule of choosing n cion wih probbiliy: Q( s, ) / τ e P( s, ) =. n Q( s, b) / τ e b = 1 The posiive prmeer τ is clled emperure, he lower he vlue of he emperure, he higher he probbiliy becomes h n cion wih high Q-vlue will be chosen. When τ 0, his becomes he greedy policy. SIMULATION ANALYSIS The gol of his nlysis is o design conroller which lerns o conrol he zone ir emperure sepoin o ' SimBuild 2004, IBPSA-USA Nionl Conference Boulder, CO, Augus 4-6, Pge 3 of 11
4 reduce opering coss by uilizing he building pssive herml sorge cpciy. The Q-Lerning lgorihm will be pplied o govern he model-free lerning procedure, nd subsequenly he opiml policy will be compred wih he resul of model-bsed opiml conrol, which is found by direc serch lgorihm. Developmen of simulion environmen A commercil building nd ssocied energy sysem model ws developed in he Simulink environmen of Mlb o model he dynmic herml response of he building nd energy consumpion of he HVAC sysem. Figure 7 depics he srucure of he simulion environmen. The firs schemic provides n overview of he models. The simulion environmen is mde up of four mjor groups of componens. The firs one consiss of he exernl nd inernl he gin models including modules processing weher d, solr rdiion, nd building inernl he gin. The second group is he building envelope modules. Using se spce modeling, he rnsien he rnsfer hrough ech consrucion elemen of he building is clculed using second-order lumped cpcince model. Previous reserch shows h second-order lumped cpcince model wih one inernl nd one exernl cpcince s well s hree resisors cn dequely pproxime he herml response of building consrucion (Goud e l., 2003). The hird group shows HVAC componens modules, which includes VAV erminl box wih rehe coil, n ir hndling uni including n economizer, cooling coil, nd circulion fn, nd finlly simple pln module including n elecricl chiller, cooling ower nd chilled wer pump. The hree groups of modules re finlly linked ogeher ino he fourh group, he herml nd humidiy blnce funcion block in he fourh schemic, in which he building zone ir emperure is upded ccording o he following equion N dt surfces z Cz = Qin + hi Ai ( Tsi Tz ) + d i= 1 m c ( T T ) + m c ( T T ) inf p Z sys p Z where, Tz, T, Ts re zone ir emperure, mbien ir emperure nd supply ir emperure; C z is he room ir herml cpciy; Qin is he convecive inernl he gin; hi, Ai, T si re he inerior convecion he rnsfer coefficien, surfce re nd emperure of he inernl surfce of he envelope of he building; m m re he mss flow re of infilrion nd inf, sys supply ir, respecively. Similrly, he zone ir humidiy is upded ccording he following funcion: dgz M ( ) ( ) / z = m inf g gz + m sys gs TZ + QL hfg d where M z is he room ir mss; g z, g, gs re moisure conen of zone ir, exernl ir nd supply ir; Q L, h fg re he len he gin o he room spce nd sndrd len he of vporizion of wer in ir respecively. The model hs been vlided wih n EnergyPlus model, here is bou 7~8% discrepncy in he lod profile beween he EnergyPlus nd Simulink models, which is considered ccepble. Simulion prmeers For convenience, he building is modeled s simple box model wih ol re of 1200 m 2, nd only one herml zone is considered. Acully, ps reserch (Liu nd Henze 2004) shows h he simplificion of building geomery nd zoning only mrginlly ffecs he opimizion. Typicl meeorologicl weher d (TMY2) for Omh, Nebrsk re seleced nd lighing power densiies ypicl of office buildings re ssumed. The uiliy re srucure nd occupncy schedule re synchronized in order o simplify he problem s shown in Figure 2. BM1 BM2 BM3 BM1 BM2 BM3 Dy N Dy N+1 Time Figure 2: Profiles of he building modes Re srucure Occupncy A new erm, building mode, is inroduced o fcilie he problem represenion. Building mode describes he chrcerisic of re srucure nd occupncy of building cerin period of ime. Figure 2 presens n exmple wih hree building modes, in which, building mode one (BM1) is defined s he ime period from midnigh o he occurrence of occupncy nd on-pek uiliy re, which is 7:00 AM in our sudy; BM2 is he ime period covering ll he hours wih occupncy nd on-pek uiliy re (7:00 AM o 17:00 PM); nd BM3 covers he remining hours of he dy, which hs no occupncy nd off-pek uiliy re. The purpose of he building modes is o simplify he opimizion problem. Insed of seing he zone ir sepoin hourly, sepoins wihin sme building mode cn be se s he sme. As resul, he number of opimizion vribles is reduced SimBuild 2004, IBPSA-USA Nionl Conference Boulder, CO, Augus 4-6, Pge 4 of 11
5 from he hours of dy (24) o he ol number of building modes. We cn define more hn hree building modes in ech dy. Menwhile, zone ir emperures re subjec o he consrins h hey lie in he rnge of 15 C o 30 C for unoccupied period nd 20 C o 24 C for occupied period. Implemenion of Reinforcemen Lerning Conrol Now we re ble o formule he problem in he frmework of reinforcemen lerning. Ech building mode is considered sge in he sequenil decision mking problem; he cion vrible is he sepoin of globl zone ir emperure, which will be discreized beween he emperure consrins corresponding o he building mode. We define he problem s n infinie horizon conrol problem. Since our gol is o minimize he ccumuled opering cos in he long-erm, he insn rewrd is defined s he cos of opering during he building mode muliplied by negive one. There re mny wys o selec he se vribles, which should compleely describe ll of he relevn informion of he conrol problem nd is environmen. As n iniil sep of he reserch, we simply define ech building mode s he only se vrible. A Simulink block for he Q-Lerning conroller is implemened ino he simulion environmen nd he clling sequence of he Q-Lerning conroller is presened in Figure 8. The Q-vlue of ech cion-se pir is sored in Q-ble. A he beginning of ech building mode, emperure sepoin mong he vilble opions for he curren se will be seleced ccording o eiher he sofmx or ε-greedy explorion mehod; he sepoin will hen be pplied by he simulion model nd simuled, nd he end of his building mode (beginning of nex mode), cos will be genered, which will be fed bck long wih he informion on he new se ino he lerning conroller. This informion will be used o upde he Q-ble. In our simulion sudy, we ssume h he cpciy of he HVAC sysem is lwys ble o rech he conrol sepoin, bu his my no be rue in n cul pplicion. In he cse where he HVAC sysem does no hve enough cpciy, he seleced cion cnno led o he expeced se rnsiion. However, even in his cse, s long s he se is fully observble nd he cul se cn be scerined, he Q-ble is sill going o be upded properly, nd hen he opiml policy will be idenified evenully. RESULTS Bse cse nd model-bsed opiml conrol cse In order o evlue he performnce of he reinforcemen lerning conroller, is resuls re compred o bse cse, which pplies ypicl nighime sebck conrol of zone ir emperure sepoin, nd model-bsed opiml conrol cse. The nighime sebck llows he sepoin of zone ir o flo o is upper bound (30 C for unoccupied period, 24 C for occupied period). The model-bsed opiml conrol is chieved by pplying direc serch lgorihm (Nelder-Med lgorihm) o find he opiml sepoin profile. The ol opering cos for he simulion period (one dy in his sudy) is seleced s he objecive funcion; opimizion vribles re he sepoins of ech building mode subjec o consrins. Figure 3 presens simple digrm of he model-bsed opiml conrol pproch. Direc serch lorihm Zone ir sepoins for ech building mode Building simulion Model Tol Cos Figure 3: Schemic of model-bsed opiml conrol Since here is no deviion in his sudy beween building model nd cul building s well s beween modeled weher nd cul weher, he model-bsed opiml conrol consiues ruly opiml scenrio. Five cses of model-bsed opimizions hve been crried ou wih he number of building modes vrying from 3 o 24. The rrngemen of building modes nd he opiml sepoin is presened in Tble 5. Two uiliy re srucures hve been esed; he firs one hs n onpek uiliy re of $0.25/kWh nd n off-pek uiliy re s $0.05/kWh; he second re srucure hs he sme off-pek re s he firs one, bu he on-pek re is incresed o $0.50/kWh, which is supposed o exggere he incenive for lod shifing. The resul of model-bsed opiml conrol nd bse cse under wo uiliy re schemes re summrized in Tble 5. Alhough he opiml sepoin vlues re differen given differen building mode nd uiliy re, he generl pern of precooling cn be found mong ll he simulion cses. The cos of one dy s simulions of opiml conrol cses nd bse cse re summrized in Tble 1. Tble 1: Cos of bse cse nd opiml conrol cses Cos [$] Sving [%] Uiliy rio Bse cse 3 BM 6 BM 9 BM 12 BM 24 BM $0.25/$0.05 $64 $55 $56 $56 $55 $57 $0.50/$0.05 $127 $100 $99 $101 $99 $102 $0.25/$ % 13% 13% 14% 11% $0.50/$ % 22% 21% 22% 20% SimBuild 2004, IBPSA-USA Nionl Conference Boulder, CO, Augus 4-6, Pge 5 of 11
6 Resuls of reinforcemen lerning conrol Differen reinforcemen lerning conrol scenrios hve been invesiged by vrying he cion spce discreizion nd he number of building modes, which represens he dimension of se spce. The size of he Q-ble is defined by he dimension of cion spce muliplied by he dimension of he se spce. Two schemes of cion spce were invesiged in he preliminry sudy (Tble 2). Acion spce Tble 2: Acion spce Off-pek building modes I [18,21,24] On-pek building modes II [16,19,22,25,28] [20,21,22,23,24] Acion spce I hs hree vlues ([18,21,24]), nd i is sme for on-pek nd off-pek periods. The cion spce II hs five cion vlues, bu i is differen o onpek period nd off-pek period. For on-pek periods, i is [20,21,22,23,24], nd [16,19,22,25,28] for off-pek period. This is becuse he upper nd lower bound of zone ir emperure is differen for on nd off-pek periods. In ll of he simulion cses, he Q-ble is iniilized wih zeros for ll enries, nd he weher d for July dy is repeed during he simulion o simplify he rining procedure. The mximum number of rining dys is 6,000. The opiml resuls for he simuled cses re summrized in Tble 3 nd Tble 4. Tble 3: Lerning conrol resuls for uiliy cos rio of 5/1 Uiliy rio: $0.25/$0.05 Acion 3 building mode 6 building mode 9 building mode spce =0.5 =0.3 =0.5 =0.3 =0.5 = /24 I 24 18/ / / /28 22/ / II / / /25/28 22 Tble 4: Lerning conrol resuls for uiliy cos rio of 10/1 Uiliy rio: $0.50/$0.05 Acion 3 building mode 6 building mode 9 building mode spce =0.5 =0.3 =0.5 =0.3 =0.5 = I / / /25 22/ / II / / 28 19/ / / /22 From hese bles i cn be deduced, he performnce of he Q-conroller is ffeced by mny fcors including dimensions of he cion spce nd se spce, on/off pek uiliy rio nd lerning re ec. Generlly speking, he cses wih higher on/off pek uiliy rio genere beer resuls. The bes resul is obined for he cse of hree building modes under uiliy re rio of 10/1. The lerning conroller found he opiml policy wihin 2,000 rining dys, nd is resul is very close o he one found by model-bsed opiml conrol s shown in Figure 4. Sepoin [C] RL-Opiml (lph = 0.5) RL-Opiml (lph = 0.3) Model-Bsed Opiml Time [hr] Figure 4: Comprison of lerning conrol wih model-bsed opiml conrol (BM = 3, uiliy rio = 10/1) Among he cses wih lower uiliy rio, he one wih 6 building modes, cion spce-i nd lerning re α = 0.5 found he bes opiml resul (Figure 5). This gives he SimBuild 2004, IBPSA-USA Nionl Conference Boulder, CO, Augus 4-6, Pge 6 of 11
7 implicion h less dimension of se spce does no necessrily led o he fser nd beer lerning. However, i is imporn o idenify he proper se spce, by which he problem cn be well represened nd he opiml conrol policy hen will be found. Sepoin [C] Time [hr] RL-Opiml Model-Bsed Opiml Figure 5: Comprison of lerning conrol wih model-bsed opiml conrol (BM = 3, uiliy rio = 10/1, α = 0.5 ) In Tble 3 nd Tble 4, i is noiceble h some opiml vlues of cerin cses hve wo or more vlues; his indices h he Q-vlues of wo or more cionse pirs re ied or very close o ech oher fer he simulion ended (6,000 dys of rining). In he exmple presened in Figure 6, se 1 (building mode 1), wo cions hve he sme Q-vlue, which re higher hn ny oher vlues. This implies h Q-conroller currenly considers h king eiher of hese wo cions would produce he sme reurn. This occurs more frequenly when higher dimensions of boh se nd cion spces re pplied. Simply sying, wih he increse of he dimension of he Q-ble, more rining is needed o le he conroller find he opiml policy. Se-Acion [1,1] Q_vlue = Se-Acion [1,5] Q_vlue = Figure 6: Lerning conrol resuls wih ied Q-vlue The phenomenon bove brings he imporn issue of he lerning conroller o enion, which cn be clled speed of lerning. As menioned before, he mximum rining dys is se 6,000 in his preliminry sudy becuse of limied compuion resources. However, i is found h in some cses he lerning conroller cnno find he opiml policy in he given rining period, such s he exmple given bove, which leds o he ied of vlues of cerin cion-se pirs in he Q- ble. Even for he cses h finlly found he opiml resul, he compuion ime is lso relively longer hn he predicive opiml conrol cses. This resul is o be expeced becuse he lerning conroller does no hve n explici building model vilble bu cn only improve incremenlly from one decision o he nex. CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK This simulion sudy shows h reinforcemen lerning conrol is fesible mehodology o find ner-opiml sepoin profile for exploiing he pssive building herml sorge cpciy. The freedom from building model mkes i especilly rcive in rel-ime conrol problems, nd heoreiclly i cn rech he rue opimum evenully, no mer wh building i is deling wih, if only he environmen could be smpled infiniely ofen. On he oher hnd, nlysis shows h he opiml policy of lerning conroller is ffeced by he dimension of he cion nd se spce, he uiliy re differenils beween on- nd off-pek, lerning re nd severl oher fcors. Lerning speed is relively low when deling wih problems wih lrge se spce nd cion spce. Fuure work is needed o ddress hese problems o exploi he power of reinforcemen lerning conrol. I ws found priculrly imporn o selec he proper cion spce nd se spce for he lerning conroller. In his sudy, he se vrible is simply defined s he building mode. I is desirble o define se vribles, which describe he herml hisory of he building nd mbien condiions. However, i is imporn o relize h here is downside ssocied wih expnding he se spce. Adding new se vribles, such s mbien condiion, cn mke he se spce represenion more pproprie, i.e., i cn represen he environmen closer. On he oher hnd, ny se vrible h is dded bu h plys no role will prolong he lerning process since explorive cions wihin irrelevn ses do no conribue o lerning he cos funcion. The resoluion of he discreizion of he coninuous cion spce lso needs o be nlyzed furher. Insed of rbirrily choosing 3 or 5 discree cion vlue, n opiml size of he cion spce needs o be idenified. One my rgue h he on/off pek uiliy rio used in his sudy is no very relisic (5/1 or 10/1). I ws emped o exggere he lod-shifing incenive from SimBuild 2004, IBPSA-USA Nionl Conference Boulder, CO, Augus 4-6, Pge 7 of 11
8 he uiliy re srucure in his simulion nlysis. However, he rel cos for ech building mode my no necessrily be he insn rewrd for he lerning conroller. Pos-processing of he rel cos my be useful o mke he lerning conroller lern fser. I is poin of fuure reserch o idenify modified rewrd signl insed of using he rel cos. One disdvnge of he reinforcemen lerning conroller is he speed of lerning. Compred wih model-bsed opiml conrol, lerning conrol needs much more rining d o find he opimum, which my no be prcicl in he perspecive of compuionl resources when lrge se nd cion spces re involved. One lernive wy o overcome his problem is o implemen se of neurl neworks o replce he funcions of he Q-ble. I is lso expeced o ccelere he lerning process of he conroller. NOMENCLUTURE s R P r ss ' ss ' (s,) V ( s) Q ( s, ) discree ime sep or sge se cion cumulive discouned rewrd (or reurn) following probbiliy of rnsiion from se s o se s under cion expeced insn rewrd on rnsiion from se s o se s under cion probbiliy of king cion in se s under he policy vlue of se s under policy vlue of king cion in se s under policy V *( s ) vlue of se s under opiml policy α REFERENCES lening re discoun fcor [1] Andresen, I. nd Brndemuehl, M. J. (1992) He sorge in building herml mss: prmeric sudy. ASHRAE Trnscions 98 (1). [2] Bellmn, R.E. (1957). Dynmic Progrmming. Princeon Universiy Press, Princeon. [3] Brun, J. E. (1990) Reducing energy coss nd pek elecricl demnd hrough opiml conrol of building herml mss. ASHRAE Trnscions 96 (2): [4] Brun, J. E., Mongomery, K.W. nd Churvedi, N. (2001) Evluing he performnce of building herml mss conrol sregies, In. J. of HVAC&R Reserch, 7 (4): [5] Brun, J. E. (2003) Lod Conrol Using Building Therml Mss, Journl of Solr Energy Engineering, Vol. 125, No. 3, pp , Americn Sociey of Mechnicl Engineers, New York, New York. [6] Conniff, J. P. (1991) Sregies for reducing pek ir-condiioning lods by using he sorge in he building srucure. ASHRAE Trnscions 97 (1): [7] Goud M.M.; Underwood C.P.; Dnher S. (2003) "Modelling he robusness properies of HVAC pln under feedbck conrol." Building Services Engineering Reserch nd Technology, 1 December 2003, Vol. 24, No. 4, pp [8] Henze, G. P., Dodier, R. H. nd Krri, M. (1997) Developmen of Predicive Opiml Conroller for Therml Energy Sorge Sysems. Inernionl Journl of HVAC&R Reserch, Vol. 3, No. 3, pp [9] Henze, G.P. nd Schoenmnn, J. (2003) Evluion of Reinforcemen Lerning Conrol for Therml Energy Sorge Sysems. Inernionl Journl of HVAC&R Reserch, Americn Sociey of Heing, Refrigering, nd Air-Condiioning Engineers, Aln, Georgi. [10] Henze, G.P., Felsmnn, C. nd Knbe, G. (2004) Evluion of Opiml Conrol for Acive nd Pssive Building Therml Sorge. Inernionl Journl of Therml Sciences, Februry [11] Kelbling, L.P., Limn, M.L., nd Moore, A.W. (1996) "Reinforcemen Lerning: A Survey", Journl of Arificil Inelligence Reserch, 4: [12] Keeney, K.R. nd Brun, J.E. (1996) A simplified mehod for deermining opiml cooling conrols sregies for herml sorge in building mss. In. J. of HVAC&R Reserch, 2 (1): [13] Keeney, K. R. nd Brun, J. E. (1997) Applicion of building precooling o reduce pek cooling requiremens. ASHRAE Trnscions 103 (1): [14] Krechmr, R.M., Young, P.M., Anderson, C.W., Hile, D.C., Anderson, M. L., Delnero, C. C. (2001) Robus Reinforcemen Lerning Conrol wih Sic nd Dynmic Sbiliy. Inernionl Journl of Robus nd Nonliner Conrol. no. 11, pp [15] Liu, S. nd Henze, G.P. (2004) Impc of Modeling Accurcy on Predicive Opiml Conrol of Acive nd Pssive Building Therml Sorge Invenory." ASHRAE Trnscions, Technicl Pper No Vol. 110, Pr 1. [16] Morris, F.B., Brun, J. E. nd Tredo, S. J. (1994) Experimenl nd simuled performnce of opi- SimBuild 2004, IBPSA-USA Nionl Conference Boulder, CO, Augus 4-6, Pge 8 of 11
9 ml conrol of building herml sorge. ASHRAE Trnscions 100 (1): [17] Rbl, A. nd Norford, L.K. (1991) Pek lod reducion by precondiioning buildings nigh, Inernionl Journl of Energy Reserch 15: [18] Suon, R.S. (1988). Lerning o predic by he mehods of emporl differences. Mchine Lerning 3: [19] Suon, R.S. nd Bro, A.G. (1998) Reinforcemen lerning: An inroducion. MIT Press, Cmbridge, MA. [20] Wkins, C. nd Dyn, P. (1992) Q-lerning, Mchine lerning, SimBuild 2004, IBPSA-USA Nionl Conference Boulder, CO, Augus 4-6, Pge 9 of 11
10 Overll Building Model Building Envelope Model HVAC Sysem Model Therml & Humidiy Blnce Funcion Figure 7: Schemic of he simulion environmen Dy N-1 Dy N Dy N+1 Building Mode 1 Building Mode 2 Building Mode M Simulion Time Zone ir sepoin Cos Selec n cion Red Q vlue Q ble Wrie Q vlue Upde he Q vlue Q Lerning Conroller Figure 8: Schemic of clling sequence of he lerning conroller SimBuild 2004, IBPSA-USA Nionl Conference Boulder, CO, Augus 4-6, Pge 10 of 11
11 Tble 5: Summry of resuls for model-bsed opiml conrol 3 building mode 6 building mode 9 building mode 12 building mode 24 building mode Time BM T_sp1 T_sp2 BM T_sp1 T_sp2 BM T_sp1 T_sp2 BM T_sp1 T_sp2 BM T_sp1 T_sp2 0: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : T_sp1 denoe he opiml sepoin under On/Off pek uiliy rio $0.25/$0.05 T_sp2 denoe he opiml sepoin under On/Off pek uiliy rio $0.5/$0.05 SimBuild 2004, IBPSA-USA Nionl Conference Boulder, CO, Augus 4-6, Pge 11 of 11
Chapter 2: Evaluative Feedback
 Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
e t dt e t dt = lim e t dt T (1 e T ) = 1
 Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
Contraction Mapping Principle Approach to Differential Equations
 epl Journl of Science echnology 0 (009) 49-53 Conrcion pping Principle pproch o Differenil Equions Bishnu P. Dhungn Deprmen of hemics, hendr Rn Cmpus ribhuvn Universiy, Khmu epl bsrc Using n eension of
epl Journl of Science echnology 0 (009) 49-53 Conrcion pping Principle pproch o Differenil Equions Bishnu P. Dhungn Deprmen of hemics, hendr Rn Cmpus ribhuvn Universiy, Khmu epl bsrc Using n eension of
S Radio transmission and network access Exercise 1-2
 S-7.330 Rdio rnsmission nd nework ccess Exercise 1 - P1 In four-symbol digil sysem wih eqully probble symbols he pulses in he figure re used in rnsmission over AWGN-chnnel. s () s () s () s () 1 3 4 )
S-7.330 Rdio rnsmission nd nework ccess Exercise 1 - P1 In four-symbol digil sysem wih eqully probble symbols he pulses in he figure re used in rnsmission over AWGN-chnnel. s () s () s () s () 1 3 4 )
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
The solution is often represented as a vector: 2xI + 4X2 + 2X3 + 4X4 + 2X5 = 4 2xI + 4X2 + 3X3 + 3X4 + 3X5 = 4. 3xI + 6X2 + 6X3 + 3X4 + 6X5 = 6.
 [~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
[~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
A new model for limit order book dynamics
 Anewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics JeffreyR.Russell UniversiyofChicgo,GrdueSchoolofBusiness TejinKim UniversiyofChicgo,DeprmenofSisics Absrc:Thispperproposesnewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics.Thelimiorderbookconsiss
Anewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics JeffreyR.Russell UniversiyofChicgo,GrdueSchoolofBusiness TejinKim UniversiyofChicgo,DeprmenofSisics Absrc:Thispperproposesnewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics.Thelimiorderbookconsiss
A Kalman filtering simulation
 A Klmn filering simulion The performnce of Klmn filering hs been esed on he bsis of wo differen dynmicl models, ssuming eiher moion wih consn elociy or wih consn ccelerion. The former is epeced o beer
A Klmn filering simulion The performnce of Klmn filering hs been esed on he bsis of wo differen dynmicl models, ssuming eiher moion wih consn elociy or wih consn ccelerion. The former is epeced o beer
Neural assembly binding in linguistic representation
 Neurl ssembly binding in linguisic represenion Frnk vn der Velde & Mrc de Kmps Cogniive Psychology Uni, Universiy of Leiden, Wssenrseweg 52, 2333 AK Leiden, The Neherlnds, vdvelde@fsw.leidenuniv.nl Absrc.
Neurl ssembly binding in linguisic represenion Frnk vn der Velde & Mrc de Kmps Cogniive Psychology Uni, Universiy of Leiden, Wssenrseweg 52, 2333 AK Leiden, The Neherlnds, vdvelde@fsw.leidenuniv.nl Absrc.
Motion. Part 2: Constant Acceleration. Acceleration. October Lab Physics. Ms. Levine 1. Acceleration. Acceleration. Units for Acceleration.
 Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
f t f a f x dx By Lin McMullin f x dx= f b f a. 2
 Accumulion: Thoughs On () By Lin McMullin f f f d = + The gols of he AP* Clculus progrm include he semen, Sudens should undersnd he definie inegrl s he ne ccumulion of chnge. 1 The Topicl Ouline includes
Accumulion: Thoughs On () By Lin McMullin f f f d = + The gols of he AP* Clculus progrm include he semen, Sudens should undersnd he definie inegrl s he ne ccumulion of chnge. 1 The Topicl Ouline includes
4.8 Improper Integrals
 4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
Reinforcement Learning. Markov Decision Processes
 einforcemen Lerning Mrkov Decision rocesses Mnfred Huber 2014 1 equenil Decision Mking N-rmed bi problems re no good wy o model sequenil decision problem Only dels wih sic decision sequences Could be miiged
einforcemen Lerning Mrkov Decision rocesses Mnfred Huber 2014 1 equenil Decision Mking N-rmed bi problems re no good wy o model sequenil decision problem Only dels wih sic decision sequences Could be miiged
September 20 Homework Solutions
 College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
Making Complex Decisions Markov Decision Processes. Making Complex Decisions: Markov Decision Problem
 Mking Comple Decisions Mrkov Decision Processes Vsn Honvr Bioinformics nd Compuionl Biology Progrm Cener for Compuionl Inelligence, Lerning, & Discovery honvr@cs.ise.edu www.cs.ise.edu/~honvr/ www.cild.ise.edu/
Mking Comple Decisions Mrkov Decision Processes Vsn Honvr Bioinformics nd Compuionl Biology Progrm Cener for Compuionl Inelligence, Lerning, & Discovery honvr@cs.ise.edu www.cs.ise.edu/~honvr/ www.cild.ise.edu/
0 for t < 0 1 for t > 0
 8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
Temperature Rise of the Earth
 Avilble online www.sciencedirec.com ScienceDirec Procedi - Socil nd Behviorl Scien ce s 88 ( 2013 ) 220 224 Socil nd Behviorl Sciences Symposium, 4 h Inernionl Science, Socil Science, Engineering nd Energy
Avilble online www.sciencedirec.com ScienceDirec Procedi - Socil nd Behviorl Scien ce s 88 ( 2013 ) 220 224 Socil nd Behviorl Sciences Symposium, 4 h Inernionl Science, Socil Science, Engineering nd Energy
Tax Audit and Vertical Externalities
 T Audi nd Vericl Eernliies Hidey Ko Misuyoshi Yngihr Ngoy Keizi Universiy Ngoy Universiy 1. Inroducion The vericl fiscl eernliies rise when he differen levels of governmens, such s he federl nd se governmens,
T Audi nd Vericl Eernliies Hidey Ko Misuyoshi Yngihr Ngoy Keizi Universiy Ngoy Universiy 1. Inroducion The vericl fiscl eernliies rise when he differen levels of governmens, such s he federl nd se governmens,
A Time Truncated Improved Group Sampling Plans for Rayleigh and Log - Logistic Distributions
 ISSNOnline : 39-8753 ISSN Prin : 347-67 An ISO 397: 7 Cerified Orgnizion Vol. 5, Issue 5, My 6 A Time Trunced Improved Group Smpling Plns for Ryleigh nd og - ogisic Disribuions P.Kvipriy, A.R. Sudmni Rmswmy
ISSNOnline : 39-8753 ISSN Prin : 347-67 An ISO 397: 7 Cerified Orgnizion Vol. 5, Issue 5, My 6 A Time Trunced Improved Group Smpling Plns for Ryleigh nd og - ogisic Disribuions P.Kvipriy, A.R. Sudmni Rmswmy
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mathematics The Integral of a Function as a Function
 ENGR 1990 Engineering Mhemics The Inegrl of Funcion s Funcion Previously, we lerned how o esime he inegrl of funcion f( ) over some inervl y dding he res of finie se of rpezoids h represen he re under
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mhemics The Inegrl of Funcion s Funcion Previously, we lerned how o esime he inegrl of funcion f( ) over some inervl y dding he res of finie se of rpezoids h represen he re under
Reinforcement Learning
 Reiforceme Corol lerig Corol polices h choose opiml cios Q lerig Covergece Chper 13 Reiforceme 1 Corol Cosider lerig o choose cios, e.g., Robo lerig o dock o bery chrger o choose cios o opimize fcory oupu
Reiforceme Corol lerig Corol polices h choose opiml cios Q lerig Covergece Chper 13 Reiforceme 1 Corol Cosider lerig o choose cios, e.g., Robo lerig o dock o bery chrger o choose cios o opimize fcory oupu
3. Renewal Limit Theorems
 Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
1.0 Electrical Systems
 . Elecricl Sysems The ypes of dynmicl sysems we will e sudying cn e modeled in erms of lgeric equions, differenil equions, or inegrl equions. We will egin y looking fmilir mhemicl models of idel resisors,
. Elecricl Sysems The ypes of dynmicl sysems we will e sudying cn e modeled in erms of lgeric equions, differenil equions, or inegrl equions. We will egin y looking fmilir mhemicl models of idel resisors,
Probability, Estimators, and Stationarity
 Chper Probbiliy, Esimors, nd Sionriy Consider signl genered by dynmicl process, R, R. Considering s funcion of ime, we re opering in he ime domin. A fundmenl wy o chrcerize he dynmics using he ime domin
Chper Probbiliy, Esimors, nd Sionriy Consider signl genered by dynmicl process, R, R. Considering s funcion of ime, we re opering in he ime domin. A fundmenl wy o chrcerize he dynmics using he ime domin
Evaporation losses as a major factor in determining allowable yield from water supply reservoirs: the case of Botswana s major reservoirs
 River Bsin Mngemen III 631 Evporion losses s mjor fcor in deermining llowble yield from wer supply reservoirs: he cse of Boswn s mjor reservoirs P. K. Kenbho & B. P. Prid Deprmen of Environmenl Science,
River Bsin Mngemen III 631 Evporion losses s mjor fcor in deermining llowble yield from wer supply reservoirs: he cse of Boswn s mjor reservoirs P. K. Kenbho & B. P. Prid Deprmen of Environmenl Science,
MATH 124 AND 125 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 2008)
 MATH 14 AND 15 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 8) The following quesions cn be used s review for Mh 14/ 15 These quesions re no cul smples of quesions h will pper on he finl em, bu hey will provide
MATH 14 AND 15 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 8) The following quesions cn be used s review for Mh 14/ 15 These quesions re no cul smples of quesions h will pper on he finl em, bu hey will provide
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 9: The High Beta Tokamak
 .65, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 9: The High e Tokmk Summry of he Properies of n Ohmic Tokmk. Advnges:. good euilibrium (smll shif) b. good sbiliy ( ) c. good confinemen ( τ nr )
.65, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 9: The High e Tokmk Summry of he Properies of n Ohmic Tokmk. Advnges:. good euilibrium (smll shif) b. good sbiliy ( ) c. good confinemen ( τ nr )
On Source and Channel Codes for Multiple Inputs and Outputs: Does Multiple Description Meet Space Time? 1
 On Source nd Chnnel Codes for Muliple Inpus nd Oupus: oes Muliple escripion Mee Spce Time? Michelle Effros Rlf Koeer 3 Andre J. Goldsmih 4 Muriel Médrd 5 ep. of Elecricl Eng., 36-93, Cliforni Insiue of
On Source nd Chnnel Codes for Muliple Inpus nd Oupus: oes Muliple escripion Mee Spce Time? Michelle Effros Rlf Koeer 3 Andre J. Goldsmih 4 Muriel Médrd 5 ep. of Elecricl Eng., 36-93, Cliforni Insiue of
Factorized Decision Forecasting via Combining Value-based and Reward-based Estimation
 Fcorized Decision Forecsing vi Combining Vlue-bsed nd Rewrd-bsed Esimion Brin D. Ziebr Crnegie Mellon Universiy Pisburgh, PA 15213 bziebr@cs.cmu.edu Absrc A powerful recen perspecive for predicing sequenil
Fcorized Decision Forecsing vi Combining Vlue-bsed nd Rewrd-bsed Esimion Brin D. Ziebr Crnegie Mellon Universiy Pisburgh, PA 15213 bziebr@cs.cmu.edu Absrc A powerful recen perspecive for predicing sequenil
REAL ANALYSIS I HOMEWORK 3. Chapter 1
 REAL ANALYSIS I HOMEWORK 3 CİHAN BAHRAN The quesions re from Sein nd Shkrchi s e. Chper 1 18. Prove he following sserion: Every mesurble funcion is he limi.e. of sequence of coninuous funcions. We firs
REAL ANALYSIS I HOMEWORK 3 CİHAN BAHRAN The quesions re from Sein nd Shkrchi s e. Chper 1 18. Prove he following sserion: Every mesurble funcion is he limi.e. of sequence of coninuous funcions. We firs
PHYSICS 1210 Exam 1 University of Wyoming 14 February points
 PHYSICS 1210 Em 1 Uniersiy of Wyoming 14 Februry 2013 150 poins This es is open-noe nd closed-book. Clculors re permied bu compuers re no. No collborion, consulion, or communicion wih oher people (oher
PHYSICS 1210 Em 1 Uniersiy of Wyoming 14 Februry 2013 150 poins This es is open-noe nd closed-book. Clculors re permied bu compuers re no. No collborion, consulion, or communicion wih oher people (oher
EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEM
 Elecronic Journl of Differenil Equions, Vol. 208 (208), No. 50, pp. 6. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mh.xse.edu or hp://ejde.mh.un.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE
Elecronic Journl of Differenil Equions, Vol. 208 (208), No. 50, pp. 6. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mh.xse.edu or hp://ejde.mh.un.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE
Compulsory Flow Q-Learning: an RL algorithm for robot navigation based on partial-policy and macro-states
 Journl of he Brzilin Compuer Sociey, 2009; 5(3):65-75. ISSN 004-6500 Compulsory Flow Q-Lerning: n RL lgorihm for robo nvigion bsed on pril-policy nd mcro-ses Vldinei Freire d Silv*, Ann Helen Reli Cos
Journl of he Brzilin Compuer Sociey, 2009; 5(3):65-75. ISSN 004-6500 Compulsory Flow Q-Lerning: n RL lgorihm for robo nvigion bsed on pril-policy nd mcro-ses Vldinei Freire d Silv*, Ann Helen Reli Cos
Optimality of Myopic Policy for a Class of Monotone Affine Restless Multi-Armed Bandit
 Univeriy of Souhern Cliforni Opimliy of Myopic Policy for Cl of Monoone Affine Rele Muli-Armed Bndi Pri Mnourifrd USC Tr Jvidi UCSD Bhkr Krihnmchri USC Dec 0, 202 Univeriy of Souhern Cliforni Inroducion
Univeriy of Souhern Cliforni Opimliy of Myopic Policy for Cl of Monoone Affine Rele Muli-Armed Bndi Pri Mnourifrd USC Tr Jvidi UCSD Bhkr Krihnmchri USC Dec 0, 202 Univeriy of Souhern Cliforni Inroducion
1 jordan.mcd Eigenvalue-eigenvector approach to solving first order ODEs. -- Jordan normal (canonical) form. Instructor: Nam Sun Wang
 jordnmcd Eigenvlue-eigenvecor pproch o solving firs order ODEs -- ordn norml (cnonicl) form Insrucor: Nm Sun Wng Consider he following se of coupled firs order ODEs d d x x 5 x x d d x d d x x x 5 x x
jordnmcd Eigenvlue-eigenvecor pproch o solving firs order ODEs -- ordn norml (cnonicl) form Insrucor: Nm Sun Wng Consider he following se of coupled firs order ODEs d d x x 5 x x d d x d d x x x 5 x x
Solutions to Problems from Chapter 2
 Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
Reinforcement learning
 CS 75 Mchine Lening Lecue b einfocemen lening Milos Huskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Sque einfocemen lening We wn o len conol policy: : X A We see emples of bu oupus e no given Insed of we ge feedbck
CS 75 Mchine Lening Lecue b einfocemen lening Milos Huskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Sque einfocemen lening We wn o len conol policy: : X A We see emples of bu oupus e no given Insed of we ge feedbck
Thermal neutron self-shielding factor in foils: a universal curve
 Proceedings of he Inernionl Conference on Reserch Recor Uilizion, Sfey, Decommissioning, Fuel nd Wse Mngemen (Snigo, Chile, -4 Nov.3) Pper IAEA-CN-/, IAEA Proceedings Series, Vienn, 5 Therml neuron self-shielding
Proceedings of he Inernionl Conference on Reserch Recor Uilizion, Sfey, Decommissioning, Fuel nd Wse Mngemen (Snigo, Chile, -4 Nov.3) Pper IAEA-CN-/, IAEA Proceedings Series, Vienn, 5 Therml neuron self-shielding
Chapter Direct Method of Interpolation
 Chper 5. Direc Mehod of Inerpolion Afer reding his chper, you should be ble o:. pply he direc mehod of inerpolion,. sole problems using he direc mehod of inerpolion, nd. use he direc mehod inerpolns o
Chper 5. Direc Mehod of Inerpolion Afer reding his chper, you should be ble o:. pply he direc mehod of inerpolion,. sole problems using he direc mehod of inerpolion, nd. use he direc mehod inerpolns o
An integral having either an infinite limit of integration or an unbounded integrand is called improper. Here are two examples.
 Improper Inegrls To his poin we hve only considered inegrls f(x) wih he is of inegrion nd b finie nd he inegrnd f(x) bounded (nd in fc coninuous excep possibly for finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegrl
Improper Inegrls To his poin we hve only considered inegrls f(x) wih he is of inegrion nd b finie nd he inegrnd f(x) bounded (nd in fc coninuous excep possibly for finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegrl
Removing Redundancy and Inconsistency in Memory- Based Collaborative Filtering
 Removing Redundncy nd Inconsisency in Memory- Bsed Collborive Filering Ki Yu Siemens AG, Corpore Technology & Universiy of Munich, Germny ki.yu.exernl@mchp.siemens. de Xiowei Xu Informion Science Deprmen
Removing Redundncy nd Inconsisency in Memory- Bsed Collborive Filering Ki Yu Siemens AG, Corpore Technology & Universiy of Munich, Germny ki.yu.exernl@mchp.siemens. de Xiowei Xu Informion Science Deprmen
Procedia Computer Science
 Procedi Compuer Science 00 (0) 000 000 Procedi Compuer Science www.elsevier.com/loce/procedi The Third Informion Sysems Inernionl Conference The Exisence of Polynomil Soluion of he Nonliner Dynmicl Sysems
Procedi Compuer Science 00 (0) 000 000 Procedi Compuer Science www.elsevier.com/loce/procedi The Third Informion Sysems Inernionl Conference The Exisence of Polynomil Soluion of he Nonliner Dynmicl Sysems
GENERALIZATION OF SOME INEQUALITIES VIA RIEMANN-LIOUVILLE FRACTIONAL CALCULUS
 - TAMKANG JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 5, Number, 7-5, June doi:5556/jkjm555 Avilble online hp://journlsmhkueduw/ - - - GENERALIZATION OF SOME INEQUALITIES VIA RIEMANN-LIOUVILLE FRACTIONAL CALCULUS MARCELA
- TAMKANG JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 5, Number, 7-5, June doi:5556/jkjm555 Avilble online hp://journlsmhkueduw/ - - - GENERALIZATION OF SOME INEQUALITIES VIA RIEMANN-LIOUVILLE FRACTIONAL CALCULUS MARCELA
SOME USEFUL MATHEMATICS
 SOME USEFU MAHEMAICS SOME USEFU MAHEMAICS I is esy o mesure n preic he behvior of n elecricl circui h conins only c volges n currens. However, mos useful elecricl signls h crry informion vry wih ime. Since
SOME USEFU MAHEMAICS SOME USEFU MAHEMAICS I is esy o mesure n preic he behvior of n elecricl circui h conins only c volges n currens. However, mos useful elecricl signls h crry informion vry wih ime. Since
Estimating the population parameter, r, q and K based on surplus production model. Wang, Chien-Hsiung
 SCTB15 Working Pper ALB 7 Esiming he populion prmeer, r, q nd K bsed on surplus producion model Wng, Chien-Hsiung Biologicl nd Fishery Division Insiue of Ocenogrphy Nionl Tiwn Universiy Tipei, Tiwn Tile:
SCTB15 Working Pper ALB 7 Esiming he populion prmeer, r, q nd K bsed on surplus producion model Wng, Chien-Hsiung Biologicl nd Fishery Division Insiue of Ocenogrphy Nionl Tiwn Universiy Tipei, Tiwn Tile:
A 1.3 m 2.5 m 2.8 m. x = m m = 8400 m. y = 4900 m 3200 m = 1700 m
 PHYS : Soluions o Chper 3 Home Work. SSM REASONING The displcemen is ecor drwn from he iniil posiion o he finl posiion. The mgniude of he displcemen is he shores disnce beween he posiions. Noe h i is onl
PHYS : Soluions o Chper 3 Home Work. SSM REASONING The displcemen is ecor drwn from he iniil posiion o he finl posiion. The mgniude of he displcemen is he shores disnce beween he posiions. Noe h i is onl
15/03/1439. Lecture 4: Linear Time Invariant (LTI) systems
 Lecre 4: Liner Time Invrin LTI sysems 2. Liner sysems, Convolion 3 lecres: Implse response, inp signls s coninm of implses. Convolion, discree-ime nd coninos-ime. LTI sysems nd convolion Specific objecives
Lecre 4: Liner Time Invrin LTI sysems 2. Liner sysems, Convolion 3 lecres: Implse response, inp signls s coninm of implses. Convolion, discree-ime nd coninos-ime. LTI sysems nd convolion Specific objecives
A new model for solving fuzzy linear fractional programming problem with ranking function
 J. ppl. Res. Ind. Eng. Vol. 4 No. 07 89 96 Journl of pplied Reserch on Indusril Engineering www.journl-prie.com new model for solving fuzzy liner frcionl progrmming prolem wih rning funcion Spn Kumr Ds
J. ppl. Res. Ind. Eng. Vol. 4 No. 07 89 96 Journl of pplied Reserch on Indusril Engineering www.journl-prie.com new model for solving fuzzy liner frcionl progrmming prolem wih rning funcion Spn Kumr Ds
Convergence of Singular Integral Operators in Weighted Lebesgue Spaces
 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS Vol. 10, No. 2, 2017, 335-347 ISSN 1307-5543 www.ejpm.com Published by New York Business Globl Convergence of Singulr Inegrl Operors in Weighed Lebesgue
EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS Vol. 10, No. 2, 2017, 335-347 ISSN 1307-5543 www.ejpm.com Published by New York Business Globl Convergence of Singulr Inegrl Operors in Weighed Lebesgue
Solutions for Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations By Tan-Cot Method
 IOSR Journl of Mhemics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578. Volume 5, Issue 3 (Jn. - Feb. 13), PP 6-11 Soluions for Nonliner Pril Differenil Equions By Tn-Co Mehod Mhmood Jwd Abdul Rsool Abu Al-Sheer Al -Rfidin Universiy
IOSR Journl of Mhemics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578. Volume 5, Issue 3 (Jn. - Feb. 13), PP 6-11 Soluions for Nonliner Pril Differenil Equions By Tn-Co Mehod Mhmood Jwd Abdul Rsool Abu Al-Sheer Al -Rfidin Universiy
LAPLACE TRANSFORM OVERCOMING PRINCIPLE DRAWBACKS IN APPLICATION OF THE VARIATIONAL ITERATION METHOD TO FRACTIONAL HEAT EQUATIONS
 Wu, G.-.: Lplce Trnsform Overcoming Principle Drwbcks in Applicion... THERMAL SIENE: Yer 22, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 257-26 257 Open forum LAPLAE TRANSFORM OVEROMING PRINIPLE DRAWBAKS IN APPLIATION OF THE VARIATIONAL
Wu, G.-.: Lplce Trnsform Overcoming Principle Drwbcks in Applicion... THERMAL SIENE: Yer 22, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 257-26 257 Open forum LAPLAE TRANSFORM OVEROMING PRINIPLE DRAWBAKS IN APPLIATION OF THE VARIATIONAL
Magnetostatics Bar Magnet. Magnetostatics Oersted s Experiment
 Mgneosics Br Mgne As fr bck s 4500 yers go, he Chinese discovered h cerin ypes of iron ore could rc ech oher nd cerin mels. Iron filings "mp" of br mgne s field Crefully suspended slivers of his mel were
Mgneosics Br Mgne As fr bck s 4500 yers go, he Chinese discovered h cerin ypes of iron ore could rc ech oher nd cerin mels. Iron filings "mp" of br mgne s field Crefully suspended slivers of his mel were
An Efficient Digital Circuit for Implementing Sequence Alignment Algorithm
 An Efficien Digil Circui for Implemening Sequence Alignmen Algorihm Vmsi Kundei Yunsi Fei (vmsik@engr.uconn.edu) (yfei@engr.uconn.edu) CSE Deprmen ECE Deprmen Universiy of Connecicu Universiy of Connecicu
An Efficien Digil Circui for Implemening Sequence Alignmen Algorihm Vmsi Kundei Yunsi Fei (vmsik@engr.uconn.edu) (yfei@engr.uconn.edu) CSE Deprmen ECE Deprmen Universiy of Connecicu Universiy of Connecicu
CONTINUOUS DYNAMIC NETWORK LOADING MODELS 1
 CONTINUOUS DYNAMIC NETWORK LOADING MODELS 1 Ricrdo Grcí*, Mª Luz López*, Alejndro Niño**, nd Doroeo Versegui* * Deprmeno de Memáics. Universidd de Csill-L Mnch ** Progrm de Invesigción en Tránsio y Trnspore.
CONTINUOUS DYNAMIC NETWORK LOADING MODELS 1 Ricrdo Grcí*, Mª Luz López*, Alejndro Niño**, nd Doroeo Versegui* * Deprmeno de Memáics. Universidd de Csill-L Mnch ** Progrm de Invesigción en Tránsio y Trnspore.
On the Pseudo-Spectral Method of Solving Linear Ordinary Differential Equations
 Journl of Mhemics nd Sisics 5 ():136-14, 9 ISS 1549-3644 9 Science Publicions On he Pseudo-Specrl Mehod of Solving Liner Ordinry Differenil Equions B.S. Ogundre Deprmen of Pure nd Applied Mhemics, Universiy
Journl of Mhemics nd Sisics 5 ():136-14, 9 ISS 1549-3644 9 Science Publicions On he Pseudo-Specrl Mehod of Solving Liner Ordinry Differenil Equions B.S. Ogundre Deprmen of Pure nd Applied Mhemics, Universiy
1. Consider a PSA initially at rest in the beginning of the left-hand end of a long ISS corridor. Assume xo = 0 on the left end of the ISS corridor.
 In Eercise 1, use sndrd recngulr Cresin coordine sysem. Le ime be represened long he horizonl is. Assume ll ccelerions nd decelerions re consn. 1. Consider PSA iniilly res in he beginning of he lef-hnd
In Eercise 1, use sndrd recngulr Cresin coordine sysem. Le ime be represened long he horizonl is. Assume ll ccelerions nd decelerions re consn. 1. Consider PSA iniilly res in he beginning of he lef-hnd
Physics 2A HW #3 Solutions
 Chper 3 Focus on Conceps: 3, 4, 6, 9 Problems: 9, 9, 3, 41, 66, 7, 75, 77 Phsics A HW #3 Soluions Focus On Conceps 3-3 (c) The ccelerion due o grvi is he sme for boh blls, despie he fc h he hve differen
Chper 3 Focus on Conceps: 3, 4, 6, 9 Problems: 9, 9, 3, 41, 66, 7, 75, 77 Phsics A HW #3 Soluions Focus On Conceps 3-3 (c) The ccelerion due o grvi is he sme for boh blls, despie he fc h he hve differen
Nonlinear System Modelling: How to Estimate the. Highest Significant Order
 IEEE Insrumenion nd Mesuremen Technology Conference nchorge,, US, - My Nonliner Sysem Modelling: ow o Esime he ighes Significn Order Neophyos Chirs, Ceri Evns nd Dvid Rees, Michel Solomou School of Elecronics,
IEEE Insrumenion nd Mesuremen Technology Conference nchorge,, US, - My Nonliner Sysem Modelling: ow o Esime he ighes Significn Order Neophyos Chirs, Ceri Evns nd Dvid Rees, Michel Solomou School of Elecronics,
TIMELINESS, ACCURACY, AND RELEVANCE IN DYNAMIC INCENTIVE CONTRACTS
 TIMELINESS, ACCURACY, AND RELEVANCE IN DYNAMIC INCENTIVE CONTRACTS by Peer O. Chrisensen Universiy of Souhern Denmrk Odense, Denmrk Gerld A. Felhm Universiy of Briish Columbi Vncouver, Cnd Chrisin Hofmnn
TIMELINESS, ACCURACY, AND RELEVANCE IN DYNAMIC INCENTIVE CONTRACTS by Peer O. Chrisensen Universiy of Souhern Denmrk Odense, Denmrk Gerld A. Felhm Universiy of Briish Columbi Vncouver, Cnd Chrisin Hofmnn
RL Lecture 7: Eligibility Traces. R. S. Sutton and A. G. Barto: Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction 1
 RL Lecure 7: Eligibiliy Traces R. S. Suon and A. G. Baro: Reinforcemen Learning: An Inroducion 1 N-sep TD Predicion Idea: Look farher ino he fuure when you do TD backup (1, 2, 3,, n seps) R. S. Suon and
RL Lecure 7: Eligibiliy Traces R. S. Suon and A. G. Baro: Reinforcemen Learning: An Inroducion 1 N-sep TD Predicion Idea: Look farher ino he fuure when you do TD backup (1, 2, 3,, n seps) R. S. Suon and
Inverse design of indoor environment using an adjoint RNG k-ε turbulence model
 Zho, X. nd Chen, Q. 019. Inverse design of indoor environmen using n djoin RNG k ε urbulence model, Acceped by Indoor Air. 1 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 1 14 15 16 17 18 19 0 1 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 4 5 6 7 8 9 40 41
Zho, X. nd Chen, Q. 019. Inverse design of indoor environmen using n djoin RNG k ε urbulence model, Acceped by Indoor Air. 1 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 1 14 15 16 17 18 19 0 1 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 4 5 6 7 8 9 40 41
1 Sterile Resources. This is the simplest case of exhaustion of a finite resource. We will use the terminology
 Cmbridge Universiy Press 978--5-8997-7 - Susinble Nurl Resource Mngemen for Scieniss nd Engineers Excerp More informion Serile Resources In his chper, we inroduce he simple concepion of scrce resource,
Cmbridge Universiy Press 978--5-8997-7 - Susinble Nurl Resource Mngemen for Scieniss nd Engineers Excerp More informion Serile Resources In his chper, we inroduce he simple concepion of scrce resource,
More on Magnetically C Coupled Coils and Ideal Transformers
 Appenix ore on gneiclly C Couple Coils Iel Trnsformers C. Equivlen Circuis for gneiclly Couple Coils A imes, i is convenien o moel mgneiclly couple coils wih n equivlen circui h oes no involve mgneic coupling.
Appenix ore on gneiclly C Couple Coils Iel Trnsformers C. Equivlen Circuis for gneiclly Couple Coils A imes, i is convenien o moel mgneiclly couple coils wih n equivlen circui h oes no involve mgneic coupling.
Some basic notation and terminology. Deterministic Finite Automata. COMP218: Decision, Computation and Language Note 1
 COMP28: Decision, Compuion nd Lnguge Noe These noes re inended minly s supplemen o he lecures nd exooks; hey will e useful for reminders ou noion nd erminology. Some sic noion nd erminology An lphe is
COMP28: Decision, Compuion nd Lnguge Noe These noes re inended minly s supplemen o he lecures nd exooks; hey will e useful for reminders ou noion nd erminology. Some sic noion nd erminology An lphe is
RESPONSE UNDER A GENERAL PERIODIC FORCE. When the external force F(t) is periodic with periodτ = 2π
 RESPONSE UNDER A GENERAL PERIODIC FORCE When he exernl force F() is periodic wih periodτ / ω,i cn be expnded in Fourier series F( ) o α ω α b ω () where τ F( ) ω d, τ,,,... () nd b τ F( ) ω d, τ,,... (3)
RESPONSE UNDER A GENERAL PERIODIC FORCE When he exernl force F() is periodic wih periodτ / ω,i cn be expnded in Fourier series F( ) o α ω α b ω () where τ F( ) ω d, τ,,,... () nd b τ F( ) ω d, τ,,... (3)
Aircraft safety modeling for time-limited dispatch
 Loughborough Universiy Insiuionl Reposiory Aircrf sfey modeling for ime-limied dispch This iem ws submied o Loughborough Universiy's Insiuionl Reposiory by he/n uhor. Ciion: PRESCOTT, D.R. nd ANDREWS,
Loughborough Universiy Insiuionl Reposiory Aircrf sfey modeling for ime-limied dispch This iem ws submied o Loughborough Universiy's Insiuionl Reposiory by he/n uhor. Ciion: PRESCOTT, D.R. nd ANDREWS,
INTEGRALS. Exercise 1. Let f : [a, b] R be bounded, and let P and Q be partitions of [a, b]. Prove that if P Q then U(P ) U(Q) and L(P ) L(Q).
![INTEGRALS. Exercise 1. Let f : [a, b] R be bounded, and let P and Q be partitions of [a, b]. Prove that if P Q then U(P ) U(Q) and L(P ) L(Q). INTEGRALS. Exercise 1. Let f : [a, b] R be bounded, and let P and Q be partitions of [a, b]. Prove that if P Q then U(P ) U(Q) and L(P ) L(Q).](/thumbs/78/77677920.jpg) INTEGRALS JOHN QUIGG Eercise. Le f : [, b] R be bounded, nd le P nd Q be priions of [, b]. Prove h if P Q hen U(P ) U(Q) nd L(P ) L(Q). Soluion: Le P = {,..., n }. Since Q is obined from P by dding finiely
INTEGRALS JOHN QUIGG Eercise. Le f : [, b] R be bounded, nd le P nd Q be priions of [, b]. Prove h if P Q hen U(P ) U(Q) nd L(P ) L(Q). Soluion: Le P = {,..., n }. Since Q is obined from P by dding finiely
AJAE appendix for Is Exchange Rate Pass-Through in Pork Meat Export Prices Constrained by the Supply of Live Hogs?
 AJAE ppendix for Is Exchnge Re Pss-Through in Por Me Expor Prices Consrined by he Supply of Live Hogs? Jen-Philippe Gervis Cnd Reserch Chir in Agri-indusries nd Inernionl Trde Cener for Reserch in he Economics
AJAE ppendix for Is Exchnge Re Pss-Through in Por Me Expor Prices Consrined by he Supply of Live Hogs? Jen-Philippe Gervis Cnd Reserch Chir in Agri-indusries nd Inernionl Trde Cener for Reserch in he Economics
A Numerical Model of Commodity Moisture Loss and Temperature Distribution During Refrigerated Storage
 A Numericl Model of Commodiy Moiure Lo nd Temperure Diribuion During Refrigered Sorge B.R. Becker nd B.A. Fricke Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Univeriy of Miouri-Kn Ciy 5 Rockhill Rod, Kn Ciy, MO 64-2499
A Numericl Model of Commodiy Moiure Lo nd Temperure Diribuion During Refrigered Sorge B.R. Becker nd B.A. Fricke Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Univeriy of Miouri-Kn Ciy 5 Rockhill Rod, Kn Ciy, MO 64-2499
5.1-The Initial-Value Problems For Ordinary Differential Equations
 5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
An introduction to the theory of SDDP algorithm
 An inroducion o he heory of SDDP algorihm V. Leclère (ENPC) Augus 1, 2014 V. Leclère Inroducion o SDDP Augus 1, 2014 1 / 21 Inroducion Large scale sochasic problem are hard o solve. Two ways of aacking
An inroducion o he heory of SDDP algorihm V. Leclère (ENPC) Augus 1, 2014 V. Leclère Inroducion o SDDP Augus 1, 2014 1 / 21 Inroducion Large scale sochasic problem are hard o solve. Two ways of aacking
Average & instantaneous velocity and acceleration Motion with constant acceleration
 Physics 7: Lecure Reminders Discussion nd Lb secions sr meeing ne week Fill ou Pink dd/drop form if you need o swich o differen secion h is FULL. Do i TODAY. Homework Ch. : 5, 7,, 3,, nd 6 Ch.: 6,, 3 Submission
Physics 7: Lecure Reminders Discussion nd Lb secions sr meeing ne week Fill ou Pink dd/drop form if you need o swich o differen secion h is FULL. Do i TODAY. Homework Ch. : 5, 7,, 3,, nd 6 Ch.: 6,, 3 Submission
Version 001 test-1 swinney (57010) 1. is constant at m/s.
 Version 001 es-1 swinne (57010) 1 This prin-ou should hve 20 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions m coninue on he nex column or pge find ll choices before nswering. CubeUniVec1x76 001 10.0 poins Acubeis1.4fee
Version 001 es-1 swinne (57010) 1 This prin-ou should hve 20 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions m coninue on he nex column or pge find ll choices before nswering. CubeUniVec1x76 001 10.0 poins Acubeis1.4fee
Think of the Relationship Between Time and Space Again
 Repor nd Opinion, 1(3),009 hp://wwwsciencepubne sciencepub@gmilcom Think of he Relionship Beween Time nd Spce Agin Yng F-cheng Compny of Ruid Cenre in Xinjing 15 Hongxing Sree, Klmyi, Xingjing 834000,
Repor nd Opinion, 1(3),009 hp://wwwsciencepubne sciencepub@gmilcom Think of he Relionship Beween Time nd Spce Agin Yng F-cheng Compny of Ruid Cenre in Xinjing 15 Hongxing Sree, Klmyi, Xingjing 834000,
Inventory Management Models with Variable Holding Cost and Salvage value
 OSR Journl of Business nd Mngemen OSR-JBM e-ssn: -X p-ssn: 9-. Volume ssue Jul. - Aug. PP - www.iosrjournls.org nvenory Mngemen Models wi Vrile Holding os nd Slvge vlue R.Mon R.Venkeswrlu Memics Dep ollege
OSR Journl of Business nd Mngemen OSR-JBM e-ssn: -X p-ssn: 9-. Volume ssue Jul. - Aug. PP - www.iosrjournls.org nvenory Mngemen Models wi Vrile Holding os nd Slvge vlue R.Mon R.Venkeswrlu Memics Dep ollege
3.1.3 INTRODUCTION TO DYNAMIC OPTIMIZATION: DISCRETE TIME PROBLEMS. A. The Hamiltonian and First-Order Conditions in a Finite Time Horizon
 3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
STATE-SPACE MODELLING. A mass balance across the tank gives:
 B. Lennox and N.F. Thornhill, 9, Sae Space Modelling, IChemE Process Managemen and Conrol Subjec Group Newsleer STE-SPACE MODELLING Inroducion: Over he pas decade or so here has been an ever increasing
B. Lennox and N.F. Thornhill, 9, Sae Space Modelling, IChemE Process Managemen and Conrol Subjec Group Newsleer STE-SPACE MODELLING Inroducion: Over he pas decade or so here has been an ever increasing
1. Introduction. 1 b b
 Journl of Mhemicl Inequliies Volume, Number 3 (007), 45 436 SOME IMPROVEMENTS OF GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITY N. ELEZOVIĆ, LJ. MARANGUNIĆ AND J. PEČARIĆ (communiced b A. Čižmešij) Absrc. In his pper some inequliies
Journl of Mhemicl Inequliies Volume, Number 3 (007), 45 436 SOME IMPROVEMENTS OF GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITY N. ELEZOVIĆ, LJ. MARANGUNIĆ AND J. PEČARIĆ (communiced b A. Čižmešij) Absrc. In his pper some inequliies
The Dynamics of Two Harvesting Species with variable Effort Rate with the Optimum Harvest Policy
 Inernionl OPEN ACCESS Journl Of Modern Engineering Reserch (IJMER) The Dynmics of Two Hrvesing Species wih vrible Effor Re wih he Opimum Hrves Policy Brhmpl Singh; nd Professor Suni Gkkhr; Deprmen of Mhemics,
Inernionl OPEN ACCESS Journl Of Modern Engineering Reserch (IJMER) The Dynmics of Two Hrvesing Species wih vrible Effor Re wih he Opimum Hrves Policy Brhmpl Singh; nd Professor Suni Gkkhr; Deprmen of Mhemics,
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( y )
 8. Lengh of Plne Curve The mos fmous heorem in ll of mhemics is he Pyhgoren Theorem. I s formulion s he disnce formul is used o find he lenghs of line segmens in he coordine plne. In his secion you ll
8. Lengh of Plne Curve The mos fmous heorem in ll of mhemics is he Pyhgoren Theorem. I s formulion s he disnce formul is used o find he lenghs of line segmens in he coordine plne. In his secion you ll
ANSWERS TO EVEN NUMBERED EXERCISES IN CHAPTER 2
 ANSWERS TO EVEN NUMBERED EXERCISES IN CHAPTER Seion Eerise -: Coninuiy of he uiliy funion Le λ ( ) be he monooni uiliy funion defined in he proof of eisene of uiliy funion If his funion is oninuous y hen
ANSWERS TO EVEN NUMBERED EXERCISES IN CHAPTER Seion Eerise -: Coninuiy of he uiliy funion Le λ ( ) be he monooni uiliy funion defined in he proof of eisene of uiliy funion If his funion is oninuous y hen
2D Motion WS. A horizontally launched projectile s initial vertical velocity is zero. Solve the following problems with this information.
 Nme D Moion WS The equions of moion h rele o projeciles were discussed in he Projecile Moion Anlsis Acii. ou found h projecile moes wih consn eloci in he horizonl direcion nd consn ccelerion in he ericl
Nme D Moion WS The equions of moion h rele o projeciles were discussed in he Projecile Moion Anlsis Acii. ou found h projecile moes wih consn eloci in he horizonl direcion nd consn ccelerion in he ericl
SOLUTION FOR A SYSTEM OF FRACTIONAL HEAT EQUATIONS OF NANOFLUID ALONG A WEDGE
 Ibrhim, R. W., e l.: Soluion for Sysem of Frcionl He Equions of THERMA SCIENCE, Yer 015, Vol. 19, Suppl. 1, pp. S51-S57 S51 SOUTION FOR A SYSTEM OF FRACTIONA HEAT EQUATIONS OF NANOFUID AONG A WEDGE by
Ibrhim, R. W., e l.: Soluion for Sysem of Frcionl He Equions of THERMA SCIENCE, Yer 015, Vol. 19, Suppl. 1, pp. S51-S57 S51 SOUTION FOR A SYSTEM OF FRACTIONA HEAT EQUATIONS OF NANOFUID AONG A WEDGE by
Mathematics 805 Final Examination Answers
 . 5 poins Se he Weiersrss M-es. Mhemics 85 Finl Eminion Answers Answer: Suppose h A R, nd f n : A R. Suppose furher h f n M n for ll A, nd h Mn converges. Then f n converges uniformly on A.. 5 poins Se
. 5 poins Se he Weiersrss M-es. Mhemics 85 Finl Eminion Answers Answer: Suppose h A R, nd f n : A R. Suppose furher h f n M n for ll A, nd h Mn converges. Then f n converges uniformly on A.. 5 poins Se
Dipartimento di Elettronica Informazione e Bioingegneria Robotics
 Diprimeno di Eleronic Inormzione e Bioingegneri Roboics From moion plnning o rjecories @ 015 robo clssiicions Robos cn be described by Applicion(seelesson1) Geomery (see lesson mechnics) Precision (see
Diprimeno di Eleronic Inormzione e Bioingegneri Roboics From moion plnning o rjecories @ 015 robo clssiicions Robos cn be described by Applicion(seelesson1) Geomery (see lesson mechnics) Precision (see
Unified Framework for Developing Testing Effort Dependent Software Reliability Growth Models
 P. K. Kpur, Omr Shnwi, Anu G. Aggrwl, Rvi Kumr Unified Frmework for Developing Tesing Effor Dependen Sofwre Relibiliy Growh Models P.K. KAPUR 1, OMAR SHATNAI, ANU G. AGGARAL 1, RAVI KUMAR 1 1 Deprmen of
P. K. Kpur, Omr Shnwi, Anu G. Aggrwl, Rvi Kumr Unified Frmework for Developing Tesing Effor Dependen Sofwre Relibiliy Growh Models P.K. KAPUR 1, OMAR SHATNAI, ANU G. AGGARAL 1, RAVI KUMAR 1 1 Deprmen of
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems
 Swiss Federl Insiue of Pge 1 The Finie Elemen Mehod for he Anlysis of Non-Liner nd Dynmic Sysems Prof. Dr. Michel Hvbro Fber Dr. Nebojs Mojsilovic Swiss Federl Insiue of ETH Zurich, Swizerlnd Mehod of
Swiss Federl Insiue of Pge 1 The Finie Elemen Mehod for he Anlysis of Non-Liner nd Dynmic Sysems Prof. Dr. Michel Hvbro Fber Dr. Nebojs Mojsilovic Swiss Federl Insiue of ETH Zurich, Swizerlnd Mehod of
Development of a New Scheme for the Solution of Initial Value Problems in Ordinary Differential Equations
 IOS Journl o Memics IOSJM ISSN: 78-78 Volume Issue July-Aug PP -9 www.iosrjournls.org Developmen o New Sceme or e Soluion o Iniil Vlue Problems in Ordinry Dierenil Equions Ogunrinde. B. dugb S. E. Deprmen
IOS Journl o Memics IOSJM ISSN: 78-78 Volume Issue July-Aug PP -9 www.iosrjournls.org Developmen o New Sceme or e Soluion o Iniil Vlue Problems in Ordinry Dierenil Equions Ogunrinde. B. dugb S. E. Deprmen
Systems Variables and Structural Controllability: An Inverted Pendulum Case
 Reserch Journl of Applied Sciences, Engineering nd echnology 6(: 46-4, 3 ISSN: 4-7459; e-issn: 4-7467 Mxwell Scienific Orgniion, 3 Submied: Jnury 5, 3 Acceped: Mrch 7, 3 Published: November, 3 Sysems Vribles
Reserch Journl of Applied Sciences, Engineering nd echnology 6(: 46-4, 3 ISSN: 4-7459; e-issn: 4-7467 Mxwell Scienific Orgniion, 3 Submied: Jnury 5, 3 Acceped: Mrch 7, 3 Published: November, 3 Sysems Vribles
10. State Space Methods
 . Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
. Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
T-Match: Matching Techniques For Driving Yagi-Uda Antennas: T-Match. 2a s. Z in. (Sections 9.5 & 9.7 of Balanis)
 3/0/018 _mch.doc Pge 1 of 6 T-Mch: Mching Techniques For Driving Ygi-Ud Anenns: T-Mch (Secions 9.5 & 9.7 of Blnis) l s l / l / in The T-Mch is shun-mching echnique h cn be used o feed he driven elemen
3/0/018 _mch.doc Pge 1 of 6 T-Mch: Mching Techniques For Driving Ygi-Ud Anenns: T-Mch (Secions 9.5 & 9.7 of Blnis) l s l / l / in The T-Mch is shun-mching echnique h cn be used o feed he driven elemen
This UR does not apply to CSR Bulk Carriers and Oil Tankers or to container ships to which UR S11A is applicable.
 (1989) (Rev.1 199) (Rev. Nov 001) (Rev. June 00) (Rev.4 July 004) (Rev.5 Jn 006) (Rev.6 My 0) (Rev.7 Nov 0) (Rev.8 June 015) Longiudinl Srengh Sndrd.1 Applicion This requiremen pplies only o seel ships
(1989) (Rev.1 199) (Rev. Nov 001) (Rev. June 00) (Rev.4 July 004) (Rev.5 Jn 006) (Rev.6 My 0) (Rev.7 Nov 0) (Rev.8 June 015) Longiudinl Srengh Sndrd.1 Applicion This requiremen pplies only o seel ships
Process Monitoring and Feedforward Control for Proactive Quality Improvement
 Inernionl Journl of Performbiliy Engineering Vol. 8, No. 6, November 0, pp. 60-64. RAMS Consulns Prined in Indi Process Monioring nd Feedforwrd Conrol for Procive Quliy Improvemen. Inroducion LIHUI SHI
Inernionl Journl of Performbiliy Engineering Vol. 8, No. 6, November 0, pp. 60-64. RAMS Consulns Prined in Indi Process Monioring nd Feedforwrd Conrol for Procive Quliy Improvemen. Inroducion LIHUI SHI
Bilateral Decision Making Under Asynchronous Time Constraint
 Inernionl Journl of Compuer Informion Sysems nd Indusril Mngemen Applicions. ISSN 50-7988 Volume 4 (0) pp. 6 c MIR Lbs, www.mirlbs.ne/ijcisim/index.hml Bilerl Decision Mking Under Asynchronous Time Consrin
Inernionl Journl of Compuer Informion Sysems nd Indusril Mngemen Applicions. ISSN 50-7988 Volume 4 (0) pp. 6 c MIR Lbs, www.mirlbs.ne/ijcisim/index.hml Bilerl Decision Mking Under Asynchronous Time Consrin
Introduction to LoggerPro
 Inroducion o LoggerPro Sr/Sop collecion Define zero Se d collecion prmeers Auoscle D Browser Open file Sensor seup window To sr d collecion, click he green Collec buon on he ool br. There is dely of second
Inroducion o LoggerPro Sr/Sop collecion Define zero Se d collecion prmeers Auoscle D Browser Open file Sensor seup window To sr d collecion, click he green Collec buon on he ool br. There is dely of second
Major Maintenance Schedule Optimization for Electric Multiple. Unit Considering Passenger Transport Demand
 Mjor Minennce Schedule Opimizion for Elecric Muliple Uni Considering Pssenger Trnspor Demnd Jinping Wu 1, Boling Lin 1*, 1 School of Trffic nd Trnsporion, Beijing Jioong Universiy, Beijing 144, Chin 1511425@bju.edu.cn,
Mjor Minennce Schedule Opimizion for Elecric Muliple Uni Considering Pssenger Trnspor Demnd Jinping Wu 1, Boling Lin 1*, 1 School of Trffic nd Trnsporion, Beijing Jioong Universiy, Beijing 144, Chin 1511425@bju.edu.cn,
ON THE STABILITY OF DELAY POPULATION DYNAMICS RELATED WITH ALLEE EFFECTS. O. A. Gumus and H. Kose
 Mhemicl nd Compuionl Applicions Vol. 7 o. pp. 56-67 O THE STABILITY O DELAY POPULATIO DYAMICS RELATED WITH ALLEE EECTS O. A. Gumus nd H. Kose Deprmen o Mhemics Selcu Universiy 47 Kony Turey ozlem@selcu.edu.r
Mhemicl nd Compuionl Applicions Vol. 7 o. pp. 56-67 O THE STABILITY O DELAY POPULATIO DYAMICS RELATED WITH ALLEE EECTS O. A. Gumus nd H. Kose Deprmen o Mhemics Selcu Universiy 47 Kony Turey ozlem@selcu.edu.r
IX.1.1 The Laplace Transform Definition 700. IX.1.2 Properties 701. IX.1.3 Examples 702. IX.1.4 Solution of IVP for ODEs 704
 Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 4, 7 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 4, 7 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 10: The High Beta Tokamak Con d and the High Flux Conserving Tokamak.
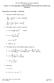 .615, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 1: The High Be Tokmk Con d nd he High Flux Conserving Tokmk Proeries of he High Tokmk 1. Evlue he MHD sfey fcor: ψ B * ( ) 1 3 ρ 1+ ν ρ ρ cosθ *
.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 1: The High Be Tokmk Con d nd he High Flux Conserving Tokmk Proeries of he High Tokmk 1. Evlue he MHD sfey fcor: ψ B * ( ) 1 3 ρ 1+ ν ρ ρ cosθ *
