Supplementary Fig. 1. Locations of thinning transects and photos of example samples. Mt Suess/Gondola Ridge transects extended metres above
|
|
|
- Loraine Smith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Fig. 1. Locations of thinning transects and photos of example samples. Mt Suess/Gondola Ridge transects extended metres above the modern surface of Mackay Glacier, and included 16 (upper), 12 (mid-lower) and 6 (lower) sampled erratics. At Low Ridge, 10 samples were collected with an elevation range of m above the ice surface.
2 Supplementary Fig. 2. Thinning of Mackay Glacier shown for the 3 most coherent transects ((a) Mt Suess/Gondola Ridge upper, with (b) as an inset of (a); (c) Gondola Ridge lower; (d) Low Ridge). Displayed are Bayesian age-elevation modelled ages (1 σ), linearly interpolated between sample elevations (1 and 2 σ). The ages were initially calculated with both the global production rate 9 (purple) and New Zealand calibration site production rate 10 (orange), which can be considered as probable minimum and maximum estimations of the absolute ages. Vertical grey bars denote minimum age markers of grounded ice retreat north of Ross Island (RI), in McMurdo Sound (MS) and of ice shelf removal in Granite Harbour (GH).
3 Supplementary Fig. 3. Estimated thinning rates of Mackay Glacier at Mt Suess/Gondola Ridge (upper) and Low Ridge. Left panels show exposure ages (2 σ) and modelled thinning profiles generated from Monte Carlo regression analysis for each transect respectively. Right panels show the corresponding thinning rate probability distributions. Thinning at Mt Suess/Gondola Ridge (upper) was estimated using Bayesian age-modelled ages and uncertainties, while at Low Ridge raw ages were alternatively used in regression analysis.
4 Supplementary Fig. 4. Staggered grounding line retreat and reverse bed slope of Mackay Glacier offshore trough. GeoMapApp multi-resolution bathymetry (a) reveals lineations and grounding-zone wedges (GZW) mapped in (b) 11. High resolution multibeam tracks and the flowline (1 km horizontal resolution) used in model experiments are also shown. (c) Longitudinal profile of Mackay Glacier trough from high resolution bathymetry data, with GZWs indicating staggered retreat upstream of the overdeepening. Bed elevation beneath the tongue was obtained from geophysical surveys 12, and the ice surface comes from airborne radar (ICECAP).
5 Supplementary Fig. 5. Model experiments of grounding line retreat and surface thinning at our transects. (a) Retreat driven by enhanced relative sea level. The pattern of surface lowering at Mt Suess/Gondola Ridge (upper) (GRU) and Low Ridge (LR), of gradual and then accelerated thinning, is largely consistent with that of enhanced ocean temperature (Fig. 4). (b) Simulated retreat over an imposed horizontal bed, with an evolving surface profile as in Fig. 4, shown for a C ocean temperature forcing scenario. Retreat lasts for ~800 years and surface lowering responds linearly. Retreat accelerates slightly towards the modern configuration, which is probably the result of a steepening surface slope and minor increases in ice flux as the grounding line approaches the high-relief Transantarctic Mountains portion. These experiments indicate that the rapid thinning recorded in our transects can be explained by a primary topographic control, largely irrespective of any single environmental forcing.
6 Location Dating Context Timing Corr. 14 C yr (2 σ) Cal. yr (2 σ) Study North of Ross Island Retreat of grounded ice 8861 ± Explorers Cove Presence of grounded ice 8340 ± Scott Coast, McMurdo Sound (multiple sites) Final unloading of grounded ice Cape Bird Retreat of grounded ice 6530 ± Marble Point Ice shelf free 5480 ± Explorers Cove Retreat of grounded ice 5370 ± Granite Harbour Ice shelf free 5480 ± Gneiss Point Ice shelf free 5220 ± Cape Bernacchi Ice shelf free 4300 ± , ,5 2,5 Corrected (corr.) 14 C ages are derived from the original study and a recent review of regional deglaciation 7. Calibrated (cal.) age ranges use the Marine09 calibration curve. A core sample that dates open water conditions and, by implication, minimum age of grounded ice retreat is marked with. One age was derived from a relative sea level curve comprising multiple samples, therefore no uncertainty is attached ( ); for calibration, we used an uncertainty of 50 years. Supplementary Table 1. Deglaciation recorded in the vicinity of Mackay Glacier.
7 Parameter Value Modern Advanced Unit Flow enhancement factor Sliding rate factor (TAM) 5 x x 10-8 Pa m 2 a -1 Sliding rate factor (Marine) 2 x x 10-5 Pa m 2 a -1 Glen s flow law exponent Sliding exponent Geothermal heat flux mw m -2 Horizontal domain resolution m Valley width m Precipitation at sea level m a -1 Precipitation lapse rate m a -1 km -1 Mean annual temp. at sea level C Temperature lapse rate -9-9 K km -1 Annual temperature range C Ocean temperature (winter) C Ocean temperature (summer) C Calving rate coefficient Relative sea level 0 0 m Degree-day factor mm K -1 d -1 Modern climate parameters were obtained from National Soil Survey Centre / Landcare Research (marked with ). Less certain parameters were tuned to simulate the desired glacier profile ( ). Reduced precipitation is assumed for the advanced profile based on ice core interpretation 8. Sliding rate factors are stated for the Transantarctic Mountains (TAM) and marine portions. Supplementary Table 2. Flowline model parameters.
8 Supplementary Note 1 Multiple onshore and offshore records constrain the timing and extent of past ice retreat in the western Ross Sea (Supplementary Table 1). For comparison between this regional evidence and our new glacier thinning transects, all 14 C dates have been corrected for marine reservoir effects and calibrated using the marine calibration curve (Marine09) as recommended by their original sources and a recent review of regional deglaciation 7. Moreover, dates obtained from offshore cores were only included if they showed linear sedimentation rates and consistent 13 C values through the core 6. Immediately north of Ross Island, a minimum age for grounding line and ice shelf retreat is recorded at 10,185 10,005 calibrated years BP, based on its core-top reservoir correction of 2,470 years 1. However, deglaciation may have occurred slightly earlier in this location if a smaller, regional, reservoir correction (e.g. 1,200 1,300 years) is used instead. Local evidence of Mackay Glacier retreat is also apparent offshore as a series of grounding-zone wedges (GZWs) preserved in the outer part of the trough (Supplementary Fig. 4). These suggest that the initial retreat of the grounding line was most likely staggered. Although we do not have data to constrain the timing and duration of these stillstands, studies of similar-sized GZWs in West Antarctica indicate that they typically form within ~120 years if the sediment flux is sufficiently high 13.
9 Supplementary References 1 McKay, R. et al. Retreat history of the Ross Ice Sheet (Shelf) since the Last Glacial Maximum from deepbasin sediment cores around Ross Island. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 260, (2008). 2 Hall, B. L. & Denton, G. H. Extent and chronology of the Ross Sea ice sheet and the Wilson Piedmont Glacier along the Scott Coast at and since the last glacial maximum. Geografiska Annaler: Series A, Physical Geography 82, (2000). 3 Hall, B. L., Baroni, C. & Denton, G. H. Holocene relative sea-level history of the Southern Victoria Land Coast, Antarctica. Global and Planetary Change 42, (2004). 4 Licht, K. J., Jennings, A. E., Andrews, J. T. & Williams, K. M. Chronology of late Wisconsin ice retreat from the western Ross Sea, Antarctica. Geology 24, (1996). 5 Hall, B. L. & Denton, G. H. New relative sea level curves for the southern Scott Coast, Antarctica: evidence for Holocene deglaciation of the western Ross Sea. Journal of Quaternary Science 14, (1999). 6 Domack, E. W., Jacobson, E. A., Shipp, S. & Anderson, J. B. Late Pleistocene Holocene retreat of the West Antarctic Ice-Sheet system in the Ross Sea: Part 2 sedimentologic and stratigraphic signature. Geological Society of America Bulletin 111, (1999). 7 Anderson, J. B. et al. Ross Sea paleo-ice sheet drainage and deglacial history during and since the LGM. Quaternary Science Reviews 100, (2014). 8 Steig, E. J. et al. Wisconsinan and Holocene climate history from an ice core at Taylor Dome, western Ross Embayment, Antarctica. Geografiska Annaler: Series A, Physical Geography 82, (2000). 9 Balco, G., Stone, J. O., Lifton, N. A. & Dunai, T. J. A complete and easily accessible means of calculating surface exposure ages or erosion rates from 10 Be and 26 Al measurements. Quaternary Geochronology 3, (2008). 10 Putnam, A. et al. In situ cosmogenic 10 Be production-rate calibration from the Southern Alps, New Zealand. Quaternary Geochronology 5, (2010). 11 Greenwood, S. L., Gyllencreutz, R., Jakobsson, M. & Anderson, J. B. Ice-flow switching and East/West Antarctic Ice Sheet roles in glaciation of the western Ross Sea. Geological Society of America Bulletin 124, (2012). 12 Calkin, P. E. Subglacial geomorphology surrounding the ice-free valleys of southern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Journal of Glaciology 13, (1974). 13 Graham, A. G. et al. Flow and retreat of the Late Quaternary Pine Island Thwaites palaeo ice stream, West Antarctica. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface ( ) 115, doi: /2009JF (2010). 14 Lal, D. Cosmic ray labeling of erosion surfaces: in situ nuclide production rates and erosion models. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 104, (1991). 15 Stone, J. O. Air pressure and cosmogenic isotope production. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth ( ) 105, (2000). 16 Desilets, D. & Zreda, M. Spatial and temporal distribution of secondary cosmic-ray nucleon intensities and applications to in situ cosmogenic dating. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 206, (2003). 17 Dunai, T. J. Scaling factors for production rates of in situ produced cosmogenic nuclides: a critical reevaluation. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 176, (2000). 18 Lifton, N. A. et al. Addressing solar modulation and long-term uncertainties in scaling secondary cosmic rays for in situ cosmogenic nuclide applications. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 239, (2005). 19 Nishiizumi, K. et al. Cosmic ray production rates of 10 Be and 26 Al in quartz from glacially polished rocks. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth ( ) 94, (1989).
UNDERSEA FEATURE NAME PROPOSAL (Sea NOTE overleaf)
 INTERNATIONAL HYDROGRAPHIC ORGANIZATION INTERGOVERNMENTAL OCEANOGRAPHIC COMMISSION (of UNESCO) UNDERSEA FEATURE NAME PROPOSAL (Sea NOTE overleaf) Note: The boxes will expand as you fill the form. Name
INTERNATIONAL HYDROGRAPHIC ORGANIZATION INTERGOVERNMENTAL OCEANOGRAPHIC COMMISSION (of UNESCO) UNDERSEA FEATURE NAME PROPOSAL (Sea NOTE overleaf) Note: The boxes will expand as you fill the form. Name
Ice Sheets and Late Quaternary Environmental Change
 Ice Sheets and Late Quaternary Environmental Change Martin J. Siegert Bristol Glaciology Centre, School of Geographical Sciences University of Bristol JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD Chichester New York Weinheim
Ice Sheets and Late Quaternary Environmental Change Martin J. Siegert Bristol Glaciology Centre, School of Geographical Sciences University of Bristol JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD Chichester New York Weinheim
Ice-stream stability on a reverse bed slope
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1600 Supplementary Information: Ice stream stability on a reverse bed Ice-stream stability on a reverse bed slope slope Stewart S.R. Jamieson 1, Andreas Vieli
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1600 Supplementary Information: Ice stream stability on a reverse bed Ice-stream stability on a reverse bed slope slope Stewart S.R. Jamieson 1, Andreas Vieli
LAST GLACIAL MAXIMUM ICE SHEET CONFIGURATION IN THE ROSS SEA
 PROJECT DESCRIPTION: COLLABORATIVE RESEARCH: TERRESTRIAL EXPOSURE-AGE CONSTRAINTS ON THE LAST GLACIAL MAXIMUM EXTENT OF THE ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET IN THE WESTERN ROSS SEA INTRODUCTION We propose to collect
PROJECT DESCRIPTION: COLLABORATIVE RESEARCH: TERRESTRIAL EXPOSURE-AGE CONSTRAINTS ON THE LAST GLACIAL MAXIMUM EXTENT OF THE ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET IN THE WESTERN ROSS SEA INTRODUCTION We propose to collect
Lake Levels and Climate Change in Maine and Eastern North America during the last 12,000 years
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities December, 2000 Lake Levels and Climate Change in Maine and Eastern North America during the last 12,000 years Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture,
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities December, 2000 Lake Levels and Climate Change in Maine and Eastern North America during the last 12,000 years Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture,
Sutherland et al: Glacial chronology, NZ
 Orbital forcing of mid-latitude southern hemisphere glaciation since 100 ka, inferred from cosmogenic nuclide ages of moraine boulders from the Cascade Plateau, southwest New Zealand Rupert Sutherland
Orbital forcing of mid-latitude southern hemisphere glaciation since 100 ka, inferred from cosmogenic nuclide ages of moraine boulders from the Cascade Plateau, southwest New Zealand Rupert Sutherland
SCIENTIFIC REPORT NERC GEF
 SCIENTIFIC REPORT NERC GEF Loan 927 Measuring changes in the dynamics of Pine Island Glacier, Antarctica A.M. Smith & E.C. King, British Antarctic Survey (BAS) pp J.B.T. Scott ABSTRACT A brief period of
SCIENTIFIC REPORT NERC GEF Loan 927 Measuring changes in the dynamics of Pine Island Glacier, Antarctica A.M. Smith & E.C. King, British Antarctic Survey (BAS) pp J.B.T. Scott ABSTRACT A brief period of
Ice on Earth: An overview and examples on physical properties
 Ice on Earth: An overview and examples on physical properties - Ice on Earth during the Pleistocene - Present-day polar and temperate ice masses - Transformation of snow to ice - Mass balance, ice deformation,
Ice on Earth: An overview and examples on physical properties - Ice on Earth during the Pleistocene - Present-day polar and temperate ice masses - Transformation of snow to ice - Mass balance, ice deformation,
How do glaciers form?
 Glaciers What is a Glacier? A large mass of moving ice that exists year round is called a glacier. Glaciers are formed when snowfall exceeds snow melt year after year Snow and ice remain on the ground
Glaciers What is a Glacier? A large mass of moving ice that exists year round is called a glacier. Glaciers are formed when snowfall exceeds snow melt year after year Snow and ice remain on the ground
APPENDIX 1: EXTENDED SAMPLE INFORMATION.
 1 APPENDIX 1: EXTENDED SAMPLE INFORMATION. Location map of the giant bar between Inya and Little Jaloman (topographic map 1:50,000). The circle marks the sampling location. Giant bar boulders (location
1 APPENDIX 1: EXTENDED SAMPLE INFORMATION. Location map of the giant bar between Inya and Little Jaloman (topographic map 1:50,000). The circle marks the sampling location. Giant bar boulders (location
UNSTOPPABLE COLLAPSE OF THE WEST ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET IS NOT HAPPENING
 UNSTOPPABLE COLLAPSE OF THE WEST ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET IS NOT HAPPENING Dr. Don J. Easterbrook, Western Washington University, Bellingham, WA May 19, 2014 A New York Times headline reads Scientists Warn
UNSTOPPABLE COLLAPSE OF THE WEST ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET IS NOT HAPPENING Dr. Don J. Easterbrook, Western Washington University, Bellingham, WA May 19, 2014 A New York Times headline reads Scientists Warn
radionuclide laboratory using procedures according to Kohl and Nishiizumi (1992), Ivy-Ochs
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2010117 APPENDIX DR1 Methodology: Cosmogenic 10 Be exposure dating The cosmogenic 10 Be samples were processed at the University of Colorado cosmogenic radionuclide laboratory using
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2010117 APPENDIX DR1 Methodology: Cosmogenic 10 Be exposure dating The cosmogenic 10 Be samples were processed at the University of Colorado cosmogenic radionuclide laboratory using
ENIGMA: something that is mysterious, puzzling, or difficult to understand.
 Lecture 12. Attempts to solve the Eccentricity Enigma ENIGMA: something that is mysterious, puzzling, or difficult to understand. Milankovitch forcing glacier responses pre-900,000 yr BP glacier responses
Lecture 12. Attempts to solve the Eccentricity Enigma ENIGMA: something that is mysterious, puzzling, or difficult to understand. Milankovitch forcing glacier responses pre-900,000 yr BP glacier responses
History. Late 18 th /early 19 th century Europeans observed that erratic boulders dispersed due to the retention of glaciers caused by climate chance
 Ice ages What is an ice age? Geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere which results in the formation and expansion of continental ice sheets, polar
Ice ages What is an ice age? Geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere which results in the formation and expansion of continental ice sheets, polar
Glacial Geomorphology Lecture 1: Glaciers & Glacial Environments. GGY 166: Geomorphology of Southern Africa
 Glacial Geomorphology Lecture 1: Glaciers & Glacial Environments GGY 166: Geomorphology of Southern Africa Relevance in Southern African Context South African landscape has been influenced by glacial action
Glacial Geomorphology Lecture 1: Glaciers & Glacial Environments GGY 166: Geomorphology of Southern Africa Relevance in Southern African Context South African landscape has been influenced by glacial action
High-resolution Geophysical Mapping of Submarine Glacial Landforms
 High-resolution Geophysical Mapping of Submarine Glacial Landforms M. Jakobsson 1, J.A. Dowdeswell 2, M. Canals 3, B.J. Todd 4, E.K. Dowdeswell 2, K.A. Hogan 5 L.A. Mayer 6 1 Stockholm University, Sweden
High-resolution Geophysical Mapping of Submarine Glacial Landforms M. Jakobsson 1, J.A. Dowdeswell 2, M. Canals 3, B.J. Todd 4, E.K. Dowdeswell 2, K.A. Hogan 5 L.A. Mayer 6 1 Stockholm University, Sweden
(Denton et al., 1991 ; Ing lfsson et al., 1998 ; Anderson, 1999 ;Denton et al.,1984), (Dowsett et al.,1996)
 16 1 Vol. 16, No. 1 2004 3 CHIN ESE JOURNAL OF POLAR RESEARCH March 2004 (, 100029) (, 100085) (, 100029) 10 Be 26 Al, 2Ma, (L GM), 200m,, (L GM), 10 Be 26 Al 1 2600 km 3, 83 %, 60 (Denton,2002),,, (Denton
16 1 Vol. 16, No. 1 2004 3 CHIN ESE JOURNAL OF POLAR RESEARCH March 2004 (, 100029) (, 100085) (, 100029) 10 Be 26 Al, 2Ma, (L GM), 200m,, (L GM), 10 Be 26 Al 1 2600 km 3, 83 %, 60 (Denton,2002),,, (Denton
Deglacial landform assemblage records fast ice-flow and retreat, Inner Hebrides, Scotland
 Deglacial landform assemblage records fast ice-flow and retreat, Inner Hebrides, Scotland D. DOVE 1*, A. FINLAYSON 1, T., BRADWELL 1,2, J. A. HOWE 3 & R. AROSIO 3 1 British Geological Survey, Murchison
Deglacial landform assemblage records fast ice-flow and retreat, Inner Hebrides, Scotland D. DOVE 1*, A. FINLAYSON 1, T., BRADWELL 1,2, J. A. HOWE 3 & R. AROSIO 3 1 British Geological Survey, Murchison
Supplementary Figure 1. Normalized glacier terminus elevation changes versus normalized glacier length changes.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normalized glacier terminus elevation changes versus normalized glacier length changes. Supplementary Figure 2. Normalized glacier lengths through time, as shown in Fig. 2 in the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normalized glacier terminus elevation changes versus normalized glacier length changes. Supplementary Figure 2. Normalized glacier lengths through time, as shown in Fig. 2 in the
Variations in valley glacier activity in the Transantarctic Mountains as indicated by associated flow bands in the Ross Ice Shelf*
 Sea Level, Ice, and Climatic Change (Proceedings of the Canberra Symposium, December 1979). IAHS Publ. no. 131. Variations in valley glacier activity in the Transantarctic Mountains as indicated by associated
Sea Level, Ice, and Climatic Change (Proceedings of the Canberra Symposium, December 1979). IAHS Publ. no. 131. Variations in valley glacier activity in the Transantarctic Mountains as indicated by associated
The State of the cryosphere
 The State of the cryosphere Course outline Introduction The cryosphere; what is it? The Earth; a unique planet Cryospheric components Classifications Lecture outlines The State of the cryosphere The State
The State of the cryosphere Course outline Introduction The cryosphere; what is it? The Earth; a unique planet Cryospheric components Classifications Lecture outlines The State of the cryosphere The State
Glacial processes and landforms NGEA01, 2014
 Glacial processes and landforms NGEA01, 2014 Cecilia Akselsson Department of Physical Geography and Ecosystem Science Lund University Geomorphological processes and landforms all over the world Periglacial
Glacial processes and landforms NGEA01, 2014 Cecilia Akselsson Department of Physical Geography and Ecosystem Science Lund University Geomorphological processes and landforms all over the world Periglacial
Glacial Modification of Terrain
 Glacial Modification Part I Stupendous glaciers and crystal snowflakes -- every form of animate or inanimate existence leaves its impress upon the soul of man. 1 -Orison Swett Marden Glacial Modification
Glacial Modification Part I Stupendous glaciers and crystal snowflakes -- every form of animate or inanimate existence leaves its impress upon the soul of man. 1 -Orison Swett Marden Glacial Modification
Geological record of Ice Stream Collapse, Pine Island Bay, West Antarctica
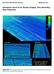 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2011212 Jakobsson et al. Geological record of Ice Stream Collapse, Pine Island Bay, West Antarctica Figure DR1. The corrugated furrows in central Pine Island Bay Trough and the iceberg
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2011212 Jakobsson et al. Geological record of Ice Stream Collapse, Pine Island Bay, West Antarctica Figure DR1. The corrugated furrows in central Pine Island Bay Trough and the iceberg
Geomorphologic Mapping by Airborne Laser Scanning in Southern Victoria Land
 Geomorphologic Mapping by Airborne Laser Scanning in Southern Victoria Land Bea Csatho, Terry Wilson, Tony Schenk, Garry McKenzie, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH William
Geomorphologic Mapping by Airborne Laser Scanning in Southern Victoria Land Bea Csatho, Terry Wilson, Tony Schenk, Garry McKenzie, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH William
common time scale developed for Greenland and Antarctic ice core records. Central to this
 1 Supplemental Material Age scale: For the dating of the EDML and EDC ice cores (Figure S1) we used for the first time a new common time scale developed for Greenland and Antarctic ice core records. Central
1 Supplemental Material Age scale: For the dating of the EDML and EDC ice cores (Figure S1) we used for the first time a new common time scale developed for Greenland and Antarctic ice core records. Central
Lecture 10 Glaciers and glaciation
 Lecture 10 Glaciers and glaciation Outline Importance of ice to people! Basics of glaciers formation, classification, mechanisms of movement Glacial landscapes erosion and deposition by glaciers and the
Lecture 10 Glaciers and glaciation Outline Importance of ice to people! Basics of glaciers formation, classification, mechanisms of movement Glacial landscapes erosion and deposition by glaciers and the
Brita Horlings
 Knut Christianson Brita Horlings brita2@uw.edu https://courses.washington.edu/ess431/ Natural Occurrences of Ice: Distribution and environmental factors of seasonal snow, sea ice, glaciers and permafrost
Knut Christianson Brita Horlings brita2@uw.edu https://courses.washington.edu/ess431/ Natural Occurrences of Ice: Distribution and environmental factors of seasonal snow, sea ice, glaciers and permafrost
Glaciology (as opposed to Glacial Geology) Why important? What are glaciers? How do they work?
 Glaciology (as opposed to Glacial Geology) Why important? What are glaciers? How do they work? Glaciers are important because of their role in creating glacial landscapes (erosional and depositional features).
Glaciology (as opposed to Glacial Geology) Why important? What are glaciers? How do they work? Glaciers are important because of their role in creating glacial landscapes (erosional and depositional features).
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas GLACIAL PROCESSES Glacial Processes The Impact of Glaciers on the Landscape Glaciations Past and Present Types of Glaciers Glacier Formation and Movement The Effects of
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas GLACIAL PROCESSES Glacial Processes The Impact of Glaciers on the Landscape Glaciations Past and Present Types of Glaciers Glacier Formation and Movement The Effects of
Ice Sheets and Glaciers
 Ice Sheets and Glaciers Technical University of Denmark Kees van der Veen Department of Geography University of Kansas Why are glaciers and ice sheets important? Large volume of fresh water stored in ice
Ice Sheets and Glaciers Technical University of Denmark Kees van der Veen Department of Geography University of Kansas Why are glaciers and ice sheets important? Large volume of fresh water stored in ice
Lecture 21: Glaciers and Paleoclimate Read: Chapter 15 Homework due Thursday Nov. 12. What we ll learn today:! Learning Objectives (LO)
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 21: Glaciers and Paleoclimate Read: Chapter 15 Homework due Thursday Nov. 12 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Glaciers and where they occur! 2. 2. Compare depositional and
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 21: Glaciers and Paleoclimate Read: Chapter 15 Homework due Thursday Nov. 12 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Glaciers and where they occur! 2. 2. Compare depositional and
Name. 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different soil horizons, A, B, C, and D, are shown.
 Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Timing and magnitude of late Pleistocene and Holocene glaciations in Yosemite National Park
 National Park Service U.S. Department of the Interior Yosemite National Park Timing and magnitude of late Pleistocene and Holocene glaciations in Yosemite National Park Greg Stock Yosemite National Park
National Park Service U.S. Department of the Interior Yosemite National Park Timing and magnitude of late Pleistocene and Holocene glaciations in Yosemite National Park Greg Stock Yosemite National Park
Supplementary Figure 1. New downcore data from this study. Triangles represent the depth of radiocarbon dates. Error bars represent 2 standard error
 Supplementary Figure 1. New downcore data from this study. Triangles represent the depth of radiocarbon dates. Error bars represent 2 standard error of measurement (s.e.m.). 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Particle
Supplementary Figure 1. New downcore data from this study. Triangles represent the depth of radiocarbon dates. Error bars represent 2 standard error of measurement (s.e.m.). 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Particle
Reconstruction of the Vistula ice stream lobe during LGM: preliminary results of the research project
 Ice, water, humans Quaternary landscape evolution in the Peribaltic Region 35th Annual conference of the German Quaternary Association DEUQUA e.v. 12th Annual Conference of the INQUA PeriBaltic WG 13th-17th
Ice, water, humans Quaternary landscape evolution in the Peribaltic Region 35th Annual conference of the German Quaternary Association DEUQUA e.v. 12th Annual Conference of the INQUA PeriBaltic WG 13th-17th
Holocene ice recession at Polygon Spur, Reedy Glacier, Antarctica
 652708HOL0010.1177/0959683616652708The HoloceneHall et al. research-article2016 Research paper Holocene ice recession at Polygon Spur, Reedy Glacier, Antarctica The Holocene 2017, Vol. 27(1) 122 129 The
652708HOL0010.1177/0959683616652708The HoloceneHall et al. research-article2016 Research paper Holocene ice recession at Polygon Spur, Reedy Glacier, Antarctica The Holocene 2017, Vol. 27(1) 122 129 The
Holocene Lower Mississippi River Avulsions: Autogenic Versus Allogenic Forcing*
 Holocene Lower Mississippi River Avulsions: Autogenic Versus Allogenic Forcing* Eric Prokocki 1,2 Search and Discovery Article #50330 (2010) Posted October 14, 2010 *Adapted from oral presentation at AAPG
Holocene Lower Mississippi River Avulsions: Autogenic Versus Allogenic Forcing* Eric Prokocki 1,2 Search and Discovery Article #50330 (2010) Posted October 14, 2010 *Adapted from oral presentation at AAPG
Ocean Ice Interactions: A
 Ocean Ice Interactions: A Cryospheric Perspective Tony Payne a.j.payne@bristol.ac.uk Steph Cornford, Rupert Gladstone and Dan Martin (LLNL) KISS short course Sept. 2013 Slide number 1/37 Outline Evidence
Ocean Ice Interactions: A Cryospheric Perspective Tony Payne a.j.payne@bristol.ac.uk Steph Cornford, Rupert Gladstone and Dan Martin (LLNL) KISS short course Sept. 2013 Slide number 1/37 Outline Evidence
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
Neogene Uplift of The Barents Sea
 Neogene Uplift of The Barents Sea W. Fjeldskaar A. Amantov Tectonor/UiS, Stavanger, Norway FORCE seminar April 4, 2013 The project (2010-2012) Funding companies Flat Objective The objective of the work
Neogene Uplift of The Barents Sea W. Fjeldskaar A. Amantov Tectonor/UiS, Stavanger, Norway FORCE seminar April 4, 2013 The project (2010-2012) Funding companies Flat Objective The objective of the work
This is an author produced version of Actively evolving subglacial conduits and eskers initiate ice shelf channels at an Antarctic grounding line.
 This is an author produced version of Actively evolving subglacial conduits and eskers initiate ice shelf channels at an Antarctic grounding line. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/113417/
This is an author produced version of Actively evolving subglacial conduits and eskers initiate ice shelf channels at an Antarctic grounding line. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/113417/
Sea level projections with semiempirical and earth system models
 Sea level projections with semiempirical and earth system models John C. Moore College of Global Change and Earth System Science, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China and Arctic Centre, University
Sea level projections with semiempirical and earth system models John C. Moore College of Global Change and Earth System Science, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China and Arctic Centre, University
Glaciers. (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 6) Science 330 Summer 2005
 Glaciers (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 6) Science 330 Summer 2005 1 Glaciers Glaciers are parts of two basic cycles Hydrologic cycle Rock cycle Glacier a thick mass of ice that originates on land from
Glaciers (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 6) Science 330 Summer 2005 1 Glaciers Glaciers are parts of two basic cycles Hydrologic cycle Rock cycle Glacier a thick mass of ice that originates on land from
Chapter 1 Section 2. Land, Water, and Climate
 Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Summer School in Glaciology, Fairbanks/McCarthy, Exercises: Glacial geology
 Bob Anderson Summer School in Glaciology, Fairbanks/McCarthy, 2010 Exercises: Glacial geology 1. Glacier thickness. We wish to estimate the local thickness of a glacier given only a topographic map of
Bob Anderson Summer School in Glaciology, Fairbanks/McCarthy, 2010 Exercises: Glacial geology 1. Glacier thickness. We wish to estimate the local thickness of a glacier given only a topographic map of
Areal Scour vs. Selective Linear Erosion
 Erosional Forms and Landscapes Erosional Landscapes Areal Scour vs. Selective Linear Erosion Cirques Form and Morphology Many Forms Red Tarn Cirque Basin English Lake District Red Tarn Cirque Basin, English
Erosional Forms and Landscapes Erosional Landscapes Areal Scour vs. Selective Linear Erosion Cirques Form and Morphology Many Forms Red Tarn Cirque Basin English Lake District Red Tarn Cirque Basin, English
Figure ES1 demonstrates that along the sledging
 UPPLEMENT AN EXCEPTIONAL SUMMER DURING THE SOUTH POLE RACE OF 1911/12 Ryan L. Fogt, Megan E. Jones, Susan Solomon, Julie M. Jones, and Chad A. Goergens This document is a supplement to An Exceptional Summer
UPPLEMENT AN EXCEPTIONAL SUMMER DURING THE SOUTH POLE RACE OF 1911/12 Ryan L. Fogt, Megan E. Jones, Susan Solomon, Julie M. Jones, and Chad A. Goergens This document is a supplement to An Exceptional Summer
Loess and dust. Jonathan A. Holmes Environmental Change Research Centre
 Loess and dust Jonathan A. Holmes Environmental Change Research Centre Why is dust important? Mineral dust is an important constituent of the solid load in Earth's atmosphere, the total atmospheric aerosol
Loess and dust Jonathan A. Holmes Environmental Change Research Centre Why is dust important? Mineral dust is an important constituent of the solid load in Earth's atmosphere, the total atmospheric aerosol
CORRELATION OF CLIMATIC AND SOLAR VARIATIONS OVER THE PAST 500 YEARS AND PREDICTING GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGES FROM RECURRING CLIMATE CYCLES
 Easterbrook, D.J., 2008, Correlation of climatic and solar variations over the past 500 years and predicting global climate changes from recurring climate cycles: International Geological Congress, Oslo,
Easterbrook, D.J., 2008, Correlation of climatic and solar variations over the past 500 years and predicting global climate changes from recurring climate cycles: International Geological Congress, Oslo,
Hydrologic Response to Extreme Warm and Cold Summers in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, East Antarctica
 Portland State University PDXScholar Geography Faculty Publications and Presentations Geography 1-1-2008 Hydrologic Response to Extreme Warm and Cold Summers in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, East Antarctica
Portland State University PDXScholar Geography Faculty Publications and Presentations Geography 1-1-2008 Hydrologic Response to Extreme Warm and Cold Summers in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, East Antarctica
Subglacial topography inferred from ice surface terrain analysis reveals a large un-surveyed basin below sea level in East Antarctica
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L16503, doi:10.1029/2008gl034728, 2008 Subglacial topography inferred from ice surface terrain analysis reveals a large un-surveyed basin below sea level in East
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L16503, doi:10.1029/2008gl034728, 2008 Subglacial topography inferred from ice surface terrain analysis reveals a large un-surveyed basin below sea level in East
FORMATION OF THE WEST ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET
 Annals of Glaciology 1988 @ nternational Glaciological Society FORMATON OF THE WEST ANTARCTC CE SHEET by D.R. Lindstrom (University of Chicago, Department of the Geophysical Sc iences, 5734 S. Ellis Avenue,
Annals of Glaciology 1988 @ nternational Glaciological Society FORMATON OF THE WEST ANTARCTC CE SHEET by D.R. Lindstrom (University of Chicago, Department of the Geophysical Sc iences, 5734 S. Ellis Avenue,
Glaciers Earth 9th Edition Chapter 18 Glaciers: summary in haiku form Key Concepts Glaciers Glaciers Glaciers Glaciers
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Earth 9 th Edition Chapter 18 : summary in haiku form Ten thousand years thence big glaciers began to melt - called "global warming." Key Concepts and types of glaciers.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Earth 9 th Edition Chapter 18 : summary in haiku form Ten thousand years thence big glaciers began to melt - called "global warming." Key Concepts and types of glaciers.
The Geology of Sebago Lake State Park
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
What is a Glacier? Types of Glaciers
 Alpine & Continental Glaciers Glacial Mass Balance Glacial Ice Formation Glacial Movement & Erosion Erosional and Depositional Landforms The Pleistocene Epoch Geomorphology of SW Manitoba Chapter 17 1
Alpine & Continental Glaciers Glacial Mass Balance Glacial Ice Formation Glacial Movement & Erosion Erosional and Depositional Landforms The Pleistocene Epoch Geomorphology of SW Manitoba Chapter 17 1
Contributions and unrealized potential contributions of cosmogenic-nuclide exposure dating to glacier chronology,
 Contributions and unrealized potential contributions of cosmogenic-nuclide exposure dating to glacier chronology, 1990-2010 Greg Balco a, a Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2455 Ridge Road, Berkeley CA 94709
Contributions and unrealized potential contributions of cosmogenic-nuclide exposure dating to glacier chronology, 1990-2010 Greg Balco a, a Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2455 Ridge Road, Berkeley CA 94709
Summary for the Greenland ice sheet
 Contribution of Greenland and Antarctica to future sea level change Catherine Ritz, Gaël Durand, Fabien Gillet-Chaulet, Olivier Gagliardini, Vincent Peyaud EDGe team, LGGE, CNRS/UJF Grenoble, France Ice
Contribution of Greenland and Antarctica to future sea level change Catherine Ritz, Gaël Durand, Fabien Gillet-Chaulet, Olivier Gagliardini, Vincent Peyaud EDGe team, LGGE, CNRS/UJF Grenoble, France Ice
Pleistocene Glaciations
 Chapter 14 Pleistocene Glaciations I. Geologic evidence 1. glacial deposits, etc. Pleistocene Glaciations 2. The Oxygen Isotope Record (1970s) II. Explanation of the glacial-interglacial periods The Milankovitch
Chapter 14 Pleistocene Glaciations I. Geologic evidence 1. glacial deposits, etc. Pleistocene Glaciations 2. The Oxygen Isotope Record (1970s) II. Explanation of the glacial-interglacial periods The Milankovitch
Landscape. Review Note Cards
 Landscape Review Note Cards Last Ice Age Pleistocene Epoch that occurred about 22,000 Years ago Glacier A large, long lasting mass of ice which forms on land and moves downhill because of gravity. Continental
Landscape Review Note Cards Last Ice Age Pleistocene Epoch that occurred about 22,000 Years ago Glacier A large, long lasting mass of ice which forms on land and moves downhill because of gravity. Continental
BELISSIMA: BELgian Ice Sheet- Shelf Ice Measurements in Antarctica
 BELISSIMA: BELgian Ice Sheet- Shelf Ice Measurements in Antarctica Frank PATTYN 1, Jean-Louis TISON 1, Denis SAMYN 1, Kenichi MATSUOKA², Howard CONWAY², Bryn HUBBARD³ (1)Laboratoire de Glaciologie, DSTE,
BELISSIMA: BELgian Ice Sheet- Shelf Ice Measurements in Antarctica Frank PATTYN 1, Jean-Louis TISON 1, Denis SAMYN 1, Kenichi MATSUOKA², Howard CONWAY², Bryn HUBBARD³ (1)Laboratoire de Glaciologie, DSTE,
Lower GRACE estimates of Antarctic sea-level contribution
 Lower GRACE estimates of Antarctic sea-level contribution Matt King 1,2, Rory Bingham 1, Philip Moore 1, Pippa Whitehouse 3, Mike Bentley 3, Glenn Milne 4 1 Newcastle University, 2 University of Tasmania,
Lower GRACE estimates of Antarctic sea-level contribution Matt King 1,2, Rory Bingham 1, Philip Moore 1, Pippa Whitehouse 3, Mike Bentley 3, Glenn Milne 4 1 Newcastle University, 2 University of Tasmania,
Amazing Ice: Glaciers and Ice Ages
 Amazing Ice: Glaciers and Ice Ages Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior
Amazing Ice: Glaciers and Ice Ages Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior
Any Questions? Glacier
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 25 13 April 2004 Any Questions? Earth Systems Today CD Click on Weather and Climate Look at the sections on El Niño Ozone Hole Glaciers Why do we care? They help control
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 25 13 April 2004 Any Questions? Earth Systems Today CD Click on Weather and Climate Look at the sections on El Niño Ozone Hole Glaciers Why do we care? They help control
Glaciers. Geology of the Hawaiian Islands. Any Questions? Earth Systems Today CD. Class April Why do we care?
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 25 13 April 2004 Any Questions? Earth Systems Today CD Click on Weather and Climate Look at the sections on El Niño Ozone Hole Glaciers Why do we care? They help control
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 25 13 April 2004 Any Questions? Earth Systems Today CD Click on Weather and Climate Look at the sections on El Niño Ozone Hole Glaciers Why do we care? They help control
Grounding line mapping in Antarctica using 15 years of DInSAR data
 Grounding line mapping in Antarctica using 15 years of DInSAR data Jérémie Mouginot 1 Eric Rignot 1,2, Bernd Scheuchl 1 1 University of California, Irvine 2 Jet Propulsion Laboratory Introduction Outline
Grounding line mapping in Antarctica using 15 years of DInSAR data Jérémie Mouginot 1 Eric Rignot 1,2, Bernd Scheuchl 1 1 University of California, Irvine 2 Jet Propulsion Laboratory Introduction Outline
Hydrologic response to extreme warm and cold summers in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, East Antarctica
 Antarctic Science page 1 of 11 (2008) & Antarctic Science Ltd 2008 doi: 10.1017/S0954102008001272 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Antarctic Science page 1 of 11 (2008) & Antarctic Science Ltd 2008 doi: 10.1017/S0954102008001272 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplemental Material Methods: The analytical methods for CO 2 measurements used at the University of Bern and at LGGE in Grenoble are based on dry extraction techniques followed by laser absorption spectroscopy
Supplemental Material Methods: The analytical methods for CO 2 measurements used at the University of Bern and at LGGE in Grenoble are based on dry extraction techniques followed by laser absorption spectroscopy
Father of Glacial theory. First investigations of glaciers and mountain geology,
 First investigations of glaciers and mountain geology, 1750-1800 Glaciation happens! -- Historical perspective It happens in cycles -- How do we know this? What are Milankovitch cycles? Sub-Milankovitch
First investigations of glaciers and mountain geology, 1750-1800 Glaciation happens! -- Historical perspective It happens in cycles -- How do we know this? What are Milankovitch cycles? Sub-Milankovitch
Introduction to Global Warming
 Introduction to Global Warming Cryosphere (including sea level) and its modelling Ralf GREVE Institute of Low Temperature Science Hokkaido University Sapporo, 2010.09.14 http://wwwice.lowtem.hokudai.ac.jp/~greve/
Introduction to Global Warming Cryosphere (including sea level) and its modelling Ralf GREVE Institute of Low Temperature Science Hokkaido University Sapporo, 2010.09.14 http://wwwice.lowtem.hokudai.ac.jp/~greve/
E Antarctic Ice Unstable, 200ft Sea Level Rise Possible - DK Greenroots
 E Antarctic Ice Unstable, 200ft Sea Level Rise Possible - DK Greenroots by FishOutofWater Thu Apr 22, 2010 at 04:04:48 PM PDT The last time CO2 levels were this high (14-20 million years ago), ice advanced
E Antarctic Ice Unstable, 200ft Sea Level Rise Possible - DK Greenroots by FishOutofWater Thu Apr 22, 2010 at 04:04:48 PM PDT The last time CO2 levels were this high (14-20 million years ago), ice advanced
Extra Credit Assignment (Chapters 4, 5, 6, and 10)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Extra Credit Assignment (Chapters 4, 5, 6, and 10) For this assignment you will require: a calculator and metric ruler. Chapter 4 Objectives:
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Extra Credit Assignment (Chapters 4, 5, 6, and 10) For this assignment you will require: a calculator and metric ruler. Chapter 4 Objectives:
Relative sea level in inner Nordfjord at 8150 cal. a BP
 Relative sea level in inner Nordfjord at 8150 cal. a BP Supporting information to Vasskog et al. Introduction The most precise way of determining past relative sea level in Scandinavia is considered to
Relative sea level in inner Nordfjord at 8150 cal. a BP Supporting information to Vasskog et al. Introduction The most precise way of determining past relative sea level in Scandinavia is considered to
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Pratice Surface Processes Test
 1. The cross section below shows the movement of wind-driven sand particles that strike a partly exposed basalt cobble located at the surface of a windy desert. Which cross section best represents the
1. The cross section below shows the movement of wind-driven sand particles that strike a partly exposed basalt cobble located at the surface of a windy desert. Which cross section best represents the
Proxy-based reconstructions of Arctic paleoclimate
 Proxy-based reconstructions of Arctic paleoclimate TODAY THE PAST Boothia Peninsula, Nunavut Prof. Sarah Finkelstein Earth Sciences, University of Toronto Finkelstein@es.utoronto.ca Outline Why does climate
Proxy-based reconstructions of Arctic paleoclimate TODAY THE PAST Boothia Peninsula, Nunavut Prof. Sarah Finkelstein Earth Sciences, University of Toronto Finkelstein@es.utoronto.ca Outline Why does climate
Effect of Ocean Warming on West Antarctic Ice Streams and Ice Shelves. Bryan Riel December 4, 2008
 Effect of Ocean Warming on West Antarctic Ice Streams and Ice Shelves Bryan Riel December 4, 2008 Ice Sheet Mass Balance/WAIS Dynamics -Mass Balance = (Ice/Snow Accumulation) (Surface melting, ice outflux,
Effect of Ocean Warming on West Antarctic Ice Streams and Ice Shelves Bryan Riel December 4, 2008 Ice Sheet Mass Balance/WAIS Dynamics -Mass Balance = (Ice/Snow Accumulation) (Surface melting, ice outflux,
Paleoceanography Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.740 Paleoceanography Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. PALEOCEANOGRAPHY 12.740 SPRING
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.740 Paleoceanography Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. PALEOCEANOGRAPHY 12.740 SPRING
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 6 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 6 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 6 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Thermokarst landforms in the Transantarctic Mountains region of Antarctica
 Thermokarst landforms in the Transantarctic Mountains region of Antarctica Permafrost, Phillips, Springman & Arenson (eds) 2003 Swets & Zeitlinger, Lisse, ISBN 90 5809 582 7 I.B. Campbell & G.G.C. Claridge
Thermokarst landforms in the Transantarctic Mountains region of Antarctica Permafrost, Phillips, Springman & Arenson (eds) 2003 Swets & Zeitlinger, Lisse, ISBN 90 5809 582 7 I.B. Campbell & G.G.C. Claridge
Assessing the ability of numerical ice sheet models to simulate grounding line migration
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004jf000202, 2005 Assessing the ability of numerical ice sheet models to simulate grounding line migration A. Vieli and A. J. Payne Centre for Polar
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004jf000202, 2005 Assessing the ability of numerical ice sheet models to simulate grounding line migration A. Vieli and A. J. Payne Centre for Polar
Moosehead Lake and the Tale of Two Rivers
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2005 45 o 53 5.09 N, 69 o 42 14.54 W Text by Kelley, A.R.; Kelley, J.T.; Belknap, D.F.; and Gontz, A.M. Department of Earth Sciences, University of Maine, Orono,
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2005 45 o 53 5.09 N, 69 o 42 14.54 W Text by Kelley, A.R.; Kelley, J.T.; Belknap, D.F.; and Gontz, A.M. Department of Earth Sciences, University of Maine, Orono,
Terrain Units PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION. Present Geology of NYS. Detailed Geologic Map of NYS
 NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
Investigating snow accumulation variability on the Antarctic Peninsula using Ground Penetrating Radar. - A tool for interpreting ice core records
 Investigating snow accumulation variability on the Antarctic Peninsula using Ground - A tool for interpreting ice core records Elizabeth R. Thomas June 2008 Scientific Report in support of Loan 824 Identifying
Investigating snow accumulation variability on the Antarctic Peninsula using Ground - A tool for interpreting ice core records Elizabeth R. Thomas June 2008 Scientific Report in support of Loan 824 Identifying
Subglacial Control on Glacier Flow in Northern Greenland
 Subglacial Control on Glacier Flow in Northern Greenland Beáta Csathó (University at Buffalo, SUNY, Buffalo, NY), C.J. van der Veen (U. of Kansas, Lawrence, KS) Ralph van Frese and Tim Leftwich (The Ohio
Subglacial Control on Glacier Flow in Northern Greenland Beáta Csathó (University at Buffalo, SUNY, Buffalo, NY), C.J. van der Veen (U. of Kansas, Lawrence, KS) Ralph van Frese and Tim Leftwich (The Ohio
6. What has been the most effective erosive agent in the climate system? a. Water b. Ice c. Wind
 Multiple Choice. 1. Heinrich Events a. Show increased abundance of warm-water species of planktic foraminifera b. Show greater intensity since the last deglaciation c. Show increased accumulation of ice-rafted
Multiple Choice. 1. Heinrich Events a. Show increased abundance of warm-water species of planktic foraminifera b. Show greater intensity since the last deglaciation c. Show increased accumulation of ice-rafted
Evidence for distribution and thickness of Athens Sub-episode and older sediments in Ottawa County, Michigan
 Evidence for distribution and thickness of Athens Sub-episode and older sediments in Ottawa County, Michigan Patrick M. Colgan Department of Geology Grand Valley State University With thanks to Al Kehew
Evidence for distribution and thickness of Athens Sub-episode and older sediments in Ottawa County, Michigan Patrick M. Colgan Department of Geology Grand Valley State University With thanks to Al Kehew
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
MISSISSIPPI RIVER DELTA OVERVIEW
 MISSISSIPPI RIVER DELTA OVERVIEW Science and Engineering Special Team Conference Louisiana State University October 9, 2012 Introduction Basics of the Mississippi Delta Natural and Human-Induced Land Loss
MISSISSIPPI RIVER DELTA OVERVIEW Science and Engineering Special Team Conference Louisiana State University October 9, 2012 Introduction Basics of the Mississippi Delta Natural and Human-Induced Land Loss
Pre-LGM open-water conditions south of the Drygalski Ice Tongue, Ross Sea, Antarctica
 Antarctic Science 19 (3), 373 377 (2007) & Antarctic Science Ltd 2007 Printed in the UK DOI: 10.1017/S0954102007000430 Pre-LGM open-water conditions south of the Drygalski Ice Tongue, Ross Sea, Antarctica
Antarctic Science 19 (3), 373 377 (2007) & Antarctic Science Ltd 2007 Printed in the UK DOI: 10.1017/S0954102007000430 Pre-LGM open-water conditions south of the Drygalski Ice Tongue, Ross Sea, Antarctica
Natural Climate Change: A Geological Perspective
 Natural Climate Change: A Geological Perspective A presentation to the Seminar on Sustainable Development NBA 573, BEE 673 Sage Hall B-11 March 4, 2005 by L. M. Cathles Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Truth
Natural Climate Change: A Geological Perspective A presentation to the Seminar on Sustainable Development NBA 573, BEE 673 Sage Hall B-11 March 4, 2005 by L. M. Cathles Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Truth
PROPOSAL DESCRIPTION: CENOZOIC FORMATION OF THE ANTARCTIC GLACIAL LANDSCAPE INVESTIGATED BY LOW-TEMPERATURE THERMOCHRONOMETRY
 PROPOSAL DESCRIPTION: CENOZOIC FORMATION OF THE ANTARCTIC GLACIAL LANDSCAPE INVESTIGATED BY LOW-TEMPERATURE THERMOCHRONOMETRY Summary: This pre-proposal outlines a drilling program aimed at investigating
PROPOSAL DESCRIPTION: CENOZOIC FORMATION OF THE ANTARCTIC GLACIAL LANDSCAPE INVESTIGATED BY LOW-TEMPERATURE THERMOCHRONOMETRY Summary: This pre-proposal outlines a drilling program aimed at investigating
Sea level contribution of Antarctica & Greenland Andrew Shepherd
 Andrew Shepherd School of Geosciences, Edinburgh Sea Subglacial level contribution lakes of Antarctica & Greenland Climate change Satellite observations Ice Sheets and Sea level Climate change Climate
Andrew Shepherd School of Geosciences, Edinburgh Sea Subglacial level contribution lakes of Antarctica & Greenland Climate change Satellite observations Ice Sheets and Sea level Climate change Climate
A Broecker Brief. Origin of the Glacial Ramp. Although there is no doubt that cycles in the Earth s orbital parameters pace glaciation,
 A Broecker Brief Origin of the Glacial Ramp Although there is no doubt that cycles in the Earth s orbital parameters pace glaciation, their physical link to the 100-kyr climate cycle remains unresolved.
A Broecker Brief Origin of the Glacial Ramp Although there is no doubt that cycles in the Earth s orbital parameters pace glaciation, their physical link to the 100-kyr climate cycle remains unresolved.
Climate Change. Unit 3
 Climate Change Unit 3 Aims Is global warming a recent short term phenomenon or should it be seen as part of long term climate change? What evidence is there of long-, medium-, and short- term climate change?
Climate Change Unit 3 Aims Is global warming a recent short term phenomenon or should it be seen as part of long term climate change? What evidence is there of long-, medium-, and short- term climate change?
Name: Mid-Year Review #2 SAR
 Name: Mid-Year Review #2 SAR Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on on the diagram below, which shows laboratory materials used for an investigation of the effects of sediment size on permeability,
Name: Mid-Year Review #2 SAR Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on on the diagram below, which shows laboratory materials used for an investigation of the effects of sediment size on permeability,
Basin-scale analysis of long-term sediment-generation rates derived from 10 Be in river sediment:
 Basin-scale analysis of long-term sediment-generation rates derived from 10 Be in river sediment: The Susquehanna River basin and beyond Joanna M. Reuter M.S. Proposal April 30, 2003 Paul Bierman, advisor
Basin-scale analysis of long-term sediment-generation rates derived from 10 Be in river sediment: The Susquehanna River basin and beyond Joanna M. Reuter M.S. Proposal April 30, 2003 Paul Bierman, advisor
The continent of Antarctica Resource N1
 The continent of Antarctica Resource N1 Prepared by Gillian Bunting Mapping and Geographic Information Centre, British Antarctic Survey February 1999 Equal area projection map of the world Resource N2
The continent of Antarctica Resource N1 Prepared by Gillian Bunting Mapping and Geographic Information Centre, British Antarctic Survey February 1999 Equal area projection map of the world Resource N2
ISSN Scientific Technical Report STR 07/05. DOI: /GFZ.b GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam
 ISSN 1610-0956 Ingo Sasgen, Robert Mulvaney, Volker Klemann and Detlef Wolf Glacial-isostatic adjustment and sea-level change near Berkner Island, Antarctica Ingo Sasgen Dep. 1: Geodesy and Remote Sensing
ISSN 1610-0956 Ingo Sasgen, Robert Mulvaney, Volker Klemann and Detlef Wolf Glacial-isostatic adjustment and sea-level change near Berkner Island, Antarctica Ingo Sasgen Dep. 1: Geodesy and Remote Sensing
Outline 23: The Ice Ages-Cenozoic Climatic History
 Outline 23: The Ice Ages-Cenozoic Climatic History Continental Glacier in Antarctica Valley Glaciers in Alaska, note the moraines Valley Glaciers in Alaska, note the moraines Mendenhall Glacier, Juneau,
Outline 23: The Ice Ages-Cenozoic Climatic History Continental Glacier in Antarctica Valley Glaciers in Alaska, note the moraines Valley Glaciers in Alaska, note the moraines Mendenhall Glacier, Juneau,
