Variations in valley glacier activity in the Transantarctic Mountains as indicated by associated flow bands in the Ross Ice Shelf*
|
|
|
- Bernard Grant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sea Level, Ice, and Climatic Change (Proceedings of the Canberra Symposium, December 1979). IAHS Publ. no Variations in valley glacier activity in the Transantarctic Mountains as indicated by associated flow bands in the Ross Ice Shelf* C. R, BENTLEY Geophysical and Polar Research Center, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin 53706, USA ABSTRACT Radar sounding records from the grid eastern Ross Ice Shelf show striking variations in basal reflectivity closely associated with the source of the ice. Ice from glaciers shows a strong basal echo, whereas on ice from between the glaciers the echo is weak or absent, presumably due to brine infiltration. The width and continuity of the strongly reflecting flow bands, as they are traced across the Ross Ice Shelf, provide information about the relative activity of the glaciers compared with that of the surrounding ice. Large changes in activity within the last 1500 years have been found. The cause is not certain, but the author believes it to be related to past oscillations of the glacier grounding lines resulting from changes in ice shelf thickness. A good correlation between glacier activity and the oxygen isotope records from ice cores at Dome C and Byrd stations strongly suggest some palaeoclimatic significance. The continuity of the glacier flow-band record precludes any major surges of the West Antarctic ice sheet in the 1500 years. Radar sounding records from the grid eastern sector of the Ross Ice Shelf show striking variations in basal reflectivity closely associated with the source of the ice. Ice from glaciers shows an echo that is at least intermittently strong, whereas ice from between glaciers reflects the radar wave weakly at best, presumably due to brine infiltration above the firn-ice boundary. There are not only large variations in reflection characteristics between glacial and interglacial bands, however, but also marked variations in the reflection characteristics within individual ice bands as they are traced downstream across the ice shelf from the glacier mouths. Here we examine in particular a group of valley glaciers that form four distinct bands between Beardmore and Nimrod glaciers, both of which are major East Antarctic outlet glaciers. This group was selected principally because of the large number of radar sounding tracks crossing their associated flow bands - about 25 when flights of the Ross Ice Shelf Geophysical and Glaciological Survey (RIGGS) are combined with those of the National Science Foundation/Scott Polar Research Institute/Technical University of Denmark cooperative programme (Fig. 1). * University of Wisconsin-Madison, Geophysical and Polar Research Center, Contribution no
2 248 C.R. Bentley JEG DS RG DOMEC BYRD Fig. 2 (a) "Quality" vs. residence 2 S time on the ice shelf for the bands corresponding to Jacobsen and Ekblad Fig. 1 Map of grid eastern portion of the Ross Ice glaciers (JEG), Davidson Glacier (DG), and Robb Glacier (RG). Black sections have high "quality", as defined in text, compared to white sections, (b) Oxygen isotope ratios vs. age in drill holes at Dome C (East Antarctica) and Byrd station (West Antarctica). Black sections correspond Shelf, showing the relationship of flight lines to the Transantarctic Mtn glaciers and the ice shelf flow band. The numbered and lettered lines denote NSF/SPRI/TUD and RIGGS flights, respectively. to relatively high SO values (algebraically), i.e. warmer temperatures; white sections to relatively low S 18 0 values. Two characteristics of the glacier bands were measured, the width and the reflection strength. In order to make an approximate correction for the downstream convergence of ice flow lines, the widths were measured as percentages of the total width of the band from the grid eastern edge of Beardmore Glacier ice to the grid eastern edge of Nimrod Glacier ice. No quantitative measure of the reflection strengths was available, so a qualitative assessment was made instead on a five-point scale (excellent, good, fair, poor, and non-existent, assigned numerical values of 4, 3, 2, 1 and O, respectively). Upon careful examination of the echograms, it became clear that there were, in three of the four bands, two sets of echoes, either one or both of which might be present in a particular location: the principal echo from the bottom of the ice shelf, and an echo from an internal reflector at a height of roughly 50 m above the ice-water boundary. Reflection strengths were assigned separately to the two sets of
3 Valley glacier activity in the Transantarctic Mtns 249 echoes, since, to a considerable degree, they vary independently of each other. Finally, a semi-quantitative "quality" factor was assigned to each reflector at each crossing of each glacier band by multiplying the relative width by the numerical reflection strength. A scale of residence time of the ice in the ice shelf, i.e. length of time since the ice at a particular spot left the corresponding glacier mouth, was developed using ice movement data from RIGGS. Velocities were first plotted for the outlet glacier bands because of the availability of velocities right at the mouths of two of them (Beardmore and Nimrod glaciers; Swithinbank, 1963). Plots of velocity vs. distance on the ice shelf downstream from the outlet glaciers were then interpolated for the valley glaciers, with correction factors near the mouths calculated for each glacier from the relative widths of the glacier mouths and the corresponding band on the nearest radar sounding track. The corrections, based on conservation of mass, are likely to lead to velocities near the glaciers that are too large rather than too small, since no account was made of a probable, although unmeasured, decrease in ice thickness between the glacier mouths and the first flight crossing. Because of the uncertainties near the glacier mouths, the residence times on the ice shelf calculated from the velocity vs. distance plots could easily be in error by loo years or more, probably on the low side. Plots of "quality" as a function of residence time for each of the valley glacier bands show pronounced downstream variations. The bottom echoes for all four glaciers have been relatively low in "quality" for the last 600 years. Prior to that there are peaks of high "quality" for each glacier lasting 50 to 150 years, but the correlation between bands is rather poor. For the internal reflector, however, the inter-band correlation is much better. All three bands show very similar patterns (Fig. 2(a)): high "quality" since about 300 years ago (the record begins at about 200 BP), between 500 and 800 BP, and more than 1150 BP (the record ends at 1350 BP), with periods of very low "quality" in between. These variations are not minor - "quality" factors along a particular band vary by an order of magnitude or more. Just what causes these striking variations is not at all clear. It seems inescapable that some sort of variation in the valley glaciers themselves has been occurring over the last 1500 years, but it is difficult to be more specific. The source of the internal reflections is not even known. The most likely possibilities are concentrated bottom crevasses and englacial moraine layers. Neither of these explanations is without difficulty: bottom crevasses elsewhere on the ice shelf seem always to show diffraction hyperbolas associated with the junction of the crevasses and the base of the ice, features that are largely absent in the bands in question. On the other hand, it is difficult to understand how moraine could regularly, but intermittently, be entrained to a height of 50 m above the glacier bed. A particularly striking feature of the record is the virtual disappearance of both basal and internal reflections associated with the glaciers about 500 years ago. This might be attributable
4 250 C.R. Bentley to rifting and brine infiltration above the firn-ice boundary, as is believed to occur between glacier bands, although there is no direct evidence of such an occurrence. However, most of the variations are not attributable to that mechanism, because the basal or near-basal echoes, even when weak, are clearly present. The most likely explanation in the author's opinion, is that past variations in the thickness of the ice shelf have caused advances and retreats in the grounding lines at the mouths of the glaciers, and that these advances and retreats, by some unknown mechanism, govern the strength of the internal reflector. This interpretation is strengthened by evidence presented by Jezek (1980) that a large shift in the grounding line of Crary Ice Rise, in the grid northwestern part of the Ross Ice Shelf, took place about 500 years ago. Changes in the width of the bands, however, while less coherent than the internal reflection changes, are nevertheless pronounced, suggesting that there were also major changes in the mass output of the glaciers. Evidence that the glacial phenomena are related to climatic changes comes from the oxygen isotope ratios in the ice cores from Byrd station (Johnsen et al., 1972) and Dome C (Lorius et al., 1979). The Dome C record shows a direct correspondence with all five of the "quality" zones in the internal reflections, with the more negative & O values corresponding to the low "quality" zones (Fig. 2(b)). At Byrd station, the four deeper zones all appear, although shifted perhaps years later; the record for the last 300 years does not exist in the Byrd station core. The amplitude of the ô 8 0 variations is between 1 and l^/oo at both stations, corresponding to a temperature change of 1 - lh. Although oxygen isotope ratios can change because of surface elevation changes, it is highly unlikely that the heights of the East and West Antarctic ice sheets have been oscillating in phase over a range of m with a period of 800 years. Thus a real atmospheric temperature change is indicated. Whether the temperature changes caused the glacial variations in some way, or both temperature and glacial changes reflect some larger-scale alterations in the Ross Ice Shelf and conceivably, in the regional sea ice cover, is an open question, although some model along the latter lines seems more likely to the author. However, the good (but not perfect) agreement between glacier band boundaries and the present flow lines as determined by the ice movement measurements precludes any major surges of West Antarctic ice within the last 1300 years or so, such as those proposed by Wilson (1978), since a surge would inevitably result in a large distortion of the historic flow bands. REFERENCES Jezek, K. C. (1980) Radar investigations of the Ross Ice Shelf, Antarctica. PhD Thesis, Geophysical and Polar Research Center, Univ. of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin. Johnsen, S. J., Dansgaard, W., Clausen, H. B. & Langway, C. C, Jr (1972) Oxygen isotope profiles through the Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets. Nature 235,
5 Valley glacier activity in the Transantarctic Mtns 251 Lorius, C, Merlivat, L., Jouzel, J. & Pourchet, M. (1979) A 30 OOO-yr isotope climatic record from Antarctic ice. Nature 280, Swithinbank, C. (1963) Ice movement of valley glaciers flowing onto the Ross Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Science 141, Wilson, A. T. (1978) Past surges in the West Antarctic ice sheet and their climatological significance. In: Antarctic Glacial History and Palaeoenvironments (ed. by E. M. van Zinderen Bakker), Balkema, Rotterdam.
6
Paleoceanography Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.740 Paleoceanography Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. PALEOCEANOGRAPHY 12.740 SPRING
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.740 Paleoceanography Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. PALEOCEANOGRAPHY 12.740 SPRING
Basal topography and thinning rates of Petermann Gletscher, northern Greenland, measured by ground-based phase-sensitive radar
 Basal topography and thinning rates of Petermann Gletscher, northern Greenland, measured by ground-based phase-sensitive radar Craig Stewart British Antarctic Survey, Natural Environment Research Council,
Basal topography and thinning rates of Petermann Gletscher, northern Greenland, measured by ground-based phase-sensitive radar Craig Stewart British Antarctic Survey, Natural Environment Research Council,
Supplementary Fig. 1. Locations of thinning transects and photos of example samples. Mt Suess/Gondola Ridge transects extended metres above
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Locations of thinning transects and photos of example samples. Mt Suess/Gondola Ridge transects extended 260 24 metres above the modern surface of Mackay Glacier, and included 16
Supplementary Fig. 1. Locations of thinning transects and photos of example samples. Mt Suess/Gondola Ridge transects extended 260 24 metres above the modern surface of Mackay Glacier, and included 16
common time scale developed for Greenland and Antarctic ice core records. Central to this
 1 Supplemental Material Age scale: For the dating of the EDML and EDC ice cores (Figure S1) we used for the first time a new common time scale developed for Greenland and Antarctic ice core records. Central
1 Supplemental Material Age scale: For the dating of the EDML and EDC ice cores (Figure S1) we used for the first time a new common time scale developed for Greenland and Antarctic ice core records. Central
AS REVEALED IN GREENLAND ICE CORES FROM 11 LOCATIONS
 Annals of Glaciology 1988 International Glaciological Society THE LAKI AND TAMBORA ERUPTIONS AS REVEALED IN GREENLAND ICE CORES FROM 11 LOCATIONS by H.B. Clausen and C.U. Hammer (Department of Glaciology,
Annals of Glaciology 1988 International Glaciological Society THE LAKI AND TAMBORA ERUPTIONS AS REVEALED IN GREENLAND ICE CORES FROM 11 LOCATIONS by H.B. Clausen and C.U. Hammer (Department of Glaciology,
Climate and Environment
 Climate and Environment Oxygen Isotope Fractionation and Measuring Ancient Temperatures Oxygen Isotope Ratio Cycles Oxygen isotope ratio cycles are cyclical variations in the ratio of the mass of oxygen
Climate and Environment Oxygen Isotope Fractionation and Measuring Ancient Temperatures Oxygen Isotope Ratio Cycles Oxygen isotope ratio cycles are cyclical variations in the ratio of the mass of oxygen
Meltdown Evidence of Climate Change from Polar Science. Eric Wolff
 Meltdown Evidence of Climate Change from Polar Science Eric Wolff (ewwo@bas.ac.uk) Why are the polar regions important for climate? Heat engine Why are the polar regions important for climate? Heat engine
Meltdown Evidence of Climate Change from Polar Science Eric Wolff (ewwo@bas.ac.uk) Why are the polar regions important for climate? Heat engine Why are the polar regions important for climate? Heat engine
Use of Geophysical Software for Interpretation of Ice-Penetrating Radar Data and Mapping of Polar Ice Sheets
 Use of Geophysical Software for Interpretation of Ice-Penetrating Radar Data and Mapping of Polar Ice Sheets Alex O. Martinez University of Kansas 2335 Irving Hill Road Lawrence, KS 66045-7612 http://cresis.ku.edu
Use of Geophysical Software for Interpretation of Ice-Penetrating Radar Data and Mapping of Polar Ice Sheets Alex O. Martinez University of Kansas 2335 Irving Hill Road Lawrence, KS 66045-7612 http://cresis.ku.edu
Any Questions? Glacier
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 25 13 April 2004 Any Questions? Earth Systems Today CD Click on Weather and Climate Look at the sections on El Niño Ozone Hole Glaciers Why do we care? They help control
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 25 13 April 2004 Any Questions? Earth Systems Today CD Click on Weather and Climate Look at the sections on El Niño Ozone Hole Glaciers Why do we care? They help control
Glaciers. Geology of the Hawaiian Islands. Any Questions? Earth Systems Today CD. Class April Why do we care?
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 25 13 April 2004 Any Questions? Earth Systems Today CD Click on Weather and Climate Look at the sections on El Niño Ozone Hole Glaciers Why do we care? They help control
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 25 13 April 2004 Any Questions? Earth Systems Today CD Click on Weather and Climate Look at the sections on El Niño Ozone Hole Glaciers Why do we care? They help control
Glacial Modification of Terrain
 Glacial Modification Part I Stupendous glaciers and crystal snowflakes -- every form of animate or inanimate existence leaves its impress upon the soul of man. 1 -Orison Swett Marden Glacial Modification
Glacial Modification Part I Stupendous glaciers and crystal snowflakes -- every form of animate or inanimate existence leaves its impress upon the soul of man. 1 -Orison Swett Marden Glacial Modification
Brita Horlings
 Knut Christianson Brita Horlings brita2@uw.edu https://courses.washington.edu/ess431/ Natural Occurrences of Ice: Distribution and environmental factors of seasonal snow, sea ice, glaciers and permafrost
Knut Christianson Brita Horlings brita2@uw.edu https://courses.washington.edu/ess431/ Natural Occurrences of Ice: Distribution and environmental factors of seasonal snow, sea ice, glaciers and permafrost
Ice Thickness and Subglacial Topography Studies by Ground Penetrating Radar during the XX Indian Antarctic Expedition
 Ice Thickness and Subglacial Topography Studies by Ground Penetrating Radar during the XX Indian Antarctic Expedition J.T. GERGAN and RENOJ J. THAYYEN Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, Dehradun, Uttaranchal
Ice Thickness and Subglacial Topography Studies by Ground Penetrating Radar during the XX Indian Antarctic Expedition J.T. GERGAN and RENOJ J. THAYYEN Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, Dehradun, Uttaranchal
L, G, THOMPSONJ E. MOSLEY-THOMPSON
 Sea Level, Jee, and C/imacic Change (Proceedings of the Canberra Symposium, December 1979). IAHS Publ. no. 131. Glaciological interpretation of microparticle concentrations from the French 95-m Dome C,
Sea Level, Jee, and C/imacic Change (Proceedings of the Canberra Symposium, December 1979). IAHS Publ. no. 131. Glaciological interpretation of microparticle concentrations from the French 95-m Dome C,
Glaciers. (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 6) Science 330 Summer 2005
 Glaciers (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 6) Science 330 Summer 2005 1 Glaciers Glaciers are parts of two basic cycles Hydrologic cycle Rock cycle Glacier a thick mass of ice that originates on land from
Glaciers (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 6) Science 330 Summer 2005 1 Glaciers Glaciers are parts of two basic cycles Hydrologic cycle Rock cycle Glacier a thick mass of ice that originates on land from
Lecture 21: Glaciers and Paleoclimate Read: Chapter 15 Homework due Thursday Nov. 12. What we ll learn today:! Learning Objectives (LO)
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 21: Glaciers and Paleoclimate Read: Chapter 15 Homework due Thursday Nov. 12 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Glaciers and where they occur! 2. 2. Compare depositional and
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 21: Glaciers and Paleoclimate Read: Chapter 15 Homework due Thursday Nov. 12 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Glaciers and where they occur! 2. 2. Compare depositional and
UNSTOPPABLE COLLAPSE OF THE WEST ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET IS NOT HAPPENING
 UNSTOPPABLE COLLAPSE OF THE WEST ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET IS NOT HAPPENING Dr. Don J. Easterbrook, Western Washington University, Bellingham, WA May 19, 2014 A New York Times headline reads Scientists Warn
UNSTOPPABLE COLLAPSE OF THE WEST ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET IS NOT HAPPENING Dr. Don J. Easterbrook, Western Washington University, Bellingham, WA May 19, 2014 A New York Times headline reads Scientists Warn
Ice on Earth: An overview and examples on physical properties
 Ice on Earth: An overview and examples on physical properties - Ice on Earth during the Pleistocene - Present-day polar and temperate ice masses - Transformation of snow to ice - Mass balance, ice deformation,
Ice on Earth: An overview and examples on physical properties - Ice on Earth during the Pleistocene - Present-day polar and temperate ice masses - Transformation of snow to ice - Mass balance, ice deformation,
SAMPLE PAGE. pulses. The Ice Age By: Sue Peterson
 Page 61 Objective sight words (pulses, intermittent, isotopes, chronicle, methane, tectonic plates, volcanism, configurations, land-locked, erratic); concepts (geological evidence and specific terminology
Page 61 Objective sight words (pulses, intermittent, isotopes, chronicle, methane, tectonic plates, volcanism, configurations, land-locked, erratic); concepts (geological evidence and specific terminology
Ice core studies from Mt Kenya, Africa, and their relationship to other tropical ice core studies
 Sea Level, Ice, and Climatic Change (Proceedings of the Canberra Symposium, December 1979). IAHS Publ. no. 131. INTRODUCTION Ice core studies from Mt Kenya, Africa, and their relationship to other tropical
Sea Level, Ice, and Climatic Change (Proceedings of the Canberra Symposium, December 1979). IAHS Publ. no. 131. INTRODUCTION Ice core studies from Mt Kenya, Africa, and their relationship to other tropical
CLIMATE CHANGE IN ARCTIC AND ALPINE AREAS
 CLIMATE CHANGE IN ARCTIC AND ALPINE AREAS 1. Introduction 2. Data sources: glaciers 3. Data sources: ice cores 4. Patterns and mechanisms 5. Feedbacks and surprises Striations (evidence of glacial erosion)
CLIMATE CHANGE IN ARCTIC AND ALPINE AREAS 1. Introduction 2. Data sources: glaciers 3. Data sources: ice cores 4. Patterns and mechanisms 5. Feedbacks and surprises Striations (evidence of glacial erosion)
Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra.
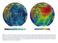 Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra. The left globe shows the seafloor bathymetry as portrayed
Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra. The left globe shows the seafloor bathymetry as portrayed
Glaciers Earth 9th Edition Chapter 18 Glaciers: summary in haiku form Key Concepts Glaciers Glaciers Glaciers Glaciers
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Earth 9 th Edition Chapter 18 : summary in haiku form Ten thousand years thence big glaciers began to melt - called "global warming." Key Concepts and types of glaciers.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Earth 9 th Edition Chapter 18 : summary in haiku form Ten thousand years thence big glaciers began to melt - called "global warming." Key Concepts and types of glaciers.
Climate Change. Unit 3
 Climate Change Unit 3 Aims Is global warming a recent short term phenomenon or should it be seen as part of long term climate change? What evidence is there of long-, medium-, and short- term climate change?
Climate Change Unit 3 Aims Is global warming a recent short term phenomenon or should it be seen as part of long term climate change? What evidence is there of long-, medium-, and short- term climate change?
SPQ Module 20 Ice Flows
 SPQ Module 20 Ice Flows When Ray, Richard & Kevin received their sleds in Southern Chili they opened them with excitement, and Kevin remarked they look like little canoes. It is perhaps appropriate that
SPQ Module 20 Ice Flows When Ray, Richard & Kevin received their sleds in Southern Chili they opened them with excitement, and Kevin remarked they look like little canoes. It is perhaps appropriate that
Ice Sheets and Glaciers
 Ice Sheets and Glaciers Technical University of Denmark Kees van der Veen Department of Geography University of Kansas Why are glaciers and ice sheets important? Large volume of fresh water stored in ice
Ice Sheets and Glaciers Technical University of Denmark Kees van der Veen Department of Geography University of Kansas Why are glaciers and ice sheets important? Large volume of fresh water stored in ice
Swath Mode Altimetry. Noel Gourmelen
 Swath Mode Altimetry Noel Gourmelen 1 Outline Background Impact case studies: Topography Rates of surface elevation change 2 Products and applications of radar altimetry over Ice Sheet, Ice Caps, Glaciers:
Swath Mode Altimetry Noel Gourmelen 1 Outline Background Impact case studies: Topography Rates of surface elevation change 2 Products and applications of radar altimetry over Ice Sheet, Ice Caps, Glaciers:
Energy and Seasons A B1. 9. Which graph best represents the general relationship between latitude and average surface temperature?
 Energy and Seasons A B1 1. Which type of surface absorbs the greatest amount of electromagnetic energy from the Sun? (1) smooth, shiny, and light colored (2) smooth, shiny, and dark colored (3) rough,
Energy and Seasons A B1 1. Which type of surface absorbs the greatest amount of electromagnetic energy from the Sun? (1) smooth, shiny, and light colored (2) smooth, shiny, and dark colored (3) rough,
History. Late 18 th /early 19 th century Europeans observed that erratic boulders dispersed due to the retention of glaciers caused by climate chance
 Ice ages What is an ice age? Geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere which results in the formation and expansion of continental ice sheets, polar
Ice ages What is an ice age? Geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere which results in the formation and expansion of continental ice sheets, polar
DETERMINATION OF ICE THICKNESS AND VOLUME OF HURD GLACIER, HURD PENINSULA, LIVINGSTONE ISLAND, ANTARCTICA
 Universidad de Granada MASTER S DEGREE IN GEOPHYSICS AND METEOROLOGY MASTER S THESIS DETERMINATION OF ICE THICKNESS AND VOLUME OF HURD GLACIER, HURD PENINSULA, LIVINGSTONE ISLAND, ANTARCTICA ÁNGEL RENTERO
Universidad de Granada MASTER S DEGREE IN GEOPHYSICS AND METEOROLOGY MASTER S THESIS DETERMINATION OF ICE THICKNESS AND VOLUME OF HURD GLACIER, HURD PENINSULA, LIVINGSTONE ISLAND, ANTARCTICA ÁNGEL RENTERO
Ice Sheets and Sea Level -- Concerns at the Coast (Teachers Guide)
 Ice Sheets and Sea Level -- Concerns at the Coast (Teachers Guide) Roughly 153 million Americans (~53% of the US population) live in coastal counties. World wide some 3 billion people live within 200 km
Ice Sheets and Sea Level -- Concerns at the Coast (Teachers Guide) Roughly 153 million Americans (~53% of the US population) live in coastal counties. World wide some 3 billion people live within 200 km
Studies of englacial water in Storglaciären using GPR - year two
 Studies of englacial water in Storglaciären using GPR - year two Robert W. Jacobel 1, Erin M. Peterson 1, Douglas R. Stone 1 and Andrew G. Fountain 2 1 Department of Physics, St. Olaf College, Northfield,
Studies of englacial water in Storglaciären using GPR - year two Robert W. Jacobel 1, Erin M. Peterson 1, Douglas R. Stone 1 and Andrew G. Fountain 2 1 Department of Physics, St. Olaf College, Northfield,
SCIENTIFIC REPORT NERC GEF
 SCIENTIFIC REPORT NERC GEF Loan 927 Measuring changes in the dynamics of Pine Island Glacier, Antarctica A.M. Smith & E.C. King, British Antarctic Survey (BAS) pp J.B.T. Scott ABSTRACT A brief period of
SCIENTIFIC REPORT NERC GEF Loan 927 Measuring changes in the dynamics of Pine Island Glacier, Antarctica A.M. Smith & E.C. King, British Antarctic Survey (BAS) pp J.B.T. Scott ABSTRACT A brief period of
A GEOLOGICAL VIEW OF CLIMATE CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING
 A GEOLOGICAL VIEW OF CLIMATE CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING Compiled by William D. Pollard, M Ray Thomasson PhD, and Lee Gerhard PhD THE ISSUE - Does the increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, resulting
A GEOLOGICAL VIEW OF CLIMATE CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING Compiled by William D. Pollard, M Ray Thomasson PhD, and Lee Gerhard PhD THE ISSUE - Does the increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, resulting
Outline 23: The Ice Ages-Cenozoic Climatic History
 Outline 23: The Ice Ages-Cenozoic Climatic History Continental Glacier in Antarctica Valley Glaciers in Alaska, note the moraines Valley Glaciers in Alaska, note the moraines Mendenhall Glacier, Juneau,
Outline 23: The Ice Ages-Cenozoic Climatic History Continental Glacier in Antarctica Valley Glaciers in Alaska, note the moraines Valley Glaciers in Alaska, note the moraines Mendenhall Glacier, Juneau,
Effect of Ocean Warming on West Antarctic Ice Streams and Ice Shelves. Bryan Riel December 4, 2008
 Effect of Ocean Warming on West Antarctic Ice Streams and Ice Shelves Bryan Riel December 4, 2008 Ice Sheet Mass Balance/WAIS Dynamics -Mass Balance = (Ice/Snow Accumulation) (Surface melting, ice outflux,
Effect of Ocean Warming on West Antarctic Ice Streams and Ice Shelves Bryan Riel December 4, 2008 Ice Sheet Mass Balance/WAIS Dynamics -Mass Balance = (Ice/Snow Accumulation) (Surface melting, ice outflux,
What lies beneath the Antarctic Ice? Adele penguins on sea ice Adele penguins on sea-ice
 What lies beneath the Antarctic Ice? Adele penguins on sea ice Adele penguins on sea-ice National Science Week 27: Antarctic Science BIOLOGICAL HISTORY FROM AN ANTARCTIC SEDIMENT CORE Background Information
What lies beneath the Antarctic Ice? Adele penguins on sea ice Adele penguins on sea-ice National Science Week 27: Antarctic Science BIOLOGICAL HISTORY FROM AN ANTARCTIC SEDIMENT CORE Background Information
Glacier Hydrology. Why should you care?
 Glacier Hydrology Why should you care? Climate Local Meteorology Surface Mass And Energy Exchange Net Mass Balance Dynamic Response Effect on Landscape Changes In Geometry Water Flow PRACTICAL MATTERS:
Glacier Hydrology Why should you care? Climate Local Meteorology Surface Mass And Energy Exchange Net Mass Balance Dynamic Response Effect on Landscape Changes In Geometry Water Flow PRACTICAL MATTERS:
Ice sheet mass balance from satellite altimetry. Kate Briggs (Mal McMillan)
 Ice sheet mass balance from satellite altimetry Kate Briggs (Mal McMillan) Outline Background Recap 25 year altimetry record Recap Measuring surface elevation with altimetry Measuring surface elevation
Ice sheet mass balance from satellite altimetry Kate Briggs (Mal McMillan) Outline Background Recap 25 year altimetry record Recap Measuring surface elevation with altimetry Measuring surface elevation
Exploring The Polar Connection to Sea Level Rise NGSS Disciplinary Core Ideas Science & Engineering Crosscutting Concepts
 Exploring The Polar Connection to Sea Level Rise NGSS Disciplinary Core Ideas Science & Engineering Crosscutting Concepts Practices MS - ESS: Earth & Space Science 1. Ask questions 2. Developing and using
Exploring The Polar Connection to Sea Level Rise NGSS Disciplinary Core Ideas Science & Engineering Crosscutting Concepts Practices MS - ESS: Earth & Space Science 1. Ask questions 2. Developing and using
Glacial Geomorphology Lecture 1: Glaciers & Glacial Environments. GGY 166: Geomorphology of Southern Africa
 Glacial Geomorphology Lecture 1: Glaciers & Glacial Environments GGY 166: Geomorphology of Southern Africa Relevance in Southern African Context South African landscape has been influenced by glacial action
Glacial Geomorphology Lecture 1: Glaciers & Glacial Environments GGY 166: Geomorphology of Southern Africa Relevance in Southern African Context South African landscape has been influenced by glacial action
8.9A - describe the historical development of evidence that supports plate tectonic theory
 8.9A - describe the historical development of evidence that supports plate tectonic theory Theory of Plate Tectonics the theory that pieces of Earth s lithosphere are in constant motion on the asthenosphere.
8.9A - describe the historical development of evidence that supports plate tectonic theory Theory of Plate Tectonics the theory that pieces of Earth s lithosphere are in constant motion on the asthenosphere.
ENIGMA: something that is mysterious, puzzling, or difficult to understand.
 Lecture 12. Attempts to solve the Eccentricity Enigma ENIGMA: something that is mysterious, puzzling, or difficult to understand. Milankovitch forcing glacier responses pre-900,000 yr BP glacier responses
Lecture 12. Attempts to solve the Eccentricity Enigma ENIGMA: something that is mysterious, puzzling, or difficult to understand. Milankovitch forcing glacier responses pre-900,000 yr BP glacier responses
DLR s TerraSAR-X contributes to international fleet of radar satellites to map the Arctic and Antarctica
 DLR s TerraSAR-X contributes to international fleet of radar satellites to map the Arctic and Antarctica The polar regions play an important role in the Earth system. The snow and ice covered ocean and
DLR s TerraSAR-X contributes to international fleet of radar satellites to map the Arctic and Antarctica The polar regions play an important role in the Earth system. The snow and ice covered ocean and
/ Past and Present Climate
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.842 / 12.301 Past and Present Climate Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Ice Sheet Paleoclimatology
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.842 / 12.301 Past and Present Climate Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Ice Sheet Paleoclimatology
BELISSIMA: BELgian Ice Sheet- Shelf Ice Measurements in Antarctica
 BELISSIMA: BELgian Ice Sheet- Shelf Ice Measurements in Antarctica Frank PATTYN 1, Jean-Louis TISON 1, Denis SAMYN 1, Kenichi MATSUOKA², Howard CONWAY², Bryn HUBBARD³ (1)Laboratoire de Glaciologie, DSTE,
BELISSIMA: BELgian Ice Sheet- Shelf Ice Measurements in Antarctica Frank PATTYN 1, Jean-Louis TISON 1, Denis SAMYN 1, Kenichi MATSUOKA², Howard CONWAY², Bryn HUBBARD³ (1)Laboratoire de Glaciologie, DSTE,
Summary for the Greenland ice sheet
 Contribution of Greenland and Antarctica to future sea level change Catherine Ritz, Gaël Durand, Fabien Gillet-Chaulet, Olivier Gagliardini, Vincent Peyaud EDGe team, LGGE, CNRS/UJF Grenoble, France Ice
Contribution of Greenland and Antarctica to future sea level change Catherine Ritz, Gaël Durand, Fabien Gillet-Chaulet, Olivier Gagliardini, Vincent Peyaud EDGe team, LGGE, CNRS/UJF Grenoble, France Ice
Fig. 1. Map of Antarctica showing the dry snow line (d.s.l.), the sectors where net ablation at the surface is predominant near the coast (ab.- fa.
 Fig. 1. Map of Antarctica showing the dry snow line (d.s.l.), the sectors where net ablation at the surface is predominant near the coast (ab.- fa.), and the drainage divides (xxxx; after Giovinetto 1963a).
Fig. 1. Map of Antarctica showing the dry snow line (d.s.l.), the sectors where net ablation at the surface is predominant near the coast (ab.- fa.), and the drainage divides (xxxx; after Giovinetto 1963a).
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas GLACIAL PROCESSES Glacial Processes The Impact of Glaciers on the Landscape Glaciations Past and Present Types of Glaciers Glacier Formation and Movement The Effects of
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas GLACIAL PROCESSES Glacial Processes The Impact of Glaciers on the Landscape Glaciations Past and Present Types of Glaciers Glacier Formation and Movement The Effects of
How do glaciers form?
 Glaciers What is a Glacier? A large mass of moving ice that exists year round is called a glacier. Glaciers are formed when snowfall exceeds snow melt year after year Snow and ice remain on the ground
Glaciers What is a Glacier? A large mass of moving ice that exists year round is called a glacier. Glaciers are formed when snowfall exceeds snow melt year after year Snow and ice remain on the ground
Chapter 15 Millennial Oscillations in Climate
 Chapter 15 Millennial Oscillations in Climate This chapter includes millennial oscillations during glaciations, millennial oscillations during the last 8000 years, causes of millennial-scale oscillations,
Chapter 15 Millennial Oscillations in Climate This chapter includes millennial oscillations during glaciations, millennial oscillations during the last 8000 years, causes of millennial-scale oscillations,
Evidence of Climate Change in Glacier Ice and Sea Ice
 Evidence of Climate Change in Glacier Ice and Sea Ice John J. Kelley Institute of Marine Science School of Fisheries and Ocean Sciences University of Alaska Fairbanks Evidence for warming of the Arctic
Evidence of Climate Change in Glacier Ice and Sea Ice John J. Kelley Institute of Marine Science School of Fisheries and Ocean Sciences University of Alaska Fairbanks Evidence for warming of the Arctic
Subglacial topography inferred from ice surface terrain analysis reveals a large un-surveyed basin below sea level in East Antarctica
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L16503, doi:10.1029/2008gl034728, 2008 Subglacial topography inferred from ice surface terrain analysis reveals a large un-surveyed basin below sea level in East
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L16503, doi:10.1029/2008gl034728, 2008 Subglacial topography inferred from ice surface terrain analysis reveals a large un-surveyed basin below sea level in East
GSC 107 Lab # 3 Calculating sea level changes
 GSC 107 Lab # 3 Calculating sea level changes Student name Student ID Background Glacial-Interglacial Cycles Climate-related sea-level changes of the last century are very minor compared with the large
GSC 107 Lab # 3 Calculating sea level changes Student name Student ID Background Glacial-Interglacial Cycles Climate-related sea-level changes of the last century are very minor compared with the large
Natural and anthropogenic climate change Lessons from ice cores
 Natural and anthropogenic climate change Lessons from ice cores Eric Wolff British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge ewwo@bas.ac.uk ASE Annual Conference 2011; ESTA/ESEU lecture Outline What is British Antarctic
Natural and anthropogenic climate change Lessons from ice cores Eric Wolff British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge ewwo@bas.ac.uk ASE Annual Conference 2011; ESTA/ESEU lecture Outline What is British Antarctic
From Isotopes to Temperature: Using Ice Core Data!
 From Isotopes to Temperature: Using Ice Core Data! Spruce W. Schoenemann schoes@uw.edu UWHS Atmospheric Sciences 211 May 2013 Dept. of Earth and Space Sciences University of Washington Seattle http://www.uwpcc.washington.edu
From Isotopes to Temperature: Using Ice Core Data! Spruce W. Schoenemann schoes@uw.edu UWHS Atmospheric Sciences 211 May 2013 Dept. of Earth and Space Sciences University of Washington Seattle http://www.uwpcc.washington.edu
New perspectives on old data: What the earth s past tells us about future sea level rise
 New perspectives on old data: What the earth s past tells us about future sea level rise Bindschadler, Science, 1998 Andrea Dutton Department of Geological Sciences University of Florida Historical record
New perspectives on old data: What the earth s past tells us about future sea level rise Bindschadler, Science, 1998 Andrea Dutton Department of Geological Sciences University of Florida Historical record
The State of the cryosphere
 The State of the cryosphere Course outline Introduction The cryosphere; what is it? The Earth; a unique planet Cryospheric components Classifications Lecture outlines The State of the cryosphere The State
The State of the cryosphere Course outline Introduction The cryosphere; what is it? The Earth; a unique planet Cryospheric components Classifications Lecture outlines The State of the cryosphere The State
Greenhouse warming, glaciers and future sea level
 Greenhouse warming, glaciers and future sea level J. Oerlemans Introduction The atmospheric concentration of a number of radiatively active trace gases (carbon, dioxide, methane, etc.) is currently increasing
Greenhouse warming, glaciers and future sea level J. Oerlemans Introduction The atmospheric concentration of a number of radiatively active trace gases (carbon, dioxide, methane, etc.) is currently increasing
IMPORTANCE OF SUBGLACIAL WATER TO ICE SHEET FLOW AND CONFIGURATION; A TEST USING DATA FROM MARIE BYRD LAND, ANTARCTICA
 IMPORTANCE OF SUBGLACIAL WATER TO ICE SHEET FLOW AND CONFIGURATION; A TEST USING DATA FROM MARIE BYRD LAND, ANTARCTICA Robert Allen Ferry Dept. of Geology and Mineralogy B.Sc. Thesis June 1979 Adviser
IMPORTANCE OF SUBGLACIAL WATER TO ICE SHEET FLOW AND CONFIGURATION; A TEST USING DATA FROM MARIE BYRD LAND, ANTARCTICA Robert Allen Ferry Dept. of Geology and Mineralogy B.Sc. Thesis June 1979 Adviser
Location of a new ice core site at Talos Dome (East Antarctica)
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 49, N. 4/5, August/October 2006 Location of a new ice core site at Talos Dome (East Antarctica) Stefano Urbini ( 1 ), Lili Cafarella ( 1 ), Achille Zirizzotti ( 1 ), Cesidio
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 49, N. 4/5, August/October 2006 Location of a new ice core site at Talos Dome (East Antarctica) Stefano Urbini ( 1 ), Lili Cafarella ( 1 ), Achille Zirizzotti ( 1 ), Cesidio
Investigating snow accumulation variability on the Antarctic Peninsula using Ground Penetrating Radar. - A tool for interpreting ice core records
 Investigating snow accumulation variability on the Antarctic Peninsula using Ground - A tool for interpreting ice core records Elizabeth R. Thomas June 2008 Scientific Report in support of Loan 824 Identifying
Investigating snow accumulation variability on the Antarctic Peninsula using Ground - A tool for interpreting ice core records Elizabeth R. Thomas June 2008 Scientific Report in support of Loan 824 Identifying
INDEX_Glaciers.pdf. mountain (alpine) glacier NLG Test bank: [Glaciers01-03.jpg] High Quality: [Moraine_med-lat_Haines_AK_.jpg]
![INDEX_Glaciers.pdf. mountain (alpine) glacier NLG Test bank: [Glaciers01-03.jpg] High Quality: [Moraine_med-lat_Haines_AK_.jpg] INDEX_Glaciers.pdf. mountain (alpine) glacier NLG Test bank: [Glaciers01-03.jpg] High Quality: [Moraine_med-lat_Haines_AK_.jpg]](/thumbs/83/88580835.jpg) Glaciers_INDEX.pdf This is an index of all terms/ideas in this question bank. Question banks are organized into topics containing related terms/ideas. Each term/idea has at least one related question,
Glaciers_INDEX.pdf This is an index of all terms/ideas in this question bank. Question banks are organized into topics containing related terms/ideas. Each term/idea has at least one related question,
Global Cooling is Here Evidence for Predicting Global Cooling for the Next Three Decades
 http://www.globalresearch.ca/index.php?context=va&aid=10783 Global Cooling is Here Evidence for Predicting Global Cooling for the Next Three Decades by Prof. Don J. Easterbrook Global Research, November
http://www.globalresearch.ca/index.php?context=va&aid=10783 Global Cooling is Here Evidence for Predicting Global Cooling for the Next Three Decades by Prof. Don J. Easterbrook Global Research, November
Evidence for a large surface ablation zone in central East Antarctica during the last Ice Age
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com R Quaternary Research 59 (2003) 114 121 www.elsevier.com/locate/yqres Evidence for a large surface ablation zone in central East Antarctica during the last Ice
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com R Quaternary Research 59 (2003) 114 121 www.elsevier.com/locate/yqres Evidence for a large surface ablation zone in central East Antarctica during the last Ice
An Investigation of Antarctic Circumpolar Current Strength in Response to Changes in Climate. Presented by Matt Laffin
 An Investigation of Antarctic Circumpolar Current Strength in Response to Changes in Climate Presented by Matt Laffin Presentation Outline Introduction to Marine Sediment as a Proxy Introduction to McCave
An Investigation of Antarctic Circumpolar Current Strength in Response to Changes in Climate Presented by Matt Laffin Presentation Outline Introduction to Marine Sediment as a Proxy Introduction to McCave
This is an author produced version of Actively evolving subglacial conduits and eskers initiate ice shelf channels at an Antarctic grounding line.
 This is an author produced version of Actively evolving subglacial conduits and eskers initiate ice shelf channels at an Antarctic grounding line. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/113417/
This is an author produced version of Actively evolving subglacial conduits and eskers initiate ice shelf channels at an Antarctic grounding line. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/113417/
ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow
![ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow](/thumbs/95/126309683.jpg) ATOC 1060-002 OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow cover, permafrost, river and lake ice, ; [3]Glaciers and
ATOC 1060-002 OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow cover, permafrost, river and lake ice, ; [3]Glaciers and
Pleistocene Glaciation (Ch.14) Geologic evidence Milankovitch cycles Glacial climate feedbacks
 Pleistocene Glaciation (Ch.14) Geologic evidence Milankovitch cycles Glacial climate feedbacks End of last ice-age rise of human civilization Modern ice-ages begin Asteroid impact end of dinosaurs Cambrian
Pleistocene Glaciation (Ch.14) Geologic evidence Milankovitch cycles Glacial climate feedbacks End of last ice-age rise of human civilization Modern ice-ages begin Asteroid impact end of dinosaurs Cambrian
Figure ES1 demonstrates that along the sledging
 UPPLEMENT AN EXCEPTIONAL SUMMER DURING THE SOUTH POLE RACE OF 1911/12 Ryan L. Fogt, Megan E. Jones, Susan Solomon, Julie M. Jones, and Chad A. Goergens This document is a supplement to An Exceptional Summer
UPPLEMENT AN EXCEPTIONAL SUMMER DURING THE SOUTH POLE RACE OF 1911/12 Ryan L. Fogt, Megan E. Jones, Susan Solomon, Julie M. Jones, and Chad A. Goergens This document is a supplement to An Exceptional Summer
SMOW. δd = 8 δ 18 O δ 18 O. Craig 1961
 SMOW δd δd = 8 δ 18 O + 10 δ 18 O Craig 1961 " # 18 O "T $ 0.695 / deg " #D "T $ 5.6 / deg "# 18 O "T $ 0.695 / deg "#D "T $ 5.6 / deg Dansgaard 1964 -9-27 Little Am. 43 m -24.2 C Wilkes 1168 m -18.6 C
SMOW δd δd = 8 δ 18 O + 10 δ 18 O Craig 1961 " # 18 O "T $ 0.695 / deg " #D "T $ 5.6 / deg "# 18 O "T $ 0.695 / deg "#D "T $ 5.6 / deg Dansgaard 1964 -9-27 Little Am. 43 m -24.2 C Wilkes 1168 m -18.6 C
ACTIVITY II: THE FATE OF THE LARSEN S, A FAMILY OF ANTARCTIC ICE SHELVES
 ACTIVITY II: THE FATE OF THE LARSEN S, A FAMILY OF ANTARCTIC ICE SHELVES Ice Shelves play a critical role in Antarctica, serving as a buffer between the ocean and the continental ice sheet covering the
ACTIVITY II: THE FATE OF THE LARSEN S, A FAMILY OF ANTARCTIC ICE SHELVES Ice Shelves play a critical role in Antarctica, serving as a buffer between the ocean and the continental ice sheet covering the
Antarctic Automatic Weather Station Field Report: Season
 Antarctic Automatic Weather Station Field Report: 1996-1997 Season Robert E. Holmes Charles R. Stearns George A. Weidner Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin-Madison Madison, WI
Antarctic Automatic Weather Station Field Report: 1996-1997 Season Robert E. Holmes Charles R. Stearns George A. Weidner Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin-Madison Madison, WI
Lake Levels and Climate Change in Maine and Eastern North America during the last 12,000 years
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities December, 2000 Lake Levels and Climate Change in Maine and Eastern North America during the last 12,000 years Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture,
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities December, 2000 Lake Levels and Climate Change in Maine and Eastern North America during the last 12,000 years Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture,
Validation of the Antarctic Snow Accumulation and Ice Discharge Basal Stress Boundary of the Southeastern Region of the Ross Ice Shelf, Antarctica
 Validation of the Antarctic Snow Accumulation and Ice Discharge Basal Stress Boundary of the Southeastern Region of the Ross Ice Shelf, Antarctica TEAM MEMBERS Ayanna Overton, junior Charlie Nelson, senior
Validation of the Antarctic Snow Accumulation and Ice Discharge Basal Stress Boundary of the Southeastern Region of the Ross Ice Shelf, Antarctica TEAM MEMBERS Ayanna Overton, junior Charlie Nelson, senior
Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra.
 Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra. The left globe shows the seafloor bathymetry as portrayed
Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra. The left globe shows the seafloor bathymetry as portrayed
MOMURDO-POLE TRAVERSE (See Bulletin, Volume II, Number 4, pages 21-22; Number 5, pages 24-25)
 MOMURDO-POLE TRAVERSE (See Bulletin, Volume, Number 4, pages 21-22; Number 5, pages 24-25) On the afternoon of 12 February, Dr. Albert P. Crary and Sveneld Evteev drove their 743 Sno-Cat up to the Amundsen-Soott
MOMURDO-POLE TRAVERSE (See Bulletin, Volume, Number 4, pages 21-22; Number 5, pages 24-25) On the afternoon of 12 February, Dr. Albert P. Crary and Sveneld Evteev drove their 743 Sno-Cat up to the Amundsen-Soott
E Antarctic Ice Unstable, 200ft Sea Level Rise Possible - DK Greenroots
 E Antarctic Ice Unstable, 200ft Sea Level Rise Possible - DK Greenroots by FishOutofWater Thu Apr 22, 2010 at 04:04:48 PM PDT The last time CO2 levels were this high (14-20 million years ago), ice advanced
E Antarctic Ice Unstable, 200ft Sea Level Rise Possible - DK Greenroots by FishOutofWater Thu Apr 22, 2010 at 04:04:48 PM PDT The last time CO2 levels were this high (14-20 million years ago), ice advanced
Rapid Changes in Oxygen Isotope Content of Ice Cores Caused by Fractionation and Trajectory Dispersion near the Edge of an Ice Shelf
 Rapid Changes in Oxygen Isotope Content of Ice Cores Caused by Fractionation and Trajectory Dispersion near the Edge of an Ice Shelf LARRY VARDIMAN ABSTRACT Oxygen isotopes in ice cores extracted from
Rapid Changes in Oxygen Isotope Content of Ice Cores Caused by Fractionation and Trajectory Dispersion near the Edge of an Ice Shelf LARRY VARDIMAN ABSTRACT Oxygen isotopes in ice cores extracted from
GPR Reflection Profiles of Clark and Commonwealth Glaciers, Dry Valleys, Antarctica
 The University of Maine DigitalCommons@UMaine Earth Science Faculty Scholarship Earth Sciences 2009 GPR Reflection Profiles of Clark and Commonwealth Glaciers, Dry Valleys, Antarctica Steven A. Arcone
The University of Maine DigitalCommons@UMaine Earth Science Faculty Scholarship Earth Sciences 2009 GPR Reflection Profiles of Clark and Commonwealth Glaciers, Dry Valleys, Antarctica Steven A. Arcone
TEACHER PAGE Trial Version
 TEACHER PAGE Trial Version * After completion of the lesson, please take a moment to fill out the feedback form on our web site (https://www.cresis.ku.edu/education/k-12/online-data-portal)* Lesson Title:
TEACHER PAGE Trial Version * After completion of the lesson, please take a moment to fill out the feedback form on our web site (https://www.cresis.ku.edu/education/k-12/online-data-portal)* Lesson Title:
Lecture 10 Glaciers and glaciation
 Lecture 10 Glaciers and glaciation Outline Importance of ice to people! Basics of glaciers formation, classification, mechanisms of movement Glacial landscapes erosion and deposition by glaciers and the
Lecture 10 Glaciers and glaciation Outline Importance of ice to people! Basics of glaciers formation, classification, mechanisms of movement Glacial landscapes erosion and deposition by glaciers and the
Terra Antartica Publication Terra Antartica Reports 2008, 14, 21-25
 Terra Antartica Reports 2008, 14, 21-25 Snow Accumulation in the Talos Dome Area: Preliminary Results M. Frezzotti 1, M. Proposito 1, S. Urbini 2 & S. Gandolfi 3 1 ENEA, Laboratory for Climate Observations,
Terra Antartica Reports 2008, 14, 21-25 Snow Accumulation in the Talos Dome Area: Preliminary Results M. Frezzotti 1, M. Proposito 1, S. Urbini 2 & S. Gandolfi 3 1 ENEA, Laboratory for Climate Observations,
Glaciers and Ice Ages
 ES 106 Glaciers and Ice Ages I. Glacier thick mass of ice accumulated over years, decades, centuries A. Function of recrystallization of fallen snow B. Types 1. alpine valley: a. high elevations worldwide
ES 106 Glaciers and Ice Ages I. Glacier thick mass of ice accumulated over years, decades, centuries A. Function of recrystallization of fallen snow B. Types 1. alpine valley: a. high elevations worldwide
Ice core-based climate research in Denmark
 June 16, 2009 Ice core-based climate research in Denmark Sune Olander Rasmussen Center coordinator and postdoc Centre for Ice and Climate Niels Bohr Institute University of Copenhagen Temperature and CO
June 16, 2009 Ice core-based climate research in Denmark Sune Olander Rasmussen Center coordinator and postdoc Centre for Ice and Climate Niels Bohr Institute University of Copenhagen Temperature and CO
Glacier Thermodynamics: Ice Temperature and Heat Transfer Processes
 Glacier Thermodynamics: Ice Temperature and Heat Transfer Processes ESS431: Principles of Glaciology ESS505: The Cryosphere Wednesday, 10/24 Ben Hills Today s Objectives: Why do we care about ice temperature?
Glacier Thermodynamics: Ice Temperature and Heat Transfer Processes ESS431: Principles of Glaciology ESS505: The Cryosphere Wednesday, 10/24 Ben Hills Today s Objectives: Why do we care about ice temperature?
The continent of Antarctica Resource N1
 The continent of Antarctica Resource N1 Prepared by Gillian Bunting Mapping and Geographic Information Centre, British Antarctic Survey February 1999 Equal area projection map of the world Resource N2
The continent of Antarctica Resource N1 Prepared by Gillian Bunting Mapping and Geographic Information Centre, British Antarctic Survey February 1999 Equal area projection map of the world Resource N2
Errata. Version 11/07/2014 1
 Version 11/7/214 1 Climate Change 213: The Physical Science Basis The Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report Page Item Correction ii Frontmatter Insert the following text: The
Version 11/7/214 1 Climate Change 213: The Physical Science Basis The Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report Page Item Correction ii Frontmatter Insert the following text: The
POLAR EXPLORER EXPLORING SEA LEVEL RISE
 POLAR EXPLORER EXPLORING SEA i LEVEL RISE Developed by: Margie Turrin, mkt@ldeo.columbia.edu As a polar explorer you and your team will be collec@ng evidence of changes occurring throughout the world that
POLAR EXPLORER EXPLORING SEA i LEVEL RISE Developed by: Margie Turrin, mkt@ldeo.columbia.edu As a polar explorer you and your team will be collec@ng evidence of changes occurring throughout the world that
U.S. Antarctic Program EH 4/12
 U.S. Antarctic Program Agenda Geography Research Stations Transportation Scientific Research Questions? Size and Distance Antarctica Area = 13,829,430 km2 Canada Area = 9,984,670 km2 US Area = 9,826,675
U.S. Antarctic Program Agenda Geography Research Stations Transportation Scientific Research Questions? Size and Distance Antarctica Area = 13,829,430 km2 Canada Area = 9,984,670 km2 US Area = 9,826,675
Meltwater produced by wind-albedo interaction stored in an East Antarctic ice shelf Supplementary Information
 Meltwater produced by wind-albedo interaction stored in an East Antarctic ice shelf Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Figure 1: (a) Upper and (b) lower surface of an englacial lake surveyed by
Meltwater produced by wind-albedo interaction stored in an East Antarctic ice shelf Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Figure 1: (a) Upper and (b) lower surface of an englacial lake surveyed by
Plate Climatology Theory* by James Edward Kamis 21 October 2014
 Plate Climatology Theory* by James Edward Kamis 21 October 2014 Synopsis The Sun, quite obviously, is the first order driver of Earth s climate, but a much neglected second order driver can contribute
Plate Climatology Theory* by James Edward Kamis 21 October 2014 Synopsis The Sun, quite obviously, is the first order driver of Earth s climate, but a much neglected second order driver can contribute
Global Warming and Changing Sea Level. Name: Part 1: Am I part of the problem?!
 Part 1: Am I part of the problem?! Name: The consumption of energy in the form of fossil fuel combustion is the largest single contributor to anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S. and the
Part 1: Am I part of the problem?! Name: The consumption of energy in the form of fossil fuel combustion is the largest single contributor to anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S. and the
Ice Dynamics at the Mouth of Ice Stream B, Antarctica
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 92, NO. B9, PAGES 8885-8894, AUGUST 1, 1987 Ice Dynamics at the Mouth of Ice Stream B, Antarctica R. A. BINDSCHADLER, 1 S. N. STEPHENSON, 2 D. R. MACAYEAL, 3 AND S.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 92, NO. B9, PAGES 8885-8894, AUGUST 1, 1987 Ice Dynamics at the Mouth of Ice Stream B, Antarctica R. A. BINDSCHADLER, 1 S. N. STEPHENSON, 2 D. R. MACAYEAL, 3 AND S.
Glaciological Models in Focus
 Department of Probability and Statistics, University of Sheffield British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge Quantifying Uncertainty on Chronologies for Palaeoclimate Reconstruction from Ice Cores Glaciological
Department of Probability and Statistics, University of Sheffield British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge Quantifying Uncertainty on Chronologies for Palaeoclimate Reconstruction from Ice Cores Glaciological
Introduction to Global Warming
 Introduction to Global Warming Cryosphere (including sea level) and its modelling Ralf GREVE Institute of Low Temperature Science Hokkaido University Sapporo, 2010.09.14 http://wwwice.lowtem.hokudai.ac.jp/~greve/
Introduction to Global Warming Cryosphere (including sea level) and its modelling Ralf GREVE Institute of Low Temperature Science Hokkaido University Sapporo, 2010.09.14 http://wwwice.lowtem.hokudai.ac.jp/~greve/
FORMATION OF THE WEST ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET
 Annals of Glaciology 1988 @ nternational Glaciological Society FORMATON OF THE WEST ANTARCTC CE SHEET by D.R. Lindstrom (University of Chicago, Department of the Geophysical Sc iences, 5734 S. Ellis Avenue,
Annals of Glaciology 1988 @ nternational Glaciological Society FORMATON OF THE WEST ANTARCTC CE SHEET by D.R. Lindstrom (University of Chicago, Department of the Geophysical Sc iences, 5734 S. Ellis Avenue,
Increased flow speed on a large East Antarctic outlet glacier due to subglacial floods
 Increased flow speed on a large East Antarctic outlet glacier due to subglacial floods LETTERS LEIGH A. STEARNS *, BENJAMIN E. SMITH AND GORDON S. HAMILTON Climate Change Institute, University of Maine,
Increased flow speed on a large East Antarctic outlet glacier due to subglacial floods LETTERS LEIGH A. STEARNS *, BENJAMIN E. SMITH AND GORDON S. HAMILTON Climate Change Institute, University of Maine,
STATE OF BALANCE OF THE ICE SHEET IN THE ANTARCTIC PENINSULA
 Annals of Glaciology 3 1 982 International Glaciological Society STATE OF BALANCE OF THE ICE SHEET IN THE ANTARCTIC PENINSULA by Christophers. M. Doake (British Antarctic Survey, Natural Environment Research
Annals of Glaciology 3 1 982 International Glaciological Society STATE OF BALANCE OF THE ICE SHEET IN THE ANTARCTIC PENINSULA by Christophers. M. Doake (British Antarctic Survey, Natural Environment Research
CORRELATION OF CLIMATIC AND SOLAR VARIATIONS OVER THE PAST 500 YEARS AND PREDICTING GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGES FROM RECURRING CLIMATE CYCLES
 Easterbrook, D.J., 2008, Correlation of climatic and solar variations over the past 500 years and predicting global climate changes from recurring climate cycles: International Geological Congress, Oslo,
Easterbrook, D.J., 2008, Correlation of climatic and solar variations over the past 500 years and predicting global climate changes from recurring climate cycles: International Geological Congress, Oslo,
