Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes. Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology
|
|
|
- Roxanne Beasley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology
2 Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics Sea ice thermodynamics and optics
3 Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics Sea ice thermodynamics and optics
4 Radiative Transfer The clear-sky radiative transfer is essentially solved major breakthrough from SHEBA ( dirty window ) Remaining issues: cloud overlap issue (CloudSat and Calipso should help) consistency between microphysics code and r.t. code in specifying cloud optical properties correct handling of the highly reflecting surface 3D radiative transfer not a big issue in the polar regions
5 Surface turbulent fluxes Fluxes over open leads can be very large during winter, ~500 W/m2 NO DATA! Lead plume Fluxes over multi-year ice are small; uncertainty in role of gravity waves in surface fluxes
6 Boundary Layer Parameterizations Existing B.L. parameterizations work poorly in the Arctic, owing to:! Static stability and strong temperature inversions! Persistent negative surface heat fluxes! Large-scale subsidence! Mixed phase and crystalline clouds Result in Incorrect vertical profiles of T, q, u Incorrect clouds incorrect surface fluxes The main issue is not lack of observations (other than leads)
7 SHEBA (Jan): Clear stable b.l. Ph.D. Thesis, Jeff Mirocha Local schemes match LES most closely for temperature
8 SHEBA (Jan): Clear stable b.l. Ph.D. Thesis, Jeff Mirocha Main problem with nonlocal schemes is diagnosis of b.l. height
9 SHEBA (Jan): Clear stable b.l. Ph.D. Thesis, Jeff Mirocha All perform worse in presence of subsidence
10 Issues: clear stable boundary layer Assessment:! 2nd order closure (best physics?) performs the worst, does not generate sufficient turbulence! 1st order, local scheme performs well for temperature in absence of subsidence! nonlocal schemes have problems with b.l. height, esp during subsidence! nonlocal mixed with K shows the best sensitivity when compared with LES To do list:! Prognostic equation for b.l. height accounting for subsidence! investigate whether there is a missing mechanism in TKE generation; LES studies of breaking waves in steep inversions
11 Cloudy Boundary Layer Main problems:! (stable b.l. issues)! Thermal b.l. different from momentum b.l.! Thermodynamics for b.l. crystalline and mixed phase clouds
12 Representation of Arctic Clouds in Models Atmospheric Model Intercomparison Project (AMIPII). Annual cycle is vaguely captured, though several are out of phase. Large variability between models. From Walsh et al. (2002)
13 Possible reasons for poor simulations of Arctic clouds Poor large scale dynamical fields Inadequate boundary layer parameterizations Incorrect surface temperature and surface state "Inadequate cloud microphysical parameterizations Inadequate vertical resolution Etc.
14 Arctic cloud microphysics: cloud phase is the dominant issue At -30C, more than half the clouds have liquid Cloud phase has a substantial impact on radiative fluxes and precipitation
15 Cloud Microphysical Models A set of prognostic equations for: Cloud drops Ice crystals Rain drops Snow Graupel Bin resolving microphysics (specifies size spectra) Bulk microphysics - Single moment (species mixing ratio) - Dual moment (+ particle concentration)
16 Microphysical elements that need parameterizing: Liquid drop nucleation Ice particle nucleation Diffusional growth Fall speed Liquid droplet size spectra Ice crystal size spectra Particle collection and aggregation Interfaces with model dynamics and thermodynamics: Large-scale advective processes Subgrid-scale supersaturation fluctuations
17 Arctic mixed-phase stratiform clouds (AMPS) Often persist continuously for days or even weeks. SHEBA cloud phase and LWP retrievals, May 4-8, 1998 (NOAA ETL).
18 Case Description The cloud layer was mixed-phase near cloud top, with continuous light snowfall reaching the surface, and occasionally surmounted by upper-level ice clouds. May 4, 1998 May 5, 1998 Green All-Ice Yellow Mixed-Phase Cloud Classification Cloud Optical Depth Courtesy of NOAA/ETL
19 A two-moment scheme (predicting both mass and number concentration) can produce long-lived mixed-phase clouds at T ~ -21 C if droplet freezing is assumed to be the dominant ice nucleation mechanism rather than deposition nucleation Two-moment scheme LWC One-moment/quasi-one-moment schemes IWC IWC IWC Results for SHEBA grid cell (May 4-5, 1998), MM5 mesoscale simulations (dx=20 km). From Morrison and Pinto (2006).
20 How does the modeled cloud layer compare with observations? Retrieved liquid boundaries and MMCR reflectivity at SHEBA (top) and modeled liquid boundaries and ice water content (bottom) for CON run.
21 Why does the Morrison et al. scheme predict mixed-phase clouds, while Reisner1/Reisner2 (single moment) predict allice clouds? Reisner1 and Reisner2 (and most other microphysics schemes) assume a continuous supply of ice nuclei The diagnosed snow number concentration is ~ 6 times larger in Reisner1 and Reisner2 than predicted by the Morrison et al. scheme. High production of ice/snow particles depletes liquid water by the Bergeron-Findeisen process.
22 Model Description Polar NCAR/PSU Fifth-Generation Mesoscale Model (MM5) version 3.6 (Bromwich et al., 2001; Cassano et al. 2001). Location of the outer (D1) and inner (D2) model domains. SHEBA # Results for the inner domain will be shown.
23 Mixed-phase rather than all-ice clouds result in overall warming of the surface due to an increase in the downwelling longwave radiative flux. Strong cloud-top radiative cooling (~ 50 K/day) and surface warming induced by the mixed-phase cloud result in a deep, surface-based, well-mixed BL. Observed and modeled sea ice surface temperature (below) and potential temperature profiles (right) for the SHEBA grid. Observed Baseline Observed Baseline Reisner1/ Reisner2 Reisner1/ Reisner2
24 Differences in surface temperature and near-surface stability induced by the mixedphase cloud result in a much larger surface turbulent flux of water vapor than in Reisner1/Reisner2. This surface flux feeds moisture into the mixed-phase cloud and balances the increased precipitation flux. Observed turbulent near-surface latent and sensible heat fluxes. Note reduction to negative values during the brief period that the cloud was glaciated. Cloud Glaciated Latent Flux Sensible Flux
25 Diabatic processes induced by mixed-phase rather than all-ice clouds result in higher surface pressure (up to 1 mb) and increased low-level subsidence. The development of mesoscale features (banding of vertical velocity and surface pressure differences parallel to the geostrophic flow) may be due to negative potential vorticity and symmetric instability circulations induced by diabatic mixed-phase cloud processes. Surface pressure difference (baseline - Reisner1) at end of simulation (0000 UTC May 6) (mb). Low-level vertical velocity difference (baseline - Reisner1) at end of simulation (0000 UTC May 6) (cm/s). * SHEBA
26 Mixed Phase Cloud Summary Mixed-phase clouds dominate cloud fraction over the Arctic Ocean for most of the year. Arctic M-P clouds are difficult to simulate, and most models incorrectly represent them as entirely crystalline. Parameterizations basing cloud phase on temperature do not have sufficient degrees of freedom and current params introduce bias of too much ice In models with separate prognostic variables for ice and liquid, simulated M-P clouds are highly sensitive to the ice crystal concentration and mode of nucleation. Heterogeneous ice nucleation is poorly understood. The dominant mode in Arctic mixed phase clouds appears to be droplet freezing (mainly contact; impact of immersion unknown). Note: deliquescence freezing is the main mode measured in field missions
27 Sea Ice Modeling Sea ice feedbacks are complex: internal sea ice processes interactions with the local atmosphere and ocean interactions with global processes Current sea ice models and parameterized interactions with the atmosphere and ocean are likely to be inadequate at simulating the climate in an altered sea ice regime. Improved parameterizations related to sea ice are not making it into climate models.
28 But what about SHEBA? SHEBA observations: #thermodynamical and optical properties and processes #exchanges at ice/atm and ice/ocean interfaces 8 years after the SHEBA field experiment, none of these observations have influenced new parameterizations in sea ice models used in GCMs
29
30 Needed Improvements to Sea Ice Models Spectral radiative transfer: surface albedo, transmission through snow, sea ice, upper ocean.! Explicit melt ponds: albedo, latent heat, salinity effects! Snow:nonlinear conduction, metamorphism, redistribution! Ice age: optics, thermal conductivity, specific heat, etc.! Formation of snow/ice Frazil ice formation Ice deformation: brine rejection;enhanced decay of ridged ice Lead width distribution: lateral melting, turbulent fluxes Ice/ocean turbulent flux for ice thickness distribution! Fast ice: detailed ocean bathymetry,granular rheology! Good data available from SHEBA
31 Impediments to improving sea ice component of climate models Sea ice modeling community focused on large scale dynamical ice/ocean interactions. Models are currently highly tuned; adding a new/better parameterization is likely to make the model simulations worse. There is no hierarchical modeling strategy to develop and evaluate new sea ice parameterizations: needed to assess how important a given parameterization is (no analogy to GCSS, ARM in the sea ice modelling world). Inadequate funding base; sea ice scientists favor field measurements in the review process; people are leaving the field. Observations/process studies and parameterization ideas are NOT presently the limiting factor in progress
32 What is needed for a parameterization to be successful: 1. Theory and detailed process modeling to focus on specific param elements 2. Conduct simulations using the process models for the entire relevant range of thermodynamical and dynamical conditions; evaluate using obs! 3. Develop new param, guided by theory and statistics, from process model simulations 4. Test new param in CRMs, SCMs (including linkages to other parameterizations); evaluate using obs! 5. Conduct sensitivity studies to see if the complexity of new param can be reduced (or needs to be increased) 6. Incorporate new param into a mesoscale model, for domain < R od (driven by lateral boundaries, not sensitive to initial conditions); evaluate using obs! 7. Examine new param in mesoscale model for larger domain simulations 8. Incorporate new param into GCM, assess impact of param on the model climate; evaluate using obs! 9. Conduct GCM sensitivity studies to understand how param alters sensitivity! Return to #1 or proceed forward
33 Summary of parameterization issues Mostly solved issues: clear sky radiative transfer surface turbulent fluxes over ice/snow Issues with major progress expected in short term cloud microphysics and interactions with aerosols Issues limited by observations: turbulent fluxes over leads new ice formation, coastal sea ice, ridges Issues limited by understanding: stable boundary layer cloud-turbulence interactions heterogeneous ice nucleation Issues limited by community barriers: sea ice thermodynamics and optics linkages between parameterizations
Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models. Richard Forbes
 Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models Richard Forbes (ECMWF) with thanks to Peter Bechtold and Martin Köhler RMetS National Meeting on Clouds and Precipitation, 16 Nov
Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models Richard Forbes (ECMWF) with thanks to Peter Bechtold and Martin Köhler RMetS National Meeting on Clouds and Precipitation, 16 Nov
Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans
 Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans Judith A. Curry and Peter J. Webster PROGRAM IN ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO USA
Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans Judith A. Curry and Peter J. Webster PROGRAM IN ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO USA
Future directions for parametrization of cloud and precipitation microphysics
 Future directions for parametrization of cloud and precipitation microphysics Richard Forbes (ECMWF) ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop, 15-17 June 2010 Cloud and Precipitation Microphysics A Complex System! Ice Nucleation
Future directions for parametrization of cloud and precipitation microphysics Richard Forbes (ECMWF) ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop, 15-17 June 2010 Cloud and Precipitation Microphysics A Complex System! Ice Nucleation
Microphysical Properties of Single and Mixed-Phase Arctic Clouds Derived From Ground-Based AERI Observations
 Microphysical Properties of Single and Mixed-Phase Arctic Clouds Derived From Ground-Based AERI Observations Dave Turner University of Wisconsin-Madison Pacific Northwest National Laboratory 8 May 2003
Microphysical Properties of Single and Mixed-Phase Arctic Clouds Derived From Ground-Based AERI Observations Dave Turner University of Wisconsin-Madison Pacific Northwest National Laboratory 8 May 2003
Intercomparison of Bulk Cloud Microphysics Schemes in Mesoscale Simulations of Springtime Arctic Mixed-Phase Stratiform Clouds
 1880 M O N T H L Y W E A T H E R R E V I E W VOLUME 134 Intercomparison of Bulk Cloud Microphysics Schemes in Mesoscale Simulations of Springtime Arctic Mixed-Phase Stratiform Clouds H. MORRISON Department
1880 M O N T H L Y W E A T H E R R E V I E W VOLUME 134 Intercomparison of Bulk Cloud Microphysics Schemes in Mesoscale Simulations of Springtime Arctic Mixed-Phase Stratiform Clouds H. MORRISON Department
The HIGHTSI ice model and plans in SURFEX
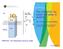 Air Snow T in Ice with snow cover T sfc x T snow Q si F si h s h s The HIGHTSI ice model and plans in SURFEX Bin Cheng and Laura Rontu Water Ice T ice h i Finnish Meteorological Institute, FI-11 Helsinki,
Air Snow T in Ice with snow cover T sfc x T snow Q si F si h s h s The HIGHTSI ice model and plans in SURFEX Bin Cheng and Laura Rontu Water Ice T ice h i Finnish Meteorological Institute, FI-11 Helsinki,
CONSTRAIN proposal for grey zone model comparison case. Adrian Hill, Paul Field, Adrian Lock, Thomas Frederikse, Stephan de Roode, Pier Siebesma
 CONSTRAIN proposal for grey zone model comparison case Adrian Hill, Paul Field, Adrian Lock, Thomas Frederikse, Stephan de Roode, Pier Siebesma Contents Introduction CONSTRAIN Overview of UM Limited Area
CONSTRAIN proposal for grey zone model comparison case Adrian Hill, Paul Field, Adrian Lock, Thomas Frederikse, Stephan de Roode, Pier Siebesma Contents Introduction CONSTRAIN Overview of UM Limited Area
An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics
 An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics M. D. Shupe Science and Technology Corporation National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Environmental Technology Laboratory Boulder, Colorado T. Uttal
An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics M. D. Shupe Science and Technology Corporation National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Environmental Technology Laboratory Boulder, Colorado T. Uttal
Numerical simulation of marine stratocumulus clouds Andreas Chlond
 Numerical simulation of marine stratocumulus clouds Andreas Chlond Marine stratus and stratocumulus cloud (MSC), which usually forms from 500 to 1000 m above the ocean surface and is a few hundred meters
Numerical simulation of marine stratocumulus clouds Andreas Chlond Marine stratus and stratocumulus cloud (MSC), which usually forms from 500 to 1000 m above the ocean surface and is a few hundred meters
Arctic Mixed-phase Clouds Simulated by a Cloud-Resolving Model: Comparison with ARM Observations and Sensitivity to Microphysics Parameterizations
 Arctic Mixed-phase Clouds Simulated by a Cloud-Resolving Model: Comparison with ARM Observations and Sensitivity to Microphysics Parameterizations Yali Luo 1,2, Kuan-Man Xu 2, Hugh Morrison 3, Greg McFarquhar
Arctic Mixed-phase Clouds Simulated by a Cloud-Resolving Model: Comparison with ARM Observations and Sensitivity to Microphysics Parameterizations Yali Luo 1,2, Kuan-Man Xu 2, Hugh Morrison 3, Greg McFarquhar
Using Cloud-Resolving Models for Parameterization Development
 Using Cloud-Resolving Models for Parameterization Development Steven K. Krueger University of Utah! 16th CMMAP Team Meeting January 7-9, 2014 What is are CRMs and why do we need them? Range of scales diagram
Using Cloud-Resolving Models for Parameterization Development Steven K. Krueger University of Utah! 16th CMMAP Team Meeting January 7-9, 2014 What is are CRMs and why do we need them? Range of scales diagram
Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model
 Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model W. O Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California
Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model W. O Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California
Radiative Climatology of the North Slope of Alaska and the Adjacent Arctic Ocean
 Radiative Climatology of the North Slope of Alaska and the Adjacent Arctic Ocean C. Marty, R. Storvold, and X. Xiong Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, Alaska K. H. Stamnes Stevens Institute
Radiative Climatology of the North Slope of Alaska and the Adjacent Arctic Ocean C. Marty, R. Storvold, and X. Xiong Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, Alaska K. H. Stamnes Stevens Institute
ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions
 ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions Themes: 1. Parametrization of microphysics 2. Representing sub-grid cloud variability 3. Constraining cloud and precipitation
ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions Themes: 1. Parametrization of microphysics 2. Representing sub-grid cloud variability 3. Constraining cloud and precipitation
Arctic Boundary Layer
 Annual Seminar 2015 Physical processes in present and future large-scale models Arctic Boundary Layer Gunilla Svensson Department of Meteorology and Bolin Centre for Climate Research Stockholm University,
Annual Seminar 2015 Physical processes in present and future large-scale models Arctic Boundary Layer Gunilla Svensson Department of Meteorology and Bolin Centre for Climate Research Stockholm University,
Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate
 Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Snow and Sea Ice Physics, Thermodynamics, Dynamics and Remote Sensing
 Snow and Sea Ice Physics, Thermodynamics, Dynamics and Remote Sensing Ryan Galley Center for Earth Observation Science Clayton H. Riddell Faculty of Earth, Environment and Resources Freezing point of seawater
Snow and Sea Ice Physics, Thermodynamics, Dynamics and Remote Sensing Ryan Galley Center for Earth Observation Science Clayton H. Riddell Faculty of Earth, Environment and Resources Freezing point of seawater
Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model
 Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman,
Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman,
Improved Atmospheric Stable Boundary Layer Formulations for Navy Seasonal Forecasting
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Improved Atmospheric Stable Boundary Layer Formulations for Navy Seasonal Forecasting Michael Tjernström Department of
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Improved Atmospheric Stable Boundary Layer Formulations for Navy Seasonal Forecasting Michael Tjernström Department of
Modeling clouds observed at SHEBA using a bulk microphysics parameterization implemented into a single-column model
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D8, 4255, doi:10.1029/2002jd002229, 2003 Modeling clouds observed at SHEBA using a bulk microphysics parameterization implemented into a single-column model
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D8, 4255, doi:10.1029/2002jd002229, 2003 Modeling clouds observed at SHEBA using a bulk microphysics parameterization implemented into a single-column model
The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science
 The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science Outline Basic Dynamical Equations Numerical Methods Initialization
The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science Outline Basic Dynamical Equations Numerical Methods Initialization
Influence of clouds on radiative fluxes in the Arctic. J. English, J. Kay, A. Gettelman CESM Workshop / PCWG Meeting June 20, 2012
 Influence of clouds on radiative fluxes in the Arctic J. English, J. Kay, A. Gettelman CESM Workshop / PCWG Meeting June 20, 2012 The complexity of arctic clouds Arctic Mixed-Phase Clouds Morrison et al.,
Influence of clouds on radiative fluxes in the Arctic J. English, J. Kay, A. Gettelman CESM Workshop / PCWG Meeting June 20, 2012 The complexity of arctic clouds Arctic Mixed-Phase Clouds Morrison et al.,
Representation of Arctic Mixed-Phase Clouds and the Wegener-Bergeron- Findeisen Process in Climate Models: Perspectives from a Cloud- Resolving Study
 University of Wyoming Wyoming Scholars Repository Atmospheric Science Faculty Publications Atmospheric Science 9-20-2011 Representation of Arctic Mixed-Phase Clouds and the Wegener-Bergeron- Findeisen
University of Wyoming Wyoming Scholars Repository Atmospheric Science Faculty Publications Atmospheric Science 9-20-2011 Representation of Arctic Mixed-Phase Clouds and the Wegener-Bergeron- Findeisen
Role of atmospheric aerosol concentration on deep convective precipitation: Cloud-resolving model simulations
 Role of atmospheric aerosol concentration on deep convective precipitation: Cloud-resolving model simulations Wei-Kuo Tao,1 Xiaowen Li,1,2 Alexander Khain,3 Toshihisa Matsui,1,2 Stephen Lang,4 and Joanne
Role of atmospheric aerosol concentration on deep convective precipitation: Cloud-resolving model simulations Wei-Kuo Tao,1 Xiaowen Li,1,2 Alexander Khain,3 Toshihisa Matsui,1,2 Stephen Lang,4 and Joanne
A Preliminary Assessment of the Simulation of Cloudiness at SHEBA by the ECMWF Model. Tony Beesley and Chris Bretherton. Univ.
 A Preliminary Assessment of the Simulation of Cloudiness at SHEBA by the ECMWF Model Tony Beesley and Chris Bretherton Univ. of Washington 16 June 1998 Introduction This report describes a preliminary
A Preliminary Assessment of the Simulation of Cloudiness at SHEBA by the ECMWF Model Tony Beesley and Chris Bretherton Univ. of Washington 16 June 1998 Introduction This report describes a preliminary
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity
 The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs
 Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs Ulrike Lohmann ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science Reading, 13.11.2006 Acknowledgements: Sylvaine Ferrachat, Corinna Hoose, Erich Roeckner,
Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs Ulrike Lohmann ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science Reading, 13.11.2006 Acknowledgements: Sylvaine Ferrachat, Corinna Hoose, Erich Roeckner,
Introduction. Effect of aerosols on precipitation: - challenging problem - no agreement between the results (quantitative and qualitative)
 Introduction Atmospheric aerosols affect the cloud mycrophysical structure & formation (observations, numerical studies) An increase of the aerosol particles: - increases CCN concentrations - decreases
Introduction Atmospheric aerosols affect the cloud mycrophysical structure & formation (observations, numerical studies) An increase of the aerosol particles: - increases CCN concentrations - decreases
Collision and Coalescence 3/3/2010. ATS 351 Lab 7 Precipitation. Droplet Growth by Collision and Coalescence. March 7, 2006
 ATS 351 Lab 7 Precipitation March 7, 2006 Droplet Growth by Collision and Coalescence Growth by condensation alone takes too long ( 15 C -) Occurs in clouds with tops warmer than 5 F Greater the speed
ATS 351 Lab 7 Precipitation March 7, 2006 Droplet Growth by Collision and Coalescence Growth by condensation alone takes too long ( 15 C -) Occurs in clouds with tops warmer than 5 F Greater the speed
Sensitivity of M-PACE mixed-phase stratocumulus to cloud condensation and ice. nuclei in a mesoscale model with two-moment bulk cloud microphysics
 Sensitivity of M-PACE mixed-phase stratocumulus to cloud condensation and ice nuclei in a mesoscale model with two-moment bulk cloud microphysics Hugh Morrison 1, James O. Pinto 1, Judith A. Curry 2, and
Sensitivity of M-PACE mixed-phase stratocumulus to cloud condensation and ice nuclei in a mesoscale model with two-moment bulk cloud microphysics Hugh Morrison 1, James O. Pinto 1, Judith A. Curry 2, and
Single-Column Modeling, General Circulation Model Parameterizations, and Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Data
 Single-Column ing, General Circulation Parameterizations, and Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Data S. F. Iacobellis, D. E. Lane and R. C. J. Somerville Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Single-Column ing, General Circulation Parameterizations, and Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Data S. F. Iacobellis, D. E. Lane and R. C. J. Somerville Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Physical Processes & Issues
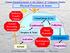 Physical Processes & Issues Radiative Transfer Climate VIS IR Cloud Drops & Ice Aerosol Processing Air quality Condensation Droplets & Xtals Cloud Dynamics Collection Aerosol Activation Hydrological Cycle
Physical Processes & Issues Radiative Transfer Climate VIS IR Cloud Drops & Ice Aerosol Processing Air quality Condensation Droplets & Xtals Cloud Dynamics Collection Aerosol Activation Hydrological Cycle
CAM Tutorial. Sea Ice Modeling 31 July 2009 David Bailey and Marika Holland, NCAR
 CAM Tutorial Sea Ice Modeling 31 July 2009 David Bailey and Marika Holland, NCAR Sea ice influences in the climate system Surface albedo in March > 0.8 < 0.1 Ice-Ocean Freshwater Exchange Contrasting the
CAM Tutorial Sea Ice Modeling 31 July 2009 David Bailey and Marika Holland, NCAR Sea ice influences in the climate system Surface albedo in March > 0.8 < 0.1 Ice-Ocean Freshwater Exchange Contrasting the
Real case simulations using spectral bin cloud microphysics: Remarks on precedence research and future activity
 Real case simulations using spectral bin cloud microphysics: Remarks on precedence research and future activity Takamichi Iguchi 1,2 (takamichi.iguchi@nasa.gov) 1 Earth System Science Interdisciplinary
Real case simulations using spectral bin cloud microphysics: Remarks on precedence research and future activity Takamichi Iguchi 1,2 (takamichi.iguchi@nasa.gov) 1 Earth System Science Interdisciplinary
Modeling of cloud microphysics: from simple concepts to sophisticated parameterizations. Part I: warm-rain microphysics
 Modeling of cloud microphysics: from simple concepts to sophisticated parameterizations. Part I: warm-rain microphysics Wojciech Grabowski National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado parameterization
Modeling of cloud microphysics: from simple concepts to sophisticated parameterizations. Part I: warm-rain microphysics Wojciech Grabowski National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado parameterization
Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM. Marika Holland NCAR
 Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM Marika Holland NCAR The Arctic is changing! Loss of Sept Arctic Sea Ice 2002 Loss of about 8% per decade Or >20% since 1979 (Courtesy I. Rigor
Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM Marika Holland NCAR The Arctic is changing! Loss of Sept Arctic Sea Ice 2002 Loss of about 8% per decade Or >20% since 1979 (Courtesy I. Rigor
Prediction of cirrus clouds in GCMs
 Prediction of cirrus clouds in GCMs Bernd Kärcher, Ulrike Burkhardt, Klaus Gierens, and Johannes Hendricks DLR Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany bernd.kaercher@dlr.de
Prediction of cirrus clouds in GCMs Bernd Kärcher, Ulrike Burkhardt, Klaus Gierens, and Johannes Hendricks DLR Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany bernd.kaercher@dlr.de
Antarctic precipitation in the LMDz and MAR climate models : comparison to CloudSat retrievals and improvement of cold microphysical processes
 Antarctic precipitation in the LMDz and MAR climate models : comparison to CloudSat retrievals and improvement of cold microphysical processes J. B. Madeleine1*, H. Gallée2, E. Vignon2, C. Genthon2, G.
Antarctic precipitation in the LMDz and MAR climate models : comparison to CloudSat retrievals and improvement of cold microphysical processes J. B. Madeleine1*, H. Gallée2, E. Vignon2, C. Genthon2, G.
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5
 Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Development and Validation of Polar WRF
 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio Development and Validation of Polar WRF David H. Bromwich 1,2, Keith M. Hines 1, and Le-Sheng Bai 1 1 Polar
Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio Development and Validation of Polar WRF David H. Bromwich 1,2, Keith M. Hines 1, and Le-Sheng Bai 1 1 Polar
Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model
 Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman,
Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman,
Assimilation of Satellite Cloud and Precipitation Observations in NWP Models: Report of a Workshop
 Assimilation of Satellite Cloud and Precipitation Observations in NWP Models: Report of a Workshop George Ohring and Fuzhong Weng Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation Ron Errico NASA/GSFC Global
Assimilation of Satellite Cloud and Precipitation Observations in NWP Models: Report of a Workshop George Ohring and Fuzhong Weng Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation Ron Errico NASA/GSFC Global
Climate models. René D. Garreaud. Departement of Geophysics Universidad de Chile
 Climate models René D. Garreaud Departement of Geophysics Universidad de Chile www.dgf.uchile.cl/rene My first toy model A system of coupled, non-linear algebraic equations X (t) = A X (t-1) Y (t) B Z
Climate models René D. Garreaud Departement of Geophysics Universidad de Chile www.dgf.uchile.cl/rene My first toy model A system of coupled, non-linear algebraic equations X (t) = A X (t-1) Y (t) B Z
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. College of Earth and Mineral Sciences
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Earth and Mineral Sciences EFFECTS OF ICE NUCLEI CONCENTRATIONS, ICE NUCLEATION MECHANISMS AND ICE CRYSTAL HABITS ON THE DYNAMICS AND MICROPHYSICS
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Earth and Mineral Sciences EFFECTS OF ICE NUCLEI CONCENTRATIONS, ICE NUCLEATION MECHANISMS AND ICE CRYSTAL HABITS ON THE DYNAMICS AND MICROPHYSICS
Snow Microphysics and the Top-Down Approach to Forecasting Winter Weather Precipitation Type
 Roger Vachalek Journey Forecaster National Weather Service Des Moines, Iowa www.snowcrystals.com Why is Snow Microphysics Important? Numerical Prediction Models better forecast areas of large scale forcing
Roger Vachalek Journey Forecaster National Weather Service Des Moines, Iowa www.snowcrystals.com Why is Snow Microphysics Important? Numerical Prediction Models better forecast areas of large scale forcing
Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model
 Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model S. F. Iacobellis, R. C. J. Somerville, D. E. Lane, and J. Berque Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model S. F. Iacobellis, R. C. J. Somerville, D. E. Lane, and J. Berque Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
RADIATIVE INFLUENCES ON THE GLACIATION TIME-SCALES OF ARCTIC MIXED-PHASE CLOUDS
 P1.26 RADIATIVE INFLUENCES ON THE GLACIATION TIME-SCALES OF ARCTIC MIXED-PHASE CLOUDS Zach Lebo, Nat Johnson, and Jerry Y. Harrington * Department of Meteorology, Pennsylvania State University, University
P1.26 RADIATIVE INFLUENCES ON THE GLACIATION TIME-SCALES OF ARCTIC MIXED-PHASE CLOUDS Zach Lebo, Nat Johnson, and Jerry Y. Harrington * Department of Meteorology, Pennsylvania State University, University
Arctic System Reanalysis Provides Highresolution Accuracy for Arctic Studies
 Arctic System Reanalysis Provides Highresolution Accuracy for Arctic Studies David H. Bromwich, Aaron Wilson, Lesheng Bai, Zhiquan Liu POLAR2018 Davos, Switzerland Arctic System Reanalysis Regional reanalysis
Arctic System Reanalysis Provides Highresolution Accuracy for Arctic Studies David H. Bromwich, Aaron Wilson, Lesheng Bai, Zhiquan Liu POLAR2018 Davos, Switzerland Arctic System Reanalysis Regional reanalysis
A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling. requirements of energy and water cycle. Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki
 A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling study for defining satellite measurement requirements of energy and water cycle Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki Motivation 1. Uncertainty of climate sensitivity
A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling study for defining satellite measurement requirements of energy and water cycle Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki Motivation 1. Uncertainty of climate sensitivity
Diagnosing Model Systematic Error for Clouds and Precipitation
 Diagnosing Model Systematic Error for Clouds and Precipitation Richard Forbes (ECMWF) With Thanks to Maike Ahlgrimm, Peter Bechtold, Martin Köhler and ECMWF colleagues, and Graeme Stephens (CSU), Julien
Diagnosing Model Systematic Error for Clouds and Precipitation Richard Forbes (ECMWF) With Thanks to Maike Ahlgrimm, Peter Bechtold, Martin Köhler and ECMWF colleagues, and Graeme Stephens (CSU), Julien
Chapter 7 Precipitation Processes
 Chapter 7 Precipitation Processes Chapter overview: Supersaturation and water availability Nucleation of liquid droplets and ice crystals Liquid droplet and ice growth by diffusion Collision and collection
Chapter 7 Precipitation Processes Chapter overview: Supersaturation and water availability Nucleation of liquid droplets and ice crystals Liquid droplet and ice growth by diffusion Collision and collection
Evaluating parameterized variables in the Community Atmospheric Model along the GCSS Pacific cross-section
 Evaluating parameterized variables in the Community Atmospheric Model along the GCSS Pacific cross-section Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Rich Neale, Jerry Olson, Dennis Shea National Center for Atmospheric
Evaluating parameterized variables in the Community Atmospheric Model along the GCSS Pacific cross-section Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Rich Neale, Jerry Olson, Dennis Shea National Center for Atmospheric
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models
 Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 6: 10-14-13 Feedbacks Climate forcings change global temperatures directly
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 6: 10-14-13 Feedbacks Climate forcings change global temperatures directly
Oceanic Eddies in the VOCALS Region of the Southeast Pacific Ocean
 Oceanic Eddies in the VOCALS Region of the Southeast Pacific Ocean Outline: Overview of VOCALS Dudley B. Chelton Oregon State University Overview of the oceanographic component of VOCALS Preliminary analysis
Oceanic Eddies in the VOCALS Region of the Southeast Pacific Ocean Outline: Overview of VOCALS Dudley B. Chelton Oregon State University Overview of the oceanographic component of VOCALS Preliminary analysis
National Center for Atmospheric Research,* Boulder, Colorado. (Manuscript received 18 June 2007, in final form 4 January 2008) ABSTRACT
 3642 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 A New Two-Moment Bulk Stratiform Cloud Microphysics Scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model, Version 3 (CAM3). Part I: Description and Numerical Tests HUGH
3642 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 A New Two-Moment Bulk Stratiform Cloud Microphysics Scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model, Version 3 (CAM3). Part I: Description and Numerical Tests HUGH
Standalone simulations: CAM3, CAM4 and CAM5
 Standalone simulations: CAM3, and CAM5 CAM5 Model Development Team Cécile Hannay, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman, Sungsu Park, Joe Tribbia, Peter Lauritzen, Andrew Conley, Hugh Morrison, Phil Rasch, Steve
Standalone simulations: CAM3, and CAM5 CAM5 Model Development Team Cécile Hannay, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman, Sungsu Park, Joe Tribbia, Peter Lauritzen, Andrew Conley, Hugh Morrison, Phil Rasch, Steve
SINGLE-COLUMN MODEL SIMULATIONS OF ARCTIC CLOUDINESS AND SURFACE RADIATIVE FLUXES DURING THE SURFACE HEAT BUDGET OF ARCTIC (SHEBA) EXPERIMENT
 SINGLE-COLUMN MODEL SIMULATIONS OF ARCTIC CLOUDINESS AND SURFACE RADIATIVE FLUXES DURING THE SURFACE HEAT BUDGET OF ARCTIC (SHEBA) EXPERIMENT By Cécile Hannay RECOMMENDED: Advisory Committee Chair Department
SINGLE-COLUMN MODEL SIMULATIONS OF ARCTIC CLOUDINESS AND SURFACE RADIATIVE FLUXES DURING THE SURFACE HEAT BUDGET OF ARCTIC (SHEBA) EXPERIMENT By Cécile Hannay RECOMMENDED: Advisory Committee Chair Department
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans
![Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans](/thumbs/96/128963638.jpg) Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D10, 4312, doi: /2002jd002643, 2003
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D10, 4312, doi:10.1029/2002jd002643, 2003 Two-dimensional cloud-resolving modeling of the atmospheric effects of Arctic leads based upon midwinter conditions
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D10, 4312, doi:10.1029/2002jd002643, 2003 Two-dimensional cloud-resolving modeling of the atmospheric effects of Arctic leads based upon midwinter conditions
Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra
 Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra emanuel.dutra@ecmwf.int Slide 1 Parameterizations training course 2015, Land-surface: Snow ECMWF Outline Snow in the climate system, an overview: Observations; Modeling;
Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra emanuel.dutra@ecmwf.int Slide 1 Parameterizations training course 2015, Land-surface: Snow ECMWF Outline Snow in the climate system, an overview: Observations; Modeling;
The Sensitivity of Springtime Arctic Mixed-Phase Stratocumulus Clouds to Surface-Layer and Cloud-Top Inversion-Layer Moisture Sources
 574 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 71 The Sensitivity of Springtime Arctic Mixed-Phase Stratocumulus Clouds to Surface-Layer and Cloud-Top Inversion-Layer Moisture
574 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 71 The Sensitivity of Springtime Arctic Mixed-Phase Stratocumulus Clouds to Surface-Layer and Cloud-Top Inversion-Layer Moisture
Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation
 Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation Adam Sobel Columbia University NCAR IMAGe Workshop, Nov. 3 2005 In the tropics, our picture of the dynamics should
Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation Adam Sobel Columbia University NCAR IMAGe Workshop, Nov. 3 2005 In the tropics, our picture of the dynamics should
Mid High Latitude Cirrus Precipitation Processes. Jon Sauer, Dan Crocker, Yanice Benitez
 Mid High Latitude Cirrus Precipitation Processes Jon Sauer, Dan Crocker, Yanice Benitez Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego, CA 92093, USA *To whom correspondence
Mid High Latitude Cirrus Precipitation Processes Jon Sauer, Dan Crocker, Yanice Benitez Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego, CA 92093, USA *To whom correspondence
Goddard Space Flight Center
 Goddard Space Flight Center Mesoscale Dynamics and Modeling Group Goddard Longwave and Shortwave Radiation Schemes in WRF v3.3 and the Current Works Roger Shi, Toshi Matsui, Wei-Kuo Tao, and Christa Peters-Lidard
Goddard Space Flight Center Mesoscale Dynamics and Modeling Group Goddard Longwave and Shortwave Radiation Schemes in WRF v3.3 and the Current Works Roger Shi, Toshi Matsui, Wei-Kuo Tao, and Christa Peters-Lidard
DEVELOPMENT AND TESTING OF AN AEROSOL / STRATUS CLOUD PARAMETERIZATION SCHEME FOR MIDDLE AND HIGH LATITUDES
 DOE/ER/6195&3 DEVELOPMENT AND TESTING OF AN AEROSOL / STRATUS CLOUD PARAMETERIZATION SCHEME FOR MIDDLE AND HIGH LATITUDES Year 3 Technical Progress Report For Period of Activity, Year 3: November 1,1996
DOE/ER/6195&3 DEVELOPMENT AND TESTING OF AN AEROSOL / STRATUS CLOUD PARAMETERIZATION SCHEME FOR MIDDLE AND HIGH LATITUDES Year 3 Technical Progress Report For Period of Activity, Year 3: November 1,1996
Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch
 Improvements in CAM5 : Moist Turbulence, Shallow Convection, and Cloud Macrophysics AMWG Meeting Feb. 10. 2010 Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch CGD.NCAR University of Washington, Seattle,
Improvements in CAM5 : Moist Turbulence, Shallow Convection, and Cloud Macrophysics AMWG Meeting Feb. 10. 2010 Sungsu Park, Chris Bretherton, and Phil Rasch CGD.NCAR University of Washington, Seattle,
Suppression of Arctic air formation with climate warming: Investigation. with a 2-dimensional cloud-resolving model
 1 Suppression of Arctic air formation with climate warming: Investigation 2 with a 2-dimensional cloud-resolving model 3 Timothy W. Cronin, 4 Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences, MIT,
1 Suppression of Arctic air formation with climate warming: Investigation 2 with a 2-dimensional cloud-resolving model 3 Timothy W. Cronin, 4 Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences, MIT,
Modeling sea-ice and its interactions with the ocean and the atmosphere
 Modeling sea-ice and its interactions with the ocean and the atmosphere H. Goosse, T. Fichefet, R. Timmermann, M. Vancoppenolle Institut d Astronomie et de Géophysique G. Lemaître. UCL, Louvain-la-Neuve,
Modeling sea-ice and its interactions with the ocean and the atmosphere H. Goosse, T. Fichefet, R. Timmermann, M. Vancoppenolle Institut d Astronomie et de Géophysique G. Lemaître. UCL, Louvain-la-Neuve,
Evaluation and Improvement of Clouds Simulated by the Global Nonhydrostatic Model NICAM and Satellite Data
 Evaluation and Improvement of Clouds Simulated by the Global Nonhydrostatic Model NICAM and Satellite Data NICAM: dx=3.5 km simulations EarthCARE satellite mission (2016?) Joint Simulator for Satellite
Evaluation and Improvement of Clouds Simulated by the Global Nonhydrostatic Model NICAM and Satellite Data NICAM: dx=3.5 km simulations EarthCARE satellite mission (2016?) Joint Simulator for Satellite
Spectral Albedos. a: dry snow. b: wet new snow. c: melting old snow. a: cold MY ice. b: melting MY ice. d: frozen pond. c: melting FY white ice
 Spectral Albedos a: dry snow b: wet new snow a: cold MY ice c: melting old snow b: melting MY ice d: frozen pond c: melting FY white ice d: melting FY blue ice e: early MY pond e: ageing ponds Extinction
Spectral Albedos a: dry snow b: wet new snow a: cold MY ice c: melting old snow b: melting MY ice d: frozen pond c: melting FY white ice d: melting FY blue ice e: early MY pond e: ageing ponds Extinction
Rogers and Yau Chapter 12: Precipitation Processes (emphasizing stratiform rain convection and severe storms will be next lecture)
 Rogers and Yau Chapter 12: Precipitation Processes (emphasizing stratiform rain convection and severe storms will be next lecture) There is a relationship between the scale of atmospheric vertical motions
Rogers and Yau Chapter 12: Precipitation Processes (emphasizing stratiform rain convection and severe storms will be next lecture) There is a relationship between the scale of atmospheric vertical motions
Precipitation Processes METR σ is the surface tension, ρ l is the water density, R v is the Gas constant for water vapor, T is the air
 Precipitation Processes METR 2011 Introduction In order to grow things on earth, they need water. The way that the earth naturally irrigates is through snowfall and rainfall. Therefore, it is important
Precipitation Processes METR 2011 Introduction In order to grow things on earth, they need water. The way that the earth naturally irrigates is through snowfall and rainfall. Therefore, it is important
Article Title: Cloud feedback mechanisms and their representation in global climate models. Article Type: Advanced Review
 Article Title: Cloud feedback mechanisms and their representation in global climate models Article Type: Advanced Review Authors: Paulo Ceppi Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading,
Article Title: Cloud feedback mechanisms and their representation in global climate models Article Type: Advanced Review Authors: Paulo Ceppi Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading,
P1.61 Impact of the mass-accomodation coefficient on cirrus
 P1.61 Impact of the mass-accomodation coefficient on cirrus Robert W. Carver and Jerry Y. Harrington Department of Meteorology, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 1. Introduction Recent
P1.61 Impact of the mass-accomodation coefficient on cirrus Robert W. Carver and Jerry Y. Harrington Department of Meteorology, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 1. Introduction Recent
A new theory for moist convection in statistical equilibrium
 A new theory for moist convection in statistical equilibrium A. Parodi(1), K. Emanuel(2) (2) CIMA Research Foundation,Savona, Italy (3) EAPS, MIT, Boston, USA True dynamics: turbulent, moist, non-boussinesq,
A new theory for moist convection in statistical equilibrium A. Parodi(1), K. Emanuel(2) (2) CIMA Research Foundation,Savona, Italy (3) EAPS, MIT, Boston, USA True dynamics: turbulent, moist, non-boussinesq,
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do?
 Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
Climate Roles of Land Surface
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
National Center for Atmospheric Research,* Boulder, Colorado S. J. GHAN. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, Washington
 3660 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 A New Two-Moment Bulk Stratiform Cloud Microphysics Scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model, Version 3 (CAM3). Part II: Single-Column and Global Results
3660 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 A New Two-Moment Bulk Stratiform Cloud Microphysics Scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model, Version 3 (CAM3). Part II: Single-Column and Global Results
Sea Ice Modeling for Climate Applications. Marika M Holland (NCAR) David Bailey (NCAR), Cecilia Bitz (U. Washington), Elizabeth Hunke (LANL)
 Sea Ice Modeling for Climate Applications Marika M Holland (NCAR) David Bailey (NCAR), Cecilia Bitz (U. Washington), Elizabeth Hunke (LANL) Surface albedo > 0.8 < 0.1 Why do we care about sea ice? Surface
Sea Ice Modeling for Climate Applications Marika M Holland (NCAR) David Bailey (NCAR), Cecilia Bitz (U. Washington), Elizabeth Hunke (LANL) Surface albedo > 0.8 < 0.1 Why do we care about sea ice? Surface
Subgrid-Scale Effects on Climate and Weather. Blackbird:Users:randall:UCLA_IPAM:UCLA_IPAM.frame
 Subgrid-Scale Effects on Climate and Weather The problem that will not die Deficiencies in the representation of cloud-dynamical processes in climate models drive much of the uncertainty surrounding predictions
Subgrid-Scale Effects on Climate and Weather The problem that will not die Deficiencies in the representation of cloud-dynamical processes in climate models drive much of the uncertainty surrounding predictions
Effects of Ice Nucleation and Crystal Habits on the Dynamics of Arctic Mixed Phase Clouds Muge Komurcu and Jerry Y. Harrington
 Effects of Ice Nucleation and Crystal Habits on the Dynamics of Arctic Mixed Phase Clouds Muge Komurcu and Jerry Y. Harrington I. INTRODUCTION Arctic Mixed-phase clouds are frequently observed during the
Effects of Ice Nucleation and Crystal Habits on the Dynamics of Arctic Mixed Phase Clouds Muge Komurcu and Jerry Y. Harrington I. INTRODUCTION Arctic Mixed-phase clouds are frequently observed during the
Arctic Clouds and Radiation Part 2
 Arctic Clouds and Radiation Part 2 Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013 No sun Arctic Winter Energy Balance 160 W m -2
Arctic Clouds and Radiation Part 2 Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013 No sun Arctic Winter Energy Balance 160 W m -2
Key Laboratory of Mesoscale Severe Weather, Ministry of Education, School of Atmospheric Sciences, Nanjing University
 Modeling Rapid Intensification of Typhoon Saomai (2006) with the Weather Research and Forecasting Model and Sensitivity to Cloud Microphysical Parameterizations Jie Ming and Yuan Wang Key Laboratory of
Modeling Rapid Intensification of Typhoon Saomai (2006) with the Weather Research and Forecasting Model and Sensitivity to Cloud Microphysical Parameterizations Jie Ming and Yuan Wang Key Laboratory of
Representing sub-grid heterogeneity of cloud and precipitation across scales
 Representing sub-grid heterogeneity of cloud and precipitation across scales ECMWF Seminar, September 2015 Richard Forbes, Maike Ahlgrimm (European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts) Thanks to
Representing sub-grid heterogeneity of cloud and precipitation across scales ECMWF Seminar, September 2015 Richard Forbes, Maike Ahlgrimm (European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts) Thanks to
Radiative Convective Equilibrium in Single Column CAM. I Kuan Hu, Brian Mapes, Richard Neale, and Andrew Gettelman 22 nd CESM Workshop
 Radiative Convective Equilibrium in Single Column CAM I Kuan Hu, Brian Mapes, Richard Neale, and Andrew Gettelman 22 nd CESM Workshop Motivation The Earth s atmosphere is an extremely thin sheet of air
Radiative Convective Equilibrium in Single Column CAM I Kuan Hu, Brian Mapes, Richard Neale, and Andrew Gettelman 22 nd CESM Workshop Motivation The Earth s atmosphere is an extremely thin sheet of air
8. Clouds and Climate
 8. Clouds and Climate 1. Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few
8. Clouds and Climate 1. Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few
The Atmosphere. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems
 The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
Benchmarking Polar WRF in the Antarctic *
 Benchmarking Polar WRF in the Antarctic * David H. Bromwich 1,2, Elad Shilo 1,3, and Keith M. Hines 1 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, USA
Benchmarking Polar WRF in the Antarctic * David H. Bromwich 1,2, Elad Shilo 1,3, and Keith M. Hines 1 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, USA
The Regional Arctic System Model (RASM) for Studying High Resolution Climate Changes in the Arctic
 The Regional Arctic System Model (RASM) for Studying High Resolution Climate Changes in the Arctic Mark W. Seefeldt, John J. Cassano, Alice K. Duvivier, and Mimi H. Hughes University of Colorado Boulder
The Regional Arctic System Model (RASM) for Studying High Resolution Climate Changes in the Arctic Mark W. Seefeldt, John J. Cassano, Alice K. Duvivier, and Mimi H. Hughes University of Colorado Boulder
Coastal Antarctic polynyas: A coupled process requiring high model resolution in the ocean and atmosphere
 Coastal Antarctic polynyas: A coupled process requiring high model resolution in the ocean and atmosphere Mike Dinniman and John Klinck Center for Coastal Physical Oceanography Old Dominion University
Coastal Antarctic polynyas: A coupled process requiring high model resolution in the ocean and atmosphere Mike Dinniman and John Klinck Center for Coastal Physical Oceanography Old Dominion University
GEWEX Cloud System Study (GCSS)
 GEWEX Cloud System Study (GCSS) The goal of GCSS is to improve the parameterization of cloud systems in GCMs (global climate models) and NWP (numerical weather prediction) models through improved physical
GEWEX Cloud System Study (GCSS) The goal of GCSS is to improve the parameterization of cloud systems in GCMs (global climate models) and NWP (numerical weather prediction) models through improved physical
Hurricanes are intense vortical (rotational) storms that develop over the tropical oceans in regions of very warm surface water.
 Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
Hurricanes: Observations and Dynamics Houze Section 10.1. Holton Section 9.7. Emanuel, K. A., 1988: Toward a general theory of hurricanes. American Scientist, 76, 371-379 (web link). http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(gh)/guides/mtr/hurr/home.rxml
Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2214 Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds Y.-C. Chen, M. W. Christensen, G. L. Stephens, and J. H. Seinfeld
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2214 Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds Y.-C. Chen, M. W. Christensen, G. L. Stephens, and J. H. Seinfeld
Chapter 7: Thermodynamics
 Chapter 7: Thermodynamics 7.1 Sea surface heat budget In Chapter 5, we have introduced the oceanic planetary boundary layer-the Ekman layer. The observed T and S in this layer are almost uniform vertically,
Chapter 7: Thermodynamics 7.1 Sea surface heat budget In Chapter 5, we have introduced the oceanic planetary boundary layer-the Ekman layer. The observed T and S in this layer are almost uniform vertically,
The Arctic Ocean's response to the NAM
 The Arctic Ocean's response to the NAM Gerd Krahmann and Martin Visbeck Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University RT 9W, Palisades, NY 10964, USA Abstract The sea ice response of the Arctic
The Arctic Ocean's response to the NAM Gerd Krahmann and Martin Visbeck Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University RT 9W, Palisades, NY 10964, USA Abstract The sea ice response of the Arctic
Monitoring Climate Change from Space
 Monitoring Climate Change from Space Richard Allan (email: r.p.allan@reading.ac.uk twitter: @rpallanuk) Department of Meteorology, University of Reading Why Monitor Earth s Climate from Space? Global Spectrum
Monitoring Climate Change from Space Richard Allan (email: r.p.allan@reading.ac.uk twitter: @rpallanuk) Department of Meteorology, University of Reading Why Monitor Earth s Climate from Space? Global Spectrum
