Coincident Observations with QuikSCAT and ASCAT of the Effects of Rain-Induced Sea Surface Stress During Hurricane Ike
|
|
|
- Maximilian Burke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Coincident Observations with QuikSCAT and ASCAT of the Effects of Rain-Induced Sea Surface Stress During Hurricane Ike David E. Weissman Hofstra University Hempstead, New York Mark A. Bourassa Center for Ocean Atmosphere Prediction Studies Florida State University Tallahassee, FL 2009 OVWST Boulder, CO 18-May
2 Studies of Interest: USING the QuikSCAT Scatterometer and NEXRAD Measurements of the 3-D Rain Volume: 1. To measure the effect of rain impacts on total sea surface roughness (Ku-band NRCS), as a function rain rate, wind speed, polarization and azimuth look direction 2. Develop a model for the change (increase or decrease) of the surface normalized radar cross section (NRCS for Ku-band) as a function of rainrate, wind speed, etc. 3. Interpret the results in terms of the interaction between wind waves and the splash products of rain impacts (ring waves, crowns and stalks; Sea Spray?)
3 From Contreras, et al, Ku-band ocean backscatter during rain. J. Geophys. Res., May 2003 Figure 1: Splash products when a raindrop falls onto a water surface. The figures are reproductions of photographs from Worthington, [1963] HOWEVER WHEN WIND SPEEDS ARE COMPARABLE TO AND EXCEED THE RAINDROP FALL VELOCITY, THE SITUATION IS DRASTICALLY DIFFERENT
4 DATA: a) QuikSCAT Level 2A NRCS data, H-pol and V-pol b) Simultaneous NEXRAD 3-D Volume Reflectivity (S-band) within scatterometer beam c) Surface winds from NOAA Hurricane Research Division Analysis and buoys
5 NEXRAD & BUOY Locations KHGX KCRP Buoy # Winds Speeds 4205: 8.6 => 10 m/s 42019: 8.5 => 11 m/s 42020: 4.5 => 5.5 m/s
6 Electromagnetic Model of the NRCS (σ ax ) Measured by the SeaWinds Scatterometer and Rain Impact NRCS, σ rn0 Use of x subscript below will represent either h or v polarization σ ax = Total measured NRCS at Receiver; Sum of Contributions from Sea Surface and Rain Volume=L2A data σ wdx = sea surface radar cross section due to wind driven roughness alone (wind-nrcs) σ rnx = sea surface radar cross section due to rain impact roughness alone (rain-nrcs) α x (r)= attenuation, in nepers/m for each polarization, function of local volume rainrate or precipitation water content σ ox (r)= surface equivalent of volumetric rain RCS, = constant * Zx (the radar reflectivity factor for Ku-band, Zx, varies with position, r ) lenx=path length of radar beam for each polarization = len/cos(θx) (rain column height, over scatterometer footprint = len, θ h =46 o & θ v =54 o ) lenx lenx 4 αx ( s) ds r σax= σox e dr + ( σwdx + σrnx) e 0 4 lenx 0 αx ( s) ds
7 σ rn0 = model function for the normalized radar cross section due to rain impact; depends on wind magnitude and rainrate After solving for the total surface NRCS = (σ wdx + σ rnx ) from a rain affected area, the wind-driven term alone is estimated from a nearby rain-free area: σ wdx. Then their ratio σ rn0 is computed, producing: σ = rn0 σ + σ ( wdx rnx ) σwdx
8 The locations of the QScat L2A cells within a rain event near the KCRP NEXRAD. The usable H- pol and V-pol points are designated with green circles or green squares respectively. QuikSCAT cell size typically 30- by-40 km.
9 Box # 2, Azimuth Angle #1 Winds = 5 m/s Upper plot: Uncorrected and corrected (for atmospheric rain) V-pol NRCS versus mean rainrate at each QSCAT cell. Lower Plot: Ratio of total surface NRCS to wind-driven NRCS vs. rainrate.
10 Box # 2, Azimuth Angle #1 Winds = 5 m/s Upper plot: Uncorrected and corrected (for atmospheric rain) H-pol NRCS versus mean rainrate at each QSCAT cell. Lower Plot: Ratio of total surface NRCS to winddriven NRCS vs. rainrate.
11 Results published in IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, October, 2008, D.E. Weissman and M.A. Bouassa Personal communication from Drs. Piotr Sobieski and Christophe Craeye, of Catholic University de Louvain, Belgium to show normalized radar cross section of rain impacting a wind driven sea
12 Theoretical model by Sobieski and Craeye
13 Theoretical model by Sobieski and Craeye
14 The theoretical results from Sobieski & Craeye is a validation of the 3-D rain reflectivity model and the attenuation and volume backscatter calculations
15 A fundamental study to:.. establish a theory on the interaction between rain and water waves, based on momentum exchanges, and to assess its relative importance regarding the wave prediction models was published by LeMehaute and Khangaonkar, J.Phys.Oceanogr, Dec Rain horizontal momentum transfer ( R ), R = raindrop mass density x rainrate x horizontal wind speed For example: for rainrate = 25 mm/hr and U 10 = 25 m/s, the ratio R / wind stress = 8.4 % However this number gives no direct indication about the roughness properties to which Ku-band radar responds.
16 SPRAY STRESS REVISITED by E.L. Andreas J.Phys.Oceanog. June Spray stress increases to the 4 th power of wind speed 2. Spray can redistribute momentum at surface; the total stress can remain same, but consists of spray stress and interfacial stress. 3. The mass flux created by spray falls back to ocean and can suppress wave growth ( knocks down the waves ) It acts like rain at winds > 30 m/s to suppress short waves. 4. His drag coefficient saturates at 35 m/s and then decreases
17 Suggested View of Physical Dependence of NRCS on Air-Sea Conditions: NRCS= SUM ( Effects of wind-wave spectrum controlled by friction velocity (at low winds/no-rain, equilibrium spectrum, Phillips, etc, Bragg scattering, U < 15 m/s) +Effects high wind spray stress and breaking (no-rain) + Effects of rain impact stress (low-to-moderate wind) + Effects of combination of high-wind sea & spray & rain
18 Wind: deg at #42035 Buoy NEXRAD Level II, Base Reflectivity,in dbz,h=500 m, KHGX,15-July-05, t=04:01 HURRICANE CLAUDETTE Azim #2 = 305 deg titude, Deg Lat Azim # 1=205 deg 27.5 Box #1=> Longitude, Deg 5
19
20 Ratio of NRCS with and without Rain, db Measured and atmospheric rain-corrected NRCS, d Measured NRCS and Atmosphere Corrected NRCS, Azim #1, Box #1, 15-July-03, KHGX H-pol Measured NRCS, "+" Corrected NRCS, "square" H-pol Mean Rainrate, Lowest Elevation, mm/hr Ratio of Total Surface NRCS with Rain/Relative to Wind Only NRCS Mean Rainrate, Lowest Elevation, mm/hr
21 Ratio of NRCS with and without Rain, db Measured and atmospheric rain-corrected NRCS, d Measured NRCS and Atmosphere Corrected NRCS, Azim #2, Box #1, 15-July-03, KHGX H-pol Measured NRCS, "+" Corrected NRCS, "square" H-pol Mean Rainrate, Lowest Elevation, mm/hr Ratio of Total Surface NRCS with Rain/Relative to Wind Only NRCS Mean Rainrate, Lowest Elevation, mm/hr
22 Ratio of NRCS with and without Rain, db Measured and atmospheric rain-corrected NRCS, Measured NRCS and Atmosphere Corrected NRCS, Azim #1, Box #1, 15-July-03, KHGX V-pol Measured NRCS, "+" Corrected NRCS, "square" V-pol Mean Rainrate, Lowest Elevation, mm/hr Ratio of Total Surface NRCS with Rain/Relative to Wind Only NRCS Mean Rainrate, Lowest Elevation, mm/hr
23 Ratio of NRCS with and without Rain, db Me easured and atmospheric rain-corrected NRCS, Measured NRCS and Atmosphere Corrected NRCS, Azim #2, Box #1, 15-July-03, KHGX -5 V-pol Measured NRCS, "+" Corrected NRCS, "square" V-pol Mean Rainrate, Lowest Elevation, mm/hr Ratio of Total Surface NRCS with Rain/Relative to Wind Only NRCS Mean Rainrate, Lowest Elevation, mm/hr
24 Summary for Hurricane Claudette: The properties of the NRCS vs Rainrate: For H-pol, there is a clear increase in NRCS with rainrate. For V-pol, there is no clear increase For V-pol, there is no clear increase on average, in NRCS, with increasing rainrate.
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 GENERAL SUMMARY At low wind speeds (< 7 m/s), the changes in NRCS caused by rain roughness was very similar for both H-pol and V-pol As the wind speed increases, and approaches the terminal velocity of gravity driven falling rain, the differences in NRCS for the two polarizations become progressively larger. This indicates there is an interaction between the rain impact roughness products and the wind driven wave roughness. It appears that rain impacts produce new roughness characteristics that have a distinct and differential polarization response.
33 ASCAT Studies During Hurricane Ike Will examine NRCS data at t=03:18 Z Location in Gulf of Mexico, south of Houston Thanks to Scott Dunbar for critical assistance
34
35 NEXRAD, Base Reflectivity,in dbz,h=500 m, KHGX, 13-Sep-08, t=03:20 5 km Resolution ASCAT Overpass Latitu ude, Deg Longitude, Deg 0
36 28 Mean Rainrates (45 km square) and Locations of ASCAT SIG0, Hurr IKE Marker symbols at Locations of SIG Latitude, deg Contour Lines of Constant Rainrate, mm/hr Longitude, deg HRD Winds: at t=01:30z, U= kts / at t=04:30z, U=50-60 kts /// ASCAT at 03:18z
37 -3.5 ASCAT NRCS vs Rainrate, Hurr Ike, 13-Sep-08, Mid-Beam Mid-Beam Incidence Angles: deg ASCAT NRCS, db Rainrate, mm/hr
38 -6-7 ASCAT NRCS vs Rainrate, Hurr Ike, 13-Sep-08, FWD & BACK BEAMS Incidence Angles: deg Back Beam - X Forward Beam - "square" -8 ASCAT NRCS, db Rainrate, mm/hr
39 Why Is This Interesting To A Meteorologist or Oceanographer The air-sea momentum exchange in hurricanes is not well understood Surface drag Which is related to surface roughness for U 10 < 25ms -1, If it continues to increase of U 10 > 25 ms -1, The drag is too great to produce strong hurricanes Unless there is a proportional increase in evaporation However, the highest winds are found in or near rain bands Therefore, it seems likely that surface drag is somehow reduced by rain Rain and sea spray likely act to reduce the surface drag Does rain act to increase sea spray via wave-wave interaction or is the process more direct? Current hurricane intensity forecasts do not consider these processes Intensity forecasts are bad but there could be other reasons Ocean mixing due to tropical cyclones could be important for climate If the drag is reduced there will be less mixing than otherwise modeled!
Corrections to Scatterometer Wind Vectors For Precipitation Effects: Using High Resolution NEXRAD and AMSR With Intercomparisons
 Corrections to Scatterometer Wind Vectors For Precipitation Effects: Using High Resolution NEXRAD and AMSR With Intercomparisons David E. Weissman Hofstra University Hempstead, New York 11549 Svetla Hristova-Veleva
Corrections to Scatterometer Wind Vectors For Precipitation Effects: Using High Resolution NEXRAD and AMSR With Intercomparisons David E. Weissman Hofstra University Hempstead, New York 11549 Svetla Hristova-Veleva
ON A GLOBAL scale, recent studies [14] have indicated
![ON A GLOBAL scale, recent studies [14] have indicated ON A GLOBAL scale, recent studies [14] have indicated](/thumbs/87/96046512.jpg) 2882 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 46, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2008 Measurements of the Effect of Rain-Induced Sea Surface Roughness on the QuikSCAT Scatterometer Radar Cross Section
2882 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 46, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2008 Measurements of the Effect of Rain-Induced Sea Surface Roughness on the QuikSCAT Scatterometer Radar Cross Section
Rain Effects on Scatterometer Systems A summary of what is known to date
 Rain Effects on Scatterometer Systems A summary of what is known to date Kyle Hilburn, Deborah K Smith, *Frank J. Wentz Remote Sensing Systems NASA Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting May 18-20, 2009
Rain Effects on Scatterometer Systems A summary of what is known to date Kyle Hilburn, Deborah K Smith, *Frank J. Wentz Remote Sensing Systems NASA Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting May 18-20, 2009
EVALUATING THE QUIKSCAT/SEAWINDS RADAR FOR MEASURING RAINRATE OVER THE OCEANS USING COLLOCATIONS WITH NEXRAD AND TRMM
 JP2.9 EVALUATING THE QUIKSCAT/SEAWINDS RADAR FOR MEASURING RAINRATE OVER THE OCEANS USING COLLOCATIONS WITH NEXRAD AND TRMM David E. Weissman* Hofstra University, Hempstead, New York 11549 Mark A. Bourassa
JP2.9 EVALUATING THE QUIKSCAT/SEAWINDS RADAR FOR MEASURING RAINRATE OVER THE OCEANS USING COLLOCATIONS WITH NEXRAD AND TRMM David E. Weissman* Hofstra University, Hempstead, New York 11549 Mark A. Bourassa
CALmRA TING THE QUIKSCA T/SEAWIN DS RADAR FOR
 CALmRA TING THE QUIKSCA T/SEAWIN DS RADAR FOR MEAS URIN G RAINRA TE OVER THE OCEANS David E. Weissman Dept. of Engineering. Hofstra University, Hempstead, New York 11549 Tel:(516) 463-5546; Fax: (516)
CALmRA TING THE QUIKSCA T/SEAWIN DS RADAR FOR MEAS URIN G RAINRA TE OVER THE OCEANS David E. Weissman Dept. of Engineering. Hofstra University, Hempstead, New York 11549 Tel:(516) 463-5546; Fax: (516)
CALIBRATING THE QUIKSCAT/SEAWINDS RADAR FOR MEASURING RAINRATE OVER THE OCEANS
 CALIBRATING THE QUIKSCAT/SEAWINDS RADAR FOR MEASURING RAINRATE OVER THE OCEANS David E. Weissman Hofstra University, Hempstead, New York 11549 Mark A. Bourassa COAPS/The Florida State University, Tallahassee,
CALIBRATING THE QUIKSCAT/SEAWINDS RADAR FOR MEASURING RAINRATE OVER THE OCEANS David E. Weissman Hofstra University, Hempstead, New York 11549 Mark A. Bourassa COAPS/The Florida State University, Tallahassee,
Calibrating the Quikscat/SeaWinds Radar for Measuring Rainrate Over the Oceans
 2814 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 41, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2003 Calibrating the Quikscat/SeaWinds Radar for Measuring Rainrate Over the Oceans David E. Weissman, Fellow, IEEE, Mark
2814 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 41, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2003 Calibrating the Quikscat/SeaWinds Radar for Measuring Rainrate Over the Oceans David E. Weissman, Fellow, IEEE, Mark
Q-Winds satellite hurricane wind retrievals and H*Wind comparisons
 Q-Winds satellite hurricane wind retrievals and H*Wind comparisons Pet Laupattarakasem and W. Linwood Jones Central Florida Remote Sensing Laboratory University of Central Florida Orlando, Florida 3816-
Q-Winds satellite hurricane wind retrievals and H*Wind comparisons Pet Laupattarakasem and W. Linwood Jones Central Florida Remote Sensing Laboratory University of Central Florida Orlando, Florida 3816-
Effect of rain on Ku band fan beam Scatterometer
 Effect of rain on Ku band fan beam Scatterometer J. Tournadre, Y. Quilfen, B. Chapron Laboratoire d'océanographie Spatiale Ifremer Brest Problem/Drawback of the use of Ku-Band for radar SCAT on the future
Effect of rain on Ku band fan beam Scatterometer J. Tournadre, Y. Quilfen, B. Chapron Laboratoire d'océanographie Spatiale Ifremer Brest Problem/Drawback of the use of Ku-Band for radar SCAT on the future
Related Improvements. A DFS Application. Mark A. Bourassa
 Related Improvements in Surface Turbulent Heat Fluxes A DFS Application Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies & Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, The Florida State University,
Related Improvements in Surface Turbulent Heat Fluxes A DFS Application Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies & Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, The Florida State University,
URSI-F Microwave Signatures Meeting 2010, Florence, Italy, October 4 8, Thomas Meissner Lucrezia Ricciardulli Frank Wentz
 URSI-F Microwave Signatures Meeting 2010, Florence, Italy, October 4 8, 2010 Wind Measurements from Active and Passive Microwave Sensors High Winds and Winds in Rain Thomas Meissner Lucrezia Ricciardulli
URSI-F Microwave Signatures Meeting 2010, Florence, Italy, October 4 8, 2010 Wind Measurements from Active and Passive Microwave Sensors High Winds and Winds in Rain Thomas Meissner Lucrezia Ricciardulli
Ultra-High Resolution ASCAT Products & Progress in Simultaneous Wind/Rain Retrieval
 Ultra-High Resolution ASCAT Products & Progress in Simultaneous Wind/Rain Retrieval David G. Long Brigham Young University Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting 18-20 May 2010 Introduction σ 0 imaging
Ultra-High Resolution ASCAT Products & Progress in Simultaneous Wind/Rain Retrieval David G. Long Brigham Young University Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting 18-20 May 2010 Introduction σ 0 imaging
SMAP Winds. Hurricane Irma Sep 5, AMS 33rd Conference on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology Ponte Vedra, Florida, 4/16 4/20, 2018
 Intensity and Size of Strong Tropical Cyclones in 2017 from NASA's SMAP L-Band Radiometer Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia Ricciardulli, Frank Wentz, Remote Sensing Systems, Santa Rosa, USA Charles Sampson, Naval
Intensity and Size of Strong Tropical Cyclones in 2017 from NASA's SMAP L-Band Radiometer Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia Ricciardulli, Frank Wentz, Remote Sensing Systems, Santa Rosa, USA Charles Sampson, Naval
Q-Winds Hurricane Retrieval Algorithm using QuikSCAT Scatterometer
 Q-Winds Hurricane Retrieval Algorithm using QuikSCAT Scatterometer Pete Laupattarakasem Doctoral Dissertation Defense March 23 rd, 2009 Presentation Outline Dissertation Objective Background Scatterometry/Radiometry
Q-Winds Hurricane Retrieval Algorithm using QuikSCAT Scatterometer Pete Laupattarakasem Doctoral Dissertation Defense March 23 rd, 2009 Presentation Outline Dissertation Objective Background Scatterometry/Radiometry
Integrating Multiple Scatterometer Observations into a Climate Data Record of Ocean Vector Winds
 Integrating Multiple Scatterometer Observations into a Climate Data Record of Ocean Vector Winds Lucrezia Ricciardulli and Frank Wentz Remote Sensing Systems, CA, USA E-mail: Ricciardulli@remss.com presented
Integrating Multiple Scatterometer Observations into a Climate Data Record of Ocean Vector Winds Lucrezia Ricciardulli and Frank Wentz Remote Sensing Systems, CA, USA E-mail: Ricciardulli@remss.com presented
Remote Sensing of Ocean Winds
 Remote Sensing of Ocean Winds Stephen Frasier Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Offshore Wind Energy IGERT Seminar 3/5/2015 Remote Sensing of Wind For wind energy applications: Wind Profilers
Remote Sensing of Ocean Winds Stephen Frasier Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Offshore Wind Energy IGERT Seminar 3/5/2015 Remote Sensing of Wind For wind energy applications: Wind Profilers
Stability in SeaWinds Quality Control
 Ocean and Sea Ice SAF Technical Note Stability in SeaWinds Quality Control Anton Verhoef, Marcos Portabella and Ad Stoffelen Version 1.0 April 2008 DOCUMENTATION CHANGE RECORD Reference: Issue / Revision:
Ocean and Sea Ice SAF Technical Note Stability in SeaWinds Quality Control Anton Verhoef, Marcos Portabella and Ad Stoffelen Version 1.0 April 2008 DOCUMENTATION CHANGE RECORD Reference: Issue / Revision:
Calibrating SeaWinds and QuikSCAT scatterometers using natural land targets
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2005-04-01 Calibrating SeaWinds and QuikSCAT scatterometers using natural land targets David G. Long david_long@byu.edu Lucas B. Kunz
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2005-04-01 Calibrating SeaWinds and QuikSCAT scatterometers using natural land targets David G. Long david_long@byu.edu Lucas B. Kunz
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture
 Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
COMPARISON OF SATELLITE DERIVED OCEAN SURFACE WIND SPEEDS AND THEIR ERROR DUE TO PRECIPITATION
 COMPARISON OF SATELLITE DERIVED OCEAN SURFACE WIND SPEEDS AND THEIR ERROR DUE TO PRECIPITATION A.-M. Blechschmidt and H. Graßl Meteorological Institute, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany ABSTRACT
COMPARISON OF SATELLITE DERIVED OCEAN SURFACE WIND SPEEDS AND THEIR ERROR DUE TO PRECIPITATION A.-M. Blechschmidt and H. Graßl Meteorological Institute, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany ABSTRACT
High Resolution Vector Wind Retrieval from SeaWinds Scatterometer Data
 High Resolution Vector Wind Retrieval from SeaWinds Scatterometer Data David G. Long Brigham Young University, 459 Clyde Building, Provo, UT 84602 long@ee.byu.edu http://www.scp.byu.edu Abstract The SeaWinds
High Resolution Vector Wind Retrieval from SeaWinds Scatterometer Data David G. Long Brigham Young University, 459 Clyde Building, Provo, UT 84602 long@ee.byu.edu http://www.scp.byu.edu Abstract The SeaWinds
RapidScat Along Coasts and in Hurricanes. Bryan Stiles, Alex Fore, Sermsak Jaruwatanadilok, and Ernesto Rodriguez May 20, 2015
 RapidScat Along Coasts and in Hurricanes Bryan Stiles, Alex Fore, Sermsak Jaruwatanadilok, and Ernesto Rodriguez May 20, 2015 Outline Description of Improved Rain Correction for RapidScat Hybrid of current
RapidScat Along Coasts and in Hurricanes Bryan Stiles, Alex Fore, Sermsak Jaruwatanadilok, and Ernesto Rodriguez May 20, 2015 Outline Description of Improved Rain Correction for RapidScat Hybrid of current
EVALUATION OF WINDSAT SURFACE WIND DATA AND ITS IMPACT ON OCEAN SURFACE WIND ANALYSES AND NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION
 5.8 EVALUATION OF WINDSAT SURFACE WIND DATA AND ITS IMPACT ON OCEAN SURFACE WIND ANALYSES AND NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION Robert Atlas* NOAA/Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, Miami,
5.8 EVALUATION OF WINDSAT SURFACE WIND DATA AND ITS IMPACT ON OCEAN SURFACE WIND ANALYSES AND NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION Robert Atlas* NOAA/Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, Miami,
Tropical cyclone (TC) detection has vastly improved
 EARLY DETECTION OF TROPICAL CYCLONES USING SEAWINDS-DERIVED VORTICITY BY RYAN J. SHARP, MARK A. BOURASSA, AND JAMES J. O BRIEN The SeaWinds instrument on QuikSCAT provides a new tool for identifying systems
EARLY DETECTION OF TROPICAL CYCLONES USING SEAWINDS-DERIVED VORTICITY BY RYAN J. SHARP, MARK A. BOURASSA, AND JAMES J. O BRIEN The SeaWinds instrument on QuikSCAT provides a new tool for identifying systems
Airborne Studies of High Wind and Rain Effects Using IWRAP
 Airborne Studies of High Wind and Rain Effects Using IWRAP Robert F. Contreras, Stephen J. Frasier, and Tao Chu OVWST Meeting July 5-7, 2006 Salt Lake City, Utah Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Airborne Studies of High Wind and Rain Effects Using IWRAP Robert F. Contreras, Stephen J. Frasier, and Tao Chu OVWST Meeting July 5-7, 2006 Salt Lake City, Utah Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
WindSat Ocean Surface Emissivity Dependence on Wind Speed in Tropical Cyclones. Amanda Mims University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
 WindSat Ocean Surface Emissivity Dependence on Wind Speed in Tropical Cyclones Amanda Mims University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Abstract Radiometers are adept at retrieving near surface ocean wind vectors.
WindSat Ocean Surface Emissivity Dependence on Wind Speed in Tropical Cyclones Amanda Mims University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Abstract Radiometers are adept at retrieving near surface ocean wind vectors.
Evaluating the effect of rain on SeaWinds scatterometer measurements
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2002jc001741, 2004 Evaluating the effect of rain on SeaWinds scatterometer measurements David W. Draper and David G. Long Department of Electrical
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2002jc001741, 2004 Evaluating the effect of rain on SeaWinds scatterometer measurements David W. Draper and David G. Long Department of Electrical
QuikSCAT Analysis of Hurricane Force Extratropical Cyclones in the Pacific Ocean
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Senior Honors Projects Honors Program at the University of Rhode Island 2010 QuikSCAT Analysis of Hurricane Force Extratropical Cyclones in the Pacific Ocean
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Senior Honors Projects Honors Program at the University of Rhode Island 2010 QuikSCAT Analysis of Hurricane Force Extratropical Cyclones in the Pacific Ocean
P7.5 STUDIES OF SEA SURFACE NORMALIZED RADAR CROSS SECTIONS OBSERVED BY CLOUDSAT
 P7.5 STUDIES OF SEA SURFACE NORMALIZED RADAR CROSS SECTIONS OBSERVED BY CLOUDSAT Ninoslav Majurec 1, Joel T. Johnson 1, and Simone Tanelli 1 ElectroScience Laboratory, The Ohio State University, Columbus,
P7.5 STUDIES OF SEA SURFACE NORMALIZED RADAR CROSS SECTIONS OBSERVED BY CLOUDSAT Ninoslav Majurec 1, Joel T. Johnson 1, and Simone Tanelli 1 ElectroScience Laboratory, The Ohio State University, Columbus,
Impact of QuikSCAT Surface Marine Winds on Wave Hindcasting
 Impact of QuikSCAT Surface Marine Winds on Wave Hindcasting V. J. Cardone, A. T. Cox, E. L. Harris, E. A. Orelup and M. J. Parsons Oceanweather Inc. Cos Cob, CT and H. C. Graber Rosensteil School of Marine
Impact of QuikSCAT Surface Marine Winds on Wave Hindcasting V. J. Cardone, A. T. Cox, E. L. Harris, E. A. Orelup and M. J. Parsons Oceanweather Inc. Cos Cob, CT and H. C. Graber Rosensteil School of Marine
Quality Control and Wind Retrieval for SeaWinds
 Quality Control and Wind Retrieval for SeaWinds by M. Portabella and A. Stoffelen Final report of the EUMETSAT QuikSCAT fellowship February 2002 Contents PREFACE... 3 1 INTRODUCTION... 5 2 PRODUCT VALIDATION...
Quality Control and Wind Retrieval for SeaWinds by M. Portabella and A. Stoffelen Final report of the EUMETSAT QuikSCAT fellowship February 2002 Contents PREFACE... 3 1 INTRODUCTION... 5 2 PRODUCT VALIDATION...
Zorana Jelenak Paul S. Chang Khalil Ahmed (OPC) Seubson Soisuvarn Qi Zhu NOAA/NESDIS/STAR-UCAR
 Near Real Time ASCAT Wind Vectors at NOAA and High Wind Issue Zorana Jelenak Paul S. Chang Khalil Ahmed (OPC) Seubson Soisuvarn Qi Zhu NOAA/NESDIS/STAR-UCAR ASCAT Wind Processing Implemented at NOAA Feb
Near Real Time ASCAT Wind Vectors at NOAA and High Wind Issue Zorana Jelenak Paul S. Chang Khalil Ahmed (OPC) Seubson Soisuvarn Qi Zhu NOAA/NESDIS/STAR-UCAR ASCAT Wind Processing Implemented at NOAA Feb
Active rain-gauge concept for liquid clouds using W-band and S-band Doppler radars
 Active rain-gauge concept for liquid clouds using W-band and S-band Doppler radars Leyda León-Colón *a, Sandra L. Cruz-Pol *a, Stephen M. Sekelsky **b a Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Univ.
Active rain-gauge concept for liquid clouds using W-band and S-band Doppler radars Leyda León-Colón *a, Sandra L. Cruz-Pol *a, Stephen M. Sekelsky **b a Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Univ.
The NASA EV-2 Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) Mission
 International Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting Kailua-Kona, Hawaii USA 6-8 May 2013 The NASA EV-2 Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) Mission Chris Ruf (1) (CYGNSS Principal Investigator),
International Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting Kailua-Kona, Hawaii USA 6-8 May 2013 The NASA EV-2 Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) Mission Chris Ruf (1) (CYGNSS Principal Investigator),
Ocean Vector Winds in Storms from the SMAP L-Band Radiometer
 International Workshop on Measuring High Wind Speeds over the Ocean 15 17 November 2016 UK Met Office, Exeter Ocean Vector Winds in Storms from the SMAP L-Band Radiometer Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia Ricciardulli,
International Workshop on Measuring High Wind Speeds over the Ocean 15 17 November 2016 UK Met Office, Exeter Ocean Vector Winds in Storms from the SMAP L-Band Radiometer Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia Ricciardulli,
Uncertainty in Ocean Surface Winds over the Nordic Seas
 Uncertainty in Ocean Surface Winds over the Nordic Seas Dmitry Dukhovskoy and Mark Bourassa Arctic Ocean Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies Florida State University Funded by the NASA OVWST,
Uncertainty in Ocean Surface Winds over the Nordic Seas Dmitry Dukhovskoy and Mark Bourassa Arctic Ocean Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies Florida State University Funded by the NASA OVWST,
THE CYGNSS NANOSATELLITE CONSTELLATION HURRICANE MISSION
 SSTDM2014, International Workshop on Small Satellites andsensor Technology for Disaster Management THE CYGNSS NANOSATELLITE CONSTELLATION HURRICANE MISSION Chris Ruf (1), Scott Gleason (2), Zorana Jelenak
SSTDM2014, International Workshop on Small Satellites andsensor Technology for Disaster Management THE CYGNSS NANOSATELLITE CONSTELLATION HURRICANE MISSION Chris Ruf (1), Scott Gleason (2), Zorana Jelenak
Rain footprints on C-band synthetic aperture radar images of the ocean - Revisited
 1 Remote Sensing of Environment December 2016, Volume 187 Pages 169-185 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.10.015 http://archimer.ifremer.fr/doc/00355/46574/ 2016 Published by Elsevier Inc. Achimer http://archimer.ifremer.fr
1 Remote Sensing of Environment December 2016, Volume 187 Pages 169-185 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.10.015 http://archimer.ifremer.fr/doc/00355/46574/ 2016 Published by Elsevier Inc. Achimer http://archimer.ifremer.fr
Investigate the influence of the Amazon rainfall on westerly wind anomalies and the 2002 Atlantic Nino using QuikScat, Altimeter and TRMM data
 Investigate the influence of the Amazon rainfall on westerly wind anomalies and the 2002 Atlantic Nino using QuikScat, Altimeter and TRMM data Rong Fu 1, Mike Young 1, Hui Wang 2, Weiqing Han 3 1 School
Investigate the influence of the Amazon rainfall on westerly wind anomalies and the 2002 Atlantic Nino using QuikScat, Altimeter and TRMM data Rong Fu 1, Mike Young 1, Hui Wang 2, Weiqing Han 3 1 School
Air-Sea Interaction in Extreme Weather Conditions
 Air-Sea Interaction in Extreme Weather Conditions Hans (J.W.) de Vries, Niels Zweers,, Vladimir Makin, Vladimir Kudryavtsev, and Gerrit Burgers, KNMI, De Bilt, NL Meteogroup, Wageningen, NL NIERSC, St.
Air-Sea Interaction in Extreme Weather Conditions Hans (J.W.) de Vries, Niels Zweers,, Vladimir Makin, Vladimir Kudryavtsev, and Gerrit Burgers, KNMI, De Bilt, NL Meteogroup, Wageningen, NL NIERSC, St.
Improving Surface Flux Parameterizations in the NRL Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System
 Improving Surface Flux Parameterizations in the NRL Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System LONG-TERM GOAL Shouping Wang Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943 Phone: (831) 656-4719
Improving Surface Flux Parameterizations in the NRL Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System LONG-TERM GOAL Shouping Wang Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943 Phone: (831) 656-4719
A NEW SAR RETRIEVAL METHOD FOR HURRICANE WIND PARAMETERS
 A NEW SAR RETRIEVAL METHOD FOR HURRICANE WIND PARAMETERS Antonio Reppucci, Susanne lehner, Johannes Schulz-Stellenfleth German Aerospace Center (DLR) Oberpfaffenhofen 82234 Wessling, Germany. Hurricane
A NEW SAR RETRIEVAL METHOD FOR HURRICANE WIND PARAMETERS Antonio Reppucci, Susanne lehner, Johannes Schulz-Stellenfleth German Aerospace Center (DLR) Oberpfaffenhofen 82234 Wessling, Germany. Hurricane
Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton
 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each & Q. 10 Q. 22 carry two marks each. Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton Q.2 The pair of variables that
Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each & Q. 10 Q. 22 carry two marks each. Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton Q.2 The pair of variables that
Climate data records from OSI SAF scatterometer winds. Anton Verhoef Jos de Kloe Jeroen Verspeek Jur Vogelzang Ad Stoffelen
 Climate data records from OSI SAF scatterometer winds Anton Verhoef Jos de Kloe Jeroen Verspeek Jur Vogelzang Ad Stoffelen Outline Motivation Planning Preparation and methods Quality Monitoring Output
Climate data records from OSI SAF scatterometer winds Anton Verhoef Jos de Kloe Jeroen Verspeek Jur Vogelzang Ad Stoffelen Outline Motivation Planning Preparation and methods Quality Monitoring Output
3D.6 ESTIMATES OF HURRICANE WIND SPEED MEASUREMENT ACCURACY USING THE AIRBORNE HURRICANE IMAGING RADIOMETER
 3D.6 ESTIMATES OF HURRICANE WIND SPEED MEASUREMENT ACCURACY USING THE AIRBORNE HURRICANE IMAGING RADIOMETER Ruba A. Amarin *, Linwood Jones 1, James Johnson 1, Christopher Ruf 2, Timothy Miller 3 and Shuyi
3D.6 ESTIMATES OF HURRICANE WIND SPEED MEASUREMENT ACCURACY USING THE AIRBORNE HURRICANE IMAGING RADIOMETER Ruba A. Amarin *, Linwood Jones 1, James Johnson 1, Christopher Ruf 2, Timothy Miller 3 and Shuyi
from the rain drops is a good indicator of rain rate. Most of the data were collected with the ship stationary and the bow held into the wind. Thus th
 Eects of Rain on Ku band Backscatter from the Ocean Robert F. Contreras Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington Seattle, WA William J. Plant William C. Keller Kenneth Hayes Jerey Nystuen
Eects of Rain on Ku band Backscatter from the Ocean Robert F. Contreras Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington Seattle, WA William J. Plant William C. Keller Kenneth Hayes Jerey Nystuen
Rain Detection and Quality Control of SeaWinds 1
 Rain Detection and Quality Control of SeaWinds 1 M. Portabella, A. Stoffelen KNMI, Postbus 201, 3730 AE De Bilt, The Netherlands Phone: +31 30 2206827, Fax: +31 30 2210843 e-mail: portabel@knmi.nl, stoffelen@knmi.nl
Rain Detection and Quality Control of SeaWinds 1 M. Portabella, A. Stoffelen KNMI, Postbus 201, 3730 AE De Bilt, The Netherlands Phone: +31 30 2206827, Fax: +31 30 2210843 e-mail: portabel@knmi.nl, stoffelen@knmi.nl
A Wind and Rain Backscatter Model Derived from AMSR and SeaWinds Data
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2007-07-13 A Wind and Rain Backscatter Model Derived from AMSR and SeaWinds Data Seth Niels Nielsen Brigham Young University -
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2007-07-13 A Wind and Rain Backscatter Model Derived from AMSR and SeaWinds Data Seth Niels Nielsen Brigham Young University -
Remote Sensing of the Ocean
 Remote Sensing of the Ocean David E. Weissman Professor Department of Engineering The Need for Environmental Observations Just by looking at images of the Earth from space, it s clear that the ocean is
Remote Sensing of the Ocean David E. Weissman Professor Department of Engineering The Need for Environmental Observations Just by looking at images of the Earth from space, it s clear that the ocean is
Analysis of Infrared Measurements of Microbreaking and Whitecaps
 Analysis of Infrared Measurements of Microbreaking and Whitecaps Andrew T. Jessup Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington 1013 NE 40th St. Seattle, WA 98105-6698 phone (206) 685-2609 fax (206)
Analysis of Infrared Measurements of Microbreaking and Whitecaps Andrew T. Jessup Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington 1013 NE 40th St. Seattle, WA 98105-6698 phone (206) 685-2609 fax (206)
WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program
 WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH On-Site Packet Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH WEATHER ON WHEELS ELEMENTARY ON-SITE HIGHLIGHTS PACKET
WEATHER ON WHEELS Elementary School Program MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH On-Site Packet Miami-Dade County Public Schools Miami, Florida MAST ACADEMY OUTREACH WEATHER ON WHEELS ELEMENTARY ON-SITE HIGHLIGHTS PACKET
Impact of the Loss of QuikSCAT on NOAA NWS Marine Warning and
 Impact of the Loss of QuikSCAT on NOAA NWS Marine Warning and Forecast Operations Joseph Sienkiewicz 1 Michael J. Brennan 2, Richard Knabb 3, Paul S. Chang 4, Hugh Cobb 2, Zorana J. Jelenak 5, Khalil A.
Impact of the Loss of QuikSCAT on NOAA NWS Marine Warning and Forecast Operations Joseph Sienkiewicz 1 Michael J. Brennan 2, Richard Knabb 3, Paul S. Chang 4, Hugh Cobb 2, Zorana J. Jelenak 5, Khalil A.
John Steffen and Mark A. Bourassa
 John Steffen and Mark A. Bourassa Funding by NASA Climate Data Records and NASA Ocean Vector Winds Science Team Florida State University Changes in surface winds due to SST gradients are poorly modeled
John Steffen and Mark A. Bourassa Funding by NASA Climate Data Records and NASA Ocean Vector Winds Science Team Florida State University Changes in surface winds due to SST gradients are poorly modeled
Department of Geosciences San Francisco State University Spring Metr 201 Monteverdi Quiz #5 Key (100 points)
 Department of Geosciences Name San Francisco State University Spring 2012 Metr 201 Monteverdi Quiz #5 Key (100 points) 1. Fill in the Blank or short definition. (3 points each for a total of 15 points)
Department of Geosciences Name San Francisco State University Spring 2012 Metr 201 Monteverdi Quiz #5 Key (100 points) 1. Fill in the Blank or short definition. (3 points each for a total of 15 points)
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Event Response
 PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
A - E R - E ON CLIMATE DATA RECORDS, TRENDS AND EXTREMES
 A - E R - E ON CLIMATE DATA RECORDS, TRENDS AND EXTREMES Ad Stoffelen, Anton Verhoef, Jeroen Verspeek, Jos de Kloe, Jur Vogelzang, Maria Belmonte : KNMI, the Netherlands Ana Trindade, Marcos Portabella
A - E R - E ON CLIMATE DATA RECORDS, TRENDS AND EXTREMES Ad Stoffelen, Anton Verhoef, Jeroen Verspeek, Jos de Kloe, Jur Vogelzang, Maria Belmonte : KNMI, the Netherlands Ana Trindade, Marcos Portabella
Friday, September 28, 2007: :30 Tim Liu & Hans Bonekamp Welcome, Organization of Joint meeting
 Friday, September 28, 2007: 8:30 Tim Liu & Hans Bonekamp Welcome, Organization of Joint meeting RESEARCH APPLICATION: Storms and Tropics 8:45-9:00 Kathryn A. Kelly, H. Ryan Jones, Jerome Patoux, James
Friday, September 28, 2007: 8:30 Tim Liu & Hans Bonekamp Welcome, Organization of Joint meeting RESEARCH APPLICATION: Storms and Tropics 8:45-9:00 Kathryn A. Kelly, H. Ryan Jones, Jerome Patoux, James
New NASA Ocean Observations and Coastal Applications
 New NASA Ocean Observations and Coastal Applications Duane Armstrong Chief, Applied Science & Technology Project Office August 20, 2014 1 Outline NASA s new Earth Science Ocean Science Missions for 2014
New NASA Ocean Observations and Coastal Applications Duane Armstrong Chief, Applied Science & Technology Project Office August 20, 2014 1 Outline NASA s new Earth Science Ocean Science Missions for 2014
Long term performance monitoring of ASCAT-A
 Long term performance monitoring of ASCAT-A Craig Anderson and Julia Figa-Saldaña EUMETSAT, Eumetsat Allee 1, 64295 Darmstadt, Germany. Abstract The Advanced Scatterometer (ASCAT) on the METOP series of
Long term performance monitoring of ASCAT-A Craig Anderson and Julia Figa-Saldaña EUMETSAT, Eumetsat Allee 1, 64295 Darmstadt, Germany. Abstract The Advanced Scatterometer (ASCAT) on the METOP series of
A two-season impact study of the Navy s WindSat surface wind retrievals in the NCEP global data assimilation system
 A two-season impact study of the Navy s WindSat surface wind retrievals in the NCEP global data assimilation system Li Bi James Jung John Le Marshall 16 April 2008 Outline WindSat overview and working
A two-season impact study of the Navy s WindSat surface wind retrievals in the NCEP global data assimilation system Li Bi James Jung John Le Marshall 16 April 2008 Outline WindSat overview and working
The impact of rain on ocean wave evolution and its feedback to the atmosphere
 HAROKOPIO UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY ATMOSPHERE AND CLIMATE DYNAMICS GROUP (ACDG) http://meteoclima.gr Coastal Hydrology and Surface Processes linked to Air/Sea Modeling: 1 st community
HAROKOPIO UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY ATMOSPHERE AND CLIMATE DYNAMICS GROUP (ACDG) http://meteoclima.gr Coastal Hydrology and Surface Processes linked to Air/Sea Modeling: 1 st community
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity
 The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
over the Northern West Florida Shelf from SeaWinds and ASCAT
 Interannual Variability of Synoptic Scale Winds over the Northern West Florida Shelf from SeaWinds and ASCAT Steve Morey Mark Bourassa Austin Todd COAPS/FSU This work is sponsored by the NASA Ocean Vector
Interannual Variability of Synoptic Scale Winds over the Northern West Florida Shelf from SeaWinds and ASCAT Steve Morey Mark Bourassa Austin Todd COAPS/FSU This work is sponsored by the NASA Ocean Vector
An Update Usage of ASCAT and OSCAT Winds at the NOAA Ocean Prediction Center (OPC), National Hurricane Center (NHC)
 An Update Usage of ASCAT and OSCAT Winds at the NOAA Ocean Prediction Center (OPC), National Hurricane Center (NHC) Joseph Sienkiewicz (OPC), Michael Brennan (NHC), Gregory McFadden (IMSG), Hugh D. Cobb
An Update Usage of ASCAT and OSCAT Winds at the NOAA Ocean Prediction Center (OPC), National Hurricane Center (NHC) Joseph Sienkiewicz (OPC), Michael Brennan (NHC), Gregory McFadden (IMSG), Hugh D. Cobb
18A.2 PREDICTION OF ATLANTIC TROPICAL CYCLONES WITH THE ADVANCED HURRICANE WRF (AHW) MODEL
 18A.2 PREDICTION OF ATLANTIC TROPICAL CYCLONES WITH THE ADVANCED HURRICANE WRF (AHW) MODEL Jimy Dudhia *, James Done, Wei Wang, Yongsheng Chen, Qingnong Xiao, Christopher Davis, Greg Holland, Richard Rotunno,
18A.2 PREDICTION OF ATLANTIC TROPICAL CYCLONES WITH THE ADVANCED HURRICANE WRF (AHW) MODEL Jimy Dudhia *, James Done, Wei Wang, Yongsheng Chen, Qingnong Xiao, Christopher Davis, Greg Holland, Richard Rotunno,
Ocean Vector Wind as Essential Climate Variable.
 Ocean Vector Wind as Essential Climate Variable Ad.Stoffelen@knmi.nl Context WCRP, World Climate Research Program WOAP, WCRP Observation Assimilation Panel GCOS, Global Climate Observing System Essential
Ocean Vector Wind as Essential Climate Variable Ad.Stoffelen@knmi.nl Context WCRP, World Climate Research Program WOAP, WCRP Observation Assimilation Panel GCOS, Global Climate Observing System Essential
STATUS ON THE USE OF SCATTEROMETER DATA AT METEO FRANCE
 STATUS ON THE USE OF SCATTEROMETER DATA AT METEO FRANCE Christophe Payan Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques, M CNRS-GAME CNRS and Météo-France Toulouse, France 9th International Winds Workshop,
STATUS ON THE USE OF SCATTEROMETER DATA AT METEO FRANCE Christophe Payan Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques, M CNRS-GAME CNRS and Météo-France Toulouse, France 9th International Winds Workshop,
THE SEAWINDS scatterometer has flown twice: once on
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 47, NO. 6, JUNE 2009 1595 A Wind and Rain Backscatter Model Derived From AMSR and SeaWinds Data Seth N. Nielsen and David G. Long, Fellow, IEEE
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 47, NO. 6, JUNE 2009 1595 A Wind and Rain Backscatter Model Derived From AMSR and SeaWinds Data Seth N. Nielsen and David G. Long, Fellow, IEEE
Bringing Consistency into High Wind Measurements with Spaceborne Microwave Radiometers and Scatterometers
 International Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting May 2-4, 2017, Scripps Bringing Consistency into High Wind Measurements with Spaceborne Microwave Radiometers and Scatterometers Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia
International Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting May 2-4, 2017, Scripps Bringing Consistency into High Wind Measurements with Spaceborne Microwave Radiometers and Scatterometers Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia
APPLICATIONS OF SEA-LEVEL PRESSURE
 APPLICATIONS OF SEA-LEVEL PRESSURE RETRIEVAL FROM SCATTEROMETER WINDS Jérôme Patoux, Ralph C. Foster and Robert A. Brown OVWST meeting Seattle, November 20, 2008 Pressure retrieval: how does it work? model
APPLICATIONS OF SEA-LEVEL PRESSURE RETRIEVAL FROM SCATTEROMETER WINDS Jérôme Patoux, Ralph C. Foster and Robert A. Brown OVWST meeting Seattle, November 20, 2008 Pressure retrieval: how does it work? model
Tuesday, September 13, 16
 Weather Weather State Objectives 4.c, 4.d, 4.h. Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? What
Weather Weather State Objectives 4.c, 4.d, 4.h. Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? Discussion What are some ways in which weather affects your everyday life? What
b. The boundary between two different air masses is called a.
 NAME Earth Science Weather WebQuest Part 1. Air Masses 1. Find out what an air mass is. http://okfirst.mesonet.org/train/meteorology/airmasses.html a. What is an air mass? An air mass is b. The boundary
NAME Earth Science Weather WebQuest Part 1. Air Masses 1. Find out what an air mass is. http://okfirst.mesonet.org/train/meteorology/airmasses.html a. What is an air mass? An air mass is b. The boundary
l(aolu) = _ " (ai - M(u,x,... ))2 (4) L c;;(u)2
 SIMULTANEOUS WIND AND RAIN RETRIEVAL USING SEA WINDS DATA David W. Draper and David G. Long Brigham Young University, MERS Laboratory: 459 CB, Provo, UT 84602 801-422-4884, FAX: 801-378-6586, draperd@et.byu.edu
SIMULTANEOUS WIND AND RAIN RETRIEVAL USING SEA WINDS DATA David W. Draper and David G. Long Brigham Young University, MERS Laboratory: 459 CB, Provo, UT 84602 801-422-4884, FAX: 801-378-6586, draperd@et.byu.edu
Earth Exploration-Satellite Service (EESS)- Active Spaceborne Remote Sensing and Operations
 Earth Exploration-Satellite Service (EESS)- Active Spaceborne Remote Sensing and Operations SRTM Radarsat JASON Seawinds TRMM Cloudsat Bryan Huneycutt (USA) Charles Wende (USA) WMO, Geneva, Switzerland
Earth Exploration-Satellite Service (EESS)- Active Spaceborne Remote Sensing and Operations SRTM Radarsat JASON Seawinds TRMM Cloudsat Bryan Huneycutt (USA) Charles Wende (USA) WMO, Geneva, Switzerland
Earth Observatory, Columbia University
 Satellite-Based Mid dlatitude Cyclone Statistics Over the Southern Ocean -- Tracks and Su urface Fluxes Xiaojun Yuan August 19, 2009 In collaboration with Jérôme Pato oux at University of Washington and
Satellite-Based Mid dlatitude Cyclone Statistics Over the Southern Ocean -- Tracks and Su urface Fluxes Xiaojun Yuan August 19, 2009 In collaboration with Jérôme Pato oux at University of Washington and
ARUBA CLIMATOLOGICAL SUMMARY 2017 PRECIPITATION
 ARUBA CLIMATOLOGICAL SUMMARY 2017 PRECIPITATION The total amount of rainfall recorded at Reina Beatrix International Airport for the year 2017 was 391.0 mm. This is 17.1 % below normal ( Figure 1 ). During
ARUBA CLIMATOLOGICAL SUMMARY 2017 PRECIPITATION The total amount of rainfall recorded at Reina Beatrix International Airport for the year 2017 was 391.0 mm. This is 17.1 % below normal ( Figure 1 ). During
IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST. (a) (b) (c)
 9B.3 IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST Tetsuya Iwabuchi *, J. J. Braun, and T. Van Hove UCAR, Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
9B.3 IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST Tetsuya Iwabuchi *, J. J. Braun, and T. Van Hove UCAR, Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
Atmospheric Processes
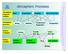 Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction in Tropical Cyclones
 Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction in Tropical Cyclones Isaac Ginis University of Rhode Island Collaborators: T. Hara, Y.Fan, I-J Moon, R. Yablonsky. ECMWF, November 10-12, 12, 2008 Air-Sea Interaction in Tropical
Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction in Tropical Cyclones Isaac Ginis University of Rhode Island Collaborators: T. Hara, Y.Fan, I-J Moon, R. Yablonsky. ECMWF, November 10-12, 12, 2008 Air-Sea Interaction in Tropical
Preliminary assessment of LAWR performance in tropical regions with high intensity convective rainfall
 Preliary assessment of LAWR performance in tropical regions with high intensity convective rainfall Chris Nielsen: DHI Water and Environment (Malaysia), Fanny Dugelay, Universitéde Nice Sophia Antipolis,
Preliary assessment of LAWR performance in tropical regions with high intensity convective rainfall Chris Nielsen: DHI Water and Environment (Malaysia), Fanny Dugelay, Universitéde Nice Sophia Antipolis,
Thermodynamic and Flux Observations of the Tropical Cyclone Surface Layer
 Thermodynamic and Flux Observations of the Tropical Cyclone Surface Layer 1. INTRODUCTION Alex M. Kowaleski and Jenni L. Evans 1 The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA Understanding tropical
Thermodynamic and Flux Observations of the Tropical Cyclone Surface Layer 1. INTRODUCTION Alex M. Kowaleski and Jenni L. Evans 1 The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA Understanding tropical
OCEAN VECTOR WINDS IN STORMS FROM THE SMAP L-BAND RADIOMETER
 Proceedings for the 2016 EUMETSAT Meteorological Satellite Conference, 26-30 September 2016, Darmstadt, Germany OCEAN VECTOR WINDS IN STORMS FROM THE SMAP L-BAND RADIOMETER Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia Ricciardulli,
Proceedings for the 2016 EUMETSAT Meteorological Satellite Conference, 26-30 September 2016, Darmstadt, Germany OCEAN VECTOR WINDS IN STORMS FROM THE SMAP L-BAND RADIOMETER Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia Ricciardulli,
Wind, Current, Wave, and Stress Coupling in the Boundary Layer and A Plan for Observing This Coupling from Space
 Wind, Current, Wave, and Stress Coupling in the Boundary Layer and A Plan for Observing This Coupling from Space Mark A. Bourassa and Qi Shi COAPS, EOAS & GFDI, Florida State University With input from
Wind, Current, Wave, and Stress Coupling in the Boundary Layer and A Plan for Observing This Coupling from Space Mark A. Bourassa and Qi Shi COAPS, EOAS & GFDI, Florida State University With input from
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY. Metr Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts. Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation.
 DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY NAME Metr 356.01 Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation. Figure 1. Surface Chart for 1500Z 7 September 2007 1 1. Pressure
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY NAME Metr 356.01 Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation. Figure 1. Surface Chart for 1500Z 7 September 2007 1 1. Pressure
Surface Wind/Stress Structure under Hurricane
 Surface Wind/Stress Structure under Hurricane W. Timothy Liu and Wenqing Tang, JPL Asymmetry Relating wind to stress 2008 NASA Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting, 19-21 November 2008, Seattle, WA Asymmetry
Surface Wind/Stress Structure under Hurricane W. Timothy Liu and Wenqing Tang, JPL Asymmetry Relating wind to stress 2008 NASA Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting, 19-21 November 2008, Seattle, WA Asymmetry
4 Forecasting Weather
 CHAPTER 2 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather? How
CHAPTER 2 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather? How
P2.57 PRECIPITATION STRUCTURE IN MIDLATITUDE CYCLONES
 P2.57 PRECIPITATION STRUCTURE IN MIDLATITUDE CYCLONES Paul R. Field 1, Robert Wood 2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado. 2. University of Washington, Seattle, Washington. 1.
P2.57 PRECIPITATION STRUCTURE IN MIDLATITUDE CYCLONES Paul R. Field 1, Robert Wood 2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado. 2. University of Washington, Seattle, Washington. 1.
Radiometric Calibration of RapidScat Using the GPM Microwave Imager
 Proceedings Radiometric Calibration of RapidScat Using the GPM Microwave Imager Ali Al-Sabbagh *, Ruaa Alsabah and Josko Zec Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Florida Institute of Technology,
Proceedings Radiometric Calibration of RapidScat Using the GPM Microwave Imager Ali Al-Sabbagh *, Ruaa Alsabah and Josko Zec Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Florida Institute of Technology,
CFRSL A STATISTICAL ALGORITHM FOR INFERRING RAIN RATE FROM THE QUIKSCAT RADIOMETER. Yanxia Wang
 A STATISTICAL ALGORITHM FOR INFERRING RAIN RATE FROM THE QUIKSCAT RADIOMETER Yanxia Wang M.S.E.E. Wuhan Technical University of Surveying&Mapping Wuhan, China, 1996 Advisor: W. Linwood Jones 1 Rain Rate
A STATISTICAL ALGORITHM FOR INFERRING RAIN RATE FROM THE QUIKSCAT RADIOMETER Yanxia Wang M.S.E.E. Wuhan Technical University of Surveying&Mapping Wuhan, China, 1996 Advisor: W. Linwood Jones 1 Rain Rate
CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: PROLOGUE The Local Environment... 1 Observation, Inference, Classification Properties of the Environment...
 CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: PROLOGUE The Local Environment... 1 Observation, Inference, Classification Properties of the Environment... 3 Measurement, Percent Deviation From Accepted Value Density... 6 Density
CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: PROLOGUE The Local Environment... 1 Observation, Inference, Classification Properties of the Environment... 3 Measurement, Percent Deviation From Accepted Value Density... 6 Density
Op#mized Tropical Cyclone Retrievals from ASCAT, OceanSAT- 2 and QuikSCAT
 Op#mized Tropical Cyclone Retrievals from ASCAT, OceanSAT- 2 and QuikSCAT Bryan W. S#les, Alex Fore, W. Lee Poulsen, Svetla- Hristova Veleva Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Ins#tute of Technology
Op#mized Tropical Cyclone Retrievals from ASCAT, OceanSAT- 2 and QuikSCAT Bryan W. S#les, Alex Fore, W. Lee Poulsen, Svetla- Hristova Veleva Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Ins#tute of Technology
El Niño, South American Monsoon, and Atlantic Niño links as detected by a. TOPEX/Jason Observations
 El Niño, South American Monsoon, and Atlantic Niño links as detected by a decade of QuikSCAT, TRMM and TOPEX/Jason Observations Rong Fu 1, Lei Huang 1, Hui Wang 2, Paola Arias 1 1 Jackson School of Geosciences,
El Niño, South American Monsoon, and Atlantic Niño links as detected by a decade of QuikSCAT, TRMM and TOPEX/Jason Observations Rong Fu 1, Lei Huang 1, Hui Wang 2, Paola Arias 1 1 Jackson School of Geosciences,
Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics
 Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics Jimy Dudhia MMM Division, NCAR 1D Ocean Mixed-Layer Model 1d model based on Pollard, Rhines and Thompson (1973) was added for hurricane forecasts Purpose is to represent
Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics Jimy Dudhia MMM Division, NCAR 1D Ocean Mixed-Layer Model 1d model based on Pollard, Rhines and Thompson (1973) was added for hurricane forecasts Purpose is to represent
Coupled Ocean Circulation and Wind-Wave Models With Data Assimilation Using Altimeter Statistics
 Coupled Ocean Circulation and Wind-Wave Models With Data Assimilation Using Altimeter Statistics Abstract ZHANG HONG, SANNASIRAJ, S.A., MD. MONIRUL ISLAM AND CHOO HENG KEK Tropical Marine Science Institute,
Coupled Ocean Circulation and Wind-Wave Models With Data Assimilation Using Altimeter Statistics Abstract ZHANG HONG, SANNASIRAJ, S.A., MD. MONIRUL ISLAM AND CHOO HENG KEK Tropical Marine Science Institute,
APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1
 APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1 1. Introduction Precipitation is one of most important environmental parameters.
APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1 1. Introduction Precipitation is one of most important environmental parameters.
Solutions Manual to Exercises for Weather & Climate, 8th ed. Appendix A Dimensions and Units 60 Appendix B Earth Measures 62 Appendix C GeoClock 63
 Solutions Manual to Exercises for Weather & Climate, 8th ed. 1 Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere 1 2 Earth Sun Geometry 4 3 The Surface Energy Budget 8 4 The Global Energy Budget 10 5 Atmospheric Moisture
Solutions Manual to Exercises for Weather & Climate, 8th ed. 1 Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere 1 2 Earth Sun Geometry 4 3 The Surface Energy Budget 8 4 The Global Energy Budget 10 5 Atmospheric Moisture
Effect of Typhoon-Driven Ocean Waves on Sea-to-Air Transfer of Dimethylsulfide (DMS)
 Effect of Typhoon-Driven Ocean Waves on Sea-to-Air Transfer of Dimethylsulfide (DMS) Peter C Chu Department of Oceanography Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, California, USA pcchu@nps.edu http://www.oc.nps.navy.mil/~chu
Effect of Typhoon-Driven Ocean Waves on Sea-to-Air Transfer of Dimethylsulfide (DMS) Peter C Chu Department of Oceanography Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, California, USA pcchu@nps.edu http://www.oc.nps.navy.mil/~chu
Sea ice extent from satellite microwave sensors
 Sea ice extent from satellite microwave sensors Maria Belmonte Rivas Introduction In 2007, the summer extent of Arctic sea ice observed by the Special Sensor Microwave Imager (SSM/I) reached its lowest
Sea ice extent from satellite microwave sensors Maria Belmonte Rivas Introduction In 2007, the summer extent of Arctic sea ice observed by the Special Sensor Microwave Imager (SSM/I) reached its lowest
Scatterometer winds.
 Scatterometer winds Ad.Stoffelen@KNMI.nl Manager NWP SAF at KNMI Manager OSI SAF at KNMI PI European OSCAT Cal/Val project Leader KNMI Satellite Winds Group www.knmi.nl/scatterometer scat@knmi.nl Overview
Scatterometer winds Ad.Stoffelen@KNMI.nl Manager NWP SAF at KNMI Manager OSI SAF at KNMI PI European OSCAT Cal/Val project Leader KNMI Satellite Winds Group www.knmi.nl/scatterometer scat@knmi.nl Overview
J16.1 PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT OF ASCAT OCEAN SURFACE VECTOR WIND (OSVW) RETRIEVALS AT NOAA OCEAN PREDICTION CENTER
 J16.1 PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT OF ASCAT OCEAN SURFACE VECTOR WIND (OSVW) RETRIEVALS AT NOAA OCEAN PREDICTION CENTER Khalil. A. Ahmad* PSGS/NOAA/NESDIS/StAR, Camp Springs, MD Joseph Sienkiewicz NOAA/NWS/NCEP/OPC,
J16.1 PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT OF ASCAT OCEAN SURFACE VECTOR WIND (OSVW) RETRIEVALS AT NOAA OCEAN PREDICTION CENTER Khalil. A. Ahmad* PSGS/NOAA/NESDIS/StAR, Camp Springs, MD Joseph Sienkiewicz NOAA/NWS/NCEP/OPC,
