Air-Sea Interaction in Extreme Weather Conditions
|
|
|
- Joella Millicent Cole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Air-Sea Interaction in Extreme Weather Conditions Hans (J.W.) de Vries, Niels Zweers,, Vladimir Makin, Vladimir Kudryavtsev, and Gerrit Burgers, KNMI, De Bilt, NL Meteogroup, Wageningen, NL NIERSC, St. Petersburg, RU Rijkswaterstaat, Lelystad, NL. Introduction The vulnerability of coastal areas, e.g. around the North Sea, for storm surges prompts for accurate forecasts, especially in cases of extreme weather. Over the North Sea wind speeds rarely exceed 5 m/s in the present climate. That means that more conventional descriptions of the boundary layer, like a Charnock relation, are adequate for use in atmospheric and oceanic models. For higher wind speeds, observational data (e.g. Powell et al. ; Holthuijsen et al. ) show that a Charnock-type drag relation in which the drag coefficient increases monotonically, is not valid anymore and that the drag coefficient levels off around m/s. In a future warmer climate, autumn storms in mid-latitude areas might well get more intensive (Baatsen et al. 5), and such wind speeds more prevalent. Models that are currently in use for weather and storm surge forecasting use a Charnock relation for the marine atmospheric boundary layer (MABL), and are not able to properly represent such events. In this paper we investigate the application of alternative parametrizations for the exchange of momentum, heat and moisture between atmosphere and ocean in a limited area atmospheric model. We will not go into the details of the parametrizations, but focus on the ability to forecast extreme storms. Because such extreme storms do not (yet) occur on the North Sea, the models are tested in the Gulf of Mexico with hurricanes Ivan () and Katrina (5).. A sea drag relation for hurricane wind speeds To include the effect of spray droplets on the drag, which becomes significant for wind speeds above m/s, and also the effects of air-flow sepraration, the standard Charnock drag relation was extended, see Zweers et al. (). The resulting drag coefficient is given in Figure, which also shows observed data by Powell et al. () and Holthuijsen et al. (). 6 5 C D (x ) 5 6 U (m s ) Fig.. Drag coefficient as function of the -m wind speed. Red is a Charnock relation, blue the extended relation from Section, green the parametrization from Section. Data points in black are from Powell et al. (), in brown from Holthuijsen et al. (). KNMI, PO Box, NL-7 AE De Bilt, mailto:hans.de.vries@knmi.nl
2 9 W 87 W 8 W 8 W 9 W 87 W 8 W 8 W N N N N N N N N 8 N 8 N 8 N 8 N N N N N N N N N 9 W 87 W 8 W 8 W 9 W 87 W 8 W 8 W Fig.. Hurricane track for Ivan (left) and Katrina (right) with the Charnock relation (red) and the extended drag parameterization (blue), in the 8h (circles), 7h (diamonds) and 96h (triangles) HIRLAM forecasts. Observed tracks according to the National Hurricane Centre are shown in black. This extended drag relation was built into the NWP model Hirlam and applied in the Gulf of Mexico for hurricanes Ivan () and Katrina (5). The Hirlam model uses a grid size of.5 X and vertical levels with the lowest level at approximately m. The dynamics time step is min. Lateral boundary conditions are taken from the European Centre (ECMWF) model archive. Figures and give some key results of these simulations. The alternative drag parametrization has little effect on the hurricane tracks (Figure ). The intensity of the storms, however, represented by the maximum -m wind speed and the pressure in the centre of the storm, becomes significantly stronger and closer to the observed values from the National Hurricane Center in comparison with a standard Charnock formulation as shown in Figure for the combination of successive Hirlam analyses. Application to storm surge The improved hurricane intensity does not automatically lead to higher storm surges, because the increased wind speeds are accompanied by decreased drag. In fact, it can be shown (Zweers et al. ) that just decreasing the drag coefficient consistently in the atmospheric and the storm surge model always leads to lower surges. To test this, the Hirlam simulations for hurricanes Ivan and Katrina were used to drive a D-version of the hydrodynamical model DelftD. Effectively, the wind stress was taken directly from Hirlam, without a separate drag relation in the storm surge model. Figures and 5 give some time series results for coastal locations. They show indeed that, despite the higher wind speeds with the extended drag relation, the peak of the surge has not increased.. The impact of spray-mediated enhanced enthalpy and reduced drag coefficients in the modelling of tropical cyclones In Section, a method was explored that decreases the momentum exchange coefficient in the MABL, but there the ensuing changes in the exchange of heat and moisture are not very large. This Section will explore a different method, based on Kudryavtsev and Makin (), and further developed in Kudryavtsev et al. (), in which the impact of spray droplets on the momentum flux is directly accounted for through a spray stress. The model produces a decrease in the drag at very high wind speeds, in agreement with available measurements in these conditions, and the air-sea exchange of enthalpy (heat and moisture) is enhanced. The wind profile is still assumed to be logarithmic with height. In Figure this drag relation is shown in green. As in Section, the new parametrization was implemented in Hirlam and applied to hurricanes Ivan and Katrina. Sea surface temperatures (SSTs) for the Hirlam surface analysis are taken from the ECMWF archive and remain fixed during the forecast period. This is a valid method in normal weather conditions
3 U max (m s ) 8 6 U max (m s ) 8 6 /9 /9 /9 /9 5/9 6/9 7/9 5/8 6/8 7/8 8/8 9/8 / Observed (NHC) Charnock Zweers et al. () /9 /9 /9 /9 5/9 6/9 7/9 5/8 6/8 7/8 8/8 9/8 /8 Fig.. Maximum -meter wind speed (top) and central pressure (bottom) in successive Hirlam analyses for hurricanes Ivan (left) and Katrina (right). Colors are as in Figure. Fig.. Storm surges simulated with DelftD in Dauphin Island and Pensacola during hurricane Ivan. Colors are as in Figure, black: observations.
4 Fig. 5. Storm surges simulated with DelftD in Gulfport and Bay Waveland Yacht Club during hurricane Katrina. Colors are as in Figure, the green curves are driven by the H*wind analysis of the Hurricane Research Division with the extended drag relation. U max (m s ) 8 6 U max (m s ) 8 6 /9 /9 /9 /9 5/9 6/9 7/9 5/8 6/8 7/8 8/8 9/8 / Observed (NHC) KMZ KMZ, SSTs reduced /9 /9 /9 /9 5/9 6/9 7/9 5/8 6/8 7/8 8/8 9/8 /8 Fig. 6. Maximum -meter wind speed (top) and central pressure (bottom) in successive Hirlam analyses for hurricanes Ivan (left) and Katrina (right). Calculations with default SSTs (block-dotted) and reduced SSTs (dashed).
5 where SSTs do not change rapidly. In hurricane conditions, however, upwelling, currents generated in the upper layer of the ocean and heat uptake by the tropical cyclone, locally reduce the SSTs. This in turn affects the enthalpy exchange and therefore the intensity of the storm. To account for this, an alternative scenario was also tested in which the SSTs were reduced with K / h in grid points where the -m wind speed exceeded m/s. Results for the maximum wind speed and central pressure in hurricanes Ivan and Katrina are given in Figure 6. This shows simulations with standard handling of the SSTs and also with the reduced SSTs. With the standard SSTs the intensity of the hurricanes are overestimated, but the rather simple reduction of the SSTs underneath the cyclones leads to much more realistic results.. Conclusions For a realistic representation of the intensity of tropical cyclones in a Limited Area NWP model, the drag needs to level off for high wind speeds. Simultaneous increase of the heat and moisture exchange with unaltered SSTs, however, leads to overestimation of tropical-cyclone intensity. But even a simple reduction of SSTs underneath the cyclone leads to much more realistic results. This suggests that a coupled NWP-ocean model is necessary for proper forecasts of extreme storms. References Baatsen, M., R. Haarsma, A. Van Delden, and H. de Vries, 5: Severe autumn storms in future western europe with a warmer atlantic ocean. Climate Dynamics, 5 (-), 99 96, doi:.7/ s Holthuijsen, L. H., M. D. Powell, and J. D. Pietrzak, : Wind and waves in extreme hurricanes. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 7 (C9), doi:.9/jc798, c9. Kudryavtsev, V. and V. Makin, : Impact of ocean spray on the dynamics of the marine atmospheric boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, (), 8, doi:.7/ s Kudryavtsev, V., V. Makin, and S. Zilitinkevich, : On the sea-surface drag and heat/mass transfer at strong winds. Scientific Reports WR -, KNMI. Powell, M. D., P. J. Vickery, and T. A. Reinhold, : Reduced drag coefficient for high wind speeds in tropical cyclones. Nature,, 79 8, doi:.8/nature8. Vatvani, D., N. C. Zweers, M. van Ormondt, A. J. Smale, J. W. de Vries, and V. K. Makin, : Storm surge and wave simulations in the gulf of mexico using a consistent drag relation for atmospheric and storm surge models. Natural Hazards and Earth System Science, (7), 99, doi:. 59/nhess Zweers, N. C., V. K. Makin, J. W. de Vries, and G. Burgers, : A sea drag relation for hurricane wind speeds. Geophys. Res. Lett., 7 (), L 8, doi:.9/gl5. Zweers, N. C., V. K. Makin, J. W. de Vries, and G. Burgers, : On the influence of changes in the drag relation on surface wind speeds and storm surge forecasts. Natural Hazards, 6 (), 7 9, doi:.7/s z. Zweers, N. C., V. K. Makin, J. W. de Vries, and V. N. Kudryavtsev, 5: The impact of spraymediated enhanced enthalpy and reduced drag coefficients in the modelling of tropical cyclones. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 55 (), 5 5, doi:.7/s
Storm surge and wave simulations in the Gulf of Mexico using a consistent drag relation for atmospheric and storm surge models
 doi:10.5194/nhess-12-2399-2012 Author(s) 2012. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Storm surge and wave simulations in the Gulf of Mexico using a consistent drag relation
doi:10.5194/nhess-12-2399-2012 Author(s) 2012. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Storm surge and wave simulations in the Gulf of Mexico using a consistent drag relation
Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction in Tropical Cyclones
 Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction in Tropical Cyclones Isaac Ginis University of Rhode Island Collaborators: T. Hara, Y.Fan, I-J Moon, R. Yablonsky. ECMWF, November 10-12, 12, 2008 Air-Sea Interaction in Tropical
Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction in Tropical Cyclones Isaac Ginis University of Rhode Island Collaborators: T. Hara, Y.Fan, I-J Moon, R. Yablonsky. ECMWF, November 10-12, 12, 2008 Air-Sea Interaction in Tropical
Improving Surface Flux Parameterizations in the NRL Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System
 Improving Surface Flux Parameterizations in the NRL Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System LONG-TERM GOAL Shouping Wang Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943 Phone: (831) 656-4719
Improving Surface Flux Parameterizations in the NRL Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System LONG-TERM GOAL Shouping Wang Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943 Phone: (831) 656-4719
18A.2 PREDICTION OF ATLANTIC TROPICAL CYCLONES WITH THE ADVANCED HURRICANE WRF (AHW) MODEL
 18A.2 PREDICTION OF ATLANTIC TROPICAL CYCLONES WITH THE ADVANCED HURRICANE WRF (AHW) MODEL Jimy Dudhia *, James Done, Wei Wang, Yongsheng Chen, Qingnong Xiao, Christopher Davis, Greg Holland, Richard Rotunno,
18A.2 PREDICTION OF ATLANTIC TROPICAL CYCLONES WITH THE ADVANCED HURRICANE WRF (AHW) MODEL Jimy Dudhia *, James Done, Wei Wang, Yongsheng Chen, Qingnong Xiao, Christopher Davis, Greg Holland, Richard Rotunno,
Importance of air-sea interaction on the coupled typhoon-wave-ocean modeling
 Importance of air-sea interaction on the coupled typhoon-wave-ocean modeling Collaborators: I. Ginis (GSO/URI) T. Hara (GSO/URI) B. Thomas (GSO/URI) H. Tolman (NCEP/NOAA) IL-JU MOON ( 文一柱 ) Cheju National
Importance of air-sea interaction on the coupled typhoon-wave-ocean modeling Collaborators: I. Ginis (GSO/URI) T. Hara (GSO/URI) B. Thomas (GSO/URI) H. Tolman (NCEP/NOAA) IL-JU MOON ( 文一柱 ) Cheju National
Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate
 Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate Will Perrie, Lanli Guo, Zhenxia Long, Bash Toulany Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth, NS Abstract
Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate Will Perrie, Lanli Guo, Zhenxia Long, Bash Toulany Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth, NS Abstract
Thermodynamic and Flux Observations of the Tropical Cyclone Surface Layer
 Thermodynamic and Flux Observations of the Tropical Cyclone Surface Layer 1. INTRODUCTION Alex M. Kowaleski and Jenni L. Evans 1 The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA Understanding tropical
Thermodynamic and Flux Observations of the Tropical Cyclone Surface Layer 1. INTRODUCTION Alex M. Kowaleski and Jenni L. Evans 1 The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA Understanding tropical
1. What type of wind is needed for a hurricane to form? Low to medium winds, blowing in the same direction (weak wind shear).
 Explain 1. What type of wind is needed for a hurricane to form? Low to medium winds, blowing in the same direction (weak wind shear). 2. What is wind shear? Any change in wind speed or direction. When
Explain 1. What type of wind is needed for a hurricane to form? Low to medium winds, blowing in the same direction (weak wind shear). 2. What is wind shear? Any change in wind speed or direction. When
HWRF Ocean: MPIPOM-TC
 HWRF v3.7a Tutorial Nanjing, China, December 2, 2015 HWRF Ocean: MPIPOM-TC Ligia Bernardet NOAA SRL Global Systems Division, Boulder CO University of Colorado CIRS, Boulder CO Acknowledgement Richard Yablonsky
HWRF v3.7a Tutorial Nanjing, China, December 2, 2015 HWRF Ocean: MPIPOM-TC Ligia Bernardet NOAA SRL Global Systems Division, Boulder CO University of Colorado CIRS, Boulder CO Acknowledgement Richard Yablonsky
A Climatology of Landfalling Hurricane Central Pressures Along the Gulf of Mexico Coast
 A Climatology of Landfalling Hurricane Central Pressures Along the Gulf of Mexico Coast David H. Levinson NOAA National Climatic Data Center Asheville, NC Peter J. Vickery Applied Research Associates,
A Climatology of Landfalling Hurricane Central Pressures Along the Gulf of Mexico Coast David H. Levinson NOAA National Climatic Data Center Asheville, NC Peter J. Vickery Applied Research Associates,
2 1-D Experiments, near surface output
 Tuning CBR A.B.C. Tijm 1 Introduction The pre 6.2 reference Hirlam versions have a positive bias in the wind direction under stable conditions (night and winter conditions), accompanied by too strong near
Tuning CBR A.B.C. Tijm 1 Introduction The pre 6.2 reference Hirlam versions have a positive bias in the wind direction under stable conditions (night and winter conditions), accompanied by too strong near
Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics
 Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics Jimy Dudhia MMM Division, NCAR 1D Ocean Mixed-Layer Model 1d model based on Pollard, Rhines and Thompson (1973) was added for hurricane forecasts Purpose is to represent
Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics Jimy Dudhia MMM Division, NCAR 1D Ocean Mixed-Layer Model 1d model based on Pollard, Rhines and Thompson (1973) was added for hurricane forecasts Purpose is to represent
Impact of sea surface temperature on COSMO forecasts of a Medicane over the western Mediterranean Sea
 Impact of sea surface temperature on COSMO forecasts of a Medicane over the western Mediterranean Sea V. Romaniello (1), P. Oddo (1), M. Tonani (1), L. Torrisi (2) and N. Pinardi (3) (1) National Institute
Impact of sea surface temperature on COSMO forecasts of a Medicane over the western Mediterranean Sea V. Romaniello (1), P. Oddo (1), M. Tonani (1), L. Torrisi (2) and N. Pinardi (3) (1) National Institute
Experimental Probabilistic Hurricane Inundation Surge Height (PHISH) Guidance
 Experimental Probabilistic Hurricane Inundation Surge Height (PHISH) Guidance DRBC Flood Advisory Committee John Kuhn - NWS/OCWWS Anne Myckow (NWS/MDL), Arthur Taylor (NWS/MDL) SLOSH Sea, Lake and Overland
Experimental Probabilistic Hurricane Inundation Surge Height (PHISH) Guidance DRBC Flood Advisory Committee John Kuhn - NWS/OCWWS Anne Myckow (NWS/MDL), Arthur Taylor (NWS/MDL) SLOSH Sea, Lake and Overland
Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones
 Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Weather Systems Tropical disturbance a cluster of thunderstorms about 250 to 600 km in diameter, originating in the tropics or sub-tropics Tropical depression a cluster
Chapter 24 Tropical Cyclones Tropical Weather Systems Tropical disturbance a cluster of thunderstorms about 250 to 600 km in diameter, originating in the tropics or sub-tropics Tropical depression a cluster
The effects of wind-driven waves and ocean spray on the drag coefficient and near-surface wind profiles over the ocean
 Acta Oceanol. Sin., 216, Vol. 35, No. 11, P. 79 85 DOI: 1.17/s13131-16-95-6 http://www.hyxb.org.cn E-mail: hyxbe@263.net The effects of wind-driven waves and ocean spray on the drag coefficient and near-surface
Acta Oceanol. Sin., 216, Vol. 35, No. 11, P. 79 85 DOI: 1.17/s13131-16-95-6 http://www.hyxb.org.cn E-mail: hyxbe@263.net The effects of wind-driven waves and ocean spray on the drag coefficient and near-surface
Global Climate Change and Human Health Cycloning out of Control: Climate Change Impacts on Natural Disasters; Cyclones
 INSTRUCTOR BACKGROUND Cyclones are one of the world s most devastating natural disasters causing billions of dollars in damages to homes, building and infrastructure annually. The United Nations estimates
INSTRUCTOR BACKGROUND Cyclones are one of the world s most devastating natural disasters causing billions of dollars in damages to homes, building and infrastructure annually. The United Nations estimates
Hurricane Katrina Tracking Lab
 Hurricane Katrina Tracking Lab Introduction: The 2005 hurricane season was the most active season on record resulting in 28 named storms. Hurricane Katrina was the eleventh named storm and would end up
Hurricane Katrina Tracking Lab Introduction: The 2005 hurricane season was the most active season on record resulting in 28 named storms. Hurricane Katrina was the eleventh named storm and would end up
Air-Sea Interaction: Physics of air-surface interactions and coupling to ocean/atmosphere BL processes
 Air-Sea Interaction: Physics of air-surface interactions and coupling to ocean/atmosphere BL processes Emphasize surface fluxes Statement of problem Present status Parameterization issues An amusing case
Air-Sea Interaction: Physics of air-surface interactions and coupling to ocean/atmosphere BL processes Emphasize surface fluxes Statement of problem Present status Parameterization issues An amusing case
Impact of the Waves on the Sea Surface Roughness Length under Idealized Like-Hurricane Wind Conditions (Part II)
 Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 2015, 5, 326-335 Published Online July 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/acs http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/acs.2015.53025 Impact of the Waves on the Sea Surface
Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 2015, 5, 326-335 Published Online July 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/acs http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/acs.2015.53025 Impact of the Waves on the Sea Surface
Improving Air-Sea Coupling Parameterizations in High-Wind Regimes
 Improving Air-Sea Coupling Parameterizations in High-Wind Regimes PI: Dr. Shuyi S. Chen Co-PI: Dr. Mark A. Donelan Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, University of Miami 4600 Rickenbacker
Improving Air-Sea Coupling Parameterizations in High-Wind Regimes PI: Dr. Shuyi S. Chen Co-PI: Dr. Mark A. Donelan Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, University of Miami 4600 Rickenbacker
The benefits and developments in ensemble wind forecasting
 The benefits and developments in ensemble wind forecasting Erik Andersson Slide 1 ECMWF European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Slide 1 ECMWF s global forecasting system High resolution forecast
The benefits and developments in ensemble wind forecasting Erik Andersson Slide 1 ECMWF European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Slide 1 ECMWF s global forecasting system High resolution forecast
Robert Weaver, Donald Slinn 1
 1 1 Robert Weaver, Donald Slinn 1 Department of Civil and Coastal Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida Supported by the US Office of Naval Research AGU Fall Meeting 2002 Poster OS72A-0342
1 1 Robert Weaver, Donald Slinn 1 Department of Civil and Coastal Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida Supported by the US Office of Naval Research AGU Fall Meeting 2002 Poster OS72A-0342
Projection of Extreme Wave Climate Change under Global Warming
 Hydrological Research Letters, 4, 15 19 (2010) Published online in J-STAGE (www.jstage.jst.go.jp/browse/hrl). DOI: 10.3178/HRL.4.15 Projection of Extreme Wave Climate Change under Global Warming Nobuhito
Hydrological Research Letters, 4, 15 19 (2010) Published online in J-STAGE (www.jstage.jst.go.jp/browse/hrl). DOI: 10.3178/HRL.4.15 Projection of Extreme Wave Climate Change under Global Warming Nobuhito
Tropical Cyclone Atmospheric Forcing 1 for Ocean Response Models: Approaches and Issues
 Tropical Cyclone Atmospheric Forcing 1 for Ocean Response Models: Approaches and Issues Vincent Cardone and Andrew Cox Oceanweather Inc. Cos Cob, CT, USA DEFINITION: 1 Specification of time and space evolution
Tropical Cyclone Atmospheric Forcing 1 for Ocean Response Models: Approaches and Issues Vincent Cardone and Andrew Cox Oceanweather Inc. Cos Cob, CT, USA DEFINITION: 1 Specification of time and space evolution
PREDICTING TROPICAL CYCLONE FORERUNNER SURGE. Abstract
 PREDICTING TROPICAL CYCLONE FORERUNNER SURGE Yi Liu 1 and Jennifer L. Irish 1 Abstract In 2008 during Hurricane Ike, a 2-m forerunner surge, early surge arrival before tropical cyclone landfall, flooded
PREDICTING TROPICAL CYCLONE FORERUNNER SURGE Yi Liu 1 and Jennifer L. Irish 1 Abstract In 2008 during Hurricane Ike, a 2-m forerunner surge, early surge arrival before tropical cyclone landfall, flooded
Huracan: evil Taino & Mayan god of winds & destruction
 Huracan: evil Taino & Mayan god of winds & destruction Profile of a Tropical Cyclone! Hurricane = typhoon = cyclone! All different words for the same thing Eye: clear area in the center Eyewall: clouds
Huracan: evil Taino & Mayan god of winds & destruction Profile of a Tropical Cyclone! Hurricane = typhoon = cyclone! All different words for the same thing Eye: clear area in the center Eyewall: clouds
Annual Number of Peer Reviewed Articles with Hurricane or Tropical Cyclone in their Titles, according to Meteorological and Geoastrophysical
 Hurricanes and Climate Kerry Emanuel Program in Atmospheres, Oceans, and Climate MIT Program Potential Intensity Role of potential ti li intensity it in storm intensity it Role of potential intensity in
Hurricanes and Climate Kerry Emanuel Program in Atmospheres, Oceans, and Climate MIT Program Potential Intensity Role of potential ti li intensity it in storm intensity it Role of potential intensity in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Probability forecasts for water levels at the coast of The Netherlands
 from Newsletter Number 114 Winter 7/8 METEOROLOGY Probability forecasts for water levels at the coast of The Netherlands doi:1.1957/gpsn56sc This article appeared in the Meteorology section of ECMWF Newsletter
from Newsletter Number 114 Winter 7/8 METEOROLOGY Probability forecasts for water levels at the coast of The Netherlands doi:1.1957/gpsn56sc This article appeared in the Meteorology section of ECMWF Newsletter
The ESSENCE project the power of a large model ensemble
 The ESSENCE project the power of a large model ensemble Andreas Sterl, Rein Haarsma, Frank Selten, Wilco Hazeleger and Henk Dijkstra (IMAU) a) b) 17 16 15 14 13 Essence ensemble world averaged observations
The ESSENCE project the power of a large model ensemble Andreas Sterl, Rein Haarsma, Frank Selten, Wilco Hazeleger and Henk Dijkstra (IMAU) a) b) 17 16 15 14 13 Essence ensemble world averaged observations
Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty
 Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty David R. Easterling National Climatic Data Center Asheville, North Carolina Overview Some examples of observed climate
Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty David R. Easterling National Climatic Data Center Asheville, North Carolina Overview Some examples of observed climate
John Steffen and Mark A. Bourassa
 John Steffen and Mark A. Bourassa Funding by NASA Climate Data Records and NASA Ocean Vector Winds Science Team Florida State University Changes in surface winds due to SST gradients are poorly modeled
John Steffen and Mark A. Bourassa Funding by NASA Climate Data Records and NASA Ocean Vector Winds Science Team Florida State University Changes in surface winds due to SST gradients are poorly modeled
The impact of rain on ocean wave evolution and its feedback to the atmosphere
 HAROKOPIO UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY ATMOSPHERE AND CLIMATE DYNAMICS GROUP (ACDG) http://meteoclima.gr Coastal Hydrology and Surface Processes linked to Air/Sea Modeling: 1 st community
HAROKOPIO UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY ATMOSPHERE AND CLIMATE DYNAMICS GROUP (ACDG) http://meteoclima.gr Coastal Hydrology and Surface Processes linked to Air/Sea Modeling: 1 st community
Exploring the Use of Dynamical Weather and Climate Models for Risk Assessment
 Exploring the Use of Dynamical Weather and Climate Models for Risk Assessment James Done Willis Research Network Fellow National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder CO, US Leverages resources in the
Exploring the Use of Dynamical Weather and Climate Models for Risk Assessment James Done Willis Research Network Fellow National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder CO, US Leverages resources in the
Tropical cyclones in ERA-40: A detection and tracking method
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35,, doi:10.1029/2008gl033880, 2008 Tropical cyclones in ERA-40: A detection and tracking method S. Kleppek, 1,2 V. Muccione, 3 C. C. Raible, 1,2 D. N. Bresch, 3 P. Koellner-Heck,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35,, doi:10.1029/2008gl033880, 2008 Tropical cyclones in ERA-40: A detection and tracking method S. Kleppek, 1,2 V. Muccione, 3 C. C. Raible, 1,2 D. N. Bresch, 3 P. Koellner-Heck,
SMALL-SCALE ATMOSPHERE-OCEAN COUPLING IN GALE-FORCE WINDS: MODELS, EXPERIMENTS, REMOTE SENSING
 SMALL-SCALE ATMOSPHERE-OCEAN COUPLING IN GALE-FORCE WINDS: MODELS, EXPERIMENTS, REMOTE SENSING YU. TROITSKAYA 1,2, D. SERGEEV 1,2, A. KANDAUROV 1,2, E. EZHOVA 1,2, O.DRUZHININ 1, I.SOUSTOVA 1,2, O.ERMAKOVA
SMALL-SCALE ATMOSPHERE-OCEAN COUPLING IN GALE-FORCE WINDS: MODELS, EXPERIMENTS, REMOTE SENSING YU. TROITSKAYA 1,2, D. SERGEEV 1,2, A. KANDAUROV 1,2, E. EZHOVA 1,2, O.DRUZHININ 1, I.SOUSTOVA 1,2, O.ERMAKOVA
Intensity of North Indian Ocean Tropical Cyclones
 Chapter 6 Intensity of North Indian Ocean Tropical Cyclones 6.1 Introduction Intensity of tropical cyclones is dependent on several parameters both thermodynamic and dynamic. It includes thermodynamic
Chapter 6 Intensity of North Indian Ocean Tropical Cyclones 6.1 Introduction Intensity of tropical cyclones is dependent on several parameters both thermodynamic and dynamic. It includes thermodynamic
Wind Speed Probability Products
 Wind Speed Probability Products Daniel Brown National Hurricane Center 2018 WMO Course 6 March 2018 Wind Speed Probabilities A Tool to Deal with Uncertainty Hurricane Irene Advisory Number 12 Issued 5:00
Wind Speed Probability Products Daniel Brown National Hurricane Center 2018 WMO Course 6 March 2018 Wind Speed Probabilities A Tool to Deal with Uncertainty Hurricane Irene Advisory Number 12 Issued 5:00
Development of Operational Storm Surge Guidance to Support Total Water Predictions
 Development of Operational Storm Surge Guidance to Support Total Water Predictions J. Feyen 1, S. Vinogradov 1,2, T. Asher 3, J. Halgren 4, Y. Funakoshi 1,5 1. NOAA/NOS//Development Laboratory 2. ERT,
Development of Operational Storm Surge Guidance to Support Total Water Predictions J. Feyen 1, S. Vinogradov 1,2, T. Asher 3, J. Halgren 4, Y. Funakoshi 1,5 1. NOAA/NOS//Development Laboratory 2. ERT,
Wind Speed Probability Products. Daniel Brown and Michael Brennan National Hurricane Center
 Wind Speed Probability Products Daniel Brown and Michael Brennan National Hurricane Center 2017 WMO Course 7 March 2017 Wind Speed Probabilities A Tool to Deal with Uncertainty Hurricane Irene Advisory
Wind Speed Probability Products Daniel Brown and Michael Brennan National Hurricane Center 2017 WMO Course 7 March 2017 Wind Speed Probabilities A Tool to Deal with Uncertainty Hurricane Irene Advisory
P1.1 THE QUALITY OF HORIZONTAL ADVECTIVE TENDENCIES IN ATMOSPHERIC MODELS FOR THE 3 RD GABLS SCM INTERCOMPARISON CASE
 P1.1 THE QUALITY OF HORIZONTAL ADVECTIVE TENDENCIES IN ATMOSPHERIC MODELS FOR THE 3 RD GABLS SCM INTERCOMPARISON CASE Fred C. Bosveld 1*, Erik van Meijgaard 1, Evert I. F. de Bruijn 1 and Gert-Jan Steeneveld
P1.1 THE QUALITY OF HORIZONTAL ADVECTIVE TENDENCIES IN ATMOSPHERIC MODELS FOR THE 3 RD GABLS SCM INTERCOMPARISON CASE Fred C. Bosveld 1*, Erik van Meijgaard 1, Evert I. F. de Bruijn 1 and Gert-Jan Steeneveld
STORM SURGE SIMULATION IN NAGASAKI DURING THE PASSAGE OF 2012 TYPHOON SANBA
 STORM SURGE SIMULATION IN NAGASAKI DURING THE PASSAGE OF 2012 TYPHOON SANBA D. P. C. Laknath 1, Kazunori Ito 1, Takahide Honda 1 and Tomoyuki Takabatake 1 As a result of global warming effect, storm surges
STORM SURGE SIMULATION IN NAGASAKI DURING THE PASSAGE OF 2012 TYPHOON SANBA D. P. C. Laknath 1, Kazunori Ito 1, Takahide Honda 1 and Tomoyuki Takabatake 1 As a result of global warming effect, storm surges
Changes in Marine Extremes. Professor Mikis Tsimplis. The LRET Research Collegium Southampton, 11 July 2 September 2011
 Changes in Marine Extremes by Professor Mikis Tsimplis The LRET Research Collegium Southampton, 11 July 2 September 2011 1 Changes in marine extremes Mikis Tsimplis, School of Law and National Oceanography
Changes in Marine Extremes by Professor Mikis Tsimplis The LRET Research Collegium Southampton, 11 July 2 September 2011 1 Changes in marine extremes Mikis Tsimplis, School of Law and National Oceanography
Outline. Extreme sea levels: past and future. Tropical cyclones 12/07/2013. North Sea Storm Surge of Understanding of coastal extremes
 Outline Extreme sea levels: past and future Svetlana Jevrejeva National Oceanography Centre, Liverpool, UK Introduction Changes in extreme sea levels in the recent past ( progress and limitation in understanding)
Outline Extreme sea levels: past and future Svetlana Jevrejeva National Oceanography Centre, Liverpool, UK Introduction Changes in extreme sea levels in the recent past ( progress and limitation in understanding)
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Event Response
 PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
ABSTRACT 1 INTRODUCTION P2G.4 HURRICANE DEFLECTION BY SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURE ANOMALIES.
 P2G.4 HURRICANE DEFLECTION BY SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURE ANOMALIES. M.E. McCulloch, J.T. Heming and J.D. Stark Met Office, Exeter, UK April 23, 2008 ABSTRACT To determine whether hurricane forecasts can be
P2G.4 HURRICANE DEFLECTION BY SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURE ANOMALIES. M.E. McCulloch, J.T. Heming and J.D. Stark Met Office, Exeter, UK April 23, 2008 ABSTRACT To determine whether hurricane forecasts can be
Cape Verde. General Climate. Recent Climate. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. Temperature. Precipitation
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
Variations of total heat flux during typhoons in the South China Sea
 78 Variations of total heat flux during typhoons in the South China Sea Wan Ruslan Ismail 1, and Tahereh Haghroosta 2,* 1 Section of Geography, School of Humanities, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Minden,
78 Variations of total heat flux during typhoons in the South China Sea Wan Ruslan Ismail 1, and Tahereh Haghroosta 2,* 1 Section of Geography, School of Humanities, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Minden,
A Hurricane Outlook for the 21st Century.
 A Hurricane Outlook for the 21st Century. Hugh Willoughby Florida International University Cat Winds Effects One 74-95 mph No real damage to building structures. Two Three Four Five 96-110 mph 111-130
A Hurricane Outlook for the 21st Century. Hugh Willoughby Florida International University Cat Winds Effects One 74-95 mph No real damage to building structures. Two Three Four Five 96-110 mph 111-130
Introduction to Meteorology & Climate. Climate & Earth System Science. Atmosphere Ocean Interactions. A: Structure of the Ocean.
 Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers
 Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 4 8/13/2012 Why inner core dynamics is important? Current TC intensity and structure forecasts contain
Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 4 8/13/2012 Why inner core dynamics is important? Current TC intensity and structure forecasts contain
July Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2017
 July Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2017 Issued: 4 th July 2017 by Professor Mark Saunders and Dr Adam Lea Dept. of Space and Climate Physics, UCL (University College London), UK Forecast
July Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2017 Issued: 4 th July 2017 by Professor Mark Saunders and Dr Adam Lea Dept. of Space and Climate Physics, UCL (University College London), UK Forecast
Mesoscale meteorological models. Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen
 Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
1. Oceans. Example 2. oxygen.
 1. Oceans a) Basic facts: There are five oceans on earth, making up about 72% of the planet s surface and holding 97% of the hydrosphere. Oceans supply the planet with most of its oxygen, play a vital
1. Oceans a) Basic facts: There are five oceans on earth, making up about 72% of the planet s surface and holding 97% of the hydrosphere. Oceans supply the planet with most of its oxygen, play a vital
Homework 8: Hurricane Damage (adapted from Pipkin et al.)
 1 Homework 8: Hurricane Damage (adapted from Pipkin et al.) Tropical cyclones have a significant impact on coastal areas of the world. In the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific Oceans they are called hurricanes
1 Homework 8: Hurricane Damage (adapted from Pipkin et al.) Tropical cyclones have a significant impact on coastal areas of the world. In the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific Oceans they are called hurricanes
Early Student Support for a Process Study of Oceanic Responses to Typhoons
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Early Student Support for a Process Study of Oceanic Responses to Typhoons Ren-Chieh Lien Applied Physics Laboratory University
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Early Student Support for a Process Study of Oceanic Responses to Typhoons Ren-Chieh Lien Applied Physics Laboratory University
ESTIMATION OF DESIGN WAVE HEIGHT AND COASTAL DEFENSE: CONSIDERATION OF GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE. Abstract
 9th International Conference on Public Communication of Science and Technology (PCST) Seoul, South Korea, 17-19 May 2006 ESTIMATION OF DESIGN WAVE HEIGHT AND COASTAL DEFENSE: CONSIDERATION OF GLOBAL CLIMATE
9th International Conference on Public Communication of Science and Technology (PCST) Seoul, South Korea, 17-19 May 2006 ESTIMATION OF DESIGN WAVE HEIGHT AND COASTAL DEFENSE: CONSIDERATION OF GLOBAL CLIMATE
Cold wake of Hurricane Frances
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15609, doi:10.1029/2007gl030160, 2007 Cold wake of Hurricane Frances Eric A. D Asaro, 1 Thomas B. Sanford, 1 P. Peter Niiler, 2 and Eric
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15609, doi:10.1029/2007gl030160, 2007 Cold wake of Hurricane Frances Eric A. D Asaro, 1 Thomas B. Sanford, 1 P. Peter Niiler, 2 and Eric
Projection of Ocean Wave Climate Change Based on Numerical Simulations
 Projection of Ocean Wave Climate Change Based on Numerical Simulations Muhammad Zikra a,*, Noriaki Hashimoto b and Kodama Mitsuyasu b a) Department of Ocean Engineering, Faculty of Marine Technology, Institut
Projection of Ocean Wave Climate Change Based on Numerical Simulations Muhammad Zikra a,*, Noriaki Hashimoto b and Kodama Mitsuyasu b a) Department of Ocean Engineering, Faculty of Marine Technology, Institut
Careful, Cyclones Can Blow You Away!
 Title: Careful, Cyclones Can Blow You Away! (Meteorology) Grade(s): 6-8 Introduction: Most people associate twisters with tornadoes, but in fact tropical twisters come from hurricanes. Hurricanes are what
Title: Careful, Cyclones Can Blow You Away! (Meteorology) Grade(s): 6-8 Introduction: Most people associate twisters with tornadoes, but in fact tropical twisters come from hurricanes. Hurricanes are what
Trends in the Character of Hurricanes and their Impact on Heavy Rainfall across the Carolinas
 Trends in the Character of Hurricanes and their Impact on Heavy Rainfall across the Carolinas Chip Konrad Carolina Integrated Science and Assessments (CISA) The Southeast Regional Climate Center Department
Trends in the Character of Hurricanes and their Impact on Heavy Rainfall across the Carolinas Chip Konrad Carolina Integrated Science and Assessments (CISA) The Southeast Regional Climate Center Department
Dynamic Effects of Airborne Water Droplets on Air-Sea Interactions: Sea-Spray and Rain
 Dynamic Effects of Airborne Water Droplets on Air-Sea Interactions: Sea-Spray and Rain Fabrice Veron University of Delaware College of Marine Studies 112C Robinson Hall Newark DE, 19716 phone: (302) 831-6658
Dynamic Effects of Airborne Water Droplets on Air-Sea Interactions: Sea-Spray and Rain Fabrice Veron University of Delaware College of Marine Studies 112C Robinson Hall Newark DE, 19716 phone: (302) 831-6658
1C.4 TROPICAL CYCLONE TORNADOES: SYNOPTIC SCALE INFLUENCES AND FORECASTING APPLICATIONS
 1C.4 TROPICAL CYCLONE TORNADOES: SYNOPTIC SCALE INFLUENCES AND FORECASTING APPLICATIONS Daniel J. Cecil and Lori A. Schultz University of Alabama in Huntsville, Huntsville, AL, 35805 1. INTRODUCTION Several
1C.4 TROPICAL CYCLONE TORNADOES: SYNOPTIC SCALE INFLUENCES AND FORECASTING APPLICATIONS Daniel J. Cecil and Lori A. Schultz University of Alabama in Huntsville, Huntsville, AL, 35805 1. INTRODUCTION Several
HWRF Ocean: The Princeton Ocean Model. HWRF Tutorial NCWCP, College Park, MD January 2018
 HWRF Ocean: The Princeton Ocean Model Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode Island HWRF Tutorial NCWCP, College Park, MD 23-25 January 2018 1 1 Why Couple a 3-D Ocean Model to
HWRF Ocean: The Princeton Ocean Model Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode Island HWRF Tutorial NCWCP, College Park, MD 23-25 January 2018 1 1 Why Couple a 3-D Ocean Model to
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture
 Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT
 REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT 2017 2019 MEMBER STATE: Netherlands 1 Principal InvestigatorP0F P: Dr. R.J. Haarsma Affiliation: Address: P.O. Box 201 3730 AE De Bilt The Netherlands E-mail: Royal Netherlands
REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT 2017 2019 MEMBER STATE: Netherlands 1 Principal InvestigatorP0F P: Dr. R.J. Haarsma Affiliation: Address: P.O. Box 201 3730 AE De Bilt The Netherlands E-mail: Royal Netherlands
KCC White Paper: The 100 Year Hurricane. Could it happen this year? Are insurers prepared? KAREN CLARK & COMPANY. June 2014
 KAREN CLARK & COMPANY KCC White Paper: The 100 Year Hurricane Could it happen this year? Are insurers prepared? June 2014 Copyright 2014 Karen Clark & Company The 100 Year Hurricane Page 1 2 COPLEY PLACE
KAREN CLARK & COMPANY KCC White Paper: The 100 Year Hurricane Could it happen this year? Are insurers prepared? June 2014 Copyright 2014 Karen Clark & Company The 100 Year Hurricane Page 1 2 COPLEY PLACE
Outlook 2008 Atlantic Hurricane Season. Kevin Lipton, Ingrid Amberger National Weather Service Albany, New York
 Outlook 2008 Atlantic Hurricane Season Kevin Lipton, Ingrid Amberger National Weather Service Albany, New York Summary 2007 Hurricane Season Two hurricanes made landfall in the Atlantic Basin at category-5
Outlook 2008 Atlantic Hurricane Season Kevin Lipton, Ingrid Amberger National Weather Service Albany, New York Summary 2007 Hurricane Season Two hurricanes made landfall in the Atlantic Basin at category-5
11/19/14. Chapter 11: Hurricanes. The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th. Lutgens Tarbuck
 Chapter 11: Hurricanes The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University! Hurricanes: " Hurricanes are intense centers of
Chapter 11: Hurricanes The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University! Hurricanes: " Hurricanes are intense centers of
11A.3 The Impact on Tropical Cyclone Predictions of a Major Upgrade to the Met Office Global Model
 11A.3 The Impact on Tropical Cyclone Predictions of a Major Upgrade to the Met Office Global Model Julian T. Heming * Met Office, Exeter, UK 1. BACKGROUND TO MODEL UPGRADE The last major upgrade to the
11A.3 The Impact on Tropical Cyclone Predictions of a Major Upgrade to the Met Office Global Model Julian T. Heming * Met Office, Exeter, UK 1. BACKGROUND TO MODEL UPGRADE The last major upgrade to the
THE ROLE PLAYED BY BLOCKING OVER THE NORTHERN HEMISPHERE ON HURRICANE KATRINA
 THE ROLE PLAYED BY BLOCKING OVER THE NORTHERN J P 3.51 HEMISPHERE ON HURRICANE KATRINA Yehia Hafez* University of Cairo, Giza, Egypt ABSTARCT On year 2005, there exist 28 tropical Atlantic storms and hurricanes
THE ROLE PLAYED BY BLOCKING OVER THE NORTHERN J P 3.51 HEMISPHERE ON HURRICANE KATRINA Yehia Hafez* University of Cairo, Giza, Egypt ABSTARCT On year 2005, there exist 28 tropical Atlantic storms and hurricanes
Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions. Magnitudes are measured differently for different hazard types:
 Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions Magnitude: this is an indication of the scale of an event, often synonymous with intensity or size. In natural systems, magnitude is also related
Storm and Storm Systems Related Vocabulary and Definitions Magnitude: this is an indication of the scale of an event, often synonymous with intensity or size. In natural systems, magnitude is also related
Simulation and Prediction of Storm Surges and Waves Driven by Hurricanes and Assessment of Coastal Flooding and Inundation
 Simulation and Prediction of Storm Surges and Waves Driven by Hurricanes and Assessment of Coastal Flooding and Inundation Yan Ding, Yaoxin Zhang, Yafei Jia, Afshin Gazerzadeh, and Mustafa S. Altinakar
Simulation and Prediction of Storm Surges and Waves Driven by Hurricanes and Assessment of Coastal Flooding and Inundation Yan Ding, Yaoxin Zhang, Yafei Jia, Afshin Gazerzadeh, and Mustafa S. Altinakar
Tampa Bay Storm Surge & Wave Vulnerability, Response to Hurricane Irma and Tools for Future Use
 Tampa Bay Storm Surge & Wave Vulnerability, Response to Hurricane Irma and Tools for Future Use Robert H. Weisberg with J. Chen, Y. Liu and L. Zheng College of Marine Science University of South Florida
Tampa Bay Storm Surge & Wave Vulnerability, Response to Hurricane Irma and Tools for Future Use Robert H. Weisberg with J. Chen, Y. Liu and L. Zheng College of Marine Science University of South Florida
Ch. 11: Hurricanes. Be able to. Define what hurricane is. Identify the life and death of a hurricane. Identify the ways we track hurricanes.
 Ch. 11: Hurricanes Be able to Define what hurricane is. Identify the life and death of a hurricane. Identify the ways we track hurricanes. What are Hurricanes? Smaller than mid-latitude cyclones. Don t
Ch. 11: Hurricanes Be able to Define what hurricane is. Identify the life and death of a hurricane. Identify the ways we track hurricanes. What are Hurricanes? Smaller than mid-latitude cyclones. Don t
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Numerical Simulations and Observations of Surface Wave Fields under an Extreme Tropical Cyclone
 SEPTEMBER 2009 F A N E T A L. 2097 Numerical Simulations and Observations of Surface Wave Fields under an Extreme Tropical Cyclone YALIN FAN, ISAAC GINIS, AND TETSU HARA Graduate School of Oceanography,
SEPTEMBER 2009 F A N E T A L. 2097 Numerical Simulations and Observations of Surface Wave Fields under an Extreme Tropical Cyclone YALIN FAN, ISAAC GINIS, AND TETSU HARA Graduate School of Oceanography,
Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models
 Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models Inna Polichtchouk & Ted Shepherd Royal Meteorological Society National Meeting 16.11.2016 MOTIVATION Question: How sensitive
Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models Inna Polichtchouk & Ted Shepherd Royal Meteorological Society National Meeting 16.11.2016 MOTIVATION Question: How sensitive
Developing a Tropical Cyclone Parametric Wind Model with Landfall Effect for Real-Time Prediction of Wind and Storm Surge
 Proceedings of 2013 IAHR Congress 2013 Tsinghua University Press, Beijing Developing a Tropical Cyclone Parametric Wind Model with Landfall Effect for Real-Time Prediction of Wind and Storm Surge Taide
Proceedings of 2013 IAHR Congress 2013 Tsinghua University Press, Beijing Developing a Tropical Cyclone Parametric Wind Model with Landfall Effect for Real-Time Prediction of Wind and Storm Surge Taide
Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton
 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each & Q. 10 Q. 22 carry two marks each. Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton Q.2 The pair of variables that
Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each & Q. 10 Q. 22 carry two marks each. Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton Q.2 The pair of variables that
July Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2016
 July Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2016 Issued: 5 th July 2016 by Professor Mark Saunders and Dr Adam Lea Dept. of Space and Climate Physics, UCL (University College London), UK Forecast
July Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2016 Issued: 5 th July 2016 by Professor Mark Saunders and Dr Adam Lea Dept. of Space and Climate Physics, UCL (University College London), UK Forecast
Modeling the North West European Shelf using Delft3D Flexible Mesh
 Modeling the North West European Shelf using Delft3D Flexible Mesh 2nd JCOMM Scientific and Technical Symposium on Storm Surges, 8-13 Nov. 2015, Key West, USA; Firmijn Zijl Outline of this presentation
Modeling the North West European Shelf using Delft3D Flexible Mesh 2nd JCOMM Scientific and Technical Symposium on Storm Surges, 8-13 Nov. 2015, Key West, USA; Firmijn Zijl Outline of this presentation
Advances in Coastal Inundation Simulation Using Unstructured-Grid Coastal Ocean Models
 Advances in Coastal Inundation Simulation Using Unstructured-Grid Coastal Ocean Models Bob Beardsley (WHOI) Changsheng Chen (UMass-Dartmouth) Bob Weisberg (U. South Florida) Joannes Westerink (U. Notre
Advances in Coastal Inundation Simulation Using Unstructured-Grid Coastal Ocean Models Bob Beardsley (WHOI) Changsheng Chen (UMass-Dartmouth) Bob Weisberg (U. South Florida) Joannes Westerink (U. Notre
August Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2015
 August Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2015 Issued: 5 th August 2015 by Professor Mark Saunders and Dr Adam Lea Dept. of Space and Climate Physics, UCL (University College London), UK
August Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2015 Issued: 5 th August 2015 by Professor Mark Saunders and Dr Adam Lea Dept. of Space and Climate Physics, UCL (University College London), UK
Impact of Typhoons on the Western Pacific Ocean DRI: Numerical Modeling of Ocean Mixed Layer Turbulence and Entrainment at High Winds
 Impact of Typhoons on the Western Pacific Ocean DRI: Numerical Modeling of Ocean Mixed Layer Turbulence and Entrainment at High Winds Ramsey R. Harcourt Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington,
Impact of Typhoons on the Western Pacific Ocean DRI: Numerical Modeling of Ocean Mixed Layer Turbulence and Entrainment at High Winds Ramsey R. Harcourt Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington,
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. What Has Changed the Proportion of Intense Hurricanes in the Last 30 Years?
 1432 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE What Has Changed the Proportion of Intense Hurricanes in the Last 30 Years? LIGUANG WU Laboratory for Atmospheres, NASA Goddard Space
1432 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE What Has Changed the Proportion of Intense Hurricanes in the Last 30 Years? LIGUANG WU Laboratory for Atmospheres, NASA Goddard Space
PROJECTION OF FUTURE STORM SURGE DUE TO CLIMATE CHANGE AND ITS UNCERTAINTY A CASE STUDY IN THE TOKYO BAY
 Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts (APAC 2011) December 14 16, 2011, Hong Kong, China PROJECTION OF FUTURE STORM SURGE DUE TO CLIMATE CHANGE AND ITS UNCERTAINTY
Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts (APAC 2011) December 14 16, 2011, Hong Kong, China PROJECTION OF FUTURE STORM SURGE DUE TO CLIMATE CHANGE AND ITS UNCERTAINTY
Development and Validation of a Coastal Surge and Inundation Prediction System
 Development and Validation of a Coastal Surge and Inundation Prediction System Andrew Condon American Society for Engineering Education Stennis Space Center, MS, 39529, USA Jay Veeramony Oceanography Division
Development and Validation of a Coastal Surge and Inundation Prediction System Andrew Condon American Society for Engineering Education Stennis Space Center, MS, 39529, USA Jay Veeramony Oceanography Division
April Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2016
 April Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2016 Issued: 5 th April 2016 by Professor Mark Saunders and Dr Adam Lea Dept. of Space and Climate Physics, UCL (University College London), UK
April Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2016 Issued: 5 th April 2016 by Professor Mark Saunders and Dr Adam Lea Dept. of Space and Climate Physics, UCL (University College London), UK
Vertical structure of the atmosphere
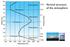 Vertical structure of the atmosphere Stratosphere ozone layer / ozone hole ultraviolet solar radiation sulfate aerosols from volcanic eruptions increasing GHG produces cooling Troposphere most clouds
Vertical structure of the atmosphere Stratosphere ozone layer / ozone hole ultraviolet solar radiation sulfate aerosols from volcanic eruptions increasing GHG produces cooling Troposphere most clouds
Horizontal resolution effects on tropical cyclone storm surges
 1 2 3 Source: AFP PHOTO/CHARISM SAYAT/AFP/Getty Images Source: kakela/ Flickr Name Author Horizontal resolution effects on tropical cyclone storm surges Nadia Bloemendaal¹, S. Muis¹, R. Haarsma², M. Verlaan³,
1 2 3 Source: AFP PHOTO/CHARISM SAYAT/AFP/Getty Images Source: kakela/ Flickr Name Author Horizontal resolution effects on tropical cyclone storm surges Nadia Bloemendaal¹, S. Muis¹, R. Haarsma², M. Verlaan³,
IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST. (a) (b) (c)
 9B.3 IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST Tetsuya Iwabuchi *, J. J. Braun, and T. Van Hove UCAR, Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
9B.3 IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST Tetsuya Iwabuchi *, J. J. Braun, and T. Van Hove UCAR, Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
Development of a Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean-Land General Circulation Model (GCM) at the Frontier Research Center for Global Change
 Chapter 1 Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulation Development of a Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean-Land General Circulation Model (GCM) at the Frontier Research Center for Global Change Project Representative Tatsushi
Chapter 1 Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulation Development of a Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean-Land General Circulation Model (GCM) at the Frontier Research Center for Global Change Project Representative Tatsushi
April Forecast Update for North Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2019
 April Forecast Update for North Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2019 Issued: 5 th April 2019 by Professor Mark Saunders and Dr Adam Lea Dept. of Space and Climate Physics, UCL (University College London),
April Forecast Update for North Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2019 Issued: 5 th April 2019 by Professor Mark Saunders and Dr Adam Lea Dept. of Space and Climate Physics, UCL (University College London),
4. Climatic changes. Past variability Future evolution
 4. Climatic changes Past variability Future evolution TROPICAL CYCLONES and CLIMATE How TCs have varied during recent and distant past? How will TC activity vary in the future? 2 CURRENT CLIMATE : how
4. Climatic changes Past variability Future evolution TROPICAL CYCLONES and CLIMATE How TCs have varied during recent and distant past? How will TC activity vary in the future? 2 CURRENT CLIMATE : how
AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast
 AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast Issued: April 10, 2018 by Dale C. S. Destin (follow @anumetservice) Director (Ag), Antigua and Barbuda Meteorological Service (ABMS) The *AnuMS (Antigua Met
AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast Issued: April 10, 2018 by Dale C. S. Destin (follow @anumetservice) Director (Ag), Antigua and Barbuda Meteorological Service (ABMS) The *AnuMS (Antigua Met
At the Midpoint of the 2008
 At the Midpoint of the 2008 Atlantic Hurricane Season Editor s note: It has been an anxious couple of weeks for those with financial interests in either on- or offshore assets in the Gulf of Mexico and
At the Midpoint of the 2008 Atlantic Hurricane Season Editor s note: It has been an anxious couple of weeks for those with financial interests in either on- or offshore assets in the Gulf of Mexico and
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity
 The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
The CBLAST-Hurricane Program and the Next-Generation Fully Coupled Atmosphere- Wave-Ocean Models for Hurricane Research and Prediction
 The CBLAST-Hurricane Program and the Next-Generation Fully Coupled Atmosphere- Wave-Ocean Models for Hurricane Research and Prediction Shuyi S. Chen 1*, James F. Price 2, Wei Zhao 1, Mark A. Donelan 1,
The CBLAST-Hurricane Program and the Next-Generation Fully Coupled Atmosphere- Wave-Ocean Models for Hurricane Research and Prediction Shuyi S. Chen 1*, James F. Price 2, Wei Zhao 1, Mark A. Donelan 1,
