hw t avid defects, hw t analyze measurement data fr imprving estimatin, defect remval, and defect preventin, hw t identify and tackle ther kinds f prc
|
|
|
- Clara Gray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 T appear (as f arch 30, 2000) in IEEE Transactins n Sftware Engineering An Experiment easuring the Eects f Persnal Sftware Prcess (PSP) Training Lutz Prechelt (prechelt@cmputer.rg) Barbara Unger (unger@ira.uka.de) Fakultat fur Infrmatik Universitat Karlsruhe D Karlsruhe, Germany +49/721/ , Fax: +49/721/ arch 30, 2000 Abstract The Persnal Sftware Prcess is a prcess imprvement methdlgy aiming at individual sftware engineers. It claims t imprve sftware quality (in particular defect cntent), effrt estimatin capability, and prcess adaptatin and imprvement capabilities. We have tested sme f these claims in an experiment cmparing the perfrmance f participants wh had just previusly received a PSP curse t a dierent grup f participants wh had received ther technical training instead. Each participant f bth grups perfrmed the same task. We fund the fllwing psitive eects: The PSP grup estimated their prductivity (thugh nt their ert) mre accurately, made fewer trivial mistakes, and their prgrams perfrmed mre careful errr-checking; further, the perfrmance variability was smaller in the PSP grup in varius respects. Hwever, the imprvements are smaller than the PSP prpnents usually assume, pssibly due t the lw actual usage f PSP techniques in the PSP grup. We cnjecture that PSP training alne des nt autmatically realize the PSP's ptential benets (as seen in sme industrial PSP success stries) when prgrammers are left alne with mtivating themselves t actually use the PSP techniques. 1 Keywrds: prcess imprvement, quality management, ert estimatin, reliability, prductivity, experiment 1 The Persnal Sftware Prcess (PSP) methdlgy The Persnal Sftware Prcess (PSP) methdlgy fr imprving the sftware prcess was intrduced in 1995 by Watts Humphrey [6]. PSP is an applicatin f the principles f the Capability aturity del (C, [5]) n the level f an individual sftware engineer. In cntrast t the C, hwever, which allws nly fr assessment f prcess quality, the PSP makes cncrete methdlgical and learning suggestins, dwn t the level f a 15-week curse with rather specic prcedural cntent. The gals f the PSP are that an individual sftware engineer learns hw t accurately estimate, plan, track, and re-plan the time required fr individual sftware develpment erts, hw t wrk accrding t a well-dened prcess, hw t dene and rene the prcess, hw t use reviews eectively and eciently fr imprving sftware quality and prductivity (by nding defects early),
2 hw t avid defects, hw t analyze measurement data fr imprving estimatin, defect remval, and defect preventin, hw t identify and tackle ther kinds f prcess deciencies. The main basic techniques used are gathering bjective measurement data n many aspects f the prcess (fr btaining a slid basis fr prcess change decisins), spelling ut the prcess int frms and scripts (fr precise cntrl f such changes and fr making the prcess repeatable), and analyzing the cllected data (fr deciding where and hw t change the prcess). 1.1 Previus evidence fr PSP eectiveness The PSP methdlgy relies a lt n bjective measurement data and s des the argumentatin f the PSP prpnents. Watts Humphrey has published data frm several PSP curses in 1996 [7] and several experience reprts frm ther PSP practitiners reprt similar results. Since n ther infrmatin was available, these results rely n the very data cllected by the curse participants during their curse exercises 1 thrugh 10, regarding real and estimated develpment time as well as inserted and remved defects, bth fr each f the varius develpment phases. These data shw fr instance that the estimatin accuracy increases cnsiderably, the number f defects intrduced per 1000 lines f cde (KLOC) decreases by a factr f tw, the number f defects per KLOC t be fund late during develpment (i.e., in test) decreases by a factr f three r mre, and prductivity is nt reduced despite the substantial verhead factr fr bkkeeping invlved when the tasks are as small as they are. See [4] fr a detailed analysis f these eects based n data frm 23 curses. Additinal evidence cmes frm industrial success reprts n PSP usage, in which the expected PSP benets were actually fund in several small industrial prjects whse engineers used PSP [3]. Unfrtunately, bth kinds f evidence have severe drawbacks. Observatins directly frm the curse are distrted in several ways. First, the prcess denitin underlying the data changes frm exercise t exercise, making exact interpretatin dicult. Secnd, the PSP curse is the Hawthrne eect [9] at its best: the participants cnstantly mnitr their perfrmance and their central bjective is imprving this perfrmance in cntrast t industrial sftware practice, where individual perfrmance is nly a means t an end. Third, individual participants may cnsciusly r subcnsciusly manipulate their time measurement and defect recrding twards better results. Furth, the exercises 4 thrugh 10 are nt nly quite simple in terms f design and implementatin cmplexity, but als have unusually clear and easyt-understand requirements, which may make the results verly ptimistic. Finally, and mst imprtantly, there is n cntrl. bdy knws hw perfrmance wuld change during these 10 prgramming assignments if n PSP training and self-mnitring ccurs at all. A validatin f the PSP by direct cmparisn t nn-psptrained persns is missing. The industrial case studies are dicult t interpret (due t their cmplex cntext) and als lack cntrl. Either cmparisns t nn-psp data are missing r they are based n a befre/after cmparisn f the same persns (nt cntrlling fr maturatin) r an A/B cmparisn t dierent prjects. Besides many ther relevant dierences, such cmparisn prjects might have engineers that are less capable than the vanguard that chse t learn PSP rst. Again, a study with a higher degree f cntrl is called fr. 1.2 Experiment mtivatin and verview When we learned the PSP urselves and then started teaching it t ur graduate students, we sn btained the impressin that the methdlgy has a lt f benets, but is nt withut prblems, t. In particular, many prgrammers appear t be unable t keep up the discipline required fr the data gathering and 2
3 fr fllwing a spelled-ut prcess script; this may als underlie sme f the PSP data quality prblems bserved by Jhnsn and Disney [8]. Furthermre, many curse participants misunderstand the cncrete techniques and prcedures taught in the PSP curse as dgmas, althugh they are meant nly as starting pints fr ne's wn prcess develpment. They d nt understand that (and hw) they shuld adapt the prpsed techniques t their wn preferences and needs. We estimated that a majrity f ur curse participants wuld prbably use little r nthing f the PSP techniques in their later daily wrk and we wndered whether, under these circumstances, PSP training wuld be mre eective than any ther technical training with respect t the PSP gals. We hence cnducted the experiment as described in Sectin 2, where we cmpared a grup f students right after a PSP curse t a grup f ther students right after a dierent (technical rather than methdlgical) curse; see Sectin 2.2. Each participant had t slve the same prgramming task (see Sectin 2.3), which was quite dierent frm all f the assignments f either curse. 2 Descriptin f the experiment 2.1 Experiment design The experiment uses a single-factr, psttestnly, inter-subject design [1]; see Table 1 fr an verview. The independent variable was whether the experimental subjects had just previusly participated in a PSP curse (experiment grup, subsequently called \P") r in an alternative curse (cmparisn grup, subsequently called \" fr \nn-psp"). Each subject f either grup slved the same task and wrked under the same cnditins. The assignment f subjects t grups culd nt be randmized; this threat is discussed in Sectin 2.6. The bserved dependent variables fr each subject were a variety f measures f persnal experience, varius estimatins f develpment time fr the task (in particular estimated ttal time), varius measurements f the develpment prcess (in particular ttal time), and varius measurements f the delivered prduct (in particular prgram reliability). grup grup P treatment PSP curse KOJAK/ther task phnewrd phnewrd bserved wrk time, estim. time, reliability, etc. We bserved several aspects f each subject's develpment prcess and sftware prduct t analyze the eects f the PSP curse in cmparisn t a mre technical curse, in particular the accuracy f the subjects' ert estimatin and the reliability f the prgrams they prduced. The results are discussed in Sectin 3. The experiment and its results are described in mre detail in a technical reprt [11], which als includes the actual experiment materials. The reprt als cntains varius less imprtant additinal measurement results nt discussed in this article. The materials and raw result data are als available in electrnic frm frm Table 1: The experiment design. Fr details see the fllwing subsectins. 2.2 Subjects Overall, 48 persns participated in the experiment, 29 in the PSP grup P and 19 in the nn-psp grup. All f them were male Cmputer Science master students. The P grup had previusly participated in a 15-week graduate lab curse intrducing the PSP methdlgy, invlving ten small prgramming assignments and ve prcess imprvement assignments, bth as described in Humphreys bk [6, Appendix D]. All but eight members f the 3
4 grup had participated in a 6-week graduate cmpact lab curse n cmpnent sftware in Java (KOJAK), invlving ve larger prgramming assignments. This curse cvered technical tpics such as Swing, Beans, and RI. It was shrter than the PSP curse, but much mre intensive, s that the verall amunt f practical prgramming experience gained was similar. The ther eight f the participants came frm ther lab curses f similar magnitude. In cntrast t all thers, wh were bliged t participate (but nt t succeed) in the experiment fr passing their curse, these eight were vlunteers. The subjects participated in the experiment between 0 t 3 mnths after their respective curse was nished. There were tw instances f the PSP curse (1997 and 1998), bth run by the same teacher and with the same cntent. On average, these 50 students were in their 8th semester at the university, they had a median prgramming experience f 8 years ttal and estimated they had a median f 600 hurs f prgramming practice beynd their assignments frm the university educatin and had written a median f LOC ttal. ne f these measures was signicantly dierent between the tw grups. During the experiment, 24 f the participants used Java (JDK), 13 used C ++ (g++), 9 used C (gcc), 1 used dula-2 (mcka), and 1 used Sather-K (sak). 8 participants drpped ut f the experiment and will be ignred in the subsequent data analysis. They chse t give up after zer t three unsuccessful attempts at passing the acceptance test that frms the end f the experiment (see Sectin 2.4). All drputs said they were frustrated by the diculty f the task; we culd nt nd any cnnectin t grup membership. The fractin f drputs is the same in the P grup (5 ut f 29, 17 percent) as in the grup (3 ut f 19, 16 percent) s that ignring the drputs des nt intrduce a bias int the experiment. This leaves 40 participants fr the evaluatin. 2.3 Experiment task The task t be slved in this experiment is called phnewrd. It cnsists f writing a prgram that encdes the digits f lng telephne numbers (prgram input) int crrespnding sequences f wrds (prgram utput, the wrds cme frm a large dictinary als prvided as input) accrding t the xed, given letter-tdigit mapping shwn in Table 2: A single digit is allwed t encde itself in the utput i n ther digit precedes it and n wrd frm the dictinary can represent the digits starting frm that pint. All pssible cmplete encdings must be fund and printed. any phne numbers have n cmplete encding at all, even with a large dictinary. Dashes and qutes in the wrds as well as dashes and slashes in the phne numbers must be ignred fr the encding but still be printed in the result. Any phne number and any wrd in the dictinary was knwn t be at mst 50 characters lng. The dictinary was knwn t be at mst wrds lng. Dictinary and phne numbers are read frm tw text les cntaining ne wrd r phne number per line. Here is an example prgram utput fr the input \ ", using a German dictinary: : Dali um : Sa 6 um : da Pik 5 The requirements fr this prgram were described thrughly in natural language and remaining ambiguities were reslved by examples f crrect and incrrect encdings. The requirements descriptin stated prgram reliability as the single tp bjective fr the participants. Prductivity, prgram eciency, etc. were t be less imprtant. Fr cmplete text f the requirements specicatin see [11, pp. 66{68]. 2.4 Experimental prcedure The experiment was run between February 1997 and Octber 1998, mstly during the semester breaks. st subjects started at 4
5 E J Q R W X D S Y F T A C I V B K U L O P G H Z Table 2: Prescribed letter-t-digit mapping fr the phnewrd task. The mapping was cnstructed such as t balance the letter frequency fr each digit acrss the German dictinary used. abut 9:30 in the mrning. Bth grups were handled exactly alike. In particular, the PSP subjects were nt specically asked t use PSP techniques. The experiment materials were printed n paper and cnsisted f tw parts. Part ne was issued at the start f the experiment and cntained a persnal infrmatin questinnaire, the task descriptin, and an ert estimatin questinnaire. After lling these questinnaires in and reading the task descriptin, the subjects wrked n the task using a specic Unix accunt that prvided the autmatic mnitring infrastructure, which nnintrusively prtcled lgin/lgut times, all cmpiled surce versins with timestamps, etc. The subjects culd mdify the setup f the accunt as necessary, make wrk pauses whenever required, and use any methds and appraches fr slving the prblem they deemed apprpriate. In particular, a few subjects imprted surce cde f reusable prcedures (fr le handling etc.) frm ther accunts and a few subjects imprted and installed small persnal tls. The input, utput, and dictinary data used in the example in the task requirements descriptin was prvided t the subjects, the large wrd dictinary later used fr evaluating all prgrams was als available. When a subject thught his prgram wrked crrectly, he culd call fr an acceptance test. This was based n randmly generating a set f 500 phne numbers, cmputing the multiset f crrespnding utputs S() using the subject's prgram, and cmputing the crrect utputs C() using a reference implementatin (\gld" prgram). The gld prgram had been written by the authrs using stepwise re- nement with semi-frmal vericatin based n precnditins and pstcnditins. The gld prgram had run crrectly right frm its rst test and n defect was ever fund in it (despite harsh prtests frm several participants and thrugh investigatins f their validity). 5 The entire expected utput C() and actual utput S() was shwn, but the acceptance test used a wrd dictinary nt available t the subjects. The utput reliability r was de- ned as the fractin f crrect utputs within all actual utputs (whether expected r incrrect), i.e. r = js() \ C()j=jS() [ C()j. T pass the acceptance test, r had t be at least 95 percent. isuse f the acceptance test as a cnvenient autmatic testing facility was avided by the fllwing reward scheme: Each participant received a payment f D 50 (apprx. 30 US dllars) fr successful participatin, i.e., passing the acceptance test, but fr each failed acceptance test, D 10 were deducted. 12 f the successful subjects nished the day they started, 10 thers required a secnd day, and the ther 18 tk between three and eleven days. Similarly, 15 subjects passed the rst acceptance test, 24 the secnd t fth, nly 1 required six. Bth f these measures shwed n signicant dierences between the tw grups. After passing the acceptance test, the subject were given part 2 f the experiment materials, a shrt pstmrtem questinnaire. After lling that in, the subjects were paid and their participatin was cmplete. 2.5 Hyptheses The experiment investigated the fllwing hyptheses (plus a few less imprtant nes nt discussed here, see [11]). Reliability: PSP-trained prgrammers prduce a mre reliable prgram fr the phnewrd task than nn-psp-trained prgrammers. Estimatin accuracy: PSP-trained prgrammers estimate the time they need
6 fr slving the phnewrd task mre accurately than nn-psp-trained prgrammers. We als srt f expect that PSP-trained prgrammers may slve the phnewrd task faster than nn-psp-trained prgrammers. Prductivity imprvement is nt an explicit claim r gal f the PSP, but fr the given task it might be a side eect f imprved quality, because lcating a prblem detected in the acceptance test is relatively dicult. 2.6 Threats t internal validity The cntrl f the independent variable is threatened by the fact that grup assignment was nt dne by randmizatin but rather was due t earlier self-selectin f the curse taken. In principle, there might be systematic dierences between the types f prgrammers taking either decisin. Hwever, we d nt believe that such dierences, if any, are substantial. Fr instance, several f the participants f the KOJAK curse and several f the vlunteers frm ther curses later chse the PSP curse and vice versa. The chice f prgramming language might als inuence ur results, because the dierent languages have dierent frequency in the tw grups. Hwever, the structure f ur task is such that the language used has nly mdest impact. In particular, neither bject-riented language features nr particular memry management mechanisms are very relevant fr the given task. (See, hwever, the discussin f prgram crashes at the end f Sectin 3.1.) 2.7 Threats t external validity There are several imprtant threats t the external validity (generalizability) f ur experiment. First, and mst imprtantly, dierent wrk cnditins than fund in the experiment may psitively r negatively inuence the eectiveness f the PSP training. This is discussed in Sectin 4. Secnd, the PSP educatin f ur subjects was nly a shrt time ag. Lng-term eects wuld be mre interesting t see. Third, ur task was unusual in several respects (small size, precise requirements, acceptance test indicates expected utputs). It is unknwn hw these prperties might inuence the cmparisn. Finally, prfessinal sftware engineers may have dierent levels f skill than ur participants. A higher skill and experience level may leave less rm fr imprvement, but may als sharpen the eye as t where imprvements are mst desirable r mst easy t achieve with PSP techniques. Cnversely, lwer skill (which will ccur, because ur students are mre skilled than mst f the nn-cmputerscientists that frequently start wrking as prgrammers tday) may leave mre rm fr imprvement but may als impede applying PSP techniques crrectly r at all. 3 Results and discussin We will nw describe and discuss the results fr estimatin accuracy, reliability, and prductivity with respect t the hyptheses. The data will be presented using bxplts (see the gures belw) indicating the individual data pints, the 10% and 90% quantiles 1 (as whiskers), the 25% and 75% quantiles (by the edges f the bx), the median (50% quantile, by a fat dt), the mean (by a capital ), and ne standard errr f the mean (by a dashed line). The tw distributins f the grups and P are shwn side-by-side. Frmal tests f the hyptheses are perfrmed by ne-sided statistical hypthesis tests fr differences f the mean r the median. We use a Wilcxn rank sum test fr cmparing medians and a btstrap resampling test [2] fr cmparing the means withut relying n the assumptin f a nrmal distributin. When we reprt fr instance \mean test p = 0:07" this means 1 Fr instance, the 10% quantile f a set f values is an interplated x such that 10% f the values are smaller r equal t x and 90% are larger r equal t x. 6
7 that the test cmparing the means f the tw grups indicates that the bserved dierence has a 7% prbability p f being purely accidental (i.e., n real dierence exists). At values at r belw 5% we will call such p-values \signicant" and believe that the dierences are real. See [11, pp.20{25] fr a mre detailed descriptin f bxplts and the tests. 3.1 Reliability We measured the reliability (as dened in Sectin 2.4) f the delivered prgrams n eight different randmly generated input data sets, in which each f the pssible letters /, {, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 had the same prbability at each psitin f each number in each le (with ne exceptin mentined belw). The data sets cntained either 100, 1000, 10000, r telephne numbers. Since sme f the prgrams were extremely slw (ver 15 secnds per input), we culd nt exercise the largest tests n all f the prgrams and will hence reprt the results fr the test sets f size 1000 nly (but see [11, pp.31{39] fr the ther results). phne numbers f length 1 r 50 had articially been made less frequent in the acceptance test. The results fr the standard data set are shwn in the rather degenerated bx plts f Figure 1. As we see, the reliability f the prgrams is generally high in bth grups, bth medians are at 100%. We d nt nd any evidence fr superir reliability in the P grup. Instead, there even is a slight advantage fr the grup, but the difference is nt signicant (median test p = 0:32, mean test p = 0:33). P utput reliability n standard data set [percent] Figure 1: Output reliability (as dened in Sectin 2.4) fr the data set with at least ne digit per phne number. P There were tw dierent 1000-number data sets, a standard ne and a surprising ne. The surprising ne used exactly the distributin f telephne numbers mentined abve with unifrmly randm lengths between 1 and 50 characters. This set is surprising because when thinking f these inputs as telephne numbers, intuitively ne wuld nt expect t see smething nt cntaining any digit at all, such as \/" r \{/-/", even thugh the requirements descriptin f the task had dened \A telephne number is an arbitrary(!) string f dashes, slashes, and digits." (emphasis is in the riginal). An empty encding must be utput fr a phne number withut digits. In cntrast, the \standard" input set suppressed numbers nt cntaining any digit and generated a new ne until at least ne digit was present. te that bth f these tests are harder than the acceptance tests: The dictinary is larger (73113 wrds versus wrds), there are twice as many phne numbers, and the critical utput reliability n surprising data set [percent] Figure 2: Output reliability fr the data set with pssibly n digit in a phne number. The results fr the surprising data set are different (Figure 2). Again, sme prgrams wrk perfectly, but many ther prgrams frm the grup and als a few frm the P grup crash 2 at the rst telephne number that cntained n digit, which resulted in a reliability f 10.7% fr the given data set. As a result the reliability is signicantly lwer in the grup (median test p = 0:00, mean test p = 0:01). te that faulty Java prgrams were mre likely t crash than faulty C r C ++ prgrams, due t the Java run time checks f array indices etc. Since the fractin f Java prgrams 2 Our measurement ignres the crash and just recrds its cnsequences: n further utput arrives.
8 P P utput reliability fr nly the Java prgrams [percent] wrk time estimatin errr [percent] Figure 3: Output reliability fr the data set with pssibly n digit in a phne number, measured nly fr the Java prgrams. is higher in the grup, the abve result may thus be biased in favr f the P grup. Therefre, we als cmpared the Java prgrams alne (see Figure 3) and fund that the abve grup dierence indeed becmes less signicant, but des nt disappear (median test p = 0:04, mean test p = 0:07). Fr the ther languages there are nt enugh data pints fr a meaningful cmparisn. These results prvide sme evidence fr higher reliability in the P grup. Specically, althugh P grup prgram reliability is nt generally higher, the P grup prgrams perfrm better errr checking and handling f unexpected situatins. See als the discussin f prgram length in Sectin 3.3. We cnclude that the reliability hypthesis is supprted, thugh nt clearly cnrmed by the experiment. 3.2 Estimatin accuracy Fr cmparing the ert estimatin capabilities f the grups, we cnsider the estimatin f the ttal wrking time the subjects made after reading the task descriptin. We cmpute the mis-estimatin in percent frm the qutient f actual and estimated time, see Figure 4. The median mis-estimatins are essentially identical (median test p = 0:48). The wrst estimatins f the grup are wrse than in the P grup, s that the mean mis-estimatin tends t be larger in the grup; but the difference is nt signicant (mean test p = 0:18). This is n cnvincing evidence that the P grup prduces better estimates. Figure 4: t wrk testim? 1 : Amunt f mis-estimatin f the ttal wrking time fr the task. st estimatins were t ptimistic, nly fur in each grup were t pessimistic. PSP estimatin is based n prgram size estimatin and histrical data n persnal prduc- pectatins the prductivity is nt larger, but Frm this pint f view, in cntrast t ur ex- 8 P estimated/actual prductivity [percent] Figure 5: actual prductivity, each measured in lines f cde per hur. prdestim : Qutient f estimated and prdactual tivity (measured in lines f cde prduced per hur). If we cmpare the subjects' expected prductivity t the actual prductivity (Figure 5), we nd the estimatins f the grup are clearly wrse than in the P grup (median test p = 0:00, mean test p = 0:00). This shws that the PSP grup knws their histrical data, but did nt prduce a size estimatin that was gd enugh fr cnverting this knwledge int an estimatin advantage. We cnclude that, verall, the hypthesis f better time estimatin in the PSP grup is nt supprted by the experiment. 3.3 Prductivity Since all subjects wrked n exactly the same task, we might take the view that their prductivity shuld best be expressed simply as the \number f tasks slved per time unit", which is just the inverse f the ttal wrking time and is shwn in Figure 6.
9 P P prductivity [1/hur] ttal wrking time [hurs] 1 Figure 6: : Prductivity measured as the inverse f ttal wrking time (number f prgrams twrk per hur, ne culd say). rather tends t be smaller in the P grup (median test p = 0:10, mean test p = 0:06). We d nt knw the degree t which the PSP bkkeeping verhead accunts fr this tendency, but prbably the degree is lw, because few subjects actually had any signicant PSP verhead (see Sectin 3.5). Hwever, the P grup generally wrte lnger prgrams, partly because f mre careful errr checking. Fr instance, in the Java prgrams the average number f `catch' statements with nn-empty exceptin handlers is signicantly larger in the P grup than in the grup (4.4 versus 2.5, p = 0:02). As we saw abve, this additinal ert tended t result in better reliability. S maybe the mre cnventinal view f prductivity as the number f lines f cde written per hur is mre apprpriate. This qutient is shwn in Figure 7; the prductivity dierence has essentially disappeared (median test p = 0:42, mean test p = 0:30). P prductivity [LOC/hur] LOC Figure 7: : Prductivity measured as the twrk number f statement LOC written per hur. Figure 8: t wrk : Ttal number f wrking hurs. As we see, the ntin f prductivity is slippery fr sftware and must be handled with care. Hwever, the hpe that the prductivity f PSP-trained persns wuld be higher is nt supprted in the experiment (and is als nt claimed by the PSP in general). 3.4 Variance within each grup One rather unexpected insight frm this experiment was that even where n imprvement f the average ccurred, the variability was usually smaller in the P grup than in the grup. The eect ccurred fr mst f the measures we have investigated. We can quantify this by prviding a btstrap resampling test fr differences f the length f the bx (\interquartile range", iqr test), which is a rather rbust measure f variability. Fr instance fr the prductivity and estimatin cmparisns shwn in the gures abve, smaller P grup variability is visible as a tendency fr the reliability n surprising inputs (Figure 2, iqr test p = 0:12) wrk time misestimatin (Figure 4, iqr test p = 0:24) and the ttal wrk time (Figure 8, iqr test p = 0:39) and is statistically signicant fr the prductivity estimatin (Figure 5, iqr test p = 0:01), the prductivity in terms f wrking time (Figure 6, iqr test p = 0:05), and the prductivity in LOC per hur (Figure 7, iqr test p = 0:04). Curiusly, if we cnsider the wrking time directly (instead f its inverse), as shwn in Fig- may be a benet. Teams with lwer interper- The reductin f variability in the PSP grup ure 8, the grup has a lwer median (median test p = 0:10), but a slightly higher mean ble, because any member culd take ver a task snal perfrmance variability can be mre exi- due t sme very slw subjects (mean test withut changing the schedule. Schedule risk p = 0:28). may als be an issue, as is utlined in [12]. 9
10 3.5 PSP usage Fr nly 6 f the 24 PSP participants (25 percent), we fund evidence 3 that they had actually used PSP techniques. This lw percentage may imply that the size f the dierences fund abve reect the degree f actual PSP use mre than the eect f PSP use. Furthermre, we fund a surprising crrelatin. Amng thse 5 PSP participants wh had given up in the experiment, as many as 4 (r 80 percent) shwed evidence f actual usage f PSP techniques a signicantly higher fractin than amng the successful participants (Fisher exact p = 0:036). Apparently the least capable subjects had a much higher inclinatin t use PSP techniques, presumably because they feel mre clearly that these techniques help them. The prgrams prduced by members f the P grup are slightly mre reliable than thse f the grup as far as rbustness against unusual (but legal) inputs is cncerned. Fr mre standard types f inputs we did nt nd a reliability dierence. The members f the P grup estimated their prductivity (in lines f cde per hur) better than the grup, but did nt prduce better ttal ert estimates. The ttal time fr nishing the task tended t be lnger in the P grup than in the grup. Hwever, at least t sme degree this additinal time is invested in the errr checking that leads t the imprved rbustness. The prductivity in lines f cde per hur was hardly dierent in bth grups. 3.6 Other results We have cllected ther measures (nt directly cnnected t ur hyptheses) as well and fund several areas where sme advantage was visible fr the P grup. Fr instance they estimated the average time required fr xing a defect r the reliability f their prgram mre accurately than the grup. Furthermre, they made fewer trivial mistakes that led t cmpilatin errrs and tended t write mre cmments int their prgrams. See [11] fr details. In the infrmal pstmrtem interview, many f the P subjects (but nne f the subjects) said smething alng the lines f \I really shuld have perfrmed design and cde reviews. Damn that I didn't." 4 Cnclusin Our experiment cmparing a grup f PSPtrained prgrammers (P grup) t a similar grup f prgrammers wh received ther training ( grup) prduced the fllwing majr ndings: 3 In all cases this evidence included a time and defect lg, in sme cases als a PSP estimatin frm. Fr many perfrmance metrics the variability within the P grup was substantially smaller than the variability within the grup. Apparently a majrity f the P grup participants did nt use PSP techniques at all. When ne cmpares these results t sme f the imprvements knwn frm the PSP curse, ne may be disappinted; fr instance, participants f a PSP curse n average achieve an at least furfld reductin f the number f defects t be fund in test during their curse exercises 1 thrugh 10. There were n such dramatic differences in this experiment. We see tw majr reasns. First, the PSP curse with its cnstant measurement and feedback is a typical Hawthrne eect situatin [9], s that results frm the curse verestimate the imprvements available in the lng run. Secnd, t few f ur subjects frm the PSP grup actually used PSP techniques during the experiment; mst f them did nt keep up the necessary selfdiscipline. We er three explanatins fr the lw degree f actual PSP usage: First, it may be a result f dierent temperaments f the prgrammers. In ur experience, a few pick up and use 10
11 the PSP techniques quite easily and enthusiastically, a majrity can adapt them nly with ert and will later use them t a mdest degree at best, and sme appear t be cmpletely unable t maintain the discipline required fr applying the PSP techniques. The prprtins may be culture-dependent, s subjects frm ther cuntries may turn ut dierent in this respect. Our curse has wn several awards fr best teaching (as evaluated by the students) in ur department, s we rule ut lw quality f teaching as a reasn. Acknwledgements We thank Oliver Gramberg fr his cntributins t ur PSP curse and ichael Philippsen fr multiple thrugh reviews f this paper and very helpful criticism. We thank the annymus reviewers fr their detailed and helpful cmments. st f all we thank mre than fty patient individuals wh guinea-pigged the experimental setup r participated in the experiment itself. Secnd, when asked shrtly befre the end f the curse, a majrity f the PSP curse participants claimed they wuld use PSP techniques fr \larger" tasks, but nt fr small nes. If ne is willing t believe this statement, it may be that we wuld have fund larger PSP benets if yur experiment had used a larger task. Third, and maybe mst imprtantly, Watts Humphrey suggests that a wrking envirnment which actively encurages PSP usage is a key ingredient fr PSP success. Our subjects were wrking alne and hence had n such envirnment. Summing up, we cnjecture that PSP training alne prvides nly a fractin f the expected benets. Later encuragement twards actual PSP use appears t be necessary befre large imprvements are realized. evertheless, we believe that, in principle, the PSP is wrthwhile and that ur experiment prvides supprt fr this pinin. Given the lw degree f use f the actual PSP techniques despite a 15-week curse, it appears a wrthwhile research tpic whether and hw the PSP benets can be btained with a much smaller training prgram than the standard PSP curse. We are pursuing such research and have already btained rst results [10]. Further, the experiment shws that we need t understand better hw t make peple use methds: what technical, scial, and rganizatinal means imprve the level f actual use f a methd as ppsed t just the level f training r infrastructure prvided? 11
12 Appendix: Raw result data Authr Bigraphies Data f the 24 successful participants f the PSP-trained grup: time estim A reli relis LOC lang Java C C Java C Java C Java Java C C C C Sather-K Java C C Java C C Java dula C Java time is the actual wrk time in hurs, estim the estimated wrk time. A is the number f acceptance tests needed. reli is the reliability n the standard data set, relis is the reliability n the \surprising" data set. LOC is the length f the delivered prgram (excluding nly empty lines), lang is the prgramming language used. Data f the 16 successful participants f the nn-psp-trained grup: time estim A reli relis LOC lang C C Java Java Java Java Java Java C Java Java Java Java Java Java Java Lutz Prechelt wrked as senir researcher at the Schl f Infrmatics, University f Karlsruhe, where he als received his diplma (1990) and his Ph.D. (1995) in Infrmatics. His research interests include sftware engineering (in particular using an empirical research apprach), cmpiler cnstructin fr parallel machines, measurement and benchmarking issues, and research methdlgy. Since April 2000 he wrks fr abaxx Technlgy, Stuttgart. Prechelt is a member f IEEE CS, AC, and GI. Barbara Unger graduated with a diplma degree in 1995 and is currently wrking as a PhD candidate in the Institute fr Prgram Structures and Data Organizatin at the University f Karlsruhe. Her main research interests are in empirical sftware engineering with a fcus n design patterns. She is a member f the IEEE and the IEEE Cmputer Sciety. References [1] Larry B. Christensen. Experimental ethdlgy. Allyn and Bacn, eedham Heights, A, 6th editin, [2] Bradley Efrn and Rbert Tibshirani. An intrductin t the Btstrap. ngraphs n statistics and applied prbability 57. Chapman and Hall, ew Yrk, Lndn, [3] Pat Fergusn, Watts S. Humphrey, Sheil Khajenri, Susan acke, and Annette atvya. Intrducing the Persnal Sftware Prcess: Three industry case studies. IEEE Cmputer, 30(5):24{31, ay [4] W. Hayes and J.W. Over. The Persnal Sftware Prcess (PSP): An empirical study f the impact f PSP n individual engineers. Technical Reprt CU/SEI-97-TR-001, Sftware Engineering Institute, Carnegie elln University, Pittsburgh, PA,
13 [5] Watts S. Humphrey. anaging the Sftware Prcess. SEI series in Sftware Engineering. Addisn Wesley, [6] Watts S. Humphrey. A Discipline fr Sftware Engineering. SEI series in Sftware Engineering. Addisn Wesley, Reading, A, [7] Watts S. Humphrey. Using a dened and measured persnal sftware prcess. IEEE Sftware, 13(3):77{88, ay [8] Philip. Jhnsn and Anne. Disney. The persnal sftware prcess: A cautinary case study. IEEE Sftware, 15(6):., vember [9] H.. Parsns. What happened at Hawthrne? Science, 183(8):922{932, arch [10] Lutz Prechelt and Gerg Grutter. Accelerating learning frm experience: Aviding defects faster. IEEE Sftware, Submitted April [11] Lutz Prechelt and Barbara Unger. A cntrlled experiment n the eects f PSP training: Detailed descriptin and evaluatin. Technical Reprt 1/1999, Fakultat fur Infrmatik, Universitat Karlsruhe, Germany, arch ftp.ira.uka.de. [12] Lutz Prechelt and Barbara Unger. Hw des individual variability inuence schedule risk?: A small simulatin with experiment data. Technical Reprt , Fakultat fur Infrmatik, Universitat Karlsruhe, Germany, September ftp.ira.uka.de. 13
CS 477/677 Analysis of Algorithms Fall 2007 Dr. George Bebis Course Project Due Date: 11/29/2007
 CS 477/677 Analysis f Algrithms Fall 2007 Dr. Gerge Bebis Curse Prject Due Date: 11/29/2007 Part1: Cmparisn f Srting Algrithms (70% f the prject grade) The bjective f the first part f the assignment is
CS 477/677 Analysis f Algrithms Fall 2007 Dr. Gerge Bebis Curse Prject Due Date: 11/29/2007 Part1: Cmparisn f Srting Algrithms (70% f the prject grade) The bjective f the first part f the assignment is
Lab 1 The Scientific Method
 INTRODUCTION The fllwing labratry exercise is designed t give yu, the student, an pprtunity t explre unknwn systems, r universes, and hypthesize pssible rules which may gvern the behavir within them. Scientific
INTRODUCTION The fllwing labratry exercise is designed t give yu, the student, an pprtunity t explre unknwn systems, r universes, and hypthesize pssible rules which may gvern the behavir within them. Scientific
A controlled experiment on the effects of PSP training: Detailed description and evaluation
 A cntrlled experiment n the effects f PSP training: Detailed descriptin and evaluatin Lutz Prechelt (prechelt@ira.uka.de) Barbara Unger (unger@ira.uka.de) Fakultät für Infrmatik Universität Karlsruhe D-76128
A cntrlled experiment n the effects f PSP training: Detailed descriptin and evaluatin Lutz Prechelt (prechelt@ira.uka.de) Barbara Unger (unger@ira.uka.de) Fakultät für Infrmatik Universität Karlsruhe D-76128
WRITING THE REPORT. Organizing the report. Title Page. Table of Contents
 WRITING THE REPORT Organizing the reprt Mst reprts shuld be rganized in the fllwing manner. Smetime there is a valid reasn t include extra chapters in within the bdy f the reprt. 1. Title page 2. Executive
WRITING THE REPORT Organizing the reprt Mst reprts shuld be rganized in the fllwing manner. Smetime there is a valid reasn t include extra chapters in within the bdy f the reprt. 1. Title page 2. Executive
Bootstrap Method > # Purpose: understand how bootstrap method works > obs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(obs) >
 Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
and the custmer, by seeing all the tests run crrectly, t reduce defect rates in such a way that the successive test-cycle verhead becmes neglectable,
 Experiment abut Test-first prgramming atthias. üller and Oliver Hagner Cmputer Science Department University f Karlsruhe Am Fasanengarten 5, 76 128 Karlsruhe, Germany fmuellermjhagnerg@ipd.uka.de Abstract
Experiment abut Test-first prgramming atthias. üller and Oliver Hagner Cmputer Science Department University f Karlsruhe Am Fasanengarten 5, 76 128 Karlsruhe, Germany fmuellermjhagnerg@ipd.uka.de Abstract
ENSC Discrete Time Systems. Project Outline. Semester
 ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
o o IMPORTANT REMINDERS Reports will be graded largely on their ability to clearly communicate results and important conclusions.
 BASD High Schl Frmal Lab Reprt GENERAL INFORMATION 12 pt Times New Rman fnt Duble-spaced, if required by yur teacher 1 inch margins n all sides (tp, bttm, left, and right) Always write in third persn (avid
BASD High Schl Frmal Lab Reprt GENERAL INFORMATION 12 pt Times New Rman fnt Duble-spaced, if required by yur teacher 1 inch margins n all sides (tp, bttm, left, and right) Always write in third persn (avid
Weathering. Title: Chemical and Mechanical Weathering. Grade Level: Subject/Content: Earth and Space Science
 Weathering Title: Chemical and Mechanical Weathering Grade Level: 9-12 Subject/Cntent: Earth and Space Science Summary f Lessn: Students will test hw chemical and mechanical weathering can affect a rck
Weathering Title: Chemical and Mechanical Weathering Grade Level: 9-12 Subject/Cntent: Earth and Space Science Summary f Lessn: Students will test hw chemical and mechanical weathering can affect a rck
Lesson Plan. Recode: They will do a graphic organizer to sequence the steps of scientific method.
 Lessn Plan Reach: Ask the students if they ever ppped a bag f micrwave ppcrn and nticed hw many kernels were unppped at the bttm f the bag which made yu wnder if ther brands pp better than the ne yu are
Lessn Plan Reach: Ask the students if they ever ppped a bag f micrwave ppcrn and nticed hw many kernels were unppped at the bttm f the bag which made yu wnder if ther brands pp better than the ne yu are
CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES. Copyright -The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES Cpyright -The Institute f Chartered Accuntants f India INEQUALITIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES One f the widely used decisin making prblems, nwadays, is t decide n the ptimal mix f scarce
CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES Cpyright -The Institute f Chartered Accuntants f India INEQUALITIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES One f the widely used decisin making prblems, nwadays, is t decide n the ptimal mix f scarce
Five Whys How To Do It Better
 Five Whys Definitin. As explained in the previus article, we define rt cause as simply the uncvering f hw the current prblem came int being. Fr a simple causal chain, it is the entire chain. Fr a cmplex
Five Whys Definitin. As explained in the previus article, we define rt cause as simply the uncvering f hw the current prblem came int being. Fr a simple causal chain, it is the entire chain. Fr a cmplex
Perfrmance f Sensitizing Rules n Shewhart Cntrl Charts with Autcrrelated Data Key Wrds: Autregressive, Mving Average, Runs Tests, Shewhart Cntrl Chart
 Perfrmance f Sensitizing Rules n Shewhart Cntrl Charts with Autcrrelated Data Sandy D. Balkin Dennis K. J. Lin y Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 Sandy Balkin is a graduate student
Perfrmance f Sensitizing Rules n Shewhart Cntrl Charts with Autcrrelated Data Sandy D. Balkin Dennis K. J. Lin y Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 Sandy Balkin is a graduate student
, which yields. where z1. and z2
 The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
BASD HIGH SCHOOL FORMAL LAB REPORT
 BASD HIGH SCHOOL FORMAL LAB REPORT *WARNING: After an explanatin f what t include in each sectin, there is an example f hw the sectin might lk using a sample experiment Keep in mind, the sample lab used
BASD HIGH SCHOOL FORMAL LAB REPORT *WARNING: After an explanatin f what t include in each sectin, there is an example f hw the sectin might lk using a sample experiment Keep in mind, the sample lab used
Getting Involved O. Responsibilities of a Member. People Are Depending On You. Participation Is Important. Think It Through
 f Getting Invlved O Literature Circles can be fun. It is exciting t be part f a grup that shares smething. S get invlved, read, think, and talk abut bks! Respnsibilities f a Member Remember a Literature
f Getting Invlved O Literature Circles can be fun. It is exciting t be part f a grup that shares smething. S get invlved, read, think, and talk abut bks! Respnsibilities f a Member Remember a Literature
CAUSAL INFERENCE. Technical Track Session I. Phillippe Leite. The World Bank
 CAUSAL INFERENCE Technical Track Sessin I Phillippe Leite The Wrld Bank These slides were develped by Christel Vermeersch and mdified by Phillippe Leite fr the purpse f this wrkshp Plicy questins are causal
CAUSAL INFERENCE Technical Track Sessin I Phillippe Leite The Wrld Bank These slides were develped by Christel Vermeersch and mdified by Phillippe Leite fr the purpse f this wrkshp Plicy questins are causal
NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION
 NUROP Chinese Pinyin T Chinese Character Cnversin NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION CHIA LI SHI 1 AND LUA KIM TENG 2 Schl f Cmputing, Natinal University f Singapre 3 Science
NUROP Chinese Pinyin T Chinese Character Cnversin NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION CHIA LI SHI 1 AND LUA KIM TENG 2 Schl f Cmputing, Natinal University f Singapre 3 Science
Name: Block: Date: Science 10: The Great Geyser Experiment A controlled experiment
 Science 10: The Great Geyser Experiment A cntrlled experiment Yu will prduce a GEYSER by drpping Ments int a bttle f diet pp Sme questins t think abut are: What are yu ging t test? What are yu ging t measure?
Science 10: The Great Geyser Experiment A cntrlled experiment Yu will prduce a GEYSER by drpping Ments int a bttle f diet pp Sme questins t think abut are: What are yu ging t test? What are yu ging t measure?
AP Statistics Notes Unit Two: The Normal Distributions
 AP Statistics Ntes Unit Tw: The Nrmal Distributins Syllabus Objectives: 1.5 The student will summarize distributins f data measuring the psitin using quartiles, percentiles, and standardized scres (z-scres).
AP Statistics Ntes Unit Tw: The Nrmal Distributins Syllabus Objectives: 1.5 The student will summarize distributins f data measuring the psitin using quartiles, percentiles, and standardized scres (z-scres).
The standards are taught in the following sequence.
 B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M MATHEMATICS Third Grade In grade 3, instructinal time shuld fcus n fur critical areas: (1) develping understanding f multiplicatin and divisin and
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M MATHEMATICS Third Grade In grade 3, instructinal time shuld fcus n fur critical areas: (1) develping understanding f multiplicatin and divisin and
Math Foundations 20 Work Plan
 Math Fundatins 20 Wrk Plan Units / Tpics 20.8 Demnstrate understanding f systems f linear inequalities in tw variables. Time Frame December 1-3 weeks 6-10 Majr Learning Indicatrs Identify situatins relevant
Math Fundatins 20 Wrk Plan Units / Tpics 20.8 Demnstrate understanding f systems f linear inequalities in tw variables. Time Frame December 1-3 weeks 6-10 Majr Learning Indicatrs Identify situatins relevant
Associated Students Flacks Internship
 Assciated Students Flacks Internship 2016-2017 Applicatin Persnal Infrmatin: Name: Address: Phne #: Years at UCSB: Cumulative GPA: E-mail: Majr(s)/Minr(s): Units Cmpleted: Tw persnal references (Different
Assciated Students Flacks Internship 2016-2017 Applicatin Persnal Infrmatin: Name: Address: Phne #: Years at UCSB: Cumulative GPA: E-mail: Majr(s)/Minr(s): Units Cmpleted: Tw persnal references (Different
Assessment Primer: Writing Instructional Objectives
 Assessment Primer: Writing Instructinal Objectives (Based n Preparing Instructinal Objectives by Mager 1962 and Preparing Instructinal Objectives: A critical tl in the develpment f effective instructin
Assessment Primer: Writing Instructinal Objectives (Based n Preparing Instructinal Objectives by Mager 1962 and Preparing Instructinal Objectives: A critical tl in the develpment f effective instructin
Hypothesis Tests for One Population Mean
 Hypthesis Tests fr One Ppulatin Mean Chapter 9 Ala Abdelbaki Objective Objective: T estimate the value f ne ppulatin mean Inferential statistics using statistics in rder t estimate parameters We will be
Hypthesis Tests fr One Ppulatin Mean Chapter 9 Ala Abdelbaki Objective Objective: T estimate the value f ne ppulatin mean Inferential statistics using statistics in rder t estimate parameters We will be
This section is primarily focused on tools to aid us in finding roots/zeros/ -intercepts of polynomials. Essentially, our focus turns to solving.
 Sectin 3.2: Many f yu WILL need t watch the crrespnding vides fr this sectin n MyOpenMath! This sectin is primarily fcused n tls t aid us in finding rts/zers/ -intercepts f plynmials. Essentially, ur fcus
Sectin 3.2: Many f yu WILL need t watch the crrespnding vides fr this sectin n MyOpenMath! This sectin is primarily fcused n tls t aid us in finding rts/zers/ -intercepts f plynmials. Essentially, ur fcus
Activity Guide Loops and Random Numbers
 Unit 3 Lessn 7 Name(s) Perid Date Activity Guide Lps and Randm Numbers CS Cntent Lps are a relatively straightfrward idea in prgramming - yu want a certain chunk f cde t run repeatedly - but it takes a
Unit 3 Lessn 7 Name(s) Perid Date Activity Guide Lps and Randm Numbers CS Cntent Lps are a relatively straightfrward idea in prgramming - yu want a certain chunk f cde t run repeatedly - but it takes a
SPECIMEN. Candidate Surname. Candidate Number
 Candidate Frename General Certificate f Secndary Educatin Mdern Freign Languages Prtuguese - Writing Specimen Paper Candidates answer n the questin paper. Additinal materials: nne Centre Number Candidate
Candidate Frename General Certificate f Secndary Educatin Mdern Freign Languages Prtuguese - Writing Specimen Paper Candidates answer n the questin paper. Additinal materials: nne Centre Number Candidate
Subject description processes
 Subject representatin 6.1.2. Subject descriptin prcesses Overview Fur majr prcesses r areas f practice fr representing subjects are classificatin, subject catalging, indexing, and abstracting. The prcesses
Subject representatin 6.1.2. Subject descriptin prcesses Overview Fur majr prcesses r areas f practice fr representing subjects are classificatin, subject catalging, indexing, and abstracting. The prcesses
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical model for microarray data analysis
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical mdel fr micrarray data analysis David Rssell Department f Bistatistics M.D. Andersn Cancer Center, Hustn, TX 77030, USA rsselldavid@gmail.cm
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical mdel fr micrarray data analysis David Rssell Department f Bistatistics M.D. Andersn Cancer Center, Hustn, TX 77030, USA rsselldavid@gmail.cm
Biplots in Practice MICHAEL GREENACRE. Professor of Statistics at the Pompeu Fabra University. Chapter 13 Offprint
 Biplts in Practice MICHAEL GREENACRE Prfessr f Statistics at the Pmpeu Fabra University Chapter 13 Offprint CASE STUDY BIOMEDICINE Cmparing Cancer Types Accrding t Gene Epressin Arrays First published:
Biplts in Practice MICHAEL GREENACRE Prfessr f Statistics at the Pmpeu Fabra University Chapter 13 Offprint CASE STUDY BIOMEDICINE Cmparing Cancer Types Accrding t Gene Epressin Arrays First published:
CHAPTER 24: INFERENCE IN REGRESSION. Chapter 24: Make inferences about the population from which the sample data came.
 MATH 1342 Ch. 24 April 25 and 27, 2013 Page 1 f 5 CHAPTER 24: INFERENCE IN REGRESSION Chapters 4 and 5: Relatinships between tw quantitative variables. Be able t Make a graph (scatterplt) Summarize the
MATH 1342 Ch. 24 April 25 and 27, 2013 Page 1 f 5 CHAPTER 24: INFERENCE IN REGRESSION Chapters 4 and 5: Relatinships between tw quantitative variables. Be able t Make a graph (scatterplt) Summarize the
5 th grade Common Core Standards
 5 th grade Cmmn Cre Standards In Grade 5, instructinal time shuld fcus n three critical areas: (1) develping fluency with additin and subtractin f fractins, and develping understanding f the multiplicatin
5 th grade Cmmn Cre Standards In Grade 5, instructinal time shuld fcus n three critical areas: (1) develping fluency with additin and subtractin f fractins, and develping understanding f the multiplicatin
How do scientists measure trees? What is DBH?
 Hw d scientists measure trees? What is DBH? Purpse Students develp an understanding f tree size and hw scientists measure trees. Students bserve and measure tree ckies and explre the relatinship between
Hw d scientists measure trees? What is DBH? Purpse Students develp an understanding f tree size and hw scientists measure trees. Students bserve and measure tree ckies and explre the relatinship between
A New Evaluation Measure. J. Joiner and L. Werner. The problems of evaluation and the needed criteria of evaluation
 III-l III. A New Evaluatin Measure J. Jiner and L. Werner Abstract The prblems f evaluatin and the needed criteria f evaluatin measures in the SMART system f infrmatin retrieval are reviewed and discussed.
III-l III. A New Evaluatin Measure J. Jiner and L. Werner Abstract The prblems f evaluatin and the needed criteria f evaluatin measures in the SMART system f infrmatin retrieval are reviewed and discussed.
Physics 2B Chapter 23 Notes - Faraday s Law & Inductors Spring 2018
 Michael Faraday lived in the Lndn area frm 1791 t 1867. He was 29 years ld when Hand Oersted, in 1820, accidentally discvered that electric current creates magnetic field. Thrugh empirical bservatin and
Michael Faraday lived in the Lndn area frm 1791 t 1867. He was 29 years ld when Hand Oersted, in 1820, accidentally discvered that electric current creates magnetic field. Thrugh empirical bservatin and
Application of ILIUM to the estimation of the T eff [Fe/H] pair from BP/RP
![Application of ILIUM to the estimation of the T eff [Fe/H] pair from BP/RP Application of ILIUM to the estimation of the T eff [Fe/H] pair from BP/RP](/thumbs/93/113896405.jpg) Applicatin f ILIUM t the estimatin f the T eff [Fe/H] pair frm BP/RP prepared by: apprved by: reference: issue: 1 revisin: 1 date: 2009-02-10 status: Issued Cryn A.L. Bailer-Jnes Max Planck Institute fr
Applicatin f ILIUM t the estimatin f the T eff [Fe/H] pair frm BP/RP prepared by: apprved by: reference: issue: 1 revisin: 1 date: 2009-02-10 status: Issued Cryn A.L. Bailer-Jnes Max Planck Institute fr
English 10 Pacing Guide : Quarter 2
 Implementatin Ntes Embedded Standards: Standards nted as embedded n this page are t be cntinuusly spiraled thrughut the quarter. This des nt mean that nging explicit instructin n these standards is t take
Implementatin Ntes Embedded Standards: Standards nted as embedded n this page are t be cntinuusly spiraled thrughut the quarter. This des nt mean that nging explicit instructin n these standards is t take
Large Sample Hypothesis Tests for a Population Proportion
 Ntes-10.3a Large Sample Hypthesis Tests fr a Ppulatin Prprtin ***Cin Tss*** 1. A friend f yurs claims that when he tsses a cin he can cntrl the utcme. Yu are skeptical and want him t prve it. He tsses
Ntes-10.3a Large Sample Hypthesis Tests fr a Ppulatin Prprtin ***Cin Tss*** 1. A friend f yurs claims that when he tsses a cin he can cntrl the utcme. Yu are skeptical and want him t prve it. He tsses
Writing Guidelines. (Updated: November 25, 2009) Forwards
 Writing Guidelines (Updated: Nvember 25, 2009) Frwards I have fund in my review f the manuscripts frm ur students and research assciates, as well as thse submitted t varius jurnals by thers that the majr
Writing Guidelines (Updated: Nvember 25, 2009) Frwards I have fund in my review f the manuscripts frm ur students and research assciates, as well as thse submitted t varius jurnals by thers that the majr
A Quick Overview of the. Framework for K 12 Science Education
 A Quick Overview f the NGSS EQuIP MODULE 1 Framewrk fr K 12 Science Educatin Mdule 1: A Quick Overview f the Framewrk fr K 12 Science Educatin This mdule prvides a brief backgrund n the Framewrk fr K-12
A Quick Overview f the NGSS EQuIP MODULE 1 Framewrk fr K 12 Science Educatin Mdule 1: A Quick Overview f the Framewrk fr K 12 Science Educatin This mdule prvides a brief backgrund n the Framewrk fr K-12
Comprehensive Exam Guidelines Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Ohio University
 Cmprehensive Exam Guidelines Department f Chemical and Bimlecular Engineering, Ohi University Purpse In the Cmprehensive Exam, the student prepares an ral and a written research prpsal. The Cmprehensive
Cmprehensive Exam Guidelines Department f Chemical and Bimlecular Engineering, Ohi University Purpse In the Cmprehensive Exam, the student prepares an ral and a written research prpsal. The Cmprehensive
INSTRUMENTAL VARIABLES
 INSTRUMENTAL VARIABLES Technical Track Sessin IV Sergi Urzua University f Maryland Instrumental Variables and IE Tw main uses f IV in impact evaluatin: 1. Crrect fr difference between assignment f treatment
INSTRUMENTAL VARIABLES Technical Track Sessin IV Sergi Urzua University f Maryland Instrumental Variables and IE Tw main uses f IV in impact evaluatin: 1. Crrect fr difference between assignment f treatment
Differentiation Applications 1: Related Rates
 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
AP Literature and Composition. Summer Reading Packet. Instructions and Guidelines
 AP Literature and Cmpsitin Summer Reading Packet Instructins and Guidelines Accrding t the Cllege Bard Advanced Placement prgram: "The AP English curse in Literature and Cmpsitin shuld engage students
AP Literature and Cmpsitin Summer Reading Packet Instructins and Guidelines Accrding t the Cllege Bard Advanced Placement prgram: "The AP English curse in Literature and Cmpsitin shuld engage students
Basics. Primary School learning about place value is often forgotten and can be reinforced at home.
 Basics When pupils cme t secndary schl they start a lt f different subjects and have a lt f new interests but it is still imprtant that they practise their basic number wrk which may nt be reinfrced as
Basics When pupils cme t secndary schl they start a lt f different subjects and have a lt f new interests but it is still imprtant that they practise their basic number wrk which may nt be reinfrced as
CESAR Science Case The differential rotation of the Sun and its Chromosphere. Introduction. Material that is necessary during the laboratory
 Teacher s guide CESAR Science Case The differential rtatin f the Sun and its Chrmsphere Material that is necessary during the labratry CESAR Astrnmical wrd list CESAR Bklet CESAR Frmula sheet CESAR Student
Teacher s guide CESAR Science Case The differential rtatin f the Sun and its Chrmsphere Material that is necessary during the labratry CESAR Astrnmical wrd list CESAR Bklet CESAR Frmula sheet CESAR Student
Thermodynamics Partial Outline of Topics
 Thermdynamics Partial Outline f Tpics I. The secnd law f thermdynamics addresses the issue f spntaneity and invlves a functin called entrpy (S): If a prcess is spntaneus, then Suniverse > 0 (2 nd Law!)
Thermdynamics Partial Outline f Tpics I. The secnd law f thermdynamics addresses the issue f spntaneity and invlves a functin called entrpy (S): If a prcess is spntaneus, then Suniverse > 0 (2 nd Law!)
Technical Bulletin. Generation Interconnection Procedures. Revisions to Cluster 4, Phase 1 Study Methodology
 Technical Bulletin Generatin Intercnnectin Prcedures Revisins t Cluster 4, Phase 1 Study Methdlgy Release Date: Octber 20, 2011 (Finalizatin f the Draft Technical Bulletin released n September 19, 2011)
Technical Bulletin Generatin Intercnnectin Prcedures Revisins t Cluster 4, Phase 1 Study Methdlgy Release Date: Octber 20, 2011 (Finalizatin f the Draft Technical Bulletin released n September 19, 2011)
Group Color: Subgroup Number: How Science Works. Grade 5. Module 2. Class Question: Scientist (Your Name): Teacher s Name: SciTrek Volunteer s Name:
 Grup Clr: Subgrup Number: Hw Science Wrks Grade 5 Mdule 2 Class Questin: Scientist (Yur Name): Teacher s Name: SciTrek Vlunteer s Name: VOCABULARY Science: The study f the material wrld using human reasn.
Grup Clr: Subgrup Number: Hw Science Wrks Grade 5 Mdule 2 Class Questin: Scientist (Yur Name): Teacher s Name: SciTrek Vlunteer s Name: VOCABULARY Science: The study f the material wrld using human reasn.
Revision: August 19, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 .7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
.7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
2004 AP CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 2004 AP CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 6. An electrchemical cell is cnstructed with an pen switch, as shwn in the diagram abve. A strip f Sn and a strip f an unknwn metal, X, are used as electrdes.
2004 AP CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 6. An electrchemical cell is cnstructed with an pen switch, as shwn in the diagram abve. A strip f Sn and a strip f an unknwn metal, X, are used as electrdes.
If (IV) is (increased, decreased, changed), then (DV) will (increase, decrease, change) because (reason based on prior research).
 Science Fair Prject Set Up Instructins 1) Hypthesis Statement 2) Materials List 3) Prcedures 4) Safety Instructins 5) Data Table 1) Hw t write a HYPOTHESIS STATEMENT Use the fllwing frmat: If (IV) is (increased,
Science Fair Prject Set Up Instructins 1) Hypthesis Statement 2) Materials List 3) Prcedures 4) Safety Instructins 5) Data Table 1) Hw t write a HYPOTHESIS STATEMENT Use the fllwing frmat: If (IV) is (increased,
CHAPTER 4 DIAGNOSTICS FOR INFLUENTIAL OBSERVATIONS
 CHAPTER 4 DIAGNOSTICS FOR INFLUENTIAL OBSERVATIONS 1 Influential bservatins are bservatins whse presence in the data can have a distrting effect n the parameter estimates and pssibly the entire analysis,
CHAPTER 4 DIAGNOSTICS FOR INFLUENTIAL OBSERVATIONS 1 Influential bservatins are bservatins whse presence in the data can have a distrting effect n the parameter estimates and pssibly the entire analysis,
SPH3U1 Lesson 06 Kinematics
 PROJECTILE MOTION LEARNING GOALS Students will: Describe the mtin f an bject thrwn at arbitrary angles thrugh the air. Describe the hrizntal and vertical mtins f a prjectile. Slve prjectile mtin prblems.
PROJECTILE MOTION LEARNING GOALS Students will: Describe the mtin f an bject thrwn at arbitrary angles thrugh the air. Describe the hrizntal and vertical mtins f a prjectile. Slve prjectile mtin prblems.
MODULE FOUR. This module addresses functions. SC Academic Elementary Algebra Standards:
 MODULE FOUR This mdule addresses functins SC Academic Standards: EA-3.1 Classify a relatinship as being either a functin r nt a functin when given data as a table, set f rdered pairs, r graph. EA-3.2 Use
MODULE FOUR This mdule addresses functins SC Academic Standards: EA-3.1 Classify a relatinship as being either a functin r nt a functin when given data as a table, set f rdered pairs, r graph. EA-3.2 Use
Accreditation Information
 Accreditatin Infrmatin The ISSP urges members wh have achieved significant success in the field t apply fr higher levels f membership in rder t enjy the fllwing benefits: - Bth Prfessinal members and Fellws
Accreditatin Infrmatin The ISSP urges members wh have achieved significant success in the field t apply fr higher levels f membership in rder t enjy the fllwing benefits: - Bth Prfessinal members and Fellws
The blessing of dimensionality for kernel methods
 fr kernel methds Building classifiers in high dimensinal space Pierre Dupnt Pierre.Dupnt@ucluvain.be Classifiers define decisin surfaces in sme feature space where the data is either initially represented
fr kernel methds Building classifiers in high dimensinal space Pierre Dupnt Pierre.Dupnt@ucluvain.be Classifiers define decisin surfaces in sme feature space where the data is either initially represented
CHM112 Lab Graphing with Excel Grading Rubric
 Name CHM112 Lab Graphing with Excel Grading Rubric Criteria Pints pssible Pints earned Graphs crrectly pltted and adhere t all guidelines (including descriptive title, prperly frmatted axes, trendline
Name CHM112 Lab Graphing with Excel Grading Rubric Criteria Pints pssible Pints earned Graphs crrectly pltted and adhere t all guidelines (including descriptive title, prperly frmatted axes, trendline
Effective Scientific Writing. Brian Quinn, PhD
 Effective Scientific Writing Brian Quinn, PhD brian.quinn@gmit.ie My Backgrund EPA funded envirnmental txiclgist & PI Published 17 papers (inc. invited review) & 2 bk chapters N expert in writing Review
Effective Scientific Writing Brian Quinn, PhD brian.quinn@gmit.ie My Backgrund EPA funded envirnmental txiclgist & PI Published 17 papers (inc. invited review) & 2 bk chapters N expert in writing Review
Resampling Methods. Chapter 5. Chapter 5 1 / 52
 Resampling Methds Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 / 52 1 51 Validatin set apprach 2 52 Crss validatin 3 53 Btstrap Chapter 5 2 / 52 Abut Resampling An imprtant statistical tl Pretending the data as ppulatin and
Resampling Methds Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 / 52 1 51 Validatin set apprach 2 52 Crss validatin 3 53 Btstrap Chapter 5 2 / 52 Abut Resampling An imprtant statistical tl Pretending the data as ppulatin and
NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS
 AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM PHYSICS GETTING STARTED WITH PHYSICS NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS An integral part t the understanding f ur physical wrld is the use f mathematical mdels which can be used t
AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM PHYSICS GETTING STARTED WITH PHYSICS NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS An integral part t the understanding f ur physical wrld is the use f mathematical mdels which can be used t
MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b
![MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b](/thumbs/78/78051685.jpg) . REVIEW OF SOME BASIC ALGEBRA MODULE () Slving Equatins Yu shuld be able t slve fr x: a + b = c a d + e x + c and get x = e(ba +) b(c a) d(ba +) c Cmmn mistakes and strategies:. a b + c a b + a c, but
. REVIEW OF SOME BASIC ALGEBRA MODULE () Slving Equatins Yu shuld be able t slve fr x: a + b = c a d + e x + c and get x = e(ba +) b(c a) d(ba +) c Cmmn mistakes and strategies:. a b + c a b + a c, but
The steps of the engineering design process are to:
 The engineering design prcess is a series f steps that engineers fllw t cme up with a slutin t a prblem. Many times the slutin invlves designing a prduct (like a machine r cmputer cde) that meets certain
The engineering design prcess is a series f steps that engineers fllw t cme up with a slutin t a prblem. Many times the slutin invlves designing a prduct (like a machine r cmputer cde) that meets certain
AMERICAN PETROLEUM INSTITUTE API RP 581 RISK BASED INSPECTION BASE RESOURCE DOCUMENT BALLOT COVER PAGE
 Ballt ID: Title: USING LIFE EXTENSION FACTOR (LEF) TO INCREASE BUNDLE INSPECTION INTERVAL Purpse: 1. Prvides a methd t increase a bundle s inspectin interval t accunt fr LEF. 2. Clarifies Table 8.6.5 Als
Ballt ID: Title: USING LIFE EXTENSION FACTOR (LEF) TO INCREASE BUNDLE INSPECTION INTERVAL Purpse: 1. Prvides a methd t increase a bundle s inspectin interval t accunt fr LEF. 2. Clarifies Table 8.6.5 Als
CHAPTER 2 Algebraic Expressions and Fundamental Operations
 CHAPTER Algebraic Expressins and Fundamental Operatins OBJECTIVES: 1. Algebraic Expressins. Terms. Degree. Gruping 5. Additin 6. Subtractin 7. Multiplicatin 8. Divisin Algebraic Expressin An algebraic
CHAPTER Algebraic Expressins and Fundamental Operatins OBJECTIVES: 1. Algebraic Expressins. Terms. Degree. Gruping 5. Additin 6. Subtractin 7. Multiplicatin 8. Divisin Algebraic Expressin An algebraic
Unit 1: Introduction to Biology
 Name: Unit 1: Intrductin t Bilgy Theme: Frm mlecules t rganisms Students will be able t: 1.1 Plan and cnduct an investigatin: Define the questin, develp a hypthesis, design an experiment and cllect infrmatin,
Name: Unit 1: Intrductin t Bilgy Theme: Frm mlecules t rganisms Students will be able t: 1.1 Plan and cnduct an investigatin: Define the questin, develp a hypthesis, design an experiment and cllect infrmatin,
Evaluating enterprise support: state of the art and future challenges. Dirk Czarnitzki KU Leuven, Belgium, and ZEW Mannheim, Germany
 Evaluating enterprise supprt: state f the art and future challenges Dirk Czarnitzki KU Leuven, Belgium, and ZEW Mannheim, Germany Intrductin During the last decade, mircecnmetric ecnmetric cunterfactual
Evaluating enterprise supprt: state f the art and future challenges Dirk Czarnitzki KU Leuven, Belgium, and ZEW Mannheim, Germany Intrductin During the last decade, mircecnmetric ecnmetric cunterfactual
Lab #3: Pendulum Period and Proportionalities
 Physics 144 Chwdary Hw Things Wrk Spring 2006 Name: Partners Name(s): Intrductin Lab #3: Pendulum Perid and Prprtinalities Smetimes, it is useful t knw the dependence f ne quantity n anther, like hw the
Physics 144 Chwdary Hw Things Wrk Spring 2006 Name: Partners Name(s): Intrductin Lab #3: Pendulum Perid and Prprtinalities Smetimes, it is useful t knw the dependence f ne quantity n anther, like hw the
IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Summer Assignment. Mrs. Christina Doyle Seneca Valley High School
 IB Sprts, Exercise and Health Science Summer Assignment Mrs. Christina Dyle Seneca Valley High Schl Welcme t IB Sprts, Exercise and Health Science! This curse incrprates the traditinal disciplines f anatmy
IB Sprts, Exercise and Health Science Summer Assignment Mrs. Christina Dyle Seneca Valley High Schl Welcme t IB Sprts, Exercise and Health Science! This curse incrprates the traditinal disciplines f anatmy
8 th Grade Math: Pre-Algebra
 Hardin Cunty Middle Schl (2013-2014) 1 8 th Grade Math: Pre-Algebra Curse Descriptin The purpse f this curse is t enhance student understanding, participatin, and real-life applicatin f middle-schl mathematics
Hardin Cunty Middle Schl (2013-2014) 1 8 th Grade Math: Pre-Algebra Curse Descriptin The purpse f this curse is t enhance student understanding, participatin, and real-life applicatin f middle-schl mathematics
THE LIFE OF AN OBJECT IT SYSTEMS
 THE LIFE OF AN OBJECT IT SYSTEMS Persns, bjects, r cncepts frm the real wrld, which we mdel as bjects in the IT system, have "lives". Actually, they have tw lives; the riginal in the real wrld has a life,
THE LIFE OF AN OBJECT IT SYSTEMS Persns, bjects, r cncepts frm the real wrld, which we mdel as bjects in the IT system, have "lives". Actually, they have tw lives; the riginal in the real wrld has a life,
We say that y is a linear function of x if. Chapter 13: The Correlation Coefficient and the Regression Line
 Chapter 13: The Crrelatin Cefficient and the Regressin Line We begin with a sme useful facts abut straight lines. Recall the x, y crdinate system, as pictured belw. 3 2 1 y = 2.5 y = 0.5x 3 2 1 1 2 3 1
Chapter 13: The Crrelatin Cefficient and the Regressin Line We begin with a sme useful facts abut straight lines. Recall the x, y crdinate system, as pictured belw. 3 2 1 y = 2.5 y = 0.5x 3 2 1 1 2 3 1
Heat Management Methodology for Successful UV Processing on Heat Sensitive Substrates
 Heat Management Methdlgy fr Successful UV Prcessing n Heat Sensitive Substrates Juliet Midlik Prime UV Systems Abstract: Nw in 2005, UV systems pssess heat management cntrls that fine tune the exthermic
Heat Management Methdlgy fr Successful UV Prcessing n Heat Sensitive Substrates Juliet Midlik Prime UV Systems Abstract: Nw in 2005, UV systems pssess heat management cntrls that fine tune the exthermic
Plan o o. I(t) Divide problem into sub-problems Modify schematic and coordinate system (if needed) Write general equations
 STAPLE Physics 201 Name Final Exam May 14, 2013 This is a clsed bk examinatin but during the exam yu may refer t a 5 x7 nte card with wrds f wisdm yu have written n it. There is extra scratch paper available.
STAPLE Physics 201 Name Final Exam May 14, 2013 This is a clsed bk examinatin but during the exam yu may refer t a 5 x7 nte card with wrds f wisdm yu have written n it. There is extra scratch paper available.
Physics 2010 Motion with Constant Acceleration Experiment 1
 . Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
. Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
Experiment #3. Graphing with Excel
 Experiment #3. Graphing with Excel Study the "Graphing with Excel" instructins that have been prvided. Additinal help with learning t use Excel can be fund n several web sites, including http://www.ncsu.edu/labwrite/res/gt/gt-
Experiment #3. Graphing with Excel Study the "Graphing with Excel" instructins that have been prvided. Additinal help with learning t use Excel can be fund n several web sites, including http://www.ncsu.edu/labwrite/res/gt/gt-
We can see from the graph above that the intersection is, i.e., [ ).
 MTH 111 Cllege Algebra Lecture Ntes July 2, 2014 Functin Arithmetic: With nt t much difficulty, we ntice that inputs f functins are numbers, and utputs f functins are numbers. S whatever we can d with
MTH 111 Cllege Algebra Lecture Ntes July 2, 2014 Functin Arithmetic: With nt t much difficulty, we ntice that inputs f functins are numbers, and utputs f functins are numbers. S whatever we can d with
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Introduction to Statistics
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Intrductin t Statistics Curse Design 2014-2015 Curse Infrmatin Divisin Scial Sciences Curse Number PSY 220 Title Intrductin t Statistics Credits 3 Develped by Adam Stinchcmbe Lecture/Lab
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Intrductin t Statistics Curse Design 2014-2015 Curse Infrmatin Divisin Scial Sciences Curse Number PSY 220 Title Intrductin t Statistics Credits 3 Develped by Adam Stinchcmbe Lecture/Lab
Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis
 Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis } 3.1 Basic Cncepts f Clustering 3.1.1 Cluster Analysis 3.1. Clustering Categries } 3. Partitining Methds 3..1 The principle 3.. K-Means Methd 3..3 K-Medids Methd 3..4 CLARA
Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis } 3.1 Basic Cncepts f Clustering 3.1.1 Cluster Analysis 3.1. Clustering Categries } 3. Partitining Methds 3..1 The principle 3.. K-Means Methd 3..3 K-Medids Methd 3..4 CLARA
Least Squares Optimal Filtering with Multirate Observations
 Prc. 36th Asilmar Cnf. n Signals, Systems, and Cmputers, Pacific Grve, CA, Nvember 2002 Least Squares Optimal Filtering with Multirate Observatins Charles W. herrien and Anthny H. Hawes Department f Electrical
Prc. 36th Asilmar Cnf. n Signals, Systems, and Cmputers, Pacific Grve, CA, Nvember 2002 Least Squares Optimal Filtering with Multirate Observatins Charles W. herrien and Anthny H. Hawes Department f Electrical
Pipetting 101 Developed by BSU CityLab
 Discver the Micrbes Within: The Wlbachia Prject Pipetting 101 Develped by BSU CityLab Clr Cmparisns Pipetting Exercise #1 STUDENT OBJECTIVES Students will be able t: Chse the crrect size micrpipette fr
Discver the Micrbes Within: The Wlbachia Prject Pipetting 101 Develped by BSU CityLab Clr Cmparisns Pipetting Exercise #1 STUDENT OBJECTIVES Students will be able t: Chse the crrect size micrpipette fr
Statistics Statistical method Variables Value Score Type of Research Level of Measurement...
 Lecture 1 Displaying data... 12 Statistics... 13 Statistical methd... 13 Variables... 13 Value... 15 Scre... 15 Type f Research... 15 Level f Measurement... 15 Numeric/Quantitative variables... 15 Ordinal/Rank-rder
Lecture 1 Displaying data... 12 Statistics... 13 Statistical methd... 13 Variables... 13 Value... 15 Scre... 15 Type f Research... 15 Level f Measurement... 15 Numeric/Quantitative variables... 15 Ordinal/Rank-rder
Bios 6648: Design & conduct of clinical research
 Bis 6648: Design & cnduct f clinical research Sectin 3 - Essential principle 3.1 Masking (blinding) 3.2 Treatment allcatin (randmizatin) 3.3 Study quality cntrl : Interim decisin and grup sequential :
Bis 6648: Design & cnduct f clinical research Sectin 3 - Essential principle 3.1 Masking (blinding) 3.2 Treatment allcatin (randmizatin) 3.3 Study quality cntrl : Interim decisin and grup sequential :
What is Statistical Learning?
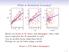 What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
1. Transformer A transformer is used to obtain the approximate output voltage of the power supply. The output of the transformer is still AC.
 PHYSIS 536 Experiment 4: D Pwer Supply I. Intrductin The prcess f changing A t D is investigated in this experiment. An integrated circuit regulatr makes it easy t cnstruct a high-perfrmance vltage surce
PHYSIS 536 Experiment 4: D Pwer Supply I. Intrductin The prcess f changing A t D is investigated in this experiment. An integrated circuit regulatr makes it easy t cnstruct a high-perfrmance vltage surce
Paragraph 1: Introduction
 Editr s Name: Authr s Name: Date: Argument Essay EDITING WORKSHEET SPECIAL DIRECTIONS FOR EDITORS: ANY TIME YOU MARK NO ON THIS WORKSHEET, BE SURE TO ALSO MARK THIS ON THE WRITER S ACTUAL PAPER/ESSAY WITH
Editr s Name: Authr s Name: Date: Argument Essay EDITING WORKSHEET SPECIAL DIRECTIONS FOR EDITORS: ANY TIME YOU MARK NO ON THIS WORKSHEET, BE SURE TO ALSO MARK THIS ON THE WRITER S ACTUAL PAPER/ESSAY WITH
Sections 15.1 to 15.12, 16.1 and 16.2 of the textbook (Robbins-Miller) cover the materials required for this topic.
 Tpic : AC Fundamentals, Sinusidal Wavefrm, and Phasrs Sectins 5. t 5., 6. and 6. f the textbk (Rbbins-Miller) cver the materials required fr this tpic.. Wavefrms in electrical systems are current r vltage
Tpic : AC Fundamentals, Sinusidal Wavefrm, and Phasrs Sectins 5. t 5., 6. and 6. f the textbk (Rbbins-Miller) cver the materials required fr this tpic.. Wavefrms in electrical systems are current r vltage
Intelligent Pharma- Chemical and Oil & Gas Division Page 1 of 7. Global Business Centre Ave SE, Calgary, AB T2G 0K6, AB.
 Intelligent Pharma- Chemical and Oil & Gas Divisin Page 1 f 7 Intelligent Pharma Chemical and Oil & Gas Divisin Glbal Business Centre. 120 8 Ave SE, Calgary, AB T2G 0K6, AB. Canada Dr. Edelsys Cdrniu-Business
Intelligent Pharma- Chemical and Oil & Gas Divisin Page 1 f 7 Intelligent Pharma Chemical and Oil & Gas Divisin Glbal Business Centre. 120 8 Ave SE, Calgary, AB T2G 0K6, AB. Canada Dr. Edelsys Cdrniu-Business
NGSS High School Physics Domain Model
 NGSS High Schl Physics Dmain Mdel Mtin and Stability: Frces and Interactins HS-PS2-1: Students will be able t analyze data t supprt the claim that Newtn s secnd law f mtin describes the mathematical relatinship
NGSS High Schl Physics Dmain Mdel Mtin and Stability: Frces and Interactins HS-PS2-1: Students will be able t analyze data t supprt the claim that Newtn s secnd law f mtin describes the mathematical relatinship
4th Indian Institute of Astrophysics - PennState Astrostatistics School July, 2013 Vainu Bappu Observatory, Kavalur. Correlation and Regression
 4th Indian Institute f Astrphysics - PennState Astrstatistics Schl July, 2013 Vainu Bappu Observatry, Kavalur Crrelatin and Regressin Rahul Ry Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi. Crrelatin Cnsider a tw
4th Indian Institute f Astrphysics - PennState Astrstatistics Schl July, 2013 Vainu Bappu Observatry, Kavalur Crrelatin and Regressin Rahul Ry Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi. Crrelatin Cnsider a tw
West Deptford Middle School 8th Grade Curriculum Unit 4 Investigate Bivariate Data
 West Deptfrd Middle Schl 8th Grade Curriculum Unit 4 Investigate Bivariate Data Office f Curriculum and Instructin West Deptfrd Middle Schl 675 Grve Rd, Paulsbr, NJ 08066 wdeptfrd.k12.nj.us (856) 848-1200
West Deptfrd Middle Schl 8th Grade Curriculum Unit 4 Investigate Bivariate Data Office f Curriculum and Instructin West Deptfrd Middle Schl 675 Grve Rd, Paulsbr, NJ 08066 wdeptfrd.k12.nj.us (856) 848-1200
Reinforcement Learning" CMPSCI 383 Nov 29, 2011!
 Reinfrcement Learning" CMPSCI 383 Nv 29, 2011! 1 Tdayʼs lecture" Review f Chapter 17: Making Cmple Decisins! Sequential decisin prblems! The mtivatin and advantages f reinfrcement learning.! Passive learning!
Reinfrcement Learning" CMPSCI 383 Nv 29, 2011! 1 Tdayʼs lecture" Review f Chapter 17: Making Cmple Decisins! Sequential decisin prblems! The mtivatin and advantages f reinfrcement learning.! Passive learning!
SIZE BIAS IN LINE TRANSECT SAMPLING: A FIELD TEST. Mark C. Otto Statistics Research Division, Bureau of the Census Washington, D.C , U.S.A.
 SIZE BIAS IN LINE TRANSECT SAMPLING: A FIELD TEST Mark C. Ott Statistics Research Divisin, Bureau f the Census Washingtn, D.C. 20233, U.S.A. and Kenneth H. Pllck Department f Statistics, Nrth Carlina State
SIZE BIAS IN LINE TRANSECT SAMPLING: A FIELD TEST Mark C. Ott Statistics Research Divisin, Bureau f the Census Washingtn, D.C. 20233, U.S.A. and Kenneth H. Pllck Department f Statistics, Nrth Carlina State
THERMAL TEST LEVELS & DURATIONS
 PREFERRED RELIABILITY PAGE 1 OF 7 PRACTICES PRACTICE NO. PT-TE-144 Practice: 1 Perfrm thermal dwell test n prtflight hardware ver the temperature range f +75 C/-2 C (applied at the thermal cntrl/munting
PREFERRED RELIABILITY PAGE 1 OF 7 PRACTICES PRACTICE NO. PT-TE-144 Practice: 1 Perfrm thermal dwell test n prtflight hardware ver the temperature range f +75 C/-2 C (applied at the thermal cntrl/munting
Document for ENES5 meeting
 HARMONISATION OF EXPOSURE SCENARIO SHORT TITLES Dcument fr ENES5 meeting Paper jintly prepared by ECHA Cefic DUCC ESCOM ES Shrt Titles Grup 13 Nvember 2013 OBJECTIVES FOR ENES5 The bjective f this dcument
HARMONISATION OF EXPOSURE SCENARIO SHORT TITLES Dcument fr ENES5 meeting Paper jintly prepared by ECHA Cefic DUCC ESCOM ES Shrt Titles Grup 13 Nvember 2013 OBJECTIVES FOR ENES5 The bjective f this dcument
UN Committee of Experts on Environmental Accounting New York, June Peter Cosier Wentworth Group of Concerned Scientists.
 UN Cmmittee f Experts n Envirnmental Accunting New Yrk, June 2011 Peter Csier Wentwrth Grup f Cncerned Scientists Speaking Ntes Peter Csier: Directr f the Wentwrth Grup Cncerned Scientists based in Sydney,
UN Cmmittee f Experts n Envirnmental Accunting New Yrk, June 2011 Peter Csier Wentwrth Grup f Cncerned Scientists Speaking Ntes Peter Csier: Directr f the Wentwrth Grup Cncerned Scientists based in Sydney,
Fall 2013 Physics 172 Recitation 3 Momentum and Springs
 Fall 03 Physics 7 Recitatin 3 Mmentum and Springs Purpse: The purpse f this recitatin is t give yu experience wrking with mmentum and the mmentum update frmula. Readings: Chapter.3-.5 Learning Objectives:.3.
Fall 03 Physics 7 Recitatin 3 Mmentum and Springs Purpse: The purpse f this recitatin is t give yu experience wrking with mmentum and the mmentum update frmula. Readings: Chapter.3-.5 Learning Objectives:.3.
Department: MATHEMATICS
 Cde: MATH 022 Title: ALGEBRA SKILLS Institute: STEM Department: MATHEMATICS Curse Descriptin: This curse prvides students wh have cmpleted MATH 021 with the necessary skills and cncepts t cntinue the study
Cde: MATH 022 Title: ALGEBRA SKILLS Institute: STEM Department: MATHEMATICS Curse Descriptin: This curse prvides students wh have cmpleted MATH 021 with the necessary skills and cncepts t cntinue the study
Please Stop Laughing at Me and Pay it Forward Final Writing Assignment
 Kirk Please Stp Laughing at Me and Pay it Frward Final Writing Assignment Our fcus fr the past few mnths has been n bullying and hw we treat ther peple. We ve played sme games, read sme articles, read
Kirk Please Stp Laughing at Me and Pay it Frward Final Writing Assignment Our fcus fr the past few mnths has been n bullying and hw we treat ther peple. We ve played sme games, read sme articles, read
