Air-Sea Interaction: Physics of air-surface interactions and coupling to ocean/atmosphere BL processes
|
|
|
- Julia Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Air-Sea Interaction: Physics of air-surface interactions and coupling to ocean/atmosphere BL processes Emphasize surface fluxes Statement of problem Present status Parameterization issues An amusing case 3/25/2008 1
2 3/25/ Flux Definitions p l s nl ns net H H H R R H Heat Net + = : ) ( : ˆ ˆ : : : wet s pw p y a x a e a l pa a s T T P c H Rain Heat j w u i w u Stress w T L H Heat Latent w T c H Sensible Heat = + = = = ρ ρ τ ρ ρ e a l w L H P E P F Water ρ / : = = ) ( ) ( ) ( : : ) ( / : / 0.61 / : r n w r n w r w n F Exchange Particle w r F Gas Exchange P E g c gh F Water L H T c H F Air s g n x x pw w net b e a l pa a s b + = = + = + = β ρ α ρ ρ
3 Present Status of Surface Flux Parameterizations P: No dependence on surface variables Radiation: Depends on albedo, emissivity, and Ts but real problem is clouds Turbulent Fluxes: Bulk Parameterization Met Flux : w x = CxU ( X s X r ) = CxU X Gas Flux : w x = kxα x X α = sol. Particles : F = V ( r) n( r) ; F deposition source = F( f d whitecap, U, u*, wave breaking, slope) 3/25/2008 3
4 3/25/ Physically-Based Parameterizations 2 )]/ ) / ( ) ( ( ][1 ) ( 4 9 exp[ ) ( 3 4 : ] 2 ) / ln( 5 [ )] / ln( [ / ] / [ : )] / ( ) / )][ln( / ( ) / [ln( )] ( ) ( [0.98* ] ) ( ) ( [ : 4 / / 2 1/ 2 1/ * 2 1/ 2 2 * u g s ca d ca a x w rw cw w a w ar x wr a x x q oq u o s sat meso y x Slope r W h U erf r a l f r n r Spray Droplet Sea S C S h z S h X X u w r Gas Flux L z z z L z z z z q T q U W U U w q Flux Met σ πη σ π κ α δ ρ ρ α α ψ ψ γ β κ + Ε = = = & Old Days: C E =1E-3 and k=0.003*u 2 and spray=s(r)*f whitecap
5 Historical perspective on turbulent fluxes: Typical moisture transfer coefficients Algorithms of UA (solid lines), COARE 2.5 (dotted lines), CCM3 (short-dashed lines), ECMWF (dot-dashed lines), NCEP (tripledot-dashed lines), and GEOS 3/25/2008 (long-dashed lines). 5
6 3/25/2008 6
7 Air-Sea transfer coefficients as a function of wind speed: latent heat flux (upper panel) and momentum flux (lower panel). The red line is the COARE algorithm version 3.0; the circles are the average of direct flux measurements from 12 ETL cruises ( ); the dashed line the original NCEP model. 3/25/2008 7
8 3/25/2008 8
9 CO2 Flux: Transfer velocity versus wind speed Hare, McGillis, Edson, Fairall Work under way on DMS and Ozone 3/25/2008 9
10 Particle Fluxes Optically relevant (.1 10 micron): Principally whitecap-bubble production Measurement and interpretation problems Some dependence on laboratory work No consensus Thermodynamically relevant ( micron) Principally breaking-wave spume production No measurements at high winds Order of magnitude uncertainty 3/25/
11 Progress in Last 5ish Years Conventional turbulent fluxes: Greatly expanded data base 5% 0-20 m/s Progress on wind-wave-stress models M-O stability functions, light-wind convective & stable Gas Fluxes: Ship-based covariance measurements Physically-based parameterization Particle Fluxes: Expanded modeling efforts 3/25/
12 Flux Parameterization Issues Representation in GCM Except for P, most observations are point time averages Concept of gustiness sufficient? Mesoscale variable? Precip, convective mass flux, Strong winds General question of turbulent fluxes, flow separation, wave momentum input Sea spray influence Waves Stress vector vs wind vector (2-D wave spectrum) z o vs wave age & wave height Breaking waves Gas and particle fluxes Distribution of stress and TKE in ocean mixed layer (P. Sullivan) Gas fluxes Bubbles Surfactants (physical vs chemical effects) Extend models to chemical reactions Particle fluxes Interpretation of measurements Source vs deposition 3/25/
13 Turbulent Fluxes at High Winds 3/25/
14 Strong wind turbulent fluxes Direct turbulent fluxes Cd or Charnock coeff Ch/Ce or zot/zoq=f(rr) Droplet mediated fluxes Momentum <ρwu> Mass flux <ρw> Enthalpy flux; partitioning Qs and Ql 3/25/
15 Evidence Strom surge models Cd/Ck ratio, Emanuel Powell drop sonde profiles Price ocean mixed layer integrations Laboratory simulations Explanations Slippery young waves (direct Cd) Moon et al Droplet mass effect (ρ<w u > Andreas Droplet stability effect (<w ρ > - Makin 3/25/
16 GOES SST imagery. Daily composites made from hourly images. GOES seems to be the most prolific SST imaging system, though at the expense of accuracy and noise level. SST cooling in these images exhibits: 1) Significant horizontal structure, i) a marked rightward bias, ii) along-track variability that is not correlated with intensity, and, 2) A rapid relaxation back toward pre-storm SST, e-folding approx 10 days. EM-APEX day 250 3/25/
17 A numerical simulation of the UO response The numerical ocean model is Price et al., 94; grid-level, high resolution, closed with PWP upper ocean mixing algorithm. The ocean IC is from pre-frances EM- APEX. The single most important thing is the hurricane stress field: a fit to HWINDS for the wind field and Powell et al. for the drag coefficient. The implicit assumption is that stressocean = stressair and so this is the null model with respect to some of the most interesting effects of surface waves. 3/25/
18 3/25/
19 A Sea-Spray Thermodynamic Parameterization Including Feedback C. W. Fairall *, J-W. Bao, and J. Wilczak NOAA Environmental Technology Laboratory (ETL) Boulder, CO 1. Background 2. Source strength 3. Feedback 4. Sensitivities 5. Model tests 3/25/
20 3/25/
21 H = ρ c C U ( T T ) s a pa H o a Original Droplet Equations Fairall/Andreas circa 1990 H = ρ L C U ( q ( T ) q ) Q l a e E s o a = ρ L F l w e E Q = ρ c F ( T T ) s w pw v o a Fv = 3 4π / 3 r Sn ( r) dr f FE = τ 3 π / r Sn ( r) dr τ r 3/25/
22 S n Surface Source Strength for Sea Spray Droplets 3/25/
23 Droplet Source Functions Fairall et al S = f ( U) S ( r) n no. f ( U ) = W = U 3 4 b Fairall, Banner, Asher Physical Model 3 4πr f Pr α πη U( h) V f / Slope S n ( r ) exp[ ( ) / = ]*[ 1 + erf ( )] / 2 3 σl 4 r σ P energy wave breaking σ surface tension r droplet radius η Kolmogorov microscale f fraction of P going into droplet production V f =droplet mean fall velocity 3/25/ u
24 Feedback 3/25/
25 Partitioning of Droplet Contribution: Stages of cooling/evaporation Simplification: consider large droplets that are ejected, cool to wet bulb temperature and re-enter ocean with negligible change in mass Stages: Cool from To to Tair = Qs Cool from Tair to Twet = Ql_a Evaporation while at Twet = Ql_b Total droplet enthapy transfer Qse=Qs+Ql_a Enthalpy Bowen ratio = Qs/Ql_a=(To-Ta)/(Ta-Twet) Qs=Qse*bowen/(1+bowen) 3/25/
26 Feedback Characterization δt a 1 β δ β δ 1 β Ta = Td = feed *( Ta Tw ) = feed * ( 1 s) γ feed = Ql Q+ ( H + Q + H ) / feed_ tune l s se sε Effect on the fluxes: H = ρ L C U[ T ( T δt )] s a e E o a a H = ρ L C U[ q ( T ) q ( T + δt )] l a e E s o s d d Q = ρ c F ( T T ) se w pw v o w Q = ρ L G( U ) hβ( T )[ q ( T δt ) q ( T + δt )] lb w e o s a a s d d 3/25/
27 Turbulent Fluxes Above the Droplet Evaporation Layer H s_ tot = H s + Qs + H sε Qlb = H s + ρc pchuδt f + Qs + H sε αql Hl _ tot = Hl + Qla + Qlb = Hl ρleceuδqa + Qla + αql 3/25/
28 Direct Transfer Coefficients Assumed in Parameterization x C d, C k U 10 (m/s) 3/25/
29 Ratio of Transfer Coefficients With Droplet Enthalpy Flux 2.8 Feedtune=0.3, 1.0, source= C d /C k source= U 10 (m/s) 3/25/
30 Feedback Sensitivity: Source Strength=0.3 3/25/
31 Model Tests (Bao and Ginis) IVAN, ISABEL GFDL operational GFDL new zo, zt WRF PLANS HWRF at high resolution matrix of tune values Explicit droplet model (Kepert/ Fairall) in HWRF Coordinate with Penn State LES work 3/25/
32 Simulation with GFDL Operational Model: Isabel 3/25/
33 But: Simulations with New Cd and Ce/Ch New Cd Ce/Ch Old Cd Ce/Ch 3/25/
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity
 The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction in Tropical Cyclones
 Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction in Tropical Cyclones Isaac Ginis University of Rhode Island Collaborators: T. Hara, Y.Fan, I-J Moon, R. Yablonsky. ECMWF, November 10-12, 12, 2008 Air-Sea Interaction in Tropical
Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction in Tropical Cyclones Isaac Ginis University of Rhode Island Collaborators: T. Hara, Y.Fan, I-J Moon, R. Yablonsky. ECMWF, November 10-12, 12, 2008 Air-Sea Interaction in Tropical
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget
 The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
Importance of air-sea interaction on the coupled typhoon-wave-ocean modeling
 Importance of air-sea interaction on the coupled typhoon-wave-ocean modeling Collaborators: I. Ginis (GSO/URI) T. Hara (GSO/URI) B. Thomas (GSO/URI) H. Tolman (NCEP/NOAA) IL-JU MOON ( 文一柱 ) Cheju National
Importance of air-sea interaction on the coupled typhoon-wave-ocean modeling Collaborators: I. Ginis (GSO/URI) T. Hara (GSO/URI) B. Thomas (GSO/URI) H. Tolman (NCEP/NOAA) IL-JU MOON ( 文一柱 ) Cheju National
Dynamic Effects of Airborne Water Droplets on Air-Sea Interactions: Sea-Spray and Rain
 Dynamic Effects of Airborne Water Droplets on Air-Sea Interactions: Sea-Spray and Rain Fabrice Veron University of Delaware College of Marine Studies 112C Robinson Hall Newark DE, 19716 phone: (302) 831-6658
Dynamic Effects of Airborne Water Droplets on Air-Sea Interactions: Sea-Spray and Rain Fabrice Veron University of Delaware College of Marine Studies 112C Robinson Hall Newark DE, 19716 phone: (302) 831-6658
Air-Sea Interaction in Extreme Weather Conditions
 Air-Sea Interaction in Extreme Weather Conditions Hans (J.W.) de Vries, Niels Zweers,, Vladimir Makin, Vladimir Kudryavtsev, and Gerrit Burgers, KNMI, De Bilt, NL Meteogroup, Wageningen, NL NIERSC, St.
Air-Sea Interaction in Extreme Weather Conditions Hans (J.W.) de Vries, Niels Zweers,, Vladimir Makin, Vladimir Kudryavtsev, and Gerrit Burgers, KNMI, De Bilt, NL Meteogroup, Wageningen, NL NIERSC, St.
Effects of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclones Simulated under Idealized Conditions
 1686 M O N T H L Y W E A T H E R R E V I E W VOLUME 136 Effects of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclones Simulated under Idealized Conditions JEFFREY S. GALL AND WILLIAM M. FRANK Department of Meteorology, The
1686 M O N T H L Y W E A T H E R R E V I E W VOLUME 136 Effects of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclones Simulated under Idealized Conditions JEFFREY S. GALL AND WILLIAM M. FRANK Department of Meteorology, The
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
The Role of Water Droplets in Air-sea Interaction: Rain and Sea Spray
 The Role of Water Droplets in Air-sea Interaction: Rain and Sea Spray Fabrice Veron Air-Sea Interaction Laboratory School of Marine Science and Policy College of Earth, Ocean, & Environment University
The Role of Water Droplets in Air-sea Interaction: Rain and Sea Spray Fabrice Veron Air-Sea Interaction Laboratory School of Marine Science and Policy College of Earth, Ocean, & Environment University
Relevant timescales: convective events diurnal intraseasonal. 3 ocean-atmosphere communication methods: freshwater flux flux momentum flux
 Radar Perspective on Air-Sea Interactions during DYNAMO Elizabeth Thompson; July 23 2013 Update Steve Rutledge, Brenda Dolan, Jim Moum, Aurelie Moulin, Chris Fairall, Bob Rilling, Mike Dixon, Scott Ellis,
Radar Perspective on Air-Sea Interactions during DYNAMO Elizabeth Thompson; July 23 2013 Update Steve Rutledge, Brenda Dolan, Jim Moum, Aurelie Moulin, Chris Fairall, Bob Rilling, Mike Dixon, Scott Ellis,
Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics
 Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics Jimy Dudhia MMM Division, NCAR 1D Ocean Mixed-Layer Model 1d model based on Pollard, Rhines and Thompson (1973) was added for hurricane forecasts Purpose is to represent
Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics Jimy Dudhia MMM Division, NCAR 1D Ocean Mixed-Layer Model 1d model based on Pollard, Rhines and Thompson (1973) was added for hurricane forecasts Purpose is to represent
6A.3 SPRAY-MEDIATED ENTHALPY FLUX TO THE ATMOSPHERE AND SALT FLUX TO THE OCEAN IN HIGH WINDS
 6A.3 SPRAY-MEDIATED ENTHALPY FLUX TO THE ATMOSPHERE AND SALT FLUX TO THE OCEAN IN HIGH WINDS Edgar L Andreas * NorthWest Research Associates, Inc., Lebanon, New Hampshire 1. INTRODUCTION Evaporating sea
6A.3 SPRAY-MEDIATED ENTHALPY FLUX TO THE ATMOSPHERE AND SALT FLUX TO THE OCEAN IN HIGH WINDS Edgar L Andreas * NorthWest Research Associates, Inc., Lebanon, New Hampshire 1. INTRODUCTION Evaporating sea
Improving Surface Flux Parameterizations in the NRL Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System
 Improving Surface Flux Parameterizations in the NRL Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System LONG-TERM GOAL Shouping Wang Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943 Phone: (831) 656-4719
Improving Surface Flux Parameterizations in the NRL Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System LONG-TERM GOAL Shouping Wang Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943 Phone: (831) 656-4719
Midlatitude storm impacts on air sea CO 2 fluxes
 CHAPTER 6 Midlatitude storm impacts on air sea CO 2 fluxes W. Perrie 1,2, W. Zhang 1,2,X.Ren 3, Z. Long 1,2 & J. Hare 4 1 Fisheries & Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth, Canada.
CHAPTER 6 Midlatitude storm impacts on air sea CO 2 fluxes W. Perrie 1,2, W. Zhang 1,2,X.Ren 3, Z. Long 1,2 & J. Hare 4 1 Fisheries & Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth, Canada.
The CBLAST-Hurricane Program and the Next-Generation Fully Coupled Atmosphere- Wave-Ocean Models for Hurricane Research and Prediction
 The CBLAST-Hurricane Program and the Next-Generation Fully Coupled Atmosphere- Wave-Ocean Models for Hurricane Research and Prediction Shuyi S. Chen 1*, James F. Price 2, Wei Zhao 1, Mark A. Donelan 1,
The CBLAST-Hurricane Program and the Next-Generation Fully Coupled Atmosphere- Wave-Ocean Models for Hurricane Research and Prediction Shuyi S. Chen 1*, James F. Price 2, Wei Zhao 1, Mark A. Donelan 1,
HWRF Ocean: MPIPOM-TC
 HWRF v3.7a Tutorial Nanjing, China, December 2, 2015 HWRF Ocean: MPIPOM-TC Ligia Bernardet NOAA SRL Global Systems Division, Boulder CO University of Colorado CIRS, Boulder CO Acknowledgement Richard Yablonsky
HWRF v3.7a Tutorial Nanjing, China, December 2, 2015 HWRF Ocean: MPIPOM-TC Ligia Bernardet NOAA SRL Global Systems Division, Boulder CO University of Colorado CIRS, Boulder CO Acknowledgement Richard Yablonsky
Thermodynamic and Flux Observations of the Tropical Cyclone Surface Layer
 Thermodynamic and Flux Observations of the Tropical Cyclone Surface Layer 1. INTRODUCTION Alex M. Kowaleski and Jenni L. Evans 1 The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA Understanding tropical
Thermodynamic and Flux Observations of the Tropical Cyclone Surface Layer 1. INTRODUCTION Alex M. Kowaleski and Jenni L. Evans 1 The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA Understanding tropical
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture
 Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Related Improvements. A DFS Application. Mark A. Bourassa
 Related Improvements in Surface Turbulent Heat Fluxes A DFS Application Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies & Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, The Florida State University,
Related Improvements in Surface Turbulent Heat Fluxes A DFS Application Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies & Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, The Florida State University,
Intercomparison of Bulk Aerodynamic Algorithms for the Computation of Sea Surface Fluxes Using TOGA COARE and TAO Data
 68 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE Intercomparison of Bulk Aerodynamic Algorithms for the Computation of Sea Surface Fluxes Using TOGA COARE and TAO Data XUBIN ZENG, MING ZHAO, AND ROBERT E. DICKINSON Institute of
68 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE Intercomparison of Bulk Aerodynamic Algorithms for the Computation of Sea Surface Fluxes Using TOGA COARE and TAO Data XUBIN ZENG, MING ZHAO, AND ROBERT E. DICKINSON Institute of
Richard M. Yablonsky University of Rhode Island. WRF for Hurricanes Tutorial Boulder, CO 25 February 2010
 Richard M. Yablonsky University of Rhode Island WRF for Hurricanes Tutorial Boulder, CO 25 February 2010 1 What is the Princeton Ocean Model? Three dimensional, primitive equation, numerical ocean model
Richard M. Yablonsky University of Rhode Island WRF for Hurricanes Tutorial Boulder, CO 25 February 2010 1 What is the Princeton Ocean Model? Three dimensional, primitive equation, numerical ocean model
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
The Impact of Sea Spray on Air-Sea Fluxes in Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean Models
 The Impact of Sea Spray on Air-Sea Fluxes in Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean Models Edgar L Andreas U. S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory 72 Lyme Road Hanover, New Hampshire 03755-1290 phone:
The Impact of Sea Spray on Air-Sea Fluxes in Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean Models Edgar L Andreas U. S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory 72 Lyme Road Hanover, New Hampshire 03755-1290 phone:
Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model
 Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model W. O Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California
Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model W. O Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California
The Impact of Sea Spray on Air-Sea Fluxes in Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean Models
 The Impact of Sea Spray on Air-Sea Fluxes in Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean Models Edgar L Andreas U. S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory 72 Lyme Road Hanover, New Hampshire 03755-1290 phone:
The Impact of Sea Spray on Air-Sea Fluxes in Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean Models Edgar L Andreas U. S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory 72 Lyme Road Hanover, New Hampshire 03755-1290 phone:
Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers
 Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 4 8/13/2012 Why inner core dynamics is important? Current TC intensity and structure forecasts contain
Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 4 8/13/2012 Why inner core dynamics is important? Current TC intensity and structure forecasts contain
Improving Air-Sea Coupling Parameterizations in High-Wind Regimes
 Improving Air-Sea Coupling Parameterizations in High-Wind Regimes PI: Dr. Shuyi S. Chen Co-PI: Dr. Mark A. Donelan Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, University of Miami 4600 Rickenbacker
Improving Air-Sea Coupling Parameterizations in High-Wind Regimes PI: Dr. Shuyi S. Chen Co-PI: Dr. Mark A. Donelan Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, University of Miami 4600 Rickenbacker
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
HWRF Surface Layer Thermodynamics Evaluation. Eric W. Uhlhorn and Joseph J. Cione HFIP Hurricane Modeling Workshop September 2012
 HWRF Surface Layer Thermodynamics Evaluation Eric W. Uhlhorn and Joseph J. Cione HFIP Hurricane Modeling Workshop 17-18 September 2012 Special thanks. HRD HWRF modeling team Gopal, Xuejin Zhang, Thiago
HWRF Surface Layer Thermodynamics Evaluation Eric W. Uhlhorn and Joseph J. Cione HFIP Hurricane Modeling Workshop 17-18 September 2012 Special thanks. HRD HWRF modeling team Gopal, Xuejin Zhang, Thiago
A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling. requirements of energy and water cycle. Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki
 A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling study for defining satellite measurement requirements of energy and water cycle Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki Motivation 1. Uncertainty of climate sensitivity
A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling study for defining satellite measurement requirements of energy and water cycle Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki Motivation 1. Uncertainty of climate sensitivity
Ship-based measurements of cloud microphysics and PBL properties in precipitating trade cumulus clouds during RICO
 Ship-based measurements of cloud microphysics and PBL properties in precipitating trade cumulus clouds during RICO Allen White and Jeff Hare, University of Colorado/CIRES Bruce Albrecht and Pavlos Kolias,
Ship-based measurements of cloud microphysics and PBL properties in precipitating trade cumulus clouds during RICO Allen White and Jeff Hare, University of Colorado/CIRES Bruce Albrecht and Pavlos Kolias,
Effects of transfer processes on marine atmospheric boundary layer or Effects of boundary layer processes on air-sea exchange
 Effects of transfer processes on marine atmospheric boundary layer or Effects of boundary layer processes on air-sea exchange Ann-Sofi Smedman Uppsala University Uppsala, Sweden Effect of transfer process
Effects of transfer processes on marine atmospheric boundary layer or Effects of boundary layer processes on air-sea exchange Ann-Sofi Smedman Uppsala University Uppsala, Sweden Effect of transfer process
Global Water Cycle. Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere. Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40.
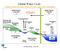 Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
New Observations of Ocean Response to a Hurricane
 New Observations of Ocean Response to a Hurricane Thomas B. Sanford and James B. Girton Applied Physics Laboratory and School of Oceanography University of Washington In collaboration with: Eric A. D Asaro
New Observations of Ocean Response to a Hurricane Thomas B. Sanford and James B. Girton Applied Physics Laboratory and School of Oceanography University of Washington In collaboration with: Eric A. D Asaro
New findings on hurricane intensity, wind field extent, and surface drag coefficient behavior
 New findings on hurricane intensity, wind field extent, and surface drag coefficient behavior Mark D. Powell NOAA Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratories Hurricane Research Division Miami
New findings on hurricane intensity, wind field extent, and surface drag coefficient behavior Mark D. Powell NOAA Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratories Hurricane Research Division Miami
Coupled Ocean-Wave Model Team (Team 8) Report
 Coupled Ocean-Wave Model Team (Team 8) Report George Halliwell (co-lead, NOAA/AOML/PhOD) Hendrik Tolman (co-lead, NOAA/NCEP) Isaac Ginis (URI) Chris Fairall (NOAA/ESRL) Shaowu Bao (NOAA/ESRL) Jian-Wen
Coupled Ocean-Wave Model Team (Team 8) Report George Halliwell (co-lead, NOAA/AOML/PhOD) Hendrik Tolman (co-lead, NOAA/NCEP) Isaac Ginis (URI) Chris Fairall (NOAA/ESRL) Shaowu Bao (NOAA/ESRL) Jian-Wen
Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration
 Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration Climatological and hydrological field work Figure 1: Estimate of the Earth s annual and global mean energy balance. Over the long term, the incoming
Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration Climatological and hydrological field work Figure 1: Estimate of the Earth s annual and global mean energy balance. Over the long term, the incoming
A new theory for moist convection in statistical equilibrium
 A new theory for moist convection in statistical equilibrium A. Parodi(1), K. Emanuel(2) (2) CIMA Research Foundation,Savona, Italy (3) EAPS, MIT, Boston, USA True dynamics: turbulent, moist, non-boussinesq,
A new theory for moist convection in statistical equilibrium A. Parodi(1), K. Emanuel(2) (2) CIMA Research Foundation,Savona, Italy (3) EAPS, MIT, Boston, USA True dynamics: turbulent, moist, non-boussinesq,
A Bulk Turbulent Air Sea Flux Algorithm for High-Wind, Spray Conditions
 JULY 2008 A N D R E A S E T A L. 1581 A Bulk Turbulent Air Sea Flux Algorithm for High-Wind, Spray Conditions EDGAR L ANDREAS NorthWest Research Associates, Inc., Lebanon, New Hampshire P. OLA G. PERSSON
JULY 2008 A N D R E A S E T A L. 1581 A Bulk Turbulent Air Sea Flux Algorithm for High-Wind, Spray Conditions EDGAR L ANDREAS NorthWest Research Associates, Inc., Lebanon, New Hampshire P. OLA G. PERSSON
Air sea satellite flux datasets and what they do (and don't) tell us about the air sea interface in the Southern Ocean
 Air sea satellite flux datasets and what they do (and don't) tell us about the air sea interface in the Southern Ocean Carol Anne Clayson Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Southern Ocean Workshop Seattle,
Air sea satellite flux datasets and what they do (and don't) tell us about the air sea interface in the Southern Ocean Carol Anne Clayson Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Southern Ocean Workshop Seattle,
Hurricane Intensity: Governing Factors and Forecasting Challenges. EAS 470 Final Paper Allison Wing
 Hurricane Intensity: Governing Factors and Forecasting Challenges EAS 470 Final Paper Allison Wing Tropical cyclones are undoubtedly among the mostly deadly and destructive natural phenomena found on Earth
Hurricane Intensity: Governing Factors and Forecasting Challenges EAS 470 Final Paper Allison Wing Tropical cyclones are undoubtedly among the mostly deadly and destructive natural phenomena found on Earth
On Surface fluxes and Clouds/Precipitation in the Tropical Eastern Atlantic
 On Surface fluxes and Clouds/Precipitation in the Tropical Eastern Atlantic Chris Fairall, NOAA/ESRL Paquita Zuidema, RSMAS/U Miami with contributions from Peter Minnett & Erica Key AMMA Team Meeting Leeds,
On Surface fluxes and Clouds/Precipitation in the Tropical Eastern Atlantic Chris Fairall, NOAA/ESRL Paquita Zuidema, RSMAS/U Miami with contributions from Peter Minnett & Erica Key AMMA Team Meeting Leeds,
Hurricanes are intense vortical (rotational) storms that develop over the tropical oceans in regions of very warm surface water.
 Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
Effects of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity
 3741 Effects of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity EDGAR LANDREAS U.S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, Hanover, New Hampshire KERRY A. EMANUEL Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
3741 Effects of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity EDGAR LANDREAS U.S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, Hanover, New Hampshire KERRY A. EMANUEL Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
Numerical Simulations of Air Sea Interaction under High Wind Conditions Using a Coupled Model: A Study of Hurricane Development
 2190 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW Numerical Simulations of Air Sea Interaction under High Wind Conditions Using a Coupled Model: A Study of Hurricane Development J.-W. BAO Cooperative Institute for Research
2190 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW Numerical Simulations of Air Sea Interaction under High Wind Conditions Using a Coupled Model: A Study of Hurricane Development J.-W. BAO Cooperative Institute for Research
18A.2 PREDICTION OF ATLANTIC TROPICAL CYCLONES WITH THE ADVANCED HURRICANE WRF (AHW) MODEL
 18A.2 PREDICTION OF ATLANTIC TROPICAL CYCLONES WITH THE ADVANCED HURRICANE WRF (AHW) MODEL Jimy Dudhia *, James Done, Wei Wang, Yongsheng Chen, Qingnong Xiao, Christopher Davis, Greg Holland, Richard Rotunno,
18A.2 PREDICTION OF ATLANTIC TROPICAL CYCLONES WITH THE ADVANCED HURRICANE WRF (AHW) MODEL Jimy Dudhia *, James Done, Wei Wang, Yongsheng Chen, Qingnong Xiao, Christopher Davis, Greg Holland, Richard Rotunno,
Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2)
 Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2) The ABL, though turbulent, is not homogeneous, and a critical role of turbulence is transport and mixing of air properties, especially in the
Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2) The ABL, though turbulent, is not homogeneous, and a critical role of turbulence is transport and mixing of air properties, especially in the
1) The energy balance at the TOA is: 4 (1 α) = σt (1 0.3) = ( ) 4. (1 α) 4σ = ( S 0 = 255 T 1
 EAS488/B8800 Climate & Climate Change Homework 2: Atmospheric Radiation and Climate, surface energy balance, and atmospheric general circulation Posted: 3/12/18; due: 3/26/18 Answer keys 1. (10 points)
EAS488/B8800 Climate & Climate Change Homework 2: Atmospheric Radiation and Climate, surface energy balance, and atmospheric general circulation Posted: 3/12/18; due: 3/26/18 Answer keys 1. (10 points)
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. The Effects of Dissipative Heating on Hurricane Intensity
 3032 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE The Effects of Dissipative Heating on Hurricane Intensity DA-LIN ZHANG AND ERIC ALTSHULER Department of Meteorology, University of Maryland, College
3032 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE The Effects of Dissipative Heating on Hurricane Intensity DA-LIN ZHANG AND ERIC ALTSHULER Department of Meteorology, University of Maryland, College
Uncertainties in sea surface turbulent flux algorithms and data sets
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. C10, 3141, doi:10.1029/2001jc000992, 2002 Uncertainties in sea surface turbulent flux algorithms and data sets Michael A. Brunke and Xubin Zeng Institute
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. C10, 3141, doi:10.1029/2001jc000992, 2002 Uncertainties in sea surface turbulent flux algorithms and data sets Michael A. Brunke and Xubin Zeng Institute
Numerical Experiments of Tropical Cyclone Seasonality over the Western North Pacific
 Numerical Experiments of Tropical Cyclone Seasonality over the Western North Pacific Dong-Kyou Lee School of Earth and Environmental Sciences Seoul National University, Korea Contributors: Suk-Jin Choi,
Numerical Experiments of Tropical Cyclone Seasonality over the Western North Pacific Dong-Kyou Lee School of Earth and Environmental Sciences Seoul National University, Korea Contributors: Suk-Jin Choi,
Aircraft Observations for ONR DRI and DYNAMO. Coupled Air-sea processes: Q. Wang, D. Khelif, L. Mahrt, S. Chen
 Aircraft Observations for ONR DRI and DYNAMO (NOAA/ONR/NSF) Coupled Air-sea processes: Q. Wang, D. Khelif, L. Mahrt, S. Chen Deep convection/mjo initiation: Dave Jorgensen, S. Chen, R. Houze Aerosol/Cloud
Aircraft Observations for ONR DRI and DYNAMO (NOAA/ONR/NSF) Coupled Air-sea processes: Q. Wang, D. Khelif, L. Mahrt, S. Chen Deep convection/mjo initiation: Dave Jorgensen, S. Chen, R. Houze Aerosol/Cloud
Momentum Flux Budget Across Air-sea Interface under Uniform and Tropical Cyclone Winds
 Momentum Flux Budget Across Air-sea Interface under Uniform and Tropical Cyclone Winds Yalin Fan 1, Isaac Ginis 2, Tetsu Hara 2 1. AOS, Princeton University / GFDL, NOAA, Princeton, New Jersey 2. Graduate
Momentum Flux Budget Across Air-sea Interface under Uniform and Tropical Cyclone Winds Yalin Fan 1, Isaac Ginis 2, Tetsu Hara 2 1. AOS, Princeton University / GFDL, NOAA, Princeton, New Jersey 2. Graduate
The Total Energy Mass Flux PBL Scheme: Overview and Performance in Shallow-Cloud Cases
 The Total Energy Mass Flux PBL Scheme: Overview and Performance in Shallow-Cloud Cases Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL Thorsten Mauritsen Max Planck Institute for Meteorology,
The Total Energy Mass Flux PBL Scheme: Overview and Performance in Shallow-Cloud Cases Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL Thorsten Mauritsen Max Planck Institute for Meteorology,
Stable and transitional (and cloudy) boundary layers in WRF. Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL
 Stable and transitional (and cloudy) boundary layers in WRF Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL WRF PBL and Land Surface options Too many options! PBL here: MYJ (traditional,
Stable and transitional (and cloudy) boundary layers in WRF Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL WRF PBL and Land Surface options Too many options! PBL here: MYJ (traditional,
How surface latent heat flux is related to lower-tropospheric stability in southern subtropical marine stratus and stratocumulus regions
 Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 1(3) 2009 368-375 DOI: 10.2478/v10085-009-0028-1 Central European Journal of Geosciences How surface latent heat flux is related to lower-tropospheric stability in southern subtropical
Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 1(3) 2009 368-375 DOI: 10.2478/v10085-009-0028-1 Central European Journal of Geosciences How surface latent heat flux is related to lower-tropospheric stability in southern subtropical
The impact of rain on ocean wave evolution and its feedback to the atmosphere
 HAROKOPIO UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY ATMOSPHERE AND CLIMATE DYNAMICS GROUP (ACDG) http://meteoclima.gr Coastal Hydrology and Surface Processes linked to Air/Sea Modeling: 1 st community
HAROKOPIO UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY ATMOSPHERE AND CLIMATE DYNAMICS GROUP (ACDG) http://meteoclima.gr Coastal Hydrology and Surface Processes linked to Air/Sea Modeling: 1 st community
Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes. Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology
 Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics
Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
Cold wake of Hurricane Frances
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15609, doi:10.1029/2007gl030160, 2007 Cold wake of Hurricane Frances Eric A. D Asaro, 1 Thomas B. Sanford, 1 P. Peter Niiler, 2 and Eric
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15609, doi:10.1029/2007gl030160, 2007 Cold wake of Hurricane Frances Eric A. D Asaro, 1 Thomas B. Sanford, 1 P. Peter Niiler, 2 and Eric
Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition. SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club
 Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club Mar 01, 2006 AGCM5 of the GFD-DENNOU CLUB edition is a three-dimensional primitive system on a sphere (Swamp Project,
Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club Mar 01, 2006 AGCM5 of the GFD-DENNOU CLUB edition is a three-dimensional primitive system on a sphere (Swamp Project,
地球系统科学前沿讲座 台风研究现状和问题 林岩銮
 地球系统科学前沿讲座 台风研究现状和问题 林岩銮 2013.3.18 Satellite image of Hurricane Floyd approaching the east coast of Florida in 1999. The image has been digitally enhanced to lend a three-dimensional perspective. Credit:
地球系统科学前沿讲座 台风研究现状和问题 林岩銮 2013.3.18 Satellite image of Hurricane Floyd approaching the east coast of Florida in 1999. The image has been digitally enhanced to lend a three-dimensional perspective. Credit:
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
A Numerical Study of a TOGA-COARE Squall-Line Using a Coupled Mesoscale Atmosphere-Ocean Model
 ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 21, NO. 5, 2004, 708 716 A Numerical Study of a TOGA-COARE Squall-Line Using a Coupled Mesoscale Atmosphere-Ocean Model Shaowu BAO, Lian XIE, and Sethu RAMAN Department
ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 21, NO. 5, 2004, 708 716 A Numerical Study of a TOGA-COARE Squall-Line Using a Coupled Mesoscale Atmosphere-Ocean Model Shaowu BAO, Lian XIE, and Sethu RAMAN Department
Turbulent fluxes. Sensible heat flux. Momentum flux = Wind stress ρc D (U-U s ) 2. Latent heat flux. ρc p C H (U-U s ) (T s -T a )
 Intertropical ocean-atmosphere coupling in a state of the art Earth System Model: Evaluating the representation of turbulent air-sea fluxes in IPSL-CM5A Alina Găinuşă-Bogdan, Pascale Braconnot Laboratoire
Intertropical ocean-atmosphere coupling in a state of the art Earth System Model: Evaluating the representation of turbulent air-sea fluxes in IPSL-CM5A Alina Găinuşă-Bogdan, Pascale Braconnot Laboratoire
Impact of Turbulence on the Intensity of Hurricanes in Numerical Models* Richard Rotunno NCAR
 Impact of Turbulence on the Intensity of Hurricanes in Numerical Models* Richard Rotunno NCAR *Based on: Bryan, G. H., and R. Rotunno, 2009: The maximum intensity of tropical cyclones in axisymmetric numerical
Impact of Turbulence on the Intensity of Hurricanes in Numerical Models* Richard Rotunno NCAR *Based on: Bryan, G. H., and R. Rotunno, 2009: The maximum intensity of tropical cyclones in axisymmetric numerical
The effects of wind-driven waves and ocean spray on the drag coefficient and near-surface wind profiles over the ocean
 Acta Oceanol. Sin., 216, Vol. 35, No. 11, P. 79 85 DOI: 1.17/s13131-16-95-6 http://www.hyxb.org.cn E-mail: hyxbe@263.net The effects of wind-driven waves and ocean spray on the drag coefficient and near-surface
Acta Oceanol. Sin., 216, Vol. 35, No. 11, P. 79 85 DOI: 1.17/s13131-16-95-6 http://www.hyxb.org.cn E-mail: hyxbe@263.net The effects of wind-driven waves and ocean spray on the drag coefficient and near-surface
Cloud parameterization and cloud prediction scheme in Eta numerical weather model
 Cloud parameterization and cloud prediction scheme in Eta numerical weather model Belgrade, 10th September, 2018 Ivan Ristić, CEO at Weather2 Ivana Kordić, meteorologist at Weather2 Introduction Models
Cloud parameterization and cloud prediction scheme in Eta numerical weather model Belgrade, 10th September, 2018 Ivan Ristić, CEO at Weather2 Ivana Kordić, meteorologist at Weather2 Introduction Models
2.1 OBSERVATIONS AND THE PARAMETERISATION OF AIR-SEA FLUXES DURING DIAMET
 2.1 OBSERVATIONS AND THE PARAMETERISATION OF AIR-SEA FLUXES DURING DIAMET Peter A. Cook * and Ian A. Renfrew School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1
2.1 OBSERVATIONS AND THE PARAMETERISATION OF AIR-SEA FLUXES DURING DIAMET Peter A. Cook * and Ian A. Renfrew School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1
OCN/ATM/ESS 587. Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics.
 OCN/ATM/ESS 587 Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics. Equation of state for seawater General T/S properties of the upper ocean Heat balance of the upper ocean Upper ocean circulation Deep circulation
OCN/ATM/ESS 587 Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics. Equation of state for seawater General T/S properties of the upper ocean Heat balance of the upper ocean Upper ocean circulation Deep circulation
HWRF Ocean: The Princeton Ocean Model. HWRF Tutorial NCWCP, College Park, MD January 2018
 HWRF Ocean: The Princeton Ocean Model Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode Island HWRF Tutorial NCWCP, College Park, MD 23-25 January 2018 1 1 Why Couple a 3-D Ocean Model to
HWRF Ocean: The Princeton Ocean Model Isaac Ginis Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode Island HWRF Tutorial NCWCP, College Park, MD 23-25 January 2018 1 1 Why Couple a 3-D Ocean Model to
Taking into account the gustiness due to free and deep convection for the representation of air-sea fluxes. - in the LMDZ model -
 Taking into account the gustiness due to free and deep convection for the representation of air-sea fluxes - in the LMDZ model - Alina Găinuşă-Bogdan, Frédéric Hourdin, Abdoul Traore, Catherine Rio, Jean-Yves
Taking into account the gustiness due to free and deep convection for the representation of air-sea fluxes - in the LMDZ model - Alina Găinuşă-Bogdan, Frédéric Hourdin, Abdoul Traore, Catherine Rio, Jean-Yves
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models
 Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
Glaciology HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION
 HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION A Heat Budget 1 Black body radiation Definition. A perfect black body is defined as a body that absorbs all radiation that falls on it. The intensity of radiation emitted by a
HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION A Heat Budget 1 Black body radiation Definition. A perfect black body is defined as a body that absorbs all radiation that falls on it. The intensity of radiation emitted by a
PUBLICATIONS. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans RESEARCH ARTICLE Special Section: Oceanic Responses and Feedbacks to Tropical Cyclones Key Points: Sea spray parameterization scheme The distribution
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans RESEARCH ARTICLE Special Section: Oceanic Responses and Feedbacks to Tropical Cyclones Key Points: Sea spray parameterization scheme The distribution
Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate
 Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation
 Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation Adam Sobel Columbia University NCAR IMAGe Workshop, Nov. 3 2005 In the tropics, our picture of the dynamics should
Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation Adam Sobel Columbia University NCAR IMAGe Workshop, Nov. 3 2005 In the tropics, our picture of the dynamics should
Exploring stochastic model uncertainty representations
 Exploring stochastic model uncertainty representations with relevance to the greyzone Sarah-Jane Lock, Martin Leutbecher, Peter Bechtold, Richard Forbes Research Department, ECMWF ECMWF November 15, 2017
Exploring stochastic model uncertainty representations with relevance to the greyzone Sarah-Jane Lock, Martin Leutbecher, Peter Bechtold, Richard Forbes Research Department, ECMWF ECMWF November 15, 2017
Tropical Cyclones-Ocean interaction as represented by a 25km resolution CGCM: the role of the coupling frequency
 HRCP Workshop 13-15 April 2016 Tropical Cyclones-Ocean interaction as represented by a 25km resolution CGCM: the role of the coupling frequency Enrico Scoccimarro (1,2), P.G. Fogli (2), K. Reed (3), S.
HRCP Workshop 13-15 April 2016 Tropical Cyclones-Ocean interaction as represented by a 25km resolution CGCM: the role of the coupling frequency Enrico Scoccimarro (1,2), P.G. Fogli (2), K. Reed (3), S.
Motivation & Goal. We investigate a way to generate PDFs from a single deterministic run
 Motivation & Goal Numerical weather prediction is limited by errors in initial conditions, model imperfections, and nonlinearity. Ensembles of an NWP model provide forecast probability density functions
Motivation & Goal Numerical weather prediction is limited by errors in initial conditions, model imperfections, and nonlinearity. Ensembles of an NWP model provide forecast probability density functions
Impact of the Waves on the Sea Surface Roughness Length under Idealized Like-Hurricane Wind Conditions (Part II)
 Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 2015, 5, 326-335 Published Online July 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/acs http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/acs.2015.53025 Impact of the Waves on the Sea Surface
Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 2015, 5, 326-335 Published Online July 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/acs http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/acs.2015.53025 Impact of the Waves on the Sea Surface
2σ e s (r,t) = e s (T)exp( rr v ρ l T ) = exp( ) 2σ R v ρ l Tln(e/e s (T)) e s (f H2 O,r,T) = f H2 O
 Formulas/Constants, Physics/Oceanography 4510/5510 B Atmospheric Physics II N A = 6.02 10 23 molecules/mole (Avogadro s number) 1 mb = 100 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/m 2 Γ d = 9.8 o C/km (dry adiabatic lapse rate)
Formulas/Constants, Physics/Oceanography 4510/5510 B Atmospheric Physics II N A = 6.02 10 23 molecules/mole (Avogadro s number) 1 mb = 100 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/m 2 Γ d = 9.8 o C/km (dry adiabatic lapse rate)
The record-setting 2005 hurricane season has
 The CBLAST-Hurricane Program and the Next- Generation Fully Coupled Atmosphere Wave Ocean Models for Hurricane Research and Prediction BY SHUYI S. CHEN, JAMES F. PRICE, WEI ZHAO, MARK A. DONELAN, AND EDWARD
The CBLAST-Hurricane Program and the Next- Generation Fully Coupled Atmosphere Wave Ocean Models for Hurricane Research and Prediction BY SHUYI S. CHEN, JAMES F. PRICE, WEI ZHAO, MARK A. DONELAN, AND EDWARD
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Temporal and spatial variations in radiation and energy fluxes across Lake Taihu
 Temporal and spatial variations in radiation and energy fluxes across Lake Taihu Wang Wei YNCenter Video Conference May 10, 2012 Outline 1. Motivation 2. Hypothesis 3. Methodology 4. Preliminary results
Temporal and spatial variations in radiation and energy fluxes across Lake Taihu Wang Wei YNCenter Video Conference May 10, 2012 Outline 1. Motivation 2. Hypothesis 3. Methodology 4. Preliminary results
On Sea Surface Roughness Parameterization and Its Effect on Tropical. Cyclone Structure and Intensity
 On Sea Surface Roughness Parameterization and Its Effect on Tropical Cyclone Structure and Intensity Zhihua Zeng Shanghai Typhoon Institute, Laboratory of Typhoon Forecast Technique/CMA, Shanghai, China
On Sea Surface Roughness Parameterization and Its Effect on Tropical Cyclone Structure and Intensity Zhihua Zeng Shanghai Typhoon Institute, Laboratory of Typhoon Forecast Technique/CMA, Shanghai, China
4D.5 INVESTIGATING THE IMPACTS OF WAVE STATE AND SEA SPRAY ON TYPHOON VIA A COUPLED ATMOSPHERE-WAVE SYSTEM: THE IDEALIZED CASE
 4D.5 INVESIGAING HE IMPACS OF WAVE SAE AND SEA SPRAY ON YPHOON VIA A COUPED AMOSPHERE-WAVE SYSEM: HE IDEAIZED CASE Bin iu 1,, Changlong Guan, and ian Xie 1 1 Department of Marine, Earth and Atmospheric
4D.5 INVESIGAING HE IMPACS OF WAVE SAE AND SEA SPRAY ON YPHOON VIA A COUPED AMOSPHERE-WAVE SYSEM: HE IDEAIZED CASE Bin iu 1,, Changlong Guan, and ian Xie 1 1 Department of Marine, Earth and Atmospheric
Papers. Sea salt emission from the coastal zone. 1. Introduction
 Papers Sea salt emission from the coastal zone OCEANOLOGIA, 42 (4), 2000. pp. 399 4. 2000, by Institute of Oceanology PAS. KEYWORDS Aerosol Sea salt Fluxes Emission Coastal zone Tomasz Petelski Maria Chomka
Papers Sea salt emission from the coastal zone OCEANOLOGIA, 42 (4), 2000. pp. 399 4. 2000, by Institute of Oceanology PAS. KEYWORDS Aerosol Sea salt Fluxes Emission Coastal zone Tomasz Petelski Maria Chomka
Chapter 4 Water Vapor
 Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Impact of wind waves on the air-sea momentum fluxes for different wind and sea state conditions and oceanic response
 Impact of wind waves on the air-sea momentum fluxes for different wind and sea state conditions and oceanic response Joanna Staneva, Heinz Günther, A. Behrens, O. Krüger, Corinna Schrum, (HZG, Germany)
Impact of wind waves on the air-sea momentum fluxes for different wind and sea state conditions and oceanic response Joanna Staneva, Heinz Günther, A. Behrens, O. Krüger, Corinna Schrum, (HZG, Germany)
ONE DIMENSIONAL CLIMATE MODEL
 JORGE A. RAMÍREZ Associate Professor Water Resources, Hydrologic and Environmental Sciences Civil Wngineering Department Fort Collins, CO 80523-1372 Phone: (970 491-7621 FAX: (970 491-7727 e-mail: Jorge.Ramirez@ColoState.edu
JORGE A. RAMÍREZ Associate Professor Water Resources, Hydrologic and Environmental Sciences Civil Wngineering Department Fort Collins, CO 80523-1372 Phone: (970 491-7621 FAX: (970 491-7727 e-mail: Jorge.Ramirez@ColoState.edu
An Investigation of Turbulent Heat Exchange in the Subtropics
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. An Investigation of Turbulent Heat Exchange in the Subtropics James B. Edson University of Connecticut, Avery Point 1080
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. An Investigation of Turbulent Heat Exchange in the Subtropics James B. Edson University of Connecticut, Avery Point 1080
Analysis of Mixing and Dynamics Associated with the Dissolution of Hurricane-Induced Cold Wakes
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Analysis of Mixing and Dynamics Associated with the Dissolution of Hurricane-Induced Cold Wakes Carol Anne Clayson Dept.
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Analysis of Mixing and Dynamics Associated with the Dissolution of Hurricane-Induced Cold Wakes Carol Anne Clayson Dept.
Next Generation HWRF. HYCOM coupling. National Centers for Environmental Prediction. HWRF & HYCOM modeling team. Environmental Modeling Center
 HWRF tutorial 1 Next Generation HWRF HYCOM coupling Hyun-Sook Kim HWRF & HYCOM modeling team 2018 HWRF Tutorial Environmental Modeling Center National Centers for Environmental Prediction US National Weather
HWRF tutorial 1 Next Generation HWRF HYCOM coupling Hyun-Sook Kim HWRF & HYCOM modeling team 2018 HWRF Tutorial Environmental Modeling Center National Centers for Environmental Prediction US National Weather
Momentum Flux Budget across the Air Sea Interface under Uniform and Tropical Cyclone Winds
 OCTOBER 2010 F A N E T A L. 2221 Momentum Flux Budget across the Air Sea Interface under Uniform and Tropical Cyclone Winds YALIN FAN Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Program, Princeton University, and
OCTOBER 2010 F A N E T A L. 2221 Momentum Flux Budget across the Air Sea Interface under Uniform and Tropical Cyclone Winds YALIN FAN Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Program, Princeton University, and
ESCI 485 Air/Sea Interaction Lesson 1 Stresses and Fluxes Dr. DeCaria
 ESCI 485 Air/Sea Interaction Lesson 1 Stresses and Fluxes Dr DeCaria References: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, Holton MOMENTUM EQUATIONS The momentum equations governing the ocean or atmosphere
ESCI 485 Air/Sea Interaction Lesson 1 Stresses and Fluxes Dr DeCaria References: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, Holton MOMENTUM EQUATIONS The momentum equations governing the ocean or atmosphere
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System
 Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Impact of Forcing/Coupling on Atmospheric and Oceanic Forecasts
 Impact of Forcing/Coupling on Atmospheric and Oceanic Forecasts herve.giordani@meteo.fr GAME/CNRM (Météo-France/CNRS),Toulouse, France Workshop, ECMWF Reading, UK, 10-12 November 2008 Oceanic state in
Impact of Forcing/Coupling on Atmospheric and Oceanic Forecasts herve.giordani@meteo.fr GAME/CNRM (Météo-France/CNRS),Toulouse, France Workshop, ECMWF Reading, UK, 10-12 November 2008 Oceanic state in
3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme
 3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme R. J. Keane and R. S. Plant 3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme p.1/17 Outline Introduction to the Plant-Craig
3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme R. J. Keane and R. S. Plant 3D experiments with a stochastic convective parameterisation scheme p.1/17 Outline Introduction to the Plant-Craig
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY. Lecture 19. Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes
 ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
