Elliptic Curve Group Core Specification. Author: Homer Hsing
|
|
|
- Cecil Richard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Elliptic Curve Group Core Specification Author: Homer Hsing Rev. 0.1 March 4, 2012
2 This page has been intentionally left blank. Rev 0.1 ii
3 Revision History Rev. Date Author Description /19/2012 Homer Hsing First Draft 02/23/ /04/2012 Homer Hsing Homer Hsing 1. correct test bench name for adding two points 2. detailed explain to the speed of scalar multiplication New and new English name of the author Rev 0.1 iii
4 Contents INTRODUCTION...1 ARCHITECTURE...2 INTERFACE...3 TIMING DIAGRAMS...5 FPGA IMPLEMENTATION...7 TEST BENCH...8 REFERENCES Rev 0.1 iv
5 1 Introduction The Elliptic Curve Group core is for computing the addition of two elements in the elliptic curve group, and the addition of identical elements in the elliptic curve group. The elliptic curve is super-singular in affine coordinates defined over a Galois field ( ), whose irreducible polynomial is. The elliptic curve group is the set of solutions ( ) over ( ) to the equation of, together with an additional point at infinity, denoted. An element in the elliptic curve group is also called a point. The elliptic curve group is abelian. The group law is as follows. Suppose ( ) ( ) ( ). Then, ( ) ( ( )) ( ) ( ) ( ) In the following, will be also called the addition of (elliptic curve group element) and. Given a positive integer, let represent the addition of identical (elliptic curve group element), i.e. ( ). Computation of proceeds as follows. 1: 2: while do 3: if is odd then 4: 5: ( ) 6: 7: return For more information about the elliptic curve group, please refer to [1]. Rev of 9
6 2 Architecture The Elliptic Curve Group core consists of two modules, one computing the addition of two elliptic curve group elements ( ) and the other computing the addition of many identical elliptic curve group elements ( ). The first module is called point_add. The second module is called point_scalar_mult. The second module builds around the first module. The module computing c P The module computing the addition of two elliptic curve group elements Rev of 9
7 3 Interface The Elliptic Curve Group core implements the signals shown in the tables below. Two modules are separately listed. Input signals are synchronous and sampled at the rising edge of the clock. Output signals are driven by flip-flops, and not directly connected to input signals by combinational logic. For signals wider than 1 bit, the range is most significant bit down to least significant bit. Signal name Table 1: Interface signals of point_add Width In/Out Description clk 1 In clock reset 1 In active high synchronous reset x1 194 In one of input data y1 194 In one of input data zero1 1 In asserted if ( ) is the point at infinity x2 194 In one of input data y2 194 In one of input data zero2 1 In asserted if ( ) is the point at infinity done 1 Out The termination signal. It is inactive low after the reset signal asserted, and is active high only if the computation is done. When the computation is done ( ) ( ) ( ). x3 194 Out Output data. Its value is valid when the done signal is asserted. y3 194 Out Output data. Its value is valid when the done signal is asserted. zero3 1 Out Output data. It is active high only if ( ) is the point at infinity. Rev of 9
8 Signal name Table 2: Interface signals of point_scalar_mult Width In/Out Description clk 1 In clock reset 1 In active high synchronous reset x1 194 In one of input data y1 194 In one of input data zero1 1 In asserted if ( ) is the point at infinity c 151 In one of input data done 1 Out The termination signal. It is inactive low after the reset signal asserted, and is active high only if the computation is done. When the computation is done ( ) ( ). x3 194 Out Output data. Its value is valid when the done signal is asserted. y3 194 Out Output data. Its value is valid when the done signal is asserted. zero3 1 Out Output data. It is active high only if ( ) is the point at infinity. Rev of 9
9 4 Timing diagrams Input timing pattern Please follow the rule when using any module of the core: When the reset signal is asserted, valid input data should be on the input signals and keep valid until the computation termination. The input data is captured at the moment when the rising edge of the clk signal meets the high value of the reset signal as shown by the blue arrow in Figure 1. r clk x y z ro x y z ro Valid input data Valid input data Valid input data Valid input data Valid input data Valid input data Figure 1: Input timing pattern of the module point_add Rev of 9
10 Output timing pattern clk do x y z ro Valid output data Valid output data Valid output data Figure 2: Output timing pattern of the module point_add Rev of 9
11 5 FPGA Implementation The core has only been verified on a Xilinx Virtex 4 XC4VLX200-11FF1513 FPGA, synthesized with Xilinx ISE For this setup related configuration files is in the directory synthesis/xilinx. The code is vendor independent in Verilog Synthesis results of the module point_add: - Number of occupied slices: 6,694 (7%) - Number of 4 input LUTs: 12,099 (6%) - Number of flip-flops: 6,141 (3%) - Minimal period: ns - Max achievable frequency: 192 MHz The module computes in 2.7 microseconds if with a 100MHz clock. Synthesis results of the module point_scalar_mult: - Number of occupied slices: 7,272 (8%) - Number of 4 input LUTs: 13,780 (7%) - Number of flip-flops: 7,451 (4%) - Minimal period: ns - Max achievable frequency: 148 MHz The module computes in milliseconds if with a 100MHz clock. Here is the order of the generator of the elliptic curve group. Rev of 9
12 6 Test bench The file testbench/simulation.do is a batch file for ModelSim to compile the HDL files, setup the wave file, and begin function simulation. In order to make it work properly, the working directory of ModelSim must be the directory of testbench. The file testbench/test_point_scalar_mult.v is the main test bench for the Elliptic Curve Group core. The test bench is self-checked. It feeds input data to the core and compares the correct result with the output of the core. If the output is wrong, the test bench will display an error message. Passing the test bench means both point_add and point_scalar_mult modules work. The file testbench/test_point_add.v is for testing point_add module alone. Rev of 9
13 7 References [1] Paulo S.L.M. Barreto, H.Y. Kim, Ben Lynn, and Michael Scott. Efficient Algorithms for Pairing-Based Cryptosystems. Rev of 9
Tate Bilinear Pairing Core Specification. Author: Homer Hsing
 Tate Bilinear Pairing Core Specification Author: Homer Hsing homer.hsing@gmail.com Rev. 0.1 March 4, 2012 This page has been intentionally left blank. www.opencores.org Rev 0.1 ii Revision History Rev.
Tate Bilinear Pairing Core Specification Author: Homer Hsing homer.hsing@gmail.com Rev. 0.1 March 4, 2012 This page has been intentionally left blank. www.opencores.org Rev 0.1 ii Revision History Rev.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 17 - Sequential Circuits 3 (Counters)
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 17 - Sequential Circuits 3 (Counters) March 19&21, 2002 John Wawrzynek Spring 2002 EECS150 - Lec13-seq3 version 2 Page 1 Counters Special sequential circuits (FSMs) that
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 17 - Sequential Circuits 3 (Counters) March 19&21, 2002 John Wawrzynek Spring 2002 EECS150 - Lec13-seq3 version 2 Page 1 Counters Special sequential circuits (FSMs) that
Laboratory Exercise #8 Introduction to Sequential Logic
 Laboratory Exercise #8 Introduction to Sequential Logic ECEN 248: Introduction to Digital Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University 2 Laboratory Exercise #8 1 Introduction
Laboratory Exercise #8 Introduction to Sequential Logic ECEN 248: Introduction to Digital Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University 2 Laboratory Exercise #8 1 Introduction
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FSMs & Counters
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FSMs & Counters April 8, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec22-counters Page 1 One-hot encoding of states. One FF per state. State Encoding Why one-hot encoding?
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FSMs & Counters April 8, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec22-counters Page 1 One-hot encoding of states. One FF per state. State Encoding Why one-hot encoding?
Laboratory Exercise #11 A Simple Digital Combination Lock
 Laboratory Exercise #11 A Simple Digital Combination Lock ECEN 248: Introduction to Digital Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University 2 Laboratory Exercise #11 1 Introduction
Laboratory Exercise #11 A Simple Digital Combination Lock ECEN 248: Introduction to Digital Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University 2 Laboratory Exercise #11 1 Introduction
Parity Checker Example. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9 - Finite State Machines 1. Formal Design Process. Formal Design Process
 Parity Checker Example A string of bits has even parity if the number of 1 s in the string is even. Design a circuit that accepts a bit-serial stream of bits and outputs a 0 if the parity thus far is even
Parity Checker Example A string of bits has even parity if the number of 1 s in the string is even. Design a circuit that accepts a bit-serial stream of bits and outputs a 0 if the parity thus far is even
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 18 - Counters
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 18 - Counters October 24, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 - Lec18-counters Page 1 Counters Special sequential circuits (FSMs) that sequence though a set outputs.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 18 - Counters October 24, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 - Lec18-counters Page 1 Counters Special sequential circuits (FSMs) that sequence though a set outputs.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 18 - Counters
 EECS50 - Digital Design Lecture 8 - Counters October 24, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS50 - Lec8-counters Page Counters Special sequential circuits (FSMs) that sequence though a set outputs. Examples:
EECS50 - Digital Design Lecture 8 - Counters October 24, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS50 - Lec8-counters Page Counters Special sequential circuits (FSMs) that sequence though a set outputs. Examples:
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 11 - Shifters & Counters. Register Summary
 EECS50 - Digital Design Lecture - Shifters & Counters February 24, 2003 John Wawrzynek Spring 2005 EECS50 - Lec-counters Page Register Summary All registers (this semester) based on Flip-flops: q 3 q 2
EECS50 - Digital Design Lecture - Shifters & Counters February 24, 2003 John Wawrzynek Spring 2005 EECS50 - Lec-counters Page Register Summary All registers (this semester) based on Flip-flops: q 3 q 2
ECEN 651: Microprogrammed Control of Digital Systems Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University
 ECEN 651: Microprogrammed Control of Digital Systems Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Prof. Mi Lu TA: Ehsan Rohani Laboratory Exercise #2 Behavioral, Dataflow, and
ECEN 651: Microprogrammed Control of Digital Systems Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Prof. Mi Lu TA: Ehsan Rohani Laboratory Exercise #2 Behavioral, Dataflow, and
or 0101 Machine
 Synchronous State Graph or Synchronous State Graph or Detector Design a state graph for a machine with: One input X, one output Z. Z= after receiving the complete sequence or Overlapped sequences are detected.
Synchronous State Graph or Synchronous State Graph or Detector Design a state graph for a machine with: One input X, one output Z. Z= after receiving the complete sequence or Overlapped sequences are detected.
6 Synchronous State Machine Design
 Design of synchronous counters. Based on the description of the problem, determine the required number n of the FFs - the smallest value of n is such that the number of states N 2 n and the desired counting
Design of synchronous counters. Based on the description of the problem, determine the required number n of the FFs - the smallest value of n is such that the number of states N 2 n and the desired counting
A Novel Efficient Hardware Implementation of Elliptic Curve Cryptography Scalar Multiplication using Vedic Multiplier
 A Novel Efficient Hardware Implementation of Elliptic Curve Cryptography Scalar Multiplication using Vedic Multiplier Rakesh K. Kadu Department of Computer Technology YCCE, Nagpur, India rakeshkadu@gmail.com
A Novel Efficient Hardware Implementation of Elliptic Curve Cryptography Scalar Multiplication using Vedic Multiplier Rakesh K. Kadu Department of Computer Technology YCCE, Nagpur, India rakeshkadu@gmail.com
ABHELSINKI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
 On Repeated Squarings in Binary Fields Kimmo Järvinen Helsinki University of Technology August 14, 2009 K. Järvinen On Repeated Squarings in Binary Fields 1/1 Introduction Repeated squaring Repeated squaring:
On Repeated Squarings in Binary Fields Kimmo Järvinen Helsinki University of Technology August 14, 2009 K. Järvinen On Repeated Squarings in Binary Fields 1/1 Introduction Repeated squaring Repeated squaring:
Hardware Implementation of Elliptic Curve Point Multiplication over GF (2 m ) for ECC protocols
 Hardware Implementation of Elliptic Curve Point Multiplication over GF (2 m ) for ECC protocols Moncef Amara University of Paris 8 LAGA laboratory Saint-Denis / France Amar Siad University of Paris 8 LAGA
Hardware Implementation of Elliptic Curve Point Multiplication over GF (2 m ) for ECC protocols Moncef Amara University of Paris 8 LAGA laboratory Saint-Denis / France Amar Siad University of Paris 8 LAGA
EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. FSMs 9/11/2007
 EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
Introduction to the Xilinx Spartan-3E
 Introduction to the Xilinx Spartan-3E Nash Kaminski Instructor: Dr. Jafar Saniie ECE597 Illinois Institute of Technology Acknowledgment: I acknowledge that all of the work (including figures and code)
Introduction to the Xilinx Spartan-3E Nash Kaminski Instructor: Dr. Jafar Saniie ECE597 Illinois Institute of Technology Acknowledgment: I acknowledge that all of the work (including figures and code)
Example: vending machine
 Example: vending machine Release item after 15 cents are deposited Single coin slot for dimes, nickels o change Reset Coin Sensor Vending Machine FSM Open Release Mechanism Clock Spring 2005 CSE370 - guest
Example: vending machine Release item after 15 cents are deposited Single coin slot for dimes, nickels o change Reset Coin Sensor Vending Machine FSM Open Release Mechanism Clock Spring 2005 CSE370 - guest
Pipelined Viterbi Decoder Using FPGA
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 5(4): 1362-1372, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: July 05, 2012 Accepted: August
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 5(4): 1362-1372, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: July 05, 2012 Accepted: August
EGR224 F 18 Assignment #4
 EGR224 F 18 Assignment #4 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Due Date: Friday (Section 10), October 19, by 5 pm (slide it under
EGR224 F 18 Assignment #4 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Due Date: Friday (Section 10), October 19, by 5 pm (slide it under
Radiation Induced Multi bit Upsets in Xilinx SRAM Based FPGAs
 LA-UR-05-6725 Radiation Induced Multi bit Upsets in Xilinx SRAM Based FPGAs Heather Quinn, Paul Graham, Jim Krone, and Michael Caffrey Los Alamos National Laboratory Sana Rezgui and Carl Carmichael Xilinx
LA-UR-05-6725 Radiation Induced Multi bit Upsets in Xilinx SRAM Based FPGAs Heather Quinn, Paul Graham, Jim Krone, and Michael Caffrey Los Alamos National Laboratory Sana Rezgui and Carl Carmichael Xilinx
COVER SHEET: Problem#: Points
 EEL 4712 Midterm 3 Spring 2017 VERSION 1 Name: UFID: Sign here to give permission for your test to be returned in class, where others might see your score: IMPORTANT: Please be neat and write (or draw)
EEL 4712 Midterm 3 Spring 2017 VERSION 1 Name: UFID: Sign here to give permission for your test to be returned in class, where others might see your score: IMPORTANT: Please be neat and write (or draw)
Implementation Of Digital Fir Filter Using Improved Table Look Up Scheme For Residue Number System
 Implementation Of Digital Fir Filter Using Improved Table Look Up Scheme For Residue Number System G.Suresh, G.Indira Devi, P.Pavankumar Abstract The use of the improved table look up Residue Number System
Implementation Of Digital Fir Filter Using Improved Table Look Up Scheme For Residue Number System G.Suresh, G.Indira Devi, P.Pavankumar Abstract The use of the improved table look up Residue Number System
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs. Cross-coupled NOR gates
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs April 16, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-blocks Page 1 Cross-coupled NOR gates remember, If both R=0 & S=0, then
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs April 16, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-blocks Page 1 Cross-coupled NOR gates remember, If both R=0 & S=0, then
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 25 Shifters and Counters. Recap
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 25 Shifters and Counters Nov. 21, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 25 Shifters and Counters Nov. 21, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 21 - Design Blocks
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 21 - Design Blocks April 3, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec21-db3 Page 1 Fixed Shifters / Rotators fixed shifters hardwire the shift amount into the circuit.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 21 - Design Blocks April 3, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec21-db3 Page 1 Fixed Shifters / Rotators fixed shifters hardwire the shift amount into the circuit.
Chapter 6. Synchronous Sequential Circuits
 Chapter 6 Synchronous Sequential Circuits In a combinational circuit, the values of the outputs are determined solely by the present values of its inputs. In a sequential circuit, the values of the outputs
Chapter 6 Synchronous Sequential Circuits In a combinational circuit, the values of the outputs are determined solely by the present values of its inputs. In a sequential circuit, the values of the outputs
Chapter 7 Sequential Logic
 Chapter 7 Sequential Logic SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} March 28, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Intro 2 Bistable Circuits 3 FF Characteristics
Chapter 7 Sequential Logic SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} March 28, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Intro 2 Bistable Circuits 3 FF Characteristics
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 16 Counters. Announcements
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 16 Counters October 20, 2011 Elad Alon Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs150 Fall 2011
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 16 Counters October 20, 2011 Elad Alon Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs150 Fall 2011
Appendix B. Review of Digital Logic. Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs
 Appendix B Review of Digital Logic Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Elect. & Comp. Eng. 2 DeMorgan Symbols NAND (A.B) = A +B NOR (A+B) = A.B AND A.B = A.B = (A +B ) OR
Appendix B Review of Digital Logic Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Elect. & Comp. Eng. 2 DeMorgan Symbols NAND (A.B) = A +B NOR (A+B) = A.B AND A.B = A.B = (A +B ) OR
EECS 579: Logic and Fault Simulation. Simulation
 EECS 579: Logic and Fault Simulation Simulation: Use of computer software models to verify correctness Fault Simulation: Use of simulation for fault analysis and ATPG Circuit description Input data for
EECS 579: Logic and Fault Simulation Simulation: Use of computer software models to verify correctness Fault Simulation: Use of simulation for fault analysis and ATPG Circuit description Input data for
FPGA Resource Utilization Estimates for NI crio LabVIEW FPGA Version: 8.6 NI-RIO Version: 3.0 Date: 8/5/2008
 FPGA Resource Utilization Estimates for NI crio-9104 LabVIEW FPGA Version: 8.6 NI-RIO Version: 3.0 Date: 8/5/2008 Note: The numbers presented in this document are estimates. Actual resource usage for your
FPGA Resource Utilization Estimates for NI crio-9104 LabVIEW FPGA Version: 8.6 NI-RIO Version: 3.0 Date: 8/5/2008 Note: The numbers presented in this document are estimates. Actual resource usage for your
Arithmetic Operators for Pairing-Based Cryptography
 Arithmetic Operators for Pairing-Based Cryptography J.-L. Beuchat 1 N. Brisebarre 2 J. Detrey 3 E. Okamoto 1 1 University of Tsukuba, Japan 2 École Normale Supérieure de Lyon, France 3 Cosec, b-it, Bonn,
Arithmetic Operators for Pairing-Based Cryptography J.-L. Beuchat 1 N. Brisebarre 2 J. Detrey 3 E. Okamoto 1 1 University of Tsukuba, Japan 2 École Normale Supérieure de Lyon, France 3 Cosec, b-it, Bonn,
Reduced-Area Constant-Coefficient and Multiple-Constant Multipliers for Xilinx FPGAs with 6-Input LUTs
 Article Reduced-Area Constant-Coefficient and Multiple-Constant Multipliers for Xilinx FPGAs with 6-Input LUTs E. George Walters III Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Penn State Erie,
Article Reduced-Area Constant-Coefficient and Multiple-Constant Multipliers for Xilinx FPGAs with 6-Input LUTs E. George Walters III Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Penn State Erie,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Introductory Digital Systems Lab (6.111) Quiz #1 - Spring 2003 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan and Prof. Don
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Introductory Digital Systems Lab (6.111) Quiz #1 - Spring 2003 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan and Prof. Don
Lab #10: Design of Finite State Machines
 Lab #10: Design of Finite State Machines ECE/COE 0501 Date of Experiment: 3/1/2017 Report Written: 3/4/2017 Submission Date: 3/15/2017 Nicholas Haver nicholas.haver@pitt.edu 1 H a v e r PURPOSE The purpose
Lab #10: Design of Finite State Machines ECE/COE 0501 Date of Experiment: 3/1/2017 Report Written: 3/4/2017 Submission Date: 3/15/2017 Nicholas Haver nicholas.haver@pitt.edu 1 H a v e r PURPOSE The purpose
FPGA accelerated multipliers over binary composite fields constructed via low hamming weight irreducible polynomials
 FPGA accelerated multipliers over binary composite fields constructed via low hamming weight irreducible polynomials C. Shu, S. Kwon and K. Gaj Abstract: The efficient design of digit-serial multipliers
FPGA accelerated multipliers over binary composite fields constructed via low hamming weight irreducible polynomials C. Shu, S. Kwon and K. Gaj Abstract: The efficient design of digit-serial multipliers
Design and FPGA Implementation of Radix-10 Algorithm for Division with Limited Precision Primitives
 Design and FPGA Implementation of Radix-10 Algorithm for Division with Limited Precision Primitives Miloš D. Ercegovac Computer Science Department Univ. of California at Los Angeles California Robert McIlhenny
Design and FPGA Implementation of Radix-10 Algorithm for Division with Limited Precision Primitives Miloš D. Ercegovac Computer Science Department Univ. of California at Los Angeles California Robert McIlhenny
Product Obsolete/Under Obsolescence. Quantization. Author: Latha Pillai
 Application Note: Virtex and Virtex-II Series XAPP615 (v1.1) June 25, 2003 R Quantization Author: Latha Pillai Summary This application note describes a reference design to do a quantization and inverse
Application Note: Virtex and Virtex-II Series XAPP615 (v1.1) June 25, 2003 R Quantization Author: Latha Pillai Summary This application note describes a reference design to do a quantization and inverse
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
CSE 140 Midterm 2 Tajana Simunic Rosing. Spring 2008
 CSE 14 Midterm 2 Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 28 Do not start the exam until you are told to. Turn off any cell phones or pagers. Write your name and PID at the top of every page. Do not separate the pages.
CSE 14 Midterm 2 Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 28 Do not start the exam until you are told to. Turn off any cell phones or pagers. Write your name and PID at the top of every page. Do not separate the pages.
High Speed Cryptoprocessor for η T Pairing on 128-bit Secure Supersingular Elliptic Curves over Characteristic Two Fields
 High Speed Cryptoprocessor for η T Pairing on 128-bit Secure Supersingular Elliptic Curves over Characteristic Two Fields Santosh Ghosh, Dipanwita Roychowdhury, and Abhijit Das Computer Science and Engineering
High Speed Cryptoprocessor for η T Pairing on 128-bit Secure Supersingular Elliptic Curves over Characteristic Two Fields Santosh Ghosh, Dipanwita Roychowdhury, and Abhijit Das Computer Science and Engineering
High Speed Cryptoprocessor for η T Pairing on 128-bit Secure Supersingular Elliptic Curves over Characteristic Two Fields
 High Speed Cryptoprocessor for η T Pairing on 128-bit Secure Supersingular Elliptic Curves over Characteristic Two Fields Santosh Ghosh, Dipanwita Roy Chowdhury, and Abhijit Das Computer Science and Engineering
High Speed Cryptoprocessor for η T Pairing on 128-bit Secure Supersingular Elliptic Curves over Characteristic Two Fields Santosh Ghosh, Dipanwita Roy Chowdhury, and Abhijit Das Computer Science and Engineering
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER /2017
 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
FPGA Resource Utilization Estimates for NI PXI-7854R. LabVIEW FPGA Version: 8.6 NI-RIO Version: 3.0 Date: 8/5/2008
 FPGA Resource Utilization Estimates for NI PXI-7854R LabVIEW FPGA Version: 8.6 NI-RIO Version: 3.0 Date: 8/5/2008 Note: The numbers presented in this document are estimates. Actual resource usage for your
FPGA Resource Utilization Estimates for NI PXI-7854R LabVIEW FPGA Version: 8.6 NI-RIO Version: 3.0 Date: 8/5/2008 Note: The numbers presented in this document are estimates. Actual resource usage for your
FSM Examples. Young Won Lim 11/6/15
 /6/5 Copyright (c) 2 25 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version.2 or any later version published
/6/5 Copyright (c) 2 25 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version.2 or any later version published
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 22 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 1
 EECS150 - igital esign Lecture 22 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 1 April 10, 2011 John Wawrzynek Spring 2011 EECS150 - Lec23-arith1 Page 1 Each cell: r i = a i XOR b i XOR c in Carry-ripple Adder Revisited
EECS150 - igital esign Lecture 22 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 1 April 10, 2011 John Wawrzynek Spring 2011 EECS150 - Lec23-arith1 Page 1 Each cell: r i = a i XOR b i XOR c in Carry-ripple Adder Revisited
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 15 SIFT2 + FSM. Recap and Outline
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 15 SIFT2 + FSM Oct. 15, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John Wawrzynek)
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 15 SIFT2 + FSM Oct. 15, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John Wawrzynek)
CSC 322: Computer Organization Lab
 CSC 322: Computer Organization Lab Lecture 3: Logic Design Dr. Haidar M. Harmanani CSC 322: Computer Organization Lab Part I: Combinational Logic Dr. Haidar M. Harmanani Logical Design of Digital Systems
CSC 322: Computer Organization Lab Lecture 3: Logic Design Dr. Haidar M. Harmanani CSC 322: Computer Organization Lab Part I: Combinational Logic Dr. Haidar M. Harmanani Logical Design of Digital Systems
Review: Designing with FSM. EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lec 09 Counters Outline.
 Review: esigning with FSM EECS 150 - Components and esign Techniques for igital Systems Lec 09 Counters 9-28-0 avid Culler Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley
Review: esigning with FSM EECS 150 - Components and esign Techniques for igital Systems Lec 09 Counters 9-28-0 avid Culler Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department
 King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page 1 of 13 COE 202: Digital Logic Design (3-0-3) Term 112 (Spring 2012) Final
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page 1 of 13 COE 202: Digital Logic Design (3-0-3) Term 112 (Spring 2012) Final
Design and Study of Enhanced Parallel FIR Filter Using Various Adders for 16 Bit Length
 International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) Design and Study of Enhanced Parallel FIR Filter Using Various Adders for 16 Bit Length D.Ashok Kumar, P.Samundiswary Abstract Now a day
International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) Design and Study of Enhanced Parallel FIR Filter Using Various Adders for 16 Bit Length D.Ashok Kumar, P.Samundiswary Abstract Now a day
Digital Control of Electric Drives
 Digital Control of Electric Drives Logic Circuits - equential Description Form, Finite tate Machine (FM) Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Ver.. J. Zdenek 27 Logic
Digital Control of Electric Drives Logic Circuits - equential Description Form, Finite tate Machine (FM) Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Ver.. J. Zdenek 27 Logic
10/12/2016. An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State. ECE 120: Introduction to Computing. Eventually, the States Form a Loop
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
FPGA-Based Elliptic Curve Cryptography for RFID Tag Using Verilog
 Journal From the SelectedWorks of Journal 2016 FPGA-Based Elliptic Curve Cryptography for RFID Tag Using Verilog M. Neelappa Dr. N. G. Kurahatti This work is licensed under a Creative Commons CC_BY-NC
Journal From the SelectedWorks of Journal 2016 FPGA-Based Elliptic Curve Cryptography for RFID Tag Using Verilog M. Neelappa Dr. N. G. Kurahatti This work is licensed under a Creative Commons CC_BY-NC
2. Accelerated Computations
 2. Accelerated Computations 2.1. Bent Function Enumeration by a Circular Pipeline Implemented on an FPGA Stuart W. Schneider Jon T. Butler 2.1.1. Background A naive approach to encoding a plaintext message
2. Accelerated Computations 2.1. Bent Function Enumeration by a Circular Pipeline Implemented on an FPGA Stuart W. Schneider Jon T. Butler 2.1.1. Background A naive approach to encoding a plaintext message
SFI Channel SDR Interface with Bus Alignment Author: Greg Burton
 Application Note: Virtex-5 FPGAs XAPP856 (v1.2) May 19, 2007 SFI-4.1 16-Channel SD Interface with Bus Alignment Author: Greg Burton Summary This application note describes an SFI-4.1 interface, a 16-channel,
Application Note: Virtex-5 FPGAs XAPP856 (v1.2) May 19, 2007 SFI-4.1 16-Channel SD Interface with Bus Alignment Author: Greg Burton Summary This application note describes an SFI-4.1 interface, a 16-channel,
International Journal of Advanced Computer Technology (IJACT)
 AN EFFICIENT DESIGN OF LOW POWER,FAST EL- LIPTIC CURVE SCALAR MULTIPLIER IN ECC USING S Jayalakshmi K R, M.Tech student, Mangalam college of engineering,kottayam,india; Ms.Hima Sara Jacob, Assistant professor,
AN EFFICIENT DESIGN OF LOW POWER,FAST EL- LIPTIC CURVE SCALAR MULTIPLIER IN ECC USING S Jayalakshmi K R, M.Tech student, Mangalam college of engineering,kottayam,india; Ms.Hima Sara Jacob, Assistant professor,
Simulation of Logic Primitives and Dynamic D-latch with Verilog-XL
 Simulation of Logic Primitives and Dynamic D-latch with Verilog-XL November 30, 2011 Robert D Angelo Tufts University Electrical and Computer Engineering EE-103 Lab 3: Part I&II Professor: Dr. Valencia
Simulation of Logic Primitives and Dynamic D-latch with Verilog-XL November 30, 2011 Robert D Angelo Tufts University Electrical and Computer Engineering EE-103 Lab 3: Part I&II Professor: Dr. Valencia
Fundamentals of Computer Systems
 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Sequential Logic Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Summer 2017 State-Holding Elements Bistable Elements S Latch Latch Positive-Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop Flip-Flop with
Fundamentals of Computer Systems Sequential Logic Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Summer 2017 State-Holding Elements Bistable Elements S Latch Latch Positive-Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop Flip-Flop with
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits
 Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Readings : Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential circuits Introduction to the concept of the
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Readings : Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential circuits Introduction to the concept of the
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD = B
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD = B Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD = B](/thumbs/84/91058397.jpg) . (a). (b). (c) S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] igital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC = B LHS = ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC But ( ) = = ABC( ) ABC( ) ABC( ) ABC( )
. (a). (b). (c) S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] igital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC = B LHS = ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC But ( ) = = ABC( ) ABC( ) ABC( ) ABC( )
FPGA-based Niederreiter Cryptosystem using Binary Goppa Codes
 FPGA-based Niederreiter Cryptosystem using Binary Goppa Codes Wen Wang 1, Jakub Szefer 1, and Ruben Niederhagen 2 1. Yale University, USA 2. Fraunhofer Institute SIT, Germany April 9, 2018 PQCrypto 2018
FPGA-based Niederreiter Cryptosystem using Binary Goppa Codes Wen Wang 1, Jakub Szefer 1, and Ruben Niederhagen 2 1. Yale University, USA 2. Fraunhofer Institute SIT, Germany April 9, 2018 PQCrypto 2018
Fast FPGA Placement Based on Quantum Model
 Fast FPGA Placement Based on Quantum Model Lingli Wang School of Microelectronics Fudan University, Shanghai, China Email: llwang@fudan.edu.cn 1 Outline Background & Motivation VPR placement Quantum Model
Fast FPGA Placement Based on Quantum Model Lingli Wang School of Microelectronics Fudan University, Shanghai, China Email: llwang@fudan.edu.cn 1 Outline Background & Motivation VPR placement Quantum Model
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 DEPARTMENT: EEE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE: EE55 SEMESTER IV UNIT : Design of Synchronous Sequential Circuits PART
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 DEPARTMENT: EEE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE: EE55 SEMESTER IV UNIT : Design of Synchronous Sequential Circuits PART
Sequential Circuit Analysis
 Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Laboratory Exercise #10 An Introduction to High-Speed Addition
 Laboratory Exercise #10 An Introduction to High-Speed Addition ECEN 248: Introduction to Digital Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University 2 Laboratory Exercise #10
Laboratory Exercise #10 An Introduction to High-Speed Addition ECEN 248: Introduction to Digital Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University 2 Laboratory Exercise #10
Roger L. Tokheim. Chapter 8 Counters Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
 Digital Electronics Principles & Applications Sixth Edition Roger L. Tokheim Chapter 8 Counters 2003 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill INTRODUCTION Overview of Counters Characteristics of Counters Ripple Up Counter
Digital Electronics Principles & Applications Sixth Edition Roger L. Tokheim Chapter 8 Counters 2003 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill INTRODUCTION Overview of Counters Characteristics of Counters Ripple Up Counter
CSE 320: Spartan3 I/O Peripheral Testing
 CSE 320: Spartan3 I/O Peripheral Testing Ujjwal Gupta, Kyle Gilsdorf Arizona State University Version 1.1 October 2, 2012 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Test code description and procedure 2 2.1 Modes...............................
CSE 320: Spartan3 I/O Peripheral Testing Ujjwal Gupta, Kyle Gilsdorf Arizona State University Version 1.1 October 2, 2012 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Test code description and procedure 2 2.1 Modes...............................
Enumeration of Bent Boolean Functions by Reconfigurable Computer
 Enumeration of Bent Boolean Functions by Reconfigurable Computer J. L. Shafer S. W. Schneider J. T. Butler P. Stănică ECE Department Department of ECE Department of Applied Math. US Naval Academy Naval
Enumeration of Bent Boolean Functions by Reconfigurable Computer J. L. Shafer S. W. Schneider J. T. Butler P. Stănică ECE Department Department of ECE Department of Applied Math. US Naval Academy Naval
Different encodings generate different circuits
 FSM State Encoding Different encodings generate different circuits no easy way to find best encoding with fewest logic gates or shortest propagation delay. Binary encoding: K states need log 2 K bits i.e.,
FSM State Encoding Different encodings generate different circuits no easy way to find best encoding with fewest logic gates or shortest propagation delay. Binary encoding: K states need log 2 K bits i.e.,
DM74LS74A Dual Positive-Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flops with Preset, Clear and Complementary Outputs
 DM74LS74A Dual Positive-Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flops with Preset, Clear and Complementary Outputs General Description This device contains two independent positive-edge-triggered D flip-flops with complementary
DM74LS74A Dual Positive-Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flops with Preset, Clear and Complementary Outputs General Description This device contains two independent positive-edge-triggered D flip-flops with complementary
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
CHW 261: Logic Design
 CHW 26: Logic Design Instructors: Prof. Hala Zayed Dr. Ahmed Shalaby http://www.bu.edu.eg/staff/halazayed4 http://bu.edu.eg/staff/ahmedshalaby4# Slide Digital Fundamentals CHAPTER 8 Counters Slide 2 Counting
CHW 26: Logic Design Instructors: Prof. Hala Zayed Dr. Ahmed Shalaby http://www.bu.edu.eg/staff/halazayed4 http://bu.edu.eg/staff/ahmedshalaby4# Slide Digital Fundamentals CHAPTER 8 Counters Slide 2 Counting
ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals. Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals
 University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall 2001 Lecture 5 Registers & Counters Part 2 Charles Kime Counters Counters are sequential circuits
University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall 2001 Lecture 5 Registers & Counters Part 2 Charles Kime Counters Counters are sequential circuits
Design of Datapath Controllers
 Design of Datapath Controllers Speaker: 俞子豪 Adviser: Prof. An-Yeu Wu ACCESS IC LAB Outline vsequential Circuit Model vfinite State Machines vuseful Modeling Techniques P. 2 Model of Sequential Circuits
Design of Datapath Controllers Speaker: 俞子豪 Adviser: Prof. An-Yeu Wu ACCESS IC LAB Outline vsequential Circuit Model vfinite State Machines vuseful Modeling Techniques P. 2 Model of Sequential Circuits
Digital Circuits ECS 371
 Digital Circuits ECS 371 Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Lecture 18 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Monday 9:00-10:30, 1:30-3:30 Tuesday 10:30-11:30 1 Announcement Reading Assignment: Chapter 7: 7-1,
Digital Circuits ECS 371 Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Lecture 18 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Monday 9:00-10:30, 1:30-3:30 Tuesday 10:30-11:30 1 Announcement Reading Assignment: Chapter 7: 7-1,
Digital Fundamentals
 Digital Fundamentals Tenth Edition Floyd Chapter 9 Sections 9-1 thru 9-5 2009 Pearson Education, Upper 2008 Pearson Saddle River, Education NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved ET285 Agenda Week 2 Quiz 0: Covered
Digital Fundamentals Tenth Edition Floyd Chapter 9 Sections 9-1 thru 9-5 2009 Pearson Education, Upper 2008 Pearson Saddle River, Education NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved ET285 Agenda Week 2 Quiz 0: Covered
An Optimized Hardware Architecture of Montgomery Multiplication Algorithm
 An Optimized Hardware Architecture of Montgomery Multiplication Algorithm Miaoqing Huang 1, Kris Gaj 2, Soonhak Kwon 3, and Tarek El-Ghazawi 1 1 The George Washington University, Washington, DC 20052,
An Optimized Hardware Architecture of Montgomery Multiplication Algorithm Miaoqing Huang 1, Kris Gaj 2, Soonhak Kwon 3, and Tarek El-Ghazawi 1 1 The George Washington University, Washington, DC 20052,
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
Review: Designing with FSM. EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lec09 Counters Outline.
 Review: Designing with FSM EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lec09 Counters 9-28-04 David Culler Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley
Review: Designing with FSM EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lec09 Counters 9-28-04 David Culler Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley
Problem Set 9 Solutions
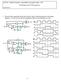 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
Efficient Hardware Calculation of Inverses in GF (2 8 )
 Efficient Hardware Calculation of Inverses in GF (2 8 ) R. W. Ward, Dr. T. C. A. Molteno 1 Physics Department University of Otago Box 56, Dunedin, New Zealand 1 Email: tim@physics.otago.ac.nz Abstract:
Efficient Hardware Calculation of Inverses in GF (2 8 ) R. W. Ward, Dr. T. C. A. Molteno 1 Physics Department University of Otago Box 56, Dunedin, New Zealand 1 Email: tim@physics.otago.ac.nz Abstract:
Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop
 EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
Lessons Learned from High-Speed Implementa6on and Benchmarking of Two Post-Quantum Public-Key Cryptosystems
 Lessons Learned from High-Speed Implementa6on and Benchmarking of Two Post-Quantum Public-Key Cryptosystems Malik Umar Sharif, Ahmed Ferozpuri, and Kris Gaj George Mason University USA Partially supported
Lessons Learned from High-Speed Implementa6on and Benchmarking of Two Post-Quantum Public-Key Cryptosystems Malik Umar Sharif, Ahmed Ferozpuri, and Kris Gaj George Mason University USA Partially supported
Review Problem 1. should be on. door state, false if light should be on when a door is open. v Describe when the dome/interior light of the car
 Review Problem 1 v Describe when the dome/interior light of the car should be on. v DriverDoorOpen = true if lefthand door open v PassDoorOpen = true if righthand door open v LightSwitch = true if light
Review Problem 1 v Describe when the dome/interior light of the car should be on. v DriverDoorOpen = true if lefthand door open v PassDoorOpen = true if righthand door open v LightSwitch = true if light
Digital Design. Sequential Logic
 Principles Of igital esign Chapter 6 Sequential Logic Chapter preview Boolean algebra 3 Logic gates and flip-flops 3 Finite-state machine 6 Logic design techniques 4 Sequential design techniques 6 Binary
Principles Of igital esign Chapter 6 Sequential Logic Chapter preview Boolean algebra 3 Logic gates and flip-flops 3 Finite-state machine 6 Logic design techniques 4 Sequential design techniques 6 Binary
Constrained Clock Shifting for Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Constrained Clock Shifting for Field Programmable Gate Arrays Deshanand P. Singh Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Toronto, Canada singhd@eecg.toronto.edu Stephen D. Brown
Constrained Clock Shifting for Field Programmable Gate Arrays Deshanand P. Singh Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Toronto, Canada singhd@eecg.toronto.edu Stephen D. Brown
Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis
 Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis Given the circuit diagram of a state machine: Analyze the combinational logic to determine flip-flop input (excitation) equations: D i = F i (Q, inputs) The input
Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis Given the circuit diagram of a state machine: Analyze the combinational logic to determine flip-flop input (excitation) equations: D i = F i (Q, inputs) The input
Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Side Channel Analysis and Protection for McEliece Implementations
 Side Channel Analysis and Protection for McEliece Implementations Thomas Eisenbarth Joint work with Cong Chen, Ingo von Maurich and Rainer Steinwandt 9/27/2016 NATO Workshop- Tel Aviv University Overview
Side Channel Analysis and Protection for McEliece Implementations Thomas Eisenbarth Joint work with Cong Chen, Ingo von Maurich and Rainer Steinwandt 9/27/2016 NATO Workshop- Tel Aviv University Overview
Design and Implementation of High Speed CRC Generators
 Department of ECE, Adhiyamaan College of Engineering, Hosur, Tamilnadu, India Design and Implementation of High Speed CRC Generators ChidambarakumarS 1, Thaky Ahmed 2, UbaidullahMM 3, VenketeshK 4, JSubhash
Department of ECE, Adhiyamaan College of Engineering, Hosur, Tamilnadu, India Design and Implementation of High Speed CRC Generators ChidambarakumarS 1, Thaky Ahmed 2, UbaidullahMM 3, VenketeshK 4, JSubhash
Sequential Logic Worksheet
 Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops
 Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops Flops Lesson 4 JK Flip Flop Ch14L4-"Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 JK Flip-Flop ve edge triggered Output Q and
Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops Flops Lesson 4 JK Flip Flop Ch14L4-"Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 JK Flip-Flop ve edge triggered Output Q and
Sequential Synchronous Circuit Analysis
 Sequential Synchronous Circuit Analysis General Model Current State at time (t) is stored in an array of flip-flops. Next State at time (t+1) is a Boolean function of State and Inputs. Outputs at time
Sequential Synchronous Circuit Analysis General Model Current State at time (t) is stored in an array of flip-flops. Next State at time (t+1) is a Boolean function of State and Inputs. Outputs at time
ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter. Lab 3. Lab 3 Gate Timing. Lab 3 Steps in designing a State Machine. Timing diagram of a DFF
 ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter Timing diagram of a DFF Lab 3 Gate Timing difference timing for difference kind of gate, cost dependence (1) Setup Time = t2-t1 (2) Propagation
ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter Timing diagram of a DFF Lab 3 Gate Timing difference timing for difference kind of gate, cost dependence (1) Setup Time = t2-t1 (2) Propagation
Lecture #4: Potpourri
 Lecture #4: Potpourri Paul Hartke Phartke@stanford.edu Stanford EE183 April 15, 2002 Tutorial/Verilog Questions? Tutorial is mostly done, right? Due tonight at Midnight (Mon 4/14/02) Turn in copies of
Lecture #4: Potpourri Paul Hartke Phartke@stanford.edu Stanford EE183 April 15, 2002 Tutorial/Verilog Questions? Tutorial is mostly done, right? Due tonight at Midnight (Mon 4/14/02) Turn in copies of
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 4. Dr. Ahmad Almulhem ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: Office:
 COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 4 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives Registers Counters Registers 0 1 n-1 A register is a group
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 4 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives Registers Counters Registers 0 1 n-1 A register is a group
DM7473 Dual Master-Slave J-K Flip-Flops with Clear and Complementary Outputs
 DM7473 Dual Master-Slave J-K Flip-Flops with Clear and Complementary Outputs General Description This device contains two independent positive pulse triggered J-K flip-flops with complementary outputs.
DM7473 Dual Master-Slave J-K Flip-Flops with Clear and Complementary Outputs General Description This device contains two independent positive pulse triggered J-K flip-flops with complementary outputs.
Hardware testing and design for testability. EE 3610 Digital Systems
 EE 3610: Digital Systems 1 Hardware testing and design for testability Introduction A Digital System requires testing before and after it is manufactured 2 Level 1: behavioral modeling and test benches
EE 3610: Digital Systems 1 Hardware testing and design for testability Introduction A Digital System requires testing before and after it is manufactured 2 Level 1: behavioral modeling and test benches
