Taking into account the gustiness due to free and deep convection for the representation of air-sea fluxes. - in the LMDZ model -
|
|
|
- Blake Tate
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Taking into account the gustiness due to free and deep convection for the representation of air-sea fluxes - in the LMDZ model - Alina Găinuşă-Bogdan, Frédéric Hourdin, Abdoul Traore, Catherine Rio, Jean-Yves Grandpeix, Jean-Louis Dufresne
2 What is gustiness? Small-scale wind variability Subgrid Redelsperger et al. (2000)
3 How can we parameterize gustiness? Free convection: Godfrey&Beljaars (1991): U eff 2 = U (βw * ) 2 Redelsperger et al. (2000): β = 0.65 Deep convection: Redelsperger et al. (2000): U g = 19.8 R R + R 2 4
4 How can we parameterize gustiness? ALE = Available lifting energy
5 How can we parameterize gustiness? Redelsperger et al. (2000): (βw * ) 2 f(r) U eff 2 = U β 2 2ALE BL + α 2ALE WK ALE = Available lifting energy
6 Simulations Old parameterization - contained ad-hoc C H enhancement at low wind speeds under unstable conditions eq.9/miller et al. (1992) No parameterization - de-activation of eq.9/miller et al. (1992) New parameterization - replacement of Miller et al. eq. 9 with full gustiness (BL+WK) 1D case TOGA
7 Simulations Old parameterization - contained ad-hoc C H enhancement at low wind speeds under unstable conditions eq.9/miller et al. (1992) No parameterization - de-activation of eq.9/miller et al. (1992) New parameterization - replacement of Miller et al. eq. 9 with full gustiness (BL+WK) Effective wind speed difference 1D case TOGA
8 Results - fluxes none - old new - old The results are what we expect for the wind stress: removing the old C H enchancement => no effect on wind stress add proper gustiness => enhanced wind stress, following effective wind speed evolution
9 Results - fluxes none - old new - old Removing the old parameterization decreases the latent heat flux New parameterization => mostly enhanced latent heat fluxes No clear change of mean sensible heat fluxes in either case, but more variability with the new parameterization
10 Results - fluxes none - old new - old Removing the old parameterization decreases the latent heat flux New parameterization => mostly enhanced latent heat fluxes No clear change of mean sensible heat fluxes in either case, but more variability with the new parameterization...is that really so?
11 Results - fluxes none - old new - old
12 Results - fluxes none - old? new - old
13 Results - fluxes none - old new - old? old parameterization old parameterization no parameterization new parameterization
14 Results - fluxes none - old new - old? old parameterization old parameterization no parameterization new parameterization
15 Conclusions 1D experiments (TOGA) Evaluation of gustiness parameterization global statistics BUT ALSO high-frequency time evolution! (process-oriented diagnostics ideal, but not often possible)
16 Conclusions 1D experiments (TOGA) Evaluation of gustiness parameterization global statistics BUT ALSO high-frequency time evolution! (process-oriented diagnostics ideal, but not often possible) Gustiness => higher, more variable wind stress higher because of effective wind speed, NOT C D (~same mean value, lower variability); more variable simply because it takes both positive and negative values + see above
17 Conclusions 1D experiments (TOGA) Evaluation of gustiness parameterization global statistics BUT ALSO high-frequency time evolution! (process-oriented diagnostics ideal, but not often possible) Gustiness => higher, more variable wind stress higher because of effective wind speed, NOT C D (~same mean value, lower variability); more variable simply because it takes both positive and negative values + see above Gustiness => ~O(25%) higher LH than without (~O(10%) higher than old parameterization); less variability also thanks to direct effect of the effective wind speed C H actually decreases (<> old parameterization, where C H increase is the reason why LH increased compared to no parameterization) q2m increases slightly (O(5%) w.r.t. old, O(10%) w.r.t. none), but systematically
18 Conclusions 1D experiments (TOGA) Evaluation of gustiness parameterization global statistics BUT ALSO high-frequency time evolution! (process-oriented diagnostics ideal, but not often possible) Gustiness => higher, more variable wind stress higher because of effective wind speed, NOT C D (~same mean value, lower variability); more variable simply because it takes both positive and negative values + see above Gustiness => ~O(25%) higher LH than without (~O(10%) higher than old parameterization); less variability also thanks to direct effect of the effective wind speed C H actually decreases (<> old parameterization, where C H increase is the reason why LH increased compared to no parameterization) q2m increases slightly (O(5%) w.r.t. old, O(10%) w.r.t. none), but systematically Gustiness => negligible differences in mean SH; slightly less variability lower CH and ΔT compensate for higher effective wind speed?
19 Results 3D, atmosphere forced with climatological SSTs, 3 years
20 Results 3D, atmosphere forced with climatological SSTs, 3 years
21 Results 3D, atmosphere forced with climatological SSTs, 3 years
22 Results 3D, atmosphere forced with climatological SSTs, 3 years
23 Results 3D, atmosphere forced with climatological SSTs, 3 years
24 Results 3D, atmosphere forced with climatological SSTs, 3 years
25 Results 3D, coupled ocean-atmosphere model, 3 years
26 Conclusionsts 3D tests Gustiness doesn t only affect the tropics! Thank you!
27 How important is gustiness? Free convection: Godfrey&Beljaars (1991): At low wind speeds, quite! U eff 2 = U (βw * ) 2 Redelsperger et al. (2000): β = 0.65 Deep convection: Redelsperger et al. (2000): U g = 19.8 R R + R 2 4
28 How important is gustiness? Wind stress At low wind speeds, quite! Latent heat flux Sensible heat flux
29 What can we use for development? 1D case TOGA The TOGA-COARE campaign: Nov. 1 st, 1992 Feb. 28, 1993 Succession of active and suppressed convection events
30 How do we parameterize gustiness? U eff 2 = U β 2 2ALE BL + α 2ALE WK
31 How do we parameterize gustiness? U eff 2 = U β 2 2ALE BL + α 2ALE WK Scalar mean of the wind speed (Redelsperger et al., 2000) = U 0 + resolved deep convection gustiness Magnitude of the mean vector wind (Redelsperger et al., 2000) = U 0 U 0, CTRL + BL gust + WK gust U 0, CTRL + BL gust U 0, CTRL + WK gust Magnitude of the mean vector wind = U 0, CTRL comparable magnitudes lower gustiness for U 0 peaks, higher for low U 0 wind enhancement higher in Dec than Dec 1992
32 How do we parameterize gustiness? U eff 2 = U β 2 2ALE BL + α 2ALE WK Horizontal wind speed deep convection gustiness Scalar mean of the wind speed (Redelsperger et al., 2000) = U 0 + resolved deep convection gustiness Magnitude of the mean vector wind (Redelsperger et al., 2000) = U 0 Magnitude of the mean vector wind = U 0, OBS Magnitude of the mean vector wind = U 0, CTRL
33 Results 3D gustiness and turbulent exchange coefficients AMIP CPL
34 Results 3D - Precipitation AMIP CPL
35 Results 3D - Precipitation
Evaluation of the IPSL climate model in a weather-forecast mode
 Evaluation of the IPSL climate model in a weather-forecast mode CFMIP/GCSS/EUCLIPSE Meeting, The Met Office, Exeter 2011 Solange Fermepin, Sandrine Bony and Laurent Fairhead Introduction Transpose AMIP
Evaluation of the IPSL climate model in a weather-forecast mode CFMIP/GCSS/EUCLIPSE Meeting, The Met Office, Exeter 2011 Solange Fermepin, Sandrine Bony and Laurent Fairhead Introduction Transpose AMIP
Turbulent fluxes. Sensible heat flux. Momentum flux = Wind stress ρc D (U-U s ) 2. Latent heat flux. ρc p C H (U-U s ) (T s -T a )
 Intertropical ocean-atmosphere coupling in a state of the art Earth System Model: Evaluating the representation of turbulent air-sea fluxes in IPSL-CM5A Alina Găinuşă-Bogdan, Pascale Braconnot Laboratoire
Intertropical ocean-atmosphere coupling in a state of the art Earth System Model: Evaluating the representation of turbulent air-sea fluxes in IPSL-CM5A Alina Găinuşă-Bogdan, Pascale Braconnot Laboratoire
Relevant timescales: convective events diurnal intraseasonal. 3 ocean-atmosphere communication methods: freshwater flux flux momentum flux
 Radar Perspective on Air-Sea Interactions during DYNAMO Elizabeth Thompson; July 23 2013 Update Steve Rutledge, Brenda Dolan, Jim Moum, Aurelie Moulin, Chris Fairall, Bob Rilling, Mike Dixon, Scott Ellis,
Radar Perspective on Air-Sea Interactions during DYNAMO Elizabeth Thompson; July 23 2013 Update Steve Rutledge, Brenda Dolan, Jim Moum, Aurelie Moulin, Chris Fairall, Bob Rilling, Mike Dixon, Scott Ellis,
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. Parameterization of Wind Gustiness for the Computation of Ocean Surface Fluxes at Different Spatial Scales
 15 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Parameterization of Wind Gustiness for the Computation of Ocean Surface Fluxes at Different Spatial Scales XUBIN ZENG Institute of Atmospheric Physics, The University of Arizona,
15 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Parameterization of Wind Gustiness for the Computation of Ocean Surface Fluxes at Different Spatial Scales XUBIN ZENG Institute of Atmospheric Physics, The University of Arizona,
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
2.1 OBSERVATIONS AND THE PARAMETERISATION OF AIR-SEA FLUXES DURING DIAMET
 2.1 OBSERVATIONS AND THE PARAMETERISATION OF AIR-SEA FLUXES DURING DIAMET Peter A. Cook * and Ian A. Renfrew School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1
2.1 OBSERVATIONS AND THE PARAMETERISATION OF AIR-SEA FLUXES DURING DIAMET Peter A. Cook * and Ian A. Renfrew School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1
Air-Sea Interaction and the MJO
 Air-Sea Interaction and the MJO Julia Slingo with thanks to Dan Bernie, Eric Guilyardi, Pete Inness, Hilary Spencer and Steve Woolnough NCAS Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling University of Reading
Air-Sea Interaction and the MJO Julia Slingo with thanks to Dan Bernie, Eric Guilyardi, Pete Inness, Hilary Spencer and Steve Woolnough NCAS Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling University of Reading
John Steffen and Mark A. Bourassa
 John Steffen and Mark A. Bourassa Funding by NASA Climate Data Records and NASA Ocean Vector Winds Science Team Florida State University Changes in surface winds due to SST gradients are poorly modeled
John Steffen and Mark A. Bourassa Funding by NASA Climate Data Records and NASA Ocean Vector Winds Science Team Florida State University Changes in surface winds due to SST gradients are poorly modeled
A "New" Mechanism for the Diurnal Variation of Convection over the Tropical Western Pacific Ocean
 A "New" Mechanism for the Diurnal Variation of Convection over the Tropical Western Pacific Ocean D. B. Parsons Atmospheric Technology Division National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Boulder,
A "New" Mechanism for the Diurnal Variation of Convection over the Tropical Western Pacific Ocean D. B. Parsons Atmospheric Technology Division National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Boulder,
Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics
 Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics Jimy Dudhia MMM Division, NCAR 1D Ocean Mixed-Layer Model 1d model based on Pollard, Rhines and Thompson (1973) was added for hurricane forecasts Purpose is to represent
Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics Jimy Dudhia MMM Division, NCAR 1D Ocean Mixed-Layer Model 1d model based on Pollard, Rhines and Thompson (1973) was added for hurricane forecasts Purpose is to represent
Aircraft Observations for ONR DRI and DYNAMO. Coupled Air-sea processes: Q. Wang, D. Khelif, L. Mahrt, S. Chen
 Aircraft Observations for ONR DRI and DYNAMO (NOAA/ONR/NSF) Coupled Air-sea processes: Q. Wang, D. Khelif, L. Mahrt, S. Chen Deep convection/mjo initiation: Dave Jorgensen, S. Chen, R. Houze Aerosol/Cloud
Aircraft Observations for ONR DRI and DYNAMO (NOAA/ONR/NSF) Coupled Air-sea processes: Q. Wang, D. Khelif, L. Mahrt, S. Chen Deep convection/mjo initiation: Dave Jorgensen, S. Chen, R. Houze Aerosol/Cloud
Tropospheric Moisture: The Crux of the MJO?
 Tropospheric Moisture: The Crux of the MJO? Chidong Zhang RSMAS, University of Miami ICGPSRO2013, May 14 16, 2013 Madden and Julian 1972 Precipitation Global Impacts of the MJO on Weather and Climate MJO
Tropospheric Moisture: The Crux of the MJO? Chidong Zhang RSMAS, University of Miami ICGPSRO2013, May 14 16, 2013 Madden and Julian 1972 Precipitation Global Impacts of the MJO on Weather and Climate MJO
Impact of Forcing/Coupling on Atmospheric and Oceanic Forecasts
 Impact of Forcing/Coupling on Atmospheric and Oceanic Forecasts herve.giordani@meteo.fr GAME/CNRM (Météo-France/CNRS),Toulouse, France Workshop, ECMWF Reading, UK, 10-12 November 2008 Oceanic state in
Impact of Forcing/Coupling on Atmospheric and Oceanic Forecasts herve.giordani@meteo.fr GAME/CNRM (Météo-France/CNRS),Toulouse, France Workshop, ECMWF Reading, UK, 10-12 November 2008 Oceanic state in
Antarctic precipitation in the LMDz and MAR climate models : comparison to CloudSat retrievals and improvement of cold microphysical processes
 Antarctic precipitation in the LMDz and MAR climate models : comparison to CloudSat retrievals and improvement of cold microphysical processes J. B. Madeleine1*, H. Gallée2, E. Vignon2, C. Genthon2, G.
Antarctic precipitation in the LMDz and MAR climate models : comparison to CloudSat retrievals and improvement of cold microphysical processes J. B. Madeleine1*, H. Gallée2, E. Vignon2, C. Genthon2, G.
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do?
 Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models
 Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models Inna Polichtchouk & Ted Shepherd Royal Meteorological Society National Meeting 16.11.2016 MOTIVATION Question: How sensitive
Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models Inna Polichtchouk & Ted Shepherd Royal Meteorological Society National Meeting 16.11.2016 MOTIVATION Question: How sensitive
Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land
 Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land surfaces in the following ways: (a) Near surface air
Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land surfaces in the following ways: (a) Near surface air
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
Validation of the JRA-55 based data set: Comparison with buoy observations
 Validation of the JRA-55 based data set: Comparison with buoy observations Hiroyuki TOMITA (Nagoya University) tomita@hyarc.nagoya-u.ac.jp 2016.01.14 OMDP extended meeting JAMSTEC@Yokohama Objectives IN
Validation of the JRA-55 based data set: Comparison with buoy observations Hiroyuki TOMITA (Nagoya University) tomita@hyarc.nagoya-u.ac.jp 2016.01.14 OMDP extended meeting JAMSTEC@Yokohama Objectives IN
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture
 Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Atmospheric Processes
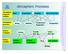 Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Convection Trigger: A key to improving GCM MJO simulation? CRM Contribution to DYNAMO and AMIE
 Convection Trigger: A key to improving GCM MJO simulation? CRM Contribution to DYNAMO and AMIE Xiaoqing Wu, Liping Deng and Sunwook Park Iowa State University 2009 DYNAMO Workshop Boulder, CO April 13-14,
Convection Trigger: A key to improving GCM MJO simulation? CRM Contribution to DYNAMO and AMIE Xiaoqing Wu, Liping Deng and Sunwook Park Iowa State University 2009 DYNAMO Workshop Boulder, CO April 13-14,
Upper-Ocean Processes and Air-Sea Interaction in the Indonesian Seas
 Upper-Ocean Processes and Air-Sea Interaction in the Indonesian Seas Janet Sprintall, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, USA Arnold L. Gordon, Asmi M. Napitu, LDEO, USA Ariane Koch-Larrouy, LEGOS, France
Upper-Ocean Processes and Air-Sea Interaction in the Indonesian Seas Janet Sprintall, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, USA Arnold L. Gordon, Asmi M. Napitu, LDEO, USA Ariane Koch-Larrouy, LEGOS, France
Mesoscale meteorological models. Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen
 Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Air Sea Process in the IndianI. Ocean and the Intraseasonal Oscillation. J.P. Duvel (LMD) H. Bellenger, J. Vialard, P.K. Xavier F.
 Air Sea Process in the IndianI Ocean and the Intraseasonal Oscillation J.P. Duvel (LMD) H. Bellenger, J. Vialard, P.K. Xavier F. Doblas Reyes Origin of the intraseasonal variability (ISV) of the convection?
Air Sea Process in the IndianI Ocean and the Intraseasonal Oscillation J.P. Duvel (LMD) H. Bellenger, J. Vialard, P.K. Xavier F. Doblas Reyes Origin of the intraseasonal variability (ISV) of the convection?
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget
 The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction in Tropical Cyclones
 Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction in Tropical Cyclones Isaac Ginis University of Rhode Island Collaborators: T. Hara, Y.Fan, I-J Moon, R. Yablonsky. ECMWF, November 10-12, 12, 2008 Air-Sea Interaction in Tropical
Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction in Tropical Cyclones Isaac Ginis University of Rhode Island Collaborators: T. Hara, Y.Fan, I-J Moon, R. Yablonsky. ECMWF, November 10-12, 12, 2008 Air-Sea Interaction in Tropical
The 5th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso-scale Weather Prediction, Nagoya University, Higashiyama Campus, Nagoya, 9 March 2015
 The 5th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso-scale Weather Prediction, Nagoya University, Higashiyama Campus, Nagoya, 9 March 2015 The effects of moisture conditions on the organization and intensity
The 5th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso-scale Weather Prediction, Nagoya University, Higashiyama Campus, Nagoya, 9 March 2015 The effects of moisture conditions on the organization and intensity
Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP
 Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP Paul Earnshaw and Sean Milton Met Office, UK Crown copyright 2005 Page 1 Overview Production and use of CEOP data Results SGP Seasonal & Diurnal cycles Other extratopical
Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP Paul Earnshaw and Sean Milton Met Office, UK Crown copyright 2005 Page 1 Overview Production and use of CEOP data Results SGP Seasonal & Diurnal cycles Other extratopical
Presentation A simple model of multiple climate regimes
 A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
MC-KPP: Efficient, flexible and accurate air-sea coupling
 MC-KPP: Efficient, flexible and accurate air-sea coupling Nick Klingaman NCAS-Climate, University of Reading Shortwave Longwave Latent Sensible Wind Prescribe SSTs and sea ice Pro: Computationally inexpensive,
MC-KPP: Efficient, flexible and accurate air-sea coupling Nick Klingaman NCAS-Climate, University of Reading Shortwave Longwave Latent Sensible Wind Prescribe SSTs and sea ice Pro: Computationally inexpensive,
Reynolds Averaging. Let u and v be two flow variables (which might or might not be velocity components), and suppose that. u t + x uv ( ) = S u,
 ! Revised January 23, 208 7:7 PM! Reynolds Averaging David Randall Introduction It is neither feasible nor desirable to consider in detail all of the small-scale fluctuations that occur in the atmosphere.
! Revised January 23, 208 7:7 PM! Reynolds Averaging David Randall Introduction It is neither feasible nor desirable to consider in detail all of the small-scale fluctuations that occur in the atmosphere.
BMKG Research on Air sea interaction modeling for YMC
 BMKG Research on Air sea interaction modeling for YMC Prof. Edvin Aldrian Director for Research and Development - BMKG First Scientific and Planning Workshop on Year of Maritime Continent, Singapore 27-3
BMKG Research on Air sea interaction modeling for YMC Prof. Edvin Aldrian Director for Research and Development - BMKG First Scientific and Planning Workshop on Year of Maritime Continent, Singapore 27-3
EFFECTS OF TROPICAL CYCLONES ON OCEAN HEAT TRANSPORT AS SIMULATED BY A HIGH RESOLUTION COUPLED GENERAL CIRCULATION MODEL
 ISTITUTO NAZIONALE di GEOFISICA e VULCANOLOGIA EFFECTS OF TROPICAL CYCLONES ON OCEAN HEAT TRANSPORT AS SIMULATED BY A HIGH RESOLUTION COUPLED GENERAL CIRCULATION MODEL E. Scoccimarro 1 S. Gualdi 12, A.
ISTITUTO NAZIONALE di GEOFISICA e VULCANOLOGIA EFFECTS OF TROPICAL CYCLONES ON OCEAN HEAT TRANSPORT AS SIMULATED BY A HIGH RESOLUTION COUPLED GENERAL CIRCULATION MODEL E. Scoccimarro 1 S. Gualdi 12, A.
THE FEASIBILITY OF EXTRACTING LOWLEVEL WIND BY TRACING LOW LEVEL MOISTURE OBSERVED IN IR IMAGERY OVER CLOUD FREE OCEAN AREA IN THE TROPICS
 THE FEASIBILITY OF EXTRACTING LOWLEVEL WIND BY TRACING LOW LEVEL MOISTURE OBSERVED IN IR IMAGERY OVER CLOUD FREE OCEAN AREA IN THE TROPICS Toshiro Ihoue and Tetsuo Nakazawa Meteorological Research Institute
THE FEASIBILITY OF EXTRACTING LOWLEVEL WIND BY TRACING LOW LEVEL MOISTURE OBSERVED IN IR IMAGERY OVER CLOUD FREE OCEAN AREA IN THE TROPICS Toshiro Ihoue and Tetsuo Nakazawa Meteorological Research Institute
Introduction to tropical meteorology and deep convection
 Introduction to tropical meteorology and deep convection TMD Lecture 1 Roger K. Smith University of Munich A satpix tour of the tropics The zonal mean circulation (Hadley circulation), Inter- Tropical
Introduction to tropical meteorology and deep convection TMD Lecture 1 Roger K. Smith University of Munich A satpix tour of the tropics The zonal mean circulation (Hadley circulation), Inter- Tropical
HWRF Surface Layer Thermodynamics Evaluation. Eric W. Uhlhorn and Joseph J. Cione HFIP Hurricane Modeling Workshop September 2012
 HWRF Surface Layer Thermodynamics Evaluation Eric W. Uhlhorn and Joseph J. Cione HFIP Hurricane Modeling Workshop 17-18 September 2012 Special thanks. HRD HWRF modeling team Gopal, Xuejin Zhang, Thiago
HWRF Surface Layer Thermodynamics Evaluation Eric W. Uhlhorn and Joseph J. Cione HFIP Hurricane Modeling Workshop 17-18 September 2012 Special thanks. HRD HWRF modeling team Gopal, Xuejin Zhang, Thiago
Recent, current & future work with NorESM-L in Bergen
 Recent, current & future work with NorESM-L in Bergen Thomas Toniazzo, Ingo Bethke, Mats Bentsen, Francois Counillon, Noel Keenlyside, and others... AMWG meeting Boulder, 10/2/2014 Low-resolution Norwegian
Recent, current & future work with NorESM-L in Bergen Thomas Toniazzo, Ingo Bethke, Mats Bentsen, Francois Counillon, Noel Keenlyside, and others... AMWG meeting Boulder, 10/2/2014 Low-resolution Norwegian
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
Shifting the diurnal cycle of parameterized deep convection over land
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L07809, doi:10.1029/2008gl036779, 2009 Shifting the diurnal cycle of parameterized deep convection over land C. Rio, 1 F. Hourdin, 1 J.-Y. Grandpeix, 1 and J.-P.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L07809, doi:10.1029/2008gl036779, 2009 Shifting the diurnal cycle of parameterized deep convection over land C. Rio, 1 F. Hourdin, 1 J.-Y. Grandpeix, 1 and J.-P.
The prognostic deep convection parametrization for operational forecast in horizontal resolutions of 8, 4 and 2 km
 The prognostic deep convection parametrization for operational forecast in horizontal resolutions of 8, 4 and 2 km Martina Tudor, Stjepan Ivatek-Šahdan and Antonio Stanešić tudor@cirus.dhz.hr Croatian
The prognostic deep convection parametrization for operational forecast in horizontal resolutions of 8, 4 and 2 km Martina Tudor, Stjepan Ivatek-Šahdan and Antonio Stanešić tudor@cirus.dhz.hr Croatian
Forecasting Polar Lows. Gunnar Noer The Norwegian Meteorological Institute in Tromsø
 Forecasting Polar Lows Gunnar Noer The Norwegian Meteorological Institute in Tromsø Longyearbyen Hopen Bear Island Jan Mayen Tromsø Gunnar Noer Senior forecaster / developer for polar meteorology The Norwegian
Forecasting Polar Lows Gunnar Noer The Norwegian Meteorological Institute in Tromsø Longyearbyen Hopen Bear Island Jan Mayen Tromsø Gunnar Noer Senior forecaster / developer for polar meteorology The Norwegian
Coastal Antarctic polynyas: A coupled process requiring high model resolution in the ocean and atmosphere
 Coastal Antarctic polynyas: A coupled process requiring high model resolution in the ocean and atmosphere Mike Dinniman and John Klinck Center for Coastal Physical Oceanography Old Dominion University
Coastal Antarctic polynyas: A coupled process requiring high model resolution in the ocean and atmosphere Mike Dinniman and John Klinck Center for Coastal Physical Oceanography Old Dominion University
Challenges in model development
 Challenges in model development Andy Brown 29/6/10 Contents How do we try to improve a model? Bottom up Top down Examples (Sensitivity to drag) Bottom up Develop new (and hopefully improved) parametrization
Challenges in model development Andy Brown 29/6/10 Contents How do we try to improve a model? Bottom up Top down Examples (Sensitivity to drag) Bottom up Develop new (and hopefully improved) parametrization
ENSO Outlook by JMA. Hiroyuki Sugimoto. El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency
 ENSO Outlook by JMA Hiroyuki Sugimoto El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Outline 1. ENSO impacts on the climate 2. Current Conditions 3. Prediction by JMA/MRI-CGCM 4. Summary
ENSO Outlook by JMA Hiroyuki Sugimoto El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Outline 1. ENSO impacts on the climate 2. Current Conditions 3. Prediction by JMA/MRI-CGCM 4. Summary
Moist static energy budget diagnostics for. monsoon research. H. Annamalai
 Moist static energy budget diagnostics for monsoon research H. Annamalai JJAS Precipitation and SST Climatology I III II Multiple regional heat sources - EIO and SPCZ still experience high precipitation
Moist static energy budget diagnostics for monsoon research H. Annamalai JJAS Precipitation and SST Climatology I III II Multiple regional heat sources - EIO and SPCZ still experience high precipitation
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models
 An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
Introduction to climate modeling. ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008
 Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans
![Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans](/thumbs/96/128963638.jpg) Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Validation of KPP in a coastal area
 Validation of KPP in a coastal area By (Météo France/SHOM) and Rémy Baraille (SHOM), Yves Morel (SHOM), Gwenaëlle Hello (Météo France), Hervé Giordani (Météo France) Contents I. Data from MOUTON2007; II.
Validation of KPP in a coastal area By (Météo France/SHOM) and Rémy Baraille (SHOM), Yves Morel (SHOM), Gwenaëlle Hello (Météo France), Hervé Giordani (Météo France) Contents I. Data from MOUTON2007; II.
Moisture modes, cloud-radiative feedbacks and the MJO
 Moisture modes, cloud-radiative feedbacks and the MJO Adam Sobel Eric Maloney with bits from Shuguang Wang, Jim Benedict; thanks also Gilles Bellon, Dargan Frierson, Daehyun Kim EUCLIPSE summer school
Moisture modes, cloud-radiative feedbacks and the MJO Adam Sobel Eric Maloney with bits from Shuguang Wang, Jim Benedict; thanks also Gilles Bellon, Dargan Frierson, Daehyun Kim EUCLIPSE summer school
Comparison of Convection Characteristics at the Tropical Western Pacific Darwin Site Between Observation and Global Climate Models Simulations
 Comparison of Convection Characteristics at the Tropical Western Pacific Darwin Site Between Observation and Global Climate Models Simulations G.J. Zhang Center for Atmospheric Sciences Scripps Institution
Comparison of Convection Characteristics at the Tropical Western Pacific Darwin Site Between Observation and Global Climate Models Simulations G.J. Zhang Center for Atmospheric Sciences Scripps Institution
A New Ocean Mixed-Layer Model Coupled into WRF
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 170 175 A New Ocean Mixed-Layer Model Coupled into WRF WANG Zi-Qian 1,2 and DUAN An-Min 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 170 175 A New Ocean Mixed-Layer Model Coupled into WRF WANG Zi-Qian 1,2 and DUAN An-Min 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR
 CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
Theoretical and Modeling Issues Related to ISO/MJO
 Theoretical and Modeling Issues Related to ISO/MJO Tim Li Department of Meteorology and IPRC University of Hawaii DYNAMO workshop, April 13-14, Boulder, Colorado 1. MJO Initiation issue: Role of air- sea
Theoretical and Modeling Issues Related to ISO/MJO Tim Li Department of Meteorology and IPRC University of Hawaii DYNAMO workshop, April 13-14, Boulder, Colorado 1. MJO Initiation issue: Role of air- sea
Reduced Complexity Frameworks for Exploring Physics Dynamics Coupling Sensitivities
 Reduced Complexity Frameworks for Exploring Physics Dynamics Coupling Sensitivities Kevin A. Reed & Adam R. Herrington School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New
Reduced Complexity Frameworks for Exploring Physics Dynamics Coupling Sensitivities Kevin A. Reed & Adam R. Herrington School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New
Air-Sea Interaction: Physics of air-surface interactions and coupling to ocean/atmosphere BL processes
 Air-Sea Interaction: Physics of air-surface interactions and coupling to ocean/atmosphere BL processes Emphasize surface fluxes Statement of problem Present status Parameterization issues An amusing case
Air-Sea Interaction: Physics of air-surface interactions and coupling to ocean/atmosphere BL processes Emphasize surface fluxes Statement of problem Present status Parameterization issues An amusing case
Effects of transfer processes on marine atmospheric boundary layer or Effects of boundary layer processes on air-sea exchange
 Effects of transfer processes on marine atmospheric boundary layer or Effects of boundary layer processes on air-sea exchange Ann-Sofi Smedman Uppsala University Uppsala, Sweden Effect of transfer process
Effects of transfer processes on marine atmospheric boundary layer or Effects of boundary layer processes on air-sea exchange Ann-Sofi Smedman Uppsala University Uppsala, Sweden Effect of transfer process
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
What you need to know in Ch. 12. Lecture Ch. 12. Atmospheric Heat Engine
 Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
A diurnally corrected highresolution
 A diurnally corrected highresolution SST analysis Andy Harris 1, Jonathan Mittaz 1,4, Gary Wick 3, Prabhat Koner 1, Eileen Maturi 2 1 NOAA-CICS, University of Maryland 2 NOAA/NESDIS/STAR 3 NOAA/OAR/ESRL
A diurnally corrected highresolution SST analysis Andy Harris 1, Jonathan Mittaz 1,4, Gary Wick 3, Prabhat Koner 1, Eileen Maturi 2 1 NOAA-CICS, University of Maryland 2 NOAA/NESDIS/STAR 3 NOAA/OAR/ESRL
Subgrid Surface Fluxes in Fair Weather Conditions during TOGA COARE: Observational Estimates and Parameterization
 62 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW VOLUME 26 Subgrid Surface Fluxes in Fair Weather Conditions during TOGA COARE: Observational Estimates and Parameterization DEAN VICKERS AND STEVEN K. ESBENSEN College of Oceanic
62 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW VOLUME 26 Subgrid Surface Fluxes in Fair Weather Conditions during TOGA COARE: Observational Estimates and Parameterization DEAN VICKERS AND STEVEN K. ESBENSEN College of Oceanic
 Convective Fluxes: Sensible and Latent Heat Convective Fluxes Convective fluxes require Vertical gradient of temperature / water AND Turbulence ( mixing ) Vertical gradient, but no turbulence: only very
Convective Fluxes: Sensible and Latent Heat Convective Fluxes Convective fluxes require Vertical gradient of temperature / water AND Turbulence ( mixing ) Vertical gradient, but no turbulence: only very
Where does the memory of convection stem from? Why can it be useful for parameterizations?
 Where does the memory of convection stem from? Why can it be useful for parameterizations? D'où vient la mémoire de la convection? En quoi cela peut-il être utile pour les paramétrisations? Maxime Colin,
Where does the memory of convection stem from? Why can it be useful for parameterizations? D'où vient la mémoire de la convection? En quoi cela peut-il être utile pour les paramétrisations? Maxime Colin,
Boundary layer parameterization and climate. Chris Bretherton. University of Washington
 Boundary layer parameterization and climate Chris Bretherton University of Washington Some PBL-related climate modeling issues PBL cloud feedbacks on tropical circulations, climate sensitivity and aerosol
Boundary layer parameterization and climate Chris Bretherton University of Washington Some PBL-related climate modeling issues PBL cloud feedbacks on tropical circulations, climate sensitivity and aerosol
Tropical Cyclones-Ocean interaction as represented by a 25km resolution CGCM: the role of the coupling frequency
 HRCP Workshop 13-15 April 2016 Tropical Cyclones-Ocean interaction as represented by a 25km resolution CGCM: the role of the coupling frequency Enrico Scoccimarro (1,2), P.G. Fogli (2), K. Reed (3), S.
HRCP Workshop 13-15 April 2016 Tropical Cyclones-Ocean interaction as represented by a 25km resolution CGCM: the role of the coupling frequency Enrico Scoccimarro (1,2), P.G. Fogli (2), K. Reed (3), S.
Assessing the Influence of Surface Wind Waves to the Global Climate by Incorporating WAVEWATCH III in CESM! Phase I: Langmuir Mixing in KPP
 Assessing the Influence of Surface Wind Waves to the Global Climate by Incorporating WAVEWATCH III in CESM Phase I: Langmuir Mixing in KPP Image: NPR.org, Deep Water Horizon Spill Qing Li Baylor Fox-Kemper,
Assessing the Influence of Surface Wind Waves to the Global Climate by Incorporating WAVEWATCH III in CESM Phase I: Langmuir Mixing in KPP Image: NPR.org, Deep Water Horizon Spill Qing Li Baylor Fox-Kemper,
Evaluation of modeled diurnally varying sea surface temperatures and the influence of surface winds
 Evaluation of modeled diurnally varying sea surface temperatures and the influence of surface winds Rachel R. Weihs and Mark A. Bourassa Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies IOVWST Meeting 6-8
Evaluation of modeled diurnally varying sea surface temperatures and the influence of surface winds Rachel R. Weihs and Mark A. Bourassa Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies IOVWST Meeting 6-8
Efficient and Accurate Bulk Parameterizations of Air Sea Fluxes for Use in General Circulation Models
 OCTOBER 2000 KARA ET AL. 1421 Efficient and Accurate Bulk Parameterizations of Air Sea Fluxes for Use in General Circulation Models A. BIROL KARA Sverdrup Technology Incorporated, Stennis Space Center,
OCTOBER 2000 KARA ET AL. 1421 Efficient and Accurate Bulk Parameterizations of Air Sea Fluxes for Use in General Circulation Models A. BIROL KARA Sverdrup Technology Incorporated, Stennis Space Center,
MJO Discussion. Eric Maloney Colorado State University. Thanks: Matthew Wheeler, Adrian Matthews, WGNE MJOTF
 MJO Discussion Eric Maloney Colorado State University Thanks: Matthew Wheeler, Adrian Matthews, WGNE MJOTF Intraseasonal OLR and Precipitation Variance Sobel et al. (2010) Peatman et al. (2013) MJO cycle
MJO Discussion Eric Maloney Colorado State University Thanks: Matthew Wheeler, Adrian Matthews, WGNE MJOTF Intraseasonal OLR and Precipitation Variance Sobel et al. (2010) Peatman et al. (2013) MJO cycle
Modelling suppressed and active convection. Comparing a numerical weather prediction, cloud-resolving and single-column model
 QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 33: 7 (7) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com) DOI:./qj.9 Modelling suppressed and active convection.
QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 33: 7 (7) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com) DOI:./qj.9 Modelling suppressed and active convection.
The Role of Water Droplets in Air-sea Interaction: Rain and Sea Spray
 The Role of Water Droplets in Air-sea Interaction: Rain and Sea Spray Fabrice Veron Air-Sea Interaction Laboratory School of Marine Science and Policy College of Earth, Ocean, & Environment University
The Role of Water Droplets in Air-sea Interaction: Rain and Sea Spray Fabrice Veron Air-Sea Interaction Laboratory School of Marine Science and Policy College of Earth, Ocean, & Environment University
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity
 The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation
 Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation Adam Sobel Columbia University NCAR IMAGe Workshop, Nov. 3 2005 In the tropics, our picture of the dynamics should
Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation Adam Sobel Columbia University NCAR IMAGe Workshop, Nov. 3 2005 In the tropics, our picture of the dynamics should
Northern Arabian Sea Circulation Autonomous Research (NASCar) DRI: A Study of Vertical Mixing Processes in the Northern Arabian Sea
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Northern Arabian Sea Circulation Autonomous Research (NASCar) DRI: A Study of Vertical Mixing Processes in the Northern
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Northern Arabian Sea Circulation Autonomous Research (NASCar) DRI: A Study of Vertical Mixing Processes in the Northern
An extended re-forecast set for ECMWF system 4. in the context of EUROSIP
 An extended re-forecast set for ECMWF system 4 in the context of EUROSIP Tim Stockdale Acknowledgements: Magdalena Balmaseda, Susanna Corti, Laura Ferranti, Kristian Mogensen, Franco Molteni, Frederic
An extended re-forecast set for ECMWF system 4 in the context of EUROSIP Tim Stockdale Acknowledgements: Magdalena Balmaseda, Susanna Corti, Laura Ferranti, Kristian Mogensen, Franco Molteni, Frederic
Model error and seasonal forecasting
 Model error and seasonal forecasting Antje Weisheimer European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts ECMWF, Reading, UK with thanks to Paco Doblas-Reyes and Tim Palmer Model error and model uncertainty
Model error and seasonal forecasting Antje Weisheimer European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts ECMWF, Reading, UK with thanks to Paco Doblas-Reyes and Tim Palmer Model error and model uncertainty
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY. Lecture 19. Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes
 ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
Deciphering the desiccation trend of the South Asian monsoon hydroclimate in a warming world
 Deciphering the desiccation trend of the South Asian monsoon hydroclimate in a warming world R. Krishnan Centre for Climate Change Research (CCCR) Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune Collaborators:
Deciphering the desiccation trend of the South Asian monsoon hydroclimate in a warming world R. Krishnan Centre for Climate Change Research (CCCR) Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune Collaborators:
A Numerical Study of a TOGA-COARE Squall-Line Using a Coupled Mesoscale Atmosphere-Ocean Model
 ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 21, NO. 5, 2004, 708 716 A Numerical Study of a TOGA-COARE Squall-Line Using a Coupled Mesoscale Atmosphere-Ocean Model Shaowu BAO, Lian XIE, and Sethu RAMAN Department
ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 21, NO. 5, 2004, 708 716 A Numerical Study of a TOGA-COARE Squall-Line Using a Coupled Mesoscale Atmosphere-Ocean Model Shaowu BAO, Lian XIE, and Sethu RAMAN Department
--Manuscript Draft-- parametrization for the LMDZ GCM. Columbia University New York, NY UNITED STATES. Jean-Yves Grandpeix
 Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences Deep convection triggering by boundary layer thermals. Part 2: Stochastic triggering parametrization for the LMDZ GCM --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title:
Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences Deep convection triggering by boundary layer thermals. Part 2: Stochastic triggering parametrization for the LMDZ GCM --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title:
Correspondence between short and long timescale systematic errors in CAM4/CAM5 explored by YOTC data
 Correspondence between short and long timescale systematic errors in CAM4/CAM5 explored by YOTC data Hsi-Yen Ma In collaboration with Shaocheng Xie, James Boyle, Stephen Klein, and Yuying Zhang Program
Correspondence between short and long timescale systematic errors in CAM4/CAM5 explored by YOTC data Hsi-Yen Ma In collaboration with Shaocheng Xie, James Boyle, Stephen Klein, and Yuying Zhang Program
8 Mechanisms for tropical rainfall responses to equatorial
 8 Mechanisms for tropical rainfall responses to equatorial heating More reading: 1. Hamouda, M. and Kucharski, F. (2019) Ekman pumping Mechanism driving Precipitation anomalies in Response to Equatorial
8 Mechanisms for tropical rainfall responses to equatorial heating More reading: 1. Hamouda, M. and Kucharski, F. (2019) Ekman pumping Mechanism driving Precipitation anomalies in Response to Equatorial
OCN/ATM/ESS 587. Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics.
 OCN/ATM/ESS 587 Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics. Equation of state for seawater General T/S properties of the upper ocean Heat balance of the upper ocean Upper ocean circulation Deep circulation
OCN/ATM/ESS 587 Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics. Equation of state for seawater General T/S properties of the upper ocean Heat balance of the upper ocean Upper ocean circulation Deep circulation
Tropical cyclone simulations and predictions with GFDL s prototype global cloud resolving model
 Tropical cyclone simulations and predictions with GFDL s prototype global cloud resolving model S.-J. Lin and GFDL model development teams NOAA/Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Workshop on High-Resolution
Tropical cyclone simulations and predictions with GFDL s prototype global cloud resolving model S.-J. Lin and GFDL model development teams NOAA/Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Workshop on High-Resolution
P R O L O G U E CORRELATION COEF. dsst/dt during wintertime (i.e., end of Feb. minus beginning of Dec, using 11-day averaged climatology)
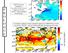 P R O L O G U E dsst/dt during wintertime (i.e., end of Feb. minus beginning of Dec, using 11-day averaged climatology) Correlation between total precipitable water (from NVAP-M) and total cloud (from
P R O L O G U E dsst/dt during wintertime (i.e., end of Feb. minus beginning of Dec, using 11-day averaged climatology) Correlation between total precipitable water (from NVAP-M) and total cloud (from
GFDL, NCEP, & SODA Upper Ocean Assimilation Systems
 GFDL, NCEP, & SODA Upper Ocean Assimilation Systems Jim Carton (UMD) With help from Gennady Chepurin, Ben Giese (TAMU), David Behringer (NCEP), Matt Harrison & Tony Rosati (GFDL) Description Goals Products
GFDL, NCEP, & SODA Upper Ocean Assimilation Systems Jim Carton (UMD) With help from Gennady Chepurin, Ben Giese (TAMU), David Behringer (NCEP), Matt Harrison & Tony Rosati (GFDL) Description Goals Products
TC/PR/RB Lecture 3 - Simulation of Random Model Errors
 TC/PR/RB Lecture 3 - Simulation of Random Model Errors Roberto Buizza (buizza@ecmwf.int) European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts http://www.ecmwf.int Roberto Buizza (buizza@ecmwf.int) 1 ECMWF
TC/PR/RB Lecture 3 - Simulation of Random Model Errors Roberto Buizza (buizza@ecmwf.int) European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts http://www.ecmwf.int Roberto Buizza (buizza@ecmwf.int) 1 ECMWF
Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS Apr 2006
 Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp. 957-960 (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS 513 12 Apr 2006 Questions 1. What is the proposed mechanism by which a uniform
Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp. 957-960 (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS 513 12 Apr 2006 Questions 1. What is the proposed mechanism by which a uniform
More on Diabatic Processes
 More on Diabatic Processes Chapter 3 Write Qtotal = Qrad + Qcond + Qsen total heating radiative heating condensationa l heating sensible heating While diabatic processes drive atmospheric motions, the
More on Diabatic Processes Chapter 3 Write Qtotal = Qrad + Qcond + Qsen total heating radiative heating condensationa l heating sensible heating While diabatic processes drive atmospheric motions, the
Uncertainties in sea surface turbulent flux algorithms and data sets
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. C10, 3141, doi:10.1029/2001jc000992, 2002 Uncertainties in sea surface turbulent flux algorithms and data sets Michael A. Brunke and Xubin Zeng Institute
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. C10, 3141, doi:10.1029/2001jc000992, 2002 Uncertainties in sea surface turbulent flux algorithms and data sets Michael A. Brunke and Xubin Zeng Institute
777 GROUNDSCHOOL Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms
 777 GROUNDSCHOOL 2018 Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms The Atmosphere Heating Transfer of heat occurs thru Radiation Advection Convection Matter changes states due to the amount of heat
777 GROUNDSCHOOL 2018 Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms The Atmosphere Heating Transfer of heat occurs thru Radiation Advection Convection Matter changes states due to the amount of heat
Dynamical versus Land-Surface Factors in the African Monsoon
 http://www.atmos.ucla.edu/~csi Dynamical versus Land-Surface Factors in the African Monsoon J. David Neelin,, UCLA Collaborators: Chia Chou, Academia Sinica, Taiwan; Hui Su, UCLA; Ning Zeng, U. Maryland
http://www.atmos.ucla.edu/~csi Dynamical versus Land-Surface Factors in the African Monsoon J. David Neelin,, UCLA Collaborators: Chia Chou, Academia Sinica, Taiwan; Hui Su, UCLA; Ning Zeng, U. Maryland
Air sea satellite flux datasets and what they do (and don't) tell us about the air sea interface in the Southern Ocean
 Air sea satellite flux datasets and what they do (and don't) tell us about the air sea interface in the Southern Ocean Carol Anne Clayson Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Southern Ocean Workshop Seattle,
Air sea satellite flux datasets and what they do (and don't) tell us about the air sea interface in the Southern Ocean Carol Anne Clayson Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Southern Ocean Workshop Seattle,
A Method for Improving Simulation of PNA Teleconnection Interannual Variation in a Climate Model
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 86 90 A Method for Improving Simulation of PNA Teleconnection Interannual Variation in a Climate Model LI Zhong-Xian 1, 2, ZHOU Tian-Jun 2,
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 86 90 A Method for Improving Simulation of PNA Teleconnection Interannual Variation in a Climate Model LI Zhong-Xian 1, 2, ZHOU Tian-Jun 2,
18A.2 PREDICTION OF ATLANTIC TROPICAL CYCLONES WITH THE ADVANCED HURRICANE WRF (AHW) MODEL
 18A.2 PREDICTION OF ATLANTIC TROPICAL CYCLONES WITH THE ADVANCED HURRICANE WRF (AHW) MODEL Jimy Dudhia *, James Done, Wei Wang, Yongsheng Chen, Qingnong Xiao, Christopher Davis, Greg Holland, Richard Rotunno,
18A.2 PREDICTION OF ATLANTIC TROPICAL CYCLONES WITH THE ADVANCED HURRICANE WRF (AHW) MODEL Jimy Dudhia *, James Done, Wei Wang, Yongsheng Chen, Qingnong Xiao, Christopher Davis, Greg Holland, Richard Rotunno,
SST Trend Based on High-resolution Datasets and Numerical Simulations
 SST Trend Based on High-resolution Datasets and Numerical Simulations Figure 1 offers the AVHRR(0.25-degree daily)-based SST trend estimates, which is roughly agree with the estimate based on Pathfinder
SST Trend Based on High-resolution Datasets and Numerical Simulations Figure 1 offers the AVHRR(0.25-degree daily)-based SST trend estimates, which is roughly agree with the estimate based on Pathfinder
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
